Machine Learning Assessment of the Impact of Global Warming on the Climate Drivers of Water Supply to Australia’s Northern Murray-Darling Basin
Abstract
:1. Introduction
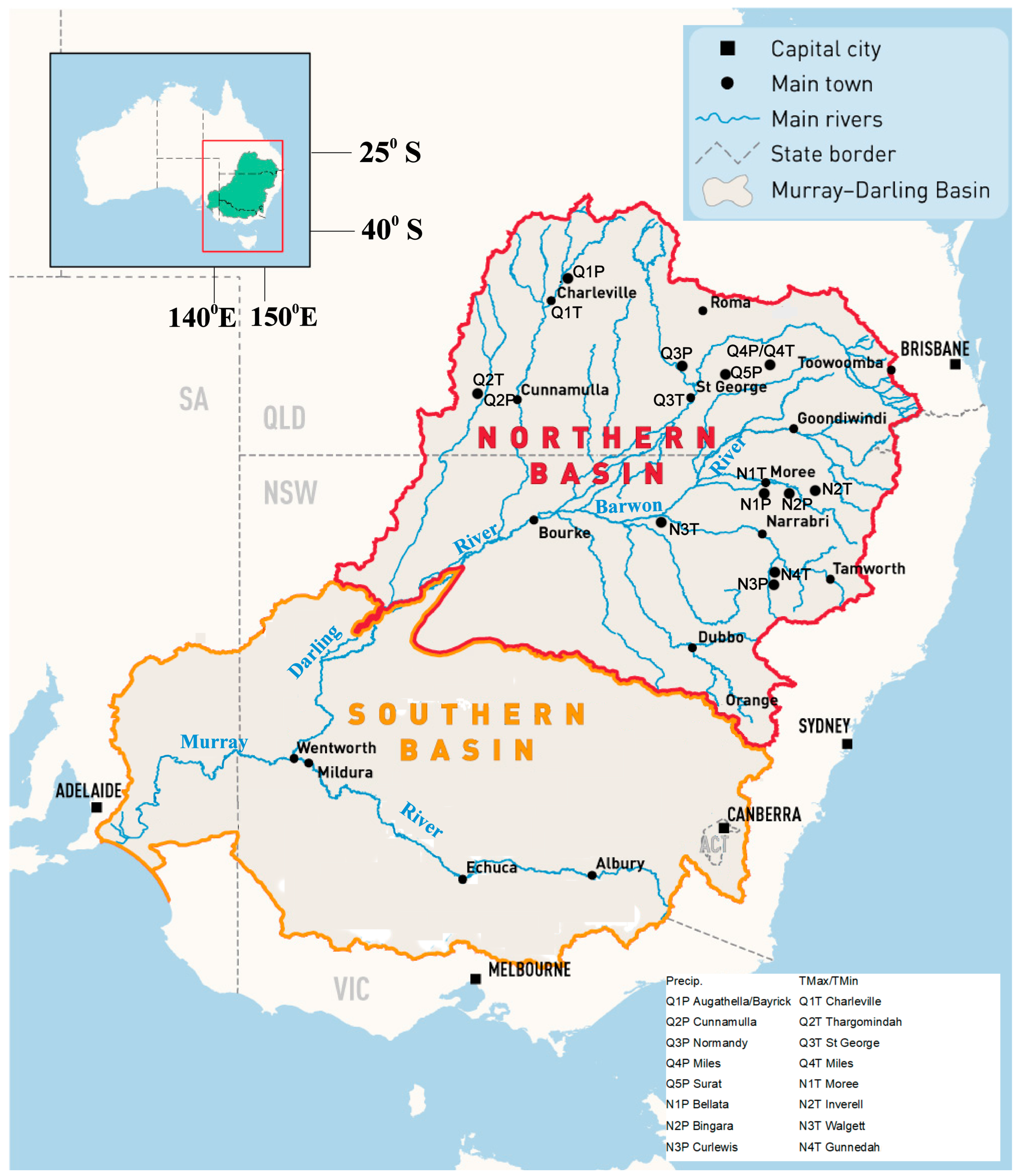
2. Data and Methodology
2.1. Data
2.2. Statistical Analysis
2.3. Wavelet Analysis
2.4. Attribute Selection
3. Results and Discussion
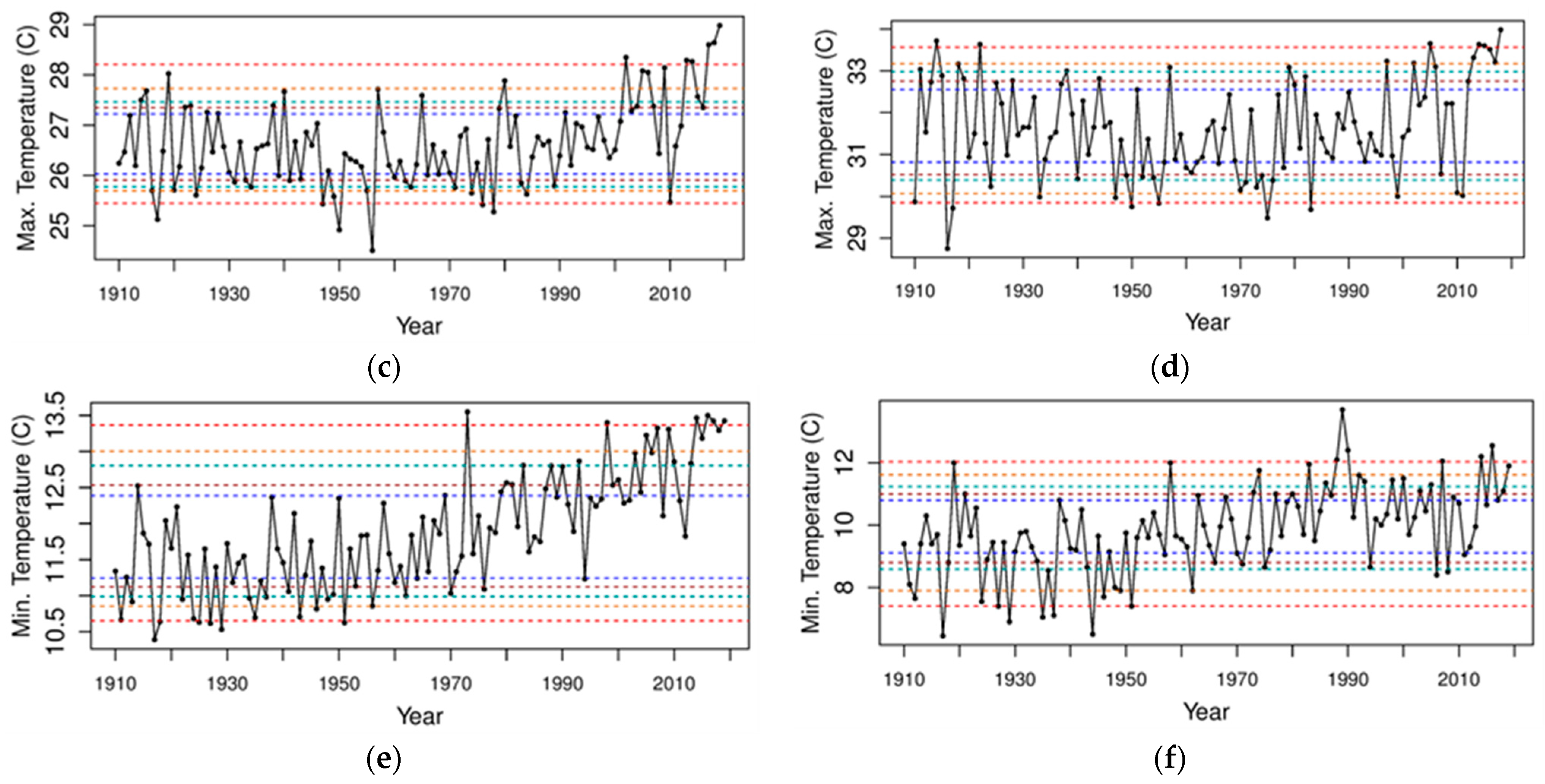
3.1. Precipitation and Temperature Time Series in the Northern Murray-Darling Basin
3.1.1. Precipitation
3.1.2. TMax
3.1.3. TMin
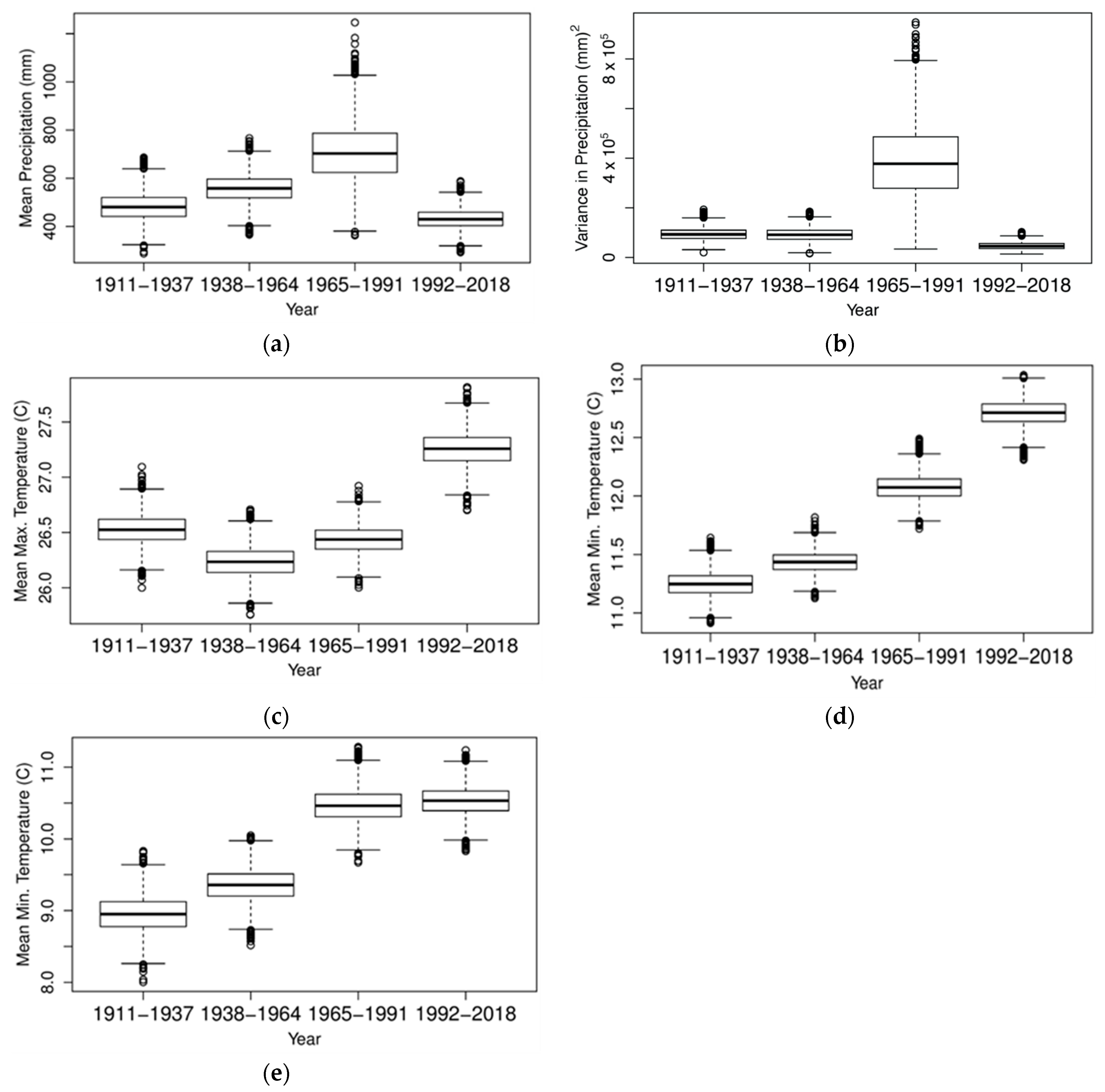
3.2. p-Values and Box–Whisker Plots for Precipitation, TMax and TMin
3.2.1. Precipitation
3.2.2. TMax
3.2.3. TMin
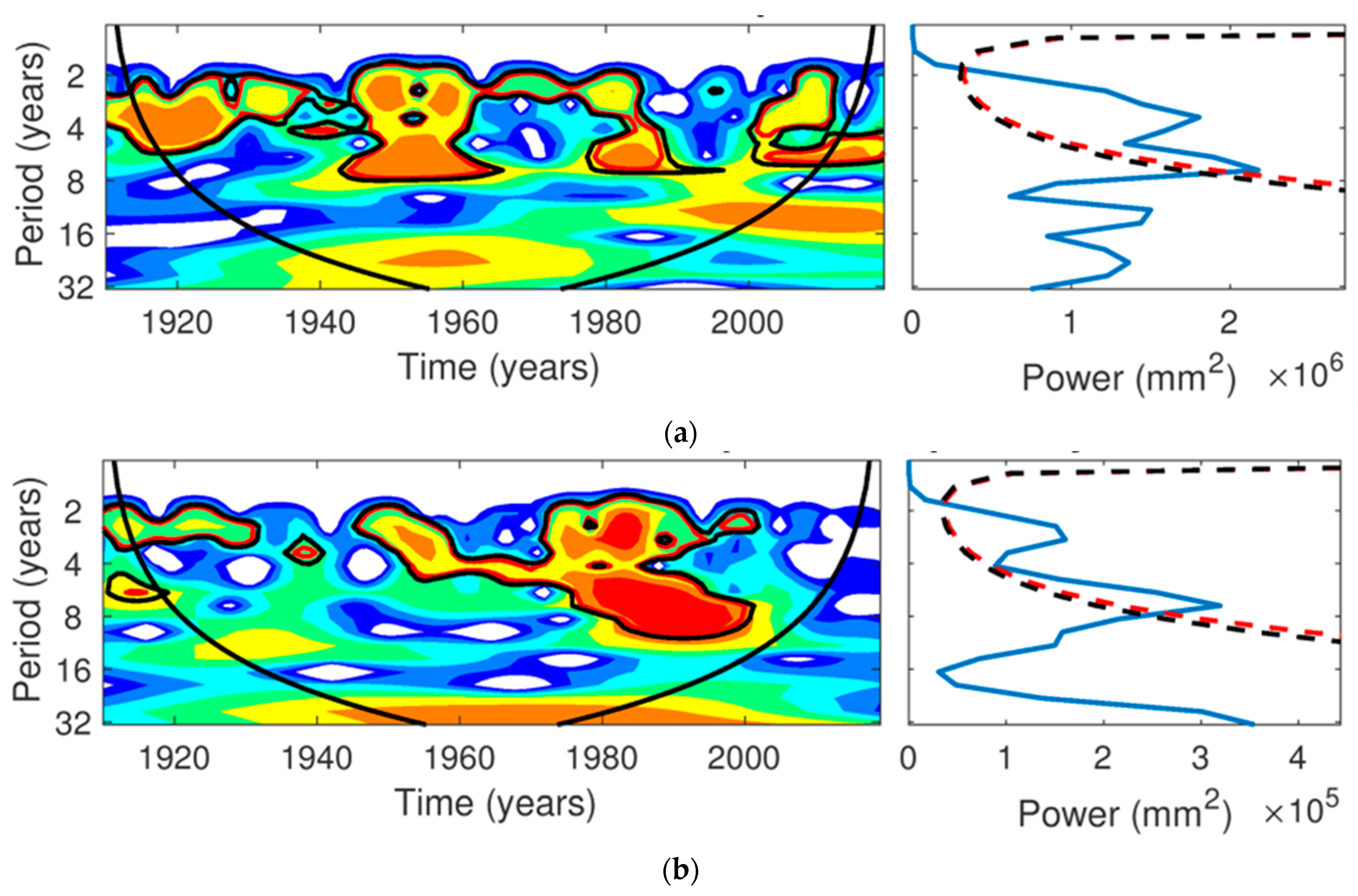
3.3. Wavelet Analysis of Temperature and Precipitation 1911–2018
3.3.1. Precipitation
3.3.2. TMax
3.3.3. TMin
3.4. Attribute Selection
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Code
References
- McBride, J.L.; Nicholls, N. Seasonal Relationships between Australian Rainfall and the Southern oscillation. Mon. Wea. Rev. 1983, 111, 1998–2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pook, M.J.; Risbey, J.S.; McIntosh, P.C. A comparative synoptic climatology of cool-season rainfall in major grain-growing regions of southern Australia. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2014, 117, 521–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Risbey, J.S.; Pook, M.J.; McIntosh, P.C.; Ummenhofer, C.C.; Meyers, G. Characteristics and variability of synoptic features associated with cool season rainfall in southeastern Australia. Int. J. Climatol. 2009, 29, 1595–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Record-Breaking La Niña Events. Available online: http://www.bom.gov.au/climate/enso/history/La-Nina-2010-12.pdf (accessed on 19 August 2022)ISBN 978-0-642-70621-8.
- Flooding in the Murray-Darling Basin. Available online: https://www.mdba.gov.au/issues-facing-basin/flooding-murray-darling-basin (accessed on 19 August 2022).
- State of the Climate 2020. Available online: https://bom.gov.au/state-of-the-climate/ (accessed on 19 August 2022).
- Science Solutions for the Murray-Darling Basin. Managing Today’s Resources for the Future. Available online: https://publications.csiro.au/rpr/download?pid=csiro:EP206574&dsid=DS1 (accessed on 19 August 2022).
- Cai, W.; Cowan, T. Southeast Australia Autumn Rainfall Reduction: A Climate-Change-Induced Poleward Shift of Ocean–Atmosphere Circulation. J. Clim. 2013, 26, 189–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speer, M.; Leslie, L.M.; MacNamara, S.; Hartigan, J. From the 1990s Climate Change Has Decreased Cool Season Catchment Precipitation and Reduced River Heights in Australia’s Southern Murray-Darling Basin. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 16136. Available online: https://www.nature.com/10.1038/s41598-021-95531-4 (accessed on 19 August 2022). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Australian Climate Influences. Available online: http://www.bom.gov.au/climate/about/australian-climate-influences.shtml (accessed on 19 August 2022).
- Murray Darling Basin. Available online: http://www.murrayriver.com.au/about-the-murray/murray-darling-basin/#agriculture (accessed on 19 August 2022).
- Characterising the Ecological Effects of Changes in the ‘Low-Flow Hydrology’ of the Barwon-Darling River. Advice to the Commonwealth Environmental Water Holder Office. Available online: https://www.environment.gov.au/system/files/resources/bb774e1f-d7fa-4825-8851-cb5e5f1b3f51/files/characterising-eco-effects-changes-low-flow-barwon-darling.pdf (accessed on 19 August 2022).
- The Australian Institute. Available online: https://australianinstitute.org.au/report/a-fish-kill-qanda/ (accessed on 19 August 2022).
- Holland, J.E.; Luck, G.W.; Finlayson, C.M. Threats to food production and water quality in the Murray-Darling Basin of Australia. Ecosyst. Serv. 2015, 12, 55–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephens, C.M.; McVicar, T.R.; Johnson, F.M.; Marshall, L.A. Revisiting pan evaporation trends in Australia a decade on. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2018, 45, 11164–11172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Independent Assessment of the 2018-19 Fish Deaths in the Lower Darling. Available online: https://www.mdba.gov.au/sites/default/files/pubs/Final-Report-Independent-Panel-fish-deaths-lower%20Darling_4.pdf (accessed on 19 August 2022).
- The Australian Landscape Water Balance Model (AWRA-L v6). Available online: http://www.bom.gov.au/water/landscape/assets/static/publications/AWRALv6_Model_Description_Report.pdf (accessed on 19 August 2022).
- Hartigan, J.; MacNamara, S.; Leslie, L.M. Application of machine learning to attribution and prediction of seasonal precipitation and temperature trends in Canberra, Australia. Climate 2020, 8, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartigan, J.; MacNamara, S.; Leslie, L.M.; Speer, M. Attribution and prediction of precipitation and temperature trends within the Sydney Catchment using machine learning. Climate 2020, 8, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Australian Climate Change Site Networks. Available online: http://www.bom.gov.au/climate/change/?ref=ftr#tabs=Tracker&tracker=site-networks (accessed on 19 August 2022).
- Hydrological Assessment of Flow Changes in the Northern Basin. Available online: https://www.mdba.gov.au/sites/default/files/pubs/1209-Hydrologic-assessment-of-flow-changes-in-the-northern-basin.pdf (accessed on 19 August 2022).
- Climate Change 2014: Synthesis Report. Contribution of Working Groups I, II and III to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Pachauri et al. Available online: https://epic.awi.de/id/eprint/37530/ (accessed on 19 August 2022).
- Morice, C.P.; Kennedy, J.J.; Rayner, N.A.; Jones, P.D. Quantifying uncertainties in global and regional temperature change using an ensemble of observational estimates: The HadCRUT4 dataset. J. Geophys. Res. 2012, 117, D08101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Centers for Environmental Information, State of the Climate: Global Climate Report for 2019, Published Online January 2020. Available online: https://www.ncdc.noaa.gov/sotc/global/201913/supplemental/page-3 (accessed on 19 August 2022).
- Good, P.I. Resampling Methods: A Practical Guide to Data Analysis; Birkhäuser: Boston, MA, USA, 2006; ISBN 978-0-8176-4386-7. [Google Scholar]
- Lau, K.M.; Weng, H. Climate signal detection using wavelet transform: How to make a time series sing. Bull. Amer. Meteorol. Soc. 1995, 76, 2391–2402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrence, C.; Compo, G.P. A Practical Guide to Wavelet Analysis. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc. 1998, 79, 61–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richman, M.B.; Leslie, L.M. Machine Learning for Attribution of Heat and Drought in Southwestern Australia. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2020, 168, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsay, H.A.; Richman, M.B.; Leslie, L.M. Seasonal tropical cyclone predictions using optimized combinations of ENSO Regions: Application to the Coral Sea region. J. Clim. 2014, 27, 8527–8542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vapnik, V. The Nature of Statistical Learning Theory; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1995; ISBN 978-1-4757-3264-1. [Google Scholar]
- Breiman, L. Random Forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hastie, T.; Tibshirani, R.; Friedman, J. The Elements of Statistical Learning: Data Mining, Inference, and Prediction; Springer Science & Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 2009; ISBN 978-0-387-84858-7. [Google Scholar]
- Maldonado, S.; Weber, R. A wrapper method for feature selection using Support Vector Machines. Inf. Sci. 2009, 179, 2208–2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Special Climate Statement 74—Extreme Rainfall and Flooding in Eastern and Central Australia in March 2021. Available online: http://www.bom.gov.au/climate/current/statements/scs74.pdf?20210621 (accessed on 19 August 2022).




| Period | Interval p-Values | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Observation | Mean & Variance | 1911–1937 vs. 1965–1991 | 1938–1964 vs. 1965–1991 | 1911–1937 vs. 1992–2018 | 1965–1991 vs. 1992–2018 | |
| Precip. | Mean Variance | 0.1 0.0168 | 0.289 0.0154 | 0.48 0.0946 | 0.0318 <0.01 | |
| April–May | TMax | Mean Variance | 0.194 0.934 | 0.0542 0.599 | <0.01 0.677 | <0.01 0.73 |
| TMin | Mean Variance | <0.01 0.726 | <0.01 0.897 | <0.01 0.318 | 0.847 0.584 | |
| Precip. | Mean Variance | 0.593 0.23 | 0.788 0.815 | 0.388 0.581 | 0.679 0.585 | |
| JJAS | TMax | Mean Variance | 0.689 0.602 | 0.577 0.474 | <0.01 0.569 | <0.01 0.935 |
| TMin | Mean Variance | 0.0230 0.913 | 0.0142 0.989 | <0.01 0.86 | <0.01 0.795 | |
| Precip. | Mean Variance | 0.225 0.664 | 0.705 0.1 | 0.0424 0.573 | 0.404 0.909 | |
| Oct–Mar | TMax | Mean Variance | 0.157 0.251 | 0.698 0.718 | 0.373 0.864 | 0.0194 0.0626 |
| TMin | Mean Variance | <0.01 0.759 | <0.01 0.94 | <0.01 0.556 | <0.01 0.211 | |
| Precip. | Mean Variance | 0.295 0.22 | 0.933 0.12 | 0.498 0.584 | 0.688 0.644 | |
| Annual | TMax | Mean Variance | 0.628 0.619 | 0.304 0.614 | <0.01 0.42 | <0.01 0.207 |
| TMin | Mean Variance | <0.01 0.859 | <0.01 0.416 | <0.01 0.825 | <0.01 0.97 | |
| Annual | April + May | JJAS | Oct–Mar |
|---|---|---|---|
| GlobalSSTA*TSSST | SOI | SOI | SOI |
| AMO*SAM | GlobalSSTA*TSSST | Niño3.4 | DMI*SAM |
| AMO*Niño3.4 | TPI | SAM | SAM |
| TPI | GlobalT | TPI | GlobalT*GlobalSSTA |
| DMI*Niño3.4 | DMI | DMI*TSSST | SOI*TPI |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Speer, M.; Hartigan, J.; Leslie, L. Machine Learning Assessment of the Impact of Global Warming on the Climate Drivers of Water Supply to Australia’s Northern Murray-Darling Basin. Water 2022, 14, 3073. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14193073
Speer M, Hartigan J, Leslie L. Machine Learning Assessment of the Impact of Global Warming on the Climate Drivers of Water Supply to Australia’s Northern Murray-Darling Basin. Water. 2022; 14(19):3073. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14193073
Chicago/Turabian StyleSpeer, Milton, Joshua Hartigan, and Lance Leslie. 2022. "Machine Learning Assessment of the Impact of Global Warming on the Climate Drivers of Water Supply to Australia’s Northern Murray-Darling Basin" Water 14, no. 19: 3073. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14193073
APA StyleSpeer, M., Hartigan, J., & Leslie, L. (2022). Machine Learning Assessment of the Impact of Global Warming on the Climate Drivers of Water Supply to Australia’s Northern Murray-Darling Basin. Water, 14(19), 3073. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14193073








