Removal of N and P in a Rotating Biological Contactor Plant: Case Study Agnita, Romania
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
- Daily average inflow: 2607 m3 (dry weather);
- Daily maximal inflow: 2971 m3 (35 L/s);
- Q max during rain: 540 m3/h (150 L/s);
Analysis
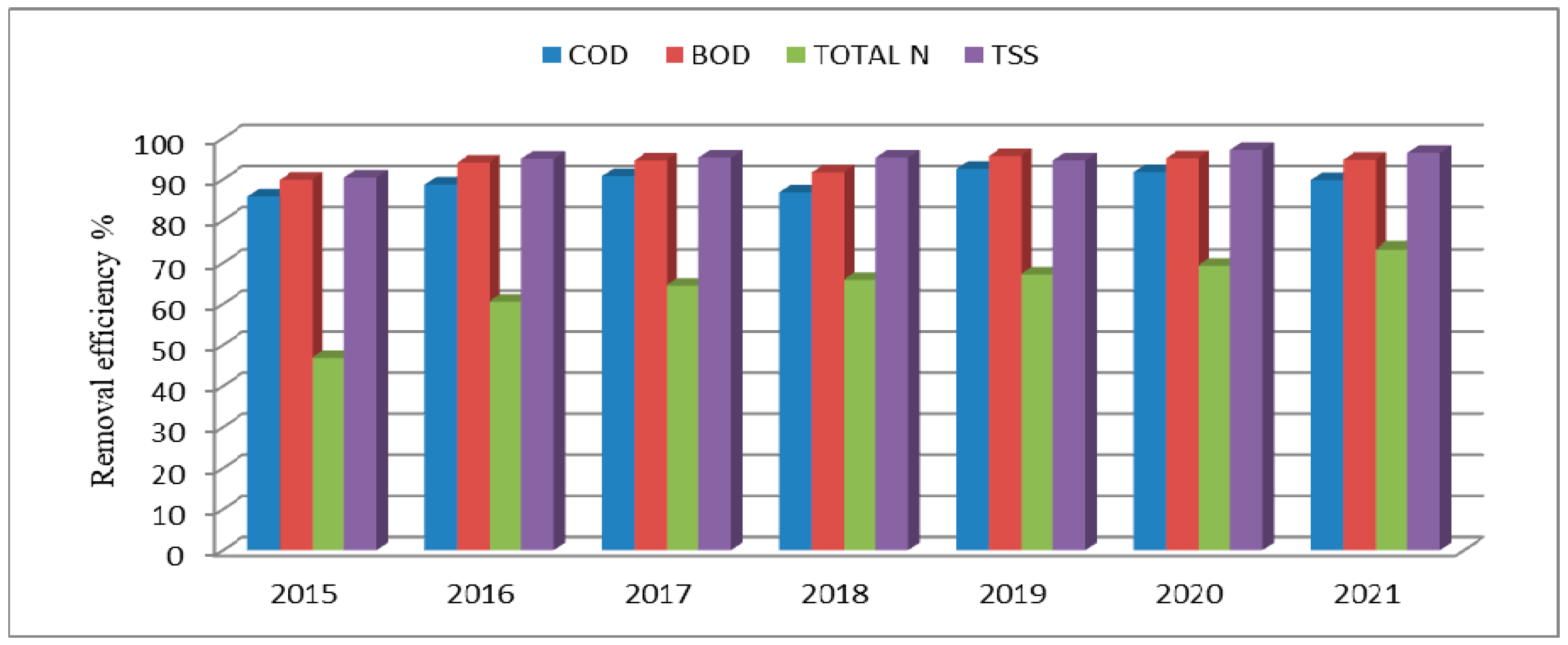
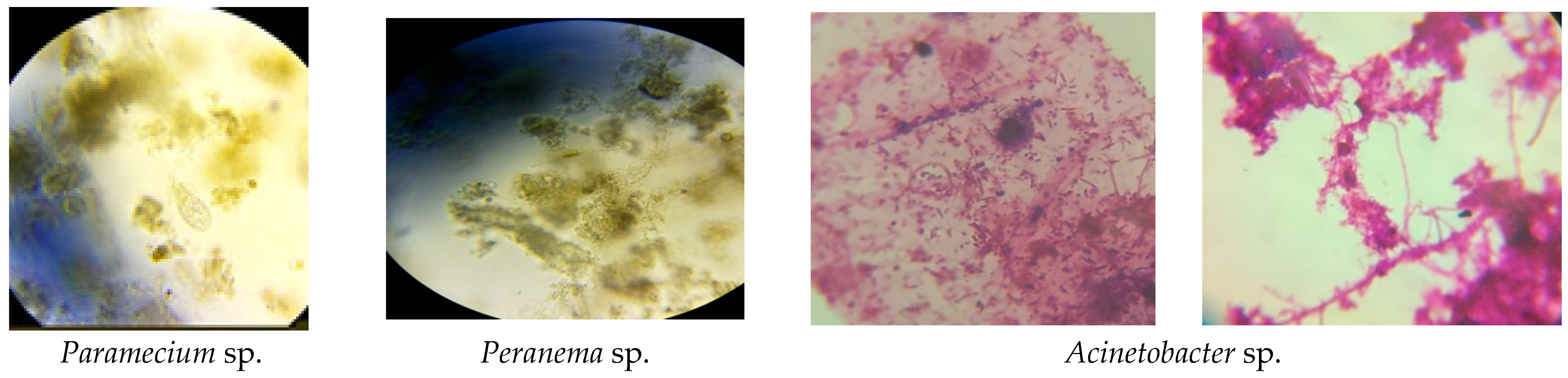
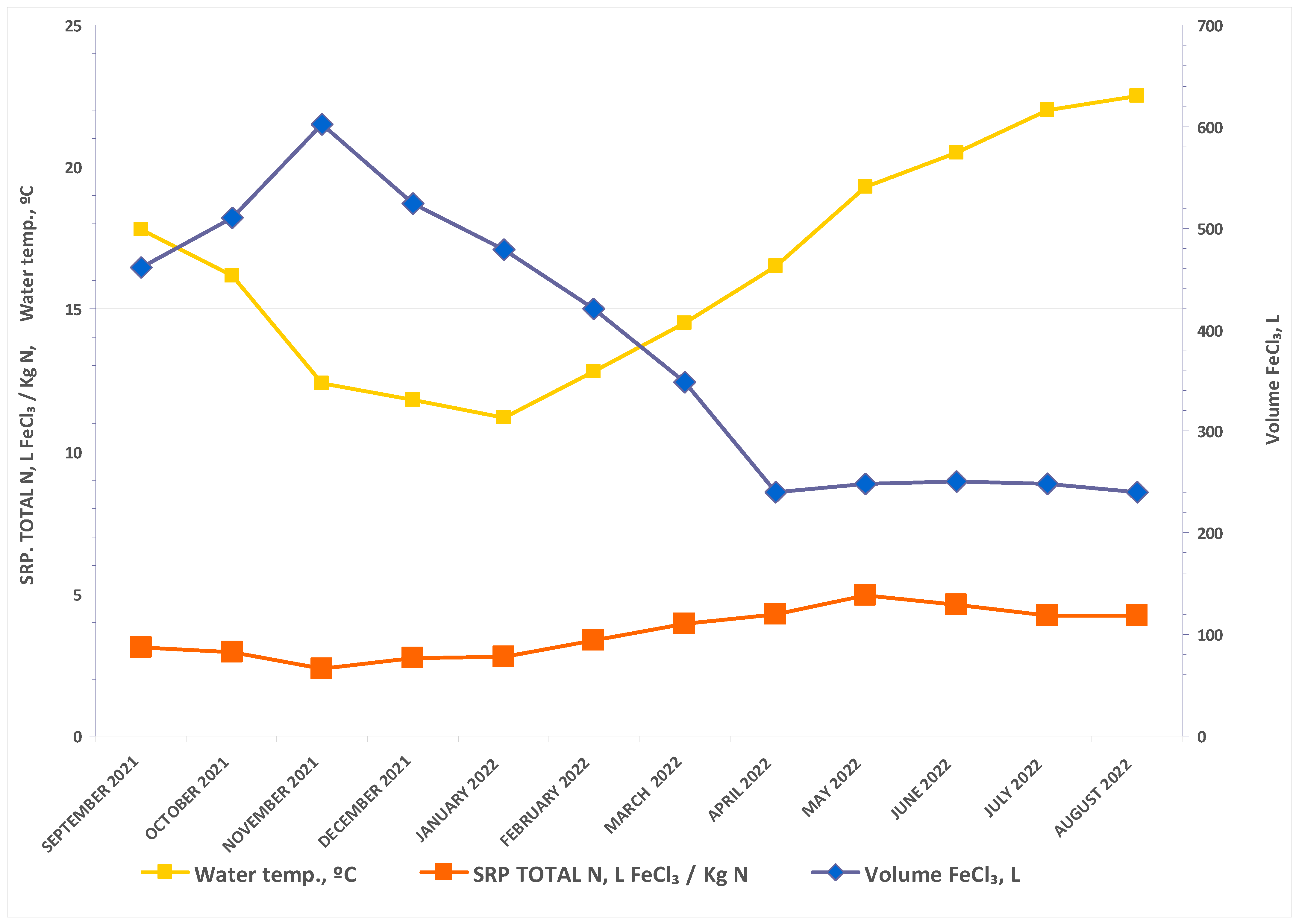
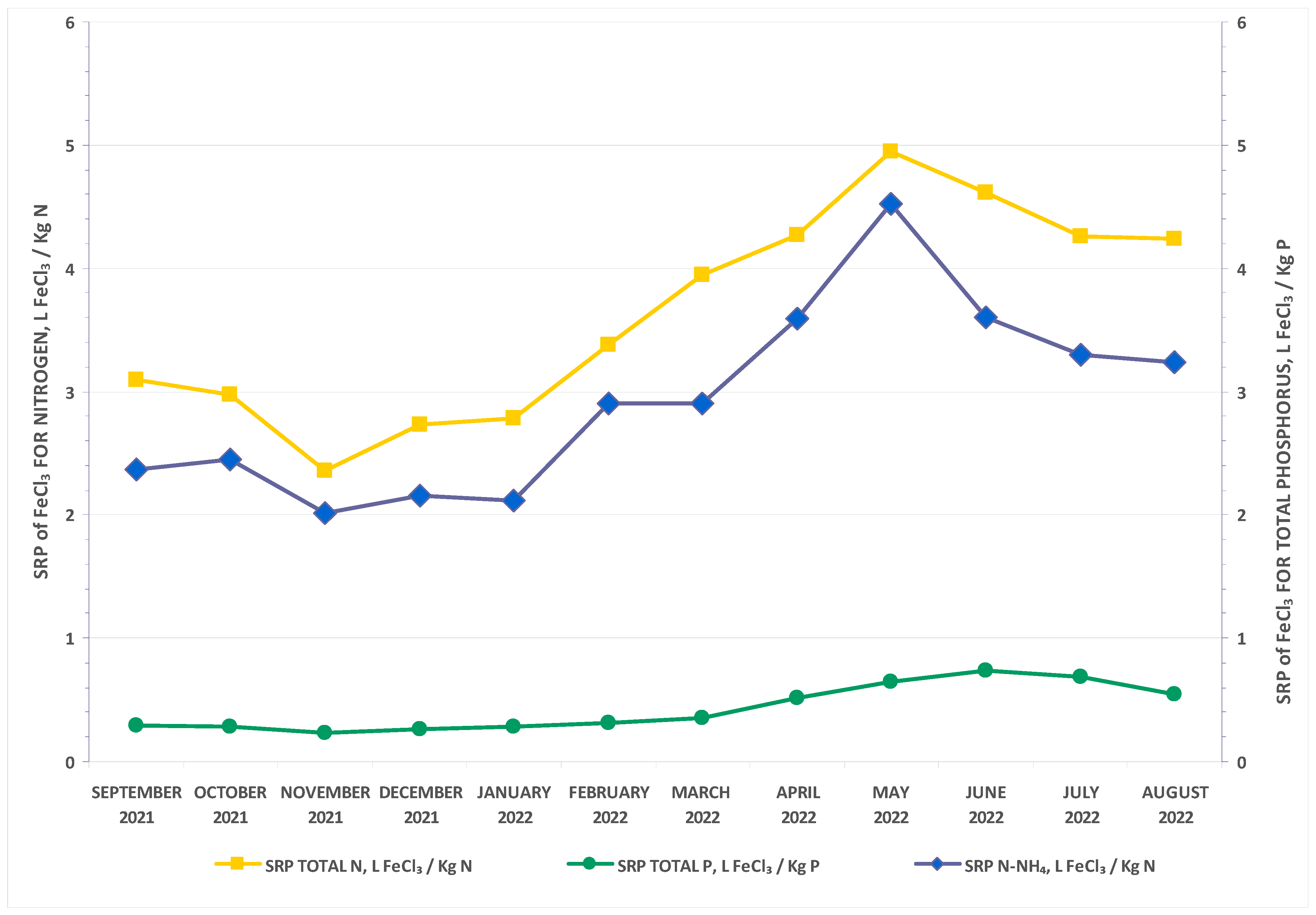
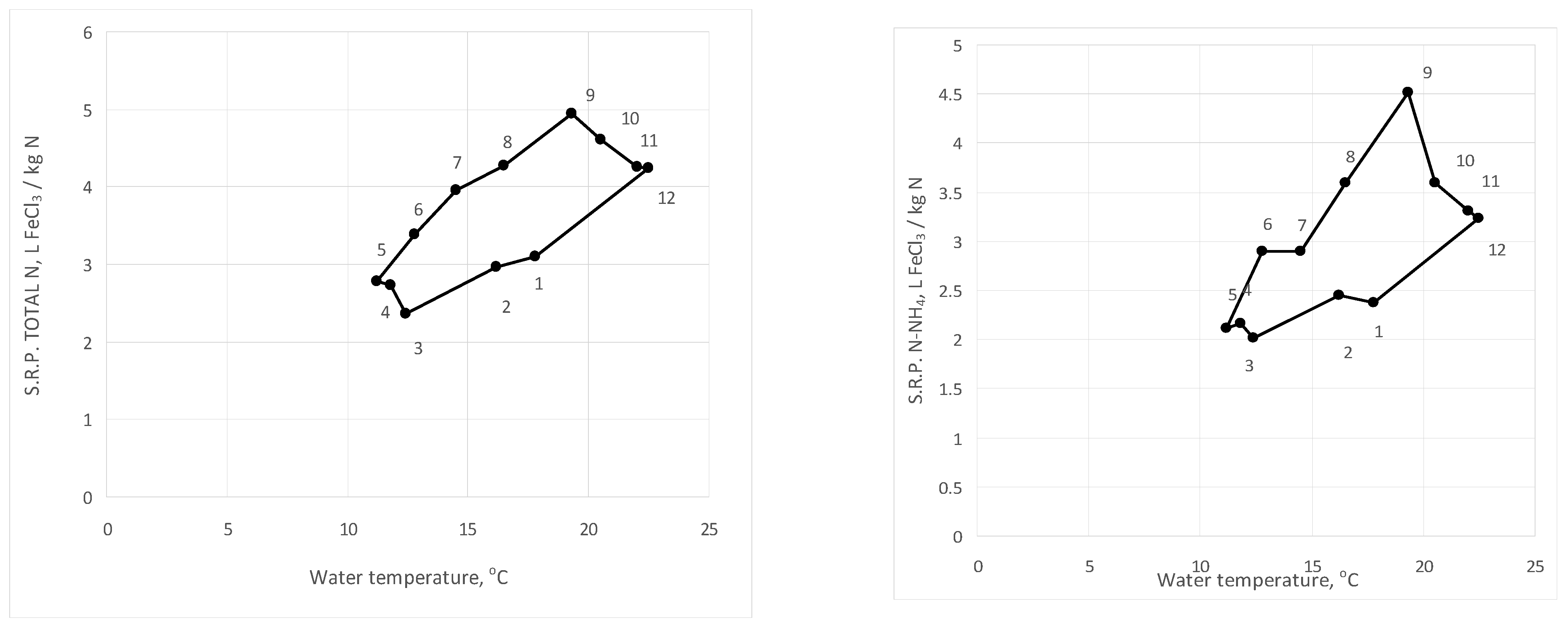
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bijekar, S.; Padariya, H.D.; Yadav, V.K.; Gacem, A.; Hasan, M.A.; Awwad, N.S.; Yadav, K.K.; Islam, S.; Park, S.; Jeon, B.-H. The State of the Art and Emerging Trends in the Wastewater Treatment in Developing Nations. Water 2022, 14, 2537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Directive 91/271/EEC—Urban Wastewater Treatment. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/EN/legal-content/summary/urban-waste-water-treatment.html (accessed on 9 October 2022).
- Emergency Ordinance 195 22/12/2005. Available online: https://www.ecolex.org/details/legislation/emergency-ordinance-no-195-of-22-december-2005-on-environmental-protection-lex-faoc197188/?xdate_min=1997&xdate_max=2014&q=marine+plastic&type=legislation (accessed on 9 October 2022).
- NORMATIV NTPA-001/28.02.2002; Norms Concerning the Limits for Pollutants Load on Industrial and Municipal Wastewater Discharged in Natural Receiving Bodies (in Romanian), Monitorul Oficial of Romania, No. 187 of 20 March 2002. Available online: https://novainstal.ro/legislatie-mediu/normativ-ntpa-001-2002/ (accessed on 14 September 2022).
- NORMATIV NTPA-002/(28/02/2002—Norms Regarding Conditions for Wastewater Discharge in Municipal Sewerage Networks and Directly Towards Wastewater Treatment Plants (Actualized Version, in Romanian), Monitorul Oficial of Romania, No. 98 of 11 May 2005. Available online: https://legislatie.just.ro/Public/DetaliiDocumentAfis/98310 (accessed on 14 September 2022).
- Strungaru, S.A.; Nicoara, M.; Jitar, O.; Moglan, I.; Plavan, G. An overview on the development and progress of water supply and wastewater treatment in Romania. Environ. Eng. Manag. J. 2019, 18, 407–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scalize, P.; Albuquerque, A.; Di Bernardo, L. Impact of alum water treatment residues on the methanogenic activity in the digestion of primary domestic wastewater sludge. Sustainability 2021, 13, 8783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Sperling, M. Activated Sludge and Aerobic Biofilm Reactors; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2015; Volume 6, ISBN 9781843391654. [Google Scholar]
- Garrone, P.; Grilli, L.; Groppi, A.; Marzano, R. Barriers and drivers in the adoption of advanced wastewater treatment technologies: A comparative analysis of Italian utilities. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 171, S69–S78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Márquez, P.; Gutiérrez, M.C.; Toledo, M.; Alhama, J.; Michán, C.; Martín, M.A. Activated sludge process versus rotating biological contactors in WWTPs: Evaluating the influence of operation and sludge bacterial content on their odor impact. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2022, 160, 775–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, G. Hydraulics of bench-scale rotating biological contactor. Wat. Res. 1997, 31, 2500–2510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortez, S.; Teixeira, P.; Oliveira, R.; Mota, M. Rotating biological contactors: A review on main factors affecting performance. Rev. Environ. Sci. Biotechnol. 2008, 7, 155–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Waqas, S.; Bilad, M.R. A review on rotating biological contactors. Indones. J. Sci. Technol. 2019, 4, 241–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, T.; Yamaya, S. Removal of hydrocarbons in a rotating biological contactor with biodrum. Process Biochem. 2005, 40, 3429–3433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popa, M.; Ungureanu, N.; Vlăduț, V. Applications of Rotating Biological Contactorsin Wastewater Treatment. Cadastre Ser. 2019, 49, 136–145. [Google Scholar]
- Hassard, F.; Biddle, J.; Cartmell, E.; Jefferson, B.; Tyrrel, S.; Stephenson, T. Rotating biological contactors for wastewater treatment—A review. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2015, 94, 285–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, B.J.; Pan, Y.; Guo, J.; Virdis, B.; Hu, S.; Chen, X.; Yuan, Z. CHAPTER 16: Denitrification Processes for Wastewater Treatment; The Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 2017; ISBN 9781782623762. [Google Scholar]
- Heylen, K.; Vanparys, B.; Wittebolle, L.; Verstraete, W.; Boon, N.; De Vos, P. Cultivation of denitrifying bacteria: Optimization of isolation conditions and diversity study. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 2637–2643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Duque, A.F.; Bessa, V.S.; Castro, P.M.L. Bacterial community dynamics in a rotating biological contactor treating 2-fluorophenol-containing wastewater. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 41, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mizyed, A.G. Review on Application of Rotating Biological Contactor in Removal of Various Pollutants from Effluent. Tech. Biochem. 2021, 2, 41–61. [Google Scholar]
- Rajta, A.; Bhatia, R.; Setia, H.; Pathania, P. Role of heterotrophic aerobic denitrifying bacteria in nitrate removal from wastewater. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2020, 128, 1261–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Numberger, D.; Ganzert, L.; Zoccarato, L.; Mühldorfer, K.; Sauer, S.; Grossart, H.P.; Greenwood, A.D. Characterization of bacterial communities in wastewater with enhanced taxonomic resolution by full-length 16S rRNA sequencing. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 9673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gumaelius, L.; Magnusson, G.; Pettersson, B.; Dalhammar, G. Comamonas denitrificans sp. nov., an efficient denitrifying bacterium isolated from activated sludge. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2001, 51, 999–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Lu, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, S.; Wang, Y.; Lei, Y.; Zhang, R.; Song, L. Simultaneous heterotrophic nitrification and aerobic denitrification (SND) for nitrogen removal: A review and future perspectives. Environ. Adv. 2022, 9, 100254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Liu, W.; Liu, W.; Xiao, L.; Ai, S.; Sun, X.; Bian, D. Simultaneous removal of organic matter and nitrogen by heterotrophic nitrification–aerobic denitrification bacteria in an air-lift multi-stage circulating integrated bioreactor. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 363, 127888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziembińska-Buczyńska, A.; Ciesielski, S.; Żabczyński, S.; Cema, G. Bacterial community structure in rotating biological contactor treating coke wastewater in relation to medium composition. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 19171–19179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fang, H.; Olson, B.H.; Asvapathanagul, P.; Wang, T.; Tsai, R.; Rosso, D. Molecular biomarkers and influential factors of denitrification in a full-scale biological nitrogen removal plant. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Holmes, D.E.; Dang, Y.; Smith, J.A. Nitrogen Cycling during Wastewater Treatment, 1st ed.; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; Volume 106, ISBN 9780128169759. [Google Scholar]
- Waqas, S.; Bilad, M.R.; Man, Z.; Wibisono, Y.; Jaafar, J.; Indra Mahlia, T.M.; Khan, A.L.; Aslam, M. Recent progress in integrated fixed-film activated sludge process for wastewater treatment: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 268, 110718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fazelipour, M.; Takdastan, A.; Borghei, S.M. Biological removal of nutrients (N & P) from urban wastewater with a modified integrated fixed-film activated sludge-oxic settling anoxic system using an anoxic sludge holding tank. Water Environ. J. 2021, 35, 830–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuśnierz, M.; Domańska, M.; Hamal, K.; Pera, A. Application of Integrated Fixed-Film Activated Sludge in a Conventional Wastewater Treatment Plant. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 5985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stuckey, D.C. Recent developments in anaerobic membrane reactors. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 122, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomczak, W.; Gryta, M. Energy-Efficient AnMBRs Technology for Treatment of Wastewaters: A Review. Energies 2022, 15, 4981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, C.F.; Chuang, S.H.; Su, J.L. Nitrogen and phosphorus removal in a combined activated sludge—RBC process. Proc. Natl. Sci. Counc. Repub. China Part A Phys. Sci. Eng. 1999, 23, 181–204. [Google Scholar]
- Teixeira, P.; Oliveira, R. Denitrification in a closed rotating biological contactor: Effect of disk submergence. Process Biochem. 2001, 37, 345–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rodziewicz, J.; Mielcarek, A.; Janczukowicz, W.; Jóźwiak, T.; Struk-Sokołowska, J.; Bryszewski, K. The share of electrochemical reduction, hydrogenotrophic and heterotrophic denitrification in nitrogen removal in rotating electrobiological contactor (REBC) treating wastewater from soilless cultivation systems. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 683, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trifi, I.M.; Trifi, B.; Djemal, A.; Hamrouni, B. Simultaneous removal of nitrates and nitrites from water by Donnan dialysis using Doehlert design. Environ. Eng. Manag. J. 2021, 20, 973–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.B.; Gupta, S.K. Simultaneous carbon and nitrogen removal from high strength domestic wastewater in an aerobic RBC biofilm. Water Res. 2001, 35, 1714–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breviar de Calcul Tehnologic—Statie de Epurare Agnita—Linia Apei; internal document; available on demand; pp. 1–21. (In Romanian)
- Mohamed, M.A.; Fouad, A.H.; ElHefny, R.M. Reviewing Rotating Biological Contactor’s Different Aspects for Wastewater Treatment with Experiment. Eng. Res. J. Fac. Eng. 2022, 51, 180–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathyapriya, K.; Chinnusamy, C. Reed Bed System: An Option for Reclamation of Polluted Water Resources: A Review. Agric. Rev. 2019, 40, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eikelboom, D.H. Process Control of Activated Sludge Plants by Microscopic Investigation; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Karczmarczyk, A.; Kowalik, W. Combination of Microscopic Tests of the Activated Sludge and Effluent Quality for More Efficient on-site Treatment. Water 2022, 14, 489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NORMATIV NTPA-011/20.03.2002; Technical Norms for Collection, Treatment and Discharge of Municipal Wastewater, Monitorul Oficial of Romania, No. 187 of 20 March 2002. Available online: https://lege5.ro/gratuit/gqytamjy/norma-tehnica-privind-colectarea-epurarea-si-evacuarea-apelor-uzate-orasenesti-ntpa-011-din-28022002 (accessed on 14 September 2022). (In Romanian).
- Rebosura, M.; Salehin, S.; Pikaar, I.; Sun, X.; Keller, J.; Sharma, K.; Yuan, Z. A comprehensive laboratory assessment of the effects of sewer-dosed iron salts on wastewater treatment processes. Water Res. 2018, 146, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghernaout, D. Water Treatment Coagulation: Dares and Trends. OALib 2020, 7, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaspar, E.; Sava, C.; Caratus, M.; Barbu, C.H. Correlations among Parameters and Indicators within a Wastewater Treatment Plant. Case Study: The Wwtp of Medias, Romania. Environ. Eng. Manag. J. 2022, 21, 831–838. [Google Scholar]
- Gaşpar, E.; Barbu, C.H. The influence of ferric chloride on the active sludge within the municipal wastewater treatment plants. Int. Multidiscip. Sci. GeoConference Surv. Geol. Min. Ecol. Manag. SGEM 2018, 18, 733–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Earhart, C.F. Uptake and Metabolism of Iron and Molybdenum. In Escherichia Coli and Salmonella: Cellular and Molecular Biology, 2nd ed.; Neidhardt, F.C., Curtiss, R., III, Ingraham, J.L., Lin, E.C.C., Low, K.B., Magasanik, B., Reznikoff, W.S., Riley, M., Schaechter, M., Eds.; ASM Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1996; pp. 1075–1090. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, B.J.; Park, J.H.; Park, T.H.; Bronstein, P.A.; Schneider, D.J.; Cartinhour, S.W.; Shuler, M.L. Effect of iron concentration on the growth rate of Pseudomonas syringae and the expression of virulence factors in hrp-inducing minimal medium. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 2720–2726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Waqas, S.; Bilad, M.R.; Man, Z.B. Performance and energy consumption evaluation of rotating biological contactor for domestic wastewater treatment. Indones. J. Sci. Technol. 2021, 6, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cvetkovic, D.; Susterstic, V.; Gordic, D.; Bojic, M.; Stosic, S. Perfomance of single-stage rotating biological contactor with supplemental aeration. Environ. Eng. Manag. J. 2014, 13, 681–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
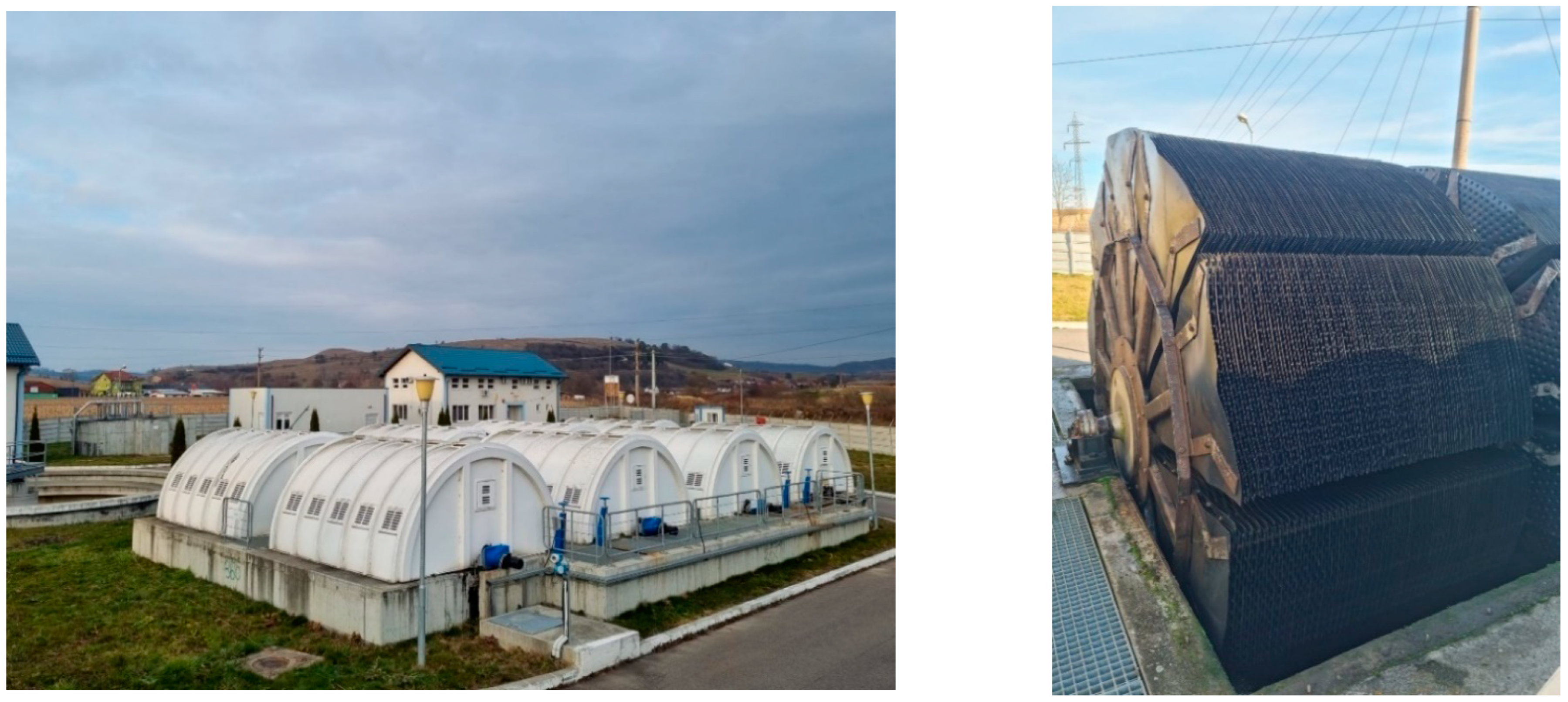



| Inflow Concentration | Inflow Load | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BOD | 220 | mg/L | 573 | kg/day |
| COD | 440 | mg/L | 1147 | kg/day |
| TSS | 256 | mg/L | 667 | kg/day |
| TKN | 45 | mg/L | 118 | kg/day |
| Total P | 9 | mg/L | 24 | kg/day |
| Characteristic | Value | Characteristic | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Type of RBC | Modular | Disc diameter (mm) | 3000 |
| Number of lines | 4 | Disc thickness (mm) | 1.5 |
| Line volume (m3) | 58.87 | Distance between discs (mm) | 20 |
| Number of modules per line | 2 | Disc material | HDPE |
| Number of biodisc sets per module | 2 | Rotation speed (min−1) | 2 |
| Number of individual discs per set | 103 (each of 10 sectors) | Water retention time (hours) | 2.17 |
| Parameter | Analytical Standard or Method | Equipment | Maximal Permitted Limits mg/L |
|---|---|---|---|
| pH | SR ISO 10523/2012, PO-01 | WTW pH/Conductivity Multimeter model 330i with SENTIX® 41 electrode | 6.5–8.5 |
| COD | SR ISO 6060/1996 | Velp eco 16 thermoreactor Merck Spectroquant® Multy Spectrophotometer | 125.0 |
| BOD | SR EN ISO 5815-1/2020 Method WTW 997,230 OxiTop, PO-07 | WTW incubator model TS 606/2-i WTW OxiTop® bottles | 25.0 |
| NH4+ | SR ISO 7150-1/2001 | WTW PhotoLab S6 Spectrophotometer | Not yet |
| Total N | SR EN 25,663:2000 Method WTW Ntot TC LR 251995, PO-09 | WTW Thermoreactor CR 2200, Merck Spectroquant® Multy Spectrophotometer | 15.0 |
| Total P | SR EN ISO 6878/2008 | WTW Thermoreactor CR 2200, Merck Spectroquant® Multy Spectrophotometer | Not yet |
| TSS | SR EN 872/2009 | Classical filtration equipment | 35.0 |
| Year | Inflow m3 | Total P, mg/L | Elimination Efficiency, % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Influent | Effluent | |||
| 2016 | 419,271 | 5.83 | 3.52 | 39.62 |
| 2017 | 351,662 | 5.76 | 3.38 | 41.32 |
| 2018 | 382,011 | 4.48 | 2.09 | 53.35 |
| 2019 | 335,185 | 5.54 | 2.7 | 51.26 |
| 2020 | 253,793 | 6.65 | 2.72 | 59.10 |
| 2021 | 307,925 | 6.67 | 3.03 | 53.46 |
| Parameter Sampling Place | 2021 | 2022 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NH4+ mg/L | Total N mg/L | NH4+ mg/L | Total N mg/L | |
| Influent | 45.35 | 47 | 40.54 | 53.09 |
| After primary settler | 33.2 | 39 | 35.22 | 46.08 |
| Removal efficiency—primary settler | 26.79 | 17.02 | 13.12 | 13.20 |
| After biodiscs | 5.01 | 13.50 | 3.80 | 15.00 |
| Removal efficiency biodiscs | 84.91 | 65.38 | 89.21 | 67.45 |
| After secondary settler | 4.16 | 10.79 | 2.38 | 11.75 |
| Removal efficiency—secondary settler | 16.97 | 20.07 | 37.37 | 21.67 |
| Total removal efficiency | 90.83 | 77.04 | 94.13 | 77.87 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gaspar, E.; Munteanu, I.; Sintea, S. Removal of N and P in a Rotating Biological Contactor Plant: Case Study Agnita, Romania. Water 2022, 14, 3670. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14223670
Gaspar E, Munteanu I, Sintea S. Removal of N and P in a Rotating Biological Contactor Plant: Case Study Agnita, Romania. Water. 2022; 14(22):3670. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14223670
Chicago/Turabian StyleGaspar, Eniko, Ioan Munteanu, and Silviu Sintea. 2022. "Removal of N and P in a Rotating Biological Contactor Plant: Case Study Agnita, Romania" Water 14, no. 22: 3670. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14223670
APA StyleGaspar, E., Munteanu, I., & Sintea, S. (2022). Removal of N and P in a Rotating Biological Contactor Plant: Case Study Agnita, Romania. Water, 14(22), 3670. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14223670







