Distribution Characteristics and Ecological Risk Assessment of Nitrogen, Phosphorus, and Some Heavy Metals in the Sediments of Yueliang Lake in Western Jilin Province, Northeast China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sample Collection and Analysis
2.3. Contamination and Risk Assessment Methods
2.3.1. Geo-Accumulation Index
2.3.2. Potential Ecological Risk Index
3. Results and Discussion
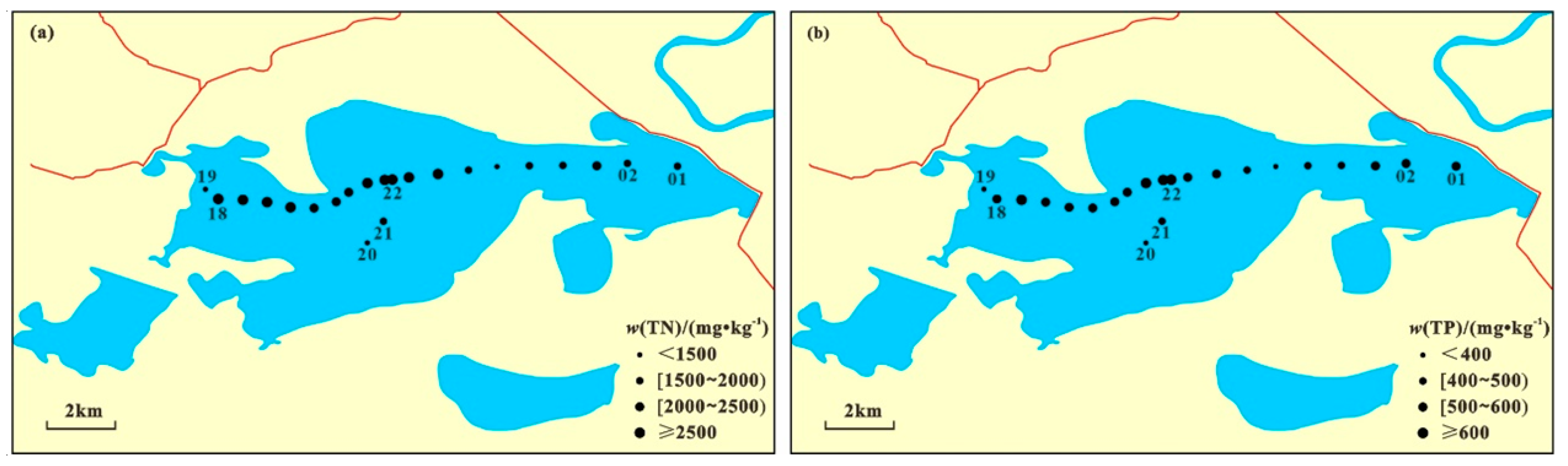
3.1. Distribution Characteristics of Nitrogen and Phosphorus
3.2. Distribution Characteristics of Organic Carbon and Nutrient Ratio
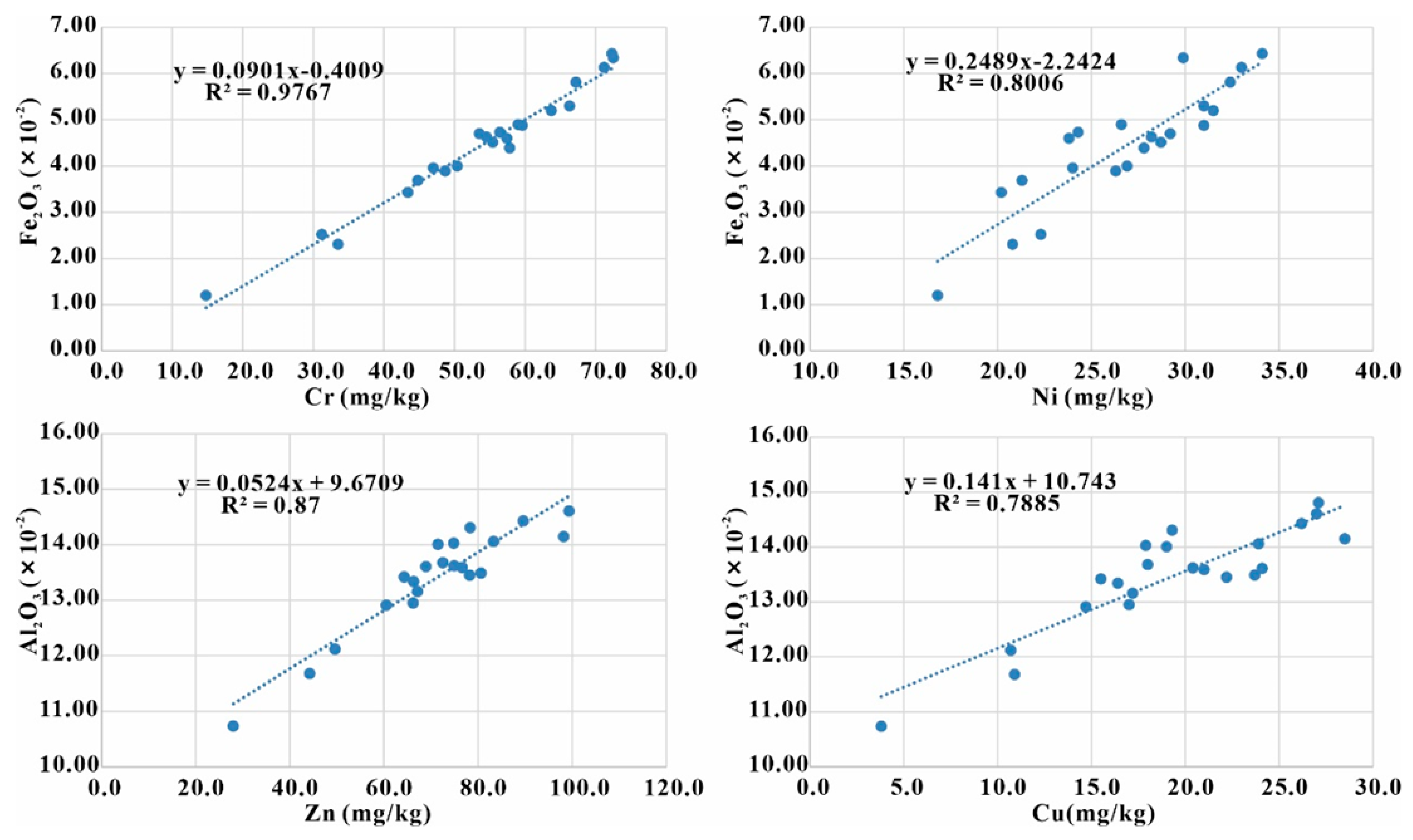
3.3. Distribution Characteristics of Heavy Metals
3.3.1. Heavy Metal Concentration of Surface Sediments
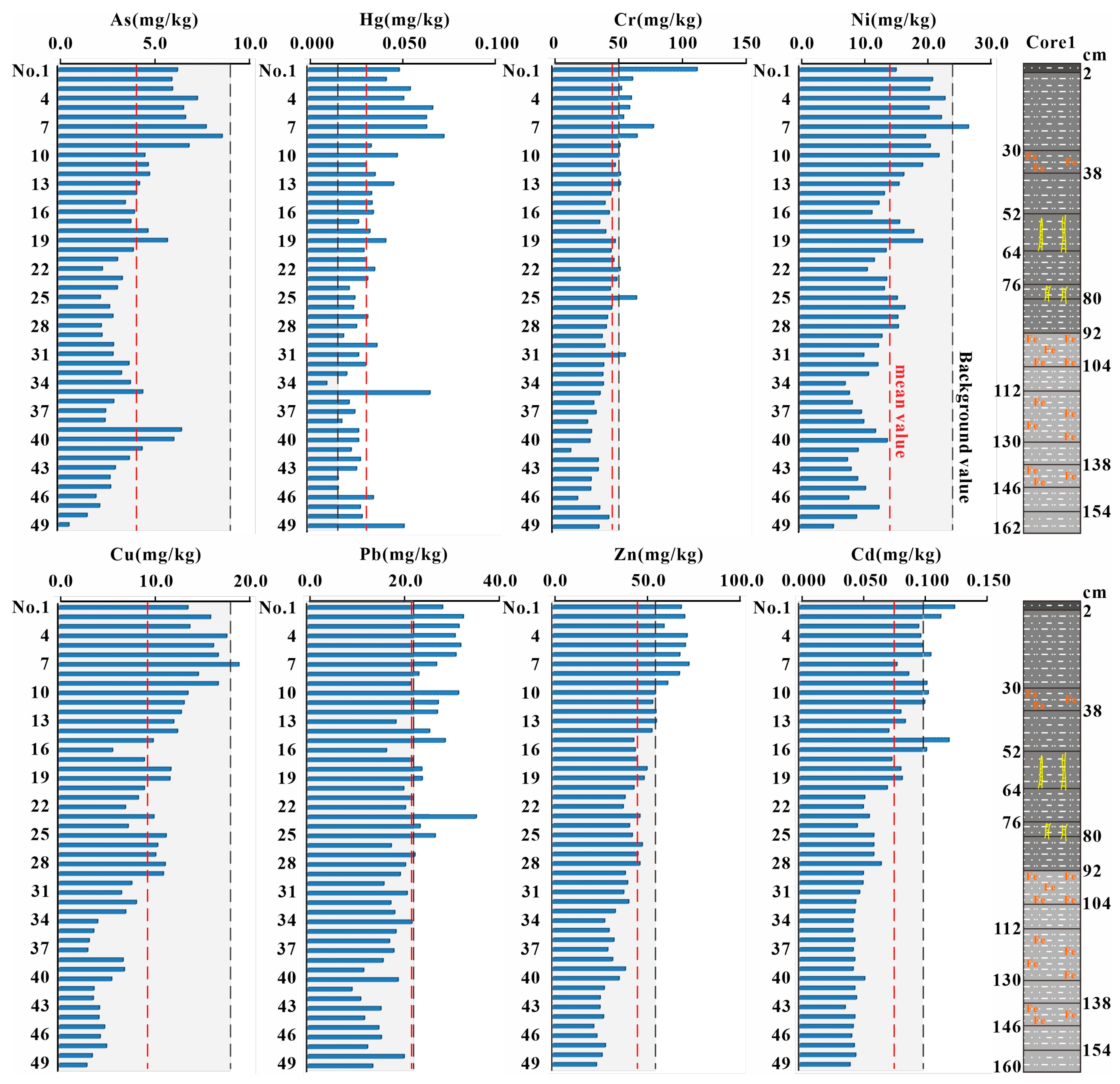
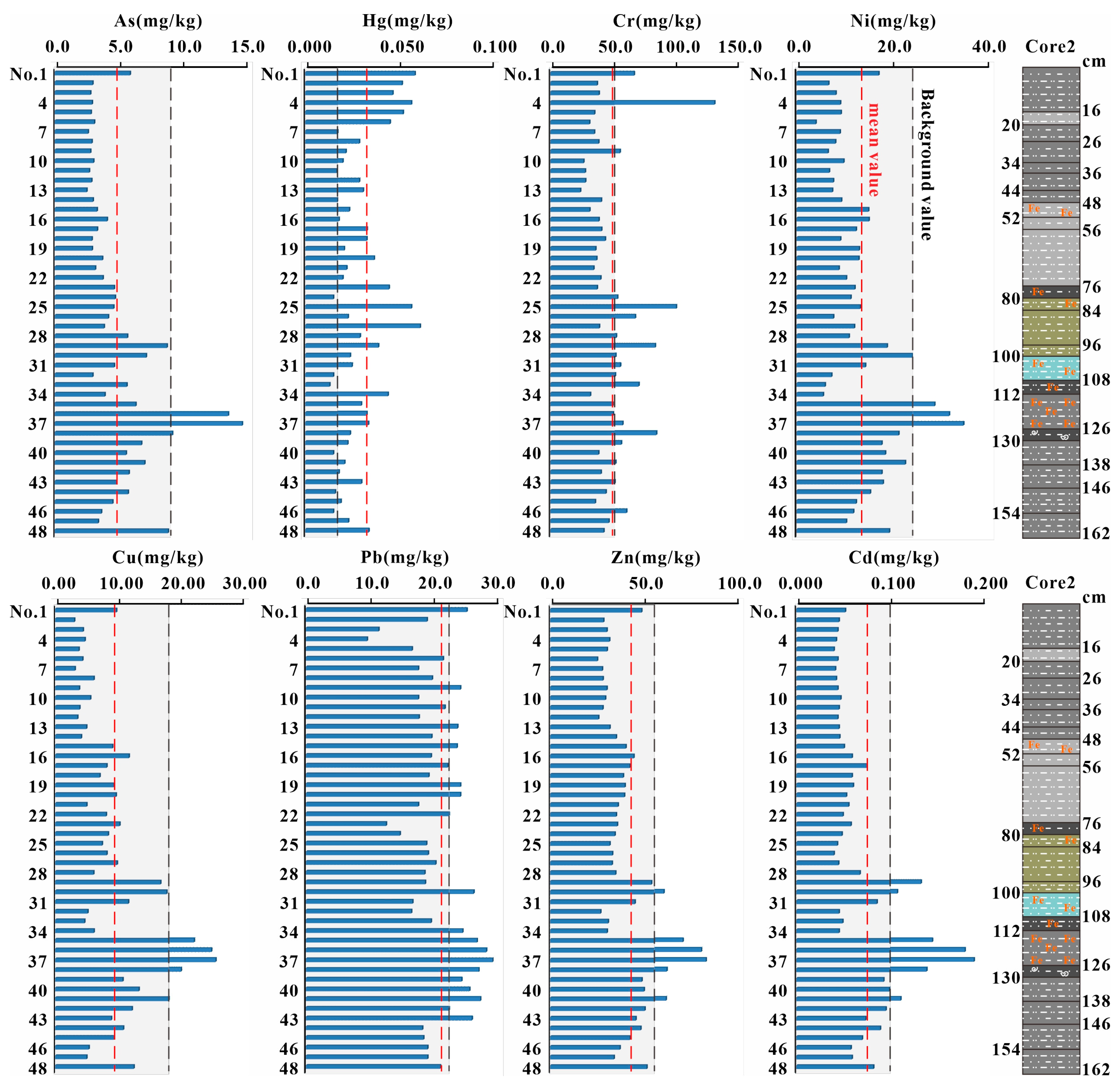
3.3.2. Concentrations and Distribution of Heavy Metals in Sediment Cores
3.4. Ecological Risk Assessment
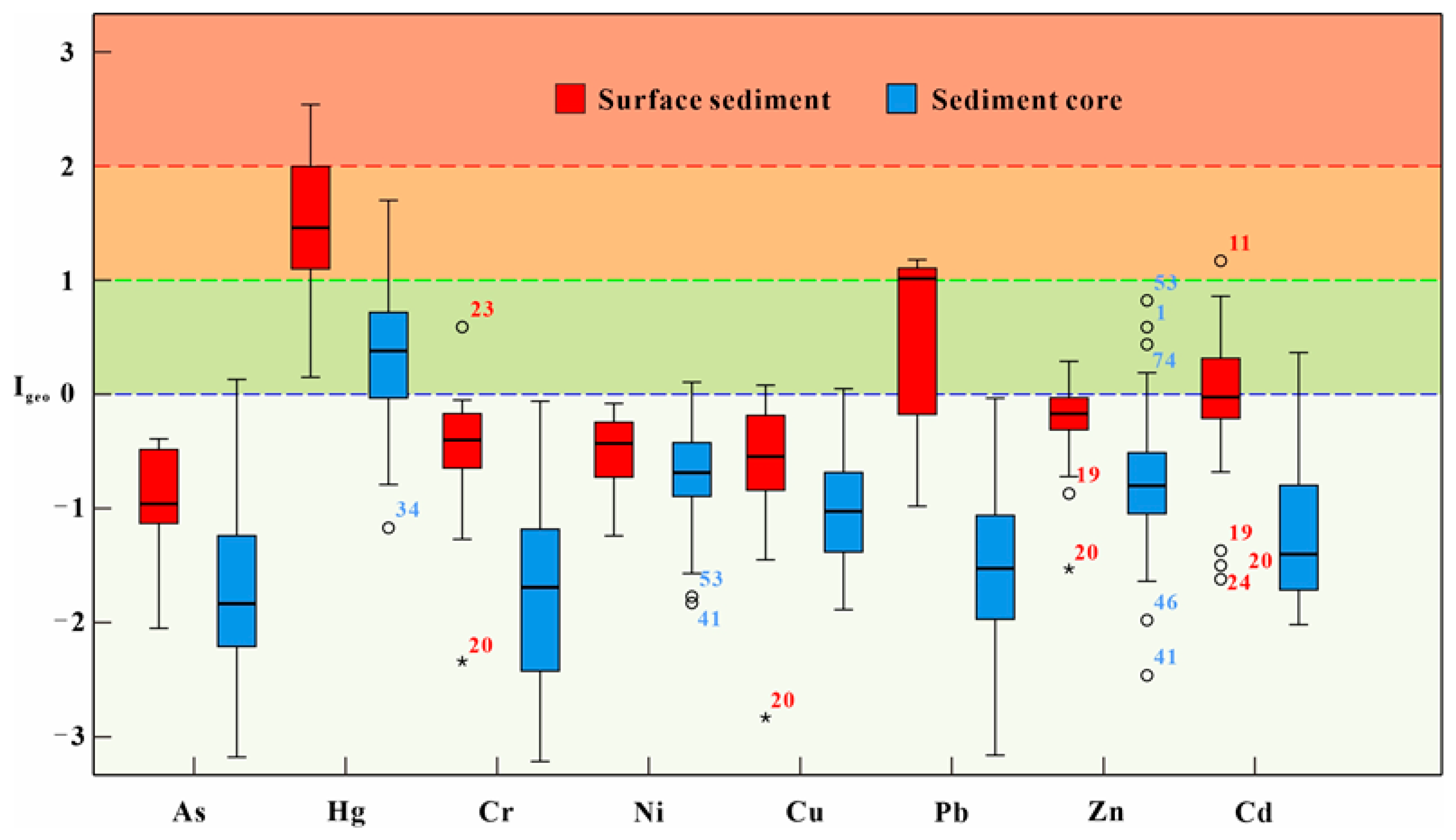
3.4.1. Evaluation of Potential Ecological Risk Index
3.4.2. Evaluation of Potential Ecological Risk Index
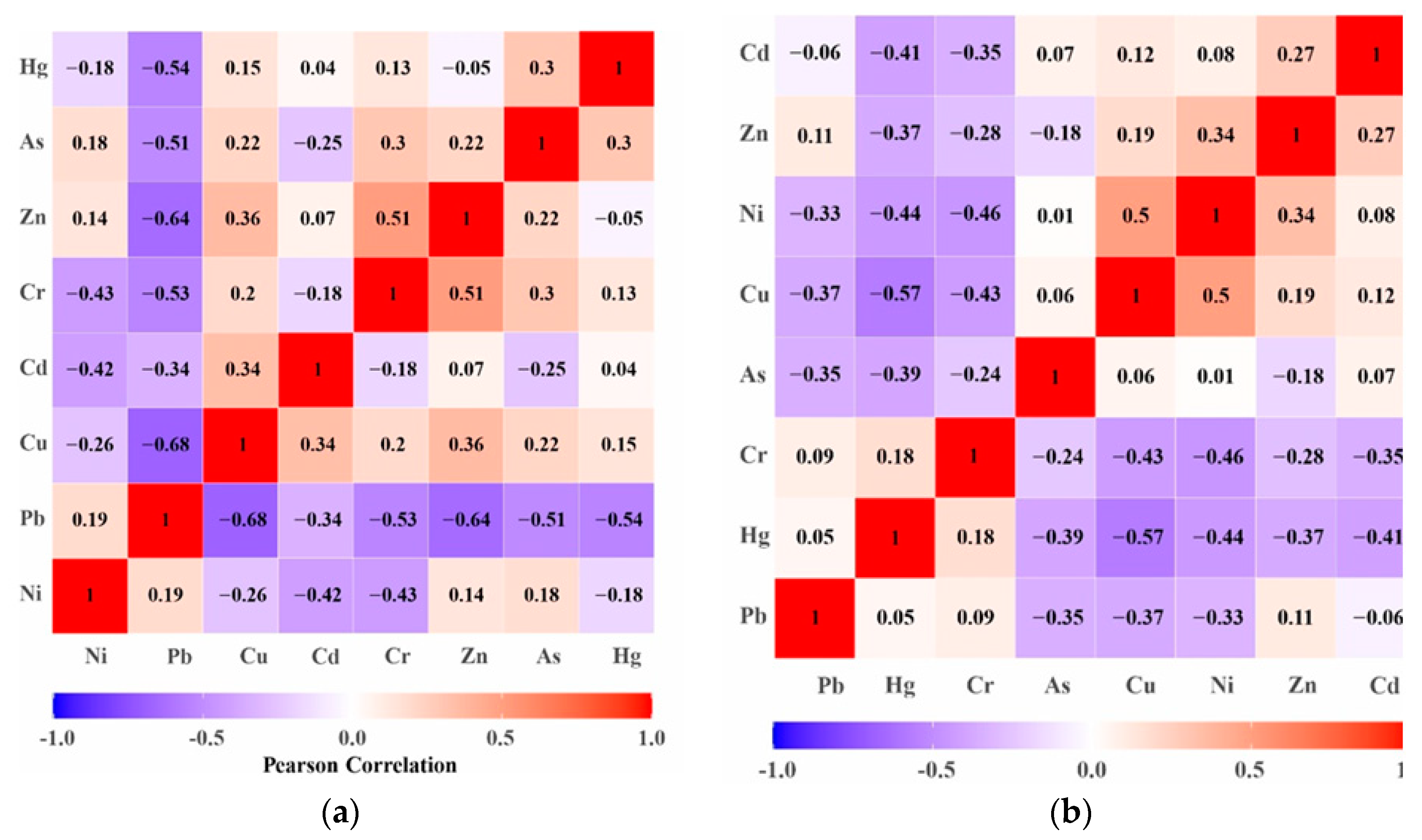
3.5. Source Identification
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, H.Y.; Jing, L.J.; Yao, Z.P.; Meng, F.S.; Teng, Y.Z. Prevalence, source and risk of antibiotic resistance genes in the sediments of Lake Tai (China) deciphered by metagenomic assembly: A comparison with other global lakes. Environ. Int. 2019, 127, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lama, G.F.C.; Errico, A.; Pasquino, V.; Mirzaei, S.; Preti, F.; Chirico, G.B. Velocity uncertainty quantification based on Riparian vegetation indices in open channels colonized by Phragmites australis. J. Ecohydraulics 2022, 7, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müllerová, J.; Gago, X.; Bučas, M.; Company, J.; Estrany, J.; Fortesa, J.; Manfreda, S.; Michez, A.; Mokroš, M.; Paulus, G.; et al. Characterizing vegetation complexity with unmanned aerial systems (UAS)—A framework and synthesis. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 131, 108156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunetti, G.F.A.; Fallico, C.; De Bartolo, S.; Severino, G. Well-Type Steady Flow in Strongly Heterogeneous Porous Media: An Experimental Study. Water Resour. Res. 2022, 58, e2021WR030717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.; Sharma, N.; Lama, G.F.; Hasan, M.; Garg, R.; Busico, G.; Alharbi, R.S. Three-Dimensional Hole Size (3DHS) Approach for Water Flow Turbulence Analysis over Emerging Sand Bars: Flume-Scale Experiments. Water 2022, 14, 1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.B.; Chen, Y.S.; Xia, W.T.; Qu, X.; Lin, L.S. Eutrophication and heavy metal pollution patterns in the water suppling lakes of China’s south-to-north water diversion project. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 711, 134543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noli, F.; Tsamos, P. Concentration of heavy metals and trace elements in soils, waters and vegetables and assessment of health risk in the vicinity of a lignite-fired power plant. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 563–564, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansour, A.T.; Alprol, A.E.; Abualnaja, K.M.; El-Beltagi, H.S.; Ramadan, K.M.A.; Ashour, M. The Using of Nanoparticles of Microalgae in Remediation of Toxic Dye from Industrial Wastewater: Kinetic and Isotherm Studies. Materials 2022, 15, 3922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abualnaja, K.M.; Alprol, A.E.; Abu-Saied, M.A.; Ashour, M.; Mansour, A.T. Removing of Anionic Dye from Aqueous Solutions by Adsorption Using of Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes and Poly (Acrylonitrile-styrene) Impregnated with Activated Carbon. Sustainability 2021, 13, 7077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, N.; Liu, L.S.; Hou, Z.L.; Wu, J.P.; Wang, Q.W.; Fu, Y.C. Pollution characteristics and risk assessment of surface sediments in the urban lakes. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 25, 22022–22037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.K.; Li, B.L.; Deng, J.M.; Qin, B.Q.; Tefsen, B. Regional-scale investigation of dissolved organic matter and lead binding in a large impacted lake with a focus on environmental risk assessment. Water Res. 2020, 172, 115478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Smith, D.S.; Benaquista, A.P.; Rossi, D.M.; Kadapuram, B.M.; Yu, M.L.; Partlow, A.S.; Burtch, N.R. Water quality impacts of small-scale hydromodification in an urban stream in Connecticut, USA. Ecol. Process. 2018, 7, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.Z.; Chen, Y.H.; Sun, W.C. Environmental Characteristics and Source Apportionment of Heavy Metals in the Sediments of a River-Lake System. Environ. Sci. 2020, 41, 2646–2652. [Google Scholar]
- Likens, G.E. Nutrients and Eutrophication: The Limitingnutrient Controversy: Proceedings; American Society of Limnology and Oceanography: Washington, DC, USA, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Alprol, A.E.; Ashour, M.; Mansour, A.T.; Alzahrani, O.M.; Mahmoud, S.F.; Gharib, S.M. Assessment of Water Quality and Phytoplankton Structure of Eight Alexandria Beaches, Southeastern Mediterranean Sea, Egypt. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garber, K.J.; Hartman, R.T. Internal phosphorus loading to shallow Edinboro Lake in northwestern Pennsylvania. Hydrobiologia 1985, 122, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lijklema, L. Phosphorus accumulation in sediments and internal loading. Aquat. Ecol. 1986, 20, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.M.; Zhu, B.D.; Zhang, J.; Wu, Y.; Liu, G.S.; Deng, B.; Zhao, M.X.; Liu, G.Q.; Du, J.Z.; Ren, J.L.; et al. Environmental change in Jiaozhou Bay recorded by nutrient components in sediments. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2010, 60, 1591–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, J.T.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, Z.B.; Wang, L.P.; Wei, L.L.; Tan, X.B. Effects of environmental factors on release of sediment nitrogen in shallow lake. J. Shandong Jianzhu Univ. 2010, 25, 58–61. [Google Scholar]
- Waajen, G.W.A.M.; Faassen, E.J.; Lürling, M. Eutrophic urban ponds suffer from cyanobacterial blooms: Dutch examples. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 9983–9994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.Y.; Teng, Y.G.; Lu, S.J.; Wang, Y.Y.; Wang, J.S. Contamination features and health risk of soil heavy metals in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 512–513, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, F.; Yang, X.L.; Zhang, Z.Q. Evaluation of water nutrition status in Yueliang Lake. Chin. J. Control. Endem. Dis. 2010, 1, 29–31. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, J.C.; Wang, S. Discussion on the construction of flood storage and detention area in Yueliang Lake. Water Resour. Hydropower Northeast China 2011, 12, 55–56. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, H.F.; Xue, B.; Yao, S.C.; Lu, X.G. Water Quality of Lakes Evolution in Songnen Plain. Wetl. Sci. 2011, 9, 120–124. [Google Scholar]
- Chai, S.L.; Gao, L.; Qiu, D.M.; Chai, Y.; Guo, J.; Xu, X.C. 210Pb and 137Cs Dating of the Sediment Core and Its Recent Accumulation Rates in Yueliang Lake in West Jilin Province. J. Jilin Univ. (Earth Sci. Ed.) 2013, 43, 134–141. [Google Scholar]
- Muller, G. Index of geoazzumulation in sediments of the Rhine river. Geojournal 1969, 2, 108–118. [Google Scholar]
- Teng, Y.G.; Tuo, X.G.; Ni, S.J.; Zhang, C.J. Applying Geo-accumulation Index to Assess Heavy Metal Pollution in Sediment: Influence of Different Geochemical Background. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 25, 7–9. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, H.; Zhang, W.B.; Yu, J.P. Distribution and Potential Ecological Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Surface Sediments of Hongze Lake. Environ. Sci. 2011, 32, 437–444. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, F. Study on the Removal of Cd(Ⅱ) from Aqueous Solutions by Bacillus Cereus RC-1: Biosorption Characteristics and Mechanism; South China University of Technology: Guangzhou, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z.Q.; Ni, S.J.; Tuo, X.G.; Zhang, C.J. Calculation of heavy metals’ toxicity coefficient in the evaluation of potential ecological risk index. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 32, 112–115. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.H.; Qian, S.M.; Xu, N.N.; Jin, X.C.; Huang, J.; Zhao, Q.H. Characteristics of Distribution of Pollutants and Evaluation in Sediment in the East Area of Chaohu Lake. Res. Environ. Sci. 2004, 17, 22–26. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Liu, X.D.; Xu, Q.; Ge, X.L.; Wang, Y.H. Phosphorous Species and Their Distribution Characters in Sediments of Miyun Reservoir. Rock Miner. Anal. 2003, 22, 81–85. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, S.L.; Ding, Y.Z. Environmental and Geochemical Characteristics of Nitrogen, Phosphorus and Heavy Metal Elements in Sediments of South Lake of Changchun. Res. Environ. Sci. 1999, 12, 40–44. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.Q. Characterization of Nitrogen Nutrient Changes in the Reservoir Water Front Zone and Surrounding Catchment Area of Mi Yun Reservoir. Master’s Thesis, Hebei University of Engineering, Handan, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, B.X.; Liu, Y.Q.; Zhang, F.; Hou, J.Z.; Zhang, H.B. Characteristics and Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Core Sediments from Lakes of Tibet. Environ. Sci. 2016, 37, 490–498. [Google Scholar]
- He, J.; Li, F.L.; Tao, L.; Zhang, A.; Zhao, Y.B. Distribution characteristics and ecological risk assessment of nitrogen, phosphorus and heavy metals in sediments of typical inland lakes: A case study of Wuhu Lake in Wuhan. Geol. Surv. China 2022, 9, 110–118. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, J.B.; Li, W.Q.; Liu, N.; Pang, Y. Characteristics of Contaminated Sediments in Yanghe Reservoir. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2007, 26, 886–893. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.N.; Ma, C.Z.; Zhang, J.T.; He, Z.S.; Huo, S.L.; Xi, B.D. Distribution characteristics of pollution from nitrogen, phosphorus, and heavy metals in sediments of Shankou Lake in Northeast China. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2018, 37, 520–529. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.J.; Zhao, Y.L. A preliminary study on the background values of eight heavy metallic elements and relevant factors on Songnen. J. Northeast Agric. Univ. 1987, 18, 113–118. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, L.X.; Ma, S.M.; Wang, Z.F. Soil eco-geochemical baseline in alluvial plains of eastern China. Geol. China 2006, 33, 1400–1405. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, Z.Y.; Pu, J.; Jilili, A. Heavy metal contamination characteristic and its assessment in surface sediments of major lakes in China. Environ. Eng. 2017, 35, 136–141. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, W.H.; Wang, J.J.; Zhang, S.Y. The Spatial Variability Characteristics and Potential Ecological Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals of Lake Sediments in the Songnen Plain. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2012, 32, 1000–1005. [Google Scholar]
- Song, G.L.; Liu, Z. Study on the Background Values of Some Elements in Deposit Sediment of the Nenjiang’s Drainage. Nat. Sci. J. Harbin Norm. Univ. 1988, 4, 100–105. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, L.N. Environmental Geochemistry of Heavy Metals in Yueliang Lake in West Jilin Province. Master’s Thesis, Jilin University, Changchun, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B.L.; Diao, G.L.; Han, X.; Zhao, B.; Xue, M.Y.; Cui, X.T.; Niu, X. Spatial Distribution and Ecological Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Surface Sediments from Songhua River. Sci. Technol. Eng. 2015, 15, 140–145. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.J.; Liu, Y.Q.; Yu, Z.S. Study on heavy metals in the sediments of Jingpo Lake. Chin. J. Environ. Eng. 1990, 11, 46–51. [Google Scholar]
- Rydberg, J.; Galman, V.; Renberg, I. Assessing the Stability of Mercury and Methylmercury in a Varved Lake Sediment Deposit. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 4391–4396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zi, Y.; Zhang, M.; Gu, X.H.; Kan, K.C.; Mao, Z.G.; Chen, H.H.; Zeng, Q.F. Impact of Enclosure Culture on Heavy Metal Content in Surface Sediments of Hongze Lake and Ecological Risk Assessment. Environ. Sci. 2021, 42, 5355–5363. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.X.; Zeng, C.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, Y.L.; Christopher, A. Traffic-related trace elements in soils along six highway segments on the Tibetan Plateau: Influence factors and spatial variation. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 581–582, 811–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, Z.F.; Zhang, Y.L.; Ding, M.J.; Li, L.H. Identification of traffic-related metals and the effects of different environments on their enrichment in roadside soils along the Qinghai–Tibet highway. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 521, 160–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, J.; Feng, C.T.; Zeng, G.M.; Gao, X.; Fang, Y.L. Spatial distribution and source identification of heavy metals in surface soils in a typical coal mine city, Lianyuan, China. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 225, 681–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| RI | Potential Ecological Risk | |
|---|---|---|
| ≤ 40 | RI ≤ 150 | Light ecological hazards |
| 40 < ≤ 80 | 150 < RI ≤ 300 | Moderate ecological hazards |
| 80 < ≤ 160 | 300 < RI ≤ 600 | Relatively strong ecological hazards |
| 160 < ≤ 320 | Strong ecological hazards | |
| > 320 | RI > 600 | Extremely strong ecological hazards |
| Name of the Lake | Heavy Metal Concentrations (mg/kg) | References | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hg | Cd | As | Cr | Ni | Cu | Pb | Zn | ||
| Yueliang Lake | 0.07 | 0.15 | 7.51 | 56.70 | 25.94 | 18.67 | 53.69 | 71.08 | This Study |
| Chagan Lake | 0.07 | 0.2 | 10.01 | 57.6 | 29.68 | 20.73 | 26.56 | 66.83 | [44] |
| Songhua River | 0.1 | 0.9 | 18.9 | 41.2 | 99 | 44.5 | 13.3 | 107 | [45] |
| Nen River | 0.027 | 0.24 | 5.2 | 26 | 24 | 21 | 5.4 | 54 | [43] |
| Jingpo Lake | 0.113 | 0.48 | 7.28 | 82.8 | 39.3 | 22.4 | 12.1 | 84.6 | [46] |
| Major Lakes in Songnen Plain | - | - | - | - | 35.07 | 29.09 | 25.57 | 189.78 | [42] |
| Major Lakes in China | 0.076 | 0.497 | 16.39 | 6.29 | 31.81 | 36.89 | 35.37 | 99.52 | [41] |
| Background Value | 0.015 | 0.099 | 9 | 50 | 24 | 18 | 22 | 54 | [39,40] |
| Items | As | Hg | Cd | Cr | Ni | Cu | Pb | Zn |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Minimum # | 0.50 | 0.01 | 0.04 | 13.60 | 5.26 | 2.91 | 9.30 | 21.90 |
| Maximum # | 8.60 | 0.07 | 0.13 | 113.00 | 26.70 | 19.00 | 35.50 | 73.20 |
| Mean # | 4.05 ± 1.80 | 0.03 ± 0.01 | 0.07 ± 0.03 | 45.15 ± 15.80 | 13.99 ± 4.97 | 9.21 ± 4.53 | 21.56 ± 6.47 | 44.08 ± 14.86 |
| Coefficient of variation * | 0.44 | 0.42 | 0.38 | 0.35 | 0.36 | 0.49 | 0.30 | 0.34 |
| Minimum * | 2.50 | 0.01 | 0.04 | 24.10 | 4.03 | 3.07 | 9.70 | 25.30 |
| Maximum * | 14.80 | 0.06 | 0.19 | 133.00 | 35.20 | 25.90 | 29.50 | 83.80 |
| Mean * | 4.84 ± 2.66 | 0.03 ± 0.01 | 0.07 ± 0.04 | 48.97 ± 20.18 | 13.44 ± 6.87 | 9.39 ± 5.74 | 20.99 ± 4.38 | 41.23 ± 13.87 |
| Coefficient of variation * | 0.55 | 0.45 | 0.52 | 0.41 | 0.51 | 0.61 | 0.21 | 0.34 |
| Background value | 9 | 0.015 | 0.099 | 50 | 24 | 18 | 22 | 54 |
| Items | Ei | RI | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| As | Hg | Cd | Cr | Ni | Cu | Pb | Zn | ||
| Minimum & | 0.06 | 66.67 | 0.59 | 3.17 | 1.06 | 3.80 | 0.52 | 14.67 | 104.34 |
| Maximum & | 11.46 | 349.33 | 4.51 | 7.10 | 7.92 | 16.98 | 1.84 | 101.11 | 444.21 |
| Mean & | 8.06 ± 2.84 | 186.60 ± 74.15 | 2.27 ± 0.73 | 5.40 ± 1.12 | 5.19 ± 1.72 | 12.20 ± 4.98 | 1.32 ± 0.31 | 46.34 ± 19.20 | 267.37 ± 92.35 |
| Minimum * | 0.59 | 26.67 | 1.36 | 0.84 | 0.81 | 2.11 | 0.41 | 11.11 | 56.00 |
| Maximum * | 16.42 | 194.99 | 13.26 | 7.32 | 7.19 | 8.08 | 1.55 | 57.99 | 252.70 |
| Mean * | 4.93 ± 2.53 | 86.17 ± 37.83 | 4.70 ± 1.81 | 2.86 ± 1.24 | 2.58 ± 1.43 | 4.83 ± 1.25 | 0.79 ± 0.27 | 20.78 ± 9.53 | 127.66 ± 44.31 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.; Wen, M.; Zheng, C.; Chai, S.; Huang, L.; Liu, P. Distribution Characteristics and Ecological Risk Assessment of Nitrogen, Phosphorus, and Some Heavy Metals in the Sediments of Yueliang Lake in Western Jilin Province, Northeast China. Water 2022, 14, 3306. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14203306
Zhang J, Liu Y, Wen M, Zheng C, Chai S, Huang L, Liu P. Distribution Characteristics and Ecological Risk Assessment of Nitrogen, Phosphorus, and Some Heavy Metals in the Sediments of Yueliang Lake in Western Jilin Province, Northeast China. Water. 2022; 14(20):3306. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14203306
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Jiali, Yinghong Liu, Meilan Wen, Chaojie Zheng, Sheli Chai, Liangliang Huang, and Panfeng Liu. 2022. "Distribution Characteristics and Ecological Risk Assessment of Nitrogen, Phosphorus, and Some Heavy Metals in the Sediments of Yueliang Lake in Western Jilin Province, Northeast China" Water 14, no. 20: 3306. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14203306
APA StyleZhang, J., Liu, Y., Wen, M., Zheng, C., Chai, S., Huang, L., & Liu, P. (2022). Distribution Characteristics and Ecological Risk Assessment of Nitrogen, Phosphorus, and Some Heavy Metals in the Sediments of Yueliang Lake in Western Jilin Province, Northeast China. Water, 14(20), 3306. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14203306






