Latitudinal Dynamics of Vibrio along the Eastern Coastline of Australia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
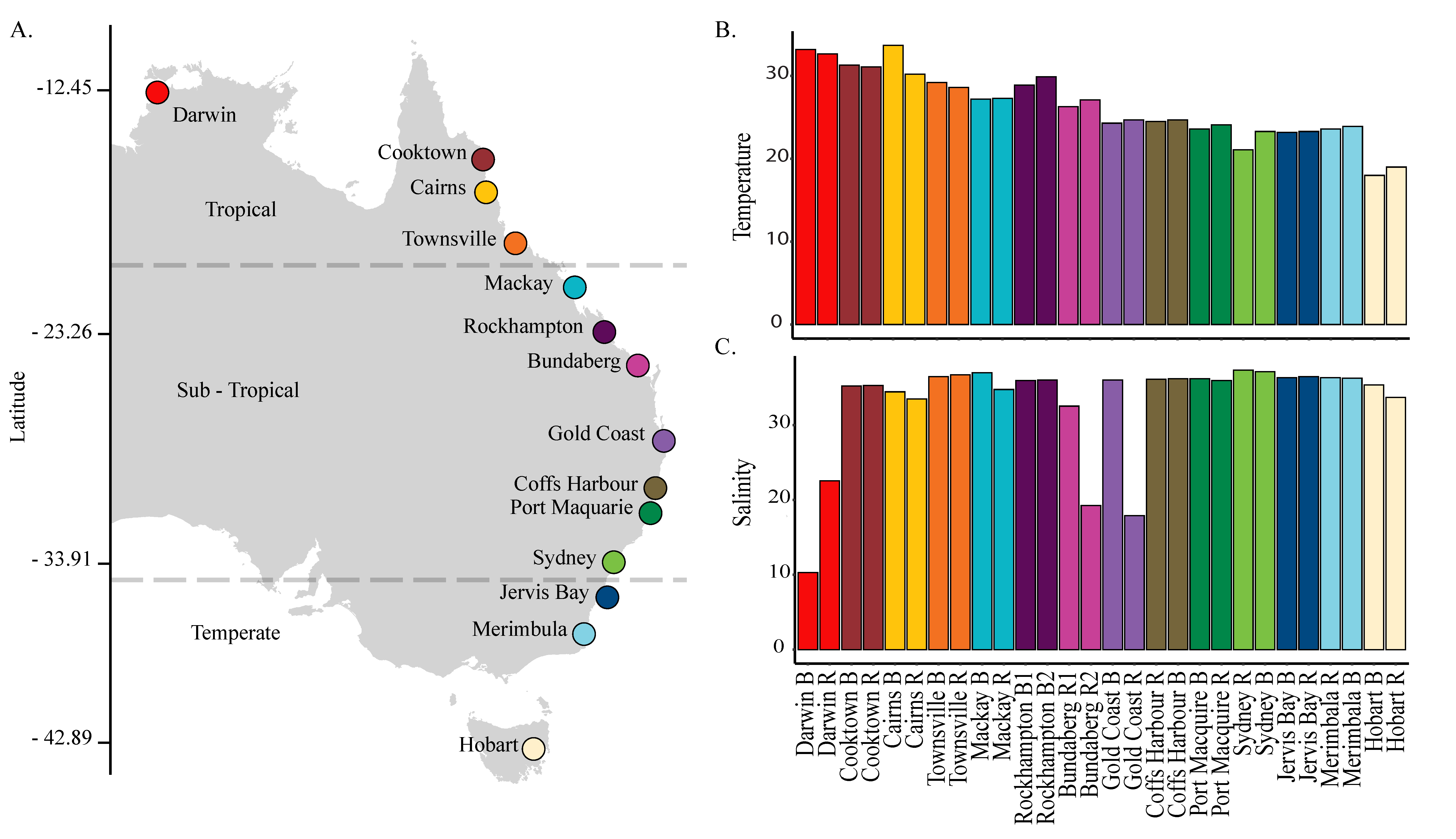
2.1. Sampling Locations and Protocol
2.2. DNA Extraction
2.3. Quantitative PCR (qPCR)
2.4. Digital Droplet Analysis
2.5. 16S rRNA Gene Amplicon Sequencing
2.6. hsp60 Sequencing
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Environmental Conditions
3.2. Quantification of the Total Bacterial Community
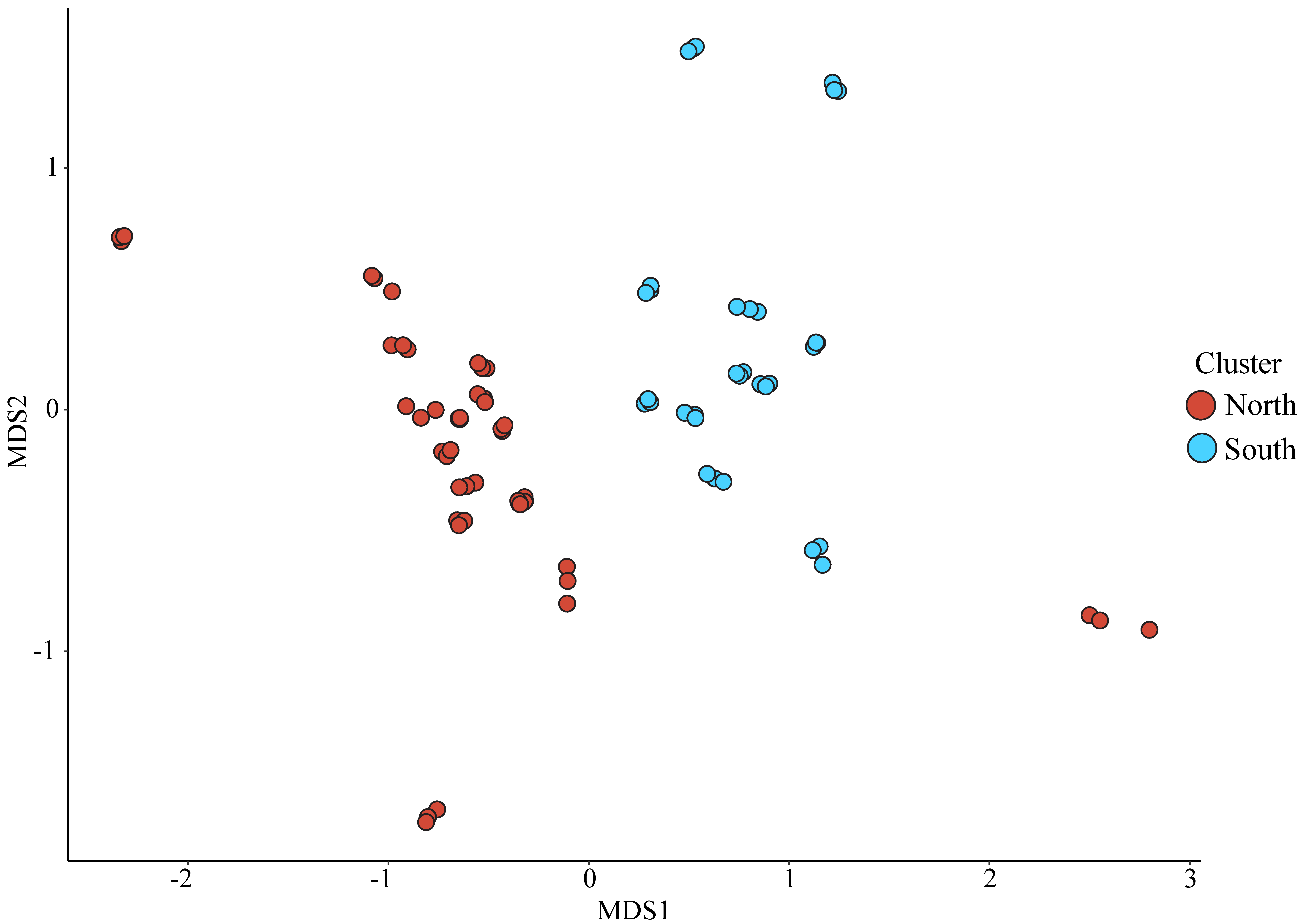
3.3. Bacterial Community Analysis
3.4. Quantification of the Total Vibrio Community
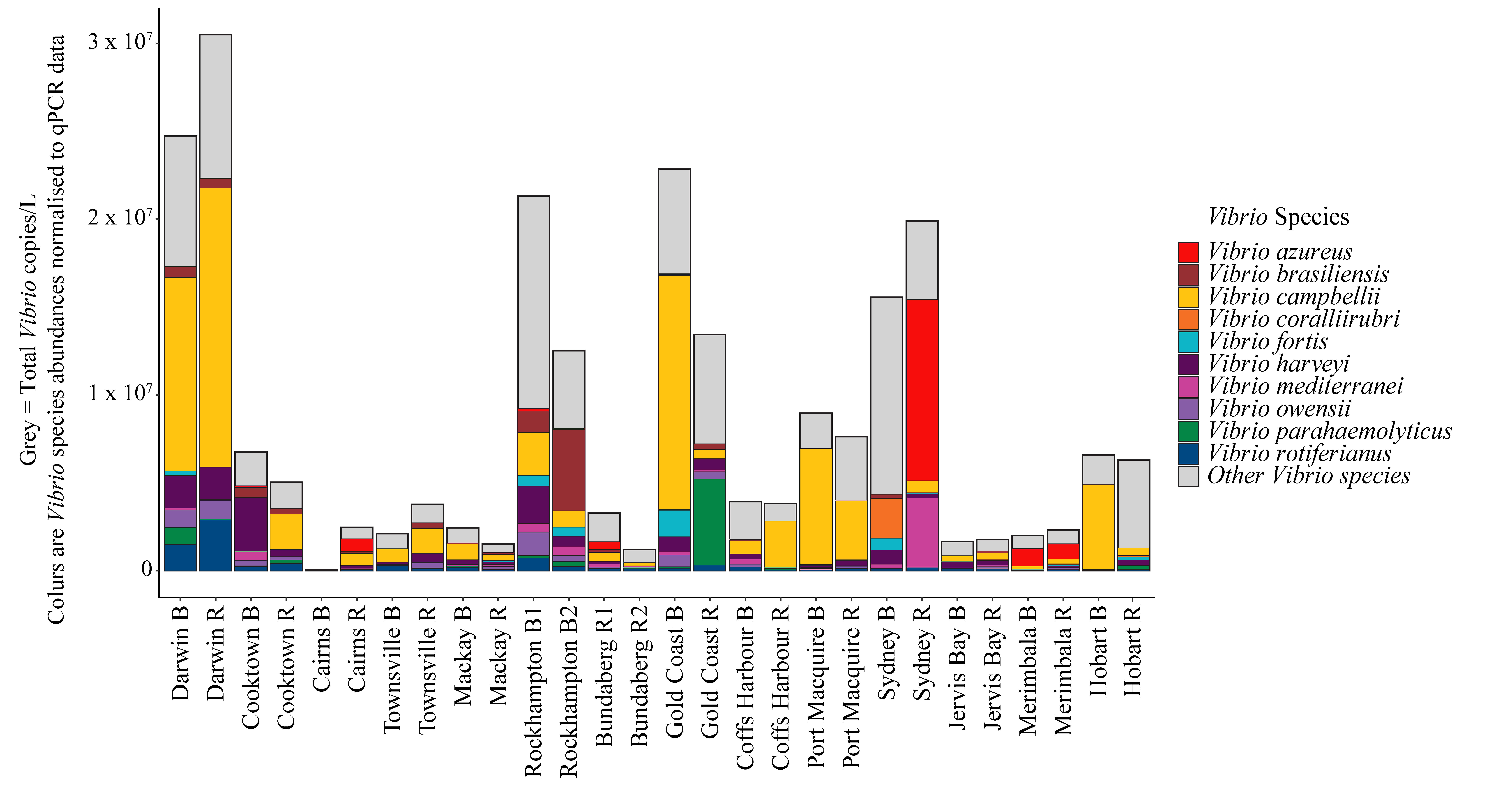
3.5. Vibrio Diversity
3.6. Potentially Pathogenic Vibrio Species: Vibrio Cholerae, Vibrio parahaemolyticus and Vibrio vulnificus
4. Discussion
4.1. Latitudinal Trends in Vibrio Abundance and Diversity
4.2. Latitudinal Patterns in Vibrio Pathogens
4.3. Implications of High Levels of Vibrio Bacteria along Australia’s East Coast
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chapin, S.F.; Zavaleta, E.S.; Eviner, V.T.; Naylor, R.L.; Vitousek, P.M.; Reynolds, H.L.; Hooper, D.U.; Lavorel, S.; Sala, O.E.; Hobbie, S.E.; et al. Consequences of changing biodiversity. Nature 2000, 405, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, A.G. Latitudinal Variations in Organic Diversity. Evolution 1960, 14, 64–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillebrand, H. Strength, slope and variability of marine latitudinal gradients. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2004, 273, 251–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pianka, E.R. Latitudinal Gradients in Species Diversity: A review of Concepts. Am. Nat. 1966, 100, 33–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunday, J.M.; Bates, A.E.; Dulvy, N.K. Thermal tolerance and the global redistribution of animals. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2012, 2, 686–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahram, M.; Hildebrand, F.; Forslund, S.K.; Anderson, J.L.; Soudzilovskaia, N.A.; Bodegom, P.M.; Bengtsson-Palme, J.; Anslan, S.; Coelho, L.P.; Harend, H.; et al. Structure and function of the global topsoil microbiome. Nature 2018, 560, 233–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raes, E.J.; Bodrossy, L.; van de Kamp, J.; Bissett, A.; Waite, A.M. Marine bacterial richness increases towards higher latitudes in the eastern Indian Ocean. Limnol. Oceanogr. Lett. 2018, 3, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, K.; Jablonski, D.; Valentine, J.W.; Rosenberg, G. Marine latitudinal diversity gradients: Tests of causal hypotheses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 3699–3702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, J.H. Two decades of homage to santa rosalia: Toward a general theory of diversity. Integr. Comp. Biol. 1981, 21, 877–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, A.P.; Brown, J.H.; Gillooly, J.F. Global biodiversity, biochemical kinetics, and the energetic-equivalence rule. Science 2002, 297, 1545–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, J.H.; Gillooly, J.F.; Allen, A.P.; Savage, V.M.; West, G.B. Toward a Metabolic Theory of Ecology. Ecol. Soc. Am. 2004, 85, 1771–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuhrman, J.A.; Steele, J.A.; Hewson, I.; Schwalbach, M.S.; Brown, M.V.; Green, J.L.; Brown, J.H. A latitudinal diversity gradient in planktonic marine bacteria. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 7774–7778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pommier, T.; Canbäck, B.; Riemann, L.; Boström, K.H.; Simu, K.; Lundberg, P.; Tunlid, A.; Hagström, Å. Global patterns of diversity and community structure in marine bacterioplankton. Mol. Ecol. 2007, 16, 867–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flombaum, P.; Gallegos, J.L.; Gordillo, R.A.; Rincón, J.; Zabala, L.L.; Jiao, N.; Karl, D.M.; Li, W.K.W.; Lomas, M.W.; Veneziano, D.; et al. Present and future global distributions of the marine Cyanobacteria Prochlorococcus and Synechococcus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 9824–9829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, J.; Liu, J.; Wang, X.; Lin, H.; Liu, J.; Zhou, S.; Sun, H.; Zhang, X.-H. Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Free-Living and Particle-Associated Vibrio Communities in the Northern Chinese Marginal Seas. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2019, 85, e00217-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Dong, K.; Jiang, G.; Tang, J.; Xu, Q.; Li, X.; Kang, Z.; Zou, S.; Chen, X.; Adams, J.M.; et al. Stochastic processes dominate marine free-living Vibrio community assembly in a subtropical gulf. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2020, 96, fiaa198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyholm, S.V.; McFall-Ngai, M.J. A lasting symbiosis: How the Hawaiian bobtail squid finds and keeps its bioluminescent bacterial partner. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 666–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Istiqomah, I.; Sukardi, M.; Isnansetyo, A. Review Vibriosis Management in Indonesian Marine Fish Farming. E3S Web Conf. 2020, 147, 01001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kushmaro, A.; Banin, E.; Loya, Y.; Stackebrandt, E.; Rosenberg, E. Vibrio shiloi sp. nov., the causative agent of bleaching of the coral Oculina patagonica. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2001, 51, 1383–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruto, M.; Labreuche, Y.; James, A.; Piel, D.; Chenivesse, S.; Petton, B.; Polz, M.F.; Le Roux, F. Ancestral gene acquisition as the key to virulence potential in environmental Vibrio populations. ISME J. 2018, 12, 2954–2966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, K.F.J.; Bondad-Reantaso, M.G. Impacts of acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease on commercial shrimp aquaculture. Rev. Sci. Tech. 2019, 38, 477–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seong Wei, L.; Wee, W. Diseases in Aquaculture. Res. J. Anim. Vet. Sci. 2014, 7, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Lafferty, K.D.; Harvell, C.D.; Conrad, J.M.; Friedman, C.S.; Kent, M.L.; Kuris, A.M.; Powell, E.N.; Rondeau, D.; Saksida, S.M. Infectious diseases affect marine fisheries and aquaculture economics. Annu. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2015, 7, 471–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, M.; Nelson, A.R.; Lopez, A.L.; Sack, D.A. Updated global burden of cholera in endemic countries. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2015, 9, e0003832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daniels, N.A.; Mackinnon, L.; Bishop, R.; Altekruse, S.; Ray, B.; Hammond, R.M.; Thompson, S.; Wilson, S.; Bean, N.H.; Griffin, P.M.; et al. Vibrio parahaemolyticus infections in the United States, 1973–1998. J. Infect. Dis. 2000, 181, 1661–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rippey, S.R. Infectious diseases associated with molluscan shellfish consumption. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 1994, 7, 419–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker-Austin, C.; Trinanes, J.; Gonzalez-Escalona, N.; Martinez-Urtaza, J. Non-Cholera Vibrios: The Microbial Barometer of Climate Change. Trends Microbiol. 2017, 25, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trinanes, J.; Martinez-Urtaza, J. Future scenarios of risk of Vibrio infections in a warming planet: A global mapping study. Lancet Planet. Health 2021, 5, e426–e435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vezzulli, L.; Colwell, R.R.; Pruzzo, C. Ocean Warming and Spread of Pathogenic Vibrios in the Aquatic Environment. Microb. Ecol. 2013, 65, 817–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eiler, A.; Johansson, M.; Bertilsson, S. Environmental influences on Vibrio populations in northern temperate and boreal coastal waters (Baltic and Skagerrak Seas). Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 6004–6011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackwell, K.D.; Oliver, J.D. The ecology of Vibrio vulnificus, Vibrio cholerae, and Vibrio parahaemolyticus in North Carolina Estuaries. J. Microbiol. 2008, 46, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Froelich, B.; Bowen, J.; Gonzalez, R.; Snedeker, A.; Noble, R. Mechanistic and statistical models of total vibrio abundance in the neuse river estuary. Water Res. 2013, 47, 5783–5793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heidelberg, J.F.; Heidelberg, K.B.; Colwell, R.R. Seasonality of chesapeake bay bacterioplankton species. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 68, 5488–5497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nigro, O.D.; Hou, A.; Vithanage, G.; Fujioka, R.S.; Steward, G.F. Temporal and spatial variability in culturable pathogenic Vibrio spp. in Lake Pontchartrain, Louisiana, following hurricanes katrina and rita. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 5384–5393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, J.W.; Good, B.; Cole, D.; Lipp, E.K. Plankton composition and environmental factors contribute to Vibrio seasonality. ISME J. 2009, 3, 1082–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wetz, J.J.; Blackwood, A.D.; Fries, J.S.; Williams, Z.F.; Noble, R.T. Trends in total Vibrio spp. and Vibrio vulnificus concentrations in the eutrophic Neuse River Estuary, North Carolina, during storm events. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2008, 53, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberbeckmann, S.; Fuchs, B.M.; Meiners, M.; Wichels, A.; Wiltshire, K.H.; Gerdts, G. Seasonal Dynamics and Modeling of a Vibrio Community in Coastal Waters of the North Sea. Microb. Ecol. 2012, 63, 543–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, J.L.; Fries, J.S.; Noble, R.T. Dynamics and predictive modelling of Vibrio spp. in the Neuse River Estuary, North Carolina, USA. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 10, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Randa, M.A.; Polz, M.F.; Lim, E. Effects of temperature and salinity on Vibrio vulnificus population dynamics as assessed by quantitative PCR. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 5469–5476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takemura, A.F.; Chien, D.M.; Polz, M.F. Associations and dynamics of vibrionaceae in the environment, from the genus to the population level. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madakumbura, G.D.; Goldenson, N.; Hall, A. Anthropogenic influence on extreme precipitation over global land areas seen in multiple observational datasets. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 3944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padovan, A.; Siboni, N.; Kaestli, M.; King, W.L.; Seymour, J.R.; Gibb, K. Occurrence and dynamics of potentially pathogenic vibrios in the wet-dry tropics of northern Australia. Mar. Environ. Res. 2021, 169, 105405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siboni, N.; Balaraju, V.; Carney, R.; Labbate, M.; Seymour, J.R. Spatiotemporal dynamics of Vibrio spp. within the Sydney Harbour estuary. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hobday, A.J.; Loug, J.M. Projected climate change in Australian marine and freshwater environments. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2011, 62, 1000–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, M.T.; Taylor, L.T.; DeLong, E.F. Quantitative analysis of small-subunit rRNA genes in mixed microbial populations via 5′-nuclease assays. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2000, 66, 4605–4614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, F.L.; Iida, T.; Swings, J. Biodiversity of Vibrios. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2004, 68, 403–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizvi, A.V.; Bej, A.K. Multiplexed real-time PCR amplification of tlh, tdh and trh genes in Vibrio parahaemolyticus and its rapid detection in shellfish and Gulf of Mexico water. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek. Int. J. Gen. Mol. Microbiol. 2010, 98, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gubala, A.J.; Proll, D.F. Molecular-beacon multiplex real-time PCR assay for detection of Vibrio cholerae. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 6424–6428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bibiloni-Isaksson, J.; Seymour, J.R.; Ingleton, T.; van de Kamp, J.; Bodrossy, L.; Brown, M.V. Spatial and temporal variability of aerobic anoxygenic photoheterotrophic bacteria along the east coast of Australia. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 18, 4485–4500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hindson, C.M.; Chevillet, J.R.; Briggs, H.A.; Gallichotte, E.N.; Ruf, I.K.; Hindson, B.J.; Vessella, R.L.; Tewari, M. Absolute quantification by droplet digital PCR versus analog real-time PCR. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 1003–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, S.; Tomita, J.; Nishioka, K.; Hisada, T.; Nishijima, M. Development of a Prokaryotic Universal Primer for Simultaneous Analysis of Bacteria and Archaea Using Next-Generation Sequencing. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e105592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illumina. 16S Metagenomic Sequencing Library. Preparing 16S Ribosomal RNA Gene Amplicons for the Illumina MiSeq System; Illumina: San Diego, CA, USA, 2013; pp. 1–28. [Google Scholar]
- Callahan, B.J.; Mcmurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.A.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, M. Cutadapt Removes Adapter Sequences from High-Throughput Sequencing Reads. EMBnet J. 2011, 17, 10–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillou, L.; Bachar, D.; Audic, S.; Bass, D.; Berney, C.; Bittner, L.; Boutte, C.; Burgaud, G.; De Vargas, C.; Decelle, J.; et al. The Protist Ribosomal Reference database (PR2): A catalog of unicellular eukaryote Small Sub-Unit rRNA sequences with curated taxonomy. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, 597–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, P. Computer program review VEGAN, a package of R functions for community ecology. J. Veg. Sci. 2003, 14, 927–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, W.L.; Siboni, N.; Kahlke, T.; Green, T.J.; Labbate, M.; Seymour, J.R. A New High Throughput Sequencing Assay for Characterizing the Diversity of Natural Vibrio Communities and Its Application to a Pacific Oyster Mortality Event. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magoč, T.; Salzberg, S.L. FLASH: Fast length adjustment of short reads to improve genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2957–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schloss, P.D.; Westcott, S.L.; Ryabin, T.; Hall, J.R.; Hartmann, M.; Hollister, E.B.; Lesniewski, R.A.; Oakley, B.B.; Parks, D.H.; Robinson, C.J.; et al. Introducing mothur: Open-source, platform-independent, community-supported software for describing and comparing microbial communities. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 7537–7541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rognes, T.; Flouri, T.; Nichols, B.; Quince, C.; Mahé, F. VSEARCH: A versatile open-source tool for metagenomics. PeerJ 2016, 4, e2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammer, Ø.; Harper, D.A.T.; Ryan, P.D. Past: Paleontological statistics software package for education and data analysis. Curr. Sci. 2001, 4, 4–9. [Google Scholar]
- Martinez Arbizu, P. PairwiseAdonis: Pairwise Multilevel Comparison Using, R Package version 0.4; GitHub, Inc.: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Whitaker, D.; Christman, M. Package ‘clustsig’, version 1.0; GitHub, Inc.: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- De Caceres, M.; Jansen, F. Indicspecies: Relationship between Species and Groups of Sites; R Package Version 1.7.5; GitHub, Inc.: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Albanese, D.; Riccadonna, S.; Donati, C.; Franceschi, P. A practical tool for maximal information coefficient analysis. GigaScience 2018, 7, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilbert, J.A.; Steele, J.A.; Caporaso, J.G.; Steinbrück, L.; Reeder, J.; Temperton, B.; Huse, S.; McHardy, A.C.; Knight, R.; Joint, I.; et al. Defining seasonal marine microbial community dynamics. ISME J. 2012, 6, 298–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Brien, J.; McParland, E.L.; Bramucci, A.R.; Siboni, N.; Ostrowski, M.; Kahlke, T.; Levine, N.M.; Brown, M.V.; van de Kamp, J.; Bodrossy, L.; et al. Biogeographical and seasonal dynamics of the marine Roseobacter community and ecological links to DMSP-producing phytoplankton. ISME Commun. 2022, 2, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, C.N.; Flowers, A.R.; Noriea, N.F.; Zimmerman, A.M.; Bowers, J.C.; DePaola, A.; Grimes, D.J. Relationships between environmental factors and pathogenic vibrios in the northern gulf of Mexico. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 7076–7084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipp, E.K.; Rodriguez-palacios, C.; Rose, J.B. The Ecology and Etiology of Newly Emerging Marine Diseases; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2001; Volume 159, pp. 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, Y.Y.; Lee, C.W.; Bong, C.W.; Lim, J.H.; Narayanan, K.; Sim, E.U.H. Environmental control of Vibrio spp. abundance and community structure in tropical waters. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2019, 95, fiz176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesy, K.; Labrenz, M.; Scales, B.S.; Kreikemeyer, B.; Oberbeckmann, S. Vibrio colonization is highly dynamic in early microplastic-associated biofilms as well as on field-collected microplastics. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Defoirdt, T.; Sorgeloos, P. Monitoring of Vibrio harveyi quorum sensing activity in real time during infection of brine shrimp larvae. ISME J. 2012, 6, 2314–2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, T.J.; Siboni, N.; King, W.L.; Labbate, M.; Seymour, J.R.; Raftos, D. Simulated Marine Heat Wave Alters Abundance and Structure of Vibrio Populations Associated with the Pacific Oyster Resulting in a Mass Mortality Event. Microb. Ecol. 2019, 77, 736–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chimetto Tonon, L.A.; Silva, B.S.D.O.; Moreira, A.P.B.; Valle, C.; Alves, N.; Cavalcanti, G.; Garcia, G.; Lopes, R.M.; Francini-Filho, R.B.; De Moura, R.L.; et al. Diversity and ecological structure of vibrios in benthic and pelagic habitats along a latitudinal gradient in the Southwest Atlantic Ocean. PeerJ 2015, 3, e731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartwick, M.A.; Berenson, A.; Whistler, C.A.; Naumova, E.N.; Jones, S.H. The seasonal microbial ecology of plankton and plankton-associated Vibrio parahaemolyticus in the northeast united states. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2021, 87, e02973-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vezzulli, L.; Baker-Austin, C.; Kirschner, A.; Pruzzo, C.; Martinez-Urtaza, J. Global emergence of environmental non-O1/O139 Vibrio cholerae infections linked with climate change: A neglected research field? Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 22, 4342–4355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker-Austin, C.; Stockley, L.; Rangdale, R.; Martinez-Urtaza, J. Environmental occurrence and clinical impact of Vibrio vulnificus and Vibrio parahaemolyticus: A European perspective. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2010, 2, 7–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker-Austin, C.; Trinanes, J.A.; Taylor, N.G.H.; Hartnell, R.; Siitonen, A.; Martinez-Urtaza, J. Emerging Vibrio risk at high latitudes in response to ocean warming. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2013, 3, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker-Austin, C.; Oliver, J.D.; Alam, M.; Ali, A.; Waldor, M.K.; Qadri, F.; Martinez-Urtaza, J. Vibrio spp. infections. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2018, 4, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doney, S.C.; Ruckelshaus, M.; Emmett Duffy, J.; Barry, J.P.; Chan, F.; English, C.A.; Galindo, H.M.; Grebmeier, J.M.; Hollowed, A.B.; Knowlton, N.; et al. Climate change impacts on marine ecosystems. Ann. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2012, 4, 11–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Williams, N.L.R.; Siboni, N.; King, W.L.; Balaraju, V.; Bramucci, A.; Seymour, J.R. Latitudinal Dynamics of Vibrio along the Eastern Coastline of Australia. Water 2022, 14, 2510. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14162510
Williams NLR, Siboni N, King WL, Balaraju V, Bramucci A, Seymour JR. Latitudinal Dynamics of Vibrio along the Eastern Coastline of Australia. Water. 2022; 14(16):2510. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14162510
Chicago/Turabian StyleWilliams, Nathan L. R., Nachshon Siboni, William L. King, Varunan Balaraju, Anna Bramucci, and Justin R. Seymour. 2022. "Latitudinal Dynamics of Vibrio along the Eastern Coastline of Australia" Water 14, no. 16: 2510. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14162510
APA StyleWilliams, N. L. R., Siboni, N., King, W. L., Balaraju, V., Bramucci, A., & Seymour, J. R. (2022). Latitudinal Dynamics of Vibrio along the Eastern Coastline of Australia. Water, 14(16), 2510. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14162510





