Impact of log(Kow) Value on the Extraction of Antibiotics from River Sediments with Pressurized Liquid Extraction
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Investigated Compounds
2.3. Preparation of Stock Solutions
2.4. Sampling and Preparation of Sediment Samples
2.5. Pressurized Liquid Extraction (PLE)
2.6. Clean-up of PLE Extracts by Solid-Phase Extraction (SPE)
2.7. Analysis of Antibiotics by Liquid Chromatography Coupled with Tandem Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS/MS)
2.8. Quality Control
2.9. Determination of the Recovery
2.10. Method Validation
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Initial Screening of PLE Methods
3.2. Influence of log(Kow), pKA, and pH on the Recovery
3.3. Recovery with Two Consecutive Extraction Steps
3.4. Method Validation
3.5. Quantification of ABs in Environmental Samples
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kumar, K.C.; Gupta, S.; Chander, Y.; Singh, A.K. Antibiotic Use in Agriculture and Its Impact on the Terrestrial Environment. In Advances in Agronomy; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2005; Volume 87, pp. 1–54. [Google Scholar]
- Aydin, S.; Aydin, M.E.; Ulvi, A.; Kilic, H. Antibiotics in Hospital Effluents: Occurrence, Contribution to Urban Wastewater, Removal in a Wastewater Treatment Plant, and Environmental Risk Assessment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 544–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michael, I.; Rizzo, L.; McArdell, C.S.; Manaia, C.M.; Merlin, C.; Schwartz, T.; Dagot, C.; Fatta-Kassinos, D. Urban Wastewater Treatment Plants as Hotspots for the Release of Antibiotics in the Environment: A Review. Water Res. 2013, 47, 957–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekwanzala, M.D.; Lehutso, R.F.; Kasonga, T.K.; Dewar, J.B.; Momba, M.N.B. Environmental Dissemination of Selected Antibiotics from Hospital Wastewater to the Aquatic Environment. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Mozaz, S.; Chamorro, S.; Marti, E.; Huerta, B.; Gros, M.; Sànchez-Melsió, A.; Borrego, C.M.; Barceló, D.; Balcázar, J.L. Occurrence of Antibiotics and Antibiotic Resistance Genes in Hospital and Urban Wastewaters and Their Impact on the Receiving River. Water Res. 2015, 69, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loos, R.; Carvalho, R.; António, D.C.; Comero, S.; Locoro, G.; Tavazzi, S.; Paracchini, B.; Ghiani, M.; Lettieri, T.; Blaha, L.; et al. EU-Wide Monitoring Survey on Emerging Polar Organic Contaminants in Wastewater Treatment Plant Effluents. Water Res. 2013, 47, 6475–6487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chunhui, Z.; Liangliang, W.; Xiangyu, G.; Xudan, H. Antibiotics in WWTP Discharge into the Chaobai River, Beijing. Arch. Environ. Prot. 2016, 42, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kümmerer, K. Antibiotics in the Aquatic Environment-A Review-Part I. Chemosphere 2009, 75, 417–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Doorslaer, X.; Dewulf, J.; Van Langenhove, H.; Demeestere, K. Fluoroquinolone Antibiotics: An Emerging Class of Environmental Micropollutants. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 500–501, 250–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, C.; Spielmeyer, A.; Frings, R.M.; Hamscher, G.; Schüttrumpf, H. From Agricultural Fields to Surface Water Systems: The Overland Transport of Veterinary Antibiotics. J. Soils Sediments 2015, 15, 1630–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felis, E.; Kalka, J.; Sochacki, A.; Kowalska, K.; Bajkacz, S.; Harnisz, M.; Korzeniewska, E. Antimicrobial Pharmaceuticals in the Aquatic Environment-Occurrence and Environmental Implications. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 866, 172813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boy-Roura, M.; Mas-Pla, J.; Petrovic, M.; Gros, M.; Soler, D.; Brusi, D.; Menció, A. Towards the Understanding of Antibiotic Occurrence and Transport in Groundwater: Findings from the Baix Fluvià Alluvial Aquifer (NE Catalonia, Spain). Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 612, 1387–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riaz, L.; Mahmood, T.; Khalid, A.; Rashid, A.; Ahmed Siddique, M.B.; Kamal, A.; Coyne, M.S. Fluoroquinolones (FQs) in the Environment: A Review on Their Abundance, Sorption and Toxicity in Soil. Chemosphere 2018, 191, 704–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolls, J. Sorption of Veterinary Pharmaceuticals in Soils: A Review. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2001, 35, 3397–3406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, S.; Aga, D.S. Analysis of Tetracycline Antibiotics in Soil: Advances in Extraction, Clean-up, and Quantification. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2007, 26, 456–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lillenberg, M.; Yurchenko, S.; Kipper, K.; Herodes, K.; Pihl, V.; Sepp, K.; Lõhmus, R.; Nei, L. Simultaneous Determination of Fluoroquinolones, Sulfonamides and Tetracyclines in Sewage Sludge by Pressurized Liquid Extraction and Liquid Chromatography Electrospray Ionization-Mass Spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2009, 1216, 5949–5954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvia, M.-V.; Fieu, M.; Vulliet, E. Determination of Tetracycline and Fluoroquinolone Antibiotics at Trace Levels in Sludge and Soil. Appl. Environ. Soil Sci. 2015, 2015, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Mo, Y.; Wu, Z.; Rad, S.; Song, X.; Zeng, H.; Bashir, S.; Kang, B.; Chen, Z. Occurrence, Distribution, and Health Risk Assessment of Quinolone Antibiotics in Water, Sediment, and Fish Species of Qingshitan Reservoir, South China. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 15777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janecko, N.; Pokludova, L.; Blahova, J.; Svobodova, Z.; Literak, I. Implications of Fluoroquinolone Contamination for the Aquatic Environment-a Review. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2016, 35, 2647–2656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Aga, D.S. Potential Ecological and Human Health Impacts of Antibiotics and Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria from Wastewater Treatment Plants. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Part B 2007, 10, 559–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halling-Sørensen, B.; Jacobsen, A.-M.; Jensen, J.; Sengeløv, G.; Vaclavik, E.; Ingerslev, F. Dissipation and Effects of Chlortetracycline and Tylosin in Two Agricultural Soils: A Field-Scale Study in Southern Denmark. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2005, 24, 802–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamscher, G.; Sczesny, S.; Höper, H.; Nau, H. Determination of Persistent Tetracycline Residues in Soil Fertilized with Liquid Manure by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography with Electrospray Ionization Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2002, 74, 1509–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haenni, M.; Dagot, C.; Chesneau, O.; Bibbal, D.; Labanowski, J.; Vialette, M.; Bouchard, D.; Martin-Laurent, F.; Calsat, L.; Nazaret, S.; et al. Environmental Contamination in a High-Income Country (France) by Antibiotics, Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria, and Antibiotic Resistance Genes: Status and Possible Causes. Environ. Int. 2022, 159, 107047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baran, W.; Sochacka, J.; Wardas, W. Toxicity and Biodegradability of Sulfonamides and Products of Their Photocatalytic Degradation in Aqueous Solutions. Chemosphere 2006, 65, 1295–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bengtsson-Palme, J.; Kristiansson, E.; Larsson, D.G.J. Environmental Factors Influencing the Development and Spread of Antibiotic Resistance. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2018, 42, fux053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larivière, A.; Lissalde, S.; Soubrand, M.; Casellas-Français, M. Overview of Multiresidues Analytical Methods for the Quantitation of Pharmaceuticals in Environmental Solid Matrixes: Comparison of Analytical Development Strategy for Sewage Sludge, Manure, Soil, and Sediment Samples. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 453–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarzenbach, R.P.; Gschwend, P.M.; Imboden, D.M. Environmental Organic Chemistry. In Wiley-Interscience, 2nd ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2003; ISBN 978-0-471-35750-6. [Google Scholar]
- Kerrigan, J.F.; Sandberg, K.D.; Engstrom, D.R.; LaPara, T.M.; Arnold, W.A. Small and Large-Scale Distribution of Four Classes of Antibiotics in Sediment: Association with Metals and Antibiotic Resistance Genes. Environ. Sci. Processes Impacts 2018, 20, 1167–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibs, J.; Heckathorn, H.A.; Meyer, M.T.; Klapinski, F.R.; Alebus, M.; Lippincott, R.L. Occurrence and Partitioning of Antibiotic Compounds Found in the Water Column and Bottom Sediments from a Stream Receiving Two Wastewater Treatment Plant Effluents in Northern New Jersey, 2008. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 458–460, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-C.; Carlson, K. Quantification of Human and Veterinary Antibiotics in Water and Sediment Using SPE/LC/MS/MS. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2007, 387, 1301–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massey, L.B.; Haggard, B.E.; Galloway, J.M.; Loftin, K.A.; Meyer, M.T.; Green, W.R. Antibiotic Fate and Transport in Three Effluent-Dominated Ozark Streams. Ecol. Eng. 2010, 36, 930–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vazquez-Roig, P.; Segarra, R.; Blasco, C.; Andreu, V.; Picó, Y. Determination of Pharmaceuticals in Soils and Sediments by Pressurized Liquid Extraction and Liquid Chromatography Tandem Mass Spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2010, 1217, 2471–2483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, B.F.; da Jelic, A.; López-Serna, R.; Mozeto, A.A.; Petrovic, M.; Barceló, D. Occurrence and Distribution of Pharmaceuticals in Surface Water, Suspended Solids and Sediments of the Ebro River Basin, Spain. Chemosphere 2011, 85, 1331–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Shi, Y.; Gao, L.; Liu, J.; Cai, Y. Occurrence of Antibiotics in Water, Sediments, Aquatic Plants, and Animals from Baiyangdian Lake in North China. Chemosphere 2012, 89, 1307–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerrigan, J.F.; Sandberg, K.D.; Engstrom, D.R.; LaPara, T.M.; Arnold, W.A. Sedimentary Record of Antibiotic Accumulation in Minnesota Lakes. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 621, 970–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senta, I.; Terzic, S.; Ahel, M. Analysis and Occurrence of Macrolide Residues in Stream Sediments and Underlying Alluvial Aquifer Downstream from a Pharmaceutical Plant. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 273, 116433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golet, E.M.; Strehler, A.; Alder, A.C.; Giger, W. Determination of Fluoroquinolone Antibacterial Agents in Sewage Sludge and Sludge-Treated Soil Using Accelerated Solvent Extraction Followed by Solid-Phase Extraction. Anal. Chem. 2002, 74, 5455–5462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Silva, J.J.; da Silva, B.F.; Stradiotto, N.R.; Petrovic, M.; Gago-Ferrero, P.; Gros, M. Pressurized Liquid Extraction (PLE) and QuEChERS Evaluation for the Analysis of Antibiotics in Agricultural Soils. MethodsX 2020, 7, 101171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.-F.; Ying, G.-G.; Zhao, J.-L.; Tao, R.; Su, H.-C.; Chen, F. Simultaneous Determination of Four Classes of Antibiotics in Sediments of the Pearl Rivers Using RRLC–MS/MS. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 3424–3432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löffler, D.; Ternes, T.A. Determination of Acidic Pharmaceuticals, Antibiotics and Ivermectin in River Sediment Using Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2003, 1021, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, Y.; Guo, X.; Hu, J.; Li, S.; Zhang, R.; Gao, Q.; Yang, X.; Chen, Q.; Sun, W. Occurrence and Risks of Antibiotics in an Urban River in Northeastern Tibetan Plateau. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 20054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, M.J.; Paíga, P.; Silva, A.; Llaguno, C.P.; Carvalho, M.; Vázquez, F.M.; Delerue-Matos, C. Antibiotics and Antidepressants Occurrence in Surface Waters and Sediments Collected in the North of Portugal. Chemosphere 2020, 239, 124729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmona, E.; Andreu, V.; Picó, Y. Multi-Residue Determination of 47 Organic Compounds in Water, Soil, Sediment and Fish—Turia River as Case Study. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2017, 146, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morales-Muñoz, S.; Luque-García, J.L.; Luque de Castro, M.D. Continuous Microwave-Assisted Extraction Coupled with Derivatization and Fluorimetric Monitoring for the Determination of Fluoroquinolone Antibacterial Agents from Soil Samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2004, 1059, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prat, M.D.; Ramil, D.; Compañó, R.; Hernández-Arteseros, J.A.; Granados, M. Determination of Flumequine and Oxolinic Acid in Sediments and Soils by Microwave-Assisted Extraction and Liquid Chromatography-Fluorescence. Anal. Chim. Acta 2006, 567, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udalova, A.Y.; Dmitrienko, S.G.; Apyari, V.V. Methods for the Separation, Preconcentration, and Determination of Tetracycline Antibiotics. J. Anal. Chem. 2015, 70, 661–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popova, I.E.; Morra, M.J.; Parikh, S.J. Pressurized Liquid Extraction of Six Tetracyclines from Agricultural Soils. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part B 2019, 54, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowara, A.; Burhenne, J.; Spiteller, M. Binding of Fluoroquinolone Carboxylic Acid Derivatives to Clay Minerals. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1997, 45, 1459–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Sun, K.; Gao, B.; Zhang, G.; Liu, X.; Zhao, Y. Adsorption of Tetracycline on Soil and Sediment: Effects of PH and the Presence of Cu(II). J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 190, 856–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Mozaz, S.; Vaz-Moreira, I.; Varela Della Giustina, S.; Llorca, M.; Barceló, D.; Schubert, S.; Berendonk, T.U.; Michael-Kordatou, I.; Fatta-Kassinos, D.; Martinez, J.L.; et al. Antibiotic Residues in Final Effluents of European Wastewater Treatment Plants and Their Impact on the Aquatic Environment. Environ. Int. 2020, 140, 105733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.-J.; Ying, G.-G.; Zhao, J.-L.; Yang, J.-F.; Wang, L.; Yang, B.; Liu, S. Trends in the Occurrence of Human and Veterinary Antibiotics in the Sediments of the Yellow River, Hai River and Liao River in Northern China. Environ. Pollut. 2011, 159, 1877–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission Commission Implementing Decision (EU) 2018/840 of 5 June 2018 Establishing a Watch List of Substances for Union-Wide Monitoring in the Field of Water Policy Pursuant to Directive 2008/105/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council and Repealing Commission Implementing Decision (EU) 2015/495. Available online: http://data.europa.eu/eli/dec_impl/2018/840/oj/eng (accessed on 3 December 2021).
- Brown, P.C.; Borowska, E.; Schwartz, T.; Horn, H. Impact of the Particulate Matter from Wastewater Discharge on the Abundance of Antibiotic Resistance Genes and Facultative Pathogenic Bacteria in Downstream River Sediments. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 649, 1171–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiaia-Hernandez, A.C.; Keller, A.; Wächter, D.; Steinlin, C.; Camenzuli, L.; Hollender, J.; Krauss, M. Long-Term Persistence of Pesticides and TPs in Archived Agricultural Soil Samples and Comparison with Pesticide Application. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 10642–10651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, M.T.; Lee, E.A.; Ferrell, G.M.; Baumgarner, J.E.; Varns, J. Scientific Investigations Report-Evaluation of Offline Tandem and Online Solid-Phase Extraction with Liquid Chromatography/Electrospray Ionization-Mass Spectrometry for Analysis of Antibiotics in Ambient Water and Comparison to an Independent Method; USGS Numbered Series 2007-5021; Lawrence Publishing Service Center: Lawrence, KS, USA, 2007; p. 28. [Google Scholar]
- Chiaia-Hernandez, A.C.; Krauss, M.; Hollender, J. Screening of Lake Sediments for Emerging Contaminants by Liquid Chromatography Atmospheric Pressure Photoionization and Electrospray Ionization Coupled to High Resolution Mass Spectrometry. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 976–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Y.; Zhang, W.; Gu, C.; Xagoraraki, I.; Li, H. Determination of Pharmaceuticals in Biosolids Using Accelerated Solvent Extraction and Liquid Chromatography/Tandem Mass Spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2011, 1218, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speltini, A.; Sturini, M.; Maraschi, F.; Profumo, A.; Albini, A. Analytical Methods for the Determination of Fluoroquinolones in Solid Environmental Matrices. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2011, 30, 1337–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bavumiragira, J.P.; Ge, J.; Yin, H. Fate and Transport of Pharmaceuticals in Water Systems: A Processes Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 823, 153635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulard, L.; Dierkes, G.; Schlüsener, M.P.; Wick, A.; Koschorreck, J.; Ternes, T.A. Spatial Distribution and Temporal Trends of Pharmaceuticals Sorbed to Suspended Particulate Matter of German Rivers. Water Res. 2020, 171, 115366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McArdell, C.S.; Molnar, E.; Suter, M.J.-F.; Giger, W. Occurrence and Fate of Macrolide Antibiotics in Wastewater Treatment Plants and in the Glatt Valley Watershed, Switzerland. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 5479–5486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PubChem. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ (accessed on 18 May 2022).
- ChemicalBook—Chemical Search Engine. Available online: https://www.chemicalbook.com/ProductIndex_DE.aspx (accessed on 18 May 2022).
- MacLeod, S.L.; McClure, E.L.; Wong, C.S. Laboratory Calibration and Field Deployment of the Polar Organic Chemical Integrative Sampler for Pharmaceuticals and Personal Care Products in Wastewater and Surface Water. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2007, 26, 2517–2529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

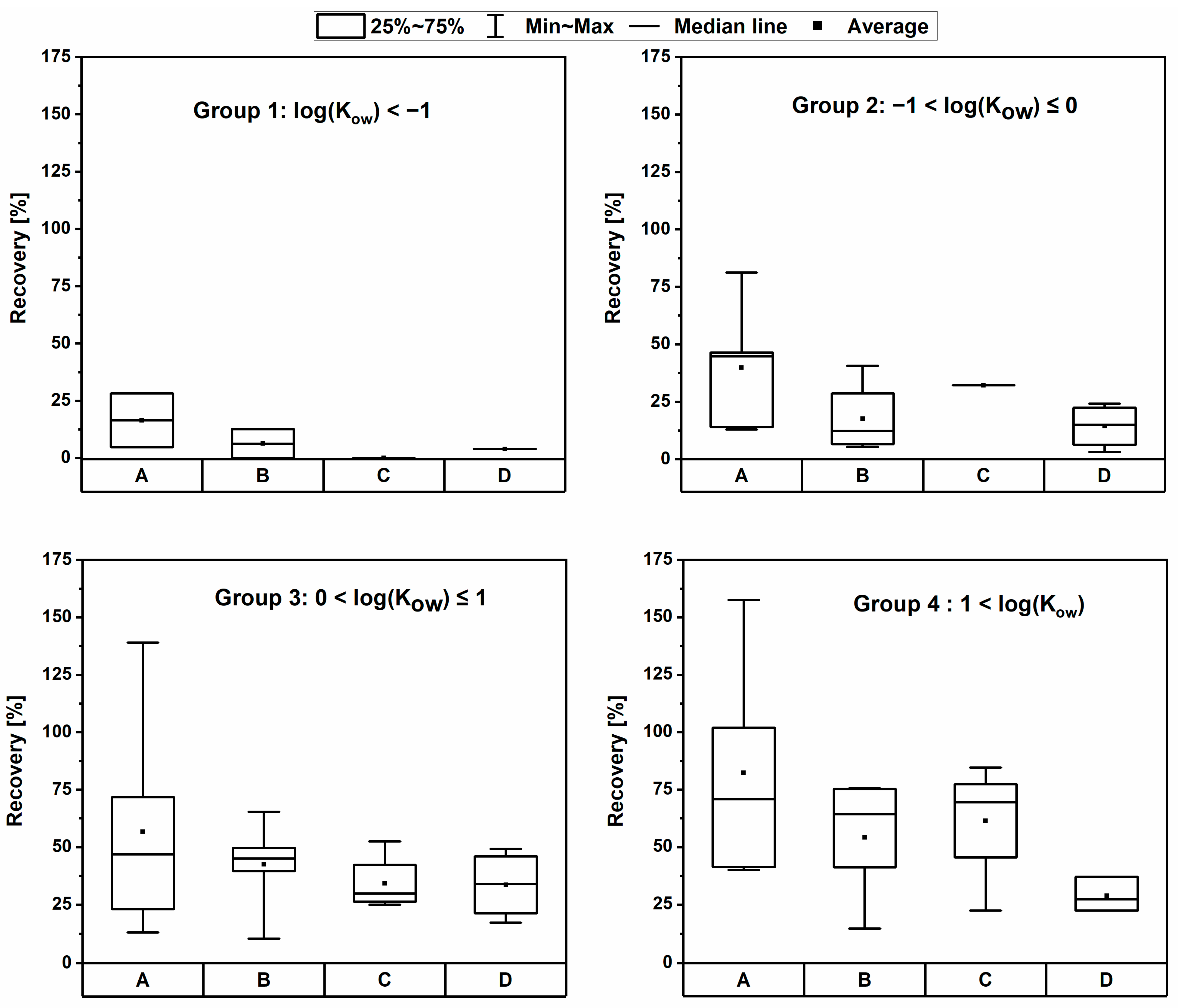
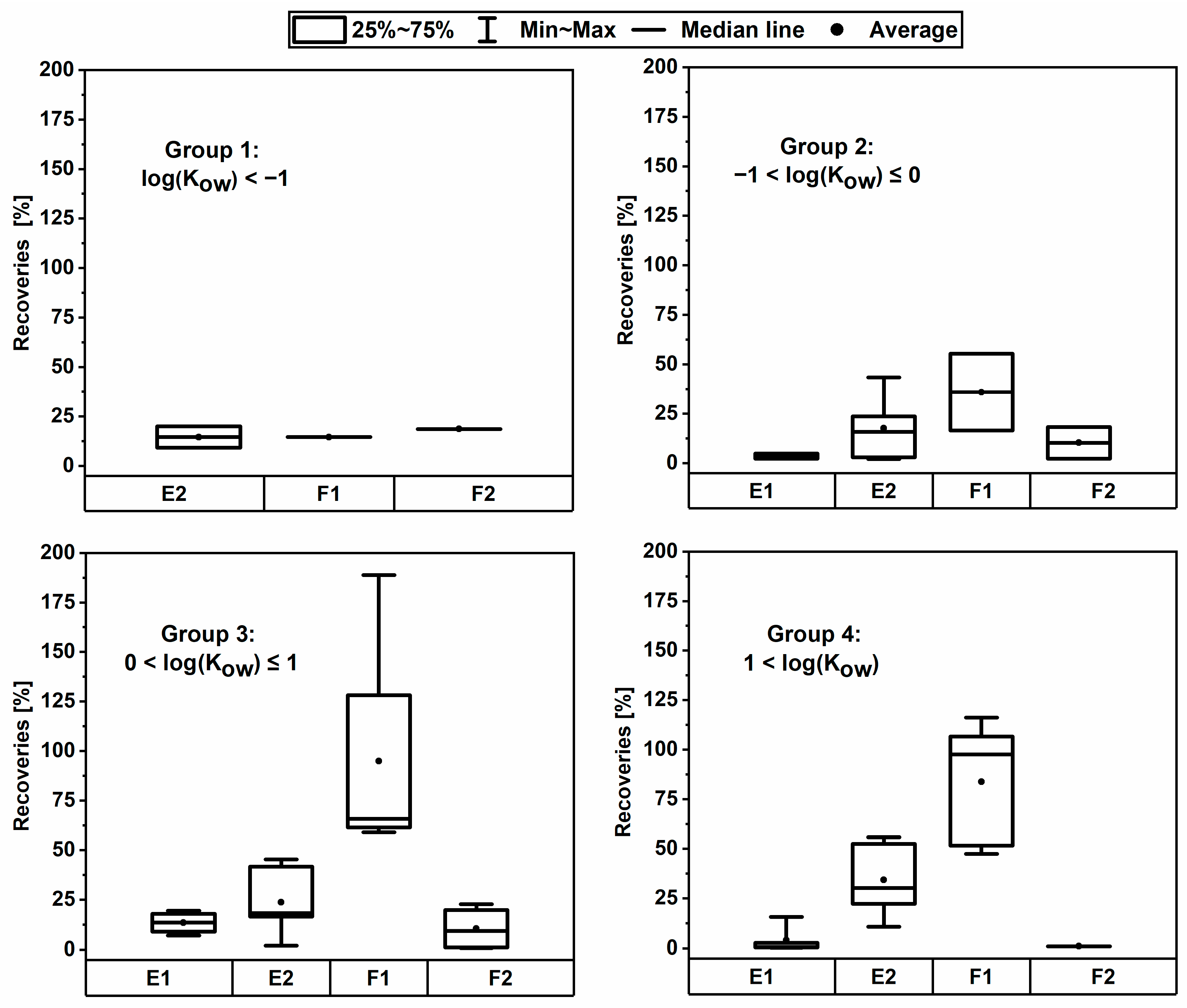
| Protocol | A (a) | B (b) | C (c) | D (a,d) | E (e) | F (a,e) | G (a) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Extraction steps | One | One | One | One | Two consecutives | Two consecutives | One | ||
| 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | ||||||
| Organic solvent | ACN | MeOH/ ACN | MeOH | MeOH + 0.2% NH4OH | EtOAc/ ACE | ACE | ACE | ACN | ACN |
| Aqueous solvent | 50 mM H3PO4 pH 2 | 0.2 M CA pH 4.5 | 50 mM phosphate buffer pH 7 | 50 mM H3PO4 pH 2 | - | 1% H3PO4 | 1% H3PO4 | 50 mM H3PO4 pH 2 | 50 mM H3PO4 pH 2 |
| Solvent ratio (%) | 50/50 | 40/40/20 | 50/50 | 50/50 | 66/33 | 66/33 | 66/33 | 50/50 | 50/50 |
| Cycles | 6 | 2 | 2 | 6 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 6 | 2 |
| Temperature (°C) | 100 | 80 | 100 | 100 | 80 | 80 | 80 | 100 | 100 |
| Static time (min) | 15 | 10 | 5 | 15 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 15 | 10 |
| Rinse volume (%) | 150 | 100 | 150 | 150 | 60 | 60 | 60 | 150 | 150 |
| Purge time (s) | 300 | 40 | 100 | 300 | 120 | 120 | 120 | 300 | 300 |
| Group No. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Log(Kow) Range | x ≤ −1 | −1 < x ≤ 0 | 0 < x ≤ 1 | 1 < x |
| Recovery [%] | 1.1–4.2 | 0.2–26.3 | 0.8–64.8 | 13.7–48.8 |
| Coefficient of variation (CV) [%] | 16–32 | 4–80 | 7–61 | 14–48 |
| Standard deviation | 0.2–1.3 | 0.9–5.1 | 0.1–12.8 | 2.4–10.4 |
| Matrix effect | 0.42–0.83 | 0.08–0.83 | 0.04–0.29 | 0.03–0.66 |
| Compounds | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Location | CFC | EFC | NFC | OFC | CTM | ETM | ETM-H2O | RTM | SDZ | SDM | SMZ | SMX | SPD | TMP | CDC | CTC | DCX | OTC | TCT |
| 1 | 2.9–4.5 | n.d. | n.d. | 0.8–1.3 | n.d. | <MLOD | 2.8 * | n.d. | <MLOD | <MLOQ | n.d. | <MLOQ | 4.2–7.0 | 0.8–1.5 | 5.5–11.0 | n.d. | <MLOQ | n.d. | n.d. |
| 2 | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | 0.3–0.4 | n.d. | n.d. | 0.8–12.8 | n.d. | <MLOD | n.d. | n.d. | <MLOQ | 2.2–3.0 | 0.5 * | 2.6–4.8 | n.d. | <MLOQ | n.d. | n.d. |
| 3 | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | 0.4–0.5 | n.d. | <MLOD | <MLOQ | n.d. | <MLOD | <MLOD | n.d. | n.d. | 4.9–8.4 | 1.0 * | 3.9–7.3 | n.d. | <MLOQ | n.d. | n.d. |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chabilan, A.; Landwehr, N.; Horn, H.; Borowska, E. Impact of log(Kow) Value on the Extraction of Antibiotics from River Sediments with Pressurized Liquid Extraction. Water 2022, 14, 2534. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14162534
Chabilan A, Landwehr N, Horn H, Borowska E. Impact of log(Kow) Value on the Extraction of Antibiotics from River Sediments with Pressurized Liquid Extraction. Water. 2022; 14(16):2534. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14162534
Chicago/Turabian StyleChabilan, Amélie, Nicolette Landwehr, Harald Horn, and Ewa Borowska. 2022. "Impact of log(Kow) Value on the Extraction of Antibiotics from River Sediments with Pressurized Liquid Extraction" Water 14, no. 16: 2534. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14162534
APA StyleChabilan, A., Landwehr, N., Horn, H., & Borowska, E. (2022). Impact of log(Kow) Value on the Extraction of Antibiotics from River Sediments with Pressurized Liquid Extraction. Water, 14(16), 2534. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14162534







