Enhancing the Efficiency of Banana Peel Bio-Coagulant in Turbid and River Water Treatment Applications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation and Modification of Banana Peel Powder
2.3. Preparation of Banana Peel Solution
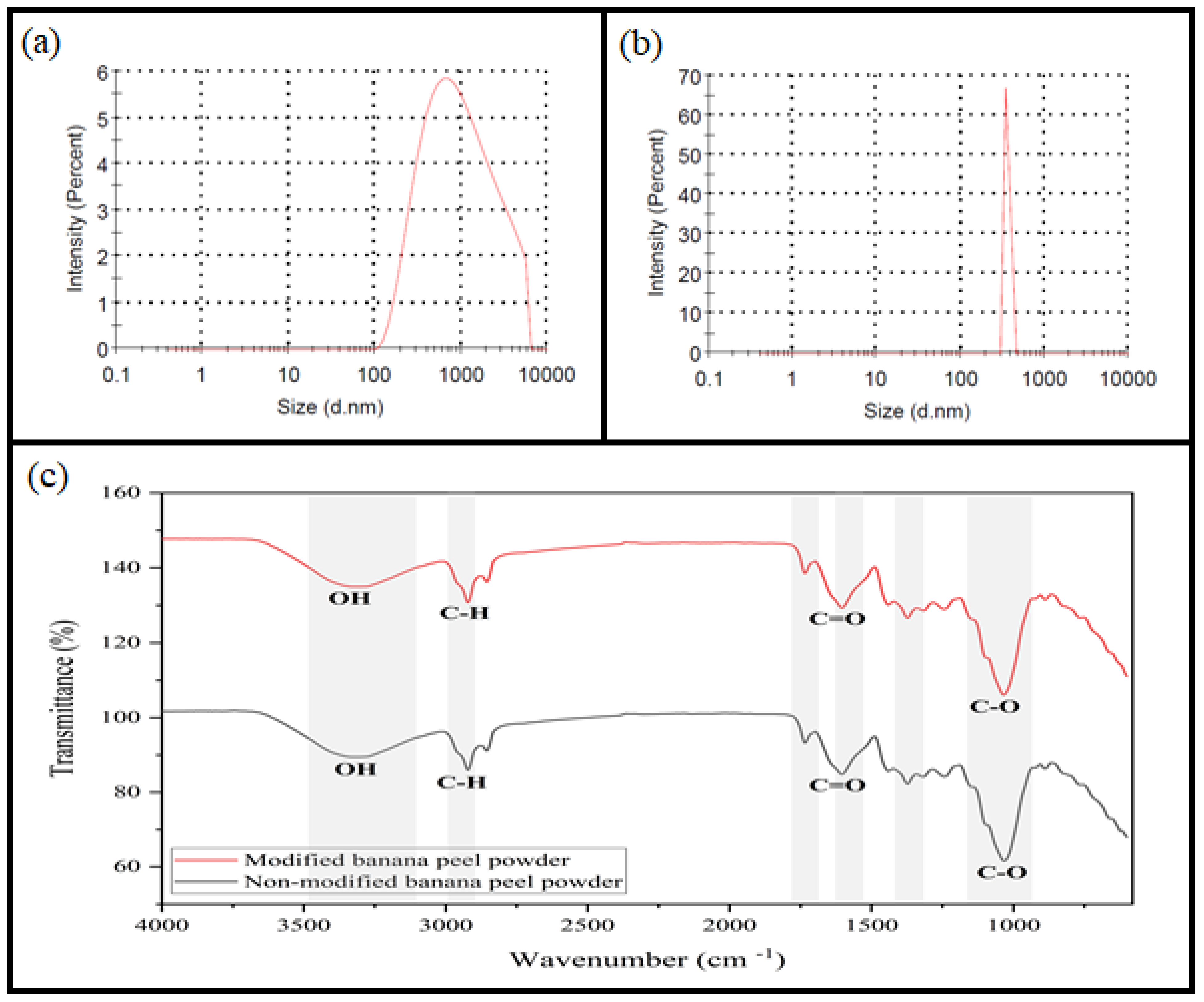
2.4. Characterization of Nano-Banana Peel Powder
2.5. Preparation and Standardization of Turbid Water
2.6. Coagulation Experiment
2.7. Characterization of River Water
3. Results
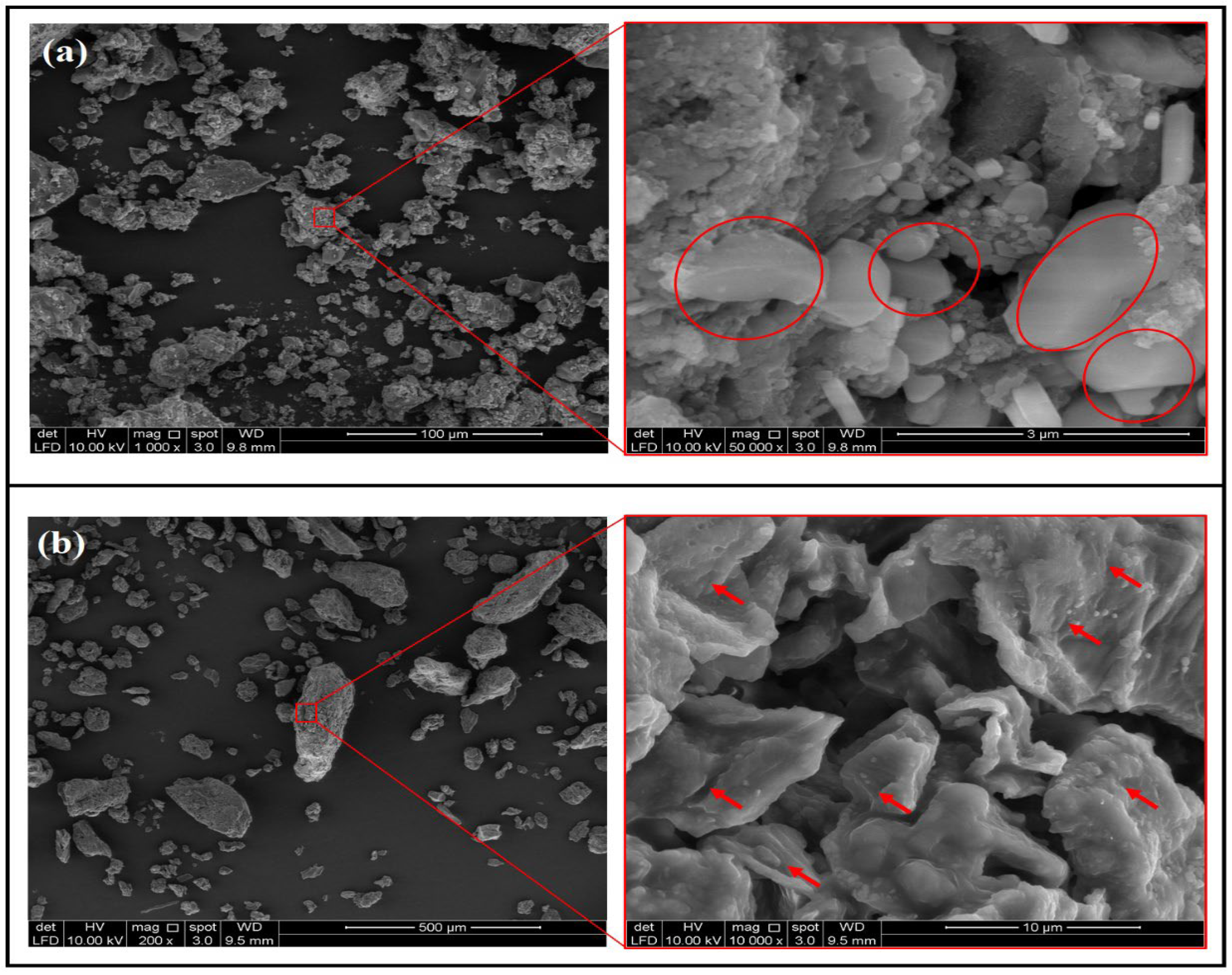
3.1. Characterization of Nano-Banana Peel Powder
3.2. Coagulation Experiment
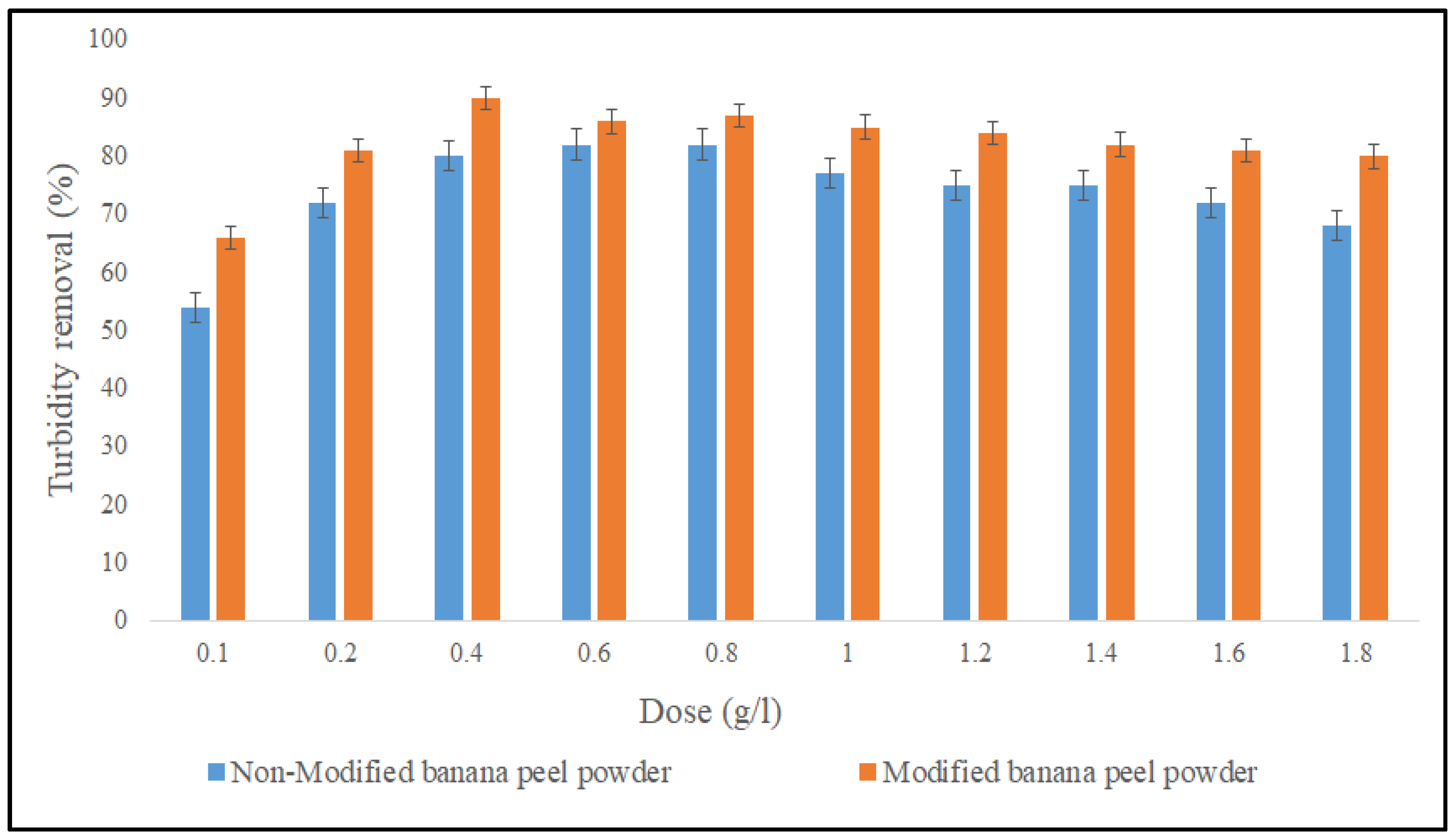
3.2.1. Effect of Dose on the Coagulation Performance
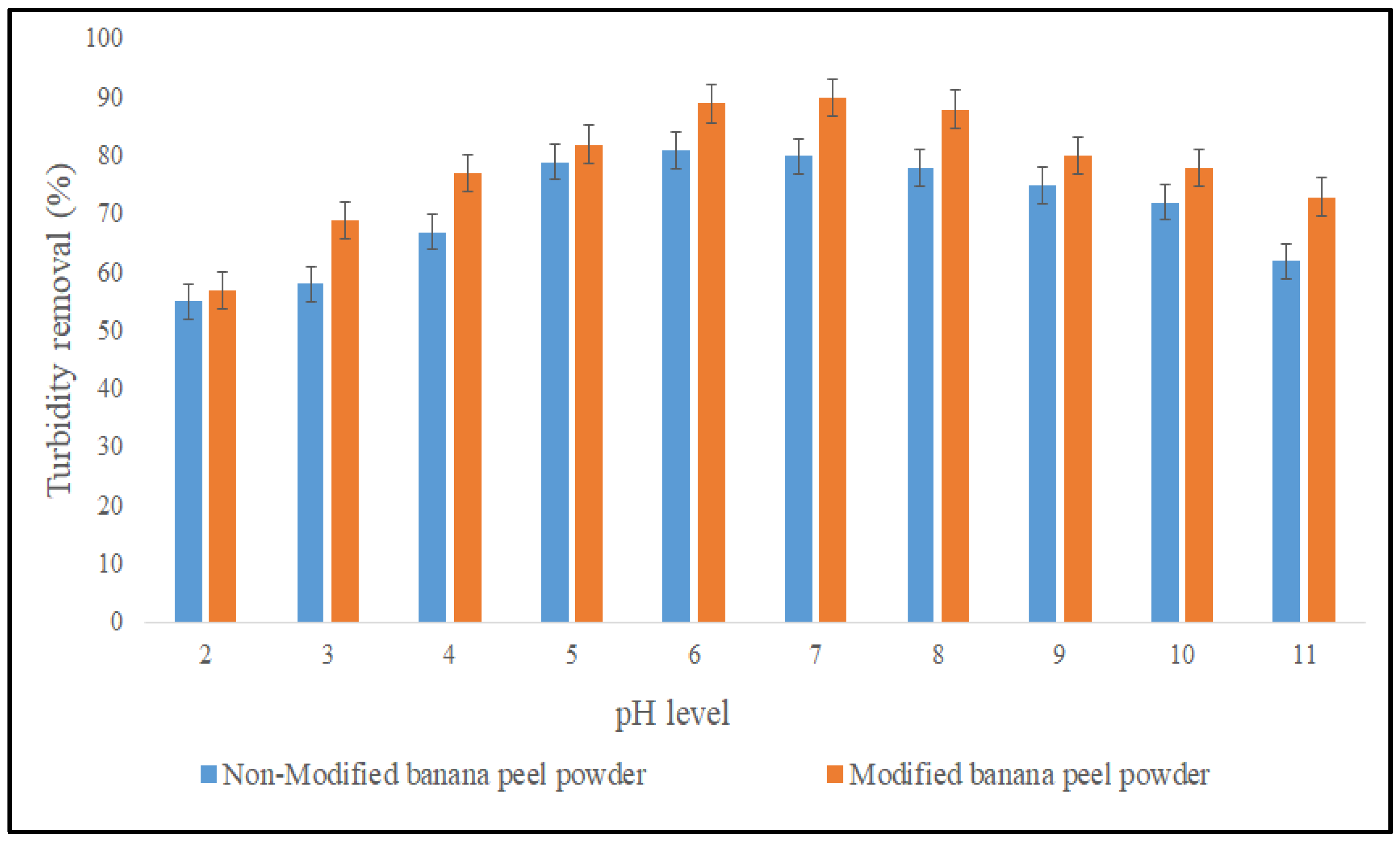
3.2.2. Effect of pH on the Coagulation Performance
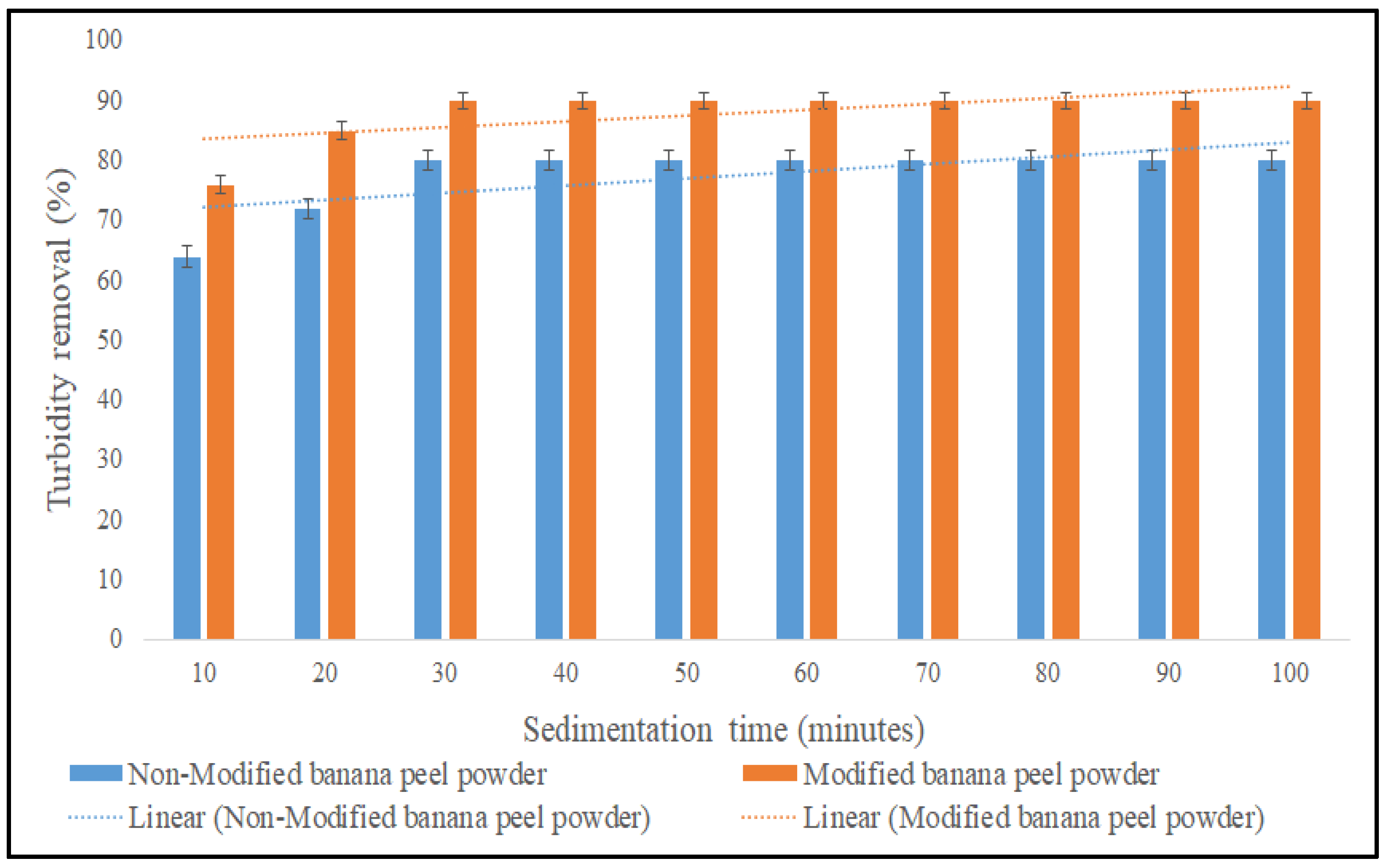
3.2.3. Effect of Sedimentation Time on the Coagulation Performance
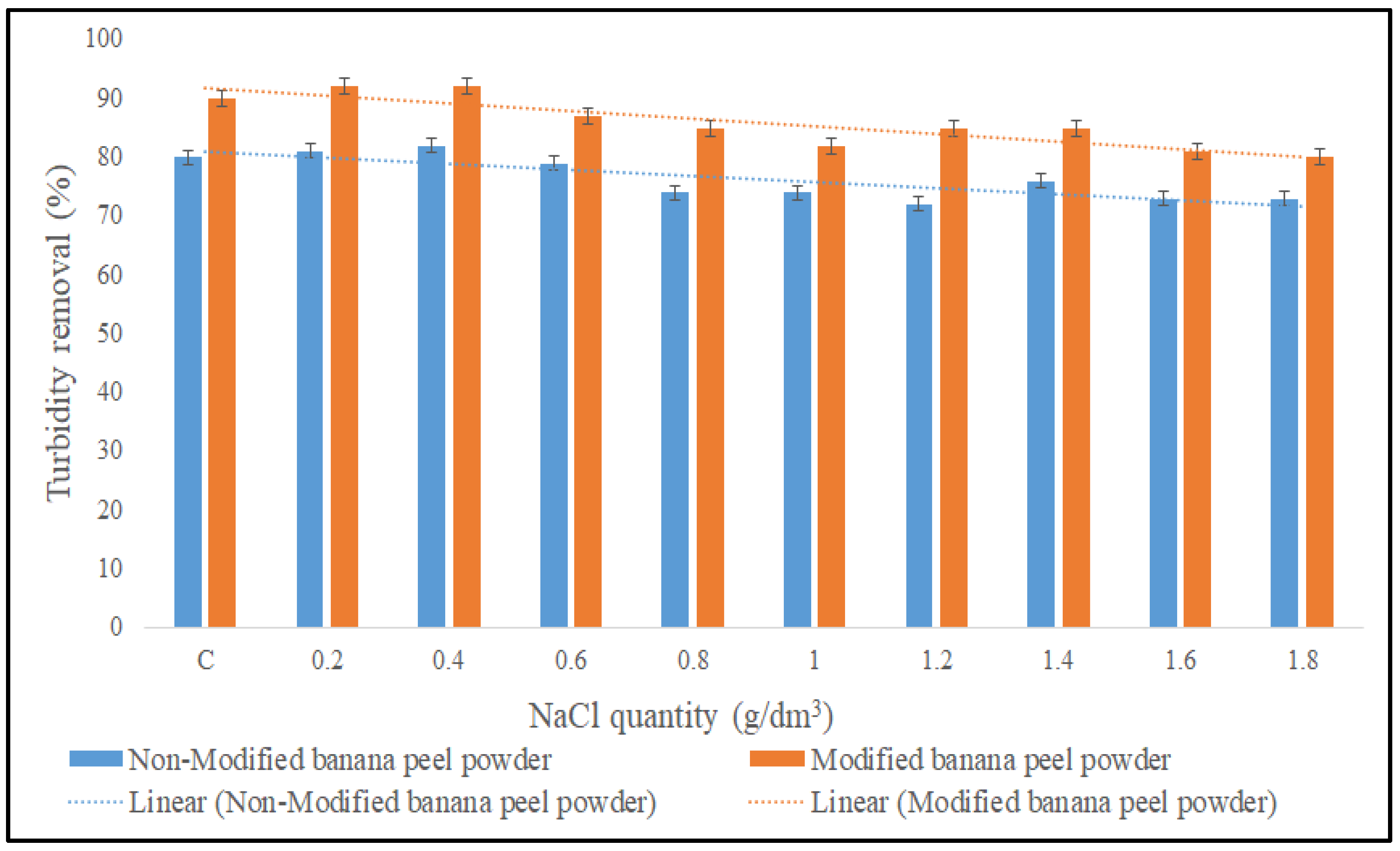
3.2.4. Effect of NaCl Quantity on the Coagulation Performance
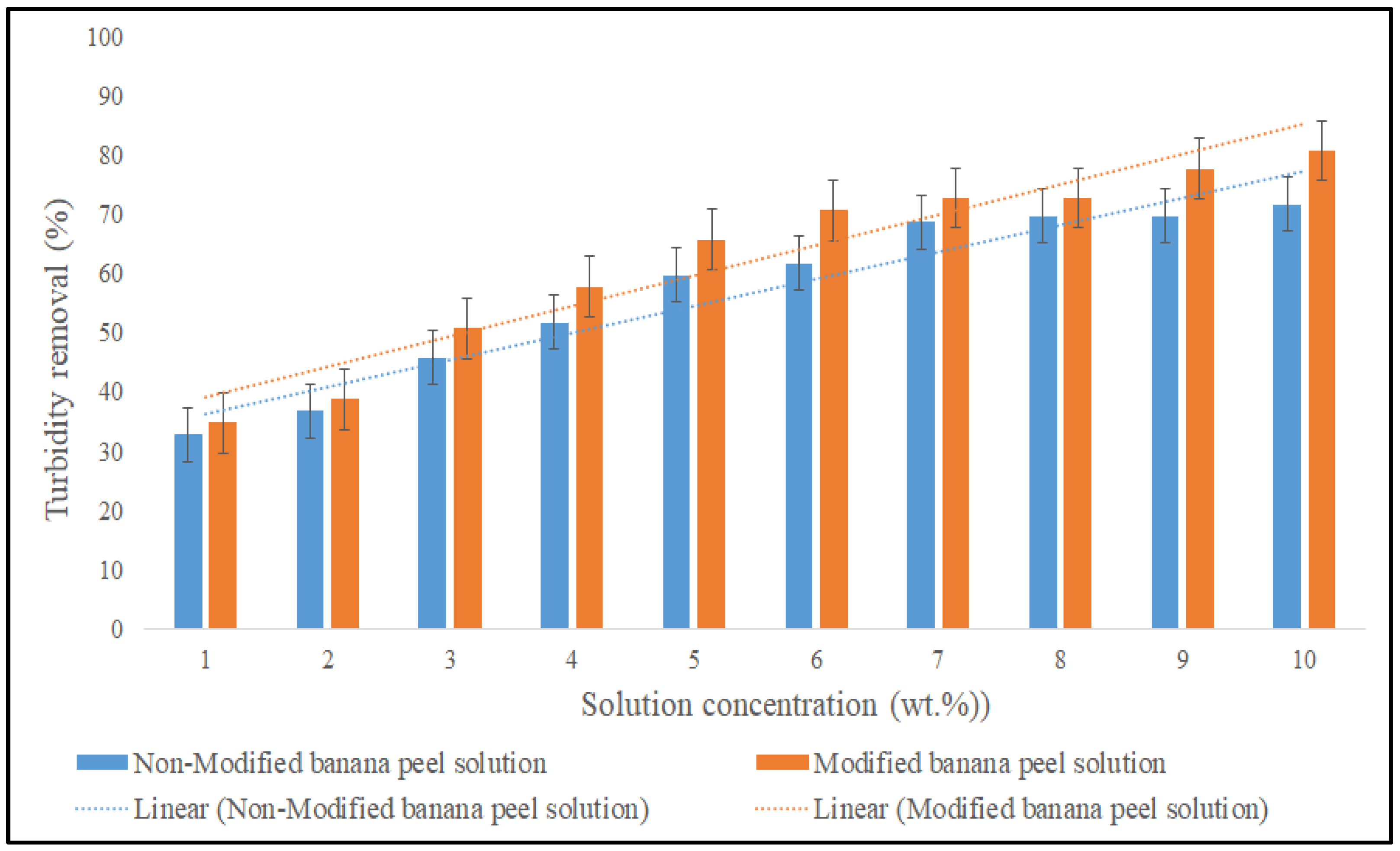
3.2.5. Effect of Powder Solution on the Coagulation Performance
3.3. Effect of Modified Banana Peel Powder on River Water Treatment
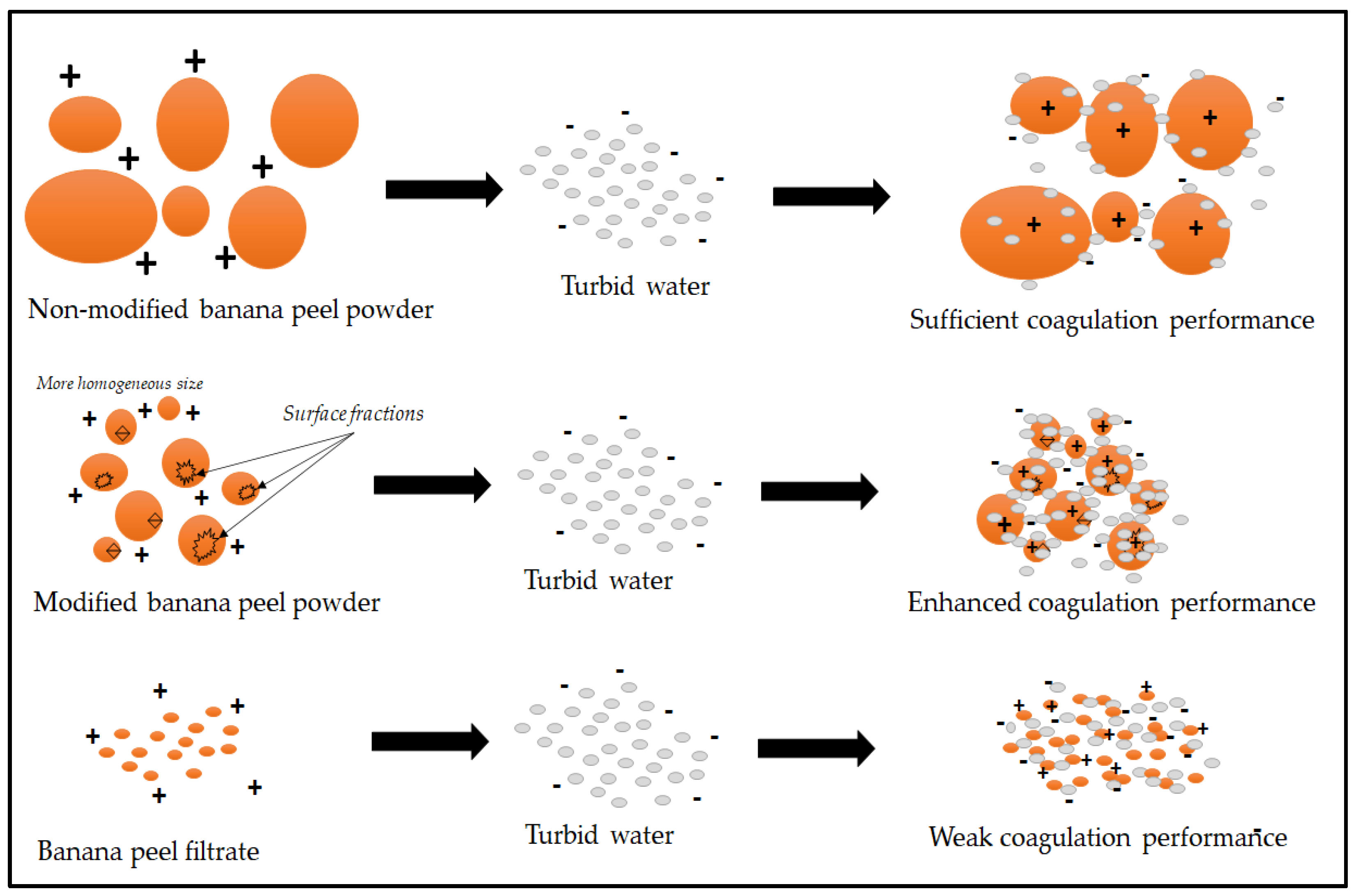
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Choy, S.; Prasad, K.M.N.; Wu, T.Y.; Ramanan, R.N. A review on common vegetables and legumes as promising plant-based natural coagulants in water clarification. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 12, 367–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mahmoodi, N.M.; Hayati, B.; Arami, M. Textile dye removal from single and ternary systems using date stones: Kinetic, isotherm, and thermodynamic studies. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2010, 55, 4638–4649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafatullah, M.; Abbas, S.Z.; Ahmad, A.; Lokhat, D. A Review of Agricultural Solid Waste Materials as Potential Adsorbents for Copper Ions from Water and Wastewater. In Air, Gas, and Water Pollution Control Using Industrial and Agricultural Solid Wastes Adsorbents; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017; pp. 197–222. [Google Scholar]
- Gandiwa, B.I.; Moyo, L.B.; Ncube, S.; Mamvura, T.A.; Mguni, L.L.; Hlabangana, N. Optimisation of using a blend of plant based natural and synthetic coagulants for water treatment: (Moringa Oleifera-Cactus Opuntia-alum blend). S. Afr. J. Chem. Eng. 2020, 34, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoodi, N.M. Synthesis of core–shell magnetic adsorbent nanoparticle and selectivity analysis for binary system dye removal. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2014, 20, 2050–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariana, M.; HPS, A.K.; Mistar, E.M.; Yahya, E.B.; Alfatah, T.; Danish, M.; Amayreh, M. Recent advances in activated carbon modification techniques for enhanced heavy metal adsorption. J. Water Process Eng. 2021, 43, 102221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oveisi, M.; Mahmoodi, N.M.; Asli, M.A. Facile and green synthesis of metal-organic framework/inorganic nanofiber using electrospinning for recyclable visible-light photocatalysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 222, 669–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoodi, N.M. Dendrimer functionalized nanoarchitecture: Synthesis and binary system dye removal. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2014, 45, 2008–2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nath, A.; Mishra, A.; Pande, P.P. A review natural polymeric coagulants in wastewater treatment. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 46, 6113–6117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahadori, A.; Clark, M.; Boyd, B. Essentials of Water Systems Design in the Oil, Gas, and Chemical Processing Industries; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Gurumath, K.; Suresh, S. Cicer Arietinum is Used as Natural Coagulant for Water Treatment. Int. Res. J. Eng. Technol. 2019, 6, 2930–2931. [Google Scholar]
- Kristianto, H. The potency of Indonesia native plants as natural coagulant: A mini review. Water Conserv. Sci. Eng. 2017, 2, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taiwo, A.S.; Adenike, K.; Aderonke, O. Efficacy of a natural coagulant protein from Moringa oleifera (Lam) seeds in treatment of Opa reservoir water, Ile-Ife, Nigeria. Heliyon 2020, 6, e03335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lek, B.L.C.; Peter, A.P.; Chong, K.H.Q.; Ragu, P.; Sethu, V.; Selvarajoo, A.; Arumugasamy, S.K. Treatment of palm oil mill effluent (POME) using chickpea (Cicer arietinum) as a natural coagulant and flocculant: Evaluation, process optimization and characterization of chickpea powder. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 6243–6255. [Google Scholar]
- Daverey, A.; Tiwari, N.; Dutta, K. Utilization of extracts of Musa paradisica (banana) peels and Dolichos lablab (Indian bean) seeds as low-cost natural coagulants for turbidity removal from water. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 34177–34183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levi, M.; Thachil, J.; Iba, T.; Levy, J.H. Coagulation abnormalities and thrombosis in patients with COVID-19. Lancet Haematol. 2020, 7, e438–e440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugwu, S.; Umuokoro, A.F.; Echiegu, E.A.; Ugwuishiwu, B.O.; Enweremadu, C.C. Comparative study of the use of natural and artificial coagulants for the treatment of sullage (domestic wastewater). Cogent Eng. 2017, 4, 1365676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoodi, N.M.; Sadeghi, U.; Maleki, A.; Hayati, B.; Najafi, F. Synthesis of cationic polymeric adsorbent and dye removal isotherm, kinetic and thermodynamic. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2014, 20, 2745–2753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohajershojaei, K.; Mahmoodi, N.M.; Khosravi, A. Immobilization of laccase enzyme onto titania nanoparticle and decolorization of dyes from single and binary systems. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 2015, 20, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoodi, N.M.; Arabloo, M.; Abdi, J. Laccase immobilized manganese ferrite nanoparticle: Synthesis and LSSVM intelligent modeling of decolorization. Water Res. 2014, 67, 216–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, J.V.M.; Andrade, P.V.; Reis, A.G.D. Moringa oleifera seed as a natural coagulant to treat low-turbidity water by in-line filtration. Rev. Ambient. Água 2019, 14, 2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristianto, H.; Kurniawan, M.A.; Soetedjo, J.N. Utilization of papaya seeds as natural coagulant for synthetic textile coloring agent wastewater treatment. Int. J. Adv. Sci. Eng. Inf. Technol. 2018, 8, 2071–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baharin, A.; Fattah, N.A.; Bakar, A.A.; Ariff, Z.M. Production of laminated natural fibre board from banana tree wastes. Procedia Chem. 2016, 19, 999–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kandeeban, M.; Malarkodi, M. Assessment of the farmers attitude towards banana cultivation and export in Coimbatore and Erode districts of Tamil Nadu. Int. J. Farm Sci. 2019, 9, 49–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aida, S.; Noriza, A.; Haswani, M.M.; Mya, S.M.Y. A study on reducing fat content of fried banana chips using a sweet pretreatment technique. Int. Food Res. J. 2016, 23, 68. [Google Scholar]
- Oladoja, N.A. Headway on natural polymeric coagulants in water and wastewater treatment operations. J. Water Process Eng. 2015, 6, 174–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvatham, S.D.; R., A.R.N. Evaluation of Wastewater Treatment Using Banana Fruit Peel Powder as Natural Coagulant. Int. Res. J. Innov. Eng. Technol. 2021, 5, 58. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, Y.; Meng, X.J.; Lu, N.N.; Jian, H.L.; Di, Y. Characteristics changes in banana peel coagulant during storage process. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 16, 7747–7756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunaratna, K.; Garcia, B.; Andersson, S.; Dalhammar, G. Screening and evaluation of natural coagulants for water treatment. Water Sci. Technol. Water Supply 2007, 7, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musselman, R. Sampling Procedure for Lake or Stream Surface Water Chemistry; Res. Note RMRS-RN-49; Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Rocky Mountain Research Station: Fort Collins, CO, USA, 2012; Volume 49, p. 11. [Google Scholar]
- Arnoldsson, E.; Bergman, M.; Matsinhe, N.; Persson, K.M. Assessment of drinking water treatment using Moringa oleifera natural coagulant. Vatten 2008, 64, 137. [Google Scholar]
- Shan, T.C.; Matar, M.A.; Makky, E.A.; Ali, E.N. The use of Moringa oleifera seed as a natural coagulant for wastewater treatment and heavy metals removal. Appl. Water Sci. 2017, 7, 1369–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eng, L.Z.; Loo, K.P. Microwave-assisted extraction of banana peel bio-flocculant and its potential in wastewater treatment. Glob. J. Eng. Technol. Adv. 2019, 1, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kamsonlian, S.; Suresh, S.; Majumder, C.B.; Chand, S. Characterization of banana and orange peels: Biosorption mechanism. Int. J. Sci. Technol. Manag. 2011, 2, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Kabenge, I.; Omulo, G.; Banadda, N.; Seay, J.; Zziwa, A.; Kiggundu, N. Characterization of banana peels wastes as potential slow pyrolysis feedstock. J. Sustain. Dev. 2018, 11, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mokhtar, N.; Priyatharishini, M.; Kristanti, R. Study on the effectiveness of banana peel coagulant in turbidity reduction of synthetic wastewater. Int. J. Eng. Technol. Sci. 2019, 6, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gloria, N. Treatment of Refinery and Petrochemical Wastewater Using Banana Peel as A Natural Coagulant. Org. Med. Chem. Int. J. 2018, 7, 141–143. [Google Scholar]
- Chong, K.H.; Kiew, P.L. Potential of banana peels as bio-flocculant for water clarification. Prog. Energy Environ. 2017, 1, 47–56. [Google Scholar]
- Yuliastri, I.R.; Rohaeti, E.; Effendi, H.; Darusman, L.K. The use of Moringa oleifera seed powder as coagulant to improve the quality of wastewater and ground water. In IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Mahmudabadi, T.Z.; Ebrahimi, A.A.; Eslami, H.; Mokhtari, M.; Salmani, M.H.; Ghaneian, M.T.; Pakdaman, M. Optimization and economic evaluation of modified coagulation–flocculation process for enhanced treatment of ceramic-tile industry wastewater. AMB Express 2018, 8, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardoso Valverde, K.; Ferri Coldebella, P.; Fernandes Silva, M.; Nishi, L.; Carvalho Bongiovani, M.; Bergamasco, R. Moringa oleifera Lam. and its potential association with aluminium sulphate in the process of coagulation/flocculation and sedimentation of surface water. Int. J. Chem. Eng. 2018, 2018, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Birima, A.; Hammad, H.A.; Desa, M.N.M.; Muda, Z.C. Extraction of natural coagulant from peanut seeds for treatment of turbid water. In IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Eskibalci, M.F.; Ozkan, M.F. An investigation of the effect of NaCl concentration on the electrocoagulation of coal preparation plant tailings. Physicochem. Probl. Miner. Process. 2018, 54, 934–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeel, S.; Zuber, M.; Zia, K.M. Microwave-assisted extraction and dyeing of chemical and bio-mordanted cotton fabric using harmal seeds as a source of natural dye. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 11100–11110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, P.D.; Mandavgane, S.A. Preparation and characterization of raw and carbon from banana peel by microwave activation: Application in citric acid adsorption. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 2435–2447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, H.T.; Scarlett, C.J.; Vuong, Q.V. Maximising recovery of phenolic compounds and antioxidant properties from banana peel using microwave assisted extraction and water. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 56, 1360–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yimer, A.; Dame, B. Papaya seed extract as coagulant for potable water treatment in the case of Tulte River for the community of Yekuset district, Ethiopia. Environ. Chall. 2021, 4, 100198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A. Removal of Mn (II) from water using chemically modified banana peels as efficient adsorbent. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2017, 7, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, J.; Yuan, Q.; Tang, H.; Yu, F.; Lv, X. A green adsorbent derived from banana peel for highly effective removal of heavy metal ions from water. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 45041–45048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasikala, S.; Muthuraman, G. Turbidity removal from surface water by natural coagulants and its potential application. Iran. J. Energy Environ. 2017, 8, 61–66. [Google Scholar]
- Dawodu, F.A.; Abonyi, C.J.; Akpomie, K.G. Feldspar-banana peel composite adsorbent for efficient crude oil removal from solution. Appl. Water Sci. 2021, 11, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munagapati, V.S.; Yarramuthi, V.; Kim, Y.; Lee, K.M.; Kim, D.S. Removal of anionic dyes (Reactive Black 5 and Congo Red) from aqueous solutions using Banana Peel Powder as an adsorbent. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 148, 601–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muhamad, N.A.N.; Juhari, N.F.; Mohamad, I.N. Efficiency of Natural Plant-Based Coagulants for Water Treatment. In IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, G.H.; Hegazy, B.E.; Fouad, H.A.; Rehab, M. Comparative study on natural products used for pollutants removal from water. J. Appl. Sci. Res. 2008, 5, 1020–1029. [Google Scholar]
- Boulaadjoul, S.; Zemmouri, H.; Bendjama, Z.; Drouiche, N. A novel use of Moringa oleifera seed powder in enhancing the primary treatment of paper mill effluent. Chemosphere 2018, 206, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Mamun, A.; Basir, A.T.A. White popinac as potential phyto-coagulant to reduce turbidity of river water. ARPN J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 2016, 11, 7180–7183. [Google Scholar]
- Mukheled, A.-S. A novel water pretreatment approach for turbidity removal using date seeds and pollen sheath. J. Water Resour. Prot. 2012, 4, 79–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Priyatharishini, M.; Mokhtar, N. Performance of jackfruit (Artocarpus heterophyllus) peel coagulant in turbidity reduction under different pH of wastewater. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 46, 1818–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurya, S.; Daverey, A. Evaluation of plant-based natural coagulants for municipal wastewater treatment. 3 Biotech 2018, 8, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilardi, G.; di Palma, L.; Verdone, N. Heavy metals adsorption by banana peels micro-powder: Equilibrium modeling by non-linear models. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2018, 26, 455–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapointe, M.; Jahandideh, H.; Farner, J.; Tufenkji, N. Identifying the best coagulant for simultaneous water treatment objectives: Interactions of mononuclear and polynuclear aluminum species with different natural organic matter fractions. J. Water Process Eng. 2021, 40, 101829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Water, S.; World Health Organization. Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality. Incorporating First Addendum 2006; World Health Organization: Geneve, Switzerland; Volume 1. Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/43428 (accessed on 31 July 2022).
- Mondal, N.K.; Kar, S. Potentiality of banana peel for removal of Congo red dye from aqueous solution: Isotherm, kinetics and thermodynamics studies. Appl. Water Sci. 2018, 8, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
| Parameter | Before Treatment | After Treatment | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Result (Mean ± SD) | Non-Modified Banana Peel Powder | Modified Banana Peel Powder | |
| Temperature (°C) | 29 | 29 | 29 |
| Turbidity (NTU) | 36.1 ± 3.4 | 8.5 ± 1.2 (76%) | 5.76 ± 1.7 (84%) |
| pH | 6.78 ± 0.1 | 6.92 ± 0.4 | 6.98 ± 0.6 |
| Color | Faint brown | Colorless | Colorless |
| Total dissolved solid (mg/L) | 43.6 ± 5.1 | 8.3 ± 1.1 | 5.7 ± 3.3 |
| Total suspended solid (mg/L) | 35.2 ± 1.3 | 11.8 ± 2.5 | 9.3 ± 1.4 |
| Chemical oxygen demand (mg/L) | 87.2 ± 4.2 | 61.8 ± 3.9 | 60.1 ± 2.8 |
| Biochemical oxygen demand (mg/L) | 31.7 ± 2.3 | 26.2 ± 1.8 | 24.4 ± 1.1 |
| Bio-Coagulant | Optimal Experimental Conditions | Turbidity Removal (%) | References | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dose (g/L) | pH | Type of Waste Water | |||
| Banana peel extract | 0.1 | 1 | Synthetic domestic wastewater | 88 | [36] |
| Moringa seed powder | 0.15 | 6–8 | Paper mill effluent | 96 | [55] |
| White popinac | 0.05 | 7 | Synthetic turbid river water | 76 | [56] |
| Iraqi date seed extract | 0.06 | 7 | Synthetic turbid water | 90 | [57] |
| Apricot seed extract | 0.03 | 7 | Raw surface water | 54 | [54] |
| Jackfruit peel extract | 0.1 | 2 | Sewage synthetic wastewater | 70 | [58] |
| Banana peel powder | 0.4 | 7 | Kaolin synthetic wastewater | 59 | [59] |
| Non-modified banana peel powder | 0.6 | 6–8 | Kaolin synthetic wastewater | 81 | This study |
| Modified banana peel powder | 0.4 | 6–8 | Kaolin synthetic wastewater | 92 | This study |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Azamzam, A.A.; Rafatullah, M.; Yahya, E.B.; Ahmad, M.I.; Lalung, J.; Alam, M.; Siddiqui, M.R. Enhancing the Efficiency of Banana Peel Bio-Coagulant in Turbid and River Water Treatment Applications. Water 2022, 14, 2473. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14162473
Azamzam AA, Rafatullah M, Yahya EB, Ahmad MI, Lalung J, Alam M, Siddiqui MR. Enhancing the Efficiency of Banana Peel Bio-Coagulant in Turbid and River Water Treatment Applications. Water. 2022; 14(16):2473. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14162473
Chicago/Turabian StyleAzamzam, Abdassalam A., Mohd Rafatullah, Esam Bashir Yahya, Mardiana Idayu Ahmad, Japareng Lalung, Mahboob Alam, and Masoom Raza Siddiqui. 2022. "Enhancing the Efficiency of Banana Peel Bio-Coagulant in Turbid and River Water Treatment Applications" Water 14, no. 16: 2473. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14162473
APA StyleAzamzam, A. A., Rafatullah, M., Yahya, E. B., Ahmad, M. I., Lalung, J., Alam, M., & Siddiqui, M. R. (2022). Enhancing the Efficiency of Banana Peel Bio-Coagulant in Turbid and River Water Treatment Applications. Water, 14(16), 2473. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14162473










