Seasonal Total Nitrogen and Phosphorus Variation, Speciation, and Composition in the Maowei Sea Affected by Riverine Flux Input, South China Sea
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
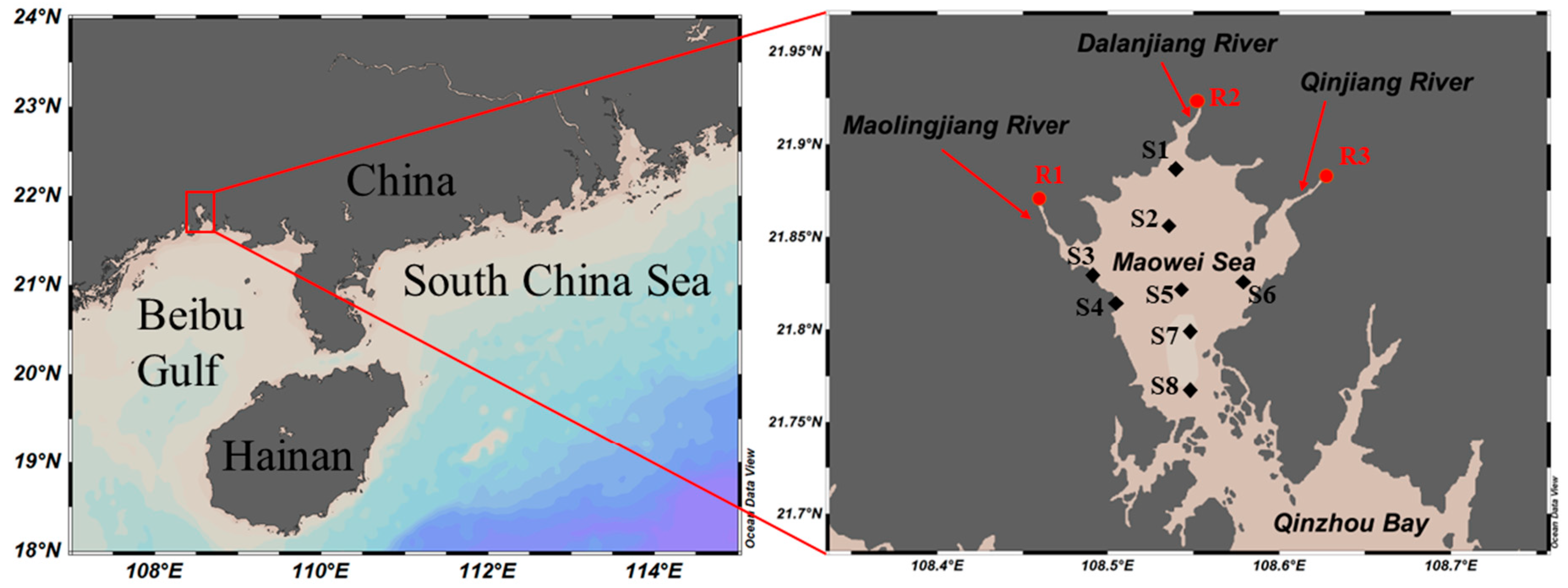
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sampling and Analytical Methods
2.3. Riverine Flows and Fluxes of TN and TP
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
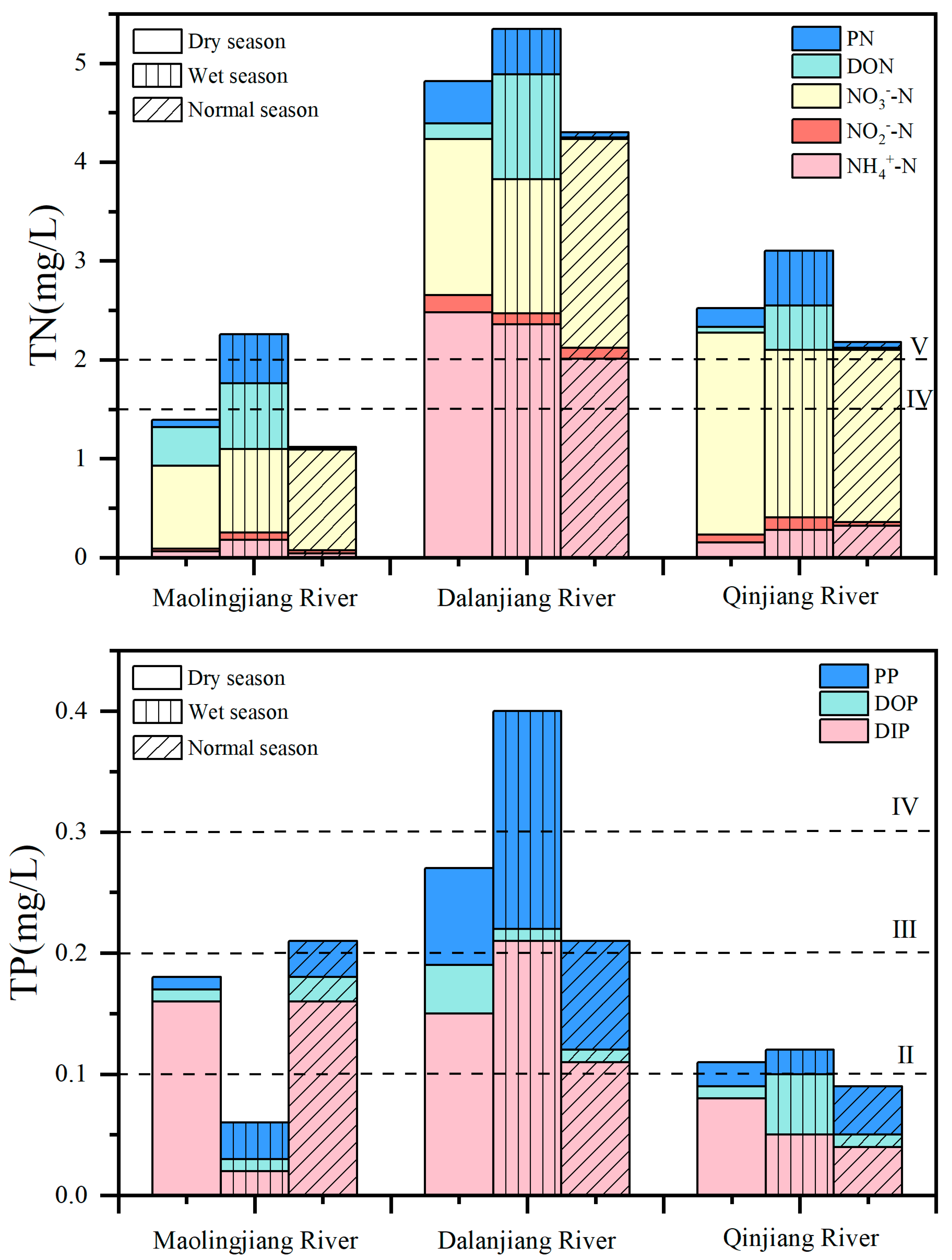
3.1. Concentration and Composition of TN and TP in Estuaries of the Maowei Sea
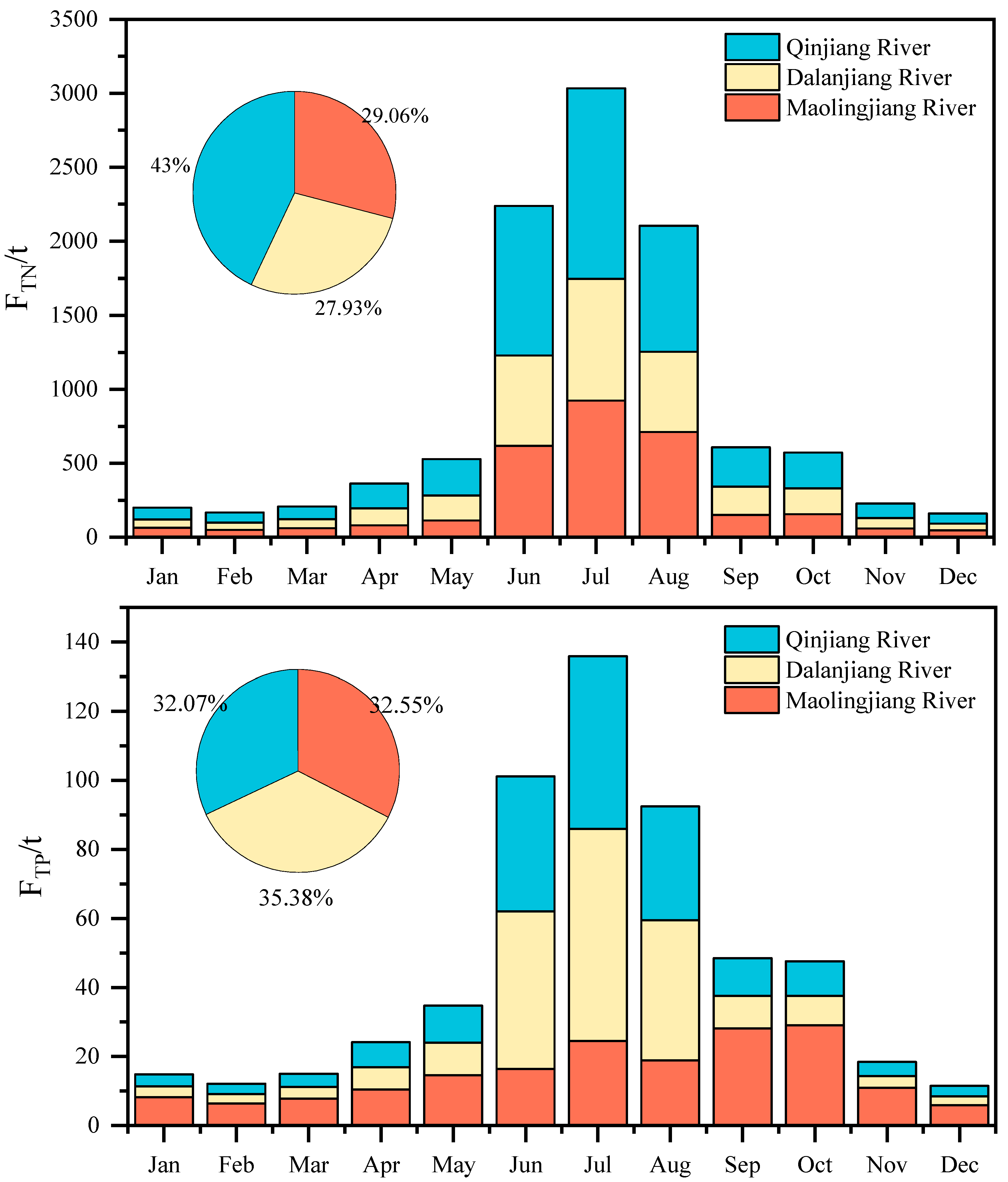
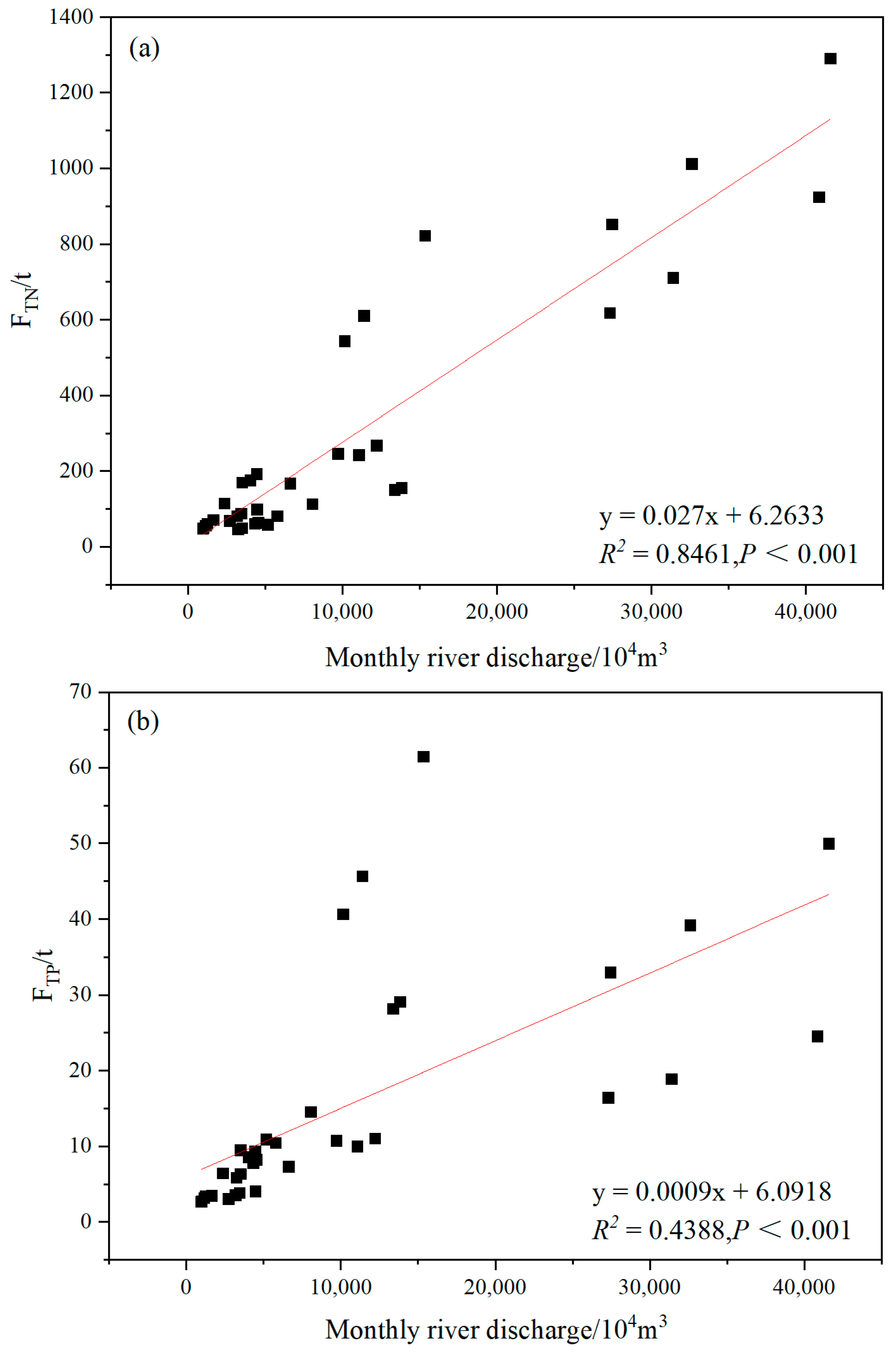
3.2. Seasonal Variations of the TN and TP Fluxes of the Rivers Discharged into the Maowei Sea
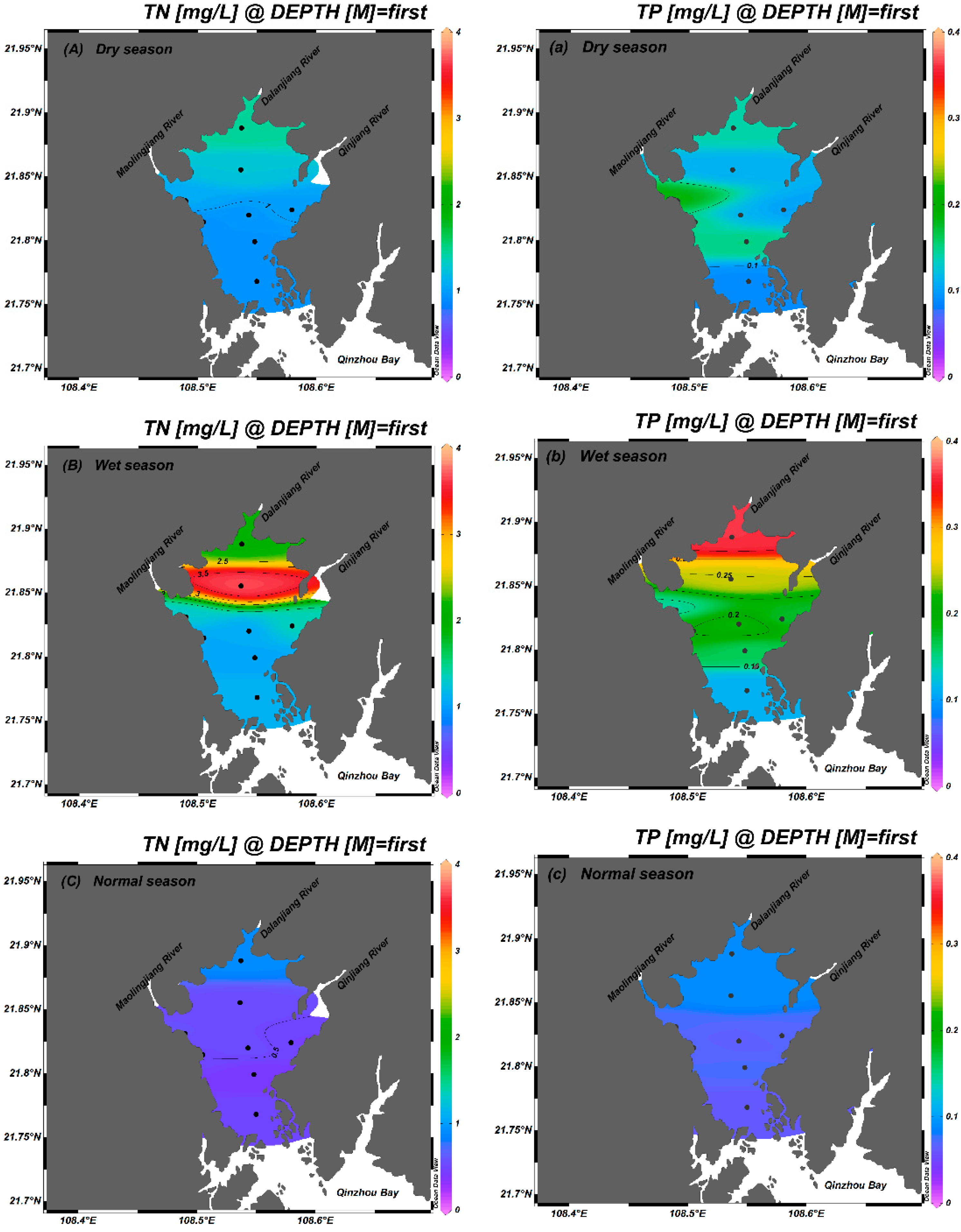
3.3. Seasonal Distribution of TN and TP in the Maowei Sea
3.4. Seasonal Variation in the Input of N/P from Rivers Estuaries of Maowei Sea and Seawater Response
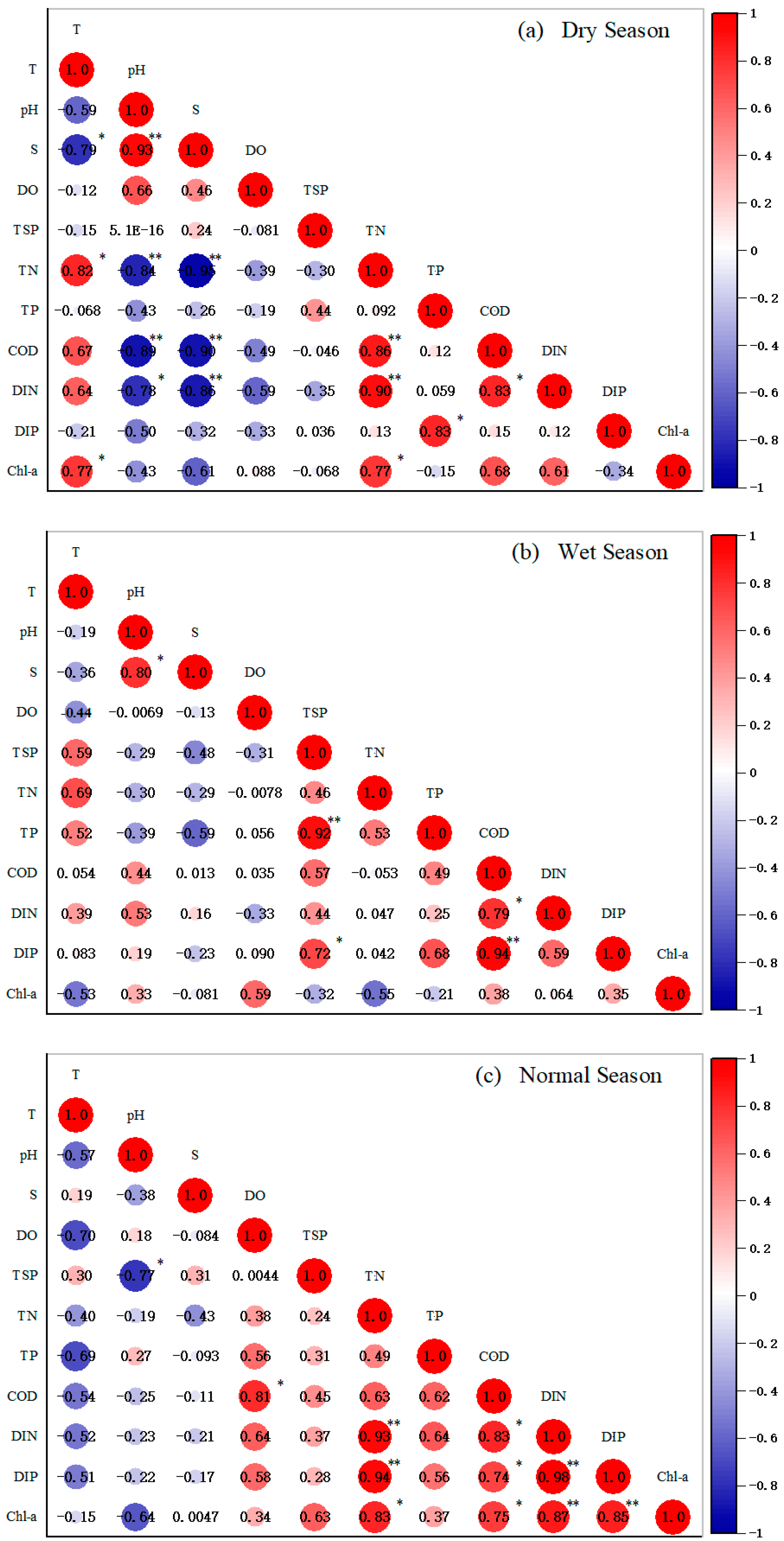
3.5. Correlation Analysis of Influencing Factors on Water Quality in Maowei Sea
4. Discussion
4.1. Concentration and Composition of N and P in the MWS Estuary and Seawater
4.2. Seasonal Variation of TN and TP Behavior in Maowei Sea Coastal Water
4.3. Nutrient Ratio Relationship and Influencing Factors in the Maowei Sea
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tuncer, G.; Karakas, T.; Balkas, T.I.; Gökçay, C.F.; Aygnn, S.; Yurteri, C.; Tuncel, G. Land-based sources of pollution along the Black Sea coast of Turkey: Concentrations and annual loads to the Black Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 1998, 36, 409–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Páez-Osuna, F.; Guerrero-Galván, S.R.; Ruiz-Fernández, A.C. Discharge of nutrients from shrimp farming to coastal waters of the Gulf of California. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 1999, 38, 585–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.L.; Yang, N.N.; Liang, S.K.; Li, K.Q.; Wang, X.L. Comparison of land-based sources with ambient estuarine concentrations of total dissolved nitrogen in Jiaozhou Bay (China). Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2016, 180, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Chen, M.; Shen, P.; Huang, H.; Dai, M.; Qi, Z. A first description of ciliate assemblages in a subtropical, eutrophic bay, South China Sea: Species assemblage and environmental correlates-Ciliate variation in a subtropical bay. Aquat. Living Resour. 2016, 29, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.J.; Lin, X.B.; Hu, W.F.; Zeng, F.; He, L.; Yin, K.D. Nitrogen cycling processes in sediments of the pearl river estuary: Spatial variations, controlling factors, and environmental implications. Catena 2021, 206, 105545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, G.; Lin, X. Bait input altered microbial community structure and increased greenhouse gases production in coastal wetland sediment. Water Res. 2022, 218, 118520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conley, D.J.; Paerl, H.F.; Howarth, R.W.; Fau-Boesch, D.F.; Boesch, D.F.; Seitzinger, S.P.; Havens, K.E.; Lancelot, C.; Likens, G.E. Controlling eutrophication: Nitrogen and phosphorus. Science 2009, 323, 1014–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zheng, B.H.; Zhang, L.; Jin, X.; Hu, X.; Liu, F.; Shao, J.B. Eutrophication characteristics and variation analysis of estuaries in China. Zhongguo Huanjing Kexue China Environ. Sci. 2016, 36, 506–516. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, V.H.; Tilman, G.D.; Nekola, J.C. Eutrophication: Impacts of excess nutrient inputs on freshwater, marine, and terrestrial ecosystems. Environ. Pollut. 1999, 100, 179–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bricker, S.B.; Longstaff, B.; Dennison, W.; Jones, A.; Boicourt, K.; Wicks, C.; Woerner, J. Effects of nutrient enrichment in the nation’s estuaries: A decade of change. Harmful Algae 2008, 8, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.B.; Zhang, P.; Dai, P.D.; Lai, J.Y.; Chen, Y. Spatiotemporal distributions of DIP and the eutrophication in Hainan Island adjacent coastal water. Zhongguo Huanjing Kexue China Environ. Sci. 2019, 39, 2541–2548. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P.; Wei, L.R.; Lai, J.Y.; Dai, P.D.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, J.B. Concentration, Composition and Fluxes of Land-based Nitrogen and Phosphorus Source Pollutants Input into Zhanjiang Bay in Summer. J. Guangdong Ocean Univ. 2019, 39, 63–72. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P.; Su, Y.; Liang, S.K.; Li, K.Q.; Li, Y.B.; Wang, X.L. Assessment of long-term water quality variation affected by high-intensity land-based inputs and land reclamation in Jiaozhou Bay, China. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 75, 210–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paerl, H.W. Coastal eutrophication and harmful algal blooms: Importance of atmospheric deposition and groundwater as “new” nitrogen and other nutrient sources. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1997, 42, 1154–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rabalais, N.N. Nitrogen in aquatic ecosystems. Ambio 2002, 31, 102–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasmund, N. Harmful Algal Blooms in Coastal Waters of the South-Eastern Baltic Sea. Balt. Coast. Ecosyst. 2002, 93–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glibert, P.M. Eutrophication, harmful algae and biodiversity—Challenging paradigms in a world of complex nutrient changes. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 124, 591–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jani, J.; Toor, G.S. Composition, sources, and bioavailability of nitrogen in a longitudinal gradient from freshwater to estuarine waters. Water Res. 2018, 137, 344–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strokal, M.; Yang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Kroeze, C.; Li, L.; Luan, S.; Wang, H.; Yang, S.; Zhang, Y. Increasing eutrophication in the coastal seas of China from 1970 to 2050. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 85, 123–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Liu, C.; Ma, Y.; Wang, X. Land-based dissolved organic nitrogen dynamics and bioavailability in Jiaozhou Bay, China. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2019, 220, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seitzinger, S.P.; Sanders, R.W. Estuarine eutrophication: The contribution of dissolved organic nitrogen. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1997, 159, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moschonas, G.; Gowen, R.J.; Paterson, R.F.; Mitchell, E.; Davidson, K. Nitrogen dynamics and phytoplankton community structure: The role of organic nutrients. Biogeochemistry 2017, 134, 125–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Officer, C.B.; Ryther, J.H. The possible importance of silicon in marine eutrophication. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1980, 3, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, D.M.; Glibert, P.M.; Burkholder, J.M. Harmful algal blooms and eutrophication: Nutrient sources, composition, and consequences. Estuaries 2002, 25, 704–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, M.; Yu, Z.; Yao, Q.; Bianchi, T.S.; Paytan, A.; Zhao, B.; Pan, H.; Peng, Y. Distribution, mixing behavior, and transformation of dissolved inorganic phosphorus and suspended particulate phosphorus along a salinity gradient in the Changjiang Estuary. Mar. Chem. 2015, 168, 124–134. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, L.Q.; Song, J.M.; Yuan, H.M.; Li, X.G.; Li, N. Distribution, partitioning and sources of dissolved and particulate nitrogen and phosphorus in the north Yellow Sea. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2016, 181, 182–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundareshwar, P.V.; Morris, J.T.; Koepfler, E.K.; Fornwalt, B. Phosphorus limitation of coastal ecosystem processes. Science 2003, 299, 563–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yuan, H.M.; Song, J.M.; Xing, J.W.; Li, X.G.; Li, N.; Duan, L.Q.; Qiu, B.X.; Wang, Q.D. Spatial and seasonal variations, partitioning and fluxes of dissolved and particulate nutrients in Jiaozhou Bay. Cont. Shelf Res. 2018, 171, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bronk, D.A.; See, J.H.; Bradley, P.; Killberg, L. DON as a source of bioavailable nitrogen for phytoplankton. Biogeosciences Discuss. 2006, 3, 1247–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, C.; Dan, S.F.; Yang, B.; Lu, D.; Ning, Z. Biogeochemistry of dissolved and particulate phosphorus speciation in the maowei sea, northern beibu gulf. J. Hydrol. 2021, 593, 125822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.X.; Zhao, S.; Song, L.R.; Wu, H.P. Analysis and assessment of nutrient status in Maowei Sea of inner Qinzhou Bay. Environ. Sci. Manag. 2017, 42, 148–153. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, Y.G.; Lin, Q.; Yu, Z.L.; Wang, X.N.; Ke, C.L.; Ning, J.J. Speciation and risk of heavy metals in sediments and human health implications of heavy metals in edible nekton in Beibu Gulf, China: A case study of Qinzhou Bay. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 101, 852–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Huang, X.; Yang, B.; Dan, S.F.; Kang, Z.; Zhou, J.; Lao, Y.; Zhong, Q.; Wu, H. Composition and Distributions of Nitrogen and Phosphorus and Assessment of Eutrophication Status in the Maowei Sea. J. Ocean Univ. China 2021, 20, 361–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.L.; Chen, X.Y.; Lai, J.X.; Jiang, F.J.; Chen, B. The distribution characteristics and seasonal variation of total dissolved nitrogen and phosphorus in the surface of Qinzhou Bay. Mar. Environ. Sci. 2017, 36, 349–353. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, B.; Zhou, J.B.; Lu, D.L.; Dan, S.F.; Zhang, D.; Lan, W.L.; Cui, D.Y. Phosphorus chemical speciation and seasonal variations in surface sediments of the Maowei Sea, northern Beibu Gulf. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 141, 61–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stepanauskas, R.; Jorgensen, N.O.; Eigaard, O.R.; Zvikas, A.; Tranvik, L.J.; Leonardson, L. Summer inputs of riverine nutrients to the Baltic Sea: Bioavailab. Eutrophication Relev. 2002, 72, 579–597. [Google Scholar]
- Oneil, J.M.; Davis, T.W.; Burford, M.A.; Gobler, C.J. The rise of harmful cyanobacteria blooms: The potential roles of eutrophication and climate change. Harmful Algae 2012, 14, 313–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.J.; Liao, R.Q.; Liu, W.L.; Kannan, K.; Ohura, T.; Wu, M.H.; Ma, J. Chlorinated polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in surface sediment from Maowei Sea, Guangxi, China: Occurrence, distribution, and source apportionment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 16241–16252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dan, S.F.; Lan, W.; Yang, B.; Han, L.; Xu, C.; Lu, D.; Kang, Z.; Huang, H.; Ning, Z. Bulk sedimentary phosphorus in relation to organic carbon, sediment textural properties and hydrodynamics in the northern Beibu Gulf, South China Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 155, 111176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.G.; Huang, H.H.; Liu, Y.; Gong, X.Y.; Liao, X.L. Non-metric multidimensional scaling and human risks of heavy metal concentrations in wild marine organisms from the Maowei Sea, the Beibu Gulf, South China Sea. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2018, 59, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Xia, P.; Li, Z.; Meng, D. Mangrove degradation and response to anthropogenic disturbance in the Maowei Sea (SW China) since 1926 AD: Mangrove- derived OM and pollen. Org. Geochem. 2016, 98, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Lao, Y.; Wang, J.; Du, J.; Liang, M.; Yang, B. Submarine groundwater-borne nutrients in a tropical bay (Maowei Sea, China) and their impacts on the oyster aquaculture. Geochem. Geophys. Geosystems 2018, 19, 932–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.T.; Hu, X.S.; Zhang, S.F.; Xie, J.; Zhang, D.; An, J.S. Distribution andpotential ecological risk assessment of heavy metals insurface sediments of Maowei Sea. Mar. Environ. Sci. 2014, 33, 187–191. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, C.; Yang, B.; Dan, S.F.; Zhang, D.; Liao, R.Q.; Lu, D.R.; Li, R.H.; Ning, Z.M.; Peng, S.Q. Spatiotemporal variations of biogenic elements and sources of sedimentary organic matter in the largest oyster mariculture bay (Maowei Sea), Southwest China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 730, 139056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Lu, D.L.; Yang, B.; Zhang, J.B.; Ning, Z.M.; Yu, K.F. Influence of natural and anthropogenic factors on spatial-temporal hydrochemistry and the susceptibility to nutrient enrichment in a subtropical estuary. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 146, 945–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guangxi Statistical Bureau. Guangxi Statistical Yearbook; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2017; pp. 366–369. [Google Scholar]
- State Bureau of Quality Technical Supervision. GB17378.4—2007; The Specification for Marine Monitoring Part 4: Seawater Analysis. China Standards Press: Beijing, China, 2007.
- Specification for Offshore Environmental Monitorin. HJ 442-2008; Part 3 Offshore Seawater Quality Monitor. China Standards Press: Beijing, China, 2008.
- GB3838-2002; MEPC, Environmental QUALITY Standards for Surface Water. Ministry of Environment Protection, People’s Republic of China, Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2002.
- Redfield, A.C.; Ketchum, B.H.; Richards, F.A. The influence of organisms on the composition of seawater. In The Sea; Hill, M.N., Ed.; Interscience Publishers: Geneva, Switzerland; John Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1963; Volume 2, pp. 26–77. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, B.; Kang, Z.J.; Lu, D.L.; Dan, S.; Ning, Z.M.; Lan, W.L.; Zhong, Q.P. Spatial variations in the abundance and chemical speciation of phosphorus across the river–sea interface in the Northern Beibu Gulf. Water 2018, 10, 1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yao, Q.Z.; Yu, Z.G.; Chen, H.T.; Liu, P.X.; Mi, T.Z. Phosphorus transport and speciation in the Changjiang (Yangtze River) system. Appl. Geochem. 2009, 24, 2186–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.L.; Du, J.Z.; Ji, T.; Wen, T.Y.; Liu, S.M.; Zhang, J. An estimation of nutrient fluxes via submarine groundwater discharge into the Sanggou Bay—A typical multi-species culture ecosystem in China. Mar. Chem. 2014, 167, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, B.; Wu, H.P.; Ma, J.X.; Luo, M.M.; Li, X. The algae community in taxon Haptophyceae at the early bloom stage of Phaeocystis globosa in Northern Beibu Gulf in winter. BioReliance 2018, 492454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, M.L.; Hong, Y.G.; Yin, J.P.; Dong, J.D.; Wang, Y.S. Evolution of the sink and source of dissolved inorganic nitrogen with salinity as a tracer during summer in the Pearl River Estuary. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 36638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wiegner, T.N.; Seitzinger, S.P.; Glibert, P.M.; Bronk, D.A. Bioavailability of dissolved organic nitrogen and carbon from nine rivers in the eastern United States. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2006, 43, 277–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, N.N. Terrigenous Input, Distribution and Bioavailability of Dissolved Organic Nitrogen in Jiaozhou Bay from 2012 to 2013; Ocean University of China: Qingdao, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, X.Y.; Zhang, G.C.; Liang, S.K.; Han, X.R. Potential bioavailability and flux of dissolved organic nitrogen at the Datong station of the Yangtze River. China Environ. Sci. 2015, 35, 3698–3706. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.M.; Li, L.W.; Zhang, G.L.; Liu, Z.; Yu, Z.G.; Ren, J.L. Impacts of human activities on nutrient transports in the Huanghe (Yellow River) estuary. J. Hydrol. 2012, 430, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, P.; Klunp, J.V.; Guo, L.D. Dynamics of dissolved and particulate phosphorus influenced by seasonal hypoxia in Green Bay, Lake Michigan. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 541, 1070–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, D.B.; Confesor, R.; Ewing, D.E.; Johnson, L.T.; Kramer, J.W.; Merryfield, B.J. Phosphorus loading to Lake Erie from the Maumee, Sandusky and Cuyahoga rivers: The importance of bioavailability. J. Great Lakes Res. 2014, 40, 502–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, P.; Chen, M.; Guo, L.D. Speciation and transformation of phosphorus and its mixing behavior in the Bay of St. Louis estuary in the northern Gulf of Mexico. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2012, 87, 283–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.H.; Guo, L.D.; Douglas, T.A.; Whitledge, T.E. Seasonal variations in nutrient concentrations and speciation in the Chena River, Alaska. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosciences 2008, 113, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vanderzee, C.; Roevros, N.; Chou, L. Phosphorus speciation, transformation and retention in the Scheldt estuary (Belgium/The Netherlands) from the freshwater tidal limits to the North Sea. Mar. Chem. 2007, 106, 76–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, P.; Guo, L.D.; Chen, M.; Cai, Y.H. Distribution, partitioning and mixing behavior of phosphorus species in the Jiulong River estuary. Mar. Chem. 2013, 157, 93–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, H.L.; Wang, X.J.; Zheng, C.M.; Wang, C.Y.; Xiao, K.; Wan, L.; Wang, X.S.; Jiang, X.W.; Guo, H.M. Estimation of submarine groundwater discharge and associated nutrient fluxes in eastern Laizhou Bay, China using 222Rn. J. Hydrol. 2016, 533, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, J.M.; Glenn, C.R.; Amato, D.W.; Dulai, H. Effect of land use and groundwater flow path on submarine groundwater discharge nutrient flux. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2015, 11, 194–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, J.; Tang, J.Y.; Li, Y.L.; Hong, Z.; Zhao, Z.Y. Restudy of constitution and distribution of inorganic nitrogen and the eutrophication in Daya Bay, Shenzhen. Mar. Environ. Sci. 2016, 35, 908–911. [Google Scholar]
- Thatoi, H.; Behera, B.C.; Mishra, R.R.; Dutta, S.K. Biodiversity and biotechnological potential of microorganisms from mangrove ecosystems: A review. Ann. Microbiol. 2013, 63, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dan, S.F.; Liu, S.M.; Udoh, E.C.; Ding, S. Nutrient biogeochemistry in the Cross River estuary system and adjacent Gulf of Guinea, South East Nigeria (West Africa). Cont. Shelf Res. 2019, 179, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.M.; Zhang, J.; Li, D.J. Phosphorus cycling in sediments of the Bohai and Yellow Seas. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2004, 59, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.M.; Hong, G.H.; Zhang, J.; Ye, X.W.; Jiang, X.L. Nutrient budgets for large Chinese estuaries. Biogeosciences 2009, 6, 2245–2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.J.; Beusen, A.H.W.; Liu, X.C.; Bouwman, A.F. Aquaculture production is a large, spatially concentrated source of nutrients in Chinese freshwater and coastal seas. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 1464–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Xiao, K.; Zhang, X.; Dan, S.F. Submarine groundwater discharge and its implication for nutrient budgets in the western Bohai Bay, China. J. Environ. Radioact. 2020, 212, 106132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, W.L.; Peng, X.Y. Eutrophication status and its impact on phytoplankton biomass in the Maowei Sea. J. Guangxi Acad. Sci. 2011, 27, 109–112. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, B.; Fang, H.Y.; Zong, Q.P.; Zhang, C.X.; Li, S.P. Distribution characteristics of nutrients and eutrophication assessment in summer in Qinzhou Bay. Mar. Sci. Bull. 2012, 31, 640–645. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, S.; Liang, T.; Zhang, S.; Wang, L.; Zhang, X.; Chen, X. Seasonal changes in nitrogen and phosphorus transport in the lower Changjiang River before the construction of the Three Gorges Dam. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2008, 79, 239–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, K.; Wang, W.X. Trace metal contamination in estuarine and coastal environments in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 421, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, X.L.; Zhai, W.D.; Hong, H.S.; Guo, W.D.; Huang, X. Distribution, fluxes and decadal changes of nutrients in the Jiulong River Estuary, Southwest Taiwan Strait. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2012, 57, 2307–2318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harding, L.W.; Adolf, J.E.; Mallonee, M.E.; Miller, W.D.; Gallegos, C.L.; Perry, E.S.; Johnson, J.M.; Seller, K.G.; Paerl, H.W. Climate effects on phytoplankton floral composition in Chesapeake Bay. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2015, 162, 53–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagy, J.D.; Boynton, W.R.; Keefe, C.W.; Wood, K.V. Hypoxia in Chesapeake Bay, 1950–2001: Long-term change in relation to nutrient loading and river flow. Estuaries 2004, 27, 634–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCoy, C.; Viso, R.; Peterson, R.N.; Libes, S.; Lewis, B.; Ledoux, J.; Voulgaris, G.; Smith, E.; Sanger, D. Radon as an indicator of limited cross-shelf mixing of submarine groundwater discharge along an open ocean beach in the South Atlantic Bight during observed hypoxia. Cont. Shelf Res. 2011, 31, 1306–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Muller-Karger, F.E.; Swarzenski, P.W. Hurricanes, submarine groundwater discharge, and Florida’s red tides. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, L11601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.W.; Kim, G.; Lim, W.; Hwang, D.W. A relationship between submarine groundwater borne nutrients traced by Ra isotopes and the intensity of dinoflagellate red-tides occurring in the southern sea of Korea. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2010, 55, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Jiao, J.J. Submarine groundwater discharge and nutrient loadings in Tolo Harbor, Hong Kong using multiple geotracer-based models, and their implications of red tide outbreaks. Water Res. 2016, 102, 11–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Townsend, A.R.; Howarth, R.W.; Bazzaz, F.A.; Booth, M.S.; Cleveland, C.C.; Collinge, S.K.; Dobson, A.P.; Epstein, P.R.; Holland, E.A.; Keeney, D.R.; et al. Human health effects of a changing global nitrogen cycle. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2003, 1, 240–246. [Google Scholar]
- Hwang, D.W.; Lee, Y.W.; Kim, G. Large submarine groundwater discharge and benthic eutrophication in Bangdu Bay on volcanic Jeju Island, Korea. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2005, 50, 1393–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galloway, J.N.; Townsend, A.R.; Erisman, J.W.; Bekunda, M.; Cai, Z.C.; Freney, J.R.; Martinelli, L.A.; Seitzinger, S.P.; Sutton, M.A. Transformation of the nitrogen cycle: Recent trends, questions, and potential solutions. Science 2008, 320, 889–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Slomp, C.P.; Van Cappellen, P. Nutrient inputs to the coastal ocean through submarine groundwater discharge: Controls and potential impact. J. Hydrol. 2004, 295, 64–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Justić, D.; Rabalais, N.N.; Turner, R.E.; Dortch, Q. Changes in nutrient structure of river-dominated coastal waters: Stoichiometric nutrient balance and its consequences. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 1995, 40, 339–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Yang, Y.; Xu, C.; Harrison, P.J. Phosphate limitation of phytoplankton growth in the Changjiang Estuary. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 1990, 9, 405–411. [Google Scholar]
- Kahlert, M. C/N/P: Ratios of freshwater benthic algae. Arch. Hydrobiol. Spec. Issue Adv. Limnol. 1998, 51, 105–114. [Google Scholar]
- Ke, Z.X.; Tan, Y.H.; Huang, L.M.; Zhang, J.L.; Lian, S.M. Relationship between phytoplankton composition and environmental factors in the surface waters of southern South China Sea in early summer of 2009. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2012, 31, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tilman, D.; Kilham, S.S.; Kilham, P. Phytoplankton community ecology: The role of limiting nutrients. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 1982, 13, 349–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, S.N.; Schindler, D.W. Influence of nitrogen to phosphorus supply ratios and physicochemical conditions on cyanobacteria and phytoplankton species composition in the Experimental Lakes Area, Canada. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1999, 56, 451–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Speciation | Parameters | Dry Season | Wet Season | Normal Season |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TN | Mean | 1.07 | 1.59 | 0.55 |
| Range | 0.93–1.44 | 1.04–3.66 | 0.40–0.89 | |
| TDN | Mean | 1.00 | 1.06 | 0.46 |
| Range | 0.85–1.24 | 0.62–1.54 | 0.31–0.75 | |
| DIN | Mean | 0.74 | 0.63 | 0.43 |
| Range | 0.64–0.89 | 0.35–1.22 | 0.31–0.73 | |
| TP | Mean | 0.129 | 0.203 | 0.073 |
| Range | 0.089–0.192 | 0.109–0.357 | 0.061–0.091 | |
| TDP | Mean | 0.103 | 0.122 | 0.059 |
| Range | 0.075–0.172 | 0.074–0.248 | 0.050–0.071 | |
| DIP | Mean | 0.100 | 0.036 | 0.030 |
| Range | 0.073–0.168 | 0.024–0.063 | 0.020–0.053 |
| Location | Sampling Time | c(TDN)/(mg/L) | c(DIN)/(mg/L) | (DIN/TDN)/% | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Delaware River, USA | July 1998 | 0.92 | 0.81 | 88 | [56] |
| Bass River, USA | July 1998 | 0.09 | 0.04 | 42 | [56] |
| Savannah River, USA | July 1998 | 0.60 | 0.48 | 80 | [56] |
| Pocomoke River, USA | August 1998 | 0.52 | 0.03 | 6 | [56] |
| Dagu River, China | July 2012 | 5.80 | 5.46 | 94.2 | [57] |
| Licun River, China | July 2012 | 13.69 | 4.95 | 36.2 | [57] |
| Loushan River, China | July 2012 | 21.64 | 6.88 | 31.8 | [57] |
| Moshui River, China | July 2012 | 11.85 | 5.66 | 47.7 | [57] |
| Datong station, Yangtze River, China | July 2013 | 2.70 | 2.31 | 85.8 | [58] |
| Huanghe Outlet, China | June–August 2009 | 3.68 | 3.14 | 85.3 | [59] |
| Zhanjiang Bay Outlet, China | July 2018 | 5.14 | 0.85 | 16.6 | [12] |
| Maolingjiang River, China | August 2018–May 2019 | 1.39 | 1.04 | 74.6 | This study |
| Dalanjiang River, China | August 2018–May 2019 | 4.51 | 4.10 | 90.9 | This study |
| Qinjiang River, China | August 2018–May 2019 | 2.33 | 2.16 | 92.4 | This study |
| Location | Sampling Time | c(TDP)/(mg/L) | c(DIP)/(mg/L) | (DIP/TDP)/% | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fox River, USA | June, August 2016 | 0.043 | 0.025 | 57.1 | [60] |
| Maumee River, USA | October 2009 | 0.107 | 0.093 | 87.0 | [61] |
| Jourdon River, USA | October 2009 | 0.006 | 0.001 | 15.8 | [62] |
| Chena River, USA | July 2005 | 0.007 | 0.006 | 93.3 | [63] |
| Scheldt River, Netherlands | April 1995–January 1996 | 0.124 | 0.022 | 17.5 | [64] |
| Jiulongjiang River, China | May 2010 | 0.082 | 0.065 | 78.9 | [65] |
| Dafengjiang River, China | December 2017 | 0.050 | 0.037 | 75.0 | [66] |
| Datong station, Yangtze River, China | September 2006 | 0.035 | 0.018 | 52.7 | [67] |
| Huanghe Outlet, China | July 2009 | 0.019 | 0.014 | 72.1 | [59] |
| Zhanjiang Bay Outlet, China | July 2018 | 0.887 | 0.629 | 70.9 | [12] |
| Maolingjiang River, China | August 2018–May 2019 | 0.127 | 0.113 | 89.5 | This study |
| Dalanjiang River, China | August 2018–May 2019 | 0.177 | 0.157 | 88.7 | This study |
| Qinjiang River, China | August 2018–May 2019 | 0.080 | 0.057 | 70.8 | This study |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ren, C.; Peng, D.; Shi, X.; Yang, S.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, J. Seasonal Total Nitrogen and Phosphorus Variation, Speciation, and Composition in the Maowei Sea Affected by Riverine Flux Input, South China Sea. Water 2022, 14, 2584. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14162584
Ren C, Peng D, Shi X, Yang S, Zhang P, Zhang J. Seasonal Total Nitrogen and Phosphorus Variation, Speciation, and Composition in the Maowei Sea Affected by Riverine Flux Input, South China Sea. Water. 2022; 14(16):2584. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14162584
Chicago/Turabian StyleRen, Chaoxing, Demeng Peng, Xiangyang Shi, Shuang Yang, Peng Zhang, and Jibiao Zhang. 2022. "Seasonal Total Nitrogen and Phosphorus Variation, Speciation, and Composition in the Maowei Sea Affected by Riverine Flux Input, South China Sea" Water 14, no. 16: 2584. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14162584
APA StyleRen, C., Peng, D., Shi, X., Yang, S., Zhang, P., & Zhang, J. (2022). Seasonal Total Nitrogen and Phosphorus Variation, Speciation, and Composition in the Maowei Sea Affected by Riverine Flux Input, South China Sea. Water, 14(16), 2584. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14162584






