The Baltic Sea under Anthropopressure—The Sea of Paradoxes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Approach
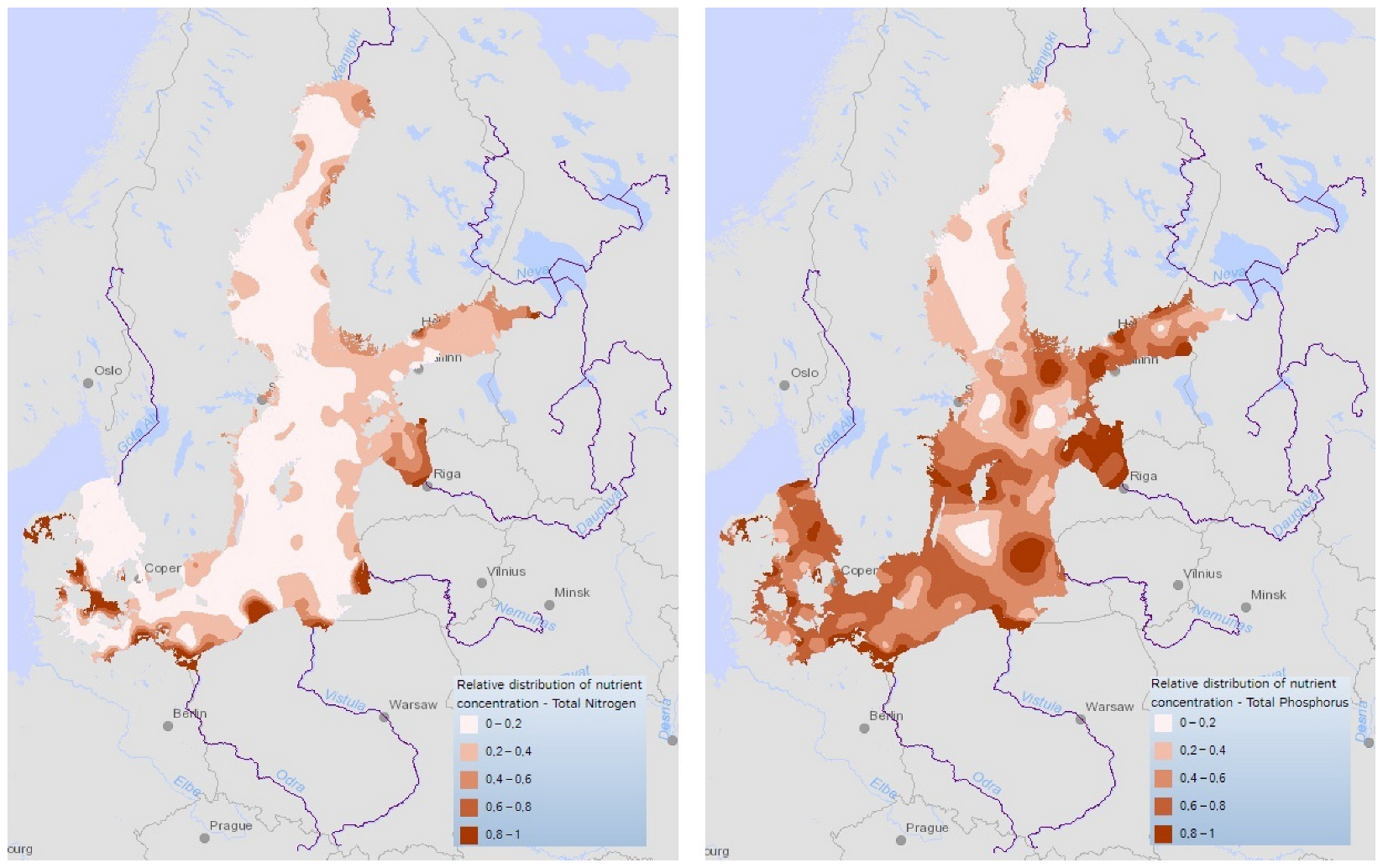
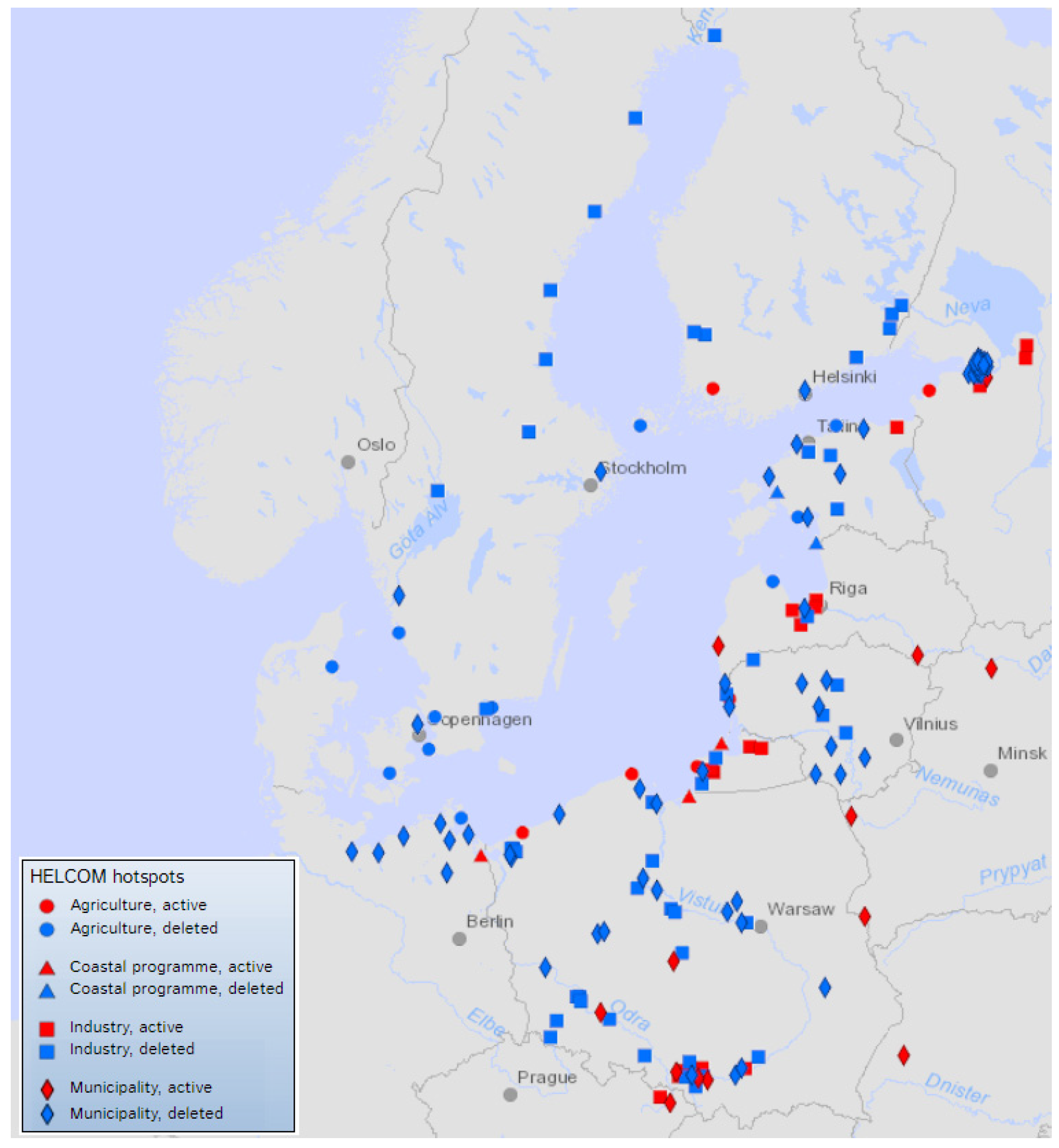
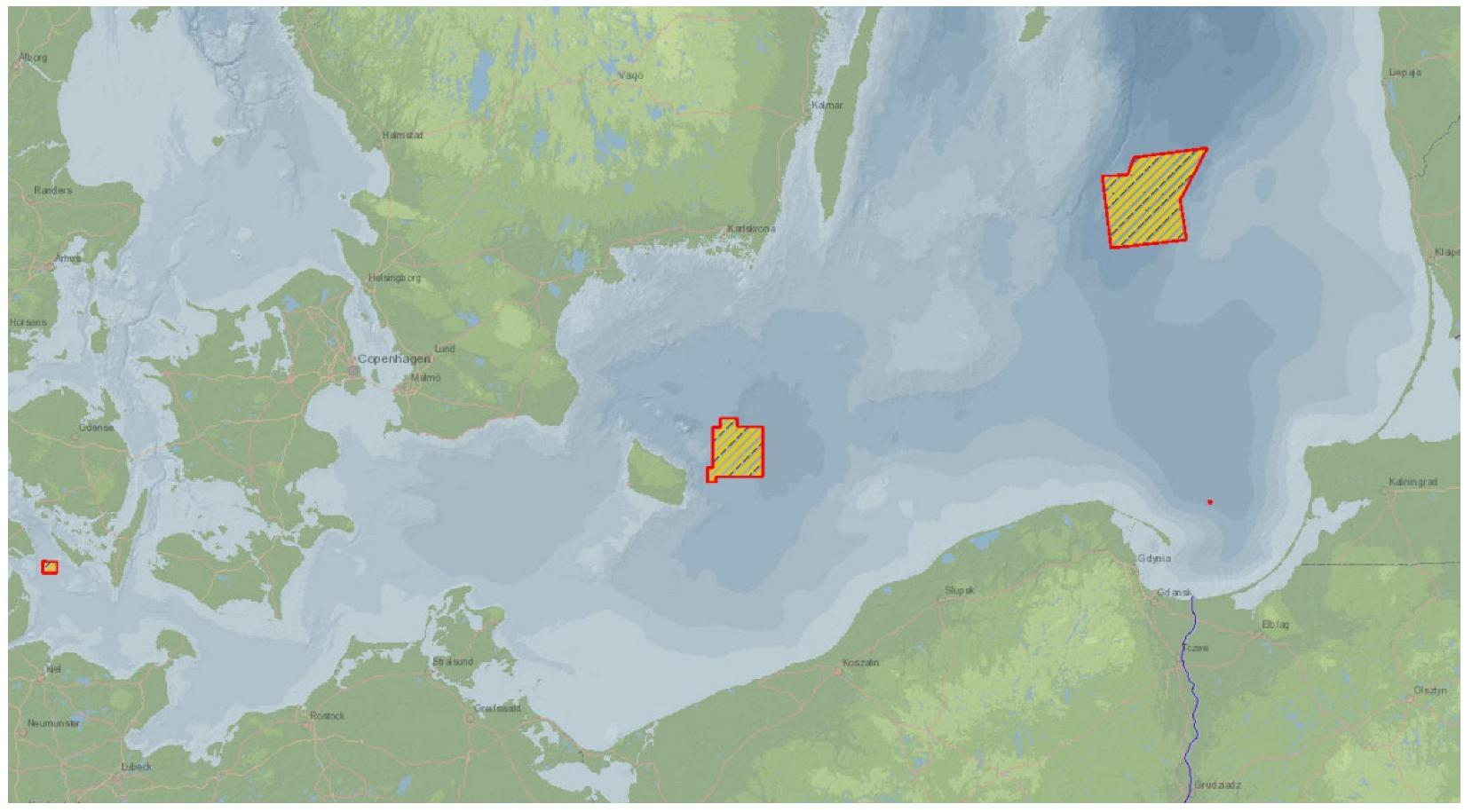
3. The Paradox of Marine Pollution
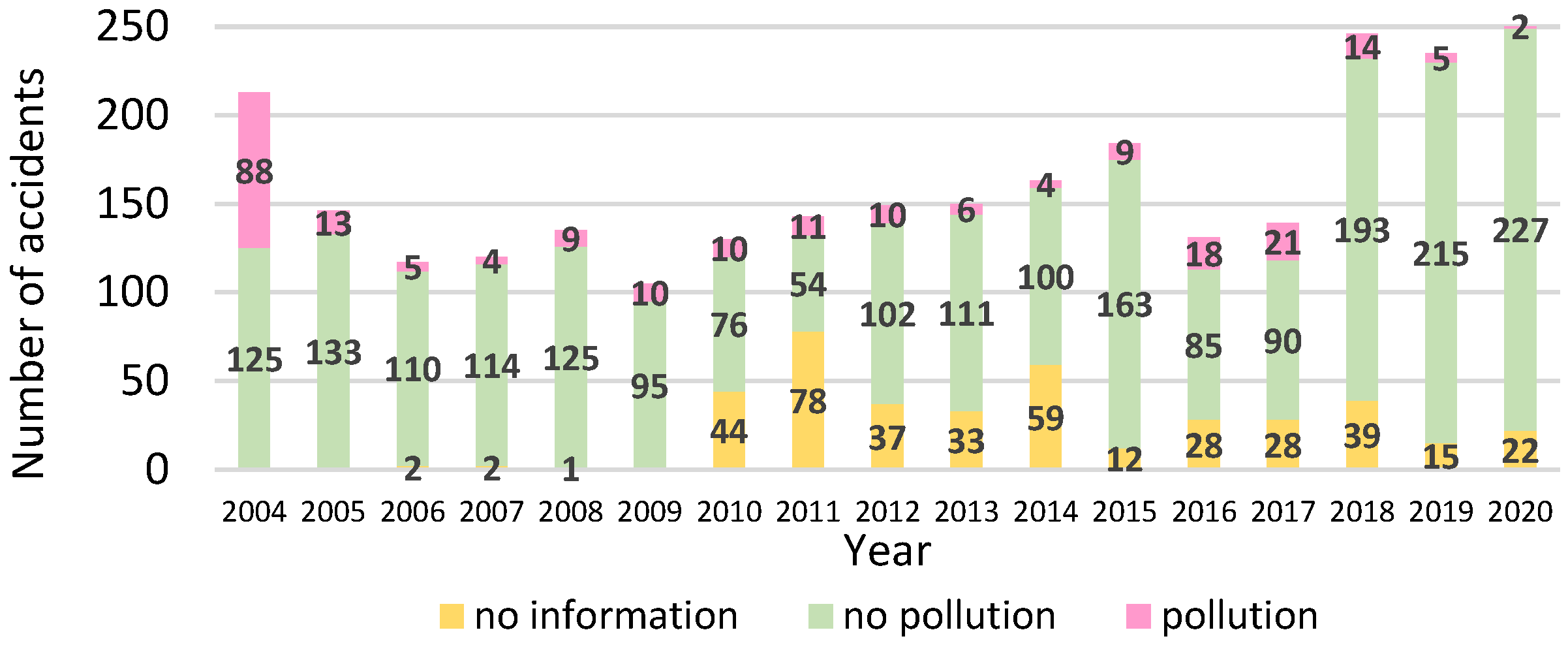
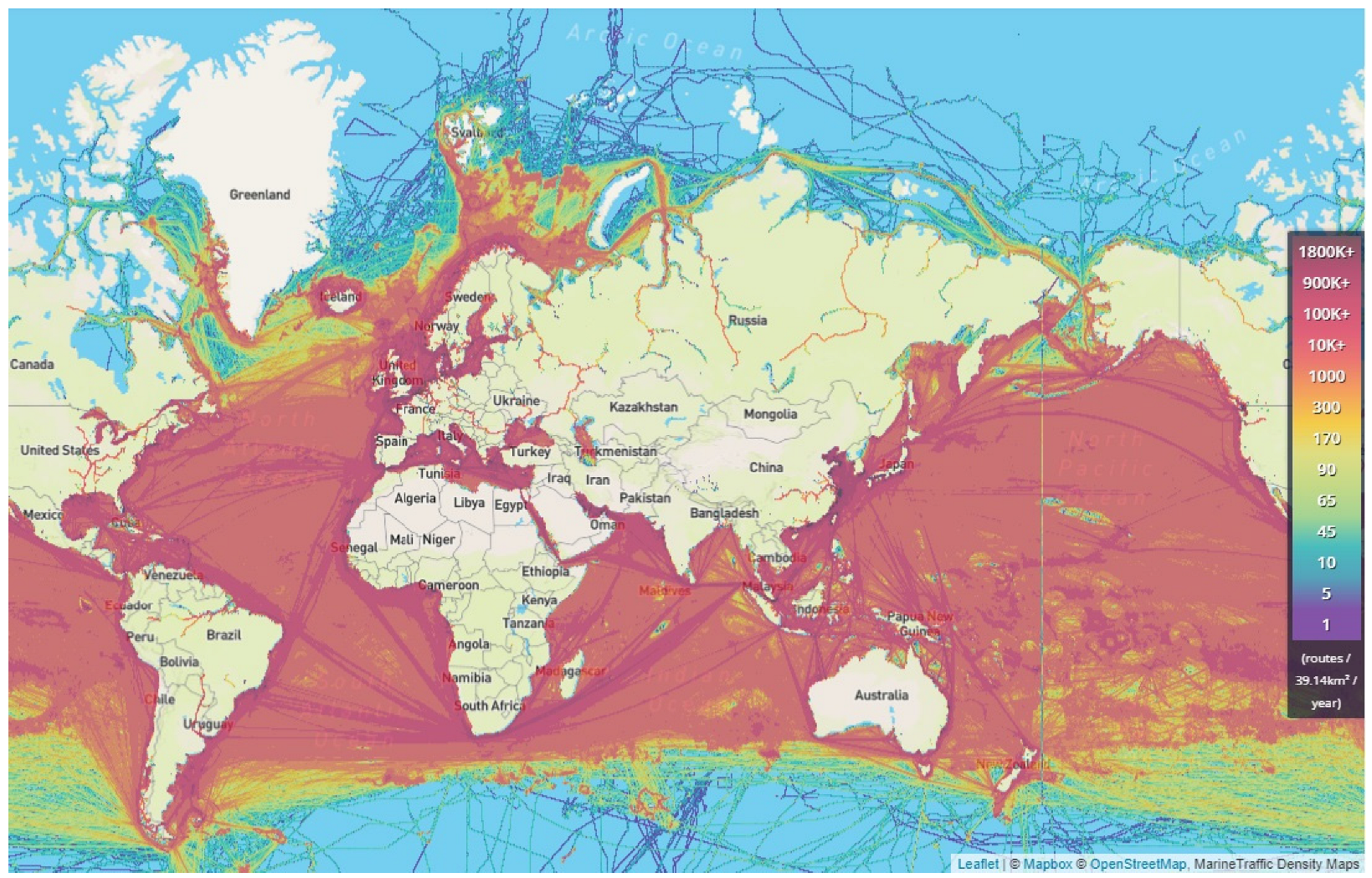
4. The Paradox of Traffic Intensity and Maritime Accidents
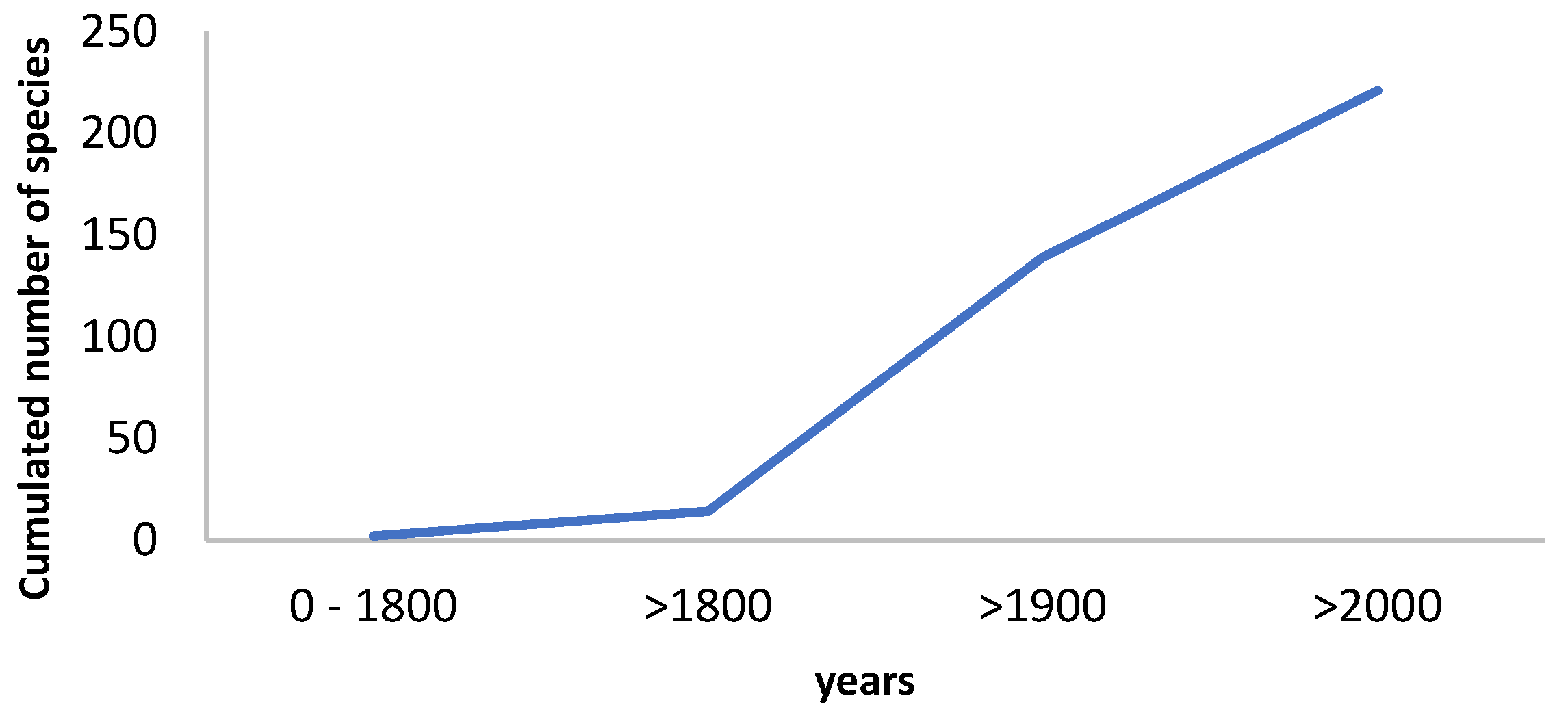
5. The Paradox of the Number of Species
6. The Paradox of Living Marine Resources
7. The Paradox of Sea Bathing
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ryden, L.; Migula, P.; Andersson, M. (Eds.) Environmental Science—Understanding, Protection, and Managing the Environment in the Baltic Sea Region; The Baltic University Press: Uppsala, Sweden, 2003; ISBN 91-970017-0-8. [Google Scholar]
- HELCOM. The Baltic marine environment 1999–2002. Balt. Sea Environ. Proc. 2003, 87. Available online: https://helcom.fi/wp-content/uploads/2019/10/BSEP87.pdf (accessed on 23 September 2022).
- Bogalecka, M.; Kołowrocki, K. The Baltic Sea circumstances for its critical infrastructure networks. J. Pol. Saf. Reliab. Assoc. Summer Saf. Reliab. Semin. 2016, 7, 37–41. [Google Scholar]
- HELCOM. Ecosystem health of the Baltic Sea 2003–2007. Balt. Sea Environ. Proc. 2010, 122. Available online: https://helcom.fi/wp-content/uploads/2019/08/BSEP122.pdf (accessed on 23 September 2022).
- HELCOM Map and Data Service. Available online: https://maps.helcom.fi/website/mapservice/index.html (accessed on 23 September 2022).
- Marine Traffic. Available online: https://marinetraffic.com (accessed on 23 September 2022).
- AquaNIS. Information System on Aquatic Non-Indigenous and Cryptogenic Species. Available online: http://www.corpi.ku.lt/databases/index.php/aquanis (accessed on 13 July 2022).
- Pietrucha-Urbanik, K.; Rak, J.R. Consumers’ perceptions of the supply of tap water in crisis situations. Energies 2020, 13, 3617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rheinheimer, G. Pollution in the Baltic Sea. Naturwissenschaften 1998, 85, 318–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dereszewska, A.; Cytawa, S. Sustainability considerations in the operation of wastewater treatment plant ‘Swarzewo’. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2016, 214, 012060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Efroymson, R.A.; Jones, D.S.; Gold, A.J. An ecological risk assessment framework for effects of onsite wastewater treatment systems and other localized sources of nutrients on aquatic ecosystem. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. 2007, 13, 574–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchobanoglous, G.; Stensel, D.; Tsuchihashi, R.; Burton, F. Wastewater Engineering. Treatment and Resource Recovery, 5th ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2014; ISBN 978-0073401188. [Google Scholar]
- HELCOM. Input of nutrients by the seven biggest rivers in the Baltic Sea region 1995–2017. Balt. Sea Environ. Proc. 2021, 178. Available online: http://www.vandensnamai.eu/3368-2/ (accessed on 23 September 2022).
- Setäläa, O.; Fleming-Lehtinen, V.; Lehtiniemi, M. Ingestion and transfer of microplastics in the planktonic food web. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 185, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auta, H.S.; Emenike, C.U.; Fauziah, S.H. Distribution and importance of microplastics in the marine environment: A review of the sources, fate, effects, and potential solutions. Environ. Int. 2017, 102, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristaldi, A.; Fiore, M.; Zuccarello, P.; Conti, G.O.; Grasso, A.; Nicolosi, I.; Copat, C.; Ferrant, M. Efficiency of wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs) for microplastic removal: A systematic review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 8014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beer, S.; Garm, A.; Huwer, A.; Dierking, J.; Nielsen, T.G. No increase in marine microplastic concentration over the last three decades—A case study from the Baltic Sea. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 621, 1272–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krasowska, K.; Dereszewska, A.; Popek, M. Preliminary approach to ecological risk assessment of microplastics in selected coastal regions of Baltic Sea. In Safety and Reliability of Systems and Processes, Summer Safety and Reliability Seminar 2022, Ciechocinek, Poland, 8–11 September 2022; Kołowrocki, K., Bogalecka, M., Dąbrowska, E., Magryta-Mut, B., Eds.; Gdynia Maritime University: Gdynia, Poland, 2022; pp. 133–142. ISBN 978-83-7421-421-6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pigłowski, M. Hazards to seafood notified in the rapid alert system for food and feed. Water, 2022; submitted. [Google Scholar]
- Graca, B.; Szewc, K.; Zakrzewska, D.; Dołęga, A.; Szczerbowska-Boruchowska, M. Sources and fate of microplastics in marine and beach sediments of the Southern Baltic Sea—A preliminary study. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 7650–7661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinja, N.; Setäläa, O.; Lehtiniemia, M. Bioturbation transports secondary microplastics to deeper layers in soft marine sediments of the northern Baltic Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 119, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Esiukova, E.; Zobkov, M.; Chubarenko, I. Data on microplastic contamination of the Baltic Sea bottom sediment samples in 2015–2016. Data Br. 2020, 28, 104887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urban-Malinga, B.; Zalewski, M.; Jakubowska, A.; Wodzinowski, T.; Malinga, M.; Pałys, B.; Dąbrowska, A. Microplastics on sandy beaches of the southern Baltic Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 155, 111170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schernewski, G.; Radtke, H.; Hauk, R.; Baresel, C.; Olshammar, M.; Osinski, R.; Oberbeckmann, S. Transport and behavior of microplastics emissions from urban sources in the Baltic Sea. Front. Environ. Sci. 2020, 8, 579361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aigars, J.; Barone, M.; Suhareva, N.; Putna-Nimane, I.; Dimante-Deimantovica, I. Occurrence and spatial distribution of microplastics in the surface waters of the Baltic Sea and the Gulf of Riga. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 172, 112860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uurasjärvi, E.; Pääkkönen, M.; Setälä, O.; Koistinen, A.; Lehtiniemi, M. Microplastics accumulate to thin layers in the stratified Baltic Sea. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 268, 115700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krasowska, K.; Heimowska, A. Behaviour of polylactide during degradation in natural aqueous environments. Water, 2022; submitted. [Google Scholar]
- Krasowska, K.; Brzeska, J.; Rutkowska, M.; Janik, H.; Sreekala, M.S.; Goda, K.; Thomas, S. Environmental degradation of ramie fibre reinforced biocomposites. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2010, 19, 937–945. [Google Scholar]
- Brzeska, J.; Heimowska, A.; Janeczek, H.; Kowalczuk, M.; Rutkowska, M. Polyurethanes based on atactic poly[(R,S)-3-hydroxybutyrate]: Preliminary degradation studies in simulated body fluids. J. Polym. Environ. 2014, 22, 176–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heimowska, A.; Krasowska, K. Influence of different environments on degradation of composites with natural fibre. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2019, 214, 012060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heimowska, A.; Morawska, M.; Bocho-Janiszewska, A. Biodegradation of poly(e-caprolactone) in natural water environments. Pol. J. Chem. Technol. 2017, 19, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Popek, M.; Dereszewska, A.; Dembska, G.; Pazikowska-Sapota, G. The impact of transport on the quality of water in the Port of Gdynia. TransNav 2022, 16, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, M. Atmospheric Emissions from Large Point Sources in Europe; Swedish NGO Secretariat on Acid Rain: Göteborg, Sweden, 2004; ISBN 919-736-918-7. [Google Scholar]
- Sonesten, L.; Undeman, E.; Svendsen, M.L.; Frank-Kamenetsky, D.; Haapaniemi, J. Inputs of hazardous substances to the Baltic Sea. Balt. Sea Environ. Proc. 2021, 179. Available online: https://helcom.fi/wp-content/uploads/2019/08/BSEP162.pdf (accessed on 23 September 2022).
- Basic Information about Pesticide Ingredients. Environmental Protection Agency. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/ingredients-used-pesticide-products/basic-information-about-pesticide-ingredients (accessed on 13 July 2022).
- McLachlan, M.; Undeman, E. Dioxins and PCBs in the Baltic Sea. Balt. Sea Environ. Proc. 2020, 171. Available online: https://helcom.fi/wp-content/uploads/2020/06/Helcom_171_Dioxins_PCBs.pdf (accessed on 23 September 2022).
- Sonnenberg, J. Shoot to kill: Control and controversy in the history of DDT science. Stanf. J. Public Health 2015. Available online: https://web.stanford.edu/group/sjph/cgi-bin/sjphsite/shoot-to-kill-control-and-controversy-in-the-history-of-ddt-science/ (accessed on 23 September 2022).
- De Zulueta, J. The end of malaria in Europe: An eradication of the disease by control measures. Parassitologia 1998, 40, 245–246. [Google Scholar]
- WHO. DDT and its Derivatives: Environmental Aspects, Environmental Health Criteria monograph No. 83; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1989; ISBN 924-154-283-7.
- Bidleman, T.F.; Jantunen, L.M.; Kurt-Karakus, P.B.; Wong, F. Chiral compounds as tracers of atmospheric sources and fate: Review and prospects for investigating climate change influences. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2012, 3, 371–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bidleman, T.; Agosta, K.; Andersson, A.; Brorström-Lundén, E.; Haglund, P.; Hansson, K.; Laudon, H.; Newton, S.; Nygren, O.; Ripszam, M.; et al. Atmospheric pathways of chlorinated pesticides and natural bromoanisoles in the northern Baltic Sea and its catchment. Ambio 2015, 44, 472–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuomisto, J. Dioxins and dioxin-like compounds: Toxicity in humans and animals, sources, and behaviour in the environment. WikiJ. Med. 2019, 6, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nevalainen, L.; Tuomisto, J.; Haapasaari, P.; Lehikoinen, A. Spatial aspects of the dioxin risk formation in the Baltic Sea: A systematic review. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 748, 142558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christiansen, C.; Leipe, T.; Witt, G.; Christoffersen, P.L.; Lund-Hansen, L.C. Selected elements, PCBs, and PAHs in sediments of the North Sea–Baltic Sea transition zone: Sources and transport as derived from the distribution pattern. Geogr. Tidsskr. 2009, 109, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikolajczyk, S.; Warenik-Bany, M.; Pajurek, M. PCDD/Fs and PCBs in Baltic fish—recent data, risk for consumers. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 171, 112763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksson, M.; Ikaheimonen, T.K.; Jakobson, E.; Nielson, S.P.; Kamarainen, M.; Luning, M.; Aust, M.-O.; Osvath, I.; Schmied, S.; Silobritiene, B.V.; et al. Thematic assessment of radioactive substances in the Baltic Sea 2011–2015. Balt. Sea Environ. Proc. 2018, 151. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/328477877_Thematic_Assessment_of_Radioactive_Substances_in_the_Baltic_Sea_2011-2015 (accessed on 23 September 2022).
- Qiao, J.; Zhang, H.; Steier, P.; Hain, K.; Hou, X.; Vartti, V.-P.; Henderson, G.M.; Eriksson, M.; Aldahan, A.; Possnert, G.; et al. An unknown source of reactor radionuclides in the Baltic Sea revealed by multi-isotope fingerprints. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szefer, P. Trace Metals in the Environment 5. Metals, Metalloids and Radionuclides in the Baltic Sea Ecosystem; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2002; ISBN 978-0-444-50352-7. [Google Scholar]
- Bergström, L.; Ahtiainen, H.; Avellan, L.; Estlander, S.; Hoikkala, L.; Ruiz, M.; Li Zweifel, U. (Eds.) First Version of the ‘State of the Baltic Sea’ Report—June 17—To be Updated in 2018; Helsinki Commission: Helsinki, Finland, 2017.
- Jaishankar, M.; Tseten, T.; Anbalagan, N.; Mathew, B.; Krishnamurthy, B. Toxicity, mechanism and health effects of some heavy metals. Interdiscip. Toxicol. 2014, 7, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lithner, G.H.; Borg, H.; Grimas, A.; Göthberg, A.; Neumann, G.; Wrásdhe, H. Metals—Trends observed 1984–1988. Ambio 1990, 7, 7–9. [Google Scholar]
- Frank-Kamenetsky, D.; Undeman, E.; Smedberg, E.; Perkola, N.; Aysto, L.; Wolf, J.; Miehe, U. Micropollutants in wastewater and sewage sludge. Balt. Sea Environ. Proc. 2022, 185. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/360699560_Micropollutants_in_wastewater_and_sewage_sludge (accessed on 23 September 2022).
- Gubelit, Y.; Polyak, Y.; Dembska, G.; Pazikowska-Sapota, G.; Zegarowski, L.; Kochura, D.; Krivorotov, D.; Podgornaya, E.; Burova, O.; Maazouzi, C. Nutrient and metal pollution of the eastern Gulf of Finland coastline: Sediments, macroalgae, microbiota. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 550, 806–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popek, M.; Dereszewska, A.; Dembska, G. Risk of heavy metals and their compounds pollution in Port Gdynia waters. In Safety and Reliability of Systems and Processes, Summer Safety and Reliability Seminar 2021, Ciechocinek, Poland, 5–9 September 2021; Kołowrocki, K., Bogalecka, M., Dąbrowska, E., Torbicki, M., Eds.; Gdynia Maritime University: Gdynia, Poland, 2021; pp. 305–315. ISBN 978-83-7421-354-7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauss, M.; Gusev, A.; Aas, W.; Hjellbrekke, A.; Ilyin, I.; Klein, H.; Nyiri, A.; Rozovskaya, O.; Shatalov, V.; Strijkina, T.; et al. Atmospheric Supply of Nitrogen, Cadmium, Lead, Mercury, PCDD/Fs, PCB-153, and B(a)P to the Baltic Sea; EMEP MSC-W TECHNICAL REPORT 3/2020; Meteorological Synthesizing Centre—West Norwegian Meteorological Institute: Oslo, Norway, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Rozkovskaya, O.; Ilyin, I.; Gusev, A. Atmospheric Emissions of Heavy Metals in the Baltic Sea Region. HELCOM Baltic Sea Environment Fact Sheet (BSEFS). 2020. Available online: https://helcom.fi/wp-content/uploads/2020/11/BSEFS_HM_emis_2018.pdf (accessed on 23 September 2022).
- International Maritime Organization. London Convention and London Protocol; IMO Publishing: London, UK, 2016; ISBN 978-928-011-644-1. [Google Scholar]
- International Maritime Organization. MARPOL, Consolidated Edition 2022; IMO Publishing: London, UK, 2022; ISBN 978-928-011-743-1. [Google Scholar]
- Suman, D. Regulation of ocean dumping by the European Economic Community. Ecol. Law Q. 1991, 18, 559–618. [Google Scholar]
- GESAMP. Guidelines or the Monitoring and Assessment of Plastic Litter and Microplastics in the Ocean; Kershaw, P.J., Turra, A., Galgani, F., Eds.; IMO/FAO/UNESCO-IOC/UNIDO/WMO/IAEA/UN/UNEP/UNDP/ISA Joint Group of Experts on the Scientific Aspects of Marine Environmental Protection: London, UK, 2019; Volume 99. [Google Scholar]
- Vuola, A. FanpLESStic-Sea 2019. Review of Existing policies and Research Related to Microplastics; FanpLESStic-Sea: Helsinki, Sweden, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Äystö, L.; Siimes, K.; Junttila, V.; Joukola, M.; Liukko, N. Emissions and Environmental Levels of Pharmaceuticals—Upscaling to the Baltic Sea Region. Project CWPharma Activity 2.3 Report. 2020. Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/10138/321722 (accessed on 23 September 2022).
- Dereszewska, A.; Cytawa, S. Effect of diclofenac concentration on activated sludge condition in biological treatment plant. Water, 2022; submitted. [Google Scholar]
- Vieno, N.; Hallgren, P.; Wallberg, P.; Pyhala, M.; Zandaryaa, S. Pharmaceuticals in the Aquatic Environment of the Baltic Sea Region—A Status Report UNESCO Emerging Pollutants in Water Series—No. 1; UNESCO Publishing: Paris, France, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Świacka, K.; Smolarz, K.; Maculewicz, J.; Caban, M. Effects of environmentally relevant concentrations of diclofenac in Mytilus trossulus. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 737, 139797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Undeman, E. Diclofenac in the Baltic Sea—Sources, transport routes and trends. Balt. Sea Environ. Proc. 2020, 170. Available online: https://portal.helcom.fi/meetings/HOD%2058-2020-738/MeetingDocuments/5-12%20Annex2%20HELCOM_diclofenac%20in%20the%20Baltic%20Sea_final_BSEP.pdf (accessed on 23 September 2022).
- Borecka, M.; Siedlewicz, G.; Haliński, L.P.; Sikora, K.; Pazdro, K.; Stepnowski, P.; Bialk-Bielinska, A. Contamination of the southern Baltic Sea waters by the residues of selected pharmaceuticals: Method development and field studies. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 94, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- HELCOM. HELCOM Hot Spots. 2022. Available online: https://helcom.fi/action-areas/industrial-municipal-releases/helcom-hot-spots/ (accessed on 23 September 2022).
- Alharbi, O.M.L.; Basheer, A.A.; Khattab, R.A.; Ali, I. Health and environmental effects of persistent organic pollutants. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 263, 442–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabisiak, J.; Olejnik, A. Sunken chemical ammunition in the Baltic Sea—Research and risk assessment—CHEMSEA scientific programme. Pol. Hyperb. Res. 2012, 2, 25–52. [Google Scholar]
- Knobloch, T.; Bełdowski, J.; Böttcher, C.; Söderström, M.; Rühl, N.-P.; Sternheim, J. Chemical munitions dumped in the Baltic Sea. Balt. Sea Environ. Proc. 2013, 142. Available online: https://helcom.fi/wp-content/uploads/2019/10/Chemical-Munitions-Dumped-in-the-Baltic-Sea-Report-of-the-ad-hoc-Expert-Group.pdf (accessed on 23 September 2022).
- Kasperek, T. Chemical Weapons Dumped in the Baltic Sea; ECE: Toruń, Poland, 1999; ISBN 83-7174-527-3. [Google Scholar]
- Korzeniewski, K. Chemical warfare agents dumped in the Baltic Sea. Oceanol. Stud. 1999, 28, 83–103. [Google Scholar]
- The Mare Foundation. Dangerous shipwrecks. Available online: https://fundacjamare.pl/en/shipwrecks/ (accessed on 23 September 2022).
- Bogalecka, M. The safety of maritime transport in the Baltic Sea region. J. Manag. Financ. 2012, 3, 570–580. [Google Scholar]
- Frank-Kamenetsky, D.; Haldin, J.; Helavuori, M.; Kaasinen, S.; Littfass, D.; Ruiz, M. HELCOM activities report for the year 2020. Balt. Sea Environ. Proc. 2021, 176. Available online: https://helcom.fi/wp-content/uploads/2021/03/HELCOM-Activities-report-2020-BSEP176.pdf (accessed on 23 September 2022).
- Bogalecka, M. How safe is the Baltic. Balt. Transp. J. 2009, 28, 37–38. [Google Scholar]
- Bogalecka, M.; Jakusik, E.; Kołowrocki, K. Data collection of last 30 years ship accidents at the Baltic Sea area. J. Pol. Saf. Reliab. Assoc. Summer Saf. Reliab. Semin. 2017, 8, 125–134. [Google Scholar]
- Bogalecka, M.; Jakusik, E.; Kołowrocki, K. Baltic Sea open waters extreme events of last 30 years caused by climate-weather hazards. J. Pol. Saf. Reliab. Assoc. Summer Saf. Reliab. Semin. 2017, 8, 135–139. [Google Scholar]
- Bogalecka, M.; Jakusik, E.; Kołowrocki, K. Baltic Sea port waters extreme events of last 30 years caused by climate-weather hazards. J. Pol. Saf. Reliab. Assoc. Summer Saf. Reliab. Semin. 2017, 8, 141–146. [Google Scholar]
- Caban, J.; Brumerčik, F.; Vrábel, J.; Ignaciuk, P.; Misztal, W.; Marczuk, A. Safety of maritime transport in the Baltic Sea. MATEC Web Conf. 2017, 134, 00003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nicolas, F.; Bakhtov, A.; Helavuori, M.; Shinoda, D. Report on Shipping Accidents in the Baltic Sea from 2014 to 2017; Helsinki Commission: Helsinki, Finland, 2018.
- HELCOM. Report on Shipping Accidents in the Baltic Sea 2018; Helsinki Commission: Helsinki, Finland, 2020.
- Niemelä, W.; Nicolas, F.; Helavuori, M.; Meski, L. HELCOM Report on Shipping Accidents in the Baltic Sea in 2019; Helsinki Commission: Helsinki, Finland, 2020.
- Niemelä, W.; Nicolas, F.; Helavuori, M.; Meski, L. HELCOM Report on Shipping Accidents in the Baltic Sea in 2020; Helsinki Commission: Helsinki, Finland, 2021.
- SSPA Consortium. Final report—Research study on the sinking sequence of MV Estonia. SSPA Res. Rep. 2008, 134. Available online: https://lounaeestlane.ee/wp-content/uploads/2019/09/0_Final_Report_Research_Study_on_the_Sinking_Sequence_of_MV_Estonia.pdf (accessed on 23 September 2022).
- ITOPF. Oil Tanker Spill Statistics 2021; ITOPF Ltd.: London, UK, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Bogalecka, M.; Dąbrowska, E. Monte Carlo simulation approach to shipping accidents consequences assessment. Water, 2022; submitted. [Google Scholar]
- Häkkinen, J.M.; Posti, A.I. Review of maritime accident involving chemicals—Special focus on the Baltic Sea. TransNav 2014, 8, 295–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pursiainen, C. (Ed.) Critical infrastructure protection in the Baltic Sea region. In Towards a Baltic Sea Region Strategy in Critical Infrastructure Protection; Nordregio: Stockholm, Sweden, 2007; ISBN 978-91-89332-66-9. [Google Scholar]
- Wilczyński, P.; Bogalecka, M. Environmental impact of the oil spill caused by the leakage of the exemplary pipeline in the South Baltic Sea. Water, 2022; submitted. [Google Scholar]
- Wilczyński, P.; Bogalecka, M. Environmental impact of oil rigs/wind farms. Water, 2022; submitted. [Google Scholar]
- Lauge, A.; Hernantes, J.; Sarriegi, J.M. Critical infrastructure dependencies: A holistic, dynamic and quantitative approach. Int. J. Crit. Infrastruct. Prot. 2015, 8, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blokus-Roszkowska, A.; Bogalecka, M.; Kołowrocki, K. Critical infrastructure networks at Baltic Sea and its seaside. J. Pol. Saf. Reliab. Assoc. Summer Saf. Reliab. Semin. 2016, 7, 7–14. [Google Scholar]
- Reuters. EU Vows to Protect Energy Network after ‘Sabotage’ of Russian Gas Pipeline. Available online: https://www.reuters.com/business/energy/mystery-gas-leaks-hit-major-russian-undersea-gas-pipelines-europe-2022-09-27/ (accessed on 23 October 2022).
- Khlebovich, W.W. Biology of brackish and hyperhaline waters. Proc. Zool. Inst. USSR Acad. Sci. Leningr. 1989, 196, 147. [Google Scholar]
- Khlebovich, W.W. Some physico-chemical and biochemical phenomena in the salinity gradient. Limnologica 1990, 20, 5–8. [Google Scholar]
- Khlebovich, W.W. Study of relation to salinity. In Methods for Study of Bivalvian Mollusks; Shkorbatov, G.L., Starobogatov, V.I., Eds.; Zoological Institute, Russian Academy of Sciences: St. Petersburg, Russia, 1990; Volume 219, pp. 87–100. [Google Scholar]
- Khlebovich, W.W.; Abramova, E.N. Some problems of crustacean taxonomy related in the phenomenon of Horohalinicum. Hydrobiologia 2000, 417, 109–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HELCOM. Biodiversity in the Baltic Sea—An integrated thematic assessment on biodiversity and nature conservation in the Baltic Sea: Executive Summary. Balt. Sea Environ. Proc 2009, 116A. Available online: https://helcom.fi/wp-content/uploads/2019/08/BSEP116A.pdf (accessed on 23 September 2022).
- Smyth, K.; Elliott, M. Effects of changing salinity on the ecology of the marine environments. In Stressors in the Marine Environment; Solan, M., Whiteley, N., Eds.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 161–174. [Google Scholar]
- Dobrzycka-Krahel, A.; Rzemykowskal, H. First records of Ponto-Caspian gammarids in the Gulf of Gdańsk (southern Baltic Sea). Oceanologia 2010, 52, 727–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrzycka-Krahel, A.; Graca, B. Laboratory study of the effect of salinity and ionic composition of water on the mortality and osmoregulation of the gammarid amphipod Dikerogammarus haemobaphes (Eichwald, 1841): Implications for understanding its invasive distribution pattern. Mar. Freshw. Behav. Physiol. 2014, 47, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrzycka-Krahel, A.; Graca, B. Effect of salinity on the distribution of Ponto-Caspian gammarids in a non-native area—Environmental and experimental study. Mar. Biol. Res. 2018, 14, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrzycka-Krahel, A.; Tarała, A.; Chabowska, A. Expansion of alien gammarids in the Vistula Lagoon and the Vistula Delta (Poland). Environ. Monit. Assess. 2013, 185, 5165–5175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrzycka-Krahel, A.; Melzer, M.; Majkowski, W. Range extension of Dikerogammarus villosus (Sowinsky, 1894) in Poland (the Baltic Sea basin) and its ability to osmoregulate in different environmental salinities. Oceanol. Hydrobiol. Stud. 2015, 44, 294–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrzycka-Krahel, A.; Majkowski, W.; Melzer, M. Length-weight relationships of Ponto-Caspian gammarids that have overcome the salinity barrier of the southern Baltic Sea coastal waters. Mar. Freshw. Behav. Physiol. 2016, 49, 407–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paavola, M.; Olenin, S.; Leppäkoski, E. Are invasive species most successful in habitats of low native species richness across European brackish water seas? Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2005, 64, 738–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gollasch, S.; Leppäkoski, E. Risk assessment and management scenarios for ballast water mediated species introductions into the Baltic Sea. Aquat. Invasions 2007, 2, 313–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surowiec, J.; Dobrzycka–Krahel, A. New data on the non–indigenous gammarids in the Vistula Delta and the Vistula Lagoon. Oceanologia 2008, 50, 443–447. [Google Scholar]
- Ojaveer, H.; Olenin, S.; Narščius, A.; Florin, A.B.; Ezhova, E.; Gollasch, S.; Jensen, K.R.; Lehtiniemi, M.; Minchin, D.; Normant-Saremba, M.; et al. Dynamics of biological invasions and pathways over time: A case study of a temperate coastal sea. Biol. Invasions 2017, 19, 799–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leppäkoski, E.; Olenin, S. The meltdown of biogeographical peculiarities of the Baltic Sea: The interaction of natural and man-made processes. Ambio 2001, 30, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leppäkoski, E.; Gollasch, S.; Gruszka, P.; Ojaveer, H.; Olenin, S.; Panov, V. The Baltic—A sea of invaders. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2002, 59, 1175–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonsdorff, E. Zoobenthic diversity-gradients in the Baltic Sea: Continuous post-glacial succession in a stressed ecosystem. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2006, 330, 383–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crooks, J.A.; Chang, A.L.; Ruiz, G.M. Aquatic pollution increases the relative success of invasive species. Biol. Invasions 2021, 13, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrzycka-Krahel, A.; Medina-Villar, S. Alien species of Mediterranean origin in the Baltic Sea Region: Current state and risk assessment. Environ. Rev. 2020, 28, 339–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Occhipinti-Ambrogi, A. Global change and marine communities: Alien species and climate change. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2007, 55, 342–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlton, J.T. Global change and biological invasions in the oceans. In Invasive Species in a Changing World; Mooney, H.A., Hobbs, R.J., Eds.; Island Press: Washington, DC, USA; Covelo, CA, USA, 2000; pp. 31–53. ISBN 1-55963-782-X. [Google Scholar]
- Dobrzycka-Krahel, A.; Kemp, J.L.; Fidalgo, M.L. Cold-tolerant traits that favour northwards movement and establishment of Mediterranean and Ponto-Caspian aquatic invertebrates. Aquat. Sci. 2022, 84, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narula, K. Ballast Water Management (BWM) Convention: Late Implementation, Huge Impact. 2017. Available online: https://maritimeindia.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/01/BALLAST-WATER-MANAGEMENT-CONVENTION-IMPLEMENTATION-AND-IMAPCT.pdf (accessed on 13 July 2022).
- Ruiz, M.; Backer, H. (Eds.) HELCOM Guide to Alien Species and Ballast Water Management in the Baltic Sea; Helsinki Commission: Helsinki, Finland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- MacKenzie, B.R.; Gislason, H.; Mollmann, C.; Koster, F.W. Impact of 21st century climate change on the Baltic Sea fish community and fisheries. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2007, 13, 1348–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EUMOFA. European Market Observatory for Fisheries and Aquaculture Products. The EU Fish Market 2021. 2021 Edition. Available online: https://www.eumofa.eu/the-eu-fish-market-2021-edition-is-now-online (accessed on 23 September 2022).
- FISH. The Fisheries Secretariat. In A Report on IUU Fishing of Baltic Sea Cod; 2007; ISBN 978-91-976859-0-0. Available online: https://www.fishsec.org/app/uploads/2011/03/1198235739_21059.pdf (accessed on 23 September 2022).
- Musielak, S.J. Natural resources of the Baltic Sea and their exploitation. In The Waterscape. Sustainable Water Management in the Baltic Sea Basin; Lundin, L.-C., Ed.; Uppsala University: Uppsala, Sweden, 2001; ISBN 91-973579-3-6. [Google Scholar]
- Kraufvelin, P.; Pekcan-Hekima, Z.; Bergström, U.; Florin, A.; Lehikoinen, A.; Mattila, J.; Arula, T.; Briekmanee, L.; Brown, E.J.; Celmer, Z.; et al. Essential coastal habitats for fish in the Baltic Sea. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2018, 204, 14–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Breitholtz, M.; Hill, C.; Bengtsson, B.E. Toxic substances and reproductive disorders in Baltic fish and crustaceans. Ambio 2001, 30, 210–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomczak, M.T. Sto lat połowów na Bałtyku—z punktu widzenia klienta smażalni ryb. Polityka 2017. Niedowiary. Available online: https://naukowy.blog.polityka.pl/2017/07/21/sto-lat-polowow-na-baltyku-z-punktu-widzenia-klienta-smazalni-ryb/ (accessed on 23 September 2022).
- Hammer, C.; Von Dorrien, C.; Ernst, P.; Grohsler, T.; Koster, F.; MacKenzie, B.; Mollmann, C.; Wegner, G.; Zimmermann, C. Fish stock development under hydrographic and hydrochemical aspects, the history of Baltic Sea fisheries and its management. In State and Evolution of the Baltic Sea, 1952–2005. A Detailed 50-Year Survey of Meteorology and Climate, Physics, Chemistry, Biology, and Marine Environment; Feistel, R., Günther, N., Wasmund, N., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons: New Jersey, NJ, USA, 2008; pp. 543–581. ISBN 978-047-197-968-5. [Google Scholar]
- MacKenzie, B.; Alheit, J.; Conley, D.J.; Holm, P.; Kinze, C.C. Ecological hypotheses for a historical reconstruction of upper trophic level biomass in the Baltic Sea and Skagerrak. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2002, 59, 173–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacKenzie, B.; Horbowy, J.; Köster, F.W. Incorporating environmental variability in stock assessment: Predicting recruitment, spawner biomass, and landings of sprat (Sprattus sprattus) in the Baltic Sea. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2008, 65, 1334–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thurow, F. Estimation of the total fish biomass in the Baltic Sea during the 20th century. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 1997, 54, 444–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draganik, B.; Ivanow, S.; Tomczak, M.; Maksimov, B.; Psuty-Lipska, I. Status of exploited Baltic flounder stocks in the southern Baltic area (ICES SD 26). Oceanol. Hydrobiol. Stud. 2007, 36, 47–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eero, M.; MacKenzie, B.R.; Karlsdóttir, H.M.; Gaumiga, R. Development of international fisheries for the eastern Baltic cod (Gadus morhua) from the late 1880s until 1938. Fish. Res. 2007, 87, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustafsson, B.G.; Schenk, F.; Blenckner, T.; Eilola, K.; Meier, H.E.M.; Müller-Karulis, B.; Neumann, T.; Ruoho-Airola, T.; Savchuk, O.P.; Zorita, E. Reconstructing the development of Baltic Sea eutrophication 1850–2006. Ambio 2012, 41, 534–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- GAIN Report, Global Agricultural Information Network. 2018; p. 11. Available online: https://catalog.data.gov/dataset/global-agricultural-information-network (accessed on 23 September 2022).
- Czapliński, P. Changes in Polish fish processing industry. Stud. Ind. Geogr. Comm. Pol. Geogr. Soc. 2018, 32, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EUMOFA. European Market Observatory for Fisheries and Aquaculture Products. The EU Fish Market 2018. 2018 Edition. Available online: https://www.eumofa.eu/the-eu-fish-market-2018-edition-is-now-online (accessed on 23 September 2022).
- EUMOFA, European Market Observatory for Fisheries and Aquaculture Products. The EU Fish Market 2019. 2019 Edition. Available online: https://www.eumofa.eu/the-eu-fish-market-2019-edition-is-now-online (accessed on 23 September 2022).
- EUMOFA. European Market Observatory for Fisheries and Aquaculture Products. The EU Fish Market 2020. 2020 Edition. Available online: https://www.eumofa.eu/the-eu-fish-market-2020-edition-is-now-online (accessed on 23 September 2022).
- EUROSTAT 2022. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/eurostat (accessed on 13 July 2022).
- Statista. Opinions on Fish Consumption in Poland. 2019. Available online: https://www.statista.com/statistics/1132823/poland-opinions-on-fish-consumption/#statisticContainer (accessed on 23 September 2022).
- Munkes, B.; Löptien, U.; Dietze, H. Cyanobacteria blooms in the Baltic Sea: A review of models and facts. Biogeosciences 2021, 18, 2347–2378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HELCOM. Climate Change in the Baltic Sea 2021 Fact Sheet. Available online: https://helcom.fi/wp-content/uploads/2021/09/Baltic-Sea-Climate-Change-Fact-Sheet-2021.pdf (accessed on 23 September 2022).
- HELCOM. Eutrophication status of the Baltic Sea 2007–2011—A concise thematic assessment. Balt. Sea Environ. Proc. 2014, 143. Available online: https://www.helcom.fi/wp-content/uploads/2019/08/BSEP143.pdf (accessed on 23 September 2022).
- HELCOM. Sources and pathways of nutrients to the Baltic Sea. Balt. Sea Environ. Proc. 2018, 158. Available online: https://www.helcom.fi/wp-content/uploads/2019/08/BSEP153.pdf (accessed on 23 September 2022).
- Mankiewicz, J.; Tarczyńska, M.; Walter, Z.; Zalewski, M. Natural toxins from cyanobacteria. Acta Biol. Crac. Ser. Bot. 2003, 45, 9–20. [Google Scholar]
- McLellan, N.L.; Manderville, R.A. Toxic mechanisms of microcystins in mammals. Toxicol. Res. 2017, 6, 391–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gobler, C.J.; Burkholder, J.M.; Davis, T.W.; Harke, M.J.; Johengen, T.; Stow, C.A.; van de Waal, D.B. The dual role of nitrogen supply in controlling the growth and toxicity of cyanobacterial blooms. Harmful Algae 2016, 54, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reckermann, M.; Omstedt, A.; Soomere, T.; Aigars, J.; Akhtar, N.; Bełdowska, M.; Bełdowski, J.; Cronin, T.; Czub, M.; Eero, M.; et al. Human impacts and their interactions in the Baltic Sea region. Earth Syst. Dyn. 2022, 13, 1–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korpinen, S.; Meski, L.; Andersen, J.H.; Laamanen, M. Human pressures and their potential impact on the Baltic Sea ecosystem. Ecol. Indic. 2012, 15, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojaveer, H.; Jaanus, A.; MacKenzie, B.R.; Martin, G.; Olenin, S.; Radziejewska, T.; Telesh, I.; Zettler, M.L. Status of biodiversity in the Baltic Sea. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e12467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zalewska, T.; Maciak, J.; Grajewska, A. Spatial and seasonal variability of beach litter along the southern coast of the Baltic Sea in 2015–2019—Recommendations for the environmental status assessment and measures. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 774, 145716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HELCOM. State of the Baltic Sea—Second HELCOM holistic assessment 2011–2016. Balt. Sea Environ. Proc. 2018, 155. Available online: http://stateofthebalticsea.helcom.fi/ (accessed on 23 September 2022).
- Trojanowski, J.; Bigus, K.; Trojanowska, C. Differences of chemical components in beaches sediments with dissimilar anthropopressure. J. Ecol. Prot. Coastline 2011, 15, 109–126. [Google Scholar]



| Year | Position in Aquaculture Production in the EU Countries | Position in Catches by Marine Areas in the EU Countries | Position in Employment in the EU Fisheries Industry and Fisheries Production | Position in Per Capita Household Nominal Expenditure on Fishery and Aquaculture Products |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2017 | 11th | 10th | n.a. | 27th |
| 2018 | 7th | 10th | 6th | 27th |
| 2019 | 8th | 8th | 6th | 27th |
| Toxins | Primary Organ Targets |
|---|---|
| Hepatotoxins—toxic chemical substances that damage the liver | |
| microcystins (MC) | liver |
| nodularins (NOD) | liver |
| Cytotoxins—toxic chemical substances that damage cells | |
| cylindrospermopsins (CYN) | liver, kidney, spleen, intestine, heart, thymus |
| Neurotoxins—toxic chemical substances destructive to nerve tissue | |
| anatoxins (ANTX-a) | nervous system |
| anatotoxins (ANTX-as) | nervous system |
| Dermatoxins—toxic chemical substances that damage skin, mucous membranes, or both | |
| aplysiatoxins | skin |
| lungbyatoxins | skin |
| lipopolisacharids (LPS) | gastro-intestinal system, respiratory system |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dobrzycka-Krahel, A.; Bogalecka, M. The Baltic Sea under Anthropopressure—The Sea of Paradoxes. Water 2022, 14, 3772. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14223772
Dobrzycka-Krahel A, Bogalecka M. The Baltic Sea under Anthropopressure—The Sea of Paradoxes. Water. 2022; 14(22):3772. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14223772
Chicago/Turabian StyleDobrzycka-Krahel, Aldona, and Magdalena Bogalecka. 2022. "The Baltic Sea under Anthropopressure—The Sea of Paradoxes" Water 14, no. 22: 3772. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14223772