Abstract
The responses of phytoplankton to nutrients vary for different natural bodies of water, which can finally affect the occurrence of phytoplankton bloom. However, the effect of high alkalinity characteristic on the nutrient thresholds of natural alkaline lake is rarely considered. Bioassay experiments were conducted to investigate the nutrient thresholds and the responses of phytoplankton growth to nutrients for the closed plateau Chenghai Lake, Southwest China, which has a high pH background of up to 9.66. The growth of the phytoplankton community was restricted by phosphorus without obvious correlation with the input of nitrogen sources. This can be explained by the nitrogen fixation function of cyanobacteria, which can meet their growth needs for nitrogen. In addition, nitrate nitrogen (NO3-N) could be utilized more efficiently than ammonia nitrogen (NH4-N) for the phytoplankton in Chenghai Lake. Interestingly, the eutrophication thresholds of soluble reactive phosphorus (SRP), NH4-N, and NO3-N should be targeted at below 0.05 mg/L, 0.30 mg/L, and 0.50 mg/L, respectively, which are higher than the usual standards for eutrophication. This can be explained by the inhibition effect of the high pH background on phytoplankton growth due to the damage to phytoplankton cells. Therefore, the prevention of phytoplankton blooms should be considered from not only the aspect of reducing nutrient input, especially phosphorus input, but also maintaining the high alkalinity characteristic in natural alkaline lake, which was formed due to the geological background of saline-alkali soil.
1. Introduction
Harmful phytoplankton blooms in natural water have aroused great concern due to their negative effects on water quality and aquatic ecosystems globally [1,2]. This poses a serious threat to the safety of drinking water, food webs, and the overall sustainability of freshwater ecosystems [3,4]. It has been reported that megafauna may be endangered by cyanotoxins released by harmful phytoplankton [5]. In addition, the expansion of phytoplankton blooms could be triggered by climate change and eutrophication [6]. It is widely believed that the reduction of nutrient input is fundamental for the control of harmful phytoplankton blooms. However, the responses of phytoplankton to nutrients vary in different natural bodies of water [3,7]. Research indicates that the thresholds for regime shifts between turbid-water and clear-water conditions in shallow lakes vary depending on basins and climates [8]. Therefore, it is important to determine the nutrient thresholds in water bodies, especially for natural water with special water quality backgrounds.
Nutrient thresholds are regarded as the critical levels of nutrients that control population shifts, such as the sudden and long-term dominance of phytoplankton blooms. The determination of nutrient thresholds is a quantifiable and meaningful approach [9]. N and P are the main material bases for phytoplankton growth, and their relationship with phytoplankton biomass is one of the important aspects in studying eutrophication [10]. It is well known that addition of N and P can not only stimulate phytoplankton growth, but also promote phosphorus release from sediment or nitrogen fixation from atmosphere [11,12]. The critical values of total nitrogen (TN) and total phosphorus (TP) for eutrophication of lakes were reported to be 0.8 mg/L and 0.05 mg/L, respectively [13]. It has been proved that the understanding and utilization of ecological thresholds is the key to the successful management of water environments [14]. The control of nutrients below threshold levels is more practical, achievable, and cost-effective than reducing them to historical levels [15].
Due to the great differences in the environment and geographical location at different altitude, plateau lakes have unique hydrological chemistry characteristics, such as high alkalinity [16]. Chenghai Lake is a typical representative of plateau lakes in southwest China with high alkalinity characteristic, which was naturally formed due to the geological background of saline-alkali soil [17,18]. Increasing salinization due to climate change might negatively affect inland water sources [19]. According to the water quality conditions of Chenghai Lake in 2018–2019, the average pH value is up to 9.42. In addition, the average values of TN and TP are 1.12 and 0.06 mg/L, respectively, which have exceeded the generally recognized concentrations for eutrophication occurrence [10,13,20,21,22]. However, the current cyanobacteria biomass in Chenghai Lake is still at a slight bloom level without large-scale phytoplankton blooms [18]. Therefore, the nutrient thresholds of natural alkaline lake might be higher than other lakes, which needs to be clarified. It has been reported that pH range has some inhibition or promotion effects on phytoplankton in various environmental backgrounds [23,24]. However, the effect of high alkalinity characteristic on the nutrient thresholds of natural alkaline lake is rarely considered. Therefore, it is important to determine the nutrient thresholds and explore the effect of high alkalinity, which are fundamental for the prevention of phytoplankton blooms in natural alkaline lakes.
Based on the aforementioned considerations, this study aims to: (1) determine the nutrient thresholds of NH4-N, NO3-N, and SRP in Chenghai Lake; (2) investigate the binding and synergistic interactions between NH4-N, NO3-N, and SRP; (3) explore the effect of high alkalinity characteristic on nutrient thresholds of natural alkaline lake.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Field Method
Chenghai Lake is located in the Yunnan Plateau, southwestern China (26°27′–26°38′ N; 100°38′–100°41′ E) with an altitude of 1503 m (Figure 1). The lake covers an area of about 72.9 square kilometers and has an average water depth of 23.7 m, and an annual average water temperature of 17.8 °C. Chenghai is a typical closed-type deep-water lake, surrounded by mountains on the east, west and north, and the terrain is flat on the south [25].
Figure 1.
Location of the study area and sampling sites.
Monthly sampling was conducted from June 2018 to May 2019 for all 15 sampling sites (Figure 1). The in-situ data of conductivity (EC), pH, and temperature (WT) were measured on site with a hand-held multi-parameter meter (MYRON L 6P, California, USA). TN, NH4-N, NO3-N, TP, and total dissolved phosphorus (TDP) were analyzed according to standard methods [25]. The phytoplankton samples were settled for 48 h after being fixed with Lugol iodine solution (2%) [26]. Cell density and community composition were determined under microscope with a Sedgwick-Rafter counting chamber [27].
2.2. Nutrient Limitation Bioassay Experiments
Water samples from site H were used for nutrient threshold and addition bioassay experiments. Zooplankton were removed by screening with a 200-μm grid to minimize the effects of grazing [28]. The water samples were cultivated in a lighted incubator within 2 °C of the in situ temperature. The light intensity was maintained at 100 μmol photon m−2 s−1 with a 14:10-h light-dark cycle. The initial physical, chemical and biological properties of the water sample used for nutrient limitation bioassay experiments are given in Table S1. For all the experiments, SRP, NO3-N, and NH4-N were added as K2HPO4·3H2O, NaNO3, and NH4Cl, respectively. The experiment was carried out over 15 days to ensure that the phytoplankton had sufficient time to adapt and grow.
The nutrient threshold bioassay experiment was conducted to explore the nutrient thresholds of SRP, NO3-N, and NH4-N. Various concentrations of SRP (0.017, 0.02, 0.03, 0.04, 0.05, 0.06, 0.08, 0.10, 0.50, 1.00 mg/L P) and fixed NO3-N (10 mg/L N) were used in the SRP threshold experiment. Various concentrations of NO3-N (0.04, 0.10, 0.20, 0.30, 0.40, 0.50, 0.80, 1.00, 1.50, 2.00 mg/L N) and fixed P (5 mg/L N) were used in the NO3-N threshold experiment. Various concentrations of NH4-N (0.04, 0.10, 0.20, 0.30, 0.40, 0.50, 0.80, 1.00, 1.50, 2.00 mg/L N) and fixed P (5 mg/L N) were used in the NH4-N threshold experiment.
A separate nutrient addition bioassay experiment was conducted with treated water samples containing individual or combined SRP, NO3-N, and NH4-N, which could assess the individual or combined effects of these nutrients on the growth of phytoplankton. A total of 30 treatments for three scenarios were designed in this experiment (Table 1).

Table 1.
Basic Schemes for Nutrient Addition Bioassay Experiment.
The growth rate (μ) for all treatments was calculated according to the exponential growth equation [9]: μ = ln(X2/X1)/(T2-T1), where X1 is the phytoplankton density at the initial incubation time point (T1), and X2 is the phytoplankton density at the last time point (T2). The Monod kinetic equation was used to calculate the maximum growth rate (µmax) and half-saturation constant (Ku) [29]. The nutrient threshold can be estimated according to the change points on the response curves.
The difference in growth response among various treatments was analyzed by one-way ANOVA [30]. The Tukey’s least significant difference procedure was used to compare multiple treatments after the event [31]. Statistical analysis was conducted using the SPSS 13.0 statistical software package (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA), and the significance level of the test used was p < 0.05 [32].
2.3. Effect of pH Range on the Growth of Phytoplankton
According to the water quality conditions of Chenghai Lake in 2018–2019, the average pH value is up to 9.42 with the highest value of 9.66. The effect of pH range on nutrient thresholds was investigated with 3 different gradients of pH value (9.17, 8.50, and 7.50). The initial pH value of the water samples from Chenghai Lake used in this study was 9.17, and all the other gradients of pH value were adjusted before cultivation. The treatments were cultivated under a light intensity of 100 μmol photon m−2 s−1 with a 14:10-h light-dark cycle. The pH of each treatment was controlled during the whole experimental period. The phytoplankton density was recorded regularly every day.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Seasonal Variation of Phytoplankton Density and Water Quality
The water quality parameters for each sampling point of Chenghai Lake from June 2018 to May 2019 are shown in Figure 2. As we can see from the monthly changes, most water quality parameters showed seasonal variations. As shown in Figure 2b, the phytoplankton density was relatively lower in autumn and spring. The highest phytoplankton density of 6.46 × 107 cells/L was found in the northern part of Chenghai Lake in May. The nutritional status for Chenghai Lake was mainly maintained at a slight bloom level according to the phytoplankton density [33].
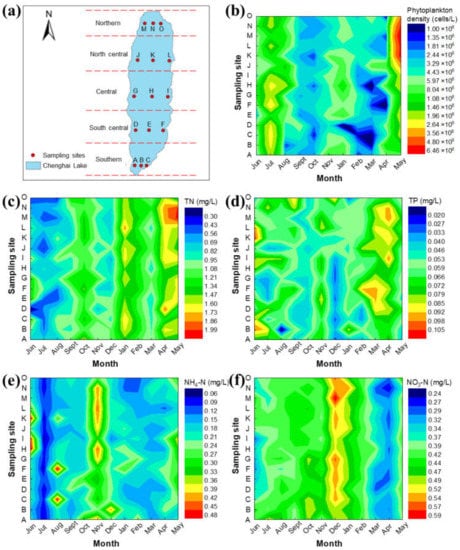
Figure 2.
Monthly variation of phytoplankton density and water quality indexes in Chenghai Lake for all the 15 sampling sites. (a) Sampling sites delineation in Chenghai Lake. The spatial and temporal distribution characteristics of (b) phytoplankton density, (c) TN, (d) TP, (e) NH4-N, and (f) NO3-N in Chenghai Lake.
Nitrogen and phosphorus are the most important nutrients for phytoplankton growth. The TN value showed a continuous upward trend during the monthly sampling, varying from 0.30 to 1.99 mg/L. The highest TN content of 1.99 mg/L also appeared in the north of Chenghai Lake in May. What’s more, the TP value was in the range from 0.02 to 0.11 mg/L. Most of the measured TN and TP values were higher than the commonly reported critical values for eutrophication [10,13,20,21,22]. In addition, NH4-N and NO3-N are also provided to illustrate the variation of different nitrogen sources (Figure 2e,f). The highest NH4-N and NO3-N values were determined to be as high as 0.43 mg/L and 0.59 mg/L, respectively. Therefore, the reduction of external nutrients is essential to ensure acceptable water quality, which can finally reduce the internal nitrogen and phosphorus load [15,34].
3.2. Nutrient Thresholds Required to Control Eutrophication in Chenghai Lake
Nitrogen and phosphorus are important nutrients that limit the growth of phytoplankton, and it is particularly important to formulate nutrient thresholds to control the occurrence of blooms [35]. The bioassay experiment is an effective tool to explore the growth response of phytoplankton under different nutrient concentrations [36]. To examine the nutrient thresholds of SRP, NO3-N, and NH4-N, the growth rate response of phytoplankton to different nutrient concentrations was explored. Figure 3 shows the growth curves fitted by nonlinear regression for SRP, NO3-N, and NH4-N, respectively. Figure 3a shows that the growth rate of phytoplankton increased with SRP addition from 0 to 0.05 mg/L P, while it remained constant with the further increase in SRP addition from 0.05 to 1.0 mg/L P. The change point on the response curve was found to be 0.05 mg/L P, which indicated that the growth of phytoplankton would be no longer restricted by P when SRP enrichment exceeded 0.05 mg/L P. Therefore, the threshold of SRP could be determined to be 0.05 mg/L P. Similarly, eutrophication thresholds of NH4-N and NO3-N were found to be 0.3 mg/L N and 0.5 mg/L N, respectively (Figure 3b,c).
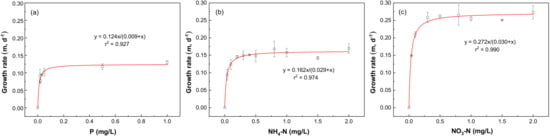
Figure 3.
Growth kinetics of phytoplankton in response to (a) SRP, (b) NH4-N, and (c) NO3-N concentrations.
The maximum growth rates (μmax) for SRP, NH4-N, and NO3-N were found to be 0.124, 0.162, and 0.272 d−1, respectively, according to the Monod equation [13]. The half-saturation constant (Ku) for SRP, NH4-N, and NO3-N were determined to be 0.009, 0.029, and 0.030 mg/L, respectively. The higher μmax/Ku ratio of NO3-N compared with NH4-N could demonstrate the higher utilization efficiency of NO3-N in Chenghai Lake.
The growth responses of phytoplankton to increasing concentrations of SRP, NH4-N, and NO3-N are shown in Figure 4. The addition of NH4-N and NO3-N alone showed little effect on the growth of phytoplankton compared with the control group. As we can see from Figure 4a, the growth rate reached a peak when the concentration of NH4-N reached 1.0 mg/L N together with P addition. This indicated that phosphorus could be the main limiting factor for the growth of phytoplankton. As for NO3-N (Figure 4b), the growth rate of phytoplankton remained almost unchanged with the increase in concentration from 0.5 mg/L N to 4.0 mg/L N which was higher than the control group. However, the growth rates of phytoplankton could be promoted by increased SRP concentration with or without nitrogen sources (Figure 4c). These results indicated that the growth of the phytoplankton community in Chenghai Lake was restricted by phosphorus without obvious correlation with the input of nitrogen sources. Similar results have been reported in Meiliang Bay of Taihu Lake, and phosphorus was also found to restrict the growth of phytoplankton [20]. This can be explained by the nitrogen fixation function of cyanobacteria, which can meet their growth needs for nitrogen [37].
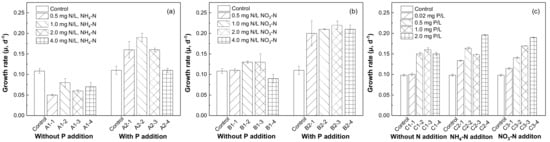
Figure 4.
Phytoplankton growth responses to various concentrations of (a) NH4-N, (b) NO3-N, and (c) SRP additions.
Figure 5 shows the growth rate of phytoplankton in response to individual or combined NH4-N, NO3-N, and SRP additions according to the nutrient addition bioassay experiment. N addition alone showed little effect on the growth rate of phytoplankton compared with the control. A significant stimulatory effect can be found with the combined addition of NO3-N and SRP. This can directly prove the stimulatory effect of NO3-N on phytoplankton growth, which is consistent with the results of nutrient threshold bioassay experiments. In addition, the stimulatory effect of SRP addition compared with the control can be further enhanced with the combined addition of NH4-N or NO3-N. However, the growth rate of phytoplankton with combined addition of “2 mg/L SRP + 5.0 mg/L NH4-N + 5.0 mg/L NO3-N” was not higher than the group with “2 mg/L SRP + 10.0 mg/L NH4-N” or “2 mg/L SRP + 10.0 mg/L NO3-N”. This indicated that the form of nitrogen source could not show similar stimulatory effect on the growth of phytoplankton under the sufficient concentration of phosphorus.
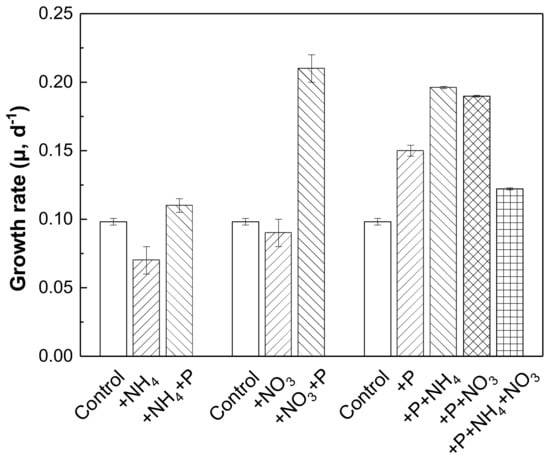
Figure 5.
Comprehensive effects of NH4-N, NO3-N, and SRP on phytoplankton growth.
3.3. Effect of High Alkalinity Background on Nutrient Thresholds
According to the above results of nutrient limitation bioassay experiments, the nutrient thresholds of Chenghai Lake are higher than other reported lakes. Only a slight level of bloom was found in Chenghai Lake with a high-nutrient environment. These results indicate that the growth of phytoplankton might be influenced by other factors in addition to nutrients. The pH range in natural water bodies has been reported to show inhibition or promotion effects on phytoplankton [23,24]. Combined with the high alkalinity characteristic in Chenghai Lake [18], the effects of pH range on the growth of phytoplankton in Chenghai Lake were also explored in this study.
As we can see from Figure 6, the phytoplankton density increased with decrease in the pH value from 9.17 to 7.50 during the cultivation. These results indicated that a relatively lower water body pH could promote the growth of phytoplankton, while the high pH background of Chenghai Lake (pH = 9.17) could limit the growth of phytoplankton. It has been reported that a high pH condition in freshwater could not promote the growth and reproduction of cyanobacteria [38]. Most phytoplankton species cannot grow properly under high alkalinity conditions, especially when pH value exceeds 9 [39,40]. Thus, the relatively higher nutrient thresholds of Chenghai Lake can be explained by the inhibition effects of the high pH background on phytoplankton growth. High pH background might alter the transport processes of membrane and the metabolic functions of cells and change the relative composition of amino acids in cellular, which can finally affect the growth of phytoplankton [40]. As a means to prevent and control phytoplankton blooms, many researchers have undertaken pH adjustment as a method in actual lake management [41,42,43]. Therefore, it is necessary to maintain the high alkalinity characteristic of Chenghai Lake, which is helpful for the prevention of phytoplankton bloom.
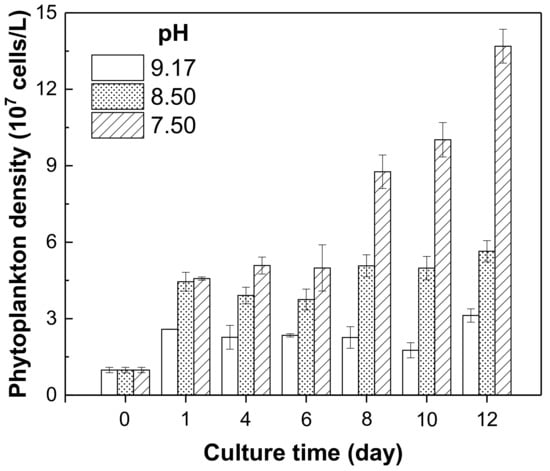
Figure 6.
Effect of different pH levels on phytoplankton growth in Chenghai Lake.
4. Conclusions
The results in this study indicated that Chenghai Lake was always maintained at a slight bloom level according to the phytoplankton density. Phosphorus was found to be the main limiting factor for the growth of phytoplankton. In addition, the utilization efficiency of NO3-N was higher than that of NH4-N in Chenghai Lake. The eutrophication thresholds of SRP, NH4-N, and NO3-N were determined to be 0.05 mg/L, 0.30 mg/L, and 0.50 mg/L, respectively. The higher nutrient thresholds can be explained by the high pH range in Chenghai Lake, which would inhibit phytoplankton growth. In addition to the reduction of nutrient input, the maintenance of high alkalinity characteristic is also necessary for the prevention of phytoplankton blooms in natural alkaline lake.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/w14172674/s1, Table S1: Physical and chemical indexes of water samples collected at site H.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.Q. and W.Q.; methodology, J.Q. and L.D.; software, L.D.; validation, J.Q. and L.D.; formal analysis, J.Q.; investigation, J.Q., L.D., and Y.S.; resources, C.H.; data curation, J.Q.; writing—original draft preparation, J.Q.; writing—review and editing, W.Q. and C.H.; supervision, J.Q. and W.Q; project administration, J.Q. and W.Q.; funding acquisition, J.Q. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was financially supported by the Funds for National Key R&D Program of China (Grant No. 2018YFE0204101), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 52170014, and 51808531).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
References
- Paerl, H.W.; Xu, H.; McCarthy, M.J.; Zhu, G.; Qin, B.; Li, Y.; Gardner, W.S. Controlling harmful cyanobacterial blooms in a hyper-eutrophic lake (Lake Taihu, China): The need for a dual nutrient (N & P) management strategy. Water Res. 2011, 45, 1973–1983. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, Z.S.; Wang, N.; Gu, L.; Sun, Y.F.; Huang, Y.; Chen, Y.F.; Yang, Z. Mixotrophic Ochromonas Addition Improves the Harmful Microcystis-Dominated Phytoplankton Community in In Situ Microcosms. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 4609–4620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, Z.Z.; Liang, D.F.; Du, H.B.; Pang, Y.; Hu, K.M.; Wang, J.J. Separation of wind’s influence on harmful cyanobacterial blooms. Water Res. 2016, 98, 280–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, N.E.; Cooke, M.E.; Shi, J.H.; Birbeck, J.A.; Westrick, J.A.; Ault, A.P. Harmful Algal Bloom Toxins in Aerosol Generated from Inland Lake Water. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 4769–4780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Xu, C.; Liu, Y.; Jeppesen, E.; Svenning, J.-C.; Wu, J.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, T.; Wang, P.; Nangombe, S.; et al. From unusual suspect to serial killer: Cyanotoxins boosted by climate change may jeopardize megafauna. Innovation 2021, 2, 100092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huisman, J.; Codd, G.A.; Paerl, H.W.; Ibelings, B.W.; Verspagen, J.M.H.; Visser, P.M. Cyanobacterial blooms. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 16, 471–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.M.; Steinman, A.D.; Tang, X.M.; Xue, Q.J.; Zhao, Y.Y.; Xie, L.Q. Response of bacterial communities to cyanobacterial harmful algal blooms in Lake Taihu, China. Harmful Algae 2017, 68, 168–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.J.; Wang, H.Z.; Liang, X.M.; Wu, S.K. Total phosphorus thresholds for regime shifts are nearly equal in subtropical and temperate shallow lakes with moderate depths and areas. Freshw. Biol. 2014, 59, 1659–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, D.-H.; Kim, M.-S. Flotation of algae for water reuse and biomass production: Role of zeta potential and surfactant to separate algal particles. Water Sci. Technol. 2015, 72, 762–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Cao, X.F.; Wang, J.; Liao, J.Q.; Sun, J.H.; Huang, Y. The threshold responses of phytoplankton community to nutrient gradient in a shallow eutrophic Chinese lake. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 61, 258–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.N.; Wang, H.J.; Wang, H.Z.; Li, Y.; Liu, M.; Liang, X.M.; Yu, Q.; Jeppesen, E.; Søndergaard, M. High ammonium loading can increase alkaline phosphatase activity and promote sediment phosphorus release: A two-month mesocosm experiment. Water Res. 2018, 145, 388–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.N.; Wang, H.J.; Wang, H.Z.; Zhang, M.; Li, Y.; Bian, S.-J.; Liang, X.-M.; Søndergaard, M.; Jeppesen, E. Effects of nitrate on phosphorus release from lake sediments. Water Res. 2021, 194, 116894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Paerl, H.W.; Qin, B.; Zhu, G.; Hall, N.S.; Wu, Y. Determining Critical Nutrient Thresholds Needed to Control Harmful Cyanobacterial Blooms in Eutrophic Lake Taihu, China. Environ. Sci. Technol. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 1051–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, S.L.; Ma, C.Z.; Xi, B.D.; Zhang, Y.L.; Wu, F.C.; Liu, H.L. Development of methods for establishing nutrient criteria in lakes and reservoirs: A review. J. Environ. Sci. 2018, 67, 54–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newell, S.E.; Davis, T.W.; Johengen, T.H.; Gossiaux, D.; Burtner, A.; Palladino, D.; McCarthy, M.J. Reduced forms of nitrogen are a driver of non-nitrogen-fixing harmful cyanobacterial blooms and toxicity in Lake Erie. Harmful Algae 2019, 81, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, W.Z.; Su, X.S.; Cui, G.; Wang, H. Microbial community structure in hypolentic zones of a brine lake in a desert plateau, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.J.; Peng, J.F.; Cao, X.F.; Xu, Y.; Yu, H.W.; Duan, G.Q.; Qu, J.H. Isotopic and chemical evidence for nitrate sources and transformation processes in a plateau lake basin in Southwest China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 711, 134856. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, D.N.; Xu, H.; Yang, M.; Lan, J.H.; Hou, W.G.; Wang, F.S.; Zhang, J.X.; Zhou, K.E.; An, Z.S.; Goldsmith, Y. Responses of cyanobacteria to climate and human activities at Lake Chenghai over the past 100 years. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 104, 755–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeppesen, E.; Beklioglu, M.; Ozkan, K.; Akyurek, Z. Salinization Increase due to Climate Change Will Have Substantial Negative Effects on Inland Waters: A Call for Multifaceted Research at the Local and Global Scale. Innovation 2020, 1, 100030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Wu, X.F.; Li, D.P.; Li, X.; Huang, Y. Annual variation of different phosphorus forms and response of algae growth in Meiliang bay of Taihu Lake. Huanjing Kexue 2015, 36, 80–86. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Yang, G.S.; Wan, R.R. Multidecadal water quality deterioration in the largest freshwater lake in China (Poyang Lake): Implications on eutrophication management. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 260, 114033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Song, C.L.; Ji, L.; Liu, Y.Q.; Xiao, J.; Cao, X.Y.; Zhou, Y.Y. Cause and effect of N/P ratio decline with eutrophication aggravation in shallow lakes. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 627, 1294–1302. [Google Scholar]
- Ni, M.; Yuan, J.L.; Liu, M.; Gu, Z.M. Assessment of water quality and phytoplankton community of Limpenaeus vannamei pond in intertidal zone of Hangzhou Bay, China. Aquac. Rep. 2018, 11, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.M.; Steinman, A.D.; Xue, Q.J.; Zhao, Y.Y.; Tang, X.M.; Xie, L.Q. Temporal patterns of phyto- and bacterioplankton and their relationships with environmental factors in Lake Taihu, China. Chemosphere 2017, 184, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.L.; Huo, S.L.; Zan, F.Y.; Xi, B.D.; Zhang, J.T.; Wu, F.C. Historical records of multiple heavy metals from dated sediment cores in Lake Chenghai, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 74, 3897–3906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, M.; Bar, N.; Basu, R.K.; Das, S.K. Comparative study of adsorptive removal of Cr (VI) ion from aqueous solution in fixed bed column by peanut shell and almond shell using empirical models and ANN. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2017, 24, 10604–10620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laskar, H.S.; Gupta, S. Phytoplankton community and limnology of Chatla floodplain wetland of Barak valley, Assam, North-East India. Knowl. Manag. Aquat. Ecosyst. 2013, 411, 06. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hwang, S.J.; Kim, H.S.; Shin, J.K.; Oh, J.M.; Kong, D.S. Grazing effects of a freshwater bivalve (Corbicula leanaPrime) and large zooplankton on phytoplankton communities in two Korean lakes. Hydrobiologia 2004, 515, 161–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monod, J. Technique, Theory and Applications of Continuous Culture. Ann. Inst. Pasteur 1950, 79, 390–410. [Google Scholar]
- Swamy, M.; Norlina, W.; Azman, W.; Suhaili, D.; Sirajudeen, K.N.S.; Mustapha, Z.; Govindasamy, C. Restoration of glutamine synthetase activity, nitric oxide levels and amelioration of oxidative stress by propolis in kainic acid mediated excitotoxicity. Afr. J. Tradit. Complementary Altern. Med. 2014, 11, 458–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valla, L.; Janson, H.; Wentzel-Larsen, T.; Slinning, K. Analysing four Norweigian population-based samples using the six-month version of the Ages and Stages Questionnaire showed few relevant clinical differences. Acta Paediatr. 2016, 105, 924–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmadel, N.M.; Harvey, J.W.; Alexander, R.B.; Schwarz, G.E.; Moore, R.B.; Eng, K.; Gomez-Velez, J.D.; Boyer, E.W.; Scott, D. Thresholds of lake and reservoir connectivity in river networks control nitrogen removal. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Du, P.; Liu, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Shou, L.; Zeng, J.; Chen, J. Phytoplankton biomass and size structure in Xiangshan Bay, China: Current state and historical comparison under accelerated eutrophication and warming. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 142, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.L.; Gagan, M.K.; Jiang, X.Z.; Xia, W.L.; Wang, S.M. Sedimentary geochemical evidence for recent eutrophication of Lake Chenghai, Yunnan, China. J. Paleolimnol. 2004, 32, 85–94. [Google Scholar]
- Abell, J.M.; Oezkundakci, D.; Hamilton, D.P. Nitrogen and phosphorus limitation of phytoplankton growth in New Zealand lakes: Implications for eutrophication control. Ecosystems 2010, 13, 966–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, A.B.G.; de Jager, V.C.L.; Janse, J.H.; Kong, X.; Liu, S.; Ye, Q.; Mooij, W.M. Spatial identification of critical nutrient loads of large shallow lakes: Implications for Lake Taihu (China). Water Res. 2017, 119, 276–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, B.J.; Barlow, J.P.; Savage, A.E. The Physiological State with Respect to Phosphorus of Cayuga Lake Phytoplankton. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1974, 19, 396–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.F.; Gao, Y.H.; Kirchman, D.L.; Cottrell, M.T.; Chen, R.; Wang, K.; Ouyang, Z.X.; Xu, Y.Y.; Chen, B.S.; Yin, K.D.; et al. Biological regulation of pH during intensive growth of phytoplankton in two eutrophic estuarine waters. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2019, 609, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hama, T.; Inoue, T.; Suzuki, R.; Kashiwazaki, H.; Wada, S.; Sasano, D.; Kosugi, N.; Ishii, M. Response of a phytoplankton community to nutrient addition under different CO2 and pH conditions. J. Oceanogr. 2016, 72, 207–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middelboe, A.L.; Hansen, P.J. Direct effects of pH and inorganic carbon on macroalgal photosynthesis and growth. Mar. Biol. Res. 2007, 3, 134–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, P.; Acharyya, T.; Babu, P.V.R.; Bandyopadhyay, D. Impact of salinity and pH on phytoplankton communities in a tropical freshwater system: An investigation with pigment analysis by HPLC. J. Environ. Monit. 2011, 13, 614–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.Y.; Durbin, E.G. Effects of pH on the growth and carbon uptake of marine phytoplankton. Mar. Ecol. Prog. 1994, 109, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, D.; Xu, Y.; Morel, F.M.M. Effects of the pH/pCO(2) control method on medium chemistry and phytoplankton growth. Biogeosciences 2009, 6, 1199–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).