The Effect and Influence Mechanism of Soil Salinity on Phosphorus Availability in Coastal Salt-Affected Soils
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Soil Properties
2.2. Soil Properties Analysis Method
2.3. Data Processing and Analysis
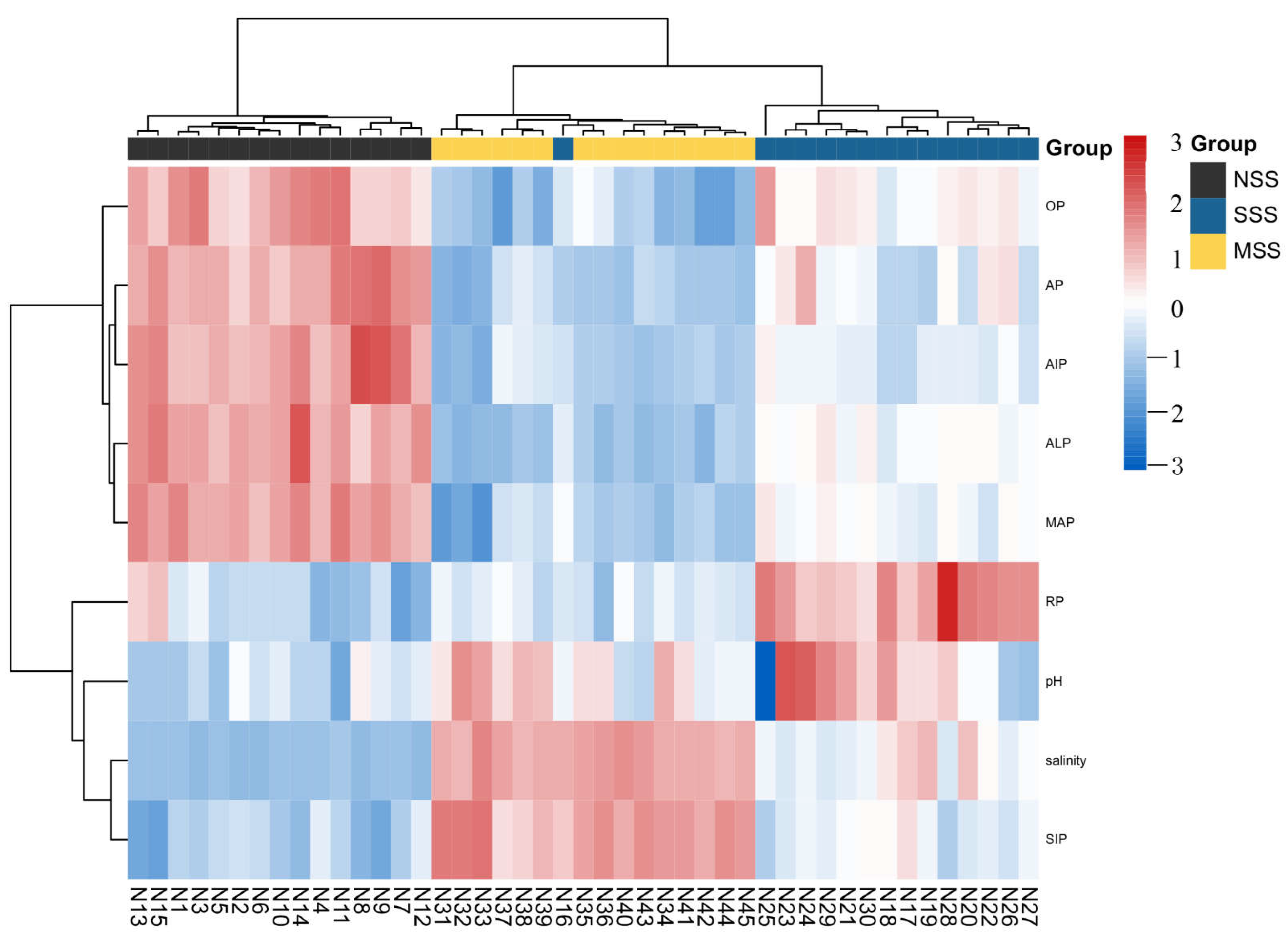
3. Result and Discussion
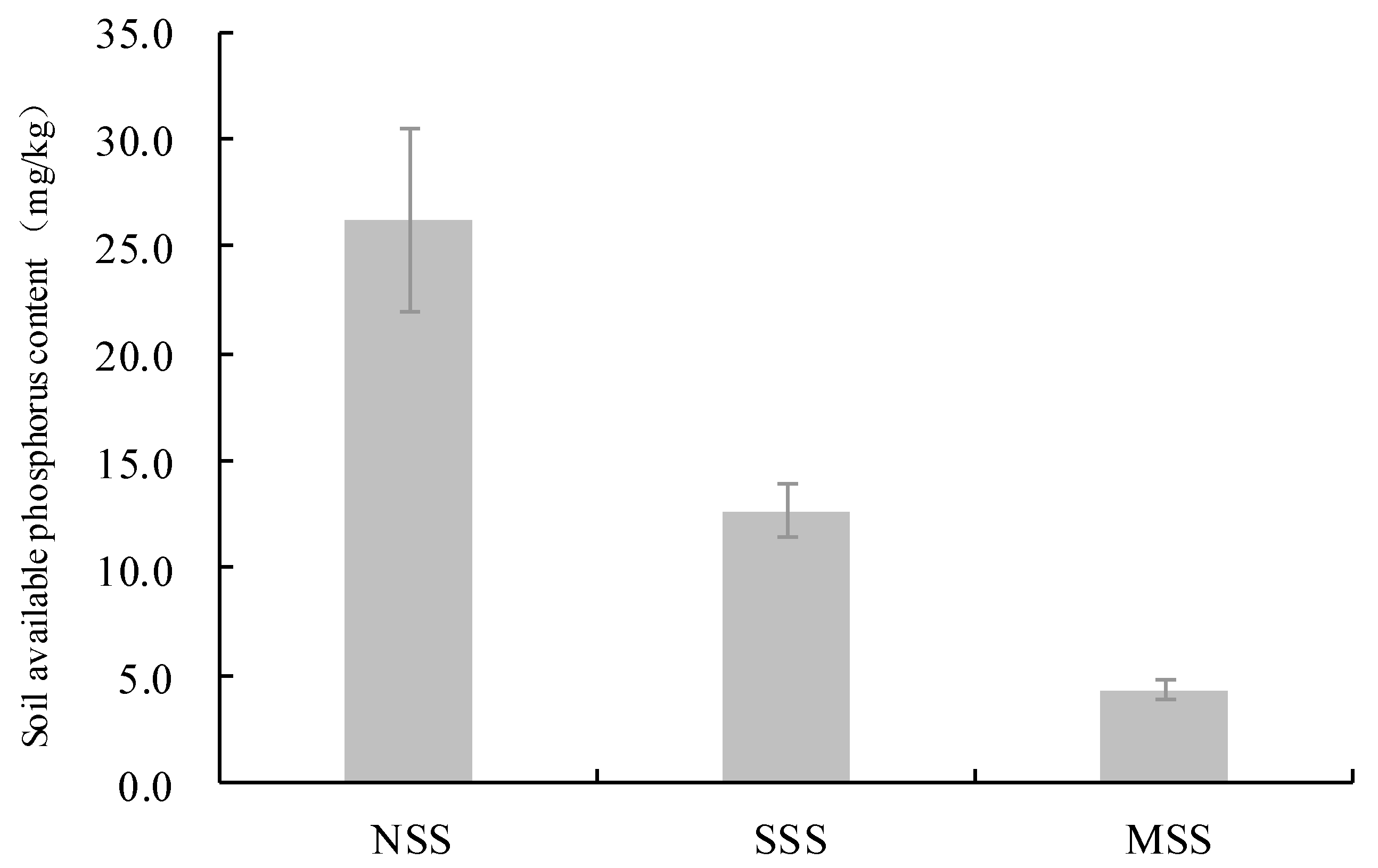
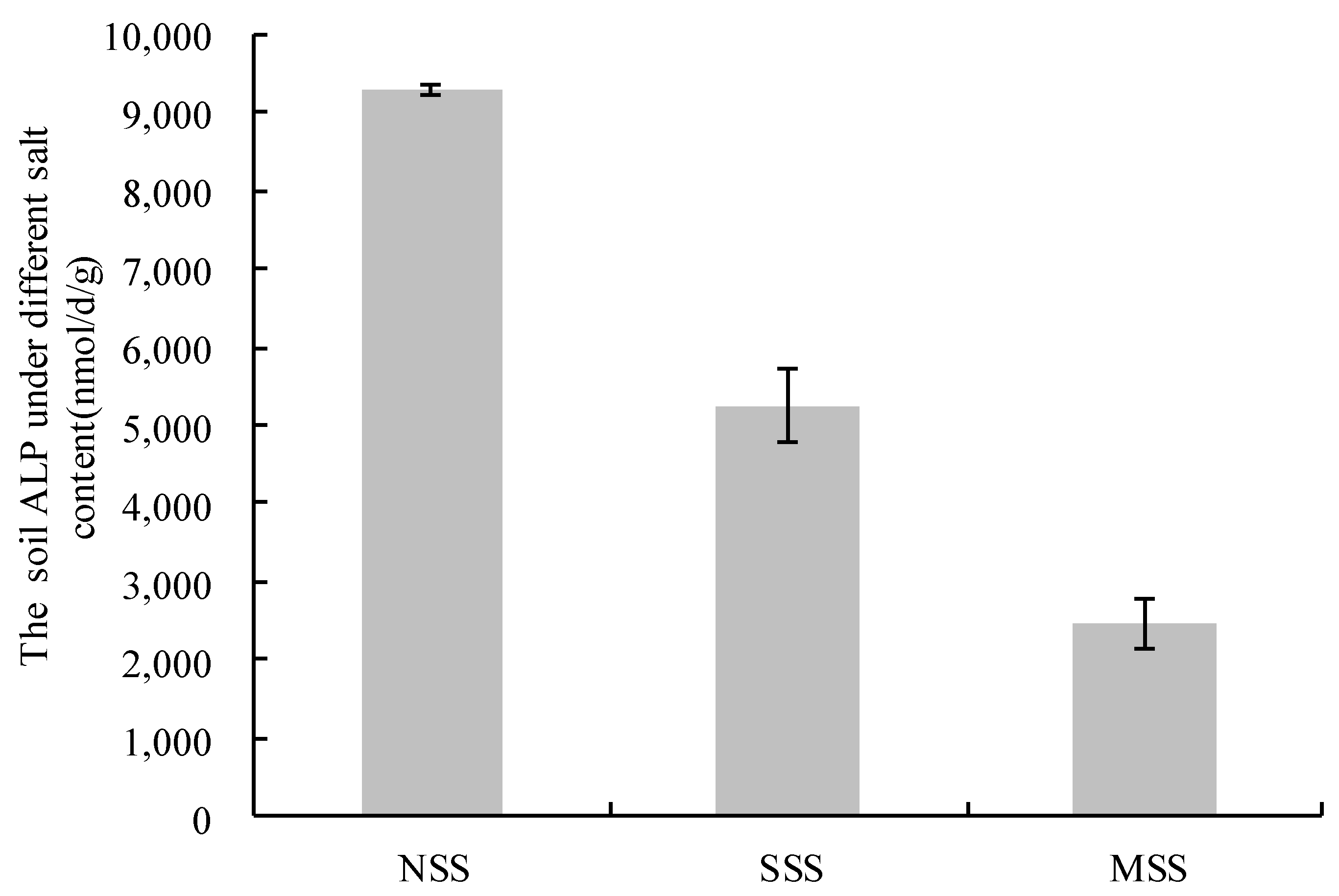
3.1. Available Phosphorus (AP) in Coastal Saline Soil with Different Salt Content
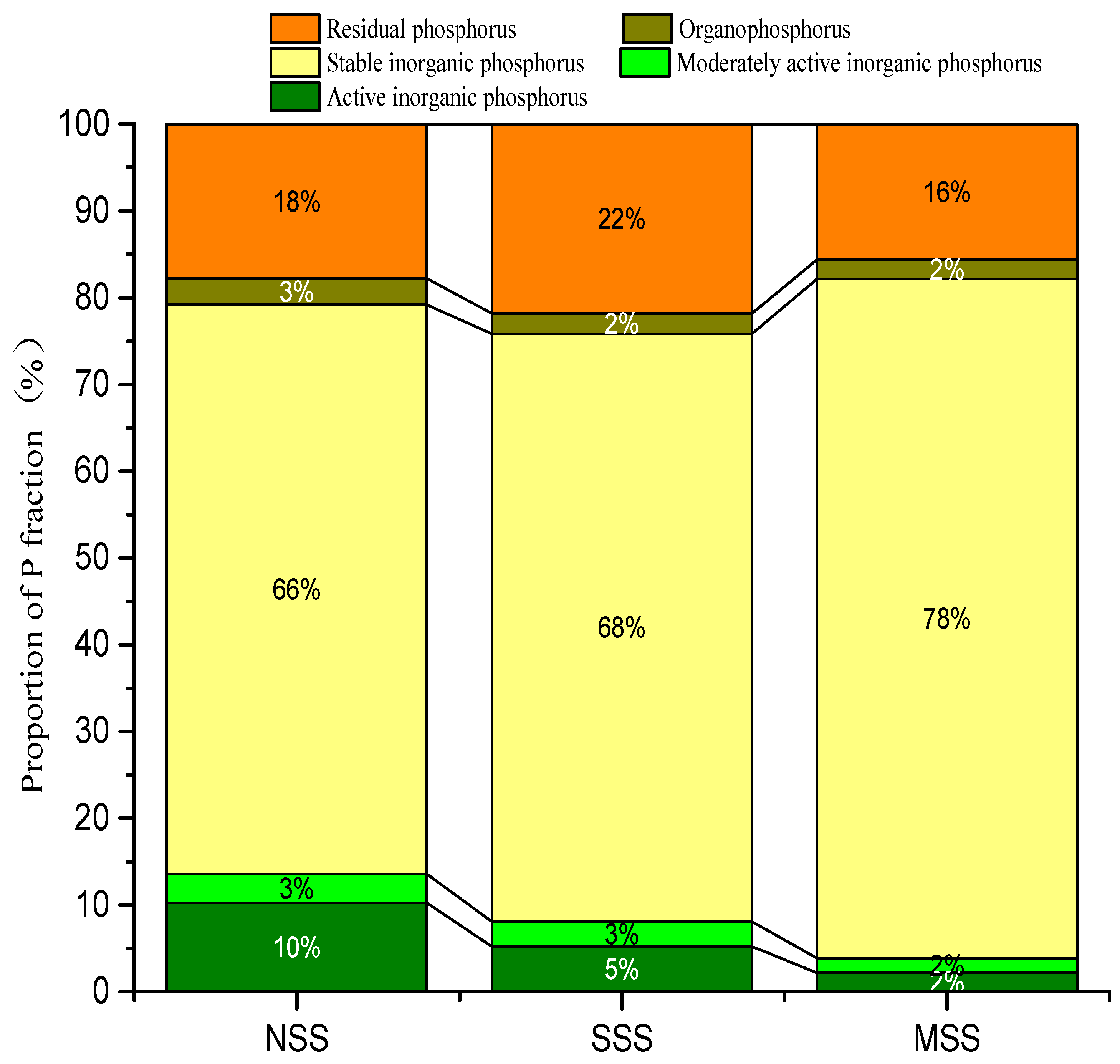
3.2. Characteristics of Various Forms of Phosphorus in Hedley Phosphorus Classification in Coastal Saline Soil with Different Salt Content
3.3. Possible Influencing Factors of Soil Available Phosphorus in Different Salinization Degrees
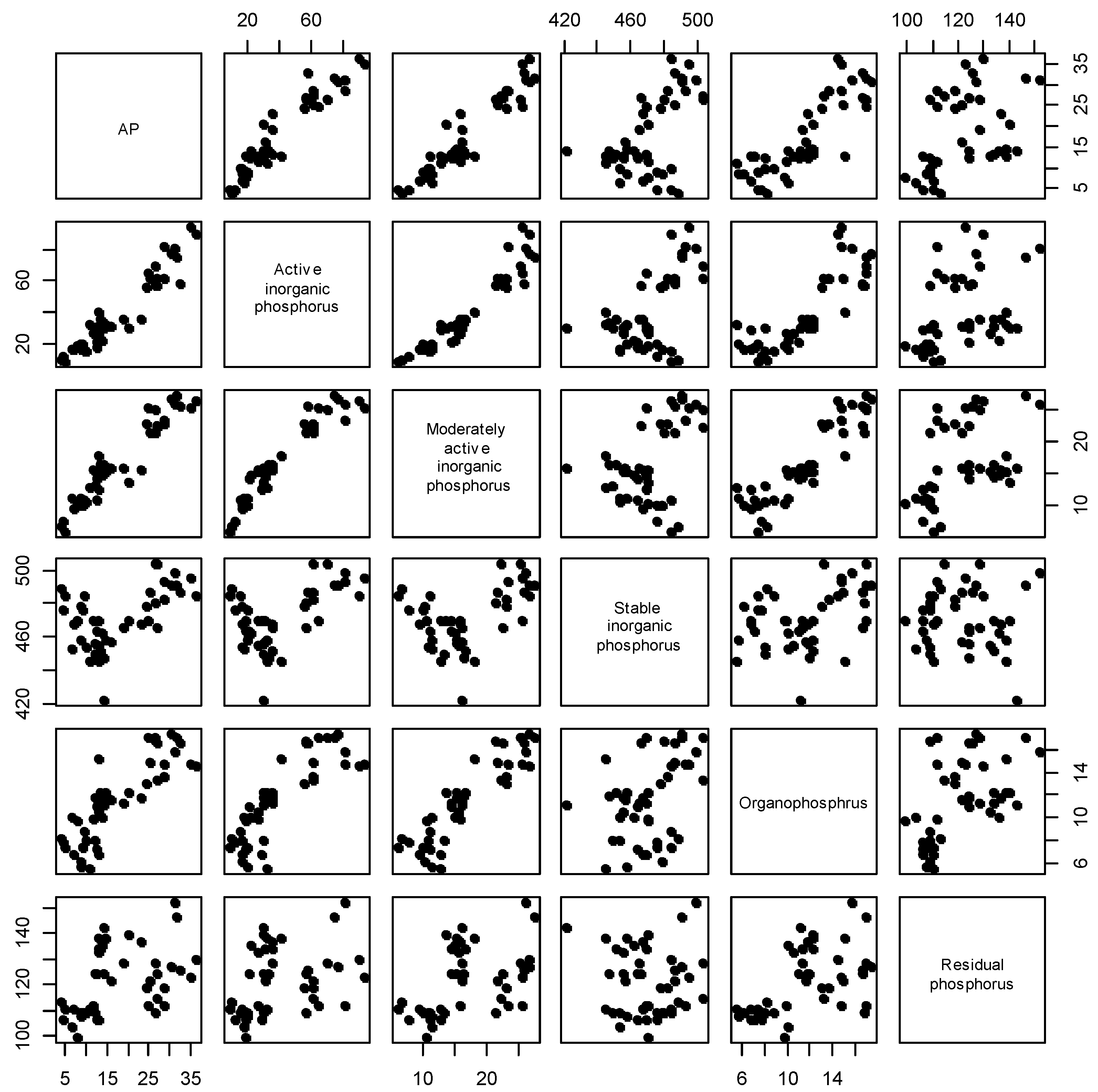
3.3.1. Relationship between Available Phosphorus and Different Phosphorus Forms in Hedley Phosphorus Classification
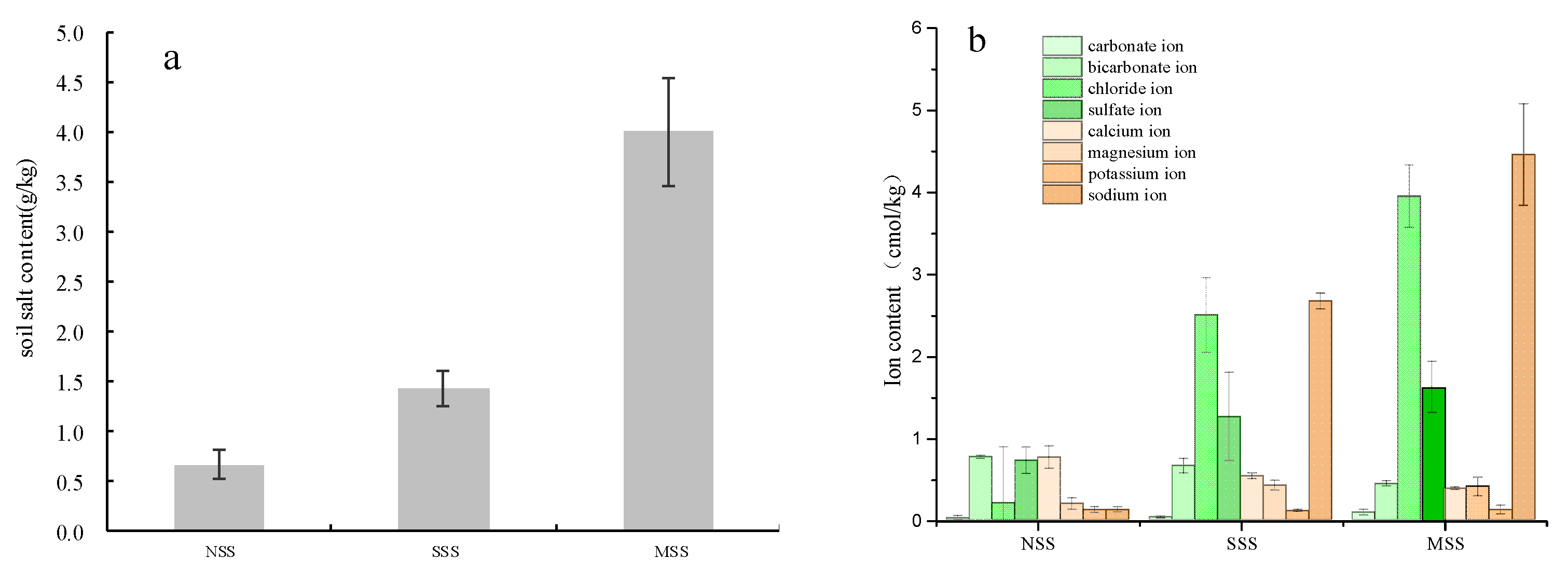
3.3.2. Soil Salinity
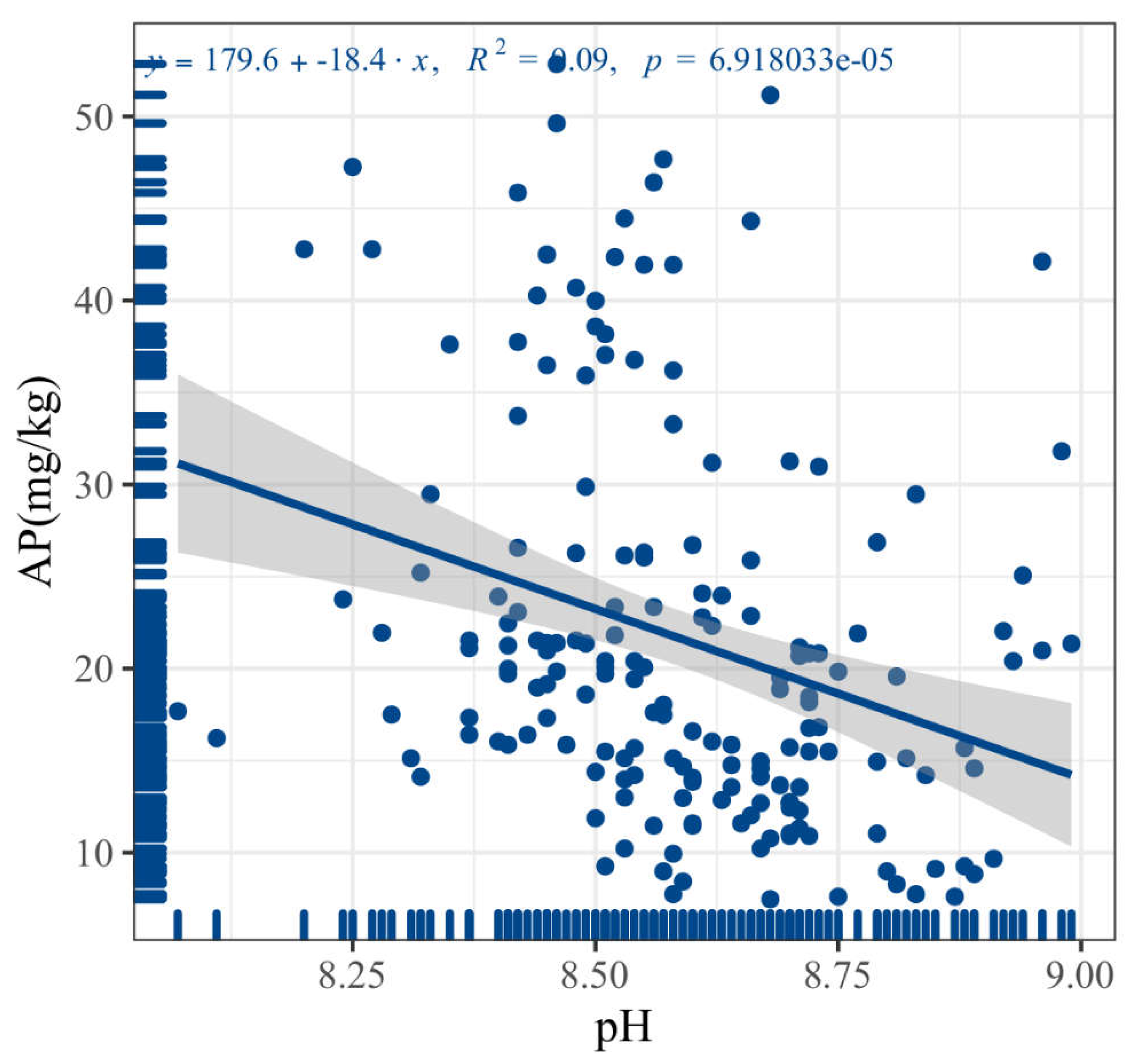
3.3.3. Soil pH Value
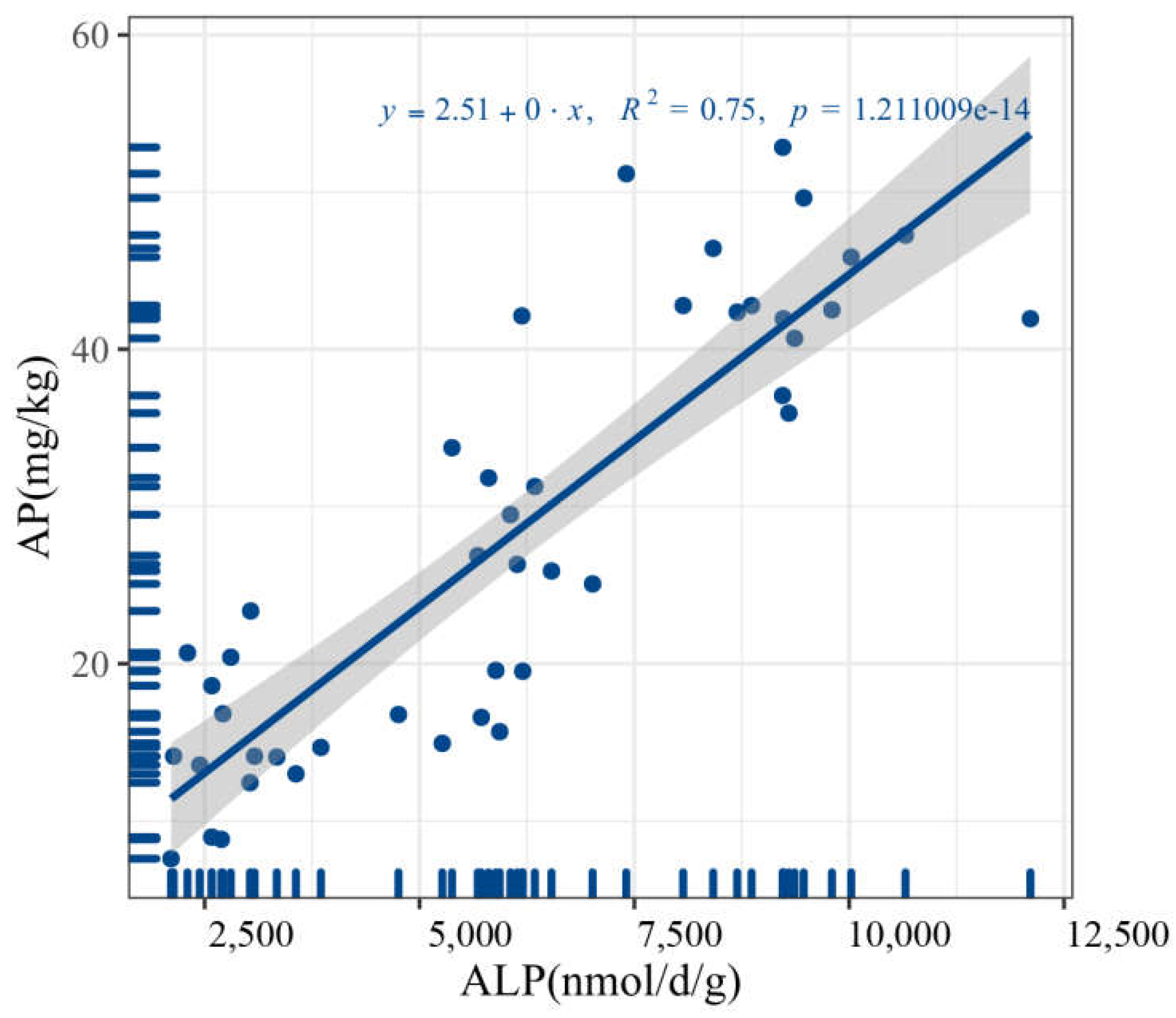
3.3.4. Soil Alkaline Phosphatase Activity
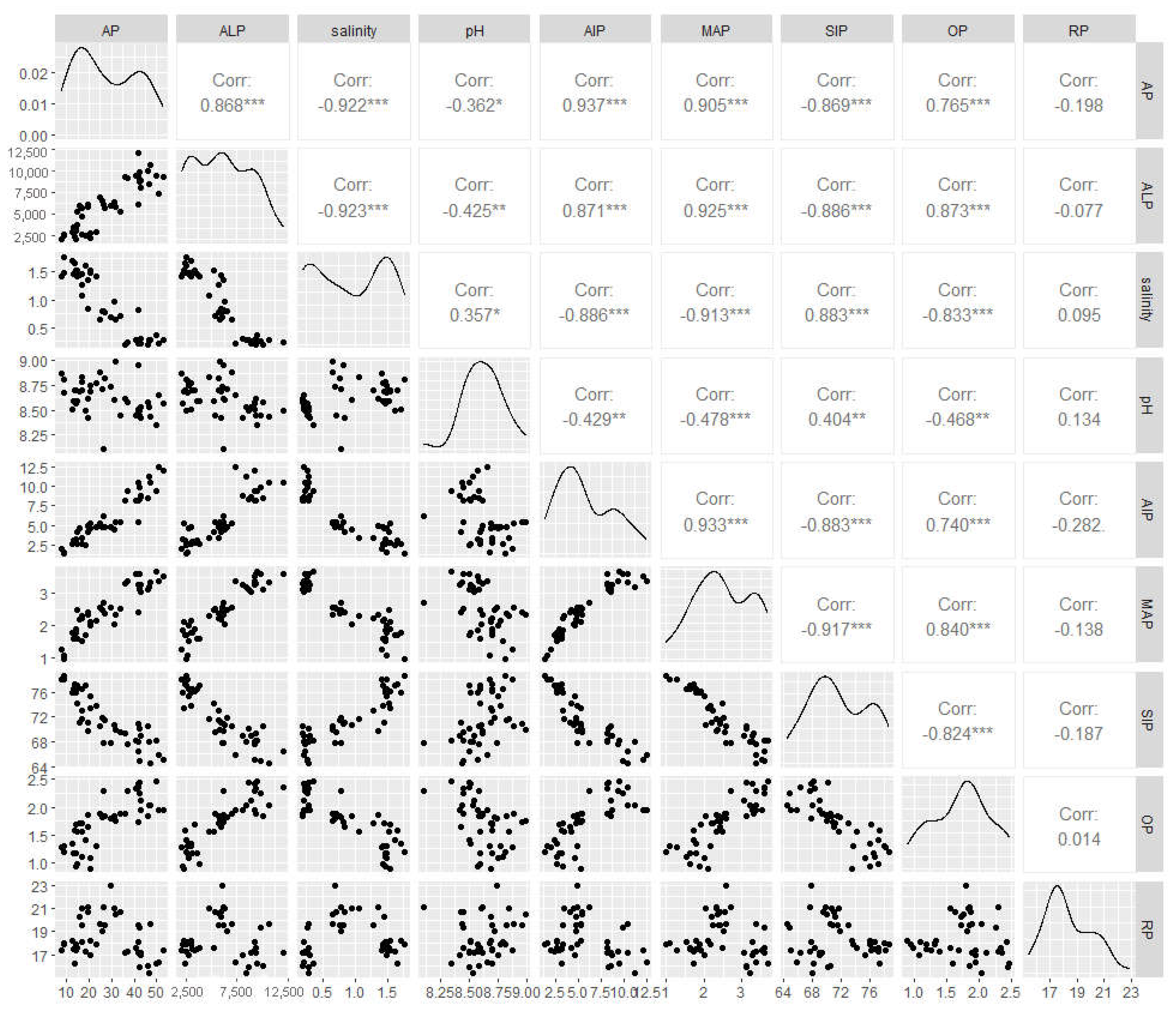
3.4. Relationships between Possible Impact Factors of Soil Available Phosphorus
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Indicators | Abbreviation |
| available phosphorus | AP |
| alkaline phosphatase activity | ALP |
| active inorganic phosphorus | AIP |
| moderately active inorganic phosphorus | MAP |
| stable inorganic phosphorus | SIP |
| Organophosphorus | OP |
References
- Yang, W.Z.; Yang, M.D.; Wen, H.Y.; Jiao, Y. Global Warming Potential of CH4 uptake and N2O emissions in saline-alkaline soils. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 191, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahbaz, M.; Ashraf, M. Improving Salinity Tolerance in Cereals. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 2013, 32, 237–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qadir, M.; Oster, J.D.; Schubert, S.; Noble, A.D.; Sahrawat, K.L. Phytoremediation of Sodic and Saline-Sodic Soils. Adv. Agron. 2007, 96, 197–247. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, G.; Li, J.; Zhang, X.; Wang, X.; Lv, Z.; Yang, J.; Shao, H.; Yu, S. GIS-mapping spatial distribution of soil salinity for Eco-restoring the Yellow River Delta in combination with Electromagnetic Induction. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 94, 306–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.G.; Deng, C.Y.; Liu, Y.; Ziru, N. Identifying change in spatial accumulation of soil salinity in an inland river watershed, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 621, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metternicht, G.I.; Zinck, J.A. Remote Sensing of Soil Salinity: Potentials and Constraints. Remote Sensitive Environ. 2003, 85, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yuan, G.; Lu, J.; Wu, J.; Wei, J. Effects of biochar and peat on salt-affected soil extract solution and wheat seedling germination in the Yellow River Delta. Arid Land Res. Manag. 2019, 34, 287–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.S. Development and prospect of the research on salt-affected soils in China. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2008, 5, 837–845. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M.; Hou, L.; Xu, S.; Ou, D.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Liu, Q. Adsorption of phosphate on tidal flat surface sediments from the Yangtze Estuary. Environ. Geol. 2002, 42, 657–665. [Google Scholar]
- Bruland, G.L.; DeMent, G. Phosphorus Sorption Dynamics of Hawaii’s Coastal Wetlands. Estuaries Coasts 2009, 32, 844–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tejada, M.; Garcia, C.; Gonzalez, J.L.; Hernandez, M.T. Use of organic amendment as a strategy for saline soil remediation: Influence on the physical, chemical and biological properties of soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2006, 38, 1413–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rietz, D.N.; Haynes, R.J. Effects of irrigation-induced salinity and sodicity on soil microbial activity. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2003, 35, 845–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, C.; Hernandez, T. Influence of salinity on the biological and biochemical activity of a calciorthird soil. Plant Soil 1996, 178, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penn, C.J.; Camberato, J.J. A critical review on soil chemical processes that control how soil pH affects phosphorus availability to plants. Agriculture 2019, 9, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, M.P.; Shah, M.T.; Patolia, J.S. Salvadora persica, a potential species for industrial oil production in semiarid saline and alkali soils. Ind. Crop Prod. 2008, 28, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, K.; Xu, H.; Zhao, S.; Shan, J.; Chen, X. Saline soil desalination by honeysuckle (Lonicera japonica Thunb.) depends on salt resistance mechanismKun. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 88, 226–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, L.L. Effects of Long-Term Located Fertilization and Paddy Field Continuous Cropping on Phosphorus Speciation in Farmland Soils. Ph.D. Thesis, Huazhong Agriculture University, Wuhan, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Perassi, I.; Borgnino, L. Adsorption and surface precipitation of phosphate onto CaCO3–montmorillonite: Effect of pH, ionic strength and competition with humic acid. Geoderma 2014, 232–234, 600–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.S.; Yao, R.J. Evaluation of soil quality in reclaimed coastal regions in North Jiangsu Province. Chin. J. Eco-Agric. 2009, 17, 410–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.G.; Shi, X.Z. Introduction to Soil Resources; Chinese Science Publication: Beijing, China, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Murphy, J.; Riley, J.P. A modified single solution method for the determination of phosphate in natural waters. Analytia Chimca Acta 1962, 27, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, S.R.; Cole, C.V.; Watanabe, F.S. Estimation of Available Phosphorus in Soils by Extraction with Sodium Bicarbonate; USDA Circular 939; US Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1954.
- Xie, X.; Pu, L.; Zhu, M.; Xu, Y.; Wang, X. Linkage between soil salinization indicators and physicochemical properties in a long-term intensive agricultural coastal reclamation area, Eastern China. J. Soil Sediments 2019, 19, 3699–3707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, S.; Kaushal, S.S. Salinization alters fluxes of bioreactive elements from stream ecosystems across land use. Biogeosciences 2015, 12, 7331–7347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, T.J.; Hardiputra, B.; Rengel, Z. Wheat, canola and grain legume access to soil phosphorus fractions differs in soils with contrasting phosphorus dynamics. Plant Soil 2010, 326, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maranguit, D.; Guillaume, T.; Kuzyakov, Y. Land-use change affects phosphorus fractions in highly weathered tropical soils. Catena 2017, 149, 385–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedley, M.J.; Stewart, J.W.B.; Chauhan, B.S. Changes in Inorganic and Organic Soil Phosphorus Fractions Induced by Cultivation Practices and by Laboratory Incubations. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1982, 46, 970–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Schmi, U. Drought and salinity: A comparison of their effects on mineral nutrition of plants. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2005, 168, 541–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.S. Characteristics of Crop Response on Different Salt Stresses/Management and the Regulation of Crop Salt Resistance. Ph.D. Thesis, Nanjing Agriculture University, Nanjing, China, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Dijk, G.V.; Lamers, L.; Loeb, R.; Westendorp, P.J.; Kuiperij, R.; van Kleef, H.H.; Klinge, M.; Smolders, A.J. Salinization lowers nutrient availability in formerly brackish freshwater wetlands; unexpected results from a long-term field experiment. Biogeochemistry 2019, 143, 67–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, J.O.; Simpson, R.J.; Moore, A.D.; Graham, P.; Chapman, D.F. Impact of phosphorus application and sheep grazing on the botanical composition of sown pasture and naturalised, native grass pasture. Aust. J. Agric. Res. 2005, 55, 1213–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevenson, F.J.; Cole, M.A. Cycles of Soils: Carbon, Nitrogen, Phosphorus, Sulfur, Micronutrients; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Xue, L.; Jiao, R. Stoichiometric imbalances and the dynamics of phosphatase activity and the abundance of phoC and phoD genes with the development of Cunninghamia lanceolata (Lamb.) Hook plantations. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2022, 173, 104373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.B.; Kang, Y.; Liu, S.H.; Liu, S.P. Alkaline phosphatase activity and its relationship to soil properties in a saline–sodic soil reclaimed by cropping wolfberry (Lycium barbarum L.) with drip irrigation. Paddy Water Environ. 2014, 12, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pant, H.K.; Warman, P.R. Enzymatic hydrolysis of soil organic phosphorus by immobilized phosphatases. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2000, 30, 306–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Shao, H.B.; Sun, J.N.; Chang, S.X. Phosphorus fractions and profile distribution in newly formed wetland soils along a salinity gradient in the Yellow River Delta in China. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2012, 175, 721–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed, S.A.; Shahzad, S.M.; Ashraf, M.; Kausar, R.; Arif, M.S.; Albasher, G.; Rizwana, H.; Shakoor, A. Interactive effect of different salinity sources and their formulations on plant growth, ionic homeostasis and seed quality of maize. Chemosphere 2022, 291, 132678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, D.; Lade, H. Plant-growth-promoting rhizobacteria to improve crop growth in saline soils: A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2014, 34, 737–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, G. Mechanisms of straw biochar’s improvement of phosphorus bioavailability in soda saline-alkali soil. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 47867–47872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, X.F.; Bai, J.H.; Lu, Q.Q.; Zhao, Q.Q.; Wang, J.J. Spatial Distribution of Phosphorus in Surface Soils of Wetlands with Different Plant Communities in the Yellow River Delta, China. Adv. Mater. Res. 2013, 726–731, 1383–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devau, N.; Le Cadre, E.; Hinsinger, P.; Jaillard, B.; Gérard, F. Soil pH controls the environmental availability of phosphorus: Experimental and mechanistic modelling approaches. Appl. Geochem. 2009, 24, 2163–2174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, C.; Liu, C.; Zhao, H.; Wang, Y. Changes of soil physico-chemical properties and enzyme activities in relation to grassland salinization. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2013, 55, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.H.; Liu, S.H.; Wan, S.Q.; Wang, R.S. Assessment of soil enzyme activities of saline–sodic soil under drip irrigation in the Songnen plain. Paddy Water Environ. 2013, 11, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.S.; Angle, J.S.; Chaney, R.L.; Delorme, T.A.; McIntosh, M. Changes in soil biological activities under reduced soil pH during Thlaspi caerulescens phytoextraction. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2006, 38, 1451–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.H.; Li, N.; Peng, J.; Chen, K.; Gao, T.Y.; Han, X.R. Efects of straw and biochar returning on soil aggregates distribution and organic carbon content in brown soil. J. Plant Nutr. Fert. 2020, 26, 1978–1986. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, W.; Zhou, Q.; Tian, Z.; Cui, Y.; Liang, Y.; Wang, H. Apply biochar to ameliorate soda saline-alkali land, improve soil function and increase corn nutrient availability in the Songnen Plain. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 722, 137428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Salinity Classification | pH | Soil Salt Content (g kg−1) | Total Phosphorus (mg kg−1) | Available Phosphorus (mg kg−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Non-saline soil | 8.77 | 0.51 | 812.45 | 44.41 |
| Slightly salinized soil | 9.00 | 1.55 | 709.95 | 21.04 |
| Moderately salinized soil | 9.30 | 2.53 | 651.20 | 11.05 |
| Soil Type | H2O-Pi | NaHCO3-Pi | NaOH-Pi | HCl-Pi | NaHCO3-Po | NaOH-Po | R-P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NSS | 1.34 | 8.79 | 0.48 | 3.70 | 2.02 | 64.78 | 18.89 |
| SSS | 0.61 | 4.60 | 0.82 | 2.74 | 1.31 | 69.09 | 20.81 |
| MSS | 0.32 | 1.87 | 0.85 | 1.66 | 1.09 | 77.90 | 16.31 |
| H2O-Pi | NaHCO3-Pi | NaHCO3-Po | NaOH-Pi | NaOH-Po | HCL-Pi | R-P | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pearson Correlation with AP | 0.805 | 0.954 | 0.560 | 0.949 | 0.878 | 0.534 | 0.442 |
| Sig. (2-tailed) | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.002 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xie, W.; Yang, J.; Gao, S.; Yao, R.; Wang, X. The Effect and Influence Mechanism of Soil Salinity on Phosphorus Availability in Coastal Salt-Affected Soils. Water 2022, 14, 2804. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14182804
Xie W, Yang J, Gao S, Yao R, Wang X. The Effect and Influence Mechanism of Soil Salinity on Phosphorus Availability in Coastal Salt-Affected Soils. Water. 2022; 14(18):2804. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14182804
Chicago/Turabian StyleXie, Wenping, Jingsong Yang, Shan Gao, Rongjiang Yao, and Xiangping Wang. 2022. "The Effect and Influence Mechanism of Soil Salinity on Phosphorus Availability in Coastal Salt-Affected Soils" Water 14, no. 18: 2804. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14182804
APA StyleXie, W., Yang, J., Gao, S., Yao, R., & Wang, X. (2022). The Effect and Influence Mechanism of Soil Salinity on Phosphorus Availability in Coastal Salt-Affected Soils. Water, 14(18), 2804. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14182804






