Nitrogen Mitigates Salt Stress and Promotes Wheat Growth in the Yellow River Delta, China
Abstract
:Highlights
- Nitrogen fertilizer (urea) application ameliorated salt damage and promoted the growth of wheat;
- 270 kg/ha nitrogen was the optimal dosage for wheat cultivation in soils of typical agricultural areas of the Yellow River delta.
- The finding is useful for rational utilization of nitrogen fertilizer and coastal saline agriculture development.
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
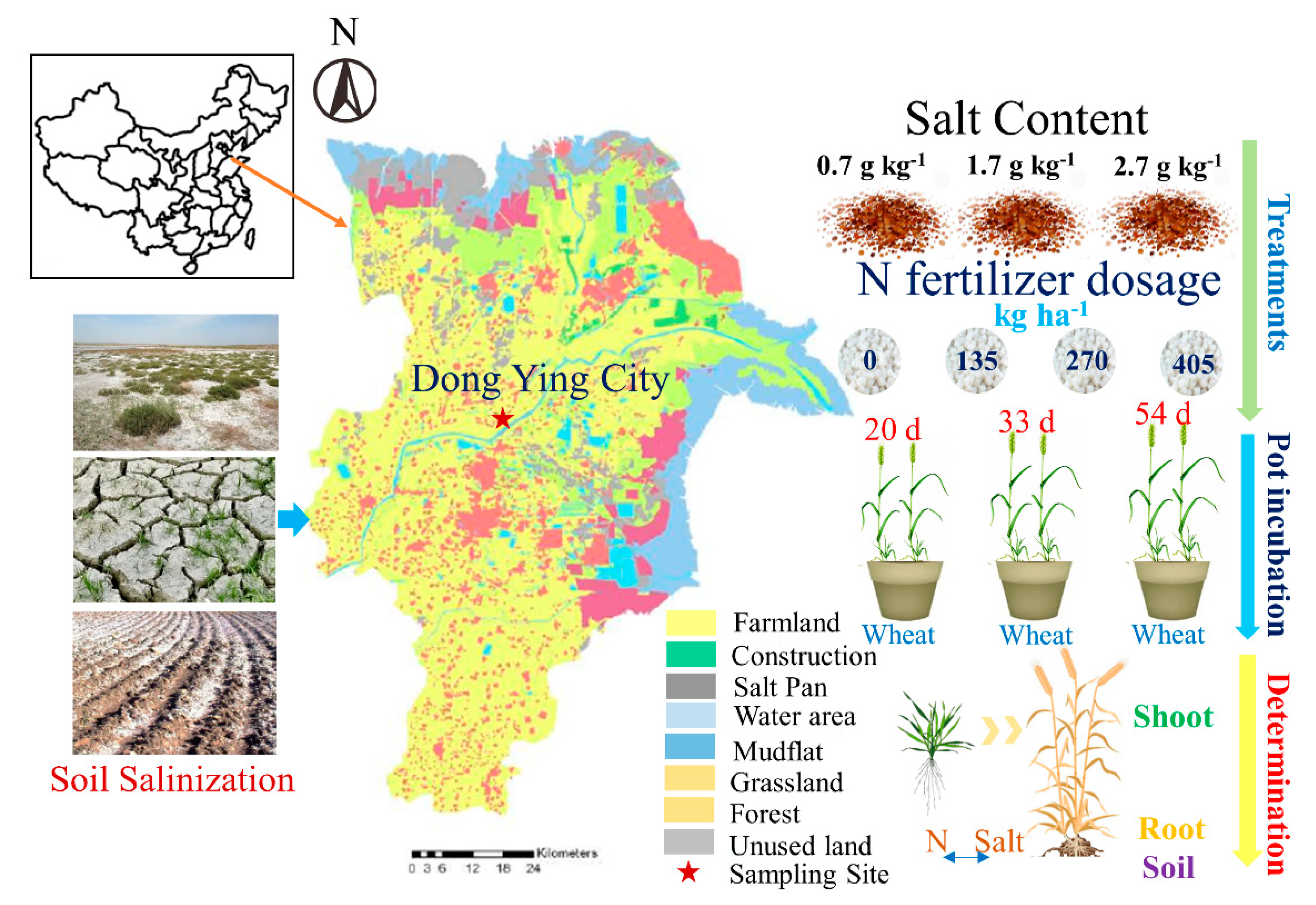
2.1. Sampling Site
2.2. Experiment Design
2.3. Data Collection
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Soil pH
3.2. Soil Total N and NO3−
3.3. Wheat Chlorophyll Content
3.4. N Concentration of Winter Wheat
3.5. Plant Height of Wheat
3.6. Wheat Weight
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of N Addition on Saline Soil Properties
4.2. Effects of N on Wheat Growth and Plant Nutrition in Saline Soil
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, L.; Bian, X.G.; Yang, R.P.; Zhou, C.L.; Tang, B.P. Assessment of organic amendments for improving coastal saline soil. Land Degrad. Dev. 2018, 29, 3204–3211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chele, K.H.; Tinte, M.M.; Piater, L.A.; Dubery, I.A.; Tugizimana, F. Soil Salinity, a Serious Environmental Issue and Plant Responses: A Metabolomics Perspective. Metabolites 2021, 11, 724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, X.F.; Pu, L.J.; Zhu, M.; Wu, T.; Xu, Y.; Wang, X.H. Effect of long-term reclamation on soil quality in agricultural reclaimed coastal saline soil, Eastern China. J. Soil Sediments 2020, 20, 3909–3920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Q.; Xia, J.B.; Yang, H.J.; Liu, J.T.; Shao, P.S. Biochar and effective microorganisms promote Sesbania cannabina growth and soil quality in the coastal saline-alkali soil of the Yellow River Delta, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 756, 143801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Wang, L.Q.; Zhou, C.J.; Shang, H.B. Sodium uptake and carbon/nitrogen metabolism by different w inter wheat genotypes during germination under salt. Chin. J. Eco-Agric. 2007, 15, 89–93. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Pu, L.; Zhu, M.; Zhang, R. The Present Situation and Hot Issues in the Salt-affected Soil Research. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2012, 67, 1233–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.K.; Shao, T.Y.; Lv, Z.X.; Yue, Y.; Liu, A.H.; Long, X.H.; Zhou, Z.S.; Gao, X.M.; Rengel, Z. The mechanisms of improving coastal saline soils by planting rice. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 703, 135529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Ji, M.C.; Yang, P.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, X. The Empirical Analysis on the Current Situation of Wheat Production in Shandong Province. J. Agric. 2014, 4, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francois, L.E.; Maas, E.V.; Donovan, T.J.; Youngs, V.L. Effect of salinity on grain-yield and quality, vegetative growth, and germination of semidwarf and durum-wheat. Agron. J. 1986, 78, 1053–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Wang, T.; Liu, K.S.; Wang, L.X.; Wang, K.; Zhou, Y. Effects of different amendments for the reclamation of coastal saline soil on soil nutrient dynamics and electrical conductivity responses. Agric. Water Manag. 2015, 159, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, J.; Wu, L.H.; Liu, X.J.; Zhang, H.; Xu, Y.J.; Gu, W.; Li, Y. Effect of Brackish Ice on Salt and Nutrient Contents of Saline Soil in Flue-Gas Desulfurization Gypsum Amended, Raised Bed Agroecosystem. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2014, 78, 1734–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.G.; Sun, R.B.; Tian, Y.P.; Guo, K.; Sun, H.Y.; Liu, X.J.; Chu, H.Y.; Liu, B.B. Long-Term Phytoremediation of Coastal Saline Soil Reveals Plant Species-Specific Patterns of Microbial Community Recruitment. mSystems 2020, 5, e00741-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhu, W.; Yang, J.S.; Yao, R.J.; Xie, W.P.; Wang, X.P.; Liu, Y.Q. Soil water-salt control and yield improvement under the effect of compound control in saline soil of the Yellow River Delta, China. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 263, 107455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cevheri, C.I.; Sakin, E.; Ramazanoglu, E. Effects of different fertilizers on some soil enzymes activity and chlorophyll contents of two cotton (G. hirsutum L.) varieties grown in a saline and non-saline soil. J. Plant Nutr. 2022, 45, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.L.; Xu, Z.R.; Xu, Y.M.; Lu, H.T.; Ji, Z.Y.; Zhou, G.S. Different Types of Fertilizers Enhanced Salt Resistance of Oat and Associated Physiological Mechanisms in Saline Soils. Agronomy 2022, 12, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.L.; Wang, Y.; Shi, X.X.; Lu, H.T.; Ren, Z.; Shi, Y.; Jiao, X.R.; Ibrahim, M.E.H.; Irshad, A.; Zhu, W.B.; et al. Optimum nitrogen management enhances growth, antioxidant ability and yield performance of rice in saline soil of coastal area of China. Chil. J. Agric. Res. 2020, 80, 629–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenelli, S.; Otto, R.; Bordonal, R.O.; Carvalho, J.L.N. How do nitrogen fertilization and cover crop influence soil C-N stocks and subsequent yields of sugarcane? Soil Tillage Res. 2021, 211, 104999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, F.; Wang, K.; Luo, Q.; Luo, C. Effects of NH4(+)-N/NO3(-)-N ratio in applied supplementary fertilizer on nitrogen metabolism, photosynthesis and growth of Isatis indigotica. China J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2009, 34, 2039–2042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.Z.; Yan, B.J.; Tan, F.Q.; Zhang, H.Q.; Ren, Z.L. Effect of Different Nitrogen Fertilizer Amount and Application Period on Wheat Quality. J. Triticeae Crops 2009, 29, 658–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Yang, S.; Yang, S.; Li, Y.; Liu, R.; Yang, Z. Effect of N Rates on Yield of Spring Wheat, Fertilizer N Recovery and N Balance. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull. 2009, 25, 137–142. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, F.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, W.; Chen, B.; Meng, Y.; Zhou, Z. Effect of N Application Rate on Growth, Yield and Fiber Quality of Cotton Grown in Saline Coastal Land. Cotton Sci. 2015, 27, 232–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.Q.; Liu, Z.P.; Cheng, A.W.; Shen, Q.R.; Chen, M.D. Influence of N and P fertilizers on sunflower grown in different saline soil on coast. Chin. J. Oil Crop Sci. 2002, 24, 61–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.x.; Gong, Y.s. Effect of Different Salinity and Nitrogen on Water and Nitrogen Use Efficiency of Spinach. Chin. J. Soil Sci. 2011, 42, 906–910. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Cao, G.; Li, X.; Zhang, H.; Wang, C.; Liu, Q.; Chen, X.; Cui, Z.; Shen, J.; Jiang, R.; et al. Closing yield gaps in China by empowering smallholder farmers. Nature 2016, 537, 671–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.P.; Hou, Z.A.; Wu, L.S.; Liang, Y.C.; Wei, C.Z. Effects of salinity and nitrogen on cotton growth in arid environment. Plant Soil 2010, 326, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Olsen, Y.S.; Dausse, A.; Garbutt, A.; Ford, H.; Thomas, D.N.; Jones, D.L. Cattle grazing drives nitrogen and carbon cycling in a temperate salt marsh. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2011, 43, 531–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apte, S.K.; Thomas, J. Possible amelioration of coastal soil salinity using halotolerant nitrogen-fixing cyanobacteria. Plant Soil 1997, 189, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, Z.; Wang, J.; Li, J.S. Determination of threshold soil salinity with consideration of salinity stress alleviation by applying nitrogen in the arid region. Irrig. Sci. 2022, 40, 283–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.M.; Li, W.J.; Xin, C.S.; Tang, W.; Eneji, A.E.; Dong, H.Z. Lint yield and nitrogen use efficiency of field-grown cotton vary with soil salinity and nitrogen application rate. Field Crops Res. 2012, 138, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daba, N.A.; Li, D.C.; Huang, J.; Han, T.F.; Zhang, L.; Ali, S.; Khan, M.N.; Du, J.X.; Liu, S.J.; Legesse, T.G.; et al. Long-Term Fertilization and Lime-Induced Soil pH Changes Affect Nitrogen Use Efficiency and Grain Yields in Acidic Soil under Wheat-Maize Rotation. Agronomy 2021, 11, 2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.J.; Zhang, Y.; Han, W.X.; Tang, A.H.; Shen, J.L.; Cui, Z.L.; Vitousek, P.; Erisman, J.W.; Goulding, K.; Christie, P.; et al. Enhanced nitrogen deposition over China. Nature 2013, 494, 459–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.D.; Ni, K.; Shi, Y.Z.; Yi, X.Y.; Zhang, Q.F.; Fang, L.; Ma, L.F.; Ruan, J.Y. Effects of long-term nitrogen application on soil acidification and solution chemistry of a tea plantation in China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2018, 252, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.F.; Gilliam, F.S.; Guo, J.Y.; Hou, E.Q.; Kuang, Y.W. Decrease in soil pH has greater effects than increase in above-ground carbon inputs on soil organic carbon in terrestrial ecosystems of China under nitrogen enrichment. J. Appl. Ecol. 2022, 59, 768–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peryea, F.J.; Burrows, R.L. Soil acidification caused by four commercial nitrogen fertilizer solutions and subsequent soil pH rebound. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 1999, 30, 525–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, M.; Hussain, F.; Ashraf, M.Y.; Qureshi, T.M.; Akhter, J.; Awan, A.R. Influence of Salinity on Nitrogen Transformations in Soil. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2012, 43, 1674–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irshad, M.; Honna, T.; Yamamoto, S.; Eneji, A.E.; Yamasaki, N. Nitrogen mineralization under saline conditions. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2005, 36, 1681–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izsaki, Z.; Ivanyi, I. Effect of N fertiliser on the nitrogen balance of the soil and on NO3-N leaching in a long-term mineral fertilisation experiment. Novenytermeles 2002, 51, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.Y.; Ma, J.A.; Chen, X.; Zhang, X.D.; Shi, Y.; Huang, B. Effect of Nitrogen Fertilizer and Maize Straw Incorporation on Nh4+-N-15 and No3--N-15 Accumulation in Black Soil of Northeast China among Three Consecutive Cropping Cycles. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2010, 10, 443–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Omar, S.A.; Ismail, M.A. Microbial populations, ammonification and nitrification in soil treated with urea and inorganic salts. Folia Microbiol. 1999, 44, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Li, Y.; Meng, Y.L.; Cao, N.; Li, D.S.; Zhou, Z.G.; Chen, B.L.; Dou, F.G. The effects of soil moisture and salinity as functions of groundwater depth on wheat growth and yield in coastal saline soils. J. Integr. Agric. 2019, 18, 2472–2482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.Y.A.; Ibrahim, M.E.H.; Zhou, G.S.; Zhu, G.L.; Elsiddig, A.M.I.; Suliman, M.S.E.; Elradi, S.B.M.; Salah, E.G.I. Interactive Impacts of Soil Salinity and Jasmonic Acid and Humic Acid on Growth Parameters, Forage Yield and Photosynthesis Parameters of Sorghum Plants. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2022, 146, 293–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Xie, Y.H.; Qin, Y.Y. Adaptive strategies of wetland plants in salt stress environment. Chin. J. Ecol. 2009, 28, 314–321. [Google Scholar]
- Shang, X.f. Effect of Salt Stress on Physiological Mechanism of Maize with Different Genotypes. Ph.D. Thesis, ShanDong Agriculture University, Tai’an, China, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, S.y.; Shang, X.f.; Wang, L.y.; Zhang, X.l. Changes of physiological characteristics and yield of different salt-sensitive maize under salt stress. Agric. Res. Arid. Areas 2010, 28, 109–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.M.; Jiang, Y.; Fu, M.M.; Zhang, Y.G.; Xu, Z.W. Effects of water addition and fertilization on soil nutrient contents and pH value of typical grassland in Inner Mongolia. Chin. J. Ecol. 2011, 30, 1642–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.Y.; Zhao, Y.M. Effects of NaCl Stress on Seed Germination and Seedling Growth of Waxy Corn. Plant Physiol. Commun. 2010, 46, 291–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, N.; Khaddar, V.K. A Study on the Effects of Soil-Salinity, Sodicity and Their Combinations on Early Seedling Growth in Wheat. J. Environ. Biol. 1995, 16, 193–199. [Google Scholar]
- Ghafoor, A.; Murtaza, G.; Rehman, M.Z.; Saifullah; Sabir, M. Reclamation and salt leaching efficiency for tile drained saline-sodic soil using marginal quality water for irrigating rice and wheat crops. Land Degrad. Dev. 2012, 23, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Liu, B.J.; Zhang, Y.H.; Lin, Z.B.; Zhu, T.B.; Sun, R.B.; Wang, X.J.; Ma, J.; Bei, Q.C.; Liu, G.; et al. Can biochar alleviate soil compaction stress on wheat growth and mitigate soil N2O emissions? Soil Biol. Biochem. 2017, 104, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marosz, A. Effect of fulvic and humic organic acids and calcium on growth and chlorophyll content of tree species grown under salt stress. Dendrobiology 2009, 62, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Sand | 67% |
| Silt | 27% |
| Clay | 6% |
| pH1:5 | 8.65 |
| Total salt | 0.7 g/kg |
| Bulk density | 1.3 g/cm3 |
| Organic matter | 10.35 g/kg |
| Total N | 0.957 g/kg |
| Available P | 11.8 mg/kg |
| Available K | 20 mg/kg |
| Number | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Treatment | N0S1 | N0S2 | N0S3 | N1S1 | N1S2 | N1S3 | N2S1 | N2S2 | N2S3 | N3S1 | N3S2 | N3S3 |
| pH/Time | N Rate | 20 Days | 33 Days | 54 Days | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | S2 | S3 | S1 | S2 | S3 | S1 | S2 | S3 | ||
| Soil pH | N0 | 8.45 a | 8.407 ab | 8.40 ab | 8.60 a | 8.46 bc | 8.37 e | 8.59 def | 8.52 ef | 8.43 f |
| N1 | 8.40 ab | 8.33 bc | 8.24 cd | 8.48 d | 8.42 cd | 8.37 e | 8.65 cdef | 8.51 def | 8.43 ab | |
| N2 | 8.34 b | 8.23 cd | 8.18 d | 8.40 de | 8.36 e | 8.29 f | 8.64 ab | 8.47 ab | 8.41 cd | |
| N3 | 8.32 bc | 8.24 cd | 8.22 d | 8.37 e | 8.30 f | 8.28 f | 8.56 bc | 8.39 ab | 8.33 cde | |
| N rate | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.001 | |||||||
| Salinity | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | |||||||
| N rate × salinity | 0.556 | 0.003 | 0.601 | |||||||
| Soil N | N Rate | 20 Days | 33 Days | 54 Days | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | S2 | S3 | S1 | S2 | S3 | S1 | S2 | S3 | ||
| Total N (g/kg) | N0 | 0.92 cde | 0.904 e | 0.912 de | 0.933 c | 0.937 c | 0.926 c | 0.643 e | 0.617 e | 0.663 e |
| N1 | 0.94 c | 0.930 cd | 0.929 cd | 0.941 bc | 0.941 bc | 0.972 ab | 0.844 d | 0.847 d | 0.809 c | |
| N2 | 1.00 b | 1.04 a | 1.02 ab | 0.974 a | 0.972 ab | 0.974 a | 0.659 c | 0.844 b | 0.861 b | |
| N3 | 1.03 ab | 1.03 a | 1.02 ab | 0.989 a | 1.00 a | 0.997 a | 1.07 a | 1.075 a | 1.06 a | |
| N rate | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.001 | |||||||
| Salinity | 0.000 | 0.595 | 0.033 | |||||||
| N rate × salinity | 0.556 | 0.520 | 0.005 | |||||||
| NO3− (mg/kg) | N0 | 13.6 d | 11.5 d | 12.4 d | 1.99 e | 2.68 e | 3.89 d | 1.25 a | 1.91 a | 1.95 a |
| N1 | 28.5 c | 31.7 c | 30.7 c | 14.8 c | 17.4 c | 17.4 c | 8.95 a | 8.96 a | 7.96 a | |
| N2 | 54.53 ab | 50.2 b | 48.3 b | 24.0 b | 29.8 b | 36.7 a | 19.0 a | 16.9 a | 19.0 a | |
| N3 | 66.8 a | 70.8 a | 60.5 ab | 44.5 a | 43.5 a | 45.1 a | 31.0 a | 31.0 a | 28.9 a | |
| N rate | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.598 | |||||||
| Salinity | 0.642 | 0.001 | 0.775 | |||||||
| N rate × salinity | 0.771 | 0.132 | 0.998 | |||||||
| Parameter | N Rate | 20 Days | 33 Days | 54 Days | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | S2 | S3 | S1 | S2 | S3 | S1 | S2 | S3 | ||
| Chlorophyll content (mg/g) | N0 | 0.033 c | 0.097 b | 0.097 a | 0.299 a | 0.266 a | 0.232 a | 0.169 f | 0.216 e | 0.253 cd |
| N1 | 0.097 a | 0.097 a | 0.097 a | 0.242 a | 0.277 a | 0.276 a | 0.249 de | 0.292 abc | 0.329 a | |
| N2 | 0.096 a | 0.096 a | 0.097 a | 0.249 a | 0.239 a | 0.222 a | 0.250 de | 0.303 ab | 0.305 ab | |
| N3 | 0.097 a | 0.096 a | 0.096 a | 0.2263 a | 0.224 a | 0.242 a | 0.269 bcd | 0.326 a | 0.317 a | |
| N rate | 0.000 | 0.303 | 0.000 | |||||||
| Salinity | 0.000 | 0.844 | 0.000 | |||||||
| N rate × salinity | 0.000 | 0.659 | 0.255 | |||||||
| Total N (g/pot) | N Rate | 20 Days | 33 Days | 54 Days | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | S2 | S3 | S1 | S2 | S3 | S1 | S2 | S3 | ||
| Shoot | N0 | 0.034 d | 0.038 cd | 0.038 cd | 0.036 d | 0.038 cd | 0.040 bcd | 0.016 e | 0.018 de | 0.020 cde |
| N1 | 0.042 abc | 0.042 abc | 0.040 bcd | 0.050 abc | 0.045 abc | 0.043 bcd | 0.025 abcd | 0.027 abc | 0.028 ab | |
| N2 | 0.049 a | 0.043 abc | 0.044 abc | 0.044 a | 0.042 abc | 0.041 abc | 0.030 a | 0.031 a | 0.032 a | |
| N3 | 0.046 ab | 0.041 bcd | 0.039 bcd | 0.043 ab | 0.043 bcd | 0.040 bcd | 0.032 a | 0.032 a | 0.022 bcde | |
| N rate | 0.679 | 0.622 | 0.000 | |||||||
| Salinity | 0.684 | 0.267 | 0.922 | |||||||
| N rate × salinity | 0.356 | 0.030 | 0.147 | |||||||
| Root | N0 | 0.018 a | 0.019 a | 0.020 a | 0.010 c | 0.012 abc | 0.011 bc | 0.007 d | 0.007 d | 0.007 d |
| N1 | 0.019 a | 0.020 a | 0.018 a | 0.011 bc | 0.012 abc | 0.012 abc | 0.011 c | 0.012 bc | 0.014 ab | |
| N2 | 0.020 a | 0.016 a | 0.017 a | 0.0140 a | 0.011 bc | 0.011 bc | 0.016 a | 0.015 a | 0.015 a | |
| N3 | 0.019 a | 0.016 a | 0.020 a | 0.013 ab | 0.011 bc | 0.010 c | 0.015 a | 0.014 ab | 0.014 ab | |
| N rate | 0.679 | 0.622 | 0.000 | |||||||
| Salinity | 0.684 | 0.267 | 0.922 | |||||||
| N rate × salinity | 0.356 | 0.030 | 0.147 | |||||||
| Parameter | N Rate | 20 Days | 33 Days | 54 Days | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | S2 | S3 | S1 | S2 | S3 | S1 | S2 | S3 | ||
| PSH (cm) | N0 | 5.74 abc | 5.08 cde | 5.08 de | 7.55 abcd | 7.26 abc | 7.02 abcd | 7.12 def | 6.99 ef | 6.92 f |
| N1 | 6.13 a | 5.51 abcd | 4.728 e | 7.24 abc | 7.22 abc | 6.85 bc | 7.18 cdef | 7.99 def | 8.07 ab | |
| N2 | 5.89 ab | 5.34 bce | 4.75 e | 7.26 abc | 7.18 abcd | 6.58 d | 8.09 ab | 7.51 ab | 7.63 cd | |
| N3 | 5.67 abcd | 5.43 cd | 4.79 e | 7.41 ab | 7.07 abcd | 6.71 cd | 8.34 bc | 7.46 ab | 7.25 cde | |
| N rate | 0.85 | 0.43 | 0.000 | |||||||
| Salinity | 0.000 | 0.002 | 0.16 | |||||||
| N rate × salinity | 0.55 | 0.95 | 0.00 | |||||||
| Dry Weight (g/pot) | N Rate | 20 Days | 33 Days | 54 Days | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | S2 | S3 | S1 | S2 | S3 | S1 | S2 | S3 | ||
| Shoot | N0 | 0.023 ab | 0.020 bc | 0.022 abc | 0.079 abc | 0.066 cde | 0.076 abcd | 0.176 de | 0.195 bcde | 0.179 cde |
| N1 | 0.023 ab | 0.028 a | 0.021 bc | 0.080 abc | 0.083 ab | 0.067 cde | 0.234 abc | 0.225 abcd | 0.176 cde | |
| N2 | 0.026 ab | 0.025 ab | 0.021 abc | 0.090 a | 0.078 abcd | 0.059 e | 0.255 a | 0.247 ab | 0.204 abcd | |
| N3 | 0.022 abc | 0.021 bc | 0.017 c | 0.088 ab | 0.074 bcd | 0.064 de | 0.226 abcd | 0.213 abcd | 0.136 c | |
| N rate | 0.069 | 0.918 | 0.019 | |||||||
| Salinity | 0.074 | 0 | 0.003 | |||||||
| N rate × salinity | 0.519 | 0.041 | 0.457 | |||||||
| Root | N0 | 0.010 cd | 0.012 abcd | 0.009 d | 0.041 a | 0.031 a | 0.035 a | 0.097 abc | 0.103 ab | 0.106 a |
| N1 | 0.010 cd | 0.013 abcd | 0.013 abc | 0.035 a | 0.033 a | 0.032 a | 0.105 a | 0.087 abcde | 0.058 ef | |
| N2 | 0.009 d | 0.013 abc | 0.014 ab | 0.037 a | 0.040 a | 0.033 a | 0.108 a | 0.091 abcd | 0.062 def | |
| N3 | 0.010 bcd | 0.0120 bcd | 0.014 a | 0.042 a | 0.038 a | 0.036 a | 0.074 bcdef | 0.070 cdef | 0.045 f | |
| N rate | 0.175 | 0.501 | 0.001 | |||||||
| Salinity | 0.007 | 0.341 | 0.002 | |||||||
| N rate × salinity | 0.35 | 0.851 | 0.193 | |||||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, Y.; Chen, X.; Shan, J.; Xian, J.; Cao, D.; Luo, Y.; Yao, R.; Zhang, X. Nitrogen Mitigates Salt Stress and Promotes Wheat Growth in the Yellow River Delta, China. Water 2022, 14, 3819. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14233819
Sun Y, Chen X, Shan J, Xian J, Cao D, Luo Y, Yao R, Zhang X. Nitrogen Mitigates Salt Stress and Promotes Wheat Growth in the Yellow River Delta, China. Water. 2022; 14(23):3819. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14233819
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Yunpeng, Xiaobing Chen, Jingjing Shan, Jingtian Xian, Dan Cao, Yongming Luo, Rongjiang Yao, and Xin Zhang. 2022. "Nitrogen Mitigates Salt Stress and Promotes Wheat Growth in the Yellow River Delta, China" Water 14, no. 23: 3819. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14233819
APA StyleSun, Y., Chen, X., Shan, J., Xian, J., Cao, D., Luo, Y., Yao, R., & Zhang, X. (2022). Nitrogen Mitigates Salt Stress and Promotes Wheat Growth in the Yellow River Delta, China. Water, 14(23), 3819. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14233819






