The Estimation of Geothermal Reservoir Temperature Based on Integrated Multicomponent Geothermometry: A Case Study in the Jizhong Depression, North China Plain
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Geological Setting
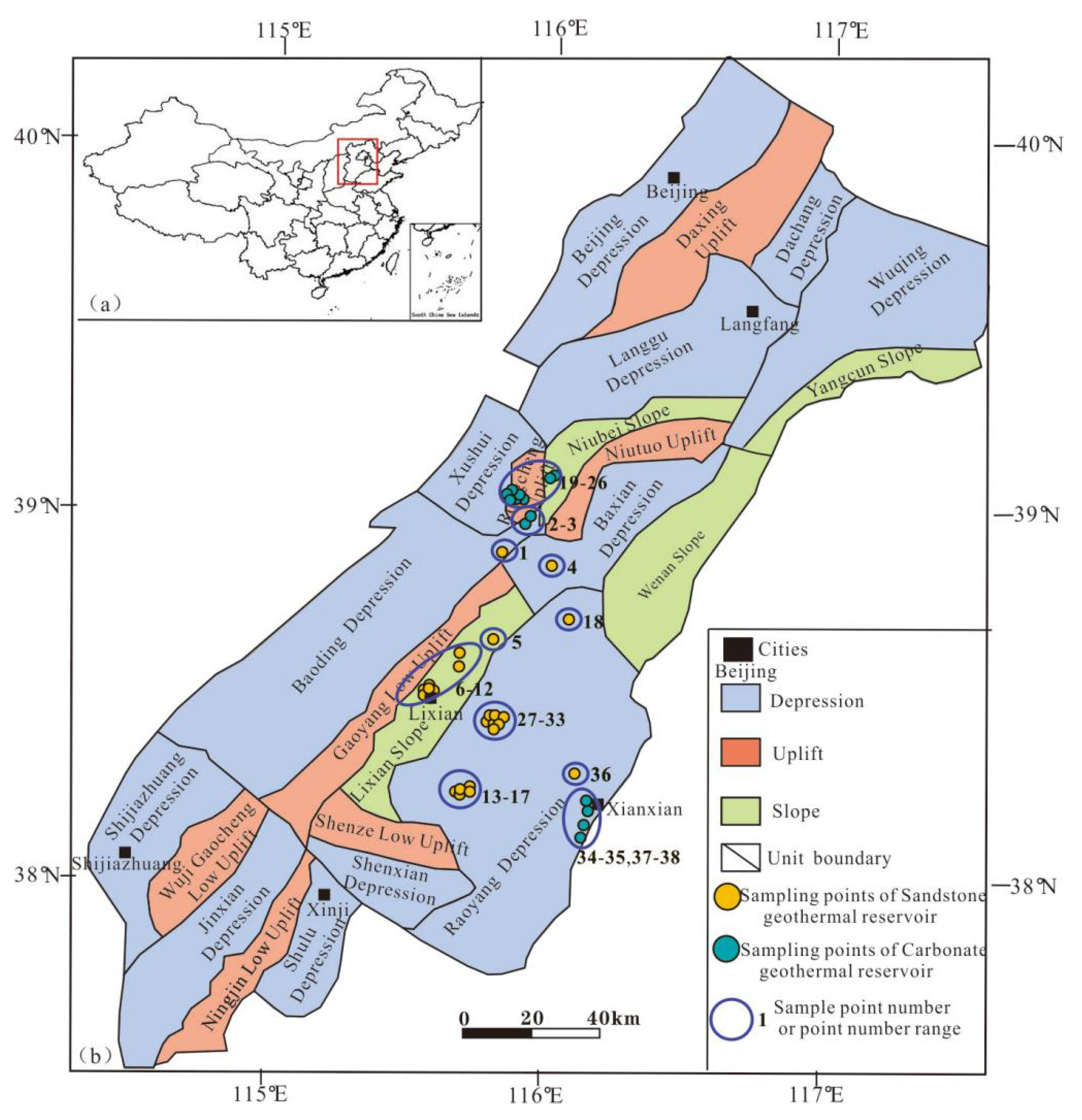
3. Material and Methods
3.1. Geothermal Fluid Samples
3.2. Geothermal Logging
3.3. Geothermometers
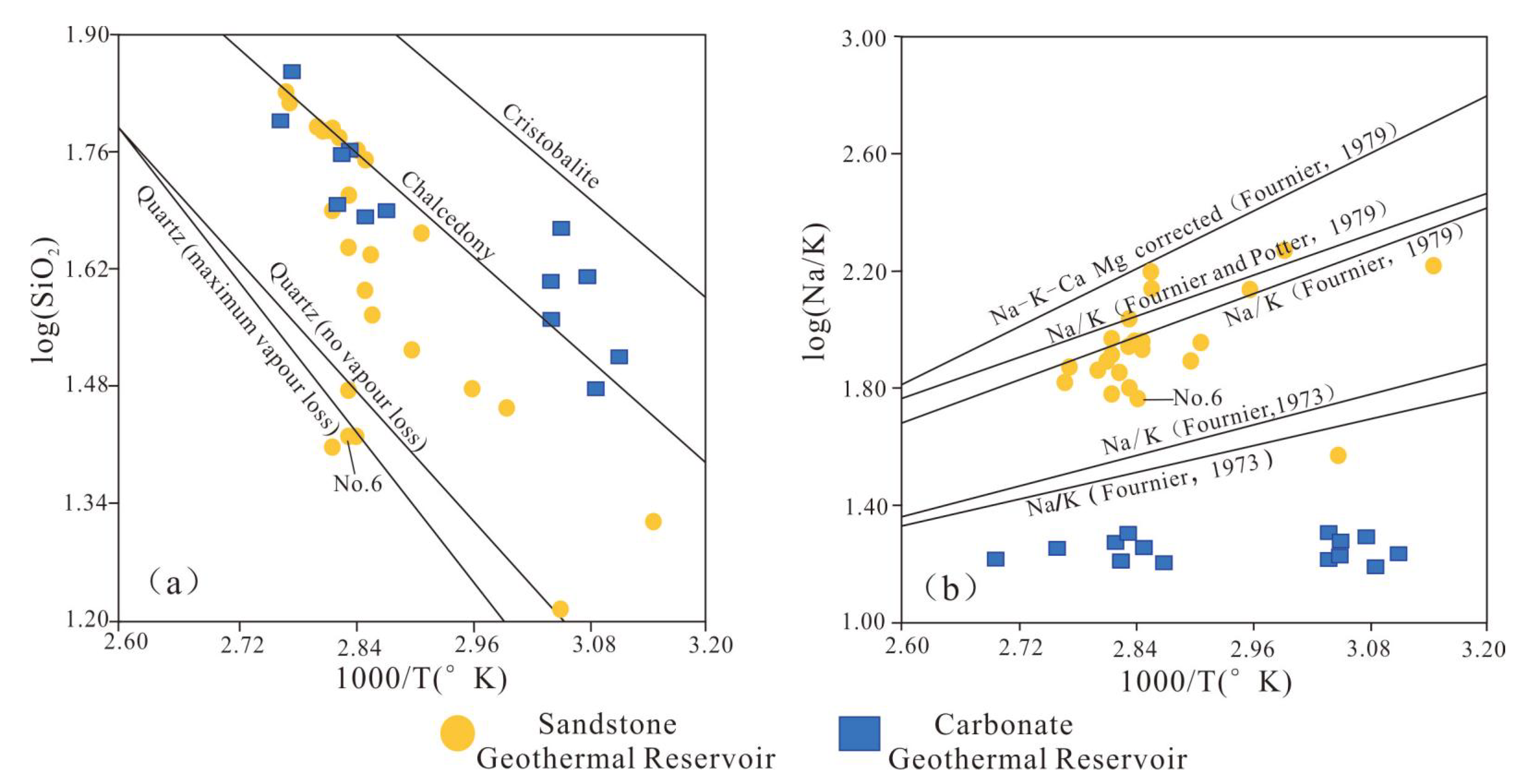
3.3.1. Cation Geothermometer
3.3.2. SiO2 Geothermometer
3.4. SI Method
3.5. Water–Rock Balance Analysis
4. Results
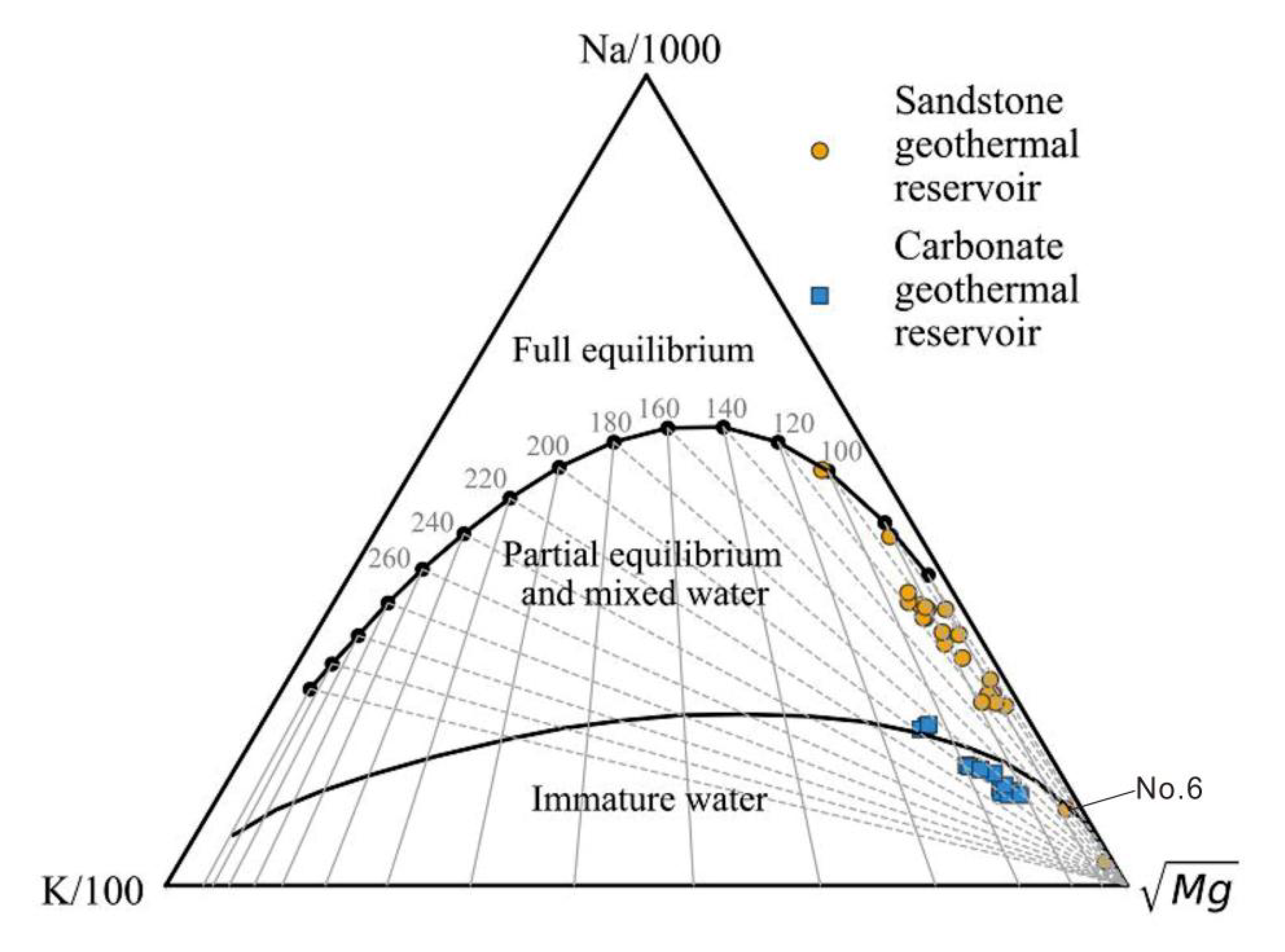
4.1. Hydrogeochemistry
4.2. Borehole Temperature Measurement
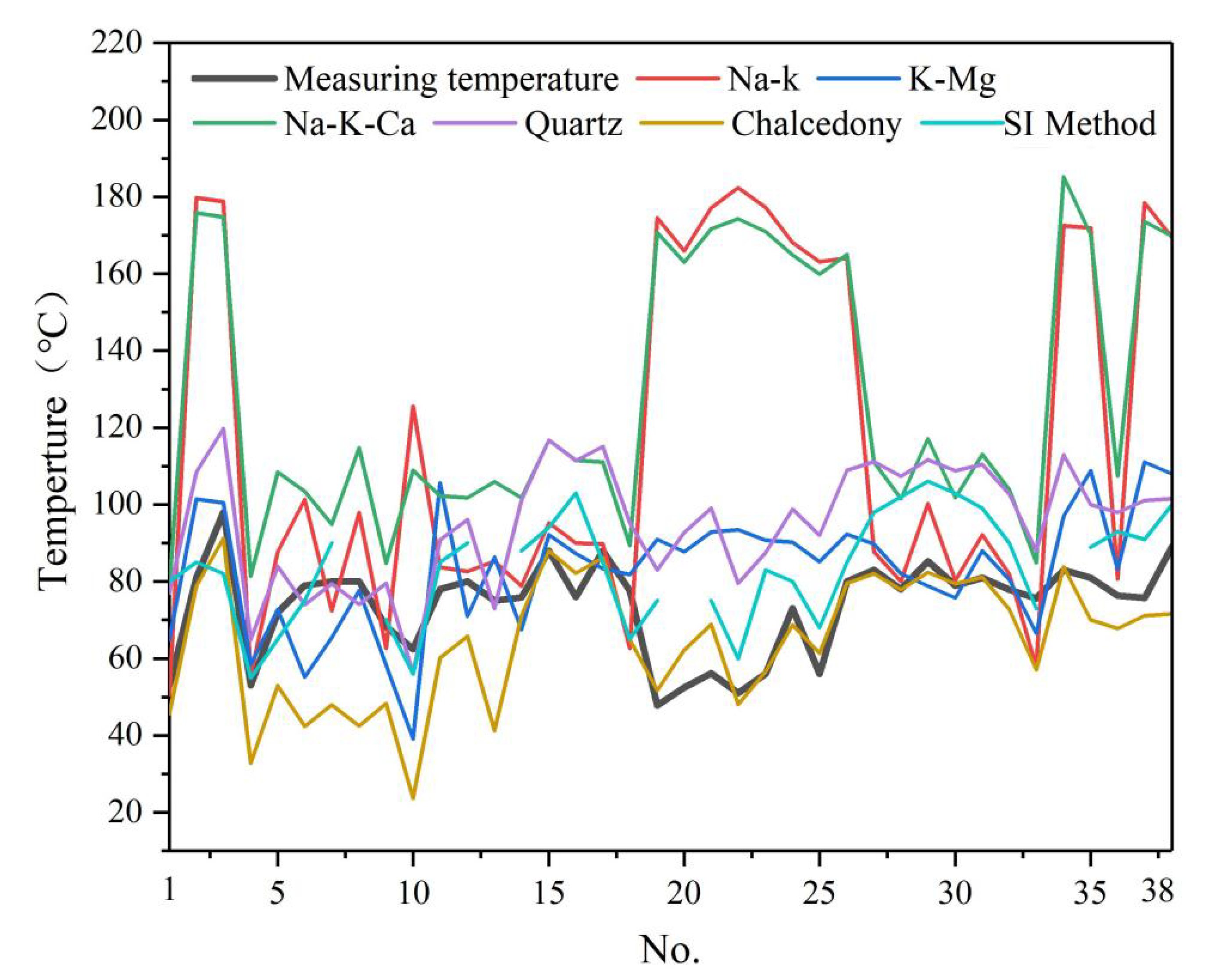
4.3. Geothermal Reservoir Temperature Estimation
4.4. SI Method
4.5. Water–Rock Balance Analysis
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions and Suggestions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, G.L.; Yin, C.X. A model for endogenous management of air pollution in the context of peak carbon neutrality targets. Bus. Econ. 2021, 8, 25–35. [Google Scholar]
- Su, H.; Chen, G.X.; Xing, L.X.; Sun, Z.X.; Cen, L.; Chen, S.F. Characteristics of the front halo elements of typical geothermal fields in Jizhong depression and their geothermal significance. Non-Ferr. Met. (Min. Segm.) 2021, 73, 88–97. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, R.H.; Zou, S.H.; Liu, C.X. Preliminary Discussion on the Development and Utilization of Shallow Geothermal Energy. J. Xuzhou Eng. Coll. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2011, 26, 69–72. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.L.; Zhang, W.; Liang, J.Y.; Lin, W.J.; Liu, Z.M.; Wang, W.L. Evaluation of Geothermal Resource Potential in China. J. Earth Sci. 2017, 38, 449–459. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, M.X. North China Geothermal; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Zhou, X.; Yu, Y.; Liu, C.H.; Zhou, H.Y. Application of Geothermometers to calculation of temperature of Geothermal Reservoirs. Mod. Geol. 2007, 4, 605–612. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Chai, R. Application of geothermometers in the geothermal system. J. Hebei Eng. Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2009, 26, 54–58. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.L.; Mu, W.Q.; Shi, J.M. Hydrogeochemical characteristics of Hot Springs in the south Segment of the Xianshui Fault Zone. Earthq. Res. 2020, 43, 287–295. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, L.; Lv, W.B.; Wang, L.B.; Wang, Y.; Li, L. Mechanisms of geothermal resource formation in the plain area of Hebei Province. Inf. Rec. Mater. 2017, 18, 174–175. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, S.S.; Zhu, C.Q.; Qiu, N.S.; Tang, B.N.; Cui, Y. Formation conditions and favorable areas for the deep geothermal resources in Xiong’an New Area. Acta Geol. Sin. 2020, 94, 2026–2035. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.L.; Lin, W.J. Main hydro-geothermal systems and their genetic models in China. Acta Geol. Sin. 2020, 94, 1923–1937. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D.Z.; Wang, Y.Y. Geothermal Resources in Nonggeothermal Anomalous Areas of HeBei Plain. J. Earth Sci. 2000, 2, 151–154. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, X.; Wang, X.W.; Guo, S.Y.; Bao, Z.D. Genetic Mechanism of Gaoyang Geothermal Field and Its Adjacent Areas. Karst China 2021, 40, 273–280. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, B.Q.; Zhu, L.X. Geochemical Survey of Geothermal Fields; Geological Press: Beijing, China, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.Y. Low-Medium Temperature Convection Type Geothermal Systerms; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- White, D.E. Saline Waters of Sedimentary Rocks; American Association of Petroleum Geologists: Tulsa, OK, USA, 1965; p. 49. [Google Scholar]
- Arnorsson, S. Chemical equilibria in Icelandic geothermal systems implications for chemical geothermometry investigations. Geothermics 1983, 12, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giggenbach, W.F. Geothermal solute equilibria. Derivation of Na-K-Mg-Ca geoindicators. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1988, 52, 2749–2765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharaka, Y.K.; Mariner, R.H. Chemical Geothermometers and Their Application to Formation Waters from Sedimentary Basins; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1989; pp. 99–117. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, J.; Mao, X.; Tong, S.; Liang, F. Using Hydrochemical Geothermometers Calculate Exchange Temperature of Deep Geothermal System in West Coastal Area of Guangdong Province. Earth Sci.-J. China Univ. Geosci. 2016, 41, 2075–2087. [Google Scholar]
- Fournier, R.O. A Revised Equation for the Na/K Geothermometer. Trans. Geotherm. Resour. Counc. 1979, 3, 221–224. [Google Scholar]
- Fournier, R.O.; Truesdell, A.H. An empirical Na-K-Ca geothermometer for natural waters. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1973, 37, 1255–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hai, K. Using Multiple Methods to Estimate Deep Geothermal Reservoirs Temperatures. Master’s Thesis, China University of Geosciences, Beijing, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, Y.Z.; Wang, F.; Yao, J.J.; Zhang, D.Z. Exploration of geothermal reservoirs temperature evaluation methods for geothermal systems. Energy Environ. 2014, 2, 10–11. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.Y.; Zhang, W.; Ma, F.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, H.X.; Wang, G.L. Geochemical characteristics of the geothermal fluid in the Rongcheng geothermal field, Xiong’an New Area. Acta Geol. Sin. 2020, 94, 1991–2001. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, H.L. Study on the Geothermal Resource Endowment Characteristics and Genesis Patterns in the Guanzhong Basin. Master’s Thesis, China University of Geosciences, Beijing, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, W.J.; Chen, X.Y.; Gan, H.N.; Yue, G.F. Geothermal, geological characteristics and exploration direction of hot dry rocks in the Xiamen bay-Zhangzhou basin, southeastern China. Acta Geol. Sin. 2020, 94, 2066–2077. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.Z.; Li, F.; Zeng, J.H.; Jin, F.M.; Zhang, W.M.; Liu, J.; Zhang, J.W. The geochemical characteristics and origin of deep geothermal water in Baxian Sag. Earth Sci. Front. 2017, 24, 210–218. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, C.L.; Xie, Z.Y.; Pei, S.Q.; Wang, S.J. Chemical characteristics of Middle Permian formation water and hydrocarbon preservation conditions in Northwest Sichuan. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2020, 600, 012041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.S.; Sun, Z.X.; Li, M.G. Application of Fixed-Al Modified log(Q/K) Graph in Hot Spring System. Earth Sci. 2004, 3, 352–356. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.; Wang, G.L.; Ma, F.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Q.L.; Zhang, H.X. Hydrogeochemistre of Geothermal Waters from Taihang Moutain–Xiong’an New area and its Indicating Singnnificance. Earth Sci. 2021, 46, 2594–2608. [Google Scholar]
- Lang, X.J. The Thermal Structure and Geothermal Genesis Mechanjsm in Guide Basin. PhD Thesis, Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, Beijing, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Shan, X.L.; Cai, Z.; Hao, G.L.; Zou, X.T.; Zhao, R.S. Estimation of Thermal Storage Temperature of Geothermal System in Changbai Mountain by Geothermometers. J. Jilin Univ. (Earth Sci. Ed.) 2019, 49, 662–672. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.R.; Pan, X.P.; Yang, Y.J.; Wang, X.L.; Liu, Z.G.; Zhang, L.H.; Zheng, K.Y. Long-Term Geochemistry changes of Geothermal water from a Geothermal well in the urban geothermal field. Beijing. Mod. Geol. 2002, 3, 318–321. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Z.Q.; Song, H.J.; Cheng, H.Z. Application of geothermometer estimate geothermal reservoir temperature of radon geothermal spring in Dasunzhuang, Pingyin county, Jinan city. Chem. Miner. Geol. 2020, 42, 44–48. [Google Scholar]




| NO. | Reservoir Lithology | Ca2+ | Mg2+ | Na+ | K+ | Cl− | HCO3− | SO4− | SiO2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Sandstone | 17.6 | 1.9 | 734.3 | 3.9 | 999.8 | 251.4 | 4.7 | 28.4 |
| 2 | Carbonate | 62.5 | 23.3 | 943.2 | 59.0 | 1162.9 | 666.3 | 37.0 | 57.4 |
| 3 | Carbonate | 53.5 | 20.0 | 859.2 | 53.0 | 1155.0 | 633.2 | 4.6 | 72.1 |
| 4 | Sandstone | 15.2 | 2.9 | 592.1 | 3.6 | 723.3 | 368.5 | 2.7 | 20.8 |
| 5 | Sandstone | 4.0 | 1.0 | 310.2 | 4.0 | 95.0 | 510.1 | 80.3 | 33.5 |
| 6 | Sandstone | 18.4 | 3.3 | 192.9 | 3.3 | 85.1 | 373.4 | 48.9 | 26.2 |
| 7 | Sandstone | 4.8 | 1.0 | 316.9 | 2.9 | 147.5 | 524.7 | 73.5 | 30.0 |
| 8 | Sandstone | 8.0 | 1.5 | 376.7 | 6.0 | 209.9 | 512.5 | 110.0 | 26.3 |
| 9 | Sandstone | 5.6 | 1.0 | 290.5 | 2.1 | 127.6 | 480.8 | 91.6 | 30.2 |
| 10 | Sandstone | 16.0 | 5.3 | 70.6 | 1.9 | 17.0 | 205.0 | 25.3 | 16.4 |
| 11 | Sandstone | 9.6 | 0.1 | 380.8 | 4.5 | 197.1 | 524.7 | 110.3 | 39.3 |
| 12 | Sandstone | 6.4 | 1.0 | 319.7 | 3.7 | 168.8 | 478.4 | 93.7 | 44.2 |
| 13 | Sandstone | 7.2 | 0.5 | 401.0 | 4.9 | 195.7 | 578.4 | 113.1 | 25.6 |
| 14 | Sandstone | 6.4 | 1.9 | 414.0 | 4.4 | 168.8 | 585.8 | 176.8 | 49.3 |
| 15 | Sandstone | 7.2 | 0.7 | 489.6 | 7.4 | 255.6 | 634.2 | 122.4 | 68.0 |
| 16 | Sandstone | 6.7 | 0.7 | 441.7 | 6.0 | 211.8 | 622.2 | 132.8 | 61.1 |
| 17 | Sandstone | 8.2 | 1.1 | 473.4 | 6.4 | 244.2 | 641.7 | 135.6 | 65.8 |
| 18 | Sandstone | 9.6 | 0.5 | 566.7 | 4.1 | 581.4 | 471.1 | 57.4 | 43.4 |
| 19 | Carbonate | 48.0 | 28.7 | 766.9 | 44.6 | 1033.0 | 644.7 | 5.6 | 32.7 |
| 20 | Carbonate | 62.0 | 31.5 | 800.3 | 41.1 | 1033.0 | 618.8 | 24.0 | 41.0 |
| 21 | Carbonate | 66.2 | 33.4 | 855.9 | 51.6 | 1127.0 | 747.7 | 3.0 | 47.1 |
| 22 | Carbonate | 70.1 | 34.4 | 827.4 | 53.6 | 1149.0 | 774.7 | 12.0 | 30.0 |
| 23 | Carbonate | 54.2 | 29.3 | 736.2 | 44.5 | 982.3 | 664.7 | 5.0 | 36.3 |
| 24 | Carbonate | 65.6 | 30.4 | 841.5 | 44.6 | 1084.0 | 685.0 | 40.4 | 46.9 |
| 25 | Carbonate | 67.9 | 34.5 | 786.9 | 38.8 | 989.1 | 683.6 | 63.6 | 40.3 |
| 26 | Carbonate | 49.7 | 25.1 | 872.3 | 43.7 | 1167.0 | 680.3 | 40.2 | 58.1 |
| 27 | Sandstone | 8.3 | 0.8 | 547.1 | 7.1 | 315.1 | 628.2 | 165.1 | 60.9 |
| 28 | Sandstone | 8.2 | 0.6 | 424.3 | 4.6 | 223.9 | 585.2 | 143.5 | 56.3 |
| 29 | Sandstone | 9.6 | 1.9 | 424.2 | 7.1 | 302.1 | 580.9 | 147.8 | 61.3 |
| 30 | Sandstone | 8.2 | 1.1 | 427.9 | 4.7 | 222.8 | 596.8 | 134.0 | 57.9 |
| 31 | Sandstone | 9.1 | 0.9 | 503.8 | 7.1 | 323.9 | 590.3 | 167.9 | 59.9 |
| 32 | Sandstone | 6.4 | 0.7 | 401.7 | 4.6 | 194.3 | 544.0 | 136.6 | 51.0 |
| 33 | Sandstone | 4.0 | 0.6 | 358.1 | 2.3 | 73.6 | 460.7 | 230.9 | 36.7 |
| 34 | Carbonate | 65.7 | 142.5 | 2201.1 | 124.4 | 3034.8 | 341.7 | 760.7 | 62.9 |
| 35 | Carbonate | 255.4 | 45.2 | 1911.0 | 107.1 | 2777.0 | 367.3 | 741.8 | 48.1 |
| 36 | Sandstone | 25.1 | 4.2 | 1138.0 | 12.6 | 1453.0 | 482.1 | 8.0 | 46.0 |
| 37 | Carbonate | 274.3 | 43.1 | 1838.0 | 112.8 | 3000.7 | 371.2 | 487.0 | 49.2 |
| 38 | Carbonate | 221.9 | 46.4 | 1944.0 | 105.1 | 2827.0 | 356.9 | 538.7 | 49.7 |
| NO. | Measuring Temperature | Na-k | K-Mg | Na-K-Ca | Quartz | Chalcedony | SI Method |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 53.0 | 50.7 | 64.9 | 78.5 | 77.1 | 45.7 | 80 |
| 2 | 81.0 | 179.8 | 101.4 | 175.8 | 108.4 | 78.9 | 85 |
| 3 | 98.0 | 178.8 | 100.5 | 174.8 | 119.7 | 91.2 | 82 |
| 4 | 53.0 | 55.8 | 58.4 | 81.4 | 64.9 | 32.9 | 55 |
| 5 | 72.0 | 87.7 | 72.8 | 108.4 | 84 | 52.9 | 65 |
| 6 | 79.0 | 101.3 | 55.2 | 103.5 | 74 | 42.3 | 75 |
| 7 | 80.0 | 72.4 | 65.4 | 94.9 | 79.4 | 48.0 | 90 |
| 8 | 80.0 | 97.8 | 77.7 | 114.7 | 74.1 | 42.5 | / |
| 9 | 68.3 | 62.7 | 58.3 | 84.8 | 79.6 | 48.3 | 70 |
| 10 | 62.4 | 125.5 | 39.2 | 108.9 | 56.1 | 23.7 | 56 |
| 11 | 78.0 | 83.7 | 105.6 | 102.2 | 90.9 | 60.2 | 85 |
| 12 | 80.0 | 82.7 | 71 | 101.8 | 96.1 | 65.8 | 90 |
| 13 | 75.0 | 85.2 | 86.3 | 105.9 | 73 | 41.3 | / |
| 14 | 75.9 | 78.9 | 67.6 | 101.8 | 101.1 | 71.1 | 88 |
| 15 | 88.0 | 95.2 | 92.2 | 116.8 | 116.7 | 88.0 | 94 |
| 16 | 76.0 | 90.0 | 87.3 | 111.5 | 111.4 | 82.2 | 103 |
| 17 | 88.0 | 89.8 | 83.3 | 111 | 115.1 | 86.2 | 85 |
| 18 | 77.6 | 62.7 | 81.8 | 89.4 | 95.3 | 64.9 | 65 |
| 19 | 50.5 | 174.5 | 91 | 170.7 | 83 | 51.8 | 75 |
| 20 | 52.4 | 165.9 | 87.7 | 163 | 92.8 | 62.2 | / |
| 21 | 56.2 | 177.1 | 92.9 | 171.7 | 99 | 68.9 | 75 |
| 22 | 51.0 | 182.3 | 93.5 | 174.3 | 79.5 | 48.1 | 60 |
| 23 | 56.0 | 177.3 | 90.7 | 170.9 | 87.5 | 56.6 | 83 |
| 24 | 73.0 | 168.1 | 90.3 | 164.9 | 98.8 | 68.7 | 80 |
| 25 | 56.0 | 163.1 | 85.1 | 159.9 | 92 | 61.4 | 68 |
| 26 | 80.0 | 164.1 | 92.3 | 165 | 108.9 | 79.6 | 85 |
| 27 | 83.0 | 87.7 | 89.8 | 111.1 | 111.2 | 82.0 | 98 |
| 28 | 78.0 | 80.0 | 82.1 | 101.5 | 107.4 | 77.9 | 102 |
| 29 | 85.2 | 100.2 | 78.9 | 117.1 | 111.6 | 82.4 | 106 |
| 30 | 79.0 | 80.3 | 75.7 | 101.8 | 108.8 | 79.4 | 103 |
| 31 | 81.0 | 92.1 | 88 | 113.1 | 110.4 | 81.1 | 99 |
| 32 | 77.9 | 81.9 | 80.5 | 103.9 | 102.7 | 72.8 | 90 |
| 33 | 75.6 | 57.8 | 66.6 | 84.9 | 88 | 57.1 | 73 |
| 34 | 83.0 | 172.5 | 97 | 185.2 | 112.9 | 83.8 | / |
| 35 | 81.0 | 171.9 | 108.8 | 170.1 | 100 | 70.0 | 89 |
| 36 | 76.4 | 80.8 | 83.2 | 107.5 | 98 | 67.8 | 93 |
| 37 | 75.7 | 178.4 | 111 | 173.6 | 101.1 | 71.1 | 91 |
| 38 | 89.1 | 169.4 | 107.9 | 169.8 | 101.5 | 71.6 | 100 |
| NO. | Type of Geothermometer | Range of Error (°C) | Average Error (°C) | Average Error Percentage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Na-k | ±1.3–131.3 | +44.7 | 68% |
| 2 | K-Mg | ±0.8–42.5 | +15.4 | 24% |
| 3 | Na-Ca-K | ±9.3–123.3 | +53.7 | 80% |
| 4 | Quartz | ±0.6–42.8 | +22.3 | 32% |
| 5 | Chalcedony | ±0–38.6 | −11.0 | 15% |
| 6 | SI method | ±1.7–27.0 | +12.6 | 18% |
| 7 | Points on the Na/K line | ±1.3–22.3 | +8.4 | 11% |
| 8 | Points on the chalcedony line | ±0–12.7 | −3.0 | 5% |
| 9 | Points on the quartz line | ±0.6–42.8 | +23.9 | 34% |
| 10 | K-Mg (in sandstone) | ±0.8–27.6 | +9.1 | 11% |
| 11 | K-Mg (in carbonate) | ±2.5–42.5 | +26.4 | 40% |
| 12 | NA-K-Ca (in sandstone) | ±9.3–46.5 | +26.4 | 34% |
| 13 | NA-K-Ca (in carbonate) | ±76.8–123.3 | +100.5 | 141% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Deng, J.; Lin, W.; Xing, L.; Chen, L. The Estimation of Geothermal Reservoir Temperature Based on Integrated Multicomponent Geothermometry: A Case Study in the Jizhong Depression, North China Plain. Water 2022, 14, 2489. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14162489
Deng J, Lin W, Xing L, Chen L. The Estimation of Geothermal Reservoir Temperature Based on Integrated Multicomponent Geothermometry: A Case Study in the Jizhong Depression, North China Plain. Water. 2022; 14(16):2489. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14162489
Chicago/Turabian StyleDeng, Junzu, Wenjing Lin, Linxiao Xing, and Li Chen. 2022. "The Estimation of Geothermal Reservoir Temperature Based on Integrated Multicomponent Geothermometry: A Case Study in the Jizhong Depression, North China Plain" Water 14, no. 16: 2489. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14162489
APA StyleDeng, J., Lin, W., Xing, L., & Chen, L. (2022). The Estimation of Geothermal Reservoir Temperature Based on Integrated Multicomponent Geothermometry: A Case Study in the Jizhong Depression, North China Plain. Water, 14(16), 2489. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14162489







