Abstract
Stormwater runoff from expressways contains high concentrations of various heavy metals. However, heavy metal removal in most current runoff treatment facilities, using infiltration and filtration, is limited and poses substantial risks. Therefore, this study proposes and evaluates a dual media system of mortar and Na-zeolite, which are inexpensive and readily available, using long-term continuous column experiments for the removal of heavy metals. The results showed significant Cu2+ removal with Na-zeolites that was improved by the addition of a thin mortar layer, while a sand layer provided negligible improvements. The removal of Cu was further enhanced by increasing mortar layer thickness. The removal of Cu2+, Zn2+, Fe3+, and Ni2+ in a mixture was enhanced as the mortar layer’s thickness increased, while the contribution of Na-zeolite was significant in 232 h experiments with a fixed empty bed contact time (EBCT) of 1.8 min. Moreover, the media were not saturated with Fe throughout the operation period. These results suggest that the dual media system is cost-effective and efficient in the removal of heavy metals from stormwater runoff via precipitation, filtration, and adsorption with a short EBCT.
Keywords:
non-point source pollution; expressway; runoff; heavy metals; adsorption; precipitation; filtration 1. Introduction
Expressways are highly impervious, resulting in higher loads of pollutants in stormwater runoff than from other non-point sources (NPSs) [1,2]. In particular, the concentration of heavy metals is significantly higher in the runoff from expressways than in those from farmland, residential areas, and commercial areas [2,3,4]. The reported total concentrations of Al, Cd, Cr, Cu, Fe, Pb, Ni, and Zn in expressway runoff were in the ranges of 4.9–0.15, 400–0.1, 1900–0.056, 9650–1, 162,000–0.334, 13,100–0.5, 19,100–5.5, and 21,060–1 μg/L, respectively, while the dissolved concentrations were 0.16–0.02, 67–1, 8.1–0.03, 21–0.026, 8.1–0.037, up to 18.8, 15.7–1.2, and 416–0.04 μg/L [2,3,4,5,6,7]. The main sources of heavy metals are vehicles and road surface wear [1,2,3,8].
NPS pollution reduction facilities that use filtration and infiltration have been designed and installed for the treatment of suspended solids (SS), organic matter, nitrogen, and phosphorus, and their removal efficiencies have been intensively studied and evaluated [9,10]. However, the substantial risks of heavy metals in runoff have not been addressed. In the Korea, an NPS pollution management plan has been established for threducing BOD, total phosphorus, and SS [11].
Infiltration facilities have shown highly variable heavy metal removal efficiencies of 25–60%, but no reliable verification process has been designed [10,12]. In addition, there is a high risk of heavy metal contamination with respect to soil near infiltration facilities. According to a survey of an infiltration facility in Tokyo, Japan, the concentration of heavy metals in soil near the facility was not significantly lower than that of the media applied in the facility [13]. Another study also reported that the soil near an infiltration facility was seriously contaminated with heavy metals [14]. Therefore, there is an urgent need for developing efficient alternatives for heavy metal removal in stormwater runoff.
It has been suggested that an adsorption–filtration system using engineered media, i.e., adsorbents, could be a better strategy for the effective removal of heavy metals in highway runoff [15,16]. The filtration medium is a critical factor in the effective pollutant reduction when using filtration, adsorption, infiltration, and precipitation [17]. The adsorbents currently studied for heavy metal removal in rainfall runoff include sandy-loam [18], zeolites [19], activated carbon [20,21], construction waste (bricks and small amounts of concrete) [20], granular ferric hydroxide (GFH), manganese dioxide, concrete, crab shells [22], calcite, zeolites, sand, iron filings [23], granulated water treatment sludge [16], activated alumina, porous concrete, activated lignite, dolomite, and iron hydroxide (FerroSorp®) [21].
Based on a literature review of various adsorption/filtration media, a preliminary survey and experiments were conducted to select the optimal media for this study. Several factors including cost, heavy metal removal efficiency, permeability, particle size, and ease of procurement were considered. Sand, GFH, biochar, zeolite, Na-zeolite, and orchid stone were tested, and Na-zeolite was selected as the optimal adsorbent based on the equilibrium adsorption capacity and adsorption kinetics. Na-zeolite is generally prepared by the impregnation of zeolite in NaCl solution to exchange metal cations in zeolite with Na+ in order to enhance metal ion removal [24]. The improved adsorption of metals by Na-zeolite suggests its use as an intermediate for specific metal doping in zeolite [25]. On the other hand, processing at a higher pH could provide enhanced efficiencies for heavy metal removal via precipitation, followed by filtration/sedimentation/flotation, because most metals form hydroxides above a certain pH [26]. Therefore, the use of an alkali agent, such as calcite and cementitious materials, presents a high potential for heavy metal removal.
In this study, a system consisting of dual adsorption/filtration media was proposed. The upper part of the filtration bed was filled with granular mortar, and the pH of the influent was increased to induce precipitation of dissolved heavy metals. The lower bed was filled with granular Na-zeolite for the adsorption and filtration of dissolved and precipitated heavy metals. A series of column experiments was performed to verify the performance and to investigate the effects of influencing factors such as the ratio of mortar to Na-zeolite layers, empty bed contact time (EBCT), and co-existing heavy metals.
It is believed that the proposed system would provide a novel alternative for the efficient removal of heavy metals in stormwater runoff within a short contact period via a combination of precipitation, filtration, and adsorption. Moreover, the system can be cost-effective because the media are readily available and cheap, with well-known properties. In addition, this study focused on long-term continuous tests for a better evaluation of the system for field applications, which is different from previous studies [17,18,19,20,21].
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
Sodium chloride (NaCl), copper(II) nitrate trihydrate (Cu(NO3)2·3H2O), zinc(II) nitrate hexahydrate (Zn(NO3)2·6H2O), iron(III) chloride hexahydrate (FeCl3·6H2O), nickel(II) nitrate hexahydrate (Ni(NO3)2·3H2O), hydrochloric acid (HCl), and sodium hydroxide (NaOH) were purchased from Merck KGaA (Darmstadt, Germany). All were of analytical grade and used as received. Distilled, deionized water (DDW) was obtained using an Aquapuri 551 system (Younglin, Anyang, Korea).
Na-zeolite was prepared by mixing 5 g of zeolite (Rex Materials Co., Ltd., Pohang, Korea) with 1 L of 1 M NaCl aqueous solution, washing with DDW, and drying at 105–110 °C for 24 h [27]. Mortar was prepared by mixing cement, sand, and water at a ratio of 5:2:1 (w:w:w). After curing, the mortar was crushed and sieved using standard #8 and #12 sieves (1.70–2.36 mm). Joomoonjin sand (Joomoonjin Silica Sand Co., Ltd., Gangneung, Korea), generally adopted for the sand filtration of runoff in Korea, was tested as a control material.
2.2. Continuous Experiments
2.2.1. Removal of Cu2+ by Various Types of Filter Media
Cu2+ was selected as a representative heavy metal in expressway runoff [20,22]. An aqueous solution of 100 mg/L Cu2+ was prepared using DDW and Cu(NO3)2·3H2O, and the pH was adjusted to 5.0 using 0.1 N HCl and 0.1 N NaOH. Meanwhile, it should be noted that the total SS (TSS) is also an important indicator of anthropogenic pollutants in stormwater runoff [28,29]. In addition, a significant fraction of the heavy metals in stormwater runoff exists as particulate form, and can be removed via TSS removal, i.e., filtration and sedimentation [2,3,4,5,6,7]. It also indicates that the TSS removal is also indicative of the metals in solid form. However, the dissolved metals are not readily removed via TSS removal; therefore, additional or separate treatments are necessary for removing them.
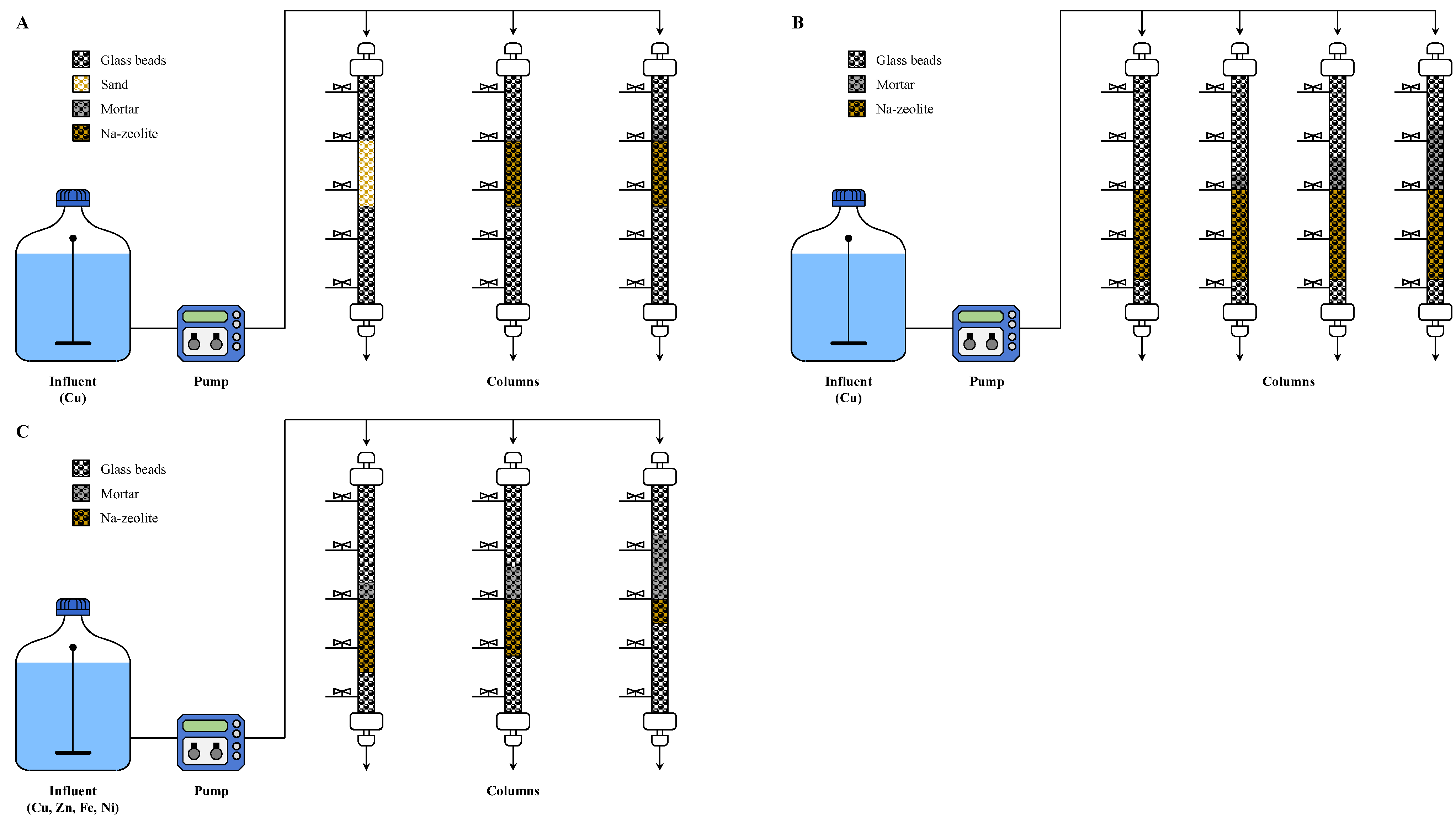
Glass columns with a length of 40 cm and an inner diameter of 1.5 cm were filled with sand or Na-zeolite (Figure 1A) corresponding to an EBCT of 1.8 min. This EBCT corresponds to a linear velocity of 20 m/h, which previously was determined by the evaluation of stormwater filtration devices of Korea [30]. The Cu2+ solution was injected onto columns at a flow rate of 8 mL/minute using a metered pump (JWS 100, JeniWell, Korea). The effluent from the columns was collected at a predetermined time interval until the concentration of Cu2+ in the effluent was equal to that of the influent. An additional experiment was performed using mortar/Na-zeolite dual media in which a mortar layer of depth producing an EBCT of 0.2 min was placed over the Na-zeolite layer to achieve a total EBCT of 2.0 min. Detailed experimental conditions are provided in Table 1.
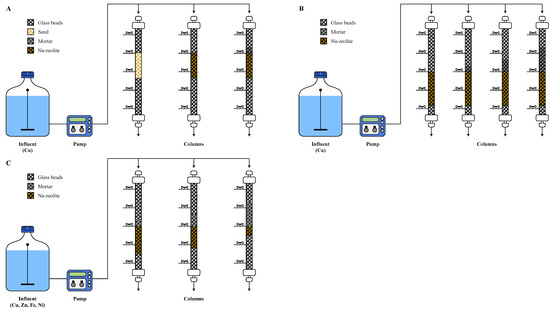
Figure 1.
Schematics of the experimental setup for (A) the removal of Cu2+ using sand, Na-zeolite, or mortar/Na-zeolite; (B) the removal of Cu2+ using mortar/Na-zeolite with different depths of mortar; and (C) the removal of a metal mixture using mortar/Na-zeolite with different ratios of mortar and Na-zeolite depths.

Table 1.
Experimental conditions for continuous Cu2+ removal.
Effluent samples were filtered through a 0.45 μm polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) filter, and the Cu2+ concentration of the filtrate was analyzed using inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectroscopy (ICP-AES, OPTIMA 5300 DV, Perkin-Elmer).
The Thomas model was used to analyze the experimental results (Equation (1)) [31,32]:
where C0 is the influent Cu concentration (mg/L), Ct is the Cu2+ concentration of effluent at time t (mg/L), kT is the Thomas model adsorption rate constant (mL/min·mg), qe is the equilibrium adsorption amount per unit mass of adsorbent (mg/g), x is the mass of adsorbent (g), and Q is the flow rate (mL/min). The Thomas model is the most widely used model for continuous adsorption, assuming that the adsorption rate depends on a reversible secondary reaction and the Langmuir kinetics of adsorption–desorption [31,32,33]. The Thomas model was used in this study, although it was expected that heavy metal removal in this study was attributable not only to adsorption but also to precipitation, because the Thomas model has been successfully used for describing column performance with a combination of various mechanisms accompanied with adsorption, such as precipitation in metal removal by iron-oxide-coated gravel [34], oxidation, and complexation, i.e., in the metal removal by humic-acid-coated sand [35], and ion exchanges [31,36].
2.2.2. Removal of Cu2+ in Mortar/Na-Zeolite Dual Filter Media
For the mortar/Na-zeolite dual media, Cu2+ adsorption was examined by changing the depth of the mortar layer to 2, 4, or 8 cm, corresponding to an EBCT of 0.31, 0.62, and 1.25 min, respectively. The depth of Na-zeolite was fixed at 11 cm (Table 2, Figure 1B). The experiments were carried out as described in Section 2.2.1 but with an influent flowrate of 10 mL/min to keep the EBCT of the Na-zeolite layer at 1.8 min.

Table 2.
Experimental conditions of mortar/Na-zeolite dual media according to EBCT.
2.2.3. Removal of Heavy Metals Mixture by Mortar/Na-Zeolite Dual Media
Considering the frequency and concentrations of metals in expressway stormwater runoff reported previously, a mixture of 1 mg/L each of Cu2+, Zn2+, Fe3+, and Ni2+ in an aqueous solution was used for the evaluation of metal removal [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,37]. A procedure using metals at higher concentrations was proposed for a quick evaluation of heavy metal removal in runoffs [22]. However, it seems reasonable to perform experiments under low concentrations of metals, although they require much longer periods. Adsorption at a high metal concentration would be faster than that at low concentrations because the rate of adsorption is generally governed by the difference in adsorbate amounts between the adsorbent and solution [38]. It should be noted that the concentration of metals in this study may not be representative because it varies significantly. The ratio of the event’s mean concentration (EMC) of Fe3+, Ni2+, and Zn2+ in stormwater runoffs to that of Cu2+ was 2.80–635.71, 0.85–5.61, and 1.20–148.57, respectively [2,3,4,5,6,7]. Therefore, the results in this study can be addressed as the metal’s relative feasibility towards precipitation and adsorption. In addition, an experimental study must be performed for the application of the system in this study for a specific case.
The effects of the ratio of mortar to Na-zeolite layers were investigated to determine the optimum configuration. Therefore, the thicknesses of the mortar and Na-zeolite layers were adjusted to 2/9 cm, 4/7 cm, and 8/3 cm, which correspond to an EBCT of 0.33/1.47, 0.65/1.15, and 1.31/0.49 min, respectively, while maintaining a total EBCT of 1.8 min [30] (Table 3, Figure 1C).

Table 3.
Mixed heavy metal removal test conditions with mortar/Na-zeolite dual media according to the ratio of media.
During the column experiments with an influent flowrate of 10 mL/min for 232 h, the effluent at the sampling port at the bottom of the mortar and Na-zeolite layers was collected for analyzing the metals using ICP-AES, as described in Section 2.2.1.
3. Results
3.1. Effects of Filter Media on Cu2+ Removal
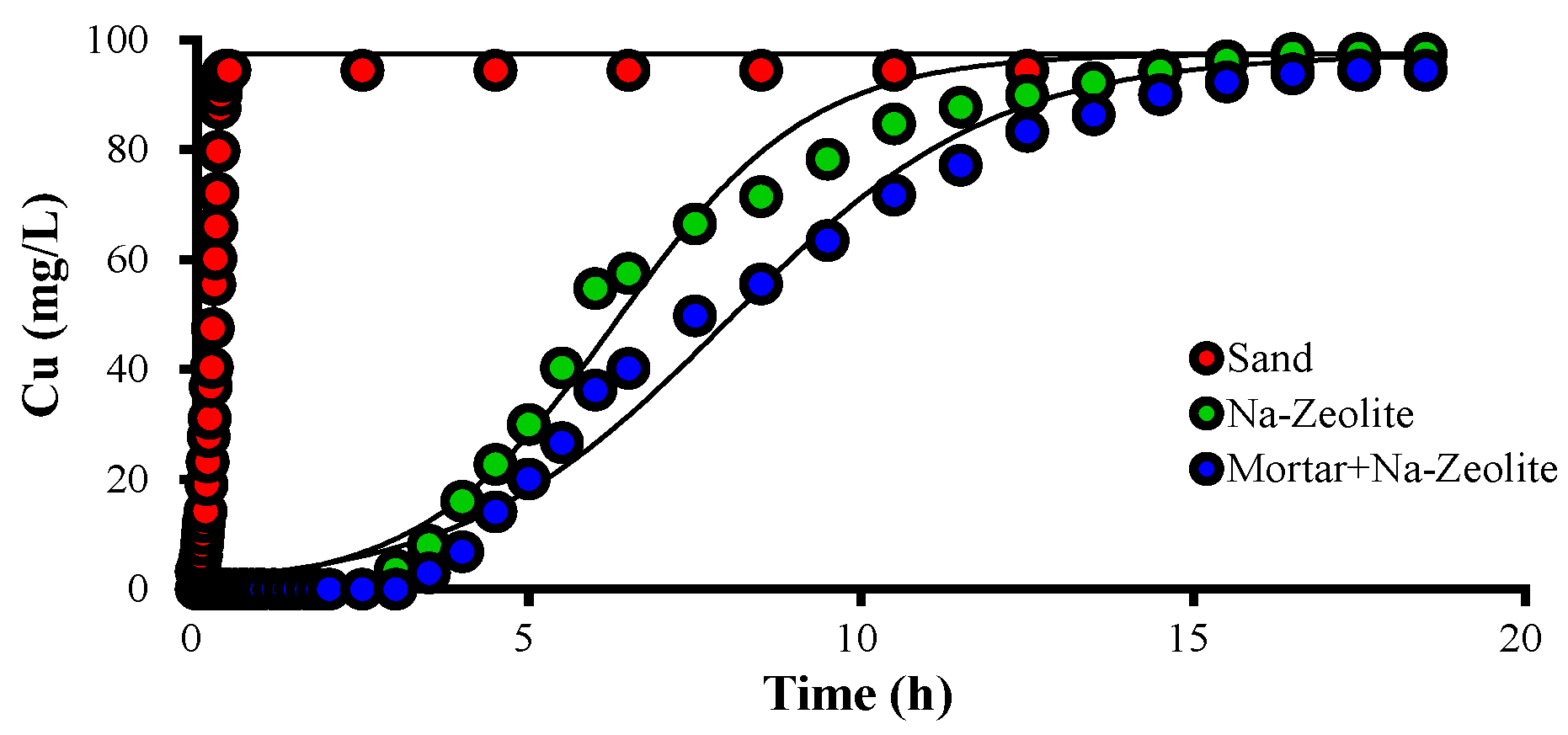
Figure 2 and Table 4 show breakthrough curves of Cu2+ and the Thomas model constants for Cu2+ removal with Na-zeolite and mortar/Na-zeolite. When the sand filter was used, the Cu2+ concentration of the effluent rapidly increased and was similar to that of the influent after 30 min of operation. In the effluent from the column using Na-zeolite, Cu2+ was not detected until 150 min of operation time, and the concentration increased to 8, 54.7, and 90.0 mg/L at 210, 360, and 750 min, respectively. In the effluent from dual mortar/Na-zeolite media, Cu was not detected until 180 min of operation, and the concentration increased to 6.8, 55.3, and 90.0 mg/L at 240, 510, and 870 min, respectively.
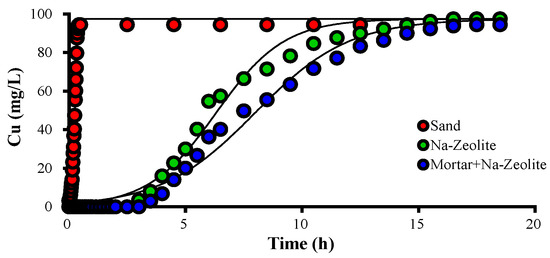
Figure 2.
Variation over time of the concentration of Cu2+ ions in the effluent collected after different media layer, in mg/L; the working temperature is 20.5 °C.

Table 4.
Adsorption constants for Cu2+ removal by sand, Na-zeolite and mortar (Cu 100 mg/L).
The qe calculated by the Thomas model was 0.35, 16.57, and 17.78 mg/g for sand, Na-zeolite, and mortar/Na-zeolite, respectively, while the equilibrium adsorption amount per volume of media layer (qL) was 0.79, 20.40, and 22.99 g/L. These data indicate the negligible removal of Cu2+ by sand, significant removal by Na-zeolite, and substantially improved removal by the addition of a layer of alkaline materials, i.e., mortar.
The kT calculated by the Thomas model was 167.2, 7.0, and 5.1 mL/min·mg for sand, Na-zeolite, and mortar/Na-zeolite, respectively. Since the Thomas model assumes that the driving force of adsorptions is the difference between adsorbate concentrations on the adsorbent’s surface and in the solution, kT increases as the adsorbate concentrations in solution increase, i.e., at smaller adsorption amounts [38], as shown in Table 4.
3.2. Effects of Mortar Amount on the Cu2+ Removal in Dual Media
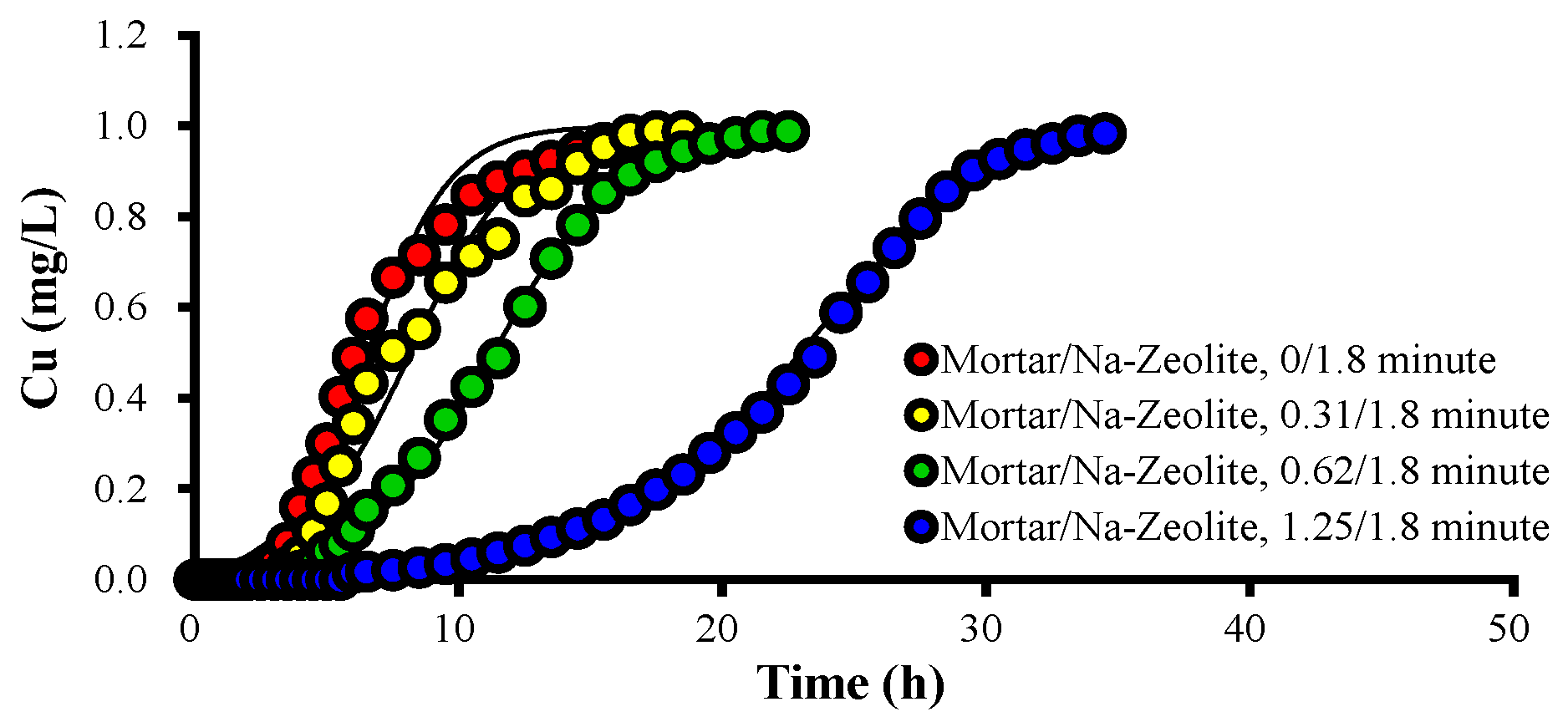
Figure 3 and Table 5 show the breakthrough curves of Cu2+ and the Thomas model constants of the mortar/Na-zeolite dual media with different amounts of mortar. When the EBCT of the mortar layer increased to 0, 0.31, 0.62, and 1.25 min, the Cu2+ concentration in the effluent was 16, 5.02, 1.9, and 0.0 mg/L, respectively, at 240 min of operation, while the time for near 50% saturation was 360 (48.9 mg/L), 450 (50.4 mg/L), 690 (48.8 mg/L), and 1410 min (48.9 mg/L).
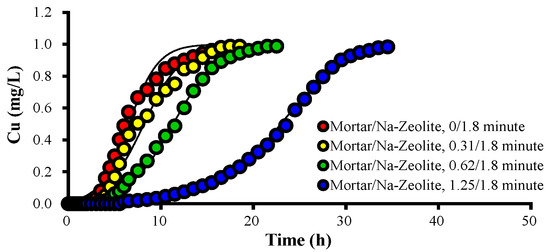
Figure 3.
Variations over time in the concentration of Cu2+ ions in the effluent collected after the dual layer, in mg/L, for different ratios of EBCTs; the working temperature is 20.5 °C.

Table 5.
Adsorption constants for Cu2+ removal with mortar/Na-zeolite dual media according to EBCT.
The qe values were 16.74, 16.01, 17.79, and 27.91 mg/g when the EBCT of the mortar layer was 0, 0.31, 0.62, and 1.25 min, respectively. Since the specific gravity of the mortar was higher than that of the zeolite, qe did not show a dramatic increase. However, qL and the total mass of removed Cu2+ (qt) increased significantly as the mortar layer’s thickness increased. On the other hand, the kT value decreased as the EBCT of the mortar layer increased, indicating that Cu adsorptions improved with increasing mortar layer depths. These data confirm that Cu2+ removal can be significantly enhanced by increasing alkali supplies.
3.3. Removal of Heavy Metals Mixture by Mortar/Na-Zeolite Dual Media
3.3.1. Removal of Heavy Metals Mixture in Mortar Layer
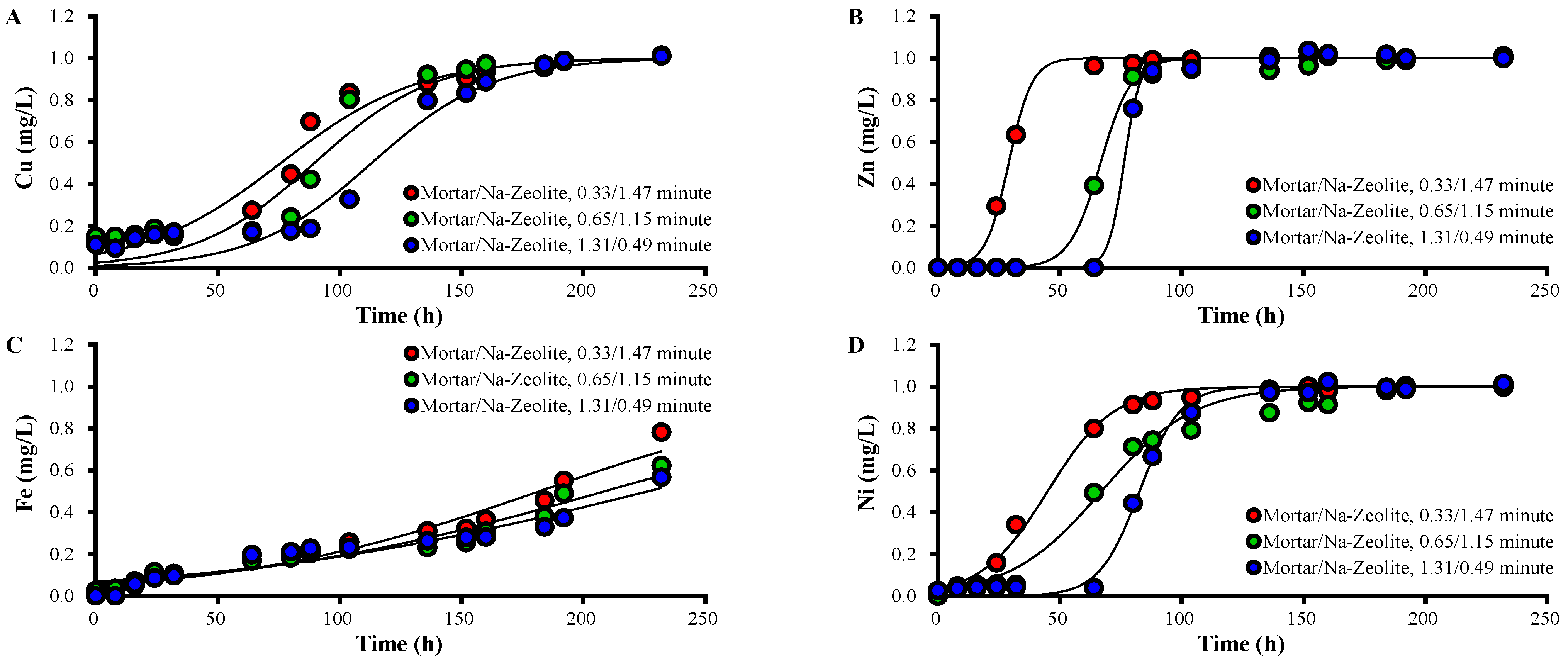
Column experiments were performed with different ratios of mortar and Na-zeolite, and breakthrough curves of each metal in the effluent of the mortar layer are presented in Figure 4, along with Thomas model constants (Table 6).
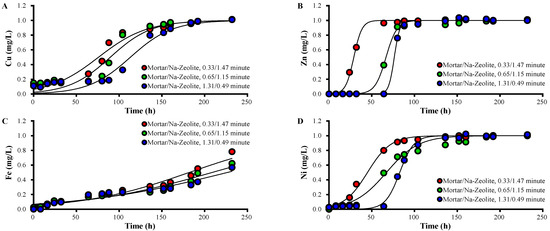
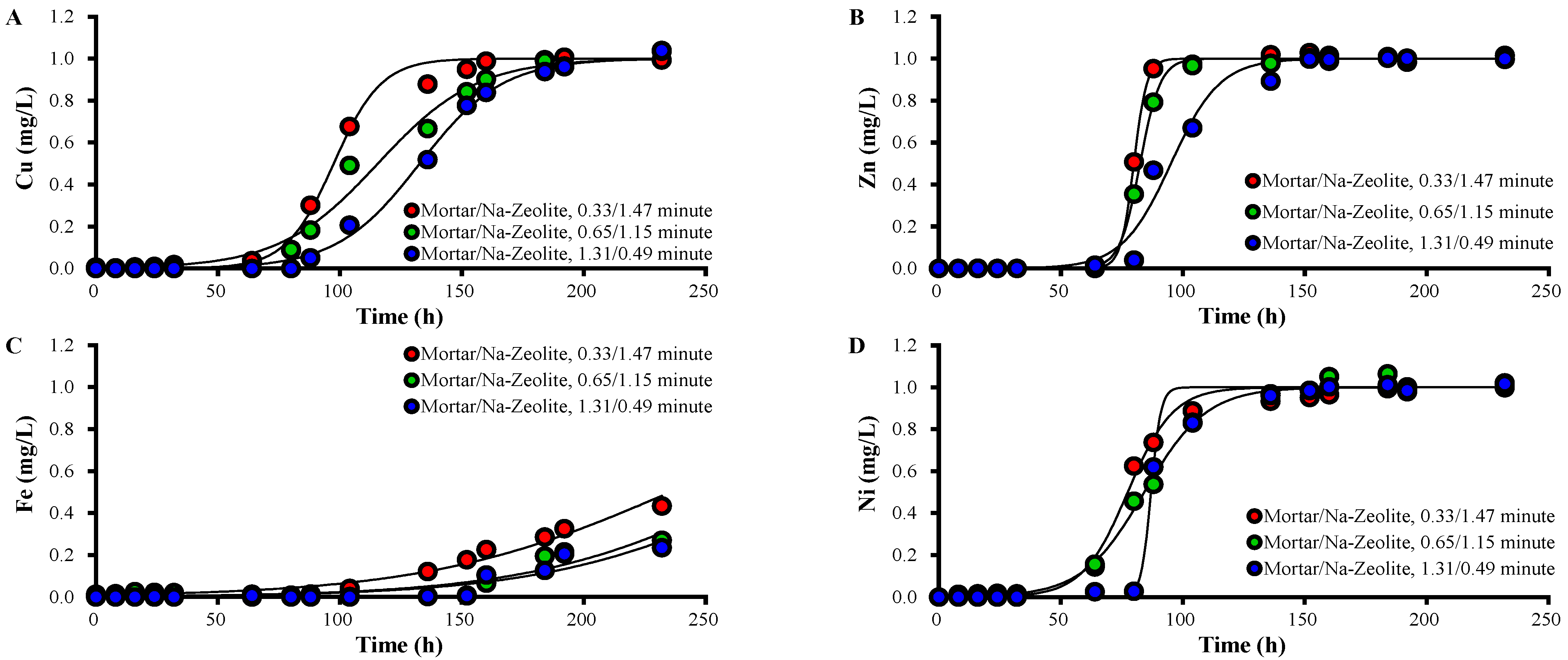
Figure 4.
Variations over time in the concentration of (A) Cu2+, (B) Zn2+, (C) Fe3+, and (D) Ni2+ ions in the effluent collected after the mortar layer from the dual system, in mg/L, for different ratios of EBCTs; the working temperature is 20.5 °C.

Table 6.
Adsorption constants for heavy metals collected from the mortar layer.
The concentrations of heavy metals in the effluent of the mortar layer decreased as the layer depth increased (Figure 4). For EBCTs of mortar/Na-zeolite of 0.33/1.47, 0.65/1.15, and 1.31/0.49 min, the 50% breakthrough times for Zn were 24–32, 64–80, and 72–80 h; those for Ni were 16–32, 40–64, and 72–88 h; those for Cu were 80–88, 93–112, and 112–136 h; those for Fe were 160–192, 208, and 208–232 h, respectively. These data indicate that heavy metals are effectively removed by the mortar. The increased qt and qL of each metal correspond to the increased EBCT of the mortar layer.
Among the heavy metals in this study, qt and qL in the mortar layer were observed in the order of Fe > Cu > Zn ≑ Ni, while kT was Zn ≑ Ni > Zn > Fe regardless of the amount of mortar, which indicates that the removal of a metal by alkali supplies was enhanced with increasing pH, where the metal forms precipitates. Fe3+ forms Fe2O3·nH2O, Fe3O4, and Fe(OH)2; Cu2+ forms CuO2 and Cu(OH)2; Zn2+ forms ZnO; Ni2+ forms NiO2 and No(OH)2 at pH 3.5, 4, 7.5, and 9, respectively [39].
3.3.2. Removal of Heavy Metals Mixture in the Entire Layers of Mortar/Na-Zeolite
The breakthrough and saturation times of each metal in the effluent of mortar/Na-zeolite dual media were prolonged with increasing mortar layer thickness (Table 5, Figure 5). The 50% breakthrough times of Zn2+ were 80, 80–88, and 88–96 h; those of Ni2+ was 64–72, 88–104, and 88 h; those of Cu2+ were 88–65, 112–136, and 136–152 h at a mortar/Na-zeolite EBCT ratio of 0.33/1.47, 0.33/1.47, and 0.33/1.47 min, respectively. However, Fe3+ did not achieve 50% breakthrough even after 232 h. These data indicate that heavy metal removal in the dual media improved due to alkali elution from the mortar layer.
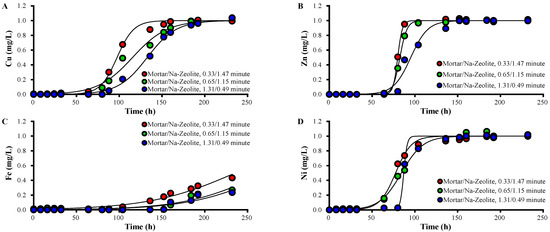
Figure 5.
Variations over time in the concentrations of (A) Cu2+, (B) Zn2+, (C) Fe3+, and (D) Ni2+ ions in the effluent collected after the Na-zeolite layer from the dual system, in mg/L, for different ratios of EBCTs; the working temperature is 20.5 °C.
The values of qt and qL of each metal increased as the mortar layer’s thickness increased (Table 7). The qt of Cu2+ was 58.5, 69.3, and 79.6 mg; that of Zn2+ was 47.9, 49.5, and 57.1 mg; that of Fe3+ was 161.6, 141.4, and 167.3 mg; and that of Ni2+ was 46.5, 50.6, and 52.2 mg when the EBCT ratio was 0.33/1.47, 0.65/1.15, and 1.31/0.49 min, respectively. The respective qL of Cu2+ was 3.0, 3.6, and 4.1 mg/L; that of Zn2+ was 2.5, 2.5, and 2.9 mg/L; that of Fe3+ was 8.3, 7.3, and 8.6 mg/L; and that of Ni2+ was 2.4, 2.6, and 2.7 mg/L. In addition, qt and qL for the dual media changed in the order of Fe3+ > Cu2+ > Zn2+ ≑ Ni2+, regardless of the EBCT, as in the mortar layer, suggesting the importance of the mortar layer.

Table 7.
Adsorption constants for heavy metals collected from the mortar/Na-zeolite dual layer.
The total mass of each metal removed per unit mass of the dual media (qe) (Table 7) was higher than that reported in previous column studies using metals mixtures, suggesting the excellence of the dual media. The removed amount of Pd2+, Cu2+, and Zn2+ was 0.21–0.57, 0.43–1.12, and 1.56–4.42 mg/g when mineral-based technical filter media were used and when their initial concentrations were 50, 100, and 400 μg/L, respectively [40]. The adsorption capacity of Cd2+ of calcite, zeolite, and iron filings was 0.48, 2.00, and 2.0 mg/g, respectively; that of Cu2+ was 0.49, 0.49, and 0.48 mg/g, respectively; that of Pb2+ was 4.66, 0.14, and 4.48 mg/g, respectively; that of Ni2+ was 1.22, 2.60, and 4.44 mg/g, respectively; that of Cr2+ was 0.016, 0.026, and 0.270 mg/g, respectively; and that of Zn was 5.0, 3.3, and 5.0 mg/g, respectively [41]. When the concentration of Cd2+, Cu2+, Ni2+, Pb2+, and Zn2+ in the influent was 0.625, 2.5, 2.5, 2.5, and 5.0 mg/L, respectively, the removed amount was approximately <0.5, 1.5–3.0, 0.5–1.5, 1.5–3.5, and 2.0–3.5 mg/g, respectively, for alumina; <0.1, 1.0–2.5, <1.0, 1.5–2.0, and 0.5–2.0 mg/g, respectively for granular activated carbon (GAC); <0.25, 1.0–2.5, 0.1–1.5, 1.0–2.0, and 2.5–3.0 mg/g, respectively, for lignite; and negligible, <0.1, <0.1, <1.0, and <0.1 mg/g, respectively, for granular ferric hydroxide [21]. The removed amount of Ni2+, Cd2+, Zn2+, Cu2+, and Pb2+ was 0.0048, 0.0034, 0.2984, 0.1024, and 0.1371 mg/g, respectively, for basalt; 0.0103, 0.0114, 0.6517, 0.2133, and 0.3004 mg/g, respectively, for zeolite; and 0.0148, 0.0127, 0.7378, 0.0233, and 0.3056 mg/g, respectively, for the layer consisting of zeolite, GAC, and a titanate nano-fibrous material [42]. In addition, the removal of Ni2+, Zn2+, and Fe3+ by an iron-oxide-coated gravel was 0.43, 1.15, and 1.13 mg/g, respectively [34].
On the other hand, kT did not show a correlation with the mortar/Na-zeolite ratio, which indicates that heavy metal removal in the mortar/Na-zeolite dual media is governed not only by mass transfer, i.e., adsorption, but also by precipitation from the mortar alkali supply and the filtration of precipitates.
3.3.3. Contribution of Each Layer in Mortar/Na-Zeolite Dual Media
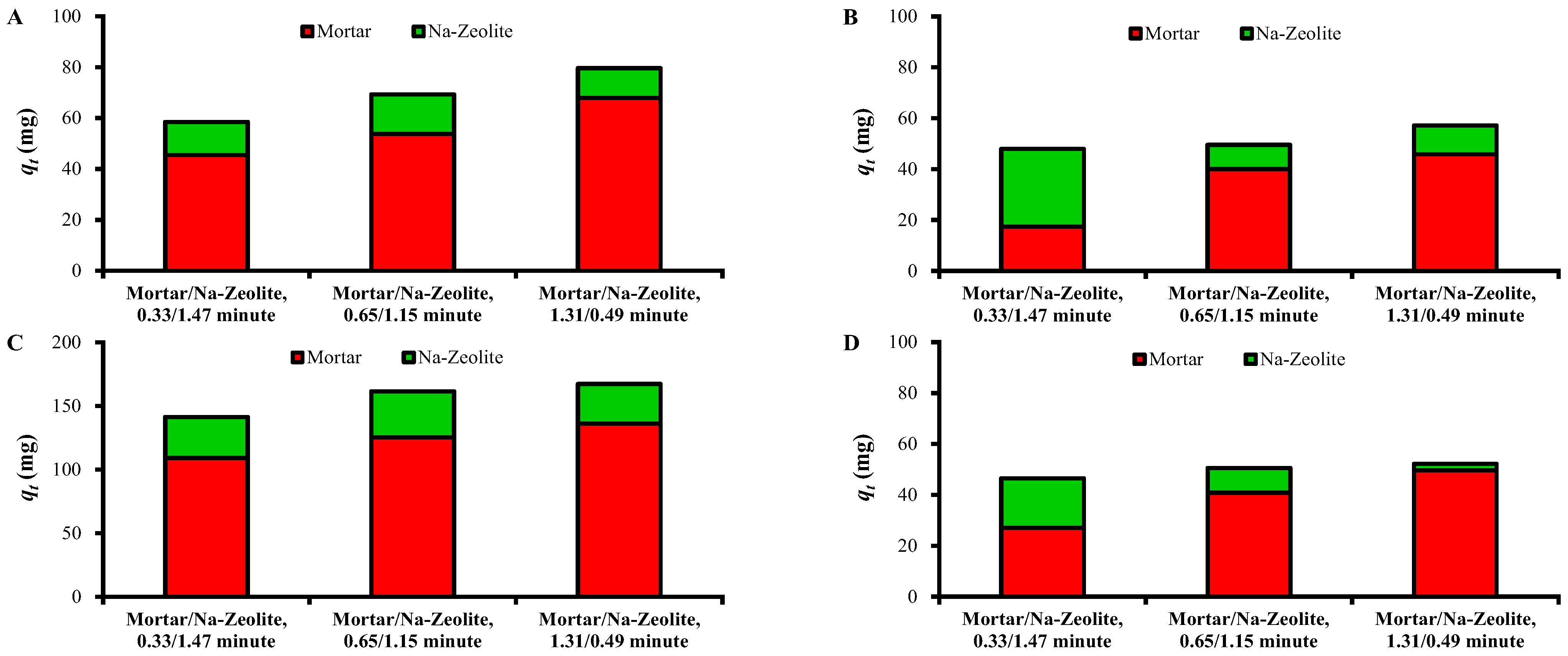
Figure 6 shows the amounts of heavy metals removed (qt in Table 6 and Table 7) in the mortar layer and Na-zeolite layer according to ratio of EBCTs of mortar and Na-zeolite layers. The qt values in the mortar layer were significantly larger than those in the Na-zeolite layer, except for Zn2+ at 0.33/1.47 min, indicating the major role of the mortar layer. The mass fraction of removed metals in the mortar layer from the dual layer was 77.9%, 77.6%, and 85.3% for Cu2+; 36.4%, 80.9%, and 80.3% for Zn2+; 77.2%, 77.5%, and 81.3% for Fe3+; and 58.0%, 80.7%, and 95.0% for Ni2+ at EBCT ratios of 0.33/1.47, 0.65/1.15, and 1.31/0.49 min, respectively.
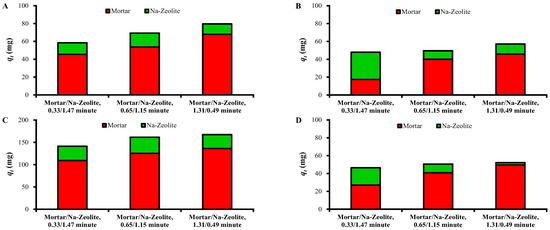
Figure 6.
Removed amounts of (A) Cu2+, (B) Zn2+, (C) Fe3+, and (D) Ni2+ in each layer of mortar/Na-zeolite dual media for different ratios of EBCTs.
The qt values of Ni2+ and Zn2+ in the mortar layer increased significantly with the increasing EBCT of the mortar layer. However, the increase was less significant for Cu2+ and Fe than the other metals, which is attributable to easier precipitation of Cu2+ and Fe3+ under low alkalinity, i.e., a thin EBCT mortar layer, resulting in better removal in the mortar layer than for Zn2+ and Ni2+ [39].
The qt of Ni2+ in the Na-zeolite layer decreased with the decreasing EBCT of the layer (Figure 6D), suggesting a contribution of the layer to Ni removal. The qt of Zn2+ was larger at 0.33/1.47 min than at 0.65/1.15 and 1.31/0.49 min. The qt values of Zn2+ and Ni2+ for the Na-zeolite layer were comparable to or significantly larger than those of Cu2+ and Fe at 0.33/1.47 min. This finding may be ascribed to the higher concentrations of Zn2+ and Ni2+ in the influent of the layer than those of Cu2+ and Fe3+ because adsorption is governed by the difference of adsorbate amounts on the adsorbent surface and in the liquid phase [38]. On the other hand, the qt values of Cu2+ and Fe3+ for the Na-zeolite layer did not show a correlation with the EBCT of the layer, which can be attributed to lower loads of Cu and Fe on the Na-zeolite layer because of the excellent removal in the mortar layer (Table 6 and Table 7).
4. Conclusions
In this study, a dual media system of mortar and Na-zeolite was investigated via continuous column experiments for the efficient removal of heavy metals in expressway stormwater runoff. First, the potential of the dual media system was evaluated. Sand, which is used widely as a filtration medium in conventional NPS pollution reduction, showed negligible Cu2+ removal, while the qe of Na-zeolite increased to as high as 16.57 mg/g at an EBCT of 1.8 min (linear velocity of 20 m/h). The addition of a thin mortar layer over the Na-zeolite layer resulted in a substantial improvement in Cu2+ removal, suggesting the high potential of the dual mortar and Na-zeolite media. By adding mortar layers corresponding to EBCTs of 0, 0.31, 0.62, and 1.25 min to the Na-zeolite layer, at a Cu2+ concentration of 100 mg/L, the qe values were 22.0, 20.5, 22.7, and 35.6 mg/g, respectively, confirming the significant role of the mortar layer.
The removal of a mixture of heavy metals commonly found in runoff at significant levels was subjected to the dual layer system under various ratios of EBCTs of mortar and Na-zeolite layers. The dual layer system showed excellent performances in the removal of all metals. In particular, the effluent concentration of Fe did not reach that of the influent after operation for 232 h. The removal of metals in the mortar layer and in the dual layers improved with an increasing EBCT of the mortar layer, confirming the important role of the layer. With the increasing EBCT of the mortar layer from 0.33/1.47 to 1.31/0.49 min, the qL of the dual layer increased from 3.0 to 4.1 g/L for Cu2+, from 2.5 to 2.9 g/L for Zn2+, from 8.3 to 8.6 g/L for Fe3+, and from 2.4 to 2.6 g/L for Ni2+. In addition, the contribution of the mortar layer to the total removal for the dual layer was 77.6–85.3%, 36.4–80.3%, 77.2–81.3%, and 58.0–95.0% for Cu2+, Zn2+, Fe3+, and Ni2+, respectively. However, the removal with Na-zeolite was also significant, indicating a synergistic effect of the layers.
The results in this study strongly suggest that a dual layer system of mortar and Na-zeolite can be an excellent alternative for heavy metal removal from stormwater runoff via the combination of alkaline precipitation, the filtration of precipitates, and adsorption. Moreover, the good performance at a short EBCT suggests that the system is suitable for compact stormwater treatment practices installed where available space is limited; the TSS can be effectively removed simultaneously in the system due to the use of granular media, i.e., mortar and Na-zeolite; moreover, the media in the system are cheap and provide cost-effective removals of pollutants in stormwater runoff. However, it is thought that the effects of real stormwater chemistry affecting the performance and clogging of the media should be investigated for successful field applications.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization and methodology, D.-G.K.; validation and formal analysis, D.-G.K. and S.-O.K.; investigation, resources, data curation, and writing—original draft preparation, D.-G.K.; writing—review and editing, D.-G.K. and S.-O.K.; visualization and supervision, S.-O.K.; project administration, and funding acquisition, S.-O.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by a National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korean government (MSIT) (No. 2022R1A2B5B02001584).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available upon request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
References
- Kim, D.-G.; Ko, S.-O. Road-Deposited Sediments Mediating the Transfer of Anthropogenic Organic Matter to Stormwater Runoff. Environ. Geochem. Health 2021, 43, 3287–3301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baum, P.; Kuch, B.; Dittmer, U. Adsorption of Metals to Particles in Urban Stormwater Runoff—Does Size Really Matter? Water 2021, 13, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijeyawardana, P.; Nanayakkara, N.; Gunasekara, C.; Karunarathna, A.; Law, D.; Pramanik, B.K. Removal of Cu, Pb and Zn from Stormwater Using an Industrially Manufactured Sawdust and Paddy Husk Derived Biochar. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2022, 28, 102640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, C.-C.; Weng, C.-H. Effects of Rainfall Patterns on Highway Runoff Pollution and Its Control. Water Environ. J. 2015, 29, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayhanian, M.; Singh, A.; Suverkropp, C.; Borroum, S. Impact of Annual Average Daily Traffic on Highway Runoff Pollutant Concentrations. J. Environ. Eng. 2003, 129, 975–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayhanian, M.; Fruchtman, B.D.; Gulliver, J.S.; Montanaro, C.; Ranieri, E.; Wuertz, S. Review of Highway Runoff Characteristics: Comparative Analysis and Universal Implications. Water Res. 2012, 46, 6609–6624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United States Department of Transportation (USDOT) and Federal Highway Administration (FHWA). Eisenhower Interstate Highway System Website. Available online: http://www.Fhwa.Dot.Gov/Interstate/Homepage.Cfm (accessed on 20 June 2017).
- Eriksson, E.; Baun, A.; Scholes, L.; Ledin, A.; Ahlman, S.; Revitt, M.; Noutsopoulos, C.; Mikkelsen, P.S. Selected Stormwater Priority Pollutants—A European Perspective. Sci. Total Environ. 2007, 383, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Lee, M. Stormwater Runoff Treatment Filtration System and Backwashing System. Water Sci. Technol. 2019, 79, 771–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.; Vymazal, J.; Malaviya, P. Application of Floating Treatment Wetlands for Stormwater Runoff: A Critical Review of the Recent Developments with Emphasis on Heavy Metals and Nutrient Removal. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 777, 146044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korea Office of Prime Minister; Ministry for Food, Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries; Korea Ministry of Knowledge Economy; Korea Ministry of Environment; Korea Ministry of Infrastructure and Transport; Korea Nation Fire Agency; Korea Rural Development Administration; Korea Forest Service. The Third Comprehensive Non-Point Sources Management Plan (2021−2025); Korea Ministry of Environment: Sejong, Korea, 2020. (In Korean)
- Bardin, J.P.; Gautier, A.; Barraud, S.; Chocat, B. The Purification Performance of Infiltration Basins Fitted with Pretreatment Facilities: A Case Study. Water Sci. Technol. 2001, 43, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hossain, M.A.; Furumai, H.; Nakajima, F.; Aryal, R.K. Heavy Metals Speciation in Soakaways Sediment and Evaluation of Metal Retention Properties of Surrounding Soil. Water Sci. Technol. 2007, 56, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmermann, J.; Dierkes, C.; Göbel, P.; Klinger, C.; Stubbe, H.; Coldewey, W.G. Metal Concentrations in Soil and Seepage Water Due to Infiltration of Roof Runoff by Long Term Numerical Modelling. Water Sci. Technol. 2005, 51, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrett, M.; Katz, L.; Taylor, S. Removal of Dissolved Heavy Metals in Highway Runoff. Transp. Res. Rec. J. Transp. Res. Board 2014, 2436, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na Nagara, V.; Sarkar, D.; Elzinga, E.J.; Datta, R. Removal of Heavy Metals from Stormwater Runoff Using Granulated Drinking Water Treatment Residuals. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2022, 28, 102636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, C.-H.; Davis, A.P. Evaluation and Optimization of Bioretention Media for Treatment of Urban Storm Water Runoff. J. Environ. Eng. 2005, 131, 1521–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, A.P.; Shokouhian, M.; Sharma, H.; Minami, C.; Winogradoff, D. Water Quality Improvement through Bioretention: Lead, Copper, and Zinc Removal. Water Environ. Res. 2003, 75, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitcher, S.K.; Slade, R.C.T.; Ward, N.I. Heavy Metal Removal from Motorway Stormwater Using Zeolites. Sci. Total Environ. 2004, 334–335, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, P.; Yang, L.; Huang, T. Adsorption Characteristics of Construction Waste for Heavy Metals from Urban Stormwater Runoff. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2015, 23, 1542–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, M.; Hilbig, H.; Badenberg, S.C.; Fassnacht, J.; Drewes, J.E.; Helmreich, B. Heavy Metal Removal Mechanisms of Sorptive Filter Materials for Road Runoff Treatment and Remobilization under De-Icing Salt Applications. Water Res. 2016, 102, 453–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ernst, C.; Katz, L.; Barrett, M. Removal of Dissolved Copper and Zinc from Highway Runoff via Adsorption. J. Sustain. Water Built. Environ. 2016, 2, 04015007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, K.R.; Xie, T.; Dastgheibi, S. Removal of Heavy Metals from Urban Stormwater Runoff Using Different Filter Materials. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 282–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Günay, A.; Arslankaya, E.; Tosun, İ. Lead Removal from Aqueous Solution by Natural and Pretreated Clinoptilolite: Adsorption Equilibrium and Kinetics. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 146, 362–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, C.R.; Rubio, J. New Basis for Adsorption of Ionic Pollutants onto Modified Zeolites. Miner. Eng. 2007, 20, 552–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.; Saunders, J.A. Effects of PH on Metals Precipitation and Sorption: Field Bioremediation and Geochemical Modeling Approaches. Vadose Zone J. 2003, 2, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taffarel, S.R.; Rubio, J. On the Removal of Mn2+ Ions by Adsorption onto Natural and Activated Chilean Zeolites. Miner. Eng. 2009, 22, 336–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todeschini, S.; Papiri, S.; Ciaponi, C. Performance of stormwater detention tanks for urban drainage systems in northern Italy. J. Environ. Manag. 2012, 101, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayhanian, M.; Rasa, E.; Vichare, A.; Leatherbarrow, J.E. Utility of Suspended Solid measurements for storm-water runoff treatment. J. Environ. Eng. 2008, 134, 712–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korea Ministry of Environment. Installation and Operation Manual of Non-Point Pollution Reduction Facility; Korea Ministry of Environment: Sejong, Korea, 2020. (In Korean)
- Thomas, H.C. Heterogeneous Ion Exchange in a Flowing System. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1944, 66, 1664–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalfa, L.; Sdiri, A.; Bagane, M.; Cervera, M.L. A Calcined Clay Fixed Bed Adsorption Studies for the Removal of Heavy Metals from Aqueous Solutions. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 278, 123935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suksabye, P.; Thiravetyan, P.; Nakbanpote, W. Column study of chromium(VI) adsorption from electroplating industry by coconut coir pith. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 160, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sizirici, B.; Yildiz, I. Simultaneous removal of organics and metals in fixed bed using gravel and iron oxide coated gravel. Results Eng. 2020, 5, 100093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faisal, A.A.H.; Abdul-Kareem, M.B.; Mohammed, A.K.; Naushad, M.; Ghfar, A.A.; Ahamad, T. Humic acid coated sand as a novel sorbent in permeable reactive barrier for environmental remediation of groundwater polluted with copper and cadmium ions. J. Water Process Eng. 2020, 36, 101373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasharrofi, S.; Rouzitalab, Z.; Maklavany, D.M.; Esmaeili, A.; Rabieezadeh, M.; Askarieh, M.; Rashidi, A.; Taghdisian, H. Adsorption of cadmium using modified zeolite-supported nanoscale zero-valent iron composites as a reactive material for PRBs. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 736, 139570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winston, R.J.; Hunt, W.F. Characterizing Runoff from Roads: Particle Size Distributions, Nutrients, and Gross Solids. J. Environ. Eng. 2017, 143, 04016074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saadi, Z.; Saadi, R.; Fazaeli, R. Fixed-Bed Adsorption Dynamics of Pb (II) Adsorption from Aqueous Solution Using Nanostructured γ-Alumina. J. Nanostruct. Chem. 2013, 3, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourbaix, M. Atlas of Electrochemical Equilibria in Aqueous Solutions, 2nd ed.; Translated from the French by James A. Franklin (except Sections I, III 5 and III 6, Which Were Originally Written in English); National Association of Corrosion Engineers: Houston, TX, USA, 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Haile, T.M.; Fuerhacker, M. Simultaneous Adsorption of Heavy Metals from Roadway Stormwater Runoff Using Different Filter Media in Column Studies. Water 2018, 10, 1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esfandiar, N.; Suri, R.; McKenzie, E.R. Competitive sorption of Cd, Cr, Cu, Ni, Pb and Zn from stormwater runoff by five low-cost sorbents; Effects of co-contaminants, humic acid, salinity and pH. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 423, 126938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sounthararajah, D.P.; Loganathan, P.; Kandasamy, J.; Vigneswaran, S. Removing heavy metals using permeable pavement system with a titanate nano-fibrous adsorbent column as a post treatment. Chemosphere 2017, 168, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).