Water Quality Predictions Based on Grey Relation Analysis Enhanced LSTM Algorithms
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods and Materials
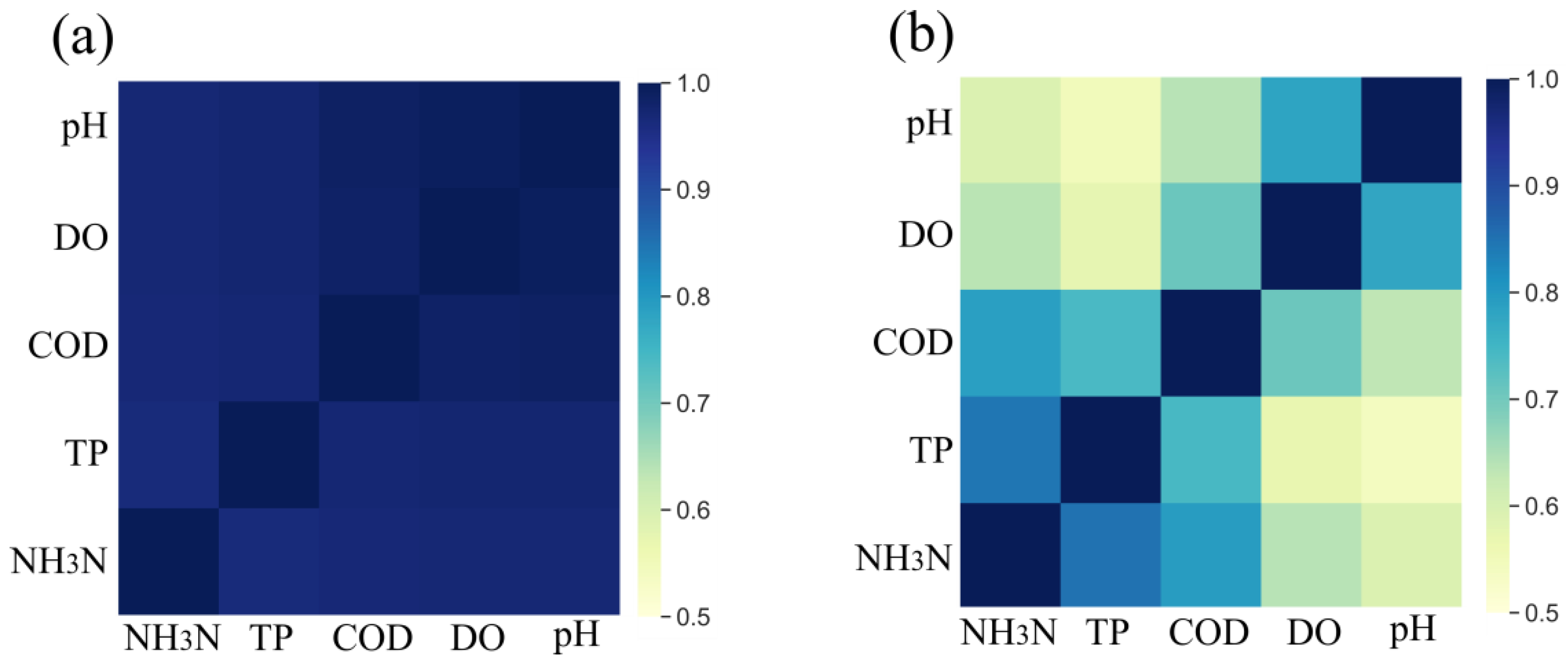
2.1. GRA Formulations
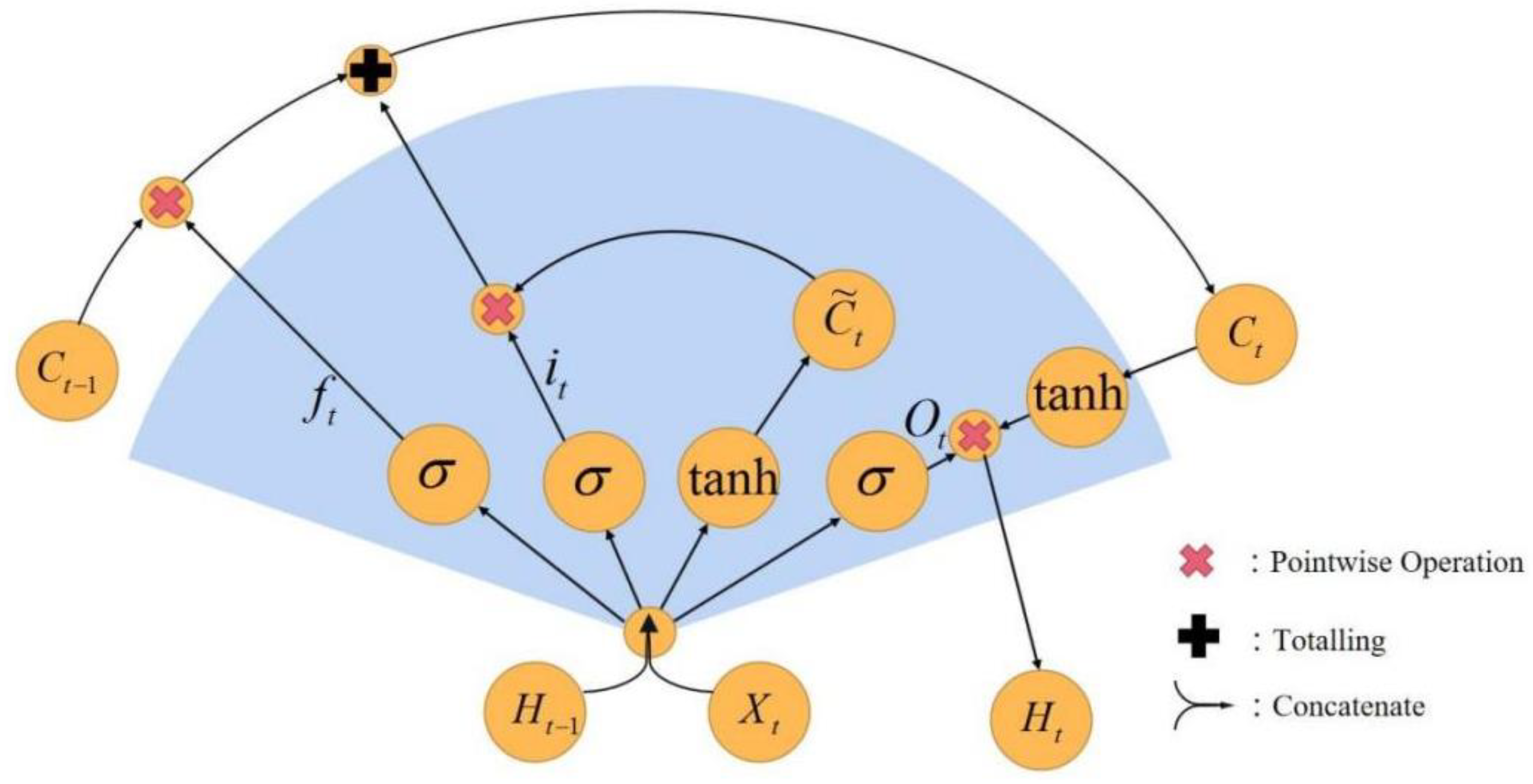
2.2. LSTM Structure
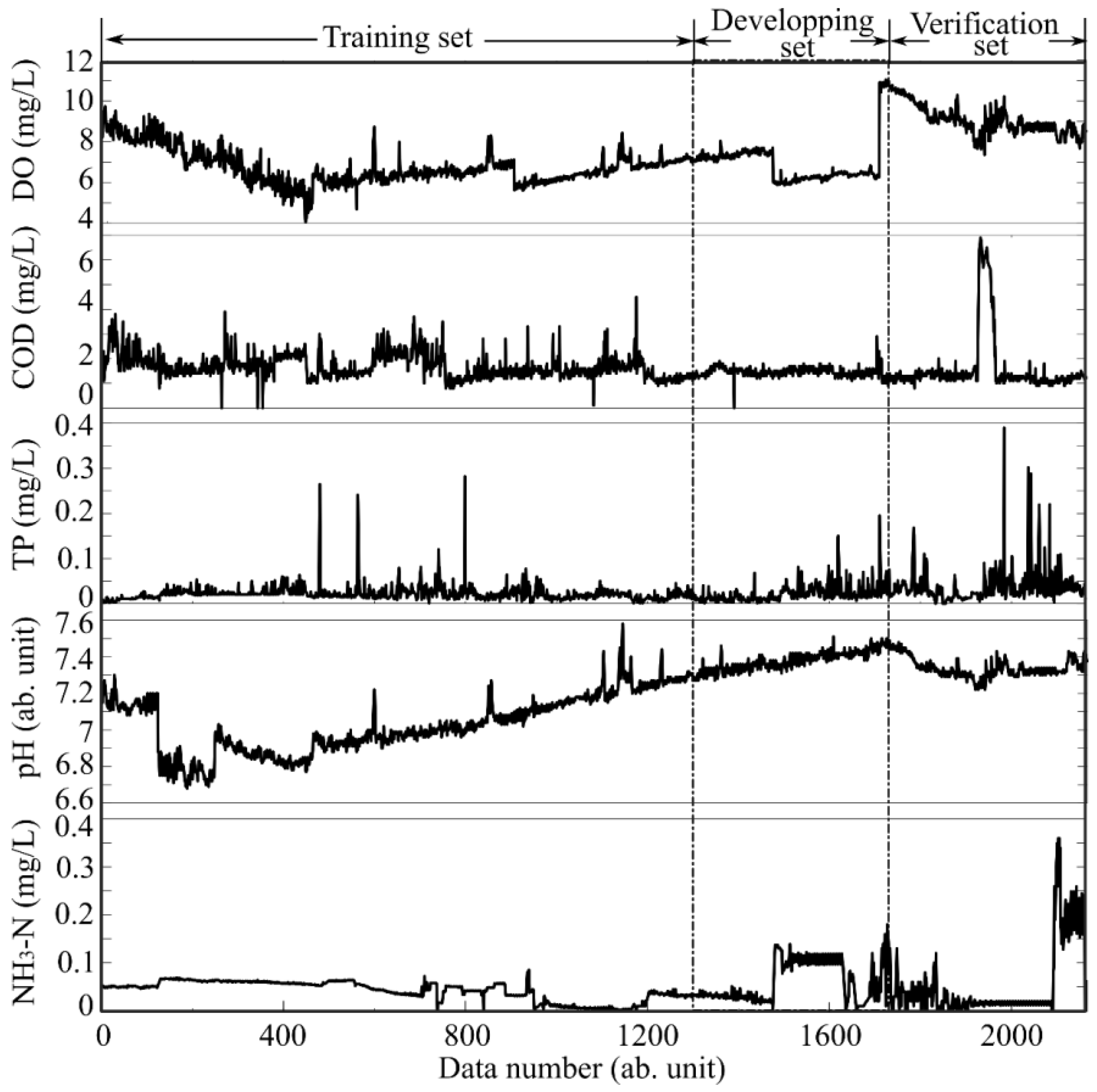
2.3. Materials
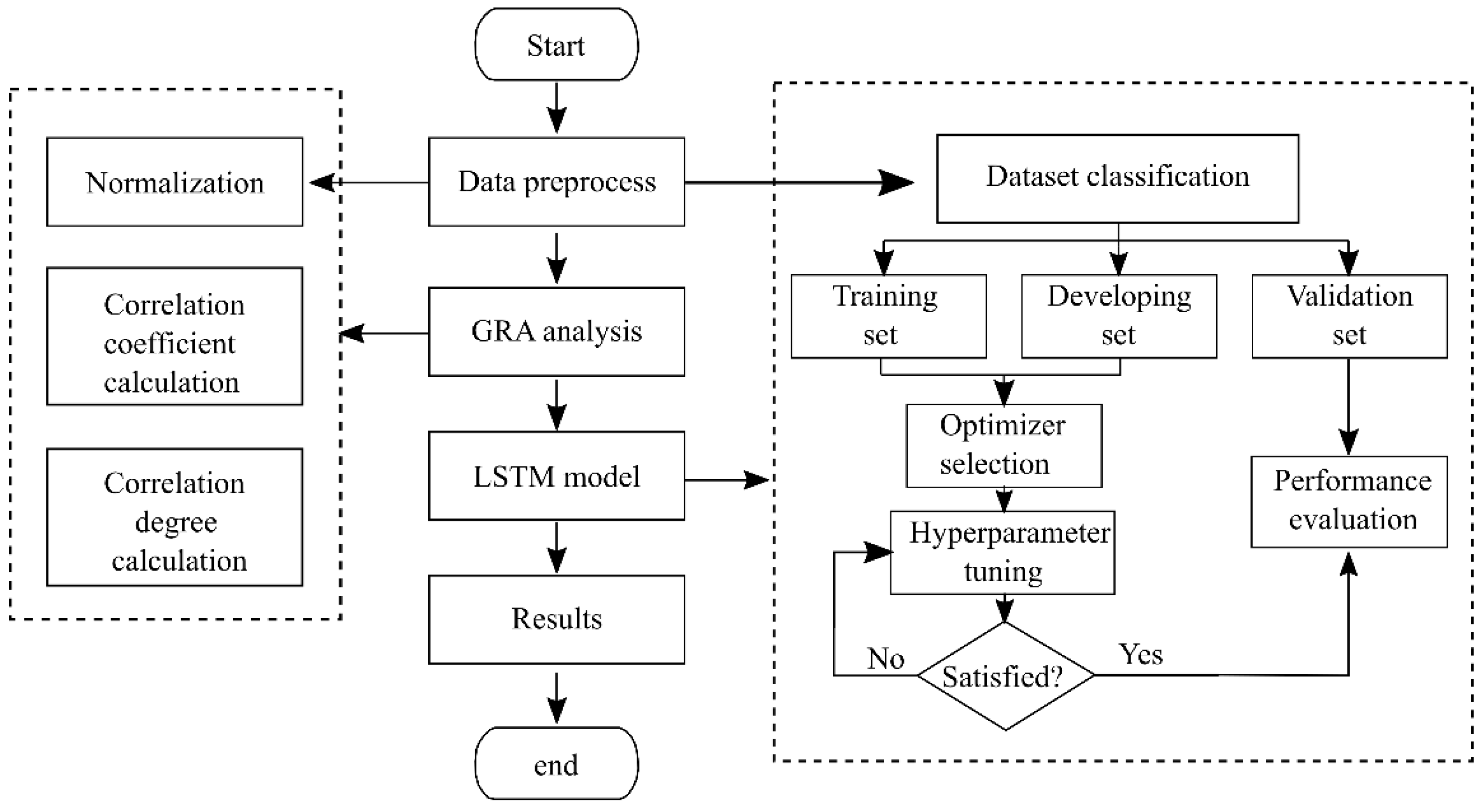
3. Modeling Flow
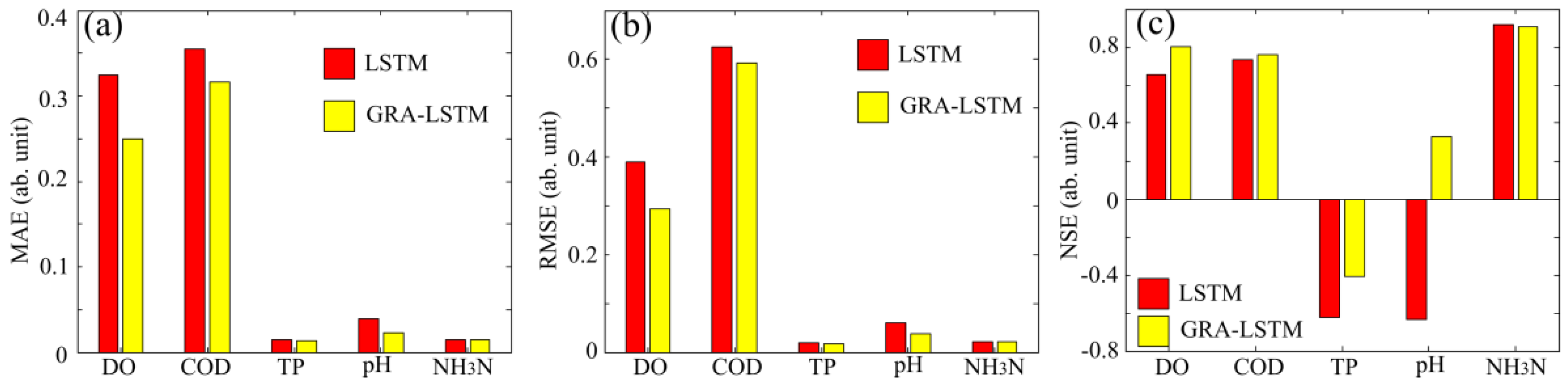
4. Results and Discussions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cao, J.; Sun, Q.; Zhao, D.; Xu, M.; Shen, Q.; Wang, D.; Wang, Y.; Ding, S. A critical review of the appearance of black-odorous waterbodies in China and treatment methods. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 385, 121511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Tai, H.; Ding, Q.; Li, D.; Xu, L.; Wei, Y. A hybrid approach of support vector regression with genetic algorithm optimization for aquaculture water quality prediction. Math. Comput. Model. 2013, 58, 458–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elçi, Ş. Effects of thermal stratification and mixing on reservoir water quality. Limnology 2008, 9, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karthik, L.; Kumar, G.; Keswani, T.; Bhattacharyya, A.; Chandar, S.S.; Bhaskara Rao, K.V. Optimised neural network model for river-nitrogen prediction utilizing a new training approach. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0239509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Liu, X.; Gao, D.; Ma, B.; Gao, X.; Cheng, M. Costs and benefits of the development methods of drinking water quality index: A systematic review. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 144, 109501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyralis, H.; Papacharalampous, G.; Langousis, A. A brief review of random forests for water scientists and practitioners and their recent history in water resources. Water 2019, 11, 910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eze, E.; Halse, S.; Ajmal, T. Developing a Novel Water Quality Prediction Model for a South African Aquaculture Farm. Water 2021, 13, 1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Ma, X. Hybrid decision tree-based machine learning models for short-term water quality prediction. Chemosphere 2020, 249, 126169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, H.R.; Dandy, G.C. The use of artificial neural networks for the prediction of water quality parameters. WRR 1996, 32, 1013–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yahya, A.S.A.; Ahmed, A.N.; Othman, F.B.; Ibrahim, R.K.; Afan, H.A.; El-Shafie, A.; Fai, C.M.; Hossain, S.; Ehteram, M.; Elshafie, A. Water quality prediction model based support vector machine model for ungauged river catchment under dual scenarios. Water 2019, 11, 1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Fang, G.; Huang, X.; Zhang, Y. Water quality prediction model of a water diversion project based on the improved artificial bee colony–backpropagation neural network. Water 2018, 10, 806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dauji, S.; Rafi, A. Spatial interpolation of SPT with artificial neural network. Eng. J. 2021, 25, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daosud, W.; Hussain, M.A.; Kittisupakorn, P. Neural network-based hybrid estimator for estimating concentration in ethylene polymerization process: An applicable approach. Eng. J. 2020, 24, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abiodun, O.I.; Jantan, A.; Omolara, A.E.; Dada, K.V.; Mohamed, N.A.; Arshad, H. State-of-the-art in artificial neural network applications: A survey. Heliyon 2018, 4, e00938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haghiabi, A.H.; Nasrolahi, A.H.; Parsaie, A. Water quality prediction using machine learning methods. WQRJ 2018, 53, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldhyani, T.H.H.; Al-Yaari, M.; Alkahtani, H.; Maashi, M. Water quality prediction using artificial intelligence algorithms. Appl. Bionics Biomech 2020, 2020, 6659314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, Z.; Liu, D. A comprehensive review of stability analysis of continuous-time recurrent neural networks. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2014, 25, 1229–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhi, N.; Kohen, E.; Mamane, H.; Shavitt, Y. Prediction of wastewater treatment quality using LSTM neural network. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 23, 101632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Lan, X.; Yao, H.; Zhou, H.; Tao, D.; Li, X. LSTM: A search space odyssey. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2016, 28, 2222–2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, Y.-L.; Chen, L. A nonlinear hybrid wind speed forecasting model using LSTM network, hysteretic ELM and Differential Evolution algorithm. Energy Convers. Manag. 2018, 173, 123–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasheed Abdul Haq, K.P.; Harigovindan, V.P. Water quality prediction for smart aquaculture using hybrid deep learning models. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 60078–60098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Wang, J.; Sangaiah, A.K.; Xie, Y.; Yin, X. Analysis and prediction of water quality using LSTM deep neural networks in IOT environment. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, S.F.; Dang, Y.G.; Fang, Z.G. Grey System Theory and Its Applications, 3rd ed.; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, X.; Du, J.; Liu, H.; Wang, Z.; Song, K. Remote estimation of soil organic matter content in the Sanjiang plain, Northeast China: The optimal band algorithm versus the GRA-ANN model. Agric. ForMeteorol. 2016, 218, 250–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, G.-W. GRA method for multiple attribute decision making with incomplete weight information in intuitionistic fuzzy setting. KBS 2010, 23, 243–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Jiang, P.; Xu, H.; Lin, G.; Guo, D.; Wu, H. Water quality prediction based on recurrent neural network and improved evidence theory: A case study of Qiantang River, China. ESPR 2019, 26, 19879–19896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ip, W.; Hu, B.; Wong, H.; Xia, J. Applications of grey relational method to river environment quality evaluation in China. J. Hydrol. 2009, 379, 284–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, G.W. Gray relational analysis method for intuitionistic fuzzy multiple attribute decision making. Expert Syst. Appl. 2011, 38, 11671–11677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yin, K. A new grey relational model based on discrete Fourier transform and its application on Chinese marine economic. MAEM 2018, 1, 79–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Wang, Y.; Xiao, F.; Wang, Y.; Sun, L. Water quality prediction method based on IGRA and LSTM. Water 2018, 10, 1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Julong, D. Introduction to grey system theory. J. Grey Syst. 1989, 1, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochreiter, S.; Schmidhuber, J. Long Short Term Memory. Neural Comput. 1997, 9, 1735–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valis, D.; Hasilova, K.; Forbelska, M.; Pietrucha-Urbanik, K. Modelling water distribution network failures and deterioration. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Industrial Engineering and Engineering Management, Singapore, 10–13 December 2017; pp. 924–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Water Quality Parameters | DO (mg/L) | NH3-N(mg/L) | pH | COD (mg/L) | TP (mg/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Minimum value | 4.05 | 0 | 6.68 | 0.8 | 0 |
| Maximum value | 11.05 | 0.36 | 7.58 | 6.90 | 0.39 |
| Average value | 7.24 | 0.048 | 7.16 | 1.62 | 0.025 |
| Standard deviation | 1.261 | 0.044 | 0.206 | 0.684 | 0.024 |
| Skewness | 0.819 | 2.762 | −0.394 | 4.082 | 6.111 |
| Hyperparameters | DO | NH3-N | pH | COD | TP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total number of LSTM layers | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| Number of neurons | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Attenuation coefficient | 0.8 | 0.1 | 0.6 | 0.6 | 0.1 |
| Learning rate | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | 0.001 |
| Patience values | 2 | 5 | 2 | 15 | 5 |
| Epoch | 200 | 200 | 200 | 200 | 200 |
| Batch size | 128 | 8 | 16 | 64 | 8 |
| Algorithm | LSTM | GRA-LSTM |
|---|---|---|
| Processor | Core i7-6700HQ CPU: 8 | Core i7-6700HQ CPU: 8 |
| Configurations | Windows 10 + python3.7 | Windows 10 + python3.7 |
| Calculation time | 220.5 s | 219.4 s |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tian, X.; Wang, Z.; Taalab, E.; Zhang, B.; Li, X.; Wang, J.; Ong, M.C.; Zhu, Z. Water Quality Predictions Based on Grey Relation Analysis Enhanced LSTM Algorithms. Water 2022, 14, 3851. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14233851
Tian X, Wang Z, Taalab E, Zhang B, Li X, Wang J, Ong MC, Zhu Z. Water Quality Predictions Based on Grey Relation Analysis Enhanced LSTM Algorithms. Water. 2022; 14(23):3851. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14233851
Chicago/Turabian StyleTian, Xiaoqing, Zhenlin Wang, Elias Taalab, Baofeng Zhang, Xiaodong Li, Jiyong Wang, Muk Chen Ong, and Zefei Zhu. 2022. "Water Quality Predictions Based on Grey Relation Analysis Enhanced LSTM Algorithms" Water 14, no. 23: 3851. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14233851
APA StyleTian, X., Wang, Z., Taalab, E., Zhang, B., Li, X., Wang, J., Ong, M. C., & Zhu, Z. (2022). Water Quality Predictions Based on Grey Relation Analysis Enhanced LSTM Algorithms. Water, 14(23), 3851. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14233851







