The State of the Art and Emerging Trends in the Wastewater Treatment in Developing Nations
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Sources of Wastewater
3. Composition of Wastewater
4. Hazardous Effects of Pollutant Consumption on Human Health
5. Population Growth and Scarcity of Safe Drinking Water in Developing Nations
6. Urban Water Cycle in Developing Nations
7. Funding for Wastewater Treatment in Developing Countries
8. Centralized and Decentralized Wastewater Treatment in Developing Countries
9. Challenges
10. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Choudhary, N.; Yadav, V.K.; Yadav, K.K.; Almohana, A.I.; Almojil, S.F.; Gnanamoorthy, G.; Kim, D.H.; Islam, S.; Kumar, P.; Jeon, B.H. Application of green synthesized MMT/Ag nanocomposite for removal of methylene blue from aqueous solution. Water 2021, 13, 3206. [Google Scholar]
- Rajendran, S.; Inwati, G.K.; Yadav, V.K.; Choudhary, N.; Solanki, M.B.; Abdellattif, M.H.; Yadav, K.K.; Gupta, N.; Islam, S.; Jeon, B.-H. Enriched catalytic activity of TiO2 nanoparticles supported by activated carbon for noxious pollutant elimination. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.H.; Pathak, B. Zinc oxide based photocatalytic degradation of persistent pesticides: A comprehensive review. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2020, 13, 100290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, V.K.; Khan, S.H.; Choudhary, N.; Tirth, V.; Kumar, P.; Ravi, R.K.; Modi, S.; Khayal, A.; Shah, M.P.; Sharma, P.; et al. Nanobioremediation: A sustainable approach towards the degradation of sodium dodecyl sulfate in the environment and simulated conditions. J. Basic Microbiol. 2022, 62, 348–360. [Google Scholar]
- Fetimi, A.; Merouani, S.; Khan, M.S.; Asghar, M.N.; Yadav, K.K.; Jeon, B.-H.; Hamachi, M.; Kebiche-Senhadji, O.; Benguerba, Y. Modeling of Textile Dye Removal from Wastewater Using Innovative Oxidation Technologies (Fe(II)/Chlorine and H2O2/Periodate Processes): Artificial Neural Network-Particle Swarm Optimization Hybrid Model. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 13818–13825. [Google Scholar]
- Yadav, V.K.; Fulekar, M.H. Biogenic synthesis of maghemite nanoparticles (γ-Fe2O3) using Tridax leaf extract and its application for removal of fly ash heavy metals (Pb, Cd). Mater. Today Proc. 2018, 5, 20704–20710. [Google Scholar]
- Yadav, V.K.; Choudhary, N.; Ali, D.; Gnanamoorthy, G.; Inwati, G.K.; Almarzoug, M.H.; Kumar, G.; Khan, S.H.; Solanki, M.B. Experimental and computational approaches for the structural study of novel Ca-rich zeolites from incense stick ash and their application for wastewater treatment. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2021, 2021, 6066906. [Google Scholar]
- Lito, P.F.; Aniceto, J.P.S.; Silva, C.M. Removal of anionic pollutants from waters and wastewaters and materials perspective for their selective sorption. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2012, 223, 6133–6155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, V.K.; Yadav, K.K.; Alam, J.; Cabral-Pinto, M.M.; Gnanamoorthy, G.; Alhoshan, M.; Kamyab, H.; Hamid, A.A.; Ali, F.A.A.; Shukla, A.K. Transformation of hazardous sacred incense sticks ash waste into less toxic product by sequential approach prior to their disposal into the water bodies. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, N.P.; Bholay, A.D.; Kapadnis, B.P.; Gaikwad, V.B. Biodegradation of model azo dye methyl red and other textile dyes by isolate bacillus circulans npp1. J. Pure Appl. Microbiol. 2016, 10, 2793–2800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnanamoorthy, G.; Karthikeyan, V.; Ali, D.; Kumar, G.; Yadav, V.K.; Narayanan, V. Global popularization of CuNiO2 and their rGO nanocomposite loveabled to the photocatalytic properties of methylene blue. Environ. Res. 2022, 204, 112338. [Google Scholar]
- Modi, S.; Yadav, V.K.; Gacem, A.; Ali, I.H.; Dave, D.; Khan, S.H.; Yadav, K.K.; Rather, S.-U.; Ahn, Y.; Son, C.T.; et al. Recent and emerging trends in remediation of methylene blue dye from wastewater by using zinc oxide nanoparticles. Water 2022, 14, 1749. [Google Scholar]
- Naik, M.R.; Mahanty, B.; Sahoo, S.K.; Jha, V.N.; Sahoo, N.K. Assessment of groundwater geochemistry using multivariate water quality index and potential health risk in industrial belt of central Odisha, India. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 303, 119161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piaskowski, K.; Świderska-Dąbrowska, R.; Zarzycki, P.K. Dye removal from water and wastewater using various physical, chemical, and biological processes. J. AOAC Int. 2018, 101, 1371–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WWAP. The United Nations World Water Development Report 2018: Nature-Based Solutions for Water; UNESCO: Paris, France, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Simha, P.; Ramanathan, A.; Thawani, B.; Jain, P.; Hussain, S.; Ganesapillai, M. Coal fly ash for the recovery of nitrogenous compounds from wastewater: Parametric considerations and system design. Arab. J. Chem. 2019, 12, 5049–5061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.H.; Yadav, V.K. Advanced oxidation processes for wastewater remediation: An overview. In Removal of Emerging Contaminants through Microbial Processes; Springer: Singapore, 2021; pp. 71–93. [Google Scholar]
- Mushtaq, F.; Zahid, M.; Bhatti, I.A.; Nasir, S.; Hussain, T. Possible applications of coal fly ash in wastewater treatment. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 240, 27–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, V.K.; Khan, S.H.; Malik, P.; Thappa, A.; Suriyaprabha, R.; Ravi, R.K.; Choudhary, N.; Kalasariya, H.; Gnanamoorthy, G. Microbial synthesis of nanoparticles and their applications for wastewater treatment. In Microbial Biotechnology: Basic Research and Applications; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 147–187. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, R.; Satyawali, Y.; Batra, V.S.; Balakrishnan, M. Submerged membrane bioreactor using fly ash filters: Trials with distillery wastewater. Water Sci. Technol. 2008, 58, 1281–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, A.; Amari, A.; Yadav, V.K.; Ismail, M.A.; Elboughdiri, N.; Fulekar, M.H.; Basnet, A. A synergistic effect of moringa oleifera-based coagulant and ultrafiltration for the wastewater treatment collected from final ETP. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2022, 2022, 1285011. [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh, D.; Ghorai, P.; Dutta, S. Chapter 4—Comparative analysis of water supply systems in megacities in developed and developing countries. In Current Directions in Water Scarcity Research; Srivastav, A.L., Madhav, S., Bhardwaj, A.K., Valsami-Jones, E., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; Volume 6, pp. 65–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, V.K.; Choudhary, N.; Khan, S.H.; Malik, P.; Inwati, G.K.; Suriyaprabha, R.; Ravi, R.K. Synthesis and characterisation of nano-biosorbents and their applications for waste water treatment. In Handbook of Research on Emerging Developments and Environmental Impacts of Ecological Chemistry; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2020; pp. 252–290. [Google Scholar]
- Adelodun, B.; Ajibade, F.O.; Ighalo, J.O.; Odey, G.; Ibrahim, R.G.; Kareem, K.Y.; Bakare, H.O.; Tiamiyu, A.O.; Ajibade, T.F.; Abdulkadir, T.S.; et al. Assessment of socioeconomic inequality based on virus-contaminated water usage in developing countries: A review. Environ. Res. 2021, 192, 110309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaitkin, M.; McCormick, S.; Torreano, J.A.-S.; Amongin, I.; Gaya, S.; Hanssen, O.N.; Johnston, R.; Slaymaker, T.; Chase, C.; Hutton, G.; et al. Estimating the cost of achieving basic water, sanitation, hygiene, and waste management services in public health-care facilities in the 46 UN designated least-developed countries: A modelling study. Lancet Glob. Health 2022, 10, e840–e849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiner, R.F.; Matthews, R.A. (Eds.) Chapter 11—Nonpoint source water pollution. In Environmental Engineering, 4th ed.; Butterworth-Heinemann: Burlington, VT, USA, 2003; pp. 233–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamwal, P.; Mittal, A.K.; Mouchel, J.M. Point and non-point microbial source pollution: A case study of Delhi. Phys. Chem. Earth 2011, 36, 490–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X. Online monitoring method of non-point source pollution of water resources in river scenic spots. Arab. J. Geosci. 2021, 14, 603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rane, N.R.; Tapase, S.; Kanojia, A.; Watharkar, A.; Salama, E.S.; Jang, M.; Yadav, K.K.; Amin, M.A.; Cabral-Pinto, M.M.; Jadhav, J.P.; et al. Molecular insights into plant–microbe interactions for sustainable remediation of contaminated environment. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 344, 126246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- León, L.F.; Soulis, E.D.; Kouwen, N.; Farquhar, G.J. Nonpoint source pollution: A distributed water quality modeling approach. Water Res. 2001, 35, 997–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwirzitz, B.; Wetzels, S.U.; Dixon, E.D. The sources and transmission routes of microbial populations throughout a meat processing facility. Npj Biofilms Microbiomes 2020, 6, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singer, H.W. The technology gap and the developing countries. Int. J. Environ. Stud. 1972, 3, 119–123. [Google Scholar]
- Kuai, P.; Li, W.; Liu, N. Evaluating the effects of land use planning for non-point source pollution based on a system dynamics approach in China. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0135572. [Google Scholar]
- Mikhak, A.; Sohrabi, A.; Kassaee, M.Z.; Feizian, M.; Najafi Disfani, M. Removal of nitrate and phosphate from water by clinoptilolite-supported iron hydroxide nanoparticle. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2017, 42, 2433–2439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hüesker, F.; Lepenies, R. Why does pesticide pollution in water persist? Environ. Sci. Policy 2022, 128, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulkhessaim, S.; Gacem, A.; Khan, S.H.; Amari, A.; Yadav, V.K.; Harharah, H.N.; Elkhaleefa, A.M.; Yadav, K.K.; Rather, S.-U.; Ahn, H.-J.; et al. Emerging trends in the remediation of persistent organic pollutants using nanomaterials and related processes: A review. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 2148. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, B. Microbes as indicators of water quality and bioremediation of polluted waters: A novel approach. In Microbial Biotechnology in Environmental Monitoring and Cleanup; Pankaj, Sharma, A., Eds.; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2018; pp. 44–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Yu, Y.; Jing, L.; Wang, X.; Feng, J.; Niu, H.; Xiao, Q.; Wang, L. Semivolatile organic pollutants in water, suspended solids, and surface sediments of the Huaihe River, Jiangsu Section, People’s Republic of China. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2004, 73, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilotta, G.S.; Brazier, R.E. Understanding the influence of suspended solids on water quality and aquatic biota. Water Res. 2008, 42, 2849–2861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Zhou, Y.; Li, L.; Xu, H.; Sun, Y.; Wang, Y. Novel synthesis of cyano-functionalized mesoporous silica nanospheres (MSN) from coal fly ash for removal of toxic metals from wastewater. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 345, 76–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, V.K.; Yadav, K.K.; Gacem, A.; Gnanamoorthy, G.; Ali, I.H.; Khan, S.H.; Jeon, B.-H.; Kamyab, H.; Inwati, G.K.; Choudhary, N. A novel approach for the synthesis of vaterite and calcite from incense sticks ash waste and their potential for remediation of dyes from aqueous solution. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2022, 29, 100756. [Google Scholar]
- Yadav, V.K.; Ali, D.; Khan, S.H.; Gnanamoorthy, G.; Choudhary, N.; Yadav, K.K.; Thai, V.N.; Hussain, S.A.; Manhrdas, S. Synthesis and characterization of amorphous iron oxide nanoparticles by the sonochemical method and their application for the remediation of heavy metals from wastewater. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1551. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, R.; Agrawal, P.R.; Kumar, R.; Gupta, G.; Ittishree. Chapter 4—Current scenario of heavy metal contamination in water. In Contamination of Water; Ahamad, A., Siddiqui, S.I., Singh, P., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2021; pp. 49–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakib, M.J.; Rahman, A.; Onyena, A.P.; Kumar, R.; Sarker, A.; Hossain, M.B.; Islam, A.R.M.T.; Islam, S.; Rahman, M.; Jolly, Y.N.; et al. A comprehensive review of heavy metal pollution in the coastal areas of Bangladesh: Abundance, bioaccumulation, health implications, and challenges. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhav, S.; Ahamad, A.; Singh, A.K.; Kushawaha, J.; Chauhan, J.S.; Sharma, S.; Singh, P. Water pollutants: Sources and impact on the environment and human health. In Sensors in Water Pollutants Monitoring: Role of Material; Pooja, D., Kumar, P., Singh, P., Patil, S., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 43–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, V.K.; Pandita, P.R. Fly ash properties and their applications as a soil ameliorant. In Amelioration Technology for Soil Sustainability; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2019; pp. 59–89. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, H. Water and climate change. In International Encyclopedia of Geography: People, the Earth, Environment and Technology; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widyarani; Wulan, D.R.; Hamidah, U.; Komarulzaman, A.; Rosmalina, R.T.; Sintawardani, N. Domestic wastewater in Indonesia: Generation, characteristics and treatment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 32397–32414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Peng, Y.; Yang, J. Transformation of dissolved organic matter during advanced coal liquefaction wastewater treatment and analysis of its molecular characteristics. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 658, 1334–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Han, F.; Zhang, X.; Liu, B.; Fan, D.; Sun, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yan, L.; Wei, D. Simultaneous nitrate and dissolved organic matter removal from wastewater treatment plant effluent in a solid-phase denitrification biofilm reactor. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 314, 123714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.-Y.; Baek, S.-R.; Kim, J.-I.; Choi, J.-W.; Hur, J.; Lee, T.-U.; Park, C.-J.; Lee, B.J. Characteristics and biodegradability of wastewater organic matter in municipal wastewater treatment plants collecting domestic wastewater and industrial discharge. Water 2017, 9, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, V.K.; Gnanamoorthy, G.; Ali, D.; Bera, S.P.; Roy, A.; Kumar, G.; Choudhary, N.; Kalasariya, H.; Basnet, A. Cytotoxicity, removal of congo red dye in aqueous solution using synthesized amorphous iron oxide nanoparticles from incense sticks ash waste. J. Nanomater. 2022, 2022, 5949595. [Google Scholar]
- Yadav, V.K.; Inwati, G.K.; Ali, D.; Gnanamoorthy, G.; Bera, S.P.; Khan, S.H.; Choudhary, N.; Kumar, G.; Chaurasia, T.P.; Basnet, A. Remediation of azure a dye from aqueous solution by using surface-modified coal fly ash extracted ferrospheres by mineral acids and toxicity assessment. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2022, 2022, 7012889. [Google Scholar]
- Dash, S.; Chaudhuri, H.; Gupta, R.; Nair, U.G. Adsorption study of modified coal fly ash with sulfonic acid as a potential adsorbent for the removal of toxic reactive dyes from aqueous solution: Kinetics and thermodynamics. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 5897–5905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cisneros, B.J. Safe sanitation in low economic development areas. Treatise Water Sci. 2011, 4, 147–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranade, V.V.; Bhandari, V.M. Industrial Wastewater Treatment, Recycling, and Reuse: An Overview; Elsevier Ltd.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girard, J. Principles of Environmental Chemistry; Jones & Bartlett Publishers: Burlington, MA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Adegoke, K.A.; Oyewole, R.O.; Lasisi, B.M.; Bello, O.S. Abatement of organic pollutants using fly ash based adsorbents. Water Sci. Technol. 2017, 76, 2580–2592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Titchou, F.E.; Zazou, H.; Afanga, H.; el Gaayda, J.; Akbour, R.A.; Hamdani, M. Removal of persistent organic pollutants (POPs) from water and wastewater by adsorption and electrocoagulation process. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2021, 13, 100575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mrowiec, B. Plastic pollutants in water environment. Environ. Prot. Nat. Resour. 2017, 28, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawat, K. Organic pollutants in wastewater and its remediation approaches using graphene adsorbent. Int. J. Agric. Appl. Sci. 2021, 2, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Raouf, M.S.; Abdul-Raheim, A.R.M. Removal of heavy metals from industrial waste water by biomass-based materials: A review. J. Pollut. Eff. Control 2016, 5, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zorn, M. Natural disasters and less developed countries. In Nature, Tourism and Ethnicity as Drivers of (De)Marginalization: Insights to Marginality from Perspective of Sustainability and Development; Pelc, S., Koderman, M., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 59–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakeem, K.R.; Akhtar, J.; Sabir, M. Soil Science: Agricultural and Environmental Prospectives; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 1–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inwati, G.K.; Kumar, P.; Roos, W.D.; Swart, H.C.; Singh, M. UV-irradiation effects on tuning LSPR of Cu/Ag nanoclusters in ion exchanged glass matrix and its thermodynamic behaviour. J. Alloy. Compd. 2020, 823, 153820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Inwati, G.K.; Mathpal, M.C.; Ghosh, S.; Roos, W.D.; Swart, H.C. Defects induced enhancement of antifungal activities of Zn doped CuO nanostructures. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 560, 150026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, P.; Inwati, G.K.; Mukherjee, T.K.; Singh, S.; Singh, M. Green silver nanoparticle and Tween-20 modulated pro-oxidant to antioxidant curcumin transformation in aqueous CTAB stabilized peanut oil emulsions. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 291, 111252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arman, N.Z.; Salmiati, S.; Aris, A.; Salim, M.R.; Nazifa, T.H.; Muhamad, M.S.; Marpongahtun, M. A review on emerging pollutants in the water environment: Existences, health effects and treatment processes. Water 2021, 13, 3258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montes-Grajales, D.; Fennix-Agudelo, M.; Miranda-Castro, W. Occurrence of personal care products as emerging chemicals of concern in water resources: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 595, 601–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daughton, C.G.; Ternes, T.A. Pharmaceuticals and personal care products in the environment: Agents of subtle change? Environ. Health Perspect. 1999, 107, 907–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geissen, V.; Mol, H.; Klumpp, E.; Umlauf, G.; Nadal, M.; van der Ploeg, M.; van de Zee, S.E.A.T.M.; Ritsema, C.J. Emerging pollutants in the environment: A challenge for water resource management. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2015, 3, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaukura, N.; Gwenzi, W.; Tavengwa, N.; Manyuchi, M.M. Biosorbents for the removal of synthetic organics and emerging pollutants: Opportunities and challenges for developing countries. Environ. Dev. 2016, 19, 84–89. [Google Scholar]
- Said, A.E.A.A.; Aly, A.A.; Abd El-Wahab, M.M.; Soliman, S.A.; Abd El-Hafez, A.A.; Helmey, V.; Goda, M.N. Application of modified bagasse as a biosorbent for reactive dyes removal from industrial wastewater. J. Water Resour. Prot. 2013, 5, 10. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, M.; Khan, A.U.; Hasan, M.A.; Yadav, K.K.; Pinto, M.M.C.; Malik, N.; Yadav, V.K.; Khan, A.H.; Islam, S.; Sharma, G.K. Agro-Nanotechnology as an Emerging Field: A Novel Sustainable Approach for Improving Plant Growth by Reducing Biotic Stress. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irannajad, M.; Kamran Haghighi, H. Removal of heavy metals from polluted solutions by zeolitic adsorbents: A review. Environ. Process. 2021, 8, 7–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaur, N.; Flora, G.; Yadav, M.; Tiwari, A. A review with recent advancements on bioremediation-based abolition of heavy metals. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2014, 16, 180–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modi, S.; Inwati, G.K.; Gacem, A.; Saquib Abullais, S.; Prajapati, R.; Yadav, V.K.; Syed, R.; Alqahtani, M.S.; Yadav, K.K.; Islam, S.; et al. Nanostructured Antibiotics and Their Emerging Medicinal Applications: An Overview of Nanoantibiotics. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, L.; Wong, Z.; Sarjadi, M.; Soloi, S.; Arshad, S.; Bidin, K.; Musta, B. Heavy metals removal from electroplating wastewater by waste fiber-based poly(Amidoxime) ligand. Water 2021, 13, 1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Lin, J.; Chen, H.; Wang, Q. Production of a novel slow-release coal fly ash microbial fertilizer for restoration of mine vegetation. Waste Manag. 2021, 124, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, M.; Hu, A.; Gad, M.; Adyari, B.; Qin, D.; Zhang, L.; Sun, Q.; Yu, C.-P. Domestic wastewater causes nitrate pollution in an agricultural watershed, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 823, 153680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondi, C.A.M.; Marks, J.L.; Wroblewski, L.B.; Raatikainen, H.S.; Lenox, S.R.; Gebhardt, K.E. Human and environmental toxicity of sodium lauryl sulfate (SLS): Evidence for safe use in household cleaning products. Environ. Health Insights. 2015, 9, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wise, A.; O’Brien, K.; Woodruff, T. Are oral contraceptives a significant contributor to the estrogenicity of drinking water? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 51–60. [Google Scholar]
- Wijaya, I.M.W.; Soedjono, E.S. Domestic wastewater in Indonesia: Challenge in the future related to nitrogen content. Int. J. GEOMATE 2018, 15, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UN Water. UN World Water Development Report 2022; UN Water: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- UNESCO; World Water Assessment Programme (United Nations); UN-Water. Nature-Based Solutions for Water. n.d. Available online: https://en.unesco.org/wwap (accessed on 3 July 2022).
- Hussain, S.; Khan, M.; Sheikh, T.M.M.; Mumtaz, M.Z.; Chohan, T.A.; Shamim, S.; Liu, Y. Zinc essentiality, toxicity, and its bacterial bioremediation: A comprehensive insight. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Research Council. Copper in Drinking Water; National Academy Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Genchi, G.; Carocci, A.; Lauria, G.; Sinicropi, M.S.; Catalano, A. Nickel: Human health and environmental toxicology. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 679. [Google Scholar]
- Genchi, G.; Sinicropi, M.S.; Lauria, G.; Carocci, A.; Catalano, A. The effects of cadmium toxicity. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 3782. [Google Scholar]
- Nagpure, N.S.; Srivastava, R.; Kumar, R.; Kushwaha, B.; Srivastava, S.K.; Kumar, P.; Dabas, A. Assessment of genotoxic and mutagenic potential of hexavalent chromium in the freshwater fish Labeo rohita (Hamilton, 1822). Drug Chem. Toxicol. 2015, 38, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Huo, X.; Yekeen, T.A.; Zheng, Q.; Zheng, M.; Xu, X. Effects of lead and cadmium exposure from electronic waste on child physical growth. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 4441–4447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thundiyil, J. Acute pesticide poisoning: A proposed classification tool. Bull. World Health Organ. 2008, 86, 205–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, R.G.; Kopfler, F.C.; Kelty, K.C.; Stober, J.A.; Ulmer, N.S. The occurrence of aluminum in drinking water. J. Am. Water Works Assoc. 1984, 76, 84–91. [Google Scholar]
- Ghafuri, Y.; Yunesian, M.; Nabizadeh, R.; Mesdaghinia, A.; Dehghani, M.H.; Alimohammadi, M. Platinum cytotoxic drugs in the municipal wastewater and drinking water, a validation method and health risk assessment. Human Ecol. Risk Assess. 2018, 24, 784–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, M.; Buchanan, J.A. Argyria, an unexpected case of skin discoloration from colloidal silver salt ingestion. J. Emerg. Med. 2020, 59, e39–e41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thevenon, F.; Shantz, A. Progress on Wastewater Treatment. 2021. Available online: https://unhabitat.org/sites/default/files/2021/08/sdg6_indicator_report_631_progress_on_wastewater_treatment_2021_english_pages.pdf (accessed on 3 July 2022).
- Mohapatra, D.P.; Kirpalani, D.M. Selenium in wastewater: Fast analysis method development and advanced oxidation treatment applications. Water Sci. Technol. 2019, 79, 842–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakakubo, K.; Nishimura, T.; Biswas, F.B.; Endo, M.; Wong, K.H.; Mashio, A.S.; Taniguchi, T.; Nishimura, T.; Maeda, K.; Hasegawa, H. Speciation analysis of inorganic selenium in wastewater using a highly selective cellulose-based adsorbent via liquid electrode plasma optical emission spectrometry. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 424, 127250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, S.K.; Jha, S.K.; Jha, V.N.; Patra, A.C.; Kulkarni, M.S. Survey of uranium in drinking water sources in India: Interim observations. Curr. Sci. 2021, 120, 1482. [Google Scholar]
- Akhtar, N.; Syakir Ishak, M.I.; Bhawani, S.A.; Umar, K. Various natural and anthropogenic factors responsible for water quality degradation: A review. Water 2021, 13, 2660. [Google Scholar]
- Mallick, J.; Singh, C.K.; AlMesfer, M.K.; Singh, V.P.; Alsubih, M. Groundwater quality studies in the kingdom of Saudi Arabia: Prevalent research and management dimensions. Water 2021, 13, 1266. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, W.; Meng, F.; Wang, F.; Liu, Q. Environmental behavior and eco-toxicity of xylene in aquatic environments: A review. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 145, 324–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dozier, M.; Lesikar, B. Drinking Water Problems: Benzene. Environ. Sci. 2009, 130221623. [Google Scholar]
- WHO. World Health Organization: Guidelines for Drinking Water Quality, 3rd ed.; Recommendations; Environmental Pollution Series A, Ecological and Biological; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2004; Volume 1, pp. 1–564.
- Hamilton, L.D.; Meinhold, A.F.; Nagy, J. Health risk assessment for radium discharged in produced waters. In Produced Water; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1992; pp. 303–314. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.; Cao, M.; Tong, D.; Finkelstein, Z.; Hoek, E. A critical review of point-of-use drinking water treatment in the United States. Npj Clean Water 2021, 4, 40. [Google Scholar]
- Bradai, M.; Han, J.; Omri AEl Funamizu, N.; Sayadi, S.; Isoda, H. Effect of linear alkylbenzene sulfonate (LAS) on human intestinal Caco-2 cells at non cytotoxic concentrations. Cytotechnology 2016, 68, 1267–1275. [Google Scholar]
- Karyab, H.; Yunesian, M.; Nasseri, S.; Mahvi, A.H.; Ahmadkhaniha, R.; Rastkari, N.; Nabizadeh, R. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in drinking water of Tehran, Iran. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2013, 11, 25. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, X.; Dong, J.; Huang, Z.; Liu, C.; Qiao, X.; Wang, X.; Zhao, X.; Zheng, B.; Shen, J. Polychlorinated biphenyls in the drinking water source of the Yangtze River: Characteristics and risk assessment. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2020, 32, 29. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Exposure to Dioxins and Dioxin-Like Substances: A Major Public Health Concern; WHO: Geneve, Switzerland, 2010.
- Taylor, K.M.; Weisskopf, M.; Shine, J. Human exposure to nitro musks and the evaluation of their potential toxicity: An overview. Environ. Health 2014, 13, 14. [Google Scholar]
- Nazari, E.; Suja, F. Effects of 17β-estradiol (E2) on aqueous organisms and its treatment problem: A review. Rev. Environ. Health 2016, 31, 465–491. [Google Scholar]
- Gadupudi, C.K.; Rice, L.; Xiao, L.; Kantamaneni, K. Endocrine disrupting compounds removal methods from wastewater in the United Kingdom: A review. Science 2021, 3, 11. [Google Scholar]
- Majam, S.; Thompson, P. Polyelectrolyte Determination in Drinking Water. Water Res. Comm. 2007, 32, 705–707. [Google Scholar]
- Ward, M.H. Too much of a good thing? Nitrate from nitrogen fertilizers and cancer. Rev. Environ. Health 2009, 24, 357–363. [Google Scholar]
- Syafrudin, M.; Kristanti, R.A.; Yuniarto, A.; Hadibarata, T.; Rhee, J.; Al-Onazi, W.A.; Algarni, T.S.; Almarri, A.H.; Al-Mohaimeed, A.M. Pesticides in drinking water—A review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 468. [Google Scholar]
- Chahal, C.; Van Den Akker, B.; Young, F.; Franco, C.; Blackbeard, J.; Monis, P. Pathogen and particle associations in wastewater: Significance and implications for treatment and disinfection processes. Adv. Appl. Microbiol. 2016, 97, 63–119. [Google Scholar]
- Pandit, A.B.; Kumar, J.K. Clean water for developing countries. Annu. Rev. Chem. Biomol. Eng. 2015, 6, 217–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, N.; Yadav, V.K.; Malik, P.; Khan, S.H.; Inwati, G.K.; Suriyaprabha, R.; Singh, B.; Yadav, A.K.; Ravi, R.K. Recovery of natural nanostructured minerals: Ferrospheres, plerospheres, cenospheres, and carbonaceous particles from fly ash. In Handbook of Research on Emerging Developments and Environmental Impacts of Ecological Chemistry; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2020; pp. 450–470. [Google Scholar]
- Pandey, P.K.; Kass, P.H.; Soupir, M.L.; Biswas, S.; Singh, V.P. Contamination of water resources by pathogenic bacteria. AMB Express 2014, 4, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Anwer, R.; Sehrawat, A.; Yadav, M.; Sehrawat, N. Assessment of bacterial pathogens in drinking water: A serious safety concern. Curr. Pharmacol. Rep. 2021, 7, 206–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gleick, P.H. Water management: Soft water paths. Nature 2002, 418, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B. Chapter 6—Human health hazards of wastewater. In High-Risk Pollutants in Wastewater; Ren, H., Zhang, X., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 125–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Singh, R.; Singh, V.K.; Bhadouria, R. Pollutants and Water Management: Resources, Strategies and Scarcity, 1st ed.; Edited The Fate of Organic Pollutants and Their Microbial Degradation in Water Bodies; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; García Molinos, J.; Heino, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, P.; Xu, J. Eutrophication causes invertebrate biodiversity loss and decreases cross-taxon congruence across anthropogenically-disturbed lakes. Environ. Int. 2021, 153, 106494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, F.; Dai, Z.; Shen, S.; Wang, S.; Lu, X. Characteristics of rural domestic wastewater with source separation. Water Sci. Technol. 2020, 83, 233–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liyanage, C.P.; Yamada, K. Impact of population growth on the water quality of natural water bodies. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CPCB. National Inventory of Sewage Treatment Plants March 2021; CPCB: New Delhi, India, 2021; Volume 183. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Meeting the MDG Drinking Water and Sanitation Target: The Urban and Rural Challenge of the Decade; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2006; p. 41.
- Gnanamoorthy, G.; Yadav, V.K.; Ali, D.; Narayanan, V.; Mohammed Saleh Katubi, K.; Alarifi, S. Trigger action of copper aminophosphate (X-CuAP) nanoparticles for enhanced electrochemical, photocatalyst and biological properties. Optical Materials 2021, 117, 111113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corcoran, E. Sick Water? The Central Role of Wastewater Management in Sustainable Development: A Rapid Response Assessment; UNEP/Earthprint: Nairobi, Kenya, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, D.; Yang, Y.; Xia, J. Hydrological cycle and water resources in a changing world: A review. Geogr. Sustain. 2021, 2, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montgomery, M.R.; Stren, R.; Cohen, B.; Reed, H.E. Cities Transformed: Demographic Change and Its Implications in the Developing World; Routledge: London, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Shabir, M.; Muhammad, Y.; Hussain, M.; Shafiq, I.; Parveen, A.; Nizami, A.S.; Jeon, B.H.; Park, Y.K. A review on recent advances in the treatment of dye-polluted wastewater. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2022, 112, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsalek, J. Urban Water Cycle Processes and Interactions; CRC Press: London, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Jia, Y.W. Theory and study methodology of dualistic water cycle in river basins under changing conditions. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2016, 47, 1219–1226. [Google Scholar]
- Bhatti, A.Z.; Farooque, A.A.; Krouglicof, N.; Peters, W.; Li, Q.; Acharya, B. Prospective Climates, and Water Availabilities under Different Projections of Environmental Changes in Prince Edward Island, Canada. Water 2022, 14, 740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidari, H.; Grigg, N.S. Effects of the COVID-19 Pandemic on the Urban Water Cycle. Adv. Environ. Eng. Res. 2021, 2, 021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koohafkan, P.; Altieri, M.; Initiative, G. A Methodological Framework for the Dynamic Conservation of Agricultural Heritage Systems; Land and Water Division, The Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) of the United Nations: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011; pp. 1–61. [Google Scholar]
- UN-Water. World Water Development Report: Water for a Sustainable World; UN-Water: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- UN-Water. The United Nations World Water Development Report 2016 on ‘Water and Jobs’; UN-Water: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Paraskevas, P.A.; Giokas, D.L.; Lekkas, T.D. Wastewater management in coastal urban areas: The case of Greece. Water Sci. Technol. 2002, 46, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Sancho, F.; Lamizana-Diallo, B.; Mateo-Sagasta, M.; Qadir, M. Economic Valuation of Wastewater: The Cost of Action and the Cost of No Action; UNEP: Nairobi, Kenya, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Hanjra, M.A.; Drechsel, P.; Mateo-Sagasta, J.; Otoo, M.; Hernández-Sancho, F. Assessing the finance and economics of resource recovery and reuse solutions across scales. In Wastewater; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 113–136. [Google Scholar]
- Massoud, M.A.; Tarhini, A.; Nasr, J.A. Decentralized approaches to wastewater treatment and management: Applicability in developing countries. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 90, 652–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnanamoorthy, G.; Ramar, K.; Ali, D.; Yadav, V.K.; Jafar ahamed, A.; Kumar, G. Synthesis and effective performance of Photocatalytic and Antimicrobial activities of Bauhinia tomentosa Linn plants using of gold nanoparticles. Opt. Mater. 2022, 123, 111945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laugesen, C.; Fryd, O. Sustainable wastewater management in developing countries. In American Society of Civil Engineers; ASCE Press: Reston, VA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyzas, G.Z.; Matis, K.A. Electroflotation process: A review. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 220, 657–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moussa, D.T.; El-Naas, M.H.; Nasser, M.; Al-Marri, M.J. A comprehensive review of electrocoagulation for water treatment: Potentials and challenges. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 186, 24–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zyłka, R.; Dabrowski, W.; Gogina, E.; Yancen, O. Trickling filter for high efficiency treatment of dairy sewage. J. Ecol. Eng. 2018, 19, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wei, W.; Gong, Y.; Yu, Q.; Li, Q.; Sun, J.; Yuan, Z. Technologies for reducing sludge production in wastewater treatment plants: State of the art. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 587–588, 510–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Kyu Kim, J.; Kim, Y.; Seung Choi, J.; Young Jeong, K. Operation of industrial-scale electron beam wastewater treatment plant. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2012, 81, 1475–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.Q.; Cui, P.; Ru, S.; Kurade, M.B.; Patil, S.M.; Yadav, K.K.; Fallatah, A.M.; Cabral-Pinto, M.M.S.; Jeon, B.H. A comprehensive review on the effects of engineered nanoparticles on microalgal treatment of pollutants from wastewater. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 344, 131121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
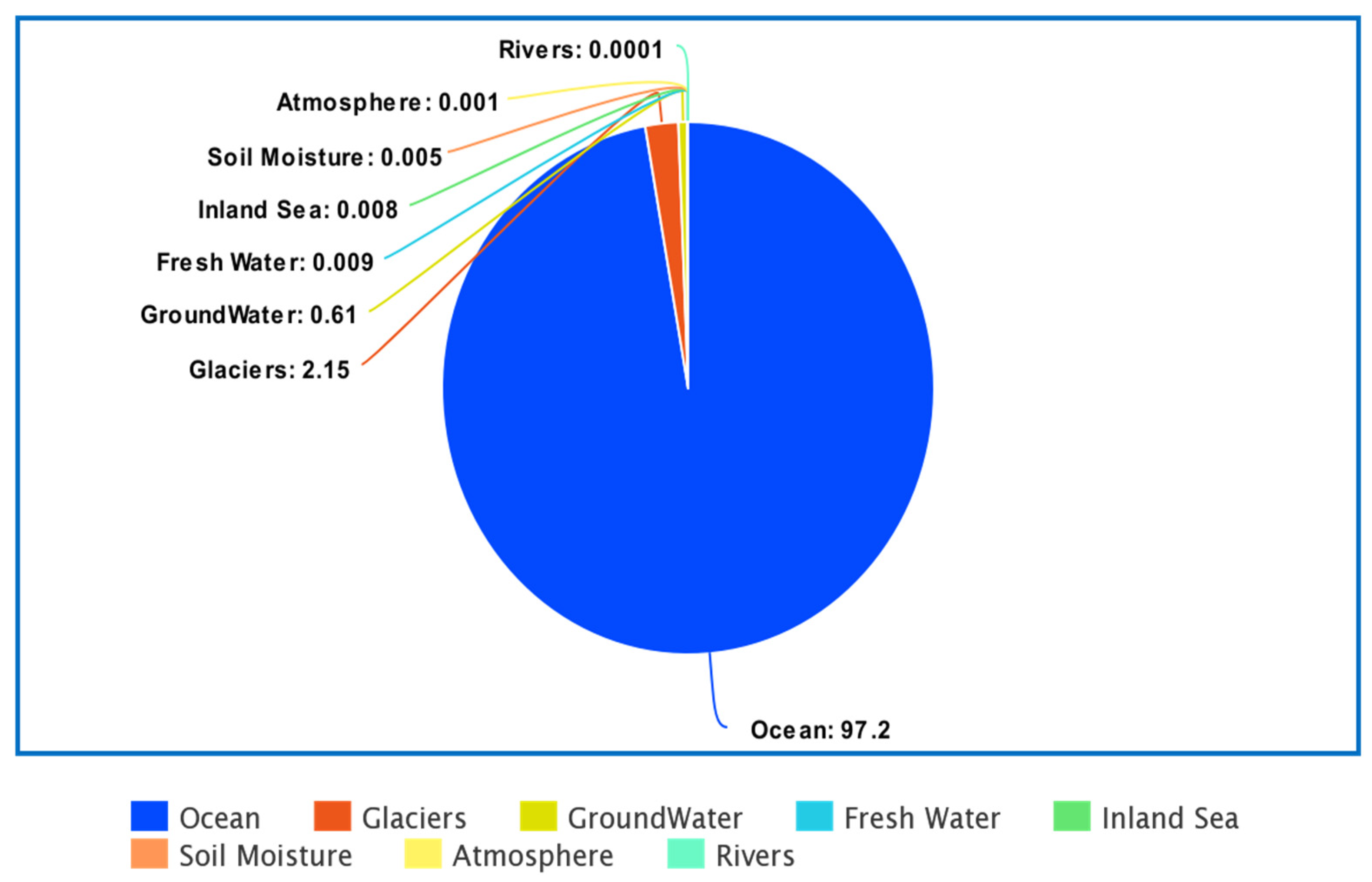
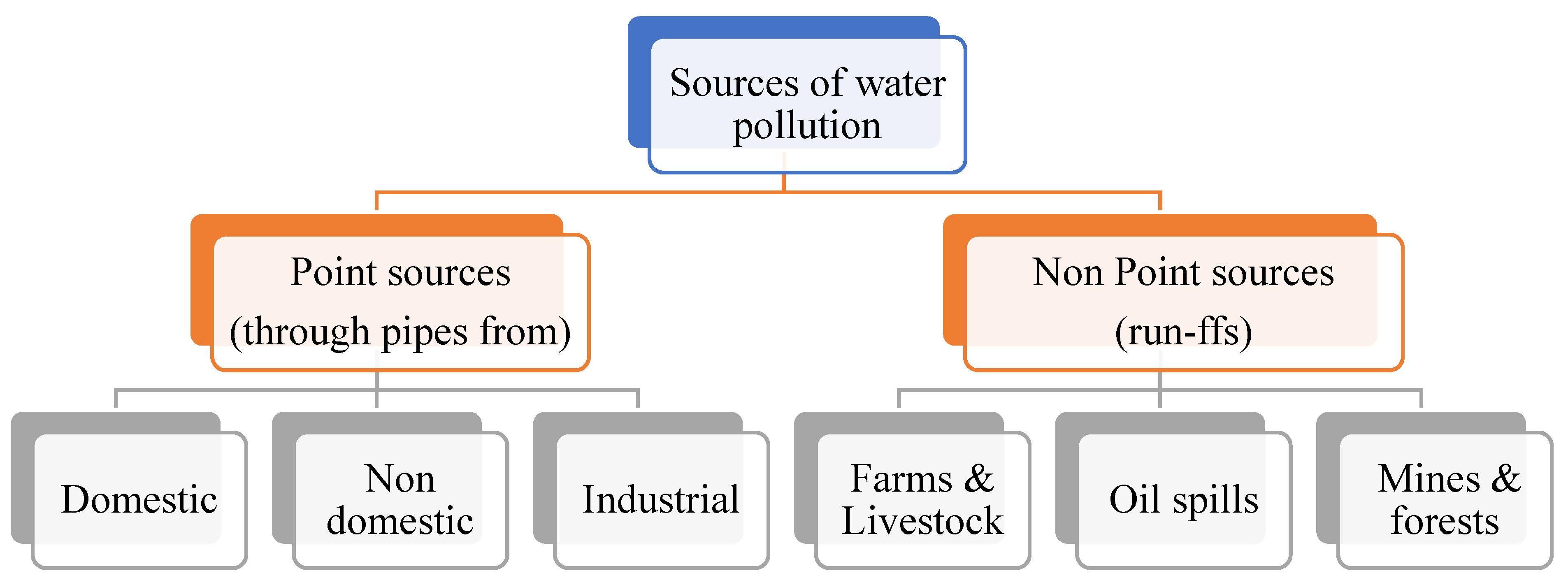
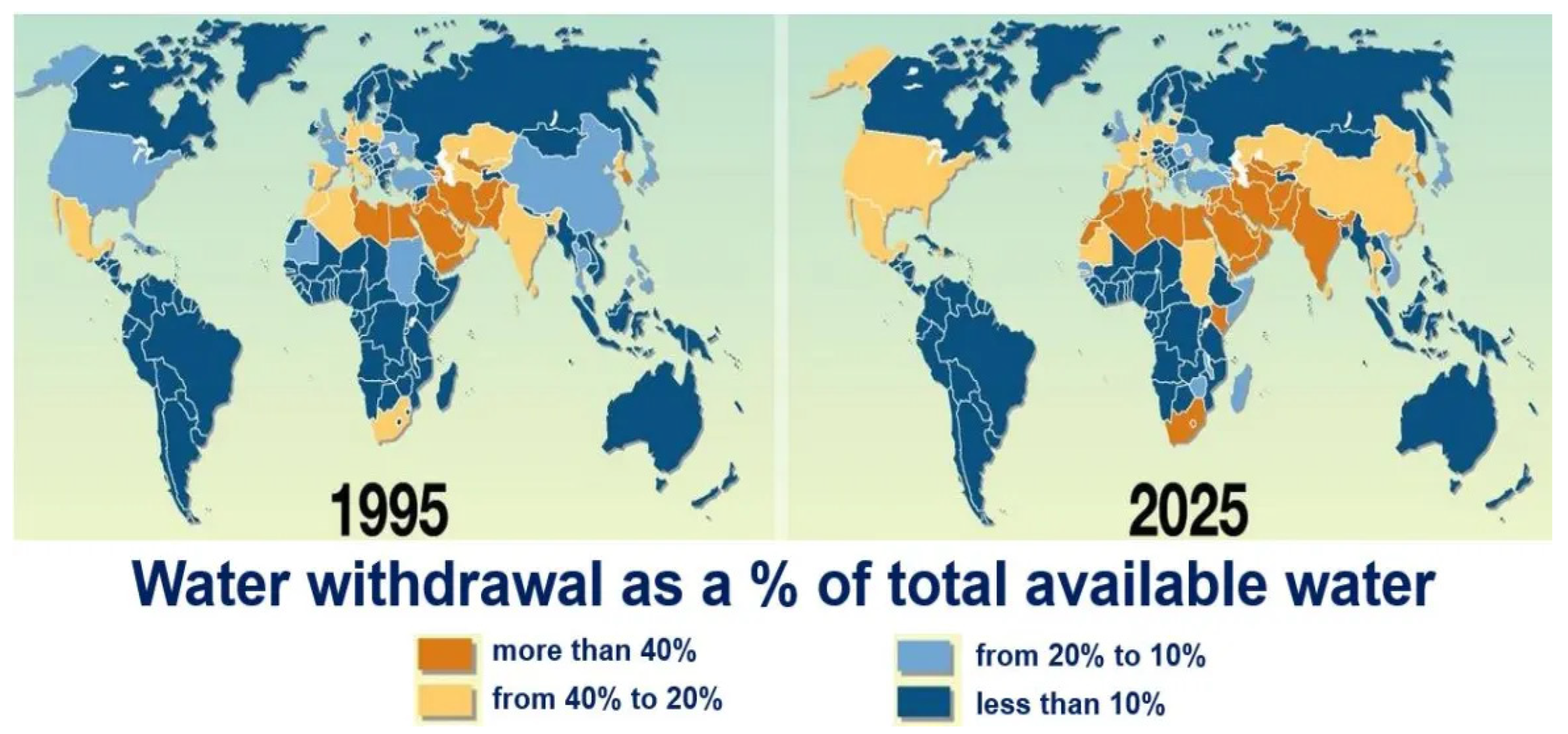


| Sources | Pollutants along with Their Effect | References |
|---|---|---|
| Waste generated from agricultural run-offs | Phosphates and nitrates in fertilizers Causes eutrophication | [34] |
| Pesticides, herbicides | [35,36] | |
| Animal waste from farms | Microorganisms (bacteria, protozoa, and viruses) that may cause water-borne diseases | [37] |
| Untreated sewage (human fecal matter + domestic waste) | Suspended solids and microorganisms Suspended solids may lead to reduced sunlight penetration in lakes, ponds other water bodies affecting aquatic flora and fauna. Pathogenic microbes from carriers may cause food and water-borne diseases like cholera, typhoid, etc. | [38,39] |
| Industrial effluents (metal-based, dyes, rubber, etc.) | Heavy metals like As, Hg, Cu, Cd, Cr, and Ni may accumulate in aquatic organisms and enter the food chain, leading to bioaccumulation. Severe to chronic diseases caused by heavy metals. | [7,8,40,41,42] |
| Underground pipes | Pb Highly toxic heavy metals may cause mental disorders among children | [43,44] |
| Domestic waste | Detergents, surfactants, may cause foaming of water bodies leading to reduced water supply to aquatic organisms. | [4,45] |
| Major Sources | Source | Composition of Effluent | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Industries | Petroleum, stainless steel, paint industries, power generation, mining, construction, and food industries. | Zinc, copper, nickel, cadmium, xylene, benzene, toluene, NORM, monocyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, chromium, lead, mercury, aluminum, radioactive molecules, platinum group metals, silver, barium, silver, arsenic, molybdenum, chloramines, radium, fluoride, nonylphenol ethoxylates (NPE), di-(2-ethylhexyl)phthalate, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, polychlorinated biphenyls, polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins, and polychlorinated dibenzo-p-furans, nitro musks (chloronitrobenzenes), oestrogenic compounds and polyelectrolytes, etc. | [75,76,77,78] |
| Domestic | Kitchen and sewage. | Fertilizer and pesticides, lead and cadmium (from batteries), plastic bags, papers, polythene bags, rotten fruits and vegetables, and linear alkyl benzene sulphonates (LAS) are the major components of washing powder and found in detergents and microbes, etc. | [79,80,81] |
| Types of Pollutants | Health Hazard | References |
|---|---|---|
| Inorganic pollutants | ||
| Zinc | Causes nausea, vomiting, and stomach cramps. | [86] |
| Copper | Vomiting, diarrhea, stomach cramps, nausea, liver damage, and kidney disease. | [87] |
| Nickel | Alters the gastrointestinal tract, respiratory system, skin, heart, and lungs; may cause epigenetic effects. | [88] |
| Cadmium | Affects the lungs, kidneys, and bone, causes fever, chills, and body pain. | [89] |
| Chromium | Mutagenic and carcinogenic. | [90] |
| Lead | Causes constipation, loss of appetite, headache, abdominal pain, causes tiredness and weakness; may lead to memory loss. | [91] |
| Mercury | Damages the kidneys, brain, vision, hearing capacity, and developing fetus. | [92] |
| Aluminum | Alzheimer’s disease. | [93] |
| Platinum group metals | Carcinogenic. | [94] |
| Silver | Skin discoloration. | [95] |
| Barium | Slows the respiratory, digestive, and cardiovascular system. Damages kidney, liver, and spleen. | [96] |
| Selenium | Causes dizziness and weakness. May lead to prostate cancer. | [97,98] |
| Uranium | Induces cancer and is toxic to the kidneys. | [99] |
| Radium | Carcinogenic. | [100] |
| Fluoride | Causes bone disorders. | [101] |
| Organic pollutants | ||
| Xylene | Influences the central nervous system (CNS) and vision. | [102] |
| Benzene | Induces vomiting, dizziness, sleepiness, and heart problems; carcinogenic. | [103] |
| Toluene | Impairs CNS causing fatigue and drowsiness. | [104] |
| NORM | Carcinogenic. | [105] |
| Chloramines | Can cause hemolytic anemia. | [106] |
| Linear alkylbenzene sulphonates (LAS) found in detergents | May cause colon cancer. | [107] |
| Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons | Consumption leads to cancer. | [108] |
| Polychlorinated biphenyls | Carcinogenic in nature. | [109] |
| Polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and Polychlorinated dibenzo-p-furans | May cause malfunctioning of the immune and endocrine systems affecting reproductive health. | [110] |
| Nitro musks (chloronitrobenzenes) | Disturbs endocrine and gynecological health. | [111] |
| Oestrogenic compounds | Affects the normal functioning of the endocrine system. | [112,113] |
| Polyelectrolytes | Affects the gastrointestinal tract and lymphoid system. | [114] |
| Nitrate | Colorectal cancer, thyroid disease, and neural tube defects. | [115] |
| Pesticides | Affects the brain and induces Parkinson’s disease, affecting reproductive and respiratory health. May be carcinogenic. | [116] |
| Pathogens | Health Hazard. | Reference |
| Campylobacter jejuni | Gastroenteritis. | [117] |
| Escherichia coli | Gastroenteritis. | |
| Salmonella spp. | Salmonellosis, typhoid, parathyroid. | |
| Shigella spp. | Bacillary dysentery. | |
| Vibrio cholerae | Cholera. | |
| Yersinia spp. | Gastroenteritis. | |
| Adenovirus | Upper respiratory infection and gastroenteritis. | |
| Astrovirus | Gastroenteritis. | |
| Coxsackie A virus | Meningitis, pneumonia, fever. | |
| Echovirus | Meningitis, paralysis, encephalitis, fever. | |
| Hepatitis A virus | Infectious hepatitis. | |
| Hepatitis E virus | Infectious hepatitis, miscarriage, and death. | |
| Human calicivirus | Epidemic gastroenteritis with severe diarrhea. | |
| Polio virus | Poliomyelitis. | |
| Reovirus | Respiratory infections, gastroenteritis. | |
| Rotavirus | Acute gastroenteritis with severe diarrhea. | |
| TT hepatitis | Hepatitis. | |
| Balantidium coli | Balantidiasis. | |
| Cryptosporidium spp. | Cryptosporidiosis. | |
| Entamoeba histolytica | Acute amoebic dysentery. | |
| Giardia duodenalis | Giardiasis. | |
| Toxoplasma gondii | Toxoplasmosis. | |
| Ascaris lumbricoides | Ascariasis. | |
| Ascaris suum | Coughing and chest pain. | |
| Hymenolepis nana | Hymenolepiasis. | |
| Necator americanus | Hookworm disease. | |
| Taenia saginata | Insomnia, anorexia. | |
| Taenia solium | Insomnia, anorexia. | |
| Toxocara canis | Fever, abdominal pain, muscle ache. | |
| Trichuris trichiura | Diarrhea, anemia, weight loss. |
| Centralized | Decentralized | |
|---|---|---|
| Definition. | The wastewater is collected and treated at a central location and then distributed using a network of a pipeline network. | Decentralized wastewater treatment is the use of a range of simple technologies to treat wastewater from near or at the point of generation. |
| Also called: | Off-site Treatment. | On-site Treatment. |
| Huge network of pipeline, excavation, manholes. | Required. | Not required. |
| Length and diameter of pipes. | Large and long. | Small and Short. |
| Waste is collected from | From long distance. | Near or at the site of a pollution source. |
| Composition of collected wastewater | A mixture of black, grey, and industrial water. | The type of water is separated from the source. |
| Owned by | State Authority | |
| Scale of operation | Large. | Small. |
| Area required | A huge area is required in a central place. | A small area is required at the site of the pollution source. |
| Investment | Huge investment is required. | Comparatively less and it is cost-effective. |
| Technical Staff | Dedicated staff are required for maintenance | Can be maintained fortuitously. |
| Preferred for | High population density region | Low population density region. |
| Affordability | People of developed countries can afford. | People in developing countries cannot afford. |
| Technology used | Combination of different advanced types of technologies | Primitive technology like septic tank/drain field. |
| A consequence of improper maintenance | Detrimental health issues at the regional level | Detrimental health issues in local areas. |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bijekar, S.; Padariya, H.D.; Yadav, V.K.; Gacem, A.; Hasan, M.A.; Awwad, N.S.; Yadav, K.K.; Islam, S.; Park, S.; Jeon, B.-H. The State of the Art and Emerging Trends in the Wastewater Treatment in Developing Nations. Water 2022, 14, 2537. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14162537
Bijekar S, Padariya HD, Yadav VK, Gacem A, Hasan MA, Awwad NS, Yadav KK, Islam S, Park S, Jeon B-H. The State of the Art and Emerging Trends in the Wastewater Treatment in Developing Nations. Water. 2022; 14(16):2537. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14162537
Chicago/Turabian StyleBijekar, Sangha, Hemanshi D. Padariya, Virendra Kumar Yadav, Amel Gacem, Mohd Abul Hasan, Nasser S. Awwad, Krishna Kumar Yadav, Saiful Islam, Sungmin Park, and Byong-Hun Jeon. 2022. "The State of the Art and Emerging Trends in the Wastewater Treatment in Developing Nations" Water 14, no. 16: 2537. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14162537








