Significant Temporal and Spatial Variability in Nutrient Concentrations in a Chinese Eutrophic Shallow Lake and Its Major Tributaries
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
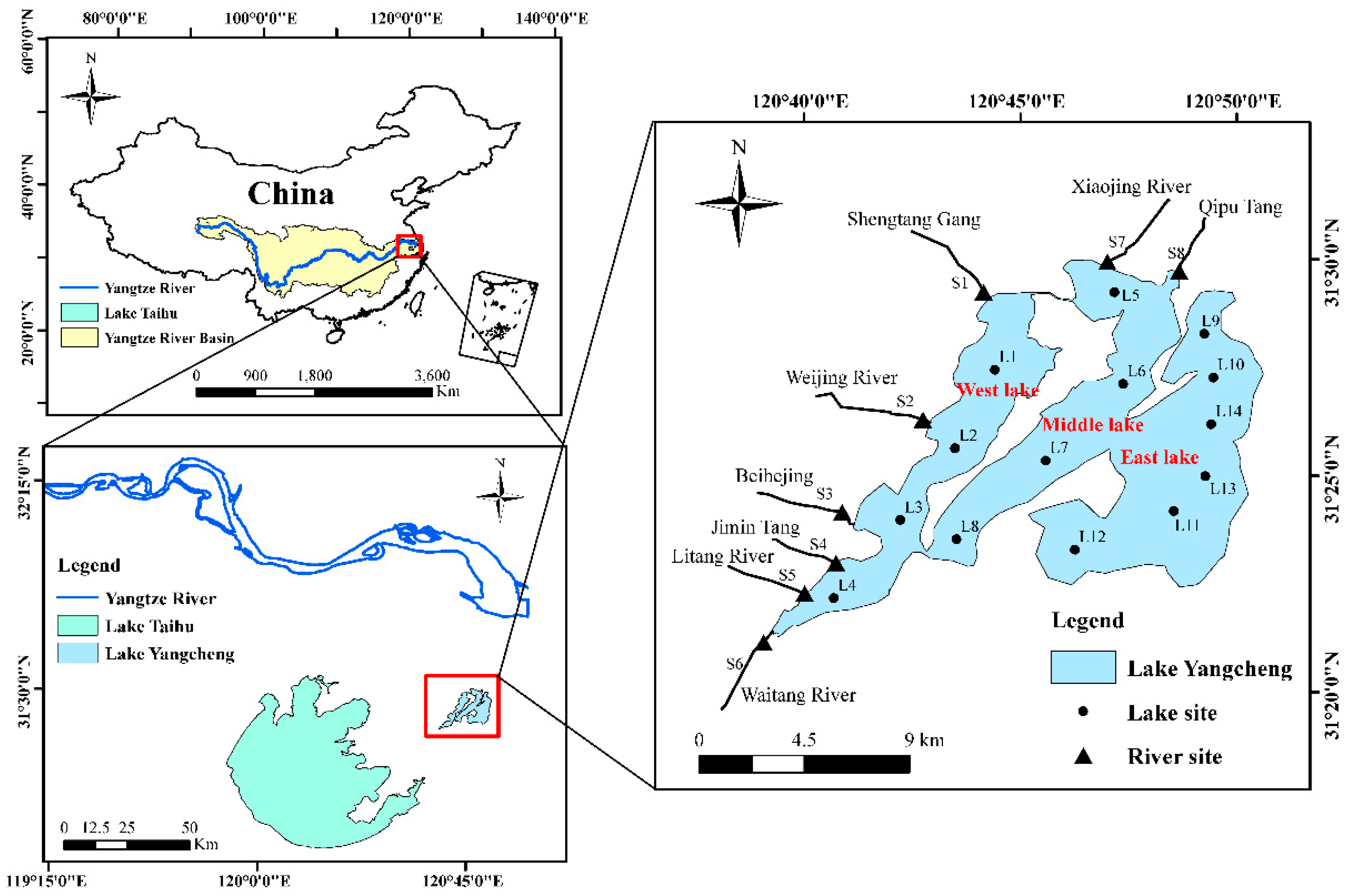
2.1. Study Area and Sample Collection
2.2. Chemical Analysis
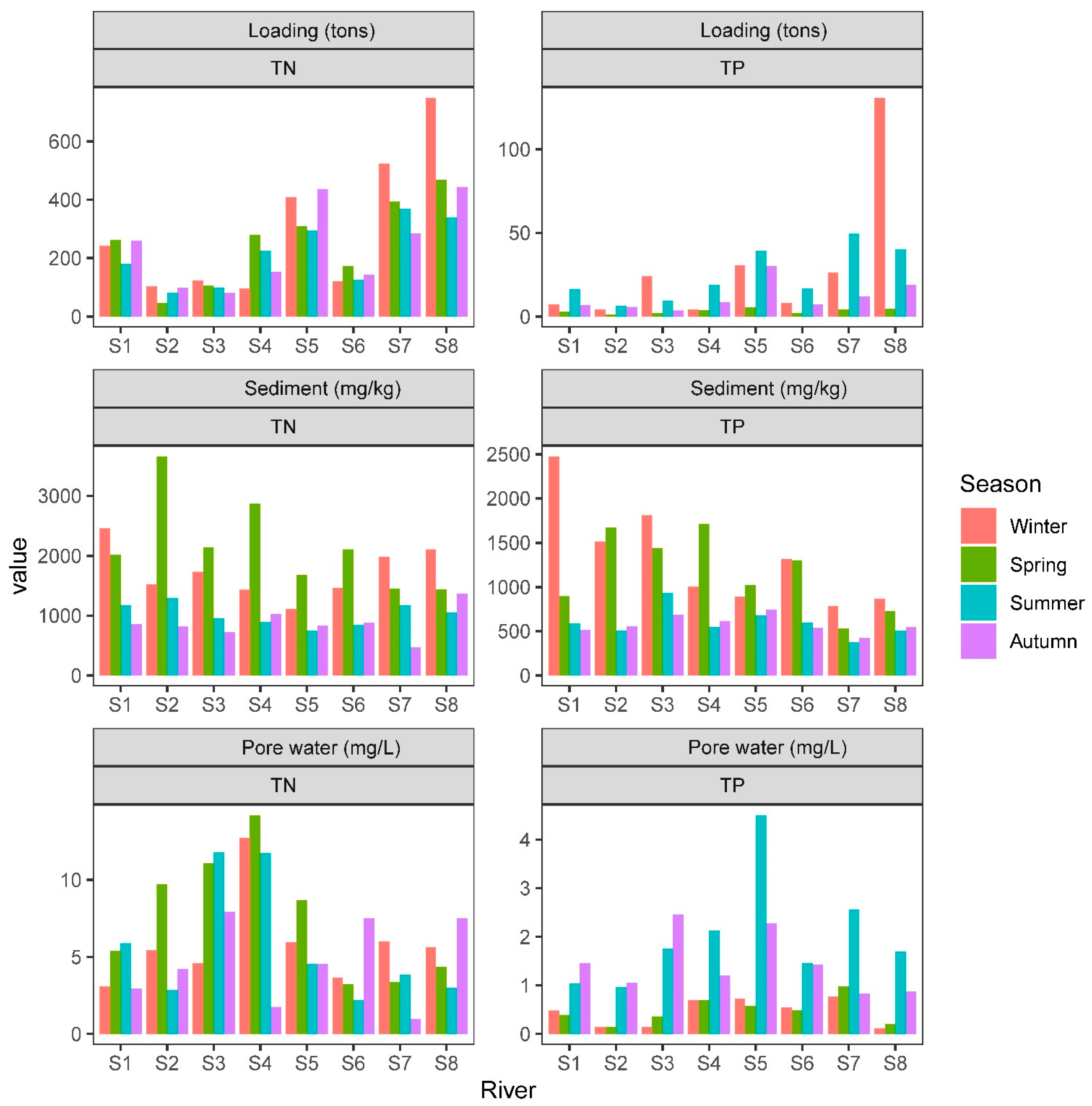
2.3. Nutrient Loading
2.4. Evaluation of Nutrient Contamination in the Sediment
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results
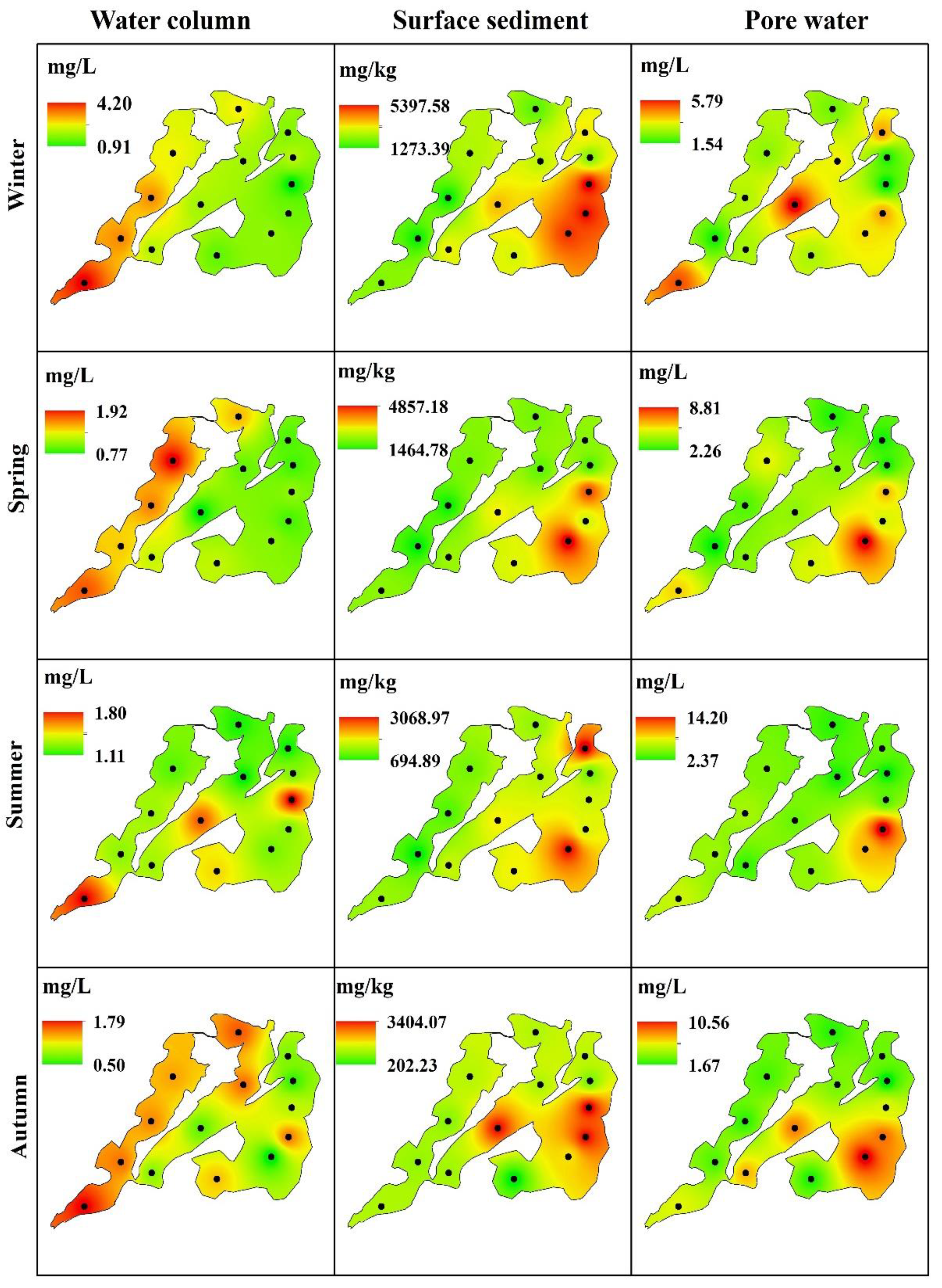
3.1. The Seasonal Variations of Nitrogen in the Lake
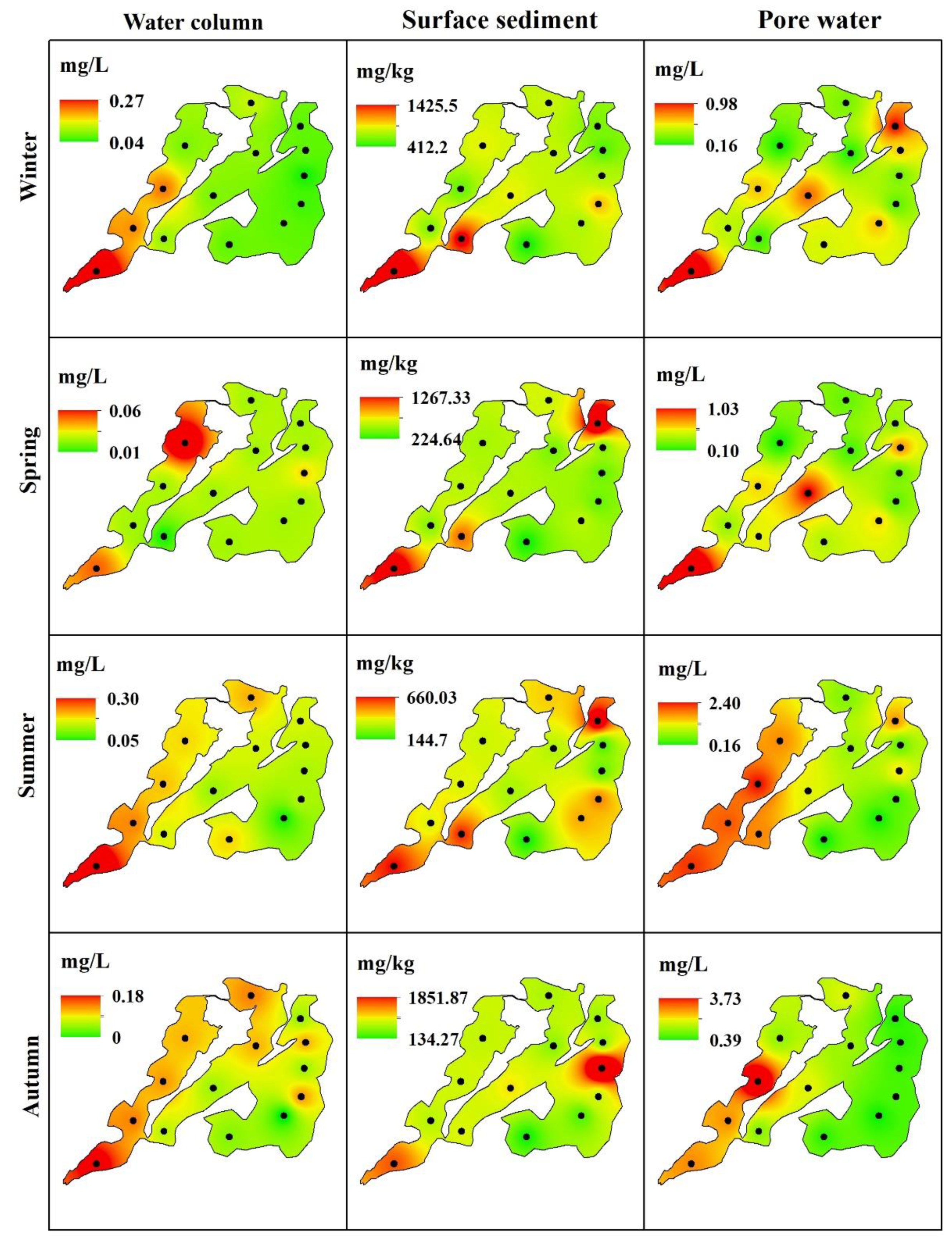
3.2. The Seasonal Variations of Phosphorus in the Lake
3.3. The Seasonal Variations of Nutrients in the Rivers
3.4. Evaluation of Nutrient Contamination in the Surface Sediment
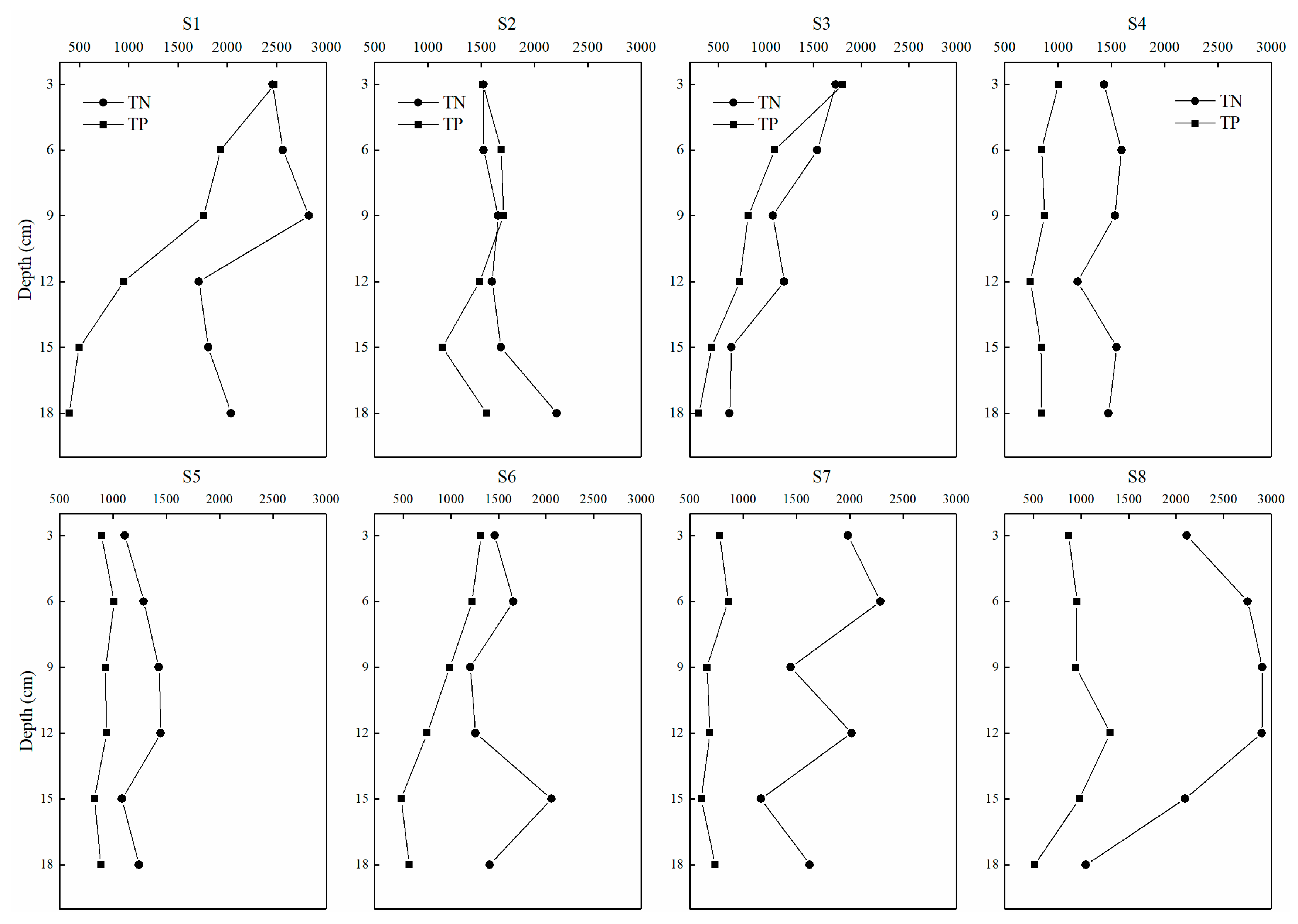
3.5. The Vertical Dynamics of Nutrients in the Deep Sediment
4. Discussion
4.1. High Nutrient Levels and Seasonal Patterns of Nutrient Limitation in the Water Column
4.2. Temporal Variations and Spatial Heterogeneity of Nutrients in the Lake Sediment
4.3. The Influence of Rivers Runoff on the Distribution of Nutrients in the Lake
4.4. Nutrient Contamination and Their Vertical Distributions in the Deep Sediment
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xu, H.; Paerl, H.W.; Qin, B.; Zhu, G.; Gaoa, G. Nitrogen and phosphorus inputs control phytoplankton growth in eutrophic Lake Taihu, China. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2010, 55, 420–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paerl, H.W.; Scott, J.T.; McCarthy, M.J.; Newell, S.E.; Gardner, W.S.; Havens, K.E.; Hoffman, D.K.; Wilhelm, S.W.; Wurtsbaugh, W.A. It Takes Two to Tango: When and Where Dual Nutrient (N & P) Reductions Are Needed to Protect Lakes and Downstream Ecosystems. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 10805–10813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sinha, E.; Michalak, A.; Balaji, V. Eutrophication will increase during the 21st century as a result of precipitation changes. Science 2017, 357, 405–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, B.; Jiang, Y.-J.; He, W.; Liu, W.-X.; Kong, X.-Z.; Jørgensen, S.E.; Xu, F.-L. The tempo-spatial variations of phytoplankton diversities and their correlation with trophic state levels in a large eutrophic Chinese lake. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 66, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, Y.-J.; He, W.; Liu, W.-X.; Qin, N.; Ouyang, H.-L.; Wang, Q.-M.; Kong, X.-Z.; He, Q.-S.; Yang, C.; Yang, B.; et al. The seasonal and spatial variations of phytoplankton community and their correlation with environmental factors in a large eutrophic Chinese lake (Lake Chaohu). Ecol. Indic. 2014, 40, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harke, M.J.; Davis, T.W.; Watson, S.B.; Gobler, C.J. Nutrient-Controlled Niche Differentiation of Western Lake Erie Cyanobacterial Populations Revealed via Metatranscriptomic Surveys. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 604–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, T.W.; Berry, D.L.; Boyer, G.L.; Gobler, C.J. The effects of temperature and nutrients on the growth and dynamics of toxic and non-toxic strains of Microcystis during cyanobacteria blooms. Harmful Algae 2009, 8, 715–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.; Steinman, A.D.; Oudsema, M.; Hassett, M.; Xie, L. The influence of nutrients limitation on phytoplankton growth and microcystins production in Spring Lake, USA. Chemosphere 2019, 234, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobler, C.J.; Burkholder, J.M.; Davis, T.W.; Harke, M.J.; Johengen, T.; Stow, C.A.; Van de Waal, D.B. The dual role of nitrogen supply in controlling the growth and toxicity of cyanobacterial blooms. Harmful Algae 2016, 54, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, V.H.; Wood, S.A.; McBride, C.G.; Atalah, J.; Hamilton, D.P.; Abell, J. Phosphorus and nitrogen loading restraints are essential for successful eutrophication control of Lake Rotorua, New Zealand. Inland Waters 2016, 6, 273–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andersen, I.M.; Williamson, T.J.; González, M.J.; Vanni, M.J. Nitrate, ammonium, and phosphorus drive seasonal nutrient limitation of chlorophytes, cyanobacteria, and diatoms in a hyper-eutrophic reservoir. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2019, 9999, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinman, A.D.; Isely, E.S.; Thompson, K. Stormwater runoff to an impaired lake: Impacts and solutions. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janssen, A.B.G.; de Jager, V.C.L.; Janse, J.H.; Kong, X.; Liu, S.; Ye, Q.; Mooij, W.M. Spatial identification of critical nutrient loads of large shallow lakes: Implications for Lake Taihu (China). Water Res. 2017, 119, 276–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijesiri, B.; Liu, A.; Deilami, K.; He, B.; Hong, N.; Yang, B.; Zhao, X.; Ayoko, G.; Goonetilleke, A. Nutrients and metals interactions between water and sediment phases: An urban river case study. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 251, 354–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ylöstalo, P.; Seppälä, J.; Kaitala, S.; Maunula, P.; Simis, S. Loadings of dissolved organic matter and nutrients from the Neva River into the Gulf of Finland—Biogeochemical composition and spatial distribution within the salinity gradient. Mar. Chem. 2016, 186, 58–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.; Li, Y.; Acharya, K. Modeling the effects of external nutrient reductions on algal blooms in hyper-eutrophic Lake Taihu, China. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 94, 164–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zou, R.; Wu, Z.; Zhao, L.; Elser, J.J.; Yu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Y. Seasonal algal blooms support sediment release of phosphorus via positive feedback in a eutrophic lake: Insights from a nutrient flux tracking modeling. Ecol. Model. 2020, 416, 108881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinman, A.D.; Spears, B. Internal Phosphorus Loading: Causes, Case Studies, and Management; J. Ross Publishing: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, S.; Chen, M.; Gong, M.; Fan, X.; Qin, B.; Xu, H.; Gao, S.; Jin, Z.; Tsang, D.C.W.; Zhang, C. Internal phosphorus loading from sediments causes seasonal nitrogen limitation for harmful algal blooms. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 625, 872–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, B.; Hu, W.; Gao, G.; Luo, L.; Zhang, J. Dynamics of sediment resuspension and the conceptual schema of nutrient release in the large shallow Lake Taihu, China. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2004, 49, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Søndergaard, M.; Bjerring, R.; Jeppesen, E. Persistent internal phosphorus loading during summer in shallow eutrophic lakes. Hydrobiologia 2013, 710, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Liang, Z.; Wu, S.; Guo, H. Internal cycling, not external loading, decides the nutrient limitation in eutrophic lake: A dynamic model with temporal Bayesian hierarchical inference. Water Res. 2017, 116, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.-L.; Tao, S.; Dawson, R.W.; Xu, Z.R. The distributions and effects of nutrients in the sediments of a shallow eutrophic Chinese lake. Hydrobiologia 2003, 492, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Xu, X.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Sun, P.; Wen, Y.; Wang, Z.; Lu, X.; Zhang, W.; Wang, X.; et al. Seasonal Pattern of Nutrient Limitation in a Eutrophic Lake and Quantitative Analysis of the Impacts from Internal Nutrient Cycling. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 13675–13686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Y.; Yang, C.; He, W.; Liu, W.-X.; Xu, F.-L. The spatial distribution of phosphorus and their correlations in surface sediments and pore water in Lake Chaohu, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 25906–25915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Ding, S.; Zhong, J.; Fan, C.; Chen, Q.; Yin, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y. Evaluation of simulated dredging to control internal phosphorus release from sediments: Focused on phosphorus transfer and resupply across the sediment-water interface. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 592, 662–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Fu, C.; Ding, G.; Fang, Y.; Yun, Y.; Norra, S. Effects of hairy crab breeding on drinking water quality in a shallow lake. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 662, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Gu, A.Z.; He, M. Quantification and genetic diversity of total and microcystin-producing Microcystis during blooming season in Tai and Yang-cheng lakes, China. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2014, 116, 1482–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Hu, Z.; Sun, Y.; Peng, Z.; Chen, L. Spatial variations of macrozoobenthos and sediment nutrients in Lake Yangcheng: Emphasis on effect of pen culture of Chinese mitten crab. J. Environ. Sci. 2015, 37, 118–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Pu, R.; Ma, R.; Wang, X.; Lai, X.; Mao, Z.; Zhang, L.; Peng, Z.; Sun, Z. Mapping Long-Term Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Pen Aquaculture in a Shallow Lake: Less Aquaculture Coming along Better Water Quality. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Wu, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, X.; Liu, X.; Li, Q.; Cai, Y. Spatial Distribution and Pollution Assessment of Nitrogen, Phosphorus and Heavy Metals in Surface Sediments of Lake Yangcheng, Jiangsu Province, China. Res. Environ. Sci. (Chin.) 2016, 29, 1590–1599. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, X.; Tu, Q. The Standard Methods for Observation and Analysis in Lake Eutrophication; Chinese Environmental Science PresS: Beijing, China, 1990; pp. 138–207. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, D.; O’Connor, D.; Nathanail, P.; Tian, L.; Ma, Y. Integrated GIS and multivariate statistical analysis for regional scale assessment of heavy metal soil contamination: A critical review. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 231, 1188–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Yang, T.; Xiong, M. Time scales of external loading and spatial heterogeneity in nutrients-chlorophyll a response: Implication on eutrophication control in a large shallow lake. Ecol. Eng. 2020, 142, 105636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, S.; He, Z.; Ma, C.; Zhang, H.; Xi, B.; Xia, X.; Xu, Y.; Wu, F. Stricter nutrient criteria are required to mitigate the impact of climate change on harmful cyanobacterial blooms. J. Hydrol. 2019, 569, 698–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Paerl, H.W.; Qin, B.; Zhu, G.; Hall, N.S.; Wu, Y. Determining Critical Nutrient Thresholds Needed to Control Harmful Cyanobacterial Blooms in Eutrophic Lake Taihu, China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 1051–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Chen, N.; Yan, Z.; Duan, S. Warming increases nutrient mobilization and gaseous nitrogen removal from sediments across cascade reservoirs. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 219, 490–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Huang, Y.; Hu, J.; Li, P.; Zhang, C.; Li, L.; Xu, P.; Zhang, J.; Chen, X. The nitrogen reduction in eutrophic water column driven by Microcystis blooms. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 385, 121578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Qin, B.; Brookes, J.D.; Yan, W.; Ji, X.; Feng, J. Spatial distribution of sediment nitrogen and phosphorus in Lake Taihu from a hydrodynamics-induced transport perspective. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 650, 1554–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chomicki, K.M.; Howell, E.T.; Defield, E.; Dumas, A.; Taylor, W.D. Factors influencing the phosphorus distribution near the mouth of the Grand River, Ontario, Lake Erie. J. Great Lakes Res. 2016, 42, 549–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Gu, X.; Zeng, Q.; Mao, Z.; Sun, M.; Gao, H. Ecological culture effects of Eriocheir sinesis and the pollutant export in reclamation areas of Lake Gucheng, Jiangsu Province). J. Lake Sci. 2013, 25, 8. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, L.; Lai, X. Simulation study of water enviroment influence on Yangcheng Lake river networks by Qipu River water diversion project. Water Rresour. Prot. 2018, 34, 88–95. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Cheung, K.C.; Poon, B.H.T.; Lan, C.Y.; Wong, M.H. Assessment of metal and nutrient concentrations in river water and sediment collected from the cities in the Pearl River Delta, South China. Chemosphere 2003, 52, 1431–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, B.; Xu, P.; Wu, Q.; Luo, L.; Zhang, Y. Environmental issues of Lake Taihu, China. Hydrobiologia 2007, 581, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhong, J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, L.; Fan, C. Fifteen-year study of environmental dredging effect on variation of nitrogen and phosphorus exchange across the sediment-water interface of an urban lake. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 219, 639–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
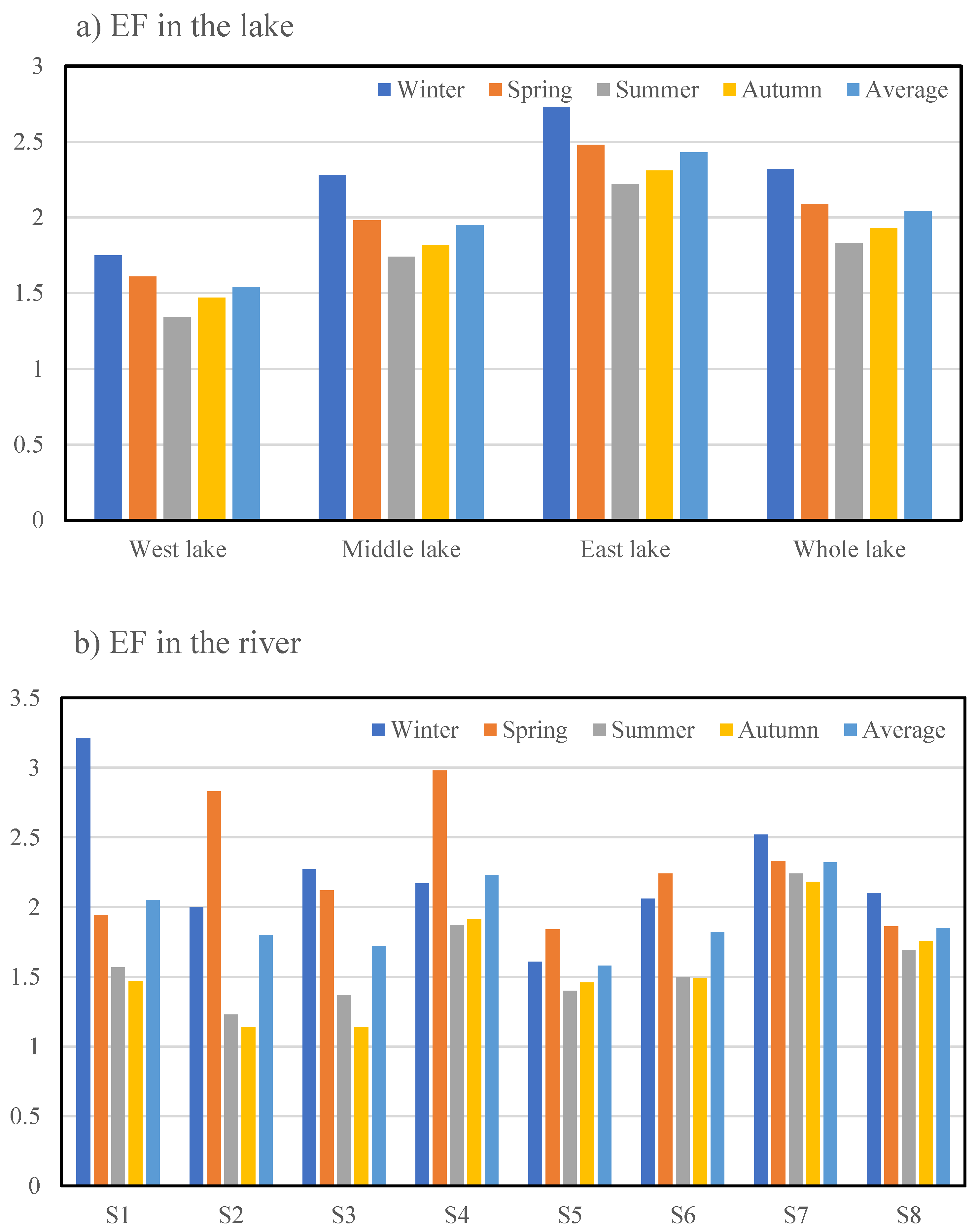

| Level | STN | STP | FF | Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | STN < 1.0 | STP < 0.5 | FF < 1.0 | Clean |
| 2 | 1.0 ≤ STN ≤ 1.5 | 0.5 ≤ STP ≤ 1.0 | 1.0 ≤ FF ≤ 1.5 | Minor contamination |
| 3 | 1.5 < STN ≤ 2.0 | 1.0 < STP ≤ 1.5 | 1.5 < FF ≤ 2.0 | Moderate contamination |
| 4 | STN > 2.0 | STP > 1.5 | FF > 2.0 | Severe contamination |
| TN | Season | West Lake | Middle Lake | East Lake | Whole Lake |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water column (mg/L) | Winter | 3.38 ± 0.67 | 2.14 ± 0.33 | 1.57 ± 0.39 | 2.25 ± 0.89 a |
| Spring | 1.69 ± 0.20 | 1.11 ± 0.31 | 0.99 ± 0.13 | 1.22 ± 0.37 b | |
| Summer | 1.38 ± 0.26 | 1.30 ± 0.26 | 1.35 ± 0.25 | 1.35 ± 0.24 b | |
| Autumn | 1.56 ± 0.17 | 1.19 ± 0.48 | 0.96 ± 0.40 | 1.19 ± 0.43 b | |
| Average | 2.00 ± 0.26 A | 1.43 ± 0.20 B | 1.22 ± 0.09 B | 1.50 ± 0.38 | |
| Surface sediment (mg/kg) | Winter | 1806.4 ± 632.6 | 2865.4 ± 861.9 | 3994.3 ± 1396.1 | 3046.7 ± 1378.6 a |
| Spring | 1814.9 ± 386.7 | 2348.9 ± 544.5 | 3139.8 ± 1219.7 | 2535.3 ± 1007.1 a | |
| Summer | 1011.6 ± 260.3 | 1540.7 ± 256.2 | 2031.5 ± 798.4 | 1599.9 ± 685.2 b | |
| Autumn | 1134.3 ± 153.7 | 1732.0 ± 1050.5 | 1825.3 ± 1311.4 | 1601.2 ± 1008.5 b | |
| Average | 1441.8 ± 342.2 A | 2121.8 ± 631.5 AB | 2747.7 ± 937.4 B | 2195.8 ± 879.9 | |
| Pore water (mg/L) | Winter | 3.10 ± 1.46 | 3.66 ± 1.52 | 3.12 ± 1.29 | 3.27 ± 1.31 a |
| Spring | 4.03 ± 1.71 | 3.40 ± 0.61 | 4.93 ± 2.42 | 4.23 ± 1.86 a | |
| Summer | 5.58 ± 0.82 | 3.19 ± 0.68 | 6.44 ± 4.50 | 5.26 ± 3.17 a | |
| Autumn | 3.33 ± 1.52 | 5.36 ± 2.94 | 5.31 ± 3.66 | 4.76 ± 2.92 a | |
| Average | 4.01 ± 1.22 A | 3.90 ± 1.29 A | 4.95 ± 2.53 A | 4.38 ± 1.86 |
| TP | Season | West Lake | Middle Lake | East Lake | Whole Lake |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water column (mg/L) | Winter | 0.17 ± 0.08 | 0.08 ± 0.01 | 0.06 ± 0.01 | 0.10 ± 0.06 a |
| Spring | 0.04 ± 0.02 | 0.02 ± 0.01 | 0.02 ± 0.004 | 0.02 ± 0.01 b | |
| Summer | 0.21 ± 0.06 | 0.14 ± 0.03 | 0.11 ± 0.04 | 0.15 ± 0.06 c | |
| Autumn | 0.14 ± 0.03 | 0.08 ± 0.04 | 0.06 ± 0.05 | 0.09 ± 0.05 a | |
| Average | 0.14 ± 0.04 A | 0.08 ± 0.02 BC | 0.06 ± 0.02 C | 0.09 ± 0.04 | |
| Surface sediment (mg/kg) | Winter | 810.8 ± 421.9 | 824.7 ± 239.7 | 594.1 ± 158.6 | 721.9 ± 277.9 a |
| Spring | 578.3 ± 314.0 | 525.5 ± 190.9 | 493.8 ± 386.8 | 527.0 ± 300.0 ab | |
| Summer | 386.9 ± 123.5 | 375.5 ± 132.5 | 346.7 ± 205.9 | 366.4 ± 155.6 b | |
| Autumn | 600.6 ± 246.6 | 488.1 ± 131.3 | 573.0 ± 639.8 | 556.6 ± 421.5 ab | |
| Average | 594.2 ± 273.7 A | 553.5 ± 151.4 A | 501.9 ± 206.9 A | 543.0 ± 201.6 | |
| Pore water (mg/L) | Winter | 0.52 ± 0.34 | 0.34 ± 0.24 | 0.48 ± 0.21 | 0.45 ± 0.25 a |
| Spring | 0.47 ± 0.40 | 0.40 ± 0.30 | 0.35 ± 0.17 | 0.40 ± 0.27 a | |
| Summer | 2.16 ± 0.25 | 1.10 ± 0.57 | 0.70 ± 0.68 | 1.23 ± 0.82 b | |
| Autumn | 2.28 ± 1.12 | 1.22 ± 0.29 | 0.47 ± 0.07 | 1.20 ± 0.96 b | |
| Average | 1.36 ± 0.45 A | 0.76 ± 0.23 BC | 0.50 ± 0.18 C | 0.82 ± 0.46 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Su, X.; Steinman, A.D.; Zhang, Y.; Ling, H.; Wu, D. Significant Temporal and Spatial Variability in Nutrient Concentrations in a Chinese Eutrophic Shallow Lake and Its Major Tributaries. Water 2022, 14, 217. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14020217
Su X, Steinman AD, Zhang Y, Ling H, Wu D. Significant Temporal and Spatial Variability in Nutrient Concentrations in a Chinese Eutrophic Shallow Lake and Its Major Tributaries. Water. 2022; 14(2):217. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14020217
Chicago/Turabian StyleSu, Xiaomei, Alan D. Steinman, Yunlin Zhang, Hong Ling, and Dan Wu. 2022. "Significant Temporal and Spatial Variability in Nutrient Concentrations in a Chinese Eutrophic Shallow Lake and Its Major Tributaries" Water 14, no. 2: 217. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14020217






