A Localized Assessment of Groundwater Quality Status Using GIS-Based Water Quality Index in Industrial Zone of Faisalabad, Pakistan
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
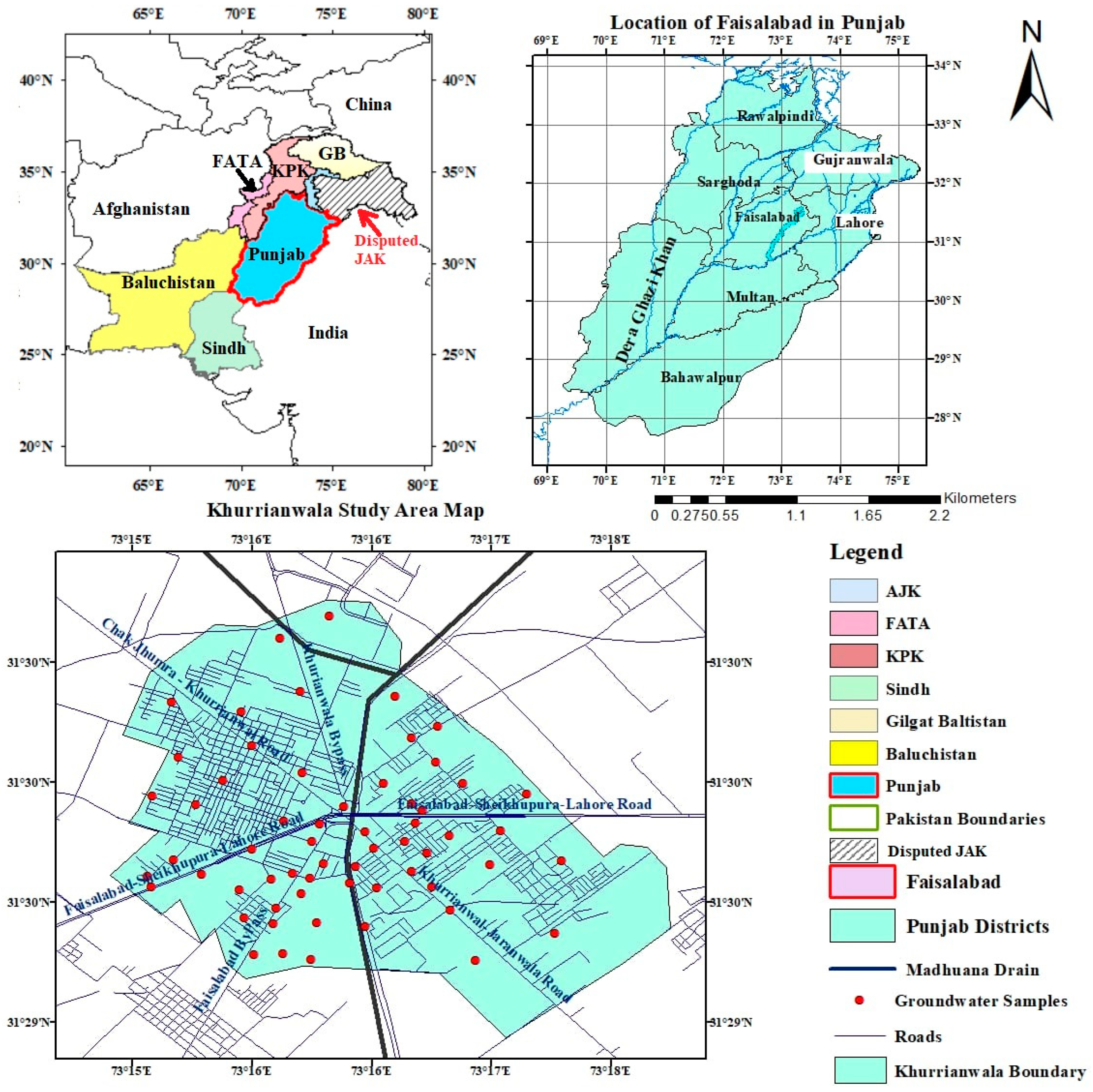
2.1. Study Area and Sampling Locations
2.2. Analysis of Samples
2.3. GIS Analysis
2.4. WQI Analysis
- = relative weightage of the ith parameter;
- = weight assigned to the ith parameter;
- n = total number of parameters.
- Q = quality rating;
- ci = concentration of each sampling parameter;
- si = permissible values of each parameter as recommended by WHO.
- SIi = subindex of ith parameter;
- Qi = quality rating of ith parameter.
3. Results
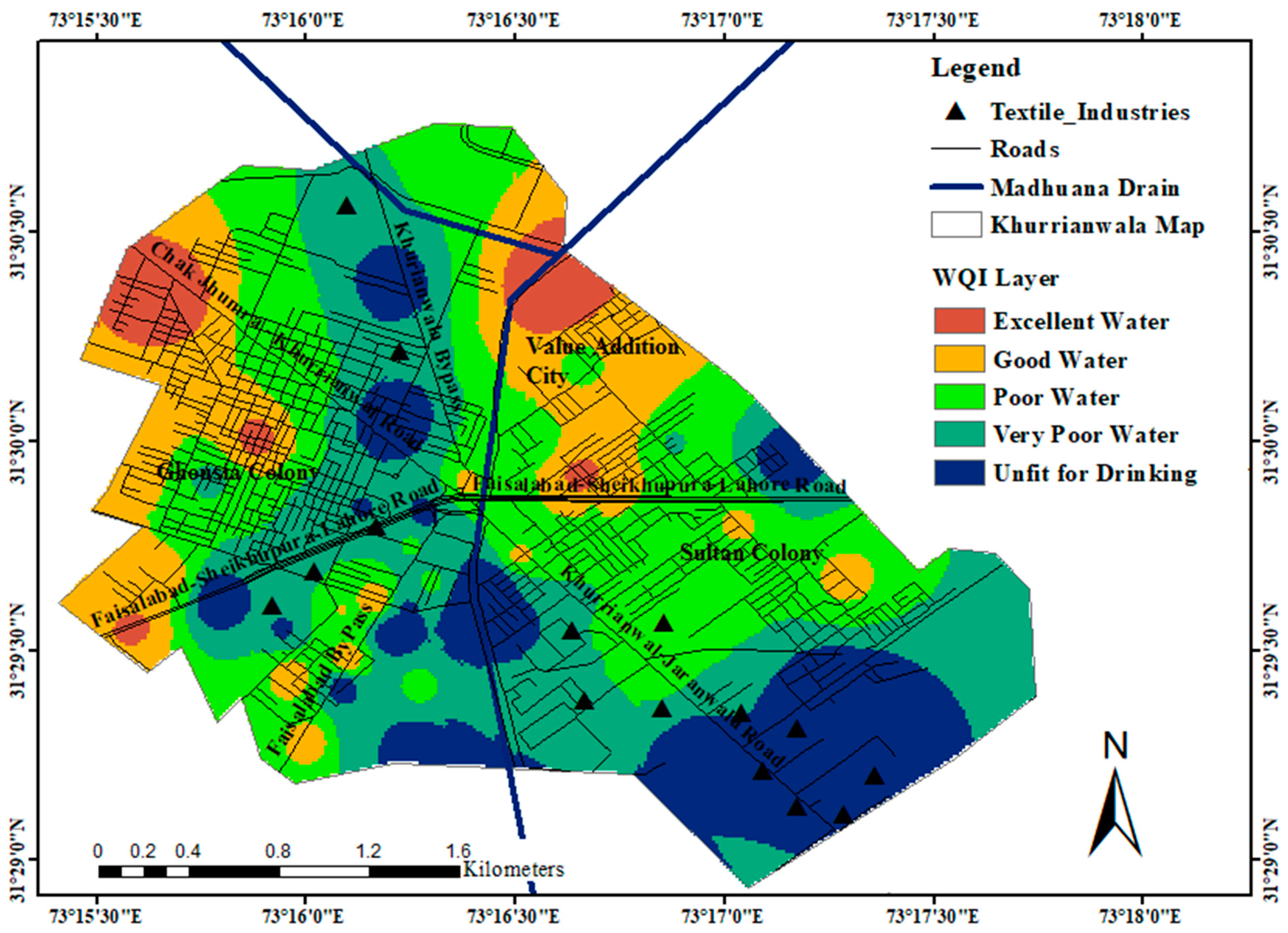
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Umar, M.; Khan, S.; Arshad, A.; Anh, D. A modified approach to quantify aquifer vulnerability to pollution towards sustainable groundwater management in Irrigated Indus Basin. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 27257–27278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saatsaz, M.; Chitsazan, M.; Eslamian, S.; Sulaiman, W.N.A. The application of groundwatermodelling to simulate the behavior of groundwaterresources in the Ramhormooz Aquifer, Iran. Int. J. Water 2011, 6, 29–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramamoorthy, P.; Rammohan, V. Assessment of groundwater potential zone using remote sensing and GIS in Varahanadhi watershed, Tamil Nadu, India. Int. J. Res. Appl. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2015, 3, 695–702. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, A.; Nasir, A.; Basheer, S.; Arslan, C.; Anwar, S. Ground water quality assessment by using geographical information system and water quality index: A case study of chokera, Faisalabad, Pakistan. Water Conserv. Manag. 2019, 3, 7–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, A.S. Improving food security and livelihood resilience through groundwater management in Pakistan. Glob. Adv. Res. J. Agric. Sci. 2015, 4, 687–710. [Google Scholar]
- Kahlown, M.A.; Ashraf, M.; Hussain, M.; Salam, H.A.; Bhatti, A.Z. Effluents on Water Resources, Sold, Cropsand; Pakistan Council of Research in Water Resources: Hyderabad, Pakistan, 2006.
- Qureshi, A.S.; Gill, M.A.; Sarwar, A. Sustainable groundwater management in Pakistan: Challenges and opportunities. Irrig. Drain. 2010, 59, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Smith, C.D.; Wang, L.; Li, Z.; Xiong, C.; Zhang, R. Combining spatial analysis and a drinking water quality index to evaluate monitoring data. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nas, B.; Berktay, A. Groundwater quality mapping in urban groundwater using GIS. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2010, 160, 215–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, B.; Wong, Y.; Ihara, M.; Nakada, N.; Yu, Z.; Sugie, Y.; Miao, Y.; Tanaka, H.; Guan, Y. Characterization of nitrosamines and nitrosamine precursors as non-point source pollutants during heavy rainfall events in an urban water environment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 424, 127552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific. State of the Environment in Asia and the Pacific (Bangkok: United Nations ESCAP); Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific: Bangkok, Thailand, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Evans, A.E.V.; Hanjra, M.A.; Jiang, Y.; Qadir, M.; Drechsel, P. Water Quality: Assessment of the Current Situation in Asia. Int. J. Water Resour. Dev. 2012, 28, 195–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, Y.J.; Shimizu, Y.; He, K.; Nik Sulaiman, N.M. Comparison among different ASEAN water quality indices for the assessment of the spatial variation of surface water quality in the Selangor river basin, Malaysia. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasir, M.S.; Nasir, A.; Rashid, H.; Shah, S.H.H. Spatial variability and long-term analysis of groundwater quality of Faisalabad industrial zone. Appl. Water Sci. 2017, 7, 3197–3205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakistan Council of Research in Water Resources (PCRWR). Water Quality Status of Pakistan, Fifth Monitoring Report 2005–2006. In National Water Quality Monitoring Programme; Pakistan Council of Research in Water Resources: Hyderabad, Pakistan, 2007; p. 133. [Google Scholar]
- Solangi, G.S.; Siyal, A.A.; Babar, M.M.; Siyal, P. Evaluation of surface water quality using the water quality index (Wqi) and the synthetic pollution index (spi): A case study of indus delta region of pakistan. Desalin. Water Treat. 2018, 118, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, Y.J.; Nakayama, R.; Shimizu, Y.; Kamiya, A.; Shen, S.; Rashid, I.Z.M.; Sulaiman, N.M.N. Toward industrial revolution 4.0: Development, validation, and application of 3D-printed IoT-based water quality monitoring system. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 324, 129230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, P.; Singh, P.K.; Sinha, R.R.; Tiwari, A.K. Assessment of groundwater quality status by using water quality index (WQI) and geographic information system (GIS) approaches: A case study of the Bokaro district, India. Appl. Water Sci. 2020, 10, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Murasingh, S. Analysis of Groundwater Potential Zones Using Electrical Resistivity, RS and GIS Techniques in a Typical Mine Area of Odisha. Master’s Thesis, Department of Civil Engineering National Institute of Technology, Rourkela, India, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Mahmood, A.; Muqbool, W.; Mumtaz, M.W.; Ahmad, F. Application of multivariate statisticaltechniques for the characterization of groundwaterquality of Lahore, Gujranwala and Sialkot (Pakistan). Pak. J. Anal. Environ. Chem. 2011, 12, 102–112. [Google Scholar]
- Arkoç, O. Application of water quality index with the aid of geographic information system in eastern thrace to assess groundwater quality. Jeol. Mühendisliği Derg. 2016, 40, 189–208. [Google Scholar]
- Imtiaz, F.; Ahmad, I.; Ahmad, S.R. Gis based evaluation of groundwater quality of western lahore using water quality index. Pak. J. Agric. Sci. 2018, 55, 653–665. [Google Scholar]
- Balakrishnan, P. Groundwater quality mapping using geographic information system (GIS): A case study of Gulbarga City, Karnataka, India. Afr. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 5, 1069–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabbir, R.; Ahmad, S.S. Use of Geographic Information System and Water Quality Index to Assess Groundwater Quality in Rawalpindi and Islamabad. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2015, 40, 2033–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- State, A. Groundwater Quality Mapping using GIS: A Case Study of Awka, Anambra state, Nigeria. Int. J. Eng. Manag. Res. 2016, 6, 579–584. [Google Scholar]
- APHA. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 20th ed.; Method. 5210 B; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg, A.E.; Clesceri, L.S.; Eaton, A.D. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Boah, D.K.; Twum, S.B.; Pelig-Ba, K.B. Mathematical computation of water quality index of Vea dam in upper east Region of Ghana. Environ. Sci. 2015, 3, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mutasher, A.K.A.; Al-Mohammed, F.M.; Aljibori, H.S.S. Groundwater quality assessment for irrigation purpose using water quality index in Green Belt project in Karbala city—Iraq. J. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2021, 16, 4060–4078. [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez, F.J.; Kahn, H.L. Clinical Methods for Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometry. Clin. Chem. Newsl. 1971, 3, 34. [Google Scholar]
- Vaiphei, S.P.; Kurakalva, R.M.; Sahadevan, D.K. Water quality index and GIS-based technique for assessment of groundwater quality in Wanaparthy watershed, Telangana, India. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 45041–45062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adimalla, N. Groundwater quality for drinking and irrigation purposes and potential health risks assessment: A case study from semiarid region of South India. Expo. Health 2019, 11, 109–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.K.; Logeshkumaran, A.; Magesh, N.S.; Godson, P.S.; Chandrasekar, N. Hydrogeochemistry and application of water quality index (WQI) for groundwater quality assessment, Anna Nagar, part of Chennai City, Tamil Nadu, India. Appl. Water Sci. 2015, 5, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chaurasia, A.K.; Pandey, H.K.; Tiwari, S.K.; Prakash, R.; Pandey, P.; Ram, A. Groundwater quality assessment using water quality index (WQI) in parts of Varanasi District, Uttar Pradesh, India. J. Geol. Soc. India 2018, 92, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Xing, B. A Comparison of the Performance of Different Interpolation Methods in Replicating Rainfall Magnitudes under Different Climatic Conditions in Chongqing Province (China). Atmosphere 2021, 12, 1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alqarawy, A.; El Osta, M.; Masoud, M.; Elsayed, S.; Gad, M. Use of Hyperspectral Reflectance and Water Quality Indices to Assess Groundwater Quality for Drinking in Arid Regions, Saudi Arabia. Water 2022, 14, 2311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, A.K.; Kumar, S.A.; Kumar, S.A.; Singh, M.P. Hydrogeochemical analysis and evaluation of surface water quality of Pratapgarh district, Uttar Pradesh, India. Appl. Water Sci. 2017, 7, 1609–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zolekar, R.B.; Todmal, R.S.; Bhagat, V.S.; Bhailume, S.A.; Korade, M.S.; Das, S. Hydrochemical characterization and geospatial analysis of groundwater for drinking and agricultural usage in Nashik district in Maharashtra, India. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2020, 23, 4433–4452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakaa, B.; Elbeltagi, A.; Boudibi, S.; Chaffaï, H.; Islam, A.R.M.; Kulimushi, L.C.; Choudhari, P.; Hani, A.; Brouziyne, Y.; Wong, Y.J. Water quality index modeling using random forest and improved SMO algorithm for support vector machine in Saf-Saf river basin. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 48491–48508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansouri, Z.; Leghrieb, Y.; Kouadri, S.; Al-Ansari, N.; Najm, H.M.; Mashaan, N.S.; Eldirderi, M.M.A.; Khedher, K.M. Hydro-Geochemistry and Groundwater Quality Assessment of Ouargla Basin, South of Algeria. Water 2022, 14, 2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Li, J.; Zhang, M.; You, D.; Zhou, Y.; Gong, Z. Groundwater Health Risk Assessment Based on Monte Carlo Model Sensitivity Analysis of Cr and As—A Case Study of Yinchuan City. Water 2022, 14, 2419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.; Zhou, Y.; Lu, Y.; Du, X. Hydrochemical Evolution and Quality Assessment of Groundwater in the Sanjiang Plain, China. Water 2022, 14, 1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Upreti, P.; Allemailem, K.S.; Almatroudi, A.; Rahmani, A.H.; Albalawi, G.M. Geospatial Assessment of Ground Water Quality and Associated Health Problems in the Western Region of India. Water 2022, 14, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nsabimana, A.; Li, P.; He, S.; He, X.; Alam, S.M.K.; Fida, M. Health Risk of the Shallow Groundwater and Its Suitability for Drinking Purpose in Tongchuan, China. Water 2021, 13, 3256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalumbe, L.; Kanyerere, T. Characterisation of Hydro-Geochemical Processes Influencing Groundwater Quality in Rural Areas: A Case Study of Soutpansberg Region, Limpopo Province, South Africa. Water 2022, 14, 1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Osta, M.; Masoud, M.; Alqarawy, A.; Elsayed, S.; Gad, M. Groundwater Suitability for Drinking and Irrigation Using Water Quality Indices and Multivariate Modeling in Makkah Al-Mukarramah Province, Saudi Arabia. Water 2022, 14, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes-Toscano, C.A.; Alfaro-Cuevas-Villanueva, R.; Cortés-Martínez, R.; Morton-Bermea, O.; Hernández-Álvarez, E.; Buenrostro-Delgado, O.; Ávila-Olivera, J.A. Hydrogeochemical Characteristics and Assessment of Drinking Water Quality in the Urban Area of Zamora, Mexico. Water 2020, 12, 556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, F.; Zhao, Z.; Yang, L.; Ma, Y.; Li, B.; Gong, L.; Liu, H. Phreatic Water Quality Assessment and Associated Hydrogeochemical Processes in an Irrigated Region Along the Upper Yellow River, Northwestern China. Water 2020, 12, 463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haider, H.; Ghumman, A.R.; Al-Salamah, I.S.; Thabit, H. Assessment Framework for Natural Groundwater Contamination in Arid Regions: Development of Indices and Wells Ranking System Using Fuzzy VIKOR Method. Water 2020, 12, 423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, L.; Mei, Y.; Yu, K.; Li, Y.; Meng, X.; Hu, F. Anthropogenic Effects on Hydrogeochemical Characterization of the Shallow Groundwater in an Arid Irrigated Plain in Northwestern China. Water 2019, 11, 2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haider, H.; Alkhowaiter, M.H.; Shafiquzzaman, M.; AlSaleem, S.S.; Almoshaogeh, M.; Alharbi, F. Spatiotemporal Water Quality Variations in Smaller Water Supply Systems: Using Modified CCME WQI from Groundwater Source to Distribution Networks. Water 2019, 11, 1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kurwadkar, S.; Kanel SRNakarmi, A. Groundwater pollution: Occurrence, detection, and remediation of organic and inorganic pollutants. Water Environ. Res. 2020, 92, 1659–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agriculture Pesticide Ordinance. 1970. Available online: https://senate.gov.pk/uploads/documents/1658381597_805.pdf (accessed on 5 October 2022).
- Altaf, S. Sustainable Urban Groundwater Governance in Faisalabad, Pakistan: Challenges and Possibilities. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Louisville, Louisville, KY, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajjad, M.M.; Wang, J.; Abbas, H.; Ullah, I.; Khan, R.; Ali, F. Impact of Climate and Land-Use Change on Groundwater Resources, Study of Faisalabad District, Pakistan. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
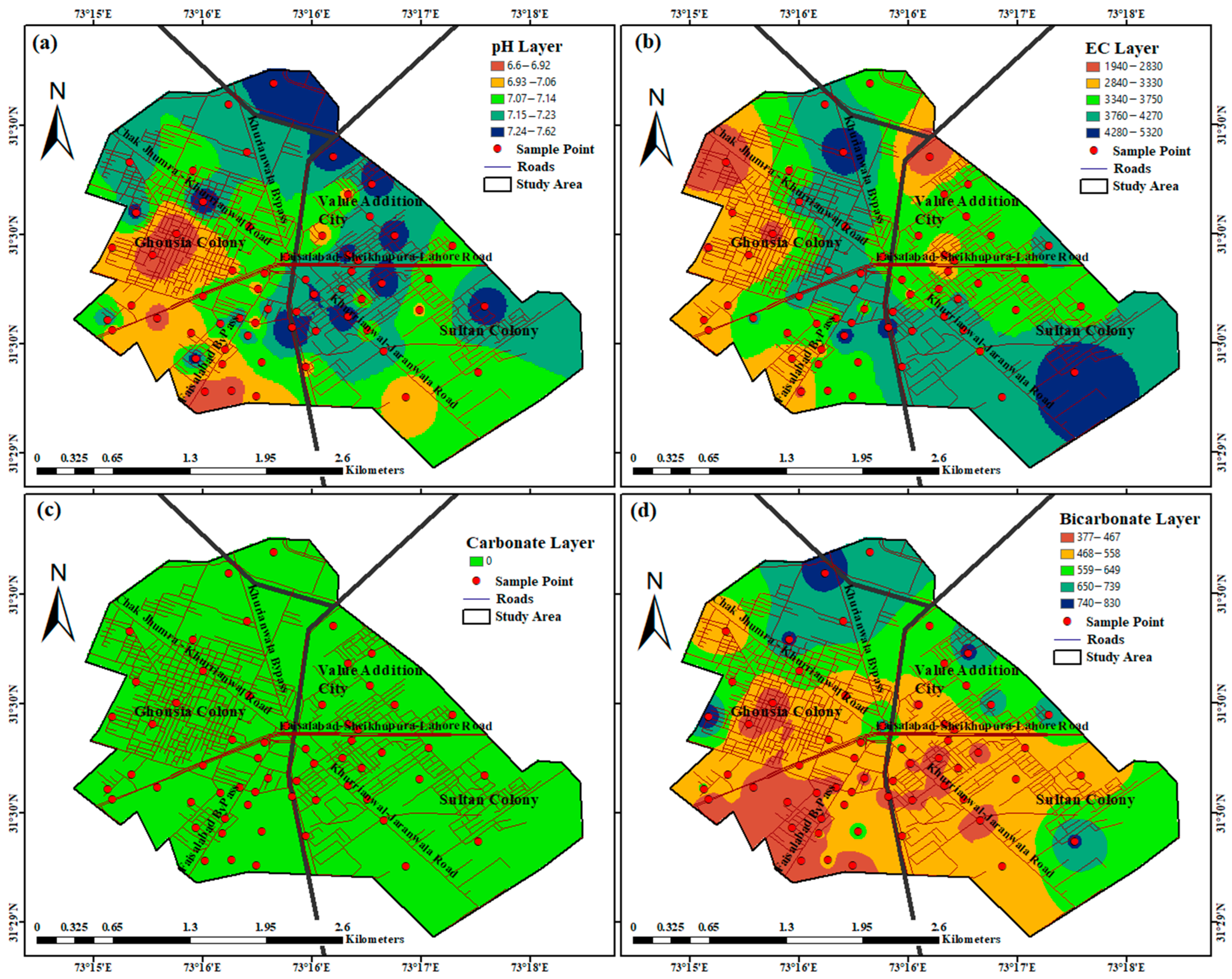

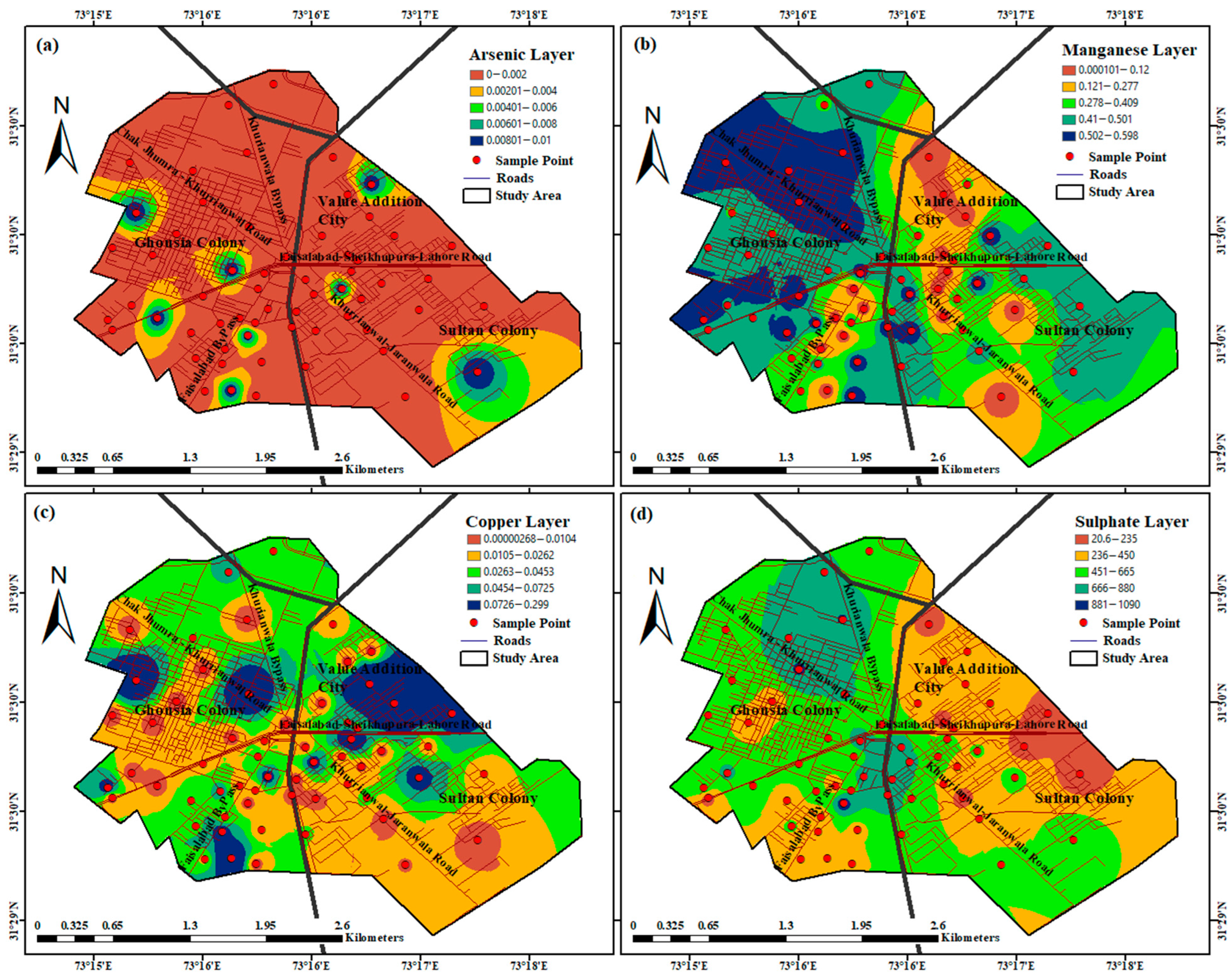

| Water Quality Parameter | Units | Minimum | Maximum | Mean | WHO Standard Values |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TDS | (mg/L) | 971 | 2660 | 1794 | 1000 |
| TSS | (mg/L) | 40.3 | 200 | 98.4 | 120 |
| pH | - | 6.5 | 7.62 | 7.07 | 7 |
| EC | (μS */cm) | 1940 | 5320 | 3581 | 197.14 |
| Mn | (mg/L) | 0.0001 | 0.598 | 0.356 | 0.5 |
| Cl | (mg/L) | 172 | 898 | 557 | 250 |
| As | (mg/L) | 0 | 0.01 | 0.001 | 50 |
| Fe | (mg/L) | 8.82 × 10−7 | 0.519 | 0.0480 | 0.3 |
| Sulfate | (mg/L) | 20.6 | 1090 | 484 | 250 |
| Turbidity | (NTU **) | 1.37 × 10−5 | 5 | 0.355 | 5 |
| Bicarbonate | (mg/L) | 377 | 830 | 519 | 120 |
| Ca | (mg/L) | 28 | 232 | 86.86 | 75 |
| Mg | (mg/L) | 243 | 1070 | 494 | 50 |
| Cu | (mg/L) | 2.68 × 10−6 | 0.299 | 0.0479 | 1 |
| Carbonate | (mg/L) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 60 |
| Cr | (mg/L) | 3.99 × 10−6 | 0.106 | 0.05 | 0.05 |
| Water Quality Parameter | WHO Standard Value | Assigned Weight | Relative Weightage |
|---|---|---|---|
| TDS (mg/L) | 1000 | 3 | 0.058 |
| TSS (mg/L) | 120 | 3 | 0.058 |
| pH | 7 | 4 | 0.078 |
| EC (μS/cm) | 197.14 | 3 | 0.058 |
| Mn (mg/L) | 0.5 | 3 | 0.058 |
| Cl (mg/L) | 250 | 3 | 0.058 |
| As (mg/L) | 50 | 5 | 0.098 |
| Fe (mg/L) | 0.3 | 4 | 0.078 |
| Sulfate (mg/L) | 250 | 3 | 0.058 |
| Turbidity (NTU) | 5 | 2 | 0.039 |
| Bicarbonate (mg/L) | 120 | 2 | 0.039 |
| Ca (mg/L) | 75 | 2 | 0.039 |
| Mg (mg/L) | 50 | 2 | 0.039 |
| Cu (mg/L) | 1 | 4 | 0.078 |
| Carbonate (mg/L) | 60 | 3 | 0.058 |
| Cr (mg/L) | 0.05 | 5 | 0.098 |
| Total | ∑wi = 51 | 1 |
| Samples 1–20 | WQI Value | Samples 20–40 | WQI Value | Sample 40–60 | WQI Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| G1 | 168.98 | G21 | 143.98 | G41 | 182.98 |
| G2 | 166.59 | G22 | 232.4 | G42 | 179.94 |
| G3 | 162.73 | G23 | 173.16 | G43 | 174.86 |
| G4 | 172.17 | G24 | 208.94 | G44 | 171.26 |
| G5 | 125.38 | G25 | 160.07 | G45 | 179.38 |
| G6 | 184.79 | G26 | 193.86 | G46 | 179.99 |
| G7 | 186.43 | G27 | 162.57 | G47 | 181.7 |
| G8 | 169.73 | G28 | 200.77 | G48 | 191.73 |
| G9 | 221.22 | G29 | 231.62 | G49 | 182.95 |
| G10 | 199.26 | G30 | 222.12 | G50 | 178.45 |
| G11 | 177.96 | G31 | 179.75 | G51 | 218.6 |
| G12 | 110.32 | G32 | 155.84 | G52 | 209.38 |
| G13 | 164.38 | G33 | 144.08 | G53 | 196.73 |
| G14 | 181.04 | G34 | 234.65 | G54 | 247.09 |
| G15 | 166.18 | G35 | 155.42 | G55 | 168.13 |
| G16 | 173.13 | G36 | 209.12 | G56 | 243.09 |
| G17 | 223.11 | G37 | 184 | G57 | 227.33 |
| G18 | 191.17 | G38 | 229.55 | G58 | 207.04 |
| G19 | 184.58 | G39 | 186.64 | G59 | 167.95 |
| G20 | 133.85 | G40 | 211.84 | G60 | 195.93 |
| SR. | WQI Range | Type of Water | % Area in Each Class |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | <50 | Excellent water | 5 |
| 2. | 50–100 | Good water | 17 |
| 3. | 100–200 | Poor water | 32 |
| 4. | 200–300 | Very poor water | 29 |
| 5. | >300 | Unfit for drinking | 17 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ullah, A.S.; Rashid, H.; Khan, S.N.; Akbar, M.U.; Arshad, A.; Rahman, M.M.; Mustafa, S. A Localized Assessment of Groundwater Quality Status Using GIS-Based Water Quality Index in Industrial Zone of Faisalabad, Pakistan. Water 2022, 14, 3342. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14203342
Ullah AS, Rashid H, Khan SN, Akbar MU, Arshad A, Rahman MM, Mustafa S. A Localized Assessment of Groundwater Quality Status Using GIS-Based Water Quality Index in Industrial Zone of Faisalabad, Pakistan. Water. 2022; 14(20):3342. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14203342
Chicago/Turabian StyleUllah, Ahsan Saif, Haroon Rashid, Shahbaz Nasir Khan, Muhammad Umar Akbar, Arfan Arshad, Md. Masudur Rahman, and Shumaila Mustafa. 2022. "A Localized Assessment of Groundwater Quality Status Using GIS-Based Water Quality Index in Industrial Zone of Faisalabad, Pakistan" Water 14, no. 20: 3342. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14203342





