The Interreg Project AdSWiM: Managed Use of Treated Wastewater for the Quality of the Adriatic Sea
Abstract
:1. Context
2. Challenges
3. Activities Carried Out
3.1. Harmonization of the Knowledge, Project Areas Modeling and Mapping, and Activities Plan (WP 3)
3.2. Innovative Analytical Solutions for Microbiological Control and Treatment of Urban Wastewaters (WP4)
3.2.1. WP 4.1: New Treatments to Reduce the Microbial Loads of Treated Wastewater
3.2.2. WP 4.2: Characterization of Treated WW and of the Seawater in Proximity of the Offshore Discharging Line
3.2.3. WP 4.3: An Electrochemical Sensor (E-Sensor) for Phosphate Detection with Improved Detection Limit
3.2.4. WP 4.4: Algae Based-Biosensors to Assess the Global Biotoxicity of Wastewater Samples
3.2.5. WP 4.5: Emerging Pathogens and Risk Assessment for Marine Environment
3.2.6. WP 4.6 Assessment of Feasibility and General Considerations from the Results of Each Task
3.3. Technologies and Strategies for Managing WWTPs Guidelines Definition and Cross-Borders Strategies (WP5)
4. Conclusions and Considerations
- -
- The OTAMBs dialogue with the Croatian bodies that carry out the same functions (perhaps a “permanent round table” or something similar can be proposed);
- -
- Each OTAMB interprets requests from the integrated water system managers and returns the results drafted by the “permanent round table” to them;
- -
- The OTAMBs are invited to participate in the permanent institutional conference, partly for the purpose of contributing what has come out during the “permanent round table” to the discussion;
- -
- The permanent institutional conference invites the relevant Minister (State representative, in Italy the Minister of Environment) to be the spokesperson (with their Croatian counterpart) at the EU Commission.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Cozzi, S.; Falconi, C.; Comici, C.; Čermelj, B.; Kovac, N.; Turk, V.; Giani, M. Recent Evolution of River Discharges in the Gulf of Trieste and Their Potential Response to Climate Changes and Anthropogenic Pressure. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2012, 115, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weissbrodt, D.G.; Winkler, M.K.H.; Wells, G.F. Responsible Science, Engineering and Education for Water Resource Recovery and Circularity. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2020, 6, 1952–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, C.M.; Mills, M.M.; Arrigo, K.R.; Berman-Frank, I.; Bopp, L.; Boyd, P.W.; Galbraith, E.D.; Geider, R.J.; Guieu, C.; Jaccard, S.L.; et al. Processes and Patterns of Oceanic Nutrient Limitation. Nat. Geosci. 2013, 6, 701–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volf, G.; Atanasova, N.; Kompare, B.; Ožanić, N. Modeling Nutrient Loads to the Northern Adriatic. J. Hydrol. 2013, 504, 182–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adami, G.; Barbieri, P.; Predonzani, S.; Rivetti, D.; Reisenhofer, E. Nutrient Distribution in Locations of the Gulf of Trieste (Northern Adriatic Sea) Suspected of Pollution. Toxicol. Environ. Chem. 1999, 68, 307–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozetič, P.; Malačič, V.; Turk, V. A Case Study of Sewage Discharge in the Shallow Coastal Area of the Northern Adriatic Sea (Gulf of Trieste). Mar. Ecol. 2008, 29, 483–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koron, N.; Ogrinc, N.; Metzger, E.; Riedel, B.; Faganeli, J. Diagenesis and benthic fluxes of nutrients and metals during experimentally induced anoxia in the Gulf of Trieste (northern Adriatic Sea). Biogeosci. Discuss. 2013, 10, 11729–11755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penezić, A.; Gašparović, B.; Cuculić, V.; Strmečki, S.; Djakovac, T.; Mlakar, M. Dissolved Trace Metals and Organic Matter Distribution in the Northern Adriatic, an Increasingly Oligotrophic Shallow Sea. Water 2022, 14, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cozzi, S.; Lipizer, M.; Cantoni, C.; Catalano, G. Nutrient balance in the ecosystem of the North Western Adriatic Sea. Chem. Ecol. 2002, 18, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipizer, M.; Cossarini, G.; Falconi, C.; Solidoro, C. Fonda Umani S Impact of different forcing factors on N: P balance in a semi-enclosed bay: The Gulf of Trieste (North Adriatic Sea). Continental Shelf Res. 2011, 31, 1651–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipizer, M.; De Vittor, C.; Falconi, C.; Comici, C.; Tamberlich, F.; Giani, M. Effects of intense physical and biological forcing factors on CNP pools in coastal waters (Gulf of Trieste, Northern Adriatic Sea). Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2012, 115, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellenic Centre for Marine Research. Mediterranean Sea-Eutrophication and Acidity Aggregated Datasets 1911/2020 V2021. Aggregated Data Products Are Generated by EMODnet Chemistry under the Support of DG MARE Call for Tenders EASME/EMFF/2016/006-Lot4, EASME/2019/OP/0003-Lot4. 2021. Available online: https://www.emodnet-chemistry.eu/products/doi?1&doi=10.6092/ep6n-tp63 (accessed on 22 March 2022).
- Kaltenböck, E.; Herndl, G.J. Ecology of Amorphous Aggregations (Marine Snow) in the Northern Adriatic Sea. IV. Dissolved Nutrients and the Autotrophic Community Associated with Marine Snow. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1992, 87, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cibic, T.; Blasutto, O.; Falconi, C.; Umani, S.F. Microphytobenthic biomass, species composition and nutrient availability in sublittoral sediments of the Gulf of Trieste (northern Adriatic Sea). Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2007, 75, 50–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granéli, E.; Carlsson, P.; Legrand, C. The Role of C, N and P in Dissolved and Particulate Organic Matter as a Nutrient Source for Phytoplankton Growth. Including Toxic Species. Aquat. Ecol. 1999, 33, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zavatarelli, M.; Raicich, F.; Bregant, D.; Russo, A.; Artegiani, A. Climatological Biogeochemical Characteristics of the Adriatic Sea. J. Mar. Syst. 1998, 18, 227–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artegiani, A.; Paschini, E.; Russo, A.; Bregant, D.; Raicich, F.; Pinardi, N. The Adriatic Sea General Circulation. Part I: Air–Sea Interactions and Water Mass Structure. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 1997, 27, 1492–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reisenhofer, E.; Adami, G.; Favretto, A. Heavy Metals and Nutrients in Coastal, Surface Seawaters (Gulf of Trieste, Northern Adriatic Sea): An Environmental Study by Factor Analysis. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 1996, 354, 729–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cibic, T.; Cerino, F.; Karuza, A.; Fornasaro, D.; Comici, C.; Cabrini, M. Structural and Functional Response of Phytoplankton to Reduced River Inputs and Anomalous Physical-Chemical Conditions in the Gulf of Trieste (Northern Adriatic Sea). Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 636, 838–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šolić, M.; Šantić, D.; Šestanović, S.; Bojanić, N.; Grbec, B.; Jozić, S.; Vrdoljak, A.; Ordulj, M.; Matić, F.; Kušpilić, G.; et al. Impact of Water Column Stability Dynamics on the Succession of Plankton Food Web Types in the Offshore Area of the Adriatic Sea. J. Sea Res. 2020, 158, 101860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, J.H.; Harvey, T.; Murray, C.; Green, N.; Reker, J. Contaminants in Europe’s Seas. Moving towards a Clean, Non Toxic Marine Environment; European Environment Agency: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Pavoni, E.; Crosera, M.; Petranich, E.; Adami, G.; Faganeli, J.; Covelli, S. Partitioning and Mixing Behaviour of Trace Elements at the Isonzo/Soča River Mouth (Gulf of Trieste, Northern Adriatic Sea). Mar. Chem. 2020, 223, 103800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Covelli, S.; Faganeli, J.; Horvat, M.; Brambati, A. Mercury Contamination of Coastal Sediments as the Result of Long-Term Cinnabar Mining Activity (Gulf of Trieste, Northern Adriatic Sea). Appl. Geochem. 2001, 16, 541–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Covelli, S.; Piani, R.; Acquavita, A.; Predonzani, S.; Faganeli, J. Transport and Dispersion of Particulate Hg Associated with a River Plume in Coastal Northern Adriatic Environments. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2007, 55, 436–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Covelli, S.; Acquavita, A.; Piani, R.; Predonzani, S.; De Vittor, C. Recent Contamination of Mercury in an Estuarine Environment (Marano Lagoon, Northern Adriatic, Italy). Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2009, 82, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrini, R.; Cidu, R.; Slejko, F.F. Thallium Contamination in the Raibl Mine Site Stream Drainage System (Eastern Alps, Italy). Mine Water Environ. 2016, 35, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bratkič, A.; Tinta, T.; Koron, N.; Guevara, S.R.; Begu, E.; Barkay, T.; Horvat, M.; Falnoga, I.; Faganeli, J. Mercury Transformations in a Coastal Water Column (Gulf of Trieste, Northern Adriatic Sea). Mar. Chem. 2018, 200, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuculić, V.; Cukrov, N.; Kwokal, Ž.; Mlakar, M. Natural and Anthropogenic Sources of Hg, Cd, Pb, Cu and Zn in Seawater and Sediment of Mljet National Park, Croatia. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2009, 81, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanković, S.; Tanaskovski, B.; Zlatić, B.; Arsenović, M.; Pezo, L. Analysis of Trace Elements in Surface Sediments, Mussels, Seagrass and Seawater along the Southeastern Adriatic Coast—A Chemometric Approach. Pure Appl. Chem. 2014, 86, 1111–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazo, P.; Cullaj, A.; Baraj, B. An Evaluation of Hg, Cr and Heavy Metals Pollution in Seawater and Sediments of Durres Bay Adriatic Sea-Albania. J. De Phys. IV (Proc.) 2003, 107, 715–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annibaldi, A.; Illuminati, S.; Truzzi, C.; Scarponi, G. SWASV Speciation of Cd, Pb and Cu for the Determination of Seawater Contamination in the Area of the Nicole Shipwreck (Ancona Coast, Central Adriatic Sea). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 62, 2813–2821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annibaldi, A.; Truzzi, C.; Illuminati, S.; Scarponi, G. Recent Sudden Decrease of Lead in Adriatic Coastal Seawater during the Years 2000–2004 in Parallel with the Phasing out of Leaded Gasoline in Italy. Mar. Chem. 2009, 113, 238–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illuminati, S.; Annibaldi, A.; Truzzi, C.; Tercier-Waeber, M.L.; Nöel, S.; Braungardt, C.B.; Achterberg, E.P.; Howell, K.A.; Turner, D.; Marini, M.; et al. In-Situ Trace Metal (Cd, Pb, Cu) Speciation along the Po River Plume (Northern Adriatic Sea) Using Submersible Systems. Mar. Chem. 2019, 212, 47–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tankere, S.P.C.; Statham, P.J. Distribution of Dissolved Cd, Cu, Ni and Zn in the Adriatic Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 1996, 32, 623–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klun, K.; Falnoga, I.; Mazej, D.; Šket, P.; Faganeli, J. Colloidal Organic Matter and Metal (Loid)s in Coastal Waters (Gulf of Trieste, Northern Adriatic Sea). Aquat. Geochem. 2019, 25, 179–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, J.-M.; Dai, M.-H.; Cauwet, G. Significance of Colloids in the Biogeochemical Cycling of Organic Carbon and Trace Metals in the Venice Lagoon (Italy). Limnol. Oceanogr. 1995, 40, 119–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camusso, M.; Crescenzio, S.; Martinotti, W.; Pettine, M.; Pagnotta, R. Behaviour of Co, Fe, Mn and Ni in the PO Estuary (Italy). Water Air Soil Pollut. 1997, 99, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwokal, Ž.; Lovrić, M. Vertical Distribution of Mercury in the Krka River Estuary. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2006, 86, 905–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiket, Z.; Ivanic, M.; Turk, M.F.; Mikac, N.; Kniewald, G. Distribution of Trace Elements in Waters of the Zrmanja River Estuary (Eastern Adriatic Coast, Croatia). Croat. Chem. Acta 2018, 91, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faganeli, J.; Horvat, M.; Covelli, S.; Fajon, V.; Logar, M.; Lipej, L.; Cermelj, B. Mercury and Methylmercury in the Gulf of Trieste (Northern Adriatic Sea). Sci. Total Environ. 2003, 304, 315–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanelli, M.; Truzzi, C.; Illuminati, S.; Girolametti, F.; Vagnoni, F.; Susmel, S.; Celussi, M.; Mion, M.; de Bortoli, N.; Franci, C.; et al. Impact of Sewage treatment plants on Nutrients Levels in North Adriatic Sea. Water 2022, 14, 569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girolametti, F.; Fanelli, M.; Ajdini, B.; Truzzi, C.; Illuminati, S.; Susmel, S.; Celussi, M.; Šangulin, J.; Annibaldi, A. Dissolved Potentially Toxic Elements (PTEs) in Relation to Sewage treatment plant Outflows in Adriatic Coastal Waters: A Two Year Monitoring Survey. Water 2022, 14, 569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonti, V.; Di Cesare, A.; Šangulin, J.; Del Negro, P.; Celussi, M. Antibiotic Resistance Genes and Potentially Pathogenic Bacteria in the Central Adriatic Sea: Are They Connected to Urban Wastewater Inputs? Water 2021, 13, 3335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobacka, J.; Ivaska, A.; Lewenstam, A. Potentiometric Ion Sensors. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 329–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talarico, D.; Cinti, S.; Arduini, F.; Amine, A.; Moscone, D.; Palleschi, G. Phosphate Detection through a Cost-Effective Carbon Black Nanoparticle-Modified Screen-Printed Electrode Embedded in a Continuous Flow System. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 7934–7939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernhart, D.N.; Wreath, A.R. Colorimetric Determination of Phosphorus by Modified Phosphomolybdate Method. Anal. Chem. 1995, 27, 440–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worsfold, P.; McKelvie, I.; Monbet, P. Determination of phosphorus in natural waters: A historical review. Anal Chim Acta 2016, 918, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neal, C.; Neal, M.; Wickham, H. Phosphate measurement in natural waters: Two examples of analytical problems associated with silica interference using phosphomolybdic acid methodologies. Sci. Total Environ 2000, 251, 511–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsilia, M.; Susmel, S. Free-Standing Plastic Electrodes: Formulation, Electrochemical Characterization and Application to Dopamine Detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 255, 1087–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbone, M.; Aneggi, E.; Figueredo, F.; Susmel, S. NiO-nanoflowers decorating a plastic electrode for the non-enzymatic amperometric detection of H2O2 in milk: Old issue, new challenge. Food Control 2022, 132, 108549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueredo, F.; Girolametti, F.; Aneggi, E.; Lekka, M.; Annibaldi, A.; Susmel, S. Plastic electrode decorated with polyhedral anion tetrabutylammonium octamolybdate [N(C4H9)4]4 Mo8O26 for nM phosphate electrochemical detection. Anal. Chim. Acta 2021, 1161, 338469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonacci, A.; Arduini, F.; Attaallah, R.; Amine, A.; Giardi, M.T.; Scognamiglio, V. A Proof-of-Concept Electrochemical Cytosensor Based on Chlamydomonas reinhardtii Functionalized Carbon Black Screen-Printed Electrodes: Detection of Escherichia coli in Wastewater as a Case Study. Biosensors 2022, 12, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldrighi, E.; Muzlovic, P.; Annibaldi, A.; Penna, A.; Manini, E.; Rosetti, E.; Esposito Renzoni, E.; Grilli, F.; Giacomini, G.; Kristovic, I.; et al. ADSWIM and WATERCARE Projects Meet Kids and Youth: The Challenge of Bringing the World of Research to School to Merge Research, Education and Communication. Water 2022, 14, 1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

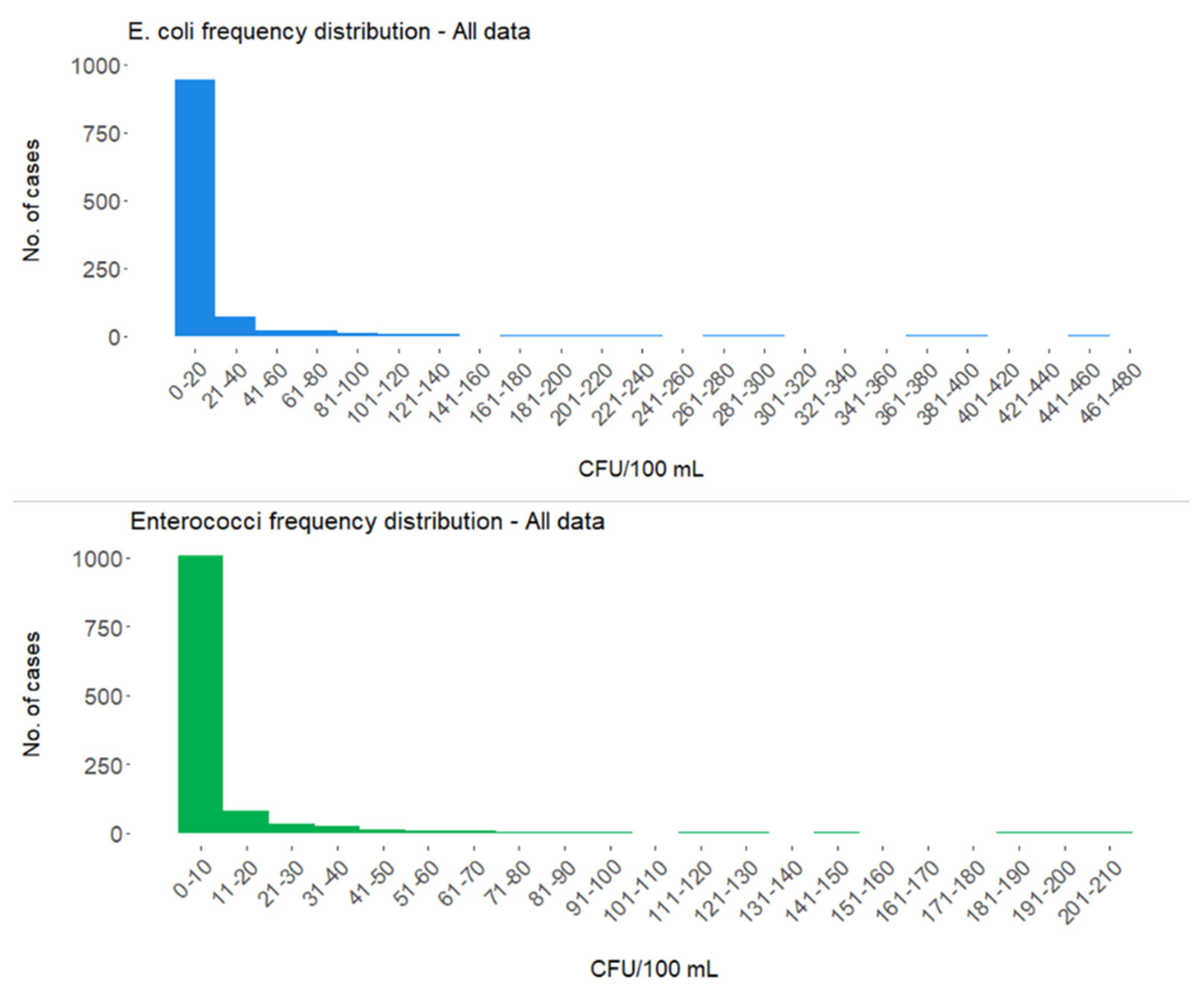

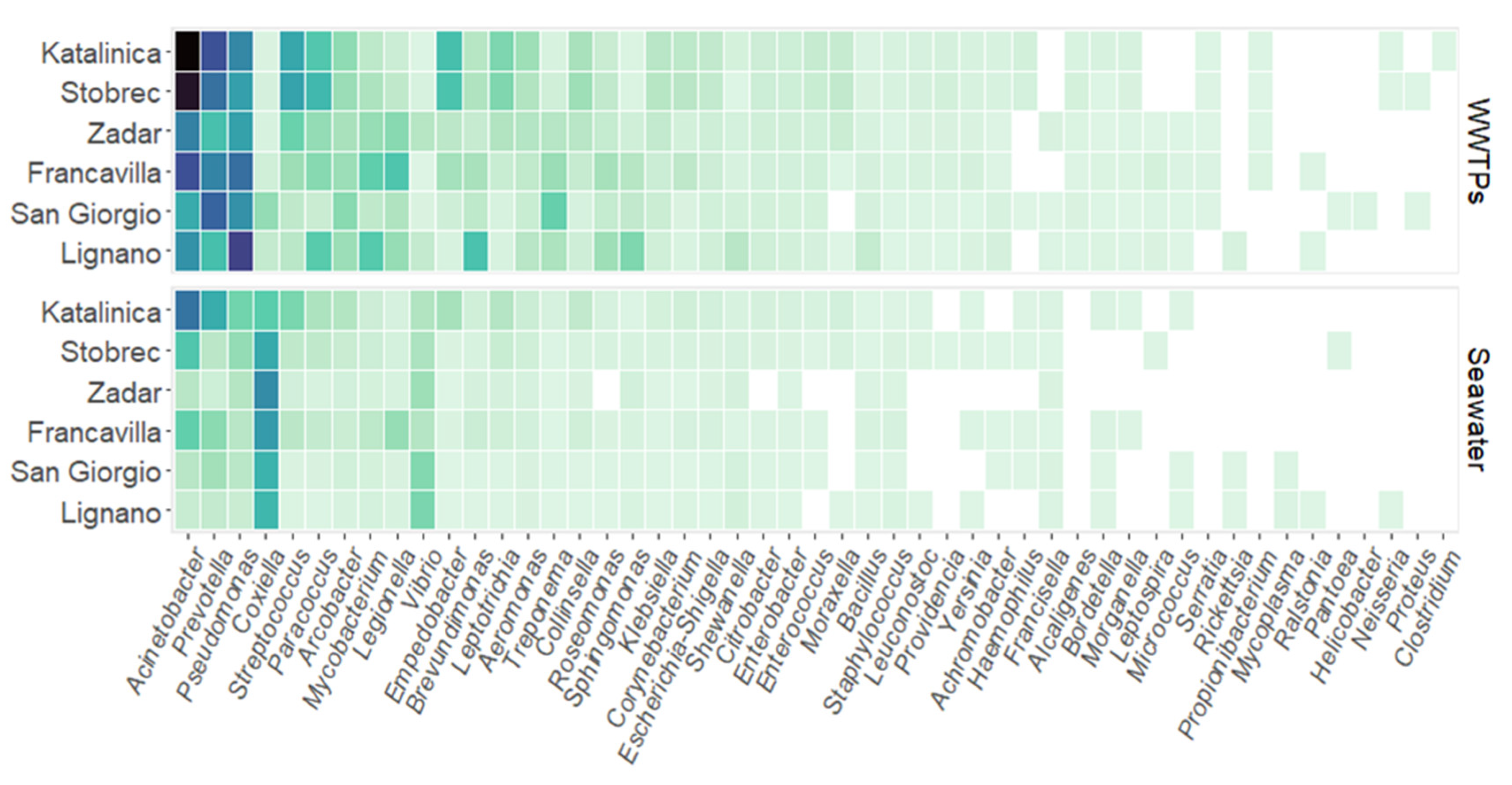
| Sampling Site (Year) | P-DIP | N-NO2 | N-NO3 | N-NH3 | Si-SiO2 | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Northern Adriatic (1991) | 3.1 ± 5.9 | 2.7 ± 2.9 | 21.9 ± 26.8 | 29 ± 18.9 | [5] | |
| Northern Adriatic (2003–2004) | 5.85–25.09 | [12] | ||||
| Northern Adriatic (1994) | 7.4 ± 0.9 | 70.8 | [13] | |||
| Northern Adriatic (1993–1994) | 3.7–6.5 | 14.43–46.6 | 6.4–14.3 | 20.2–118.8 | [14] | |
| Northern Adriatic surface | 1.5–3.8 | 8.1–44.5 | 14.3–158.1 | [15] | ||
| Northern Adriatic bottom | 0.6–2.2 | 5.6–17.5 | 37.6–70.8 | [16] | ||
| Gulf of Trieste (1992–1993) | <3–~30 | <70–~350 | ~14–~70 | <140~700 | [17] | |
| Gulf of Trieste (2006–2007) | ~0–13 | ~0–122.6 | <7.4–46.8 | ~0–191 | [18] | |
| Medium Adriatic (MSW, June–September) | 2.51 ± 1.58 | 0.99 ± 0.90 | 7.9 ± 9.5 | 16.67 ± 8.231 | [19] |
| Sampling Year | DIN | DIP | Si-SiO2 | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2001–2006 | 10.4–19.2 | 0.7–1.8 | 39–56 | EMODnet chemistry portal |
| 2006–2011 | ~14 | 0.7–1.3 | 34–48 | |
| 2011–2016 | ~21.4 | 0.7–0.9 | 17–34 | |
| 2015–2020 | 15.5–27 | 0.6–0.8 | 18.5–21.5 |
| Location, Sampling Year | Hg | Cd | Pb | As | Cr | Cu | Zn | Ni | Mn | Fe | Al | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Marano Lagoon (Italy), 2004 | 4.1–52.4 | nd | nd | nd | nd | nd | nd | nd | nd | nd | nd | [22] |
| Gulf of Trieste (Italy), 2011–2012 | 0.2–15 | nd | nd | nd | nd | nd | nd | nd | nd | nd | nd | [24] |
| Mljet National Park (Croatia), 2005–2008 | 0.5–24.2 (T) | 6.4–18.7 | 14.6–55.2 | nd | nd | 169–391 | 83.6–1098 | nd | nd | nd | nd | [25] |
| Southeast Adriatic coast (Montenegro) 2005–2007 | 200–2000 | 0–7400 | 1300–10,800 | 500–3100 | nd | 1400–19,700 | 400–36,100 | 2100–21,500 | 2400–20,000 | 3000–61,400 | nd | [26] |
| Durres Bay (Albania), 1999–2002 | 76.6–101.1 (T) | 121–187 (T) | 165–539 (T) | nd | 2992–3674 (T) | 170–990 (T) | 1111–5962 (T) | 440–1078 (T) | 66–308 (T) | 605–1210 (T) | nd | [27] |
| Ancona (Italy), 2005 | nd | 14 ± 1 | 30 ± 6 | nd | nd | 400 ± 38 | nd | nd | nd | nd | nd | [28] |
| Central Adriatic Sea, 2004 | nd | 15 ± 3 | 27 ± 12 | nd | nd | 597 ± 330 | nd | nd | nd | nd | nd | [29] |
| Po Plume (Italy), 2002 | nd | 14 ± 5 | 68 ± 43 | nd | nd | 337 ± 159 | nd | nd | nd | nd | nd | [30] |
| Mediterranean Sea, 1995 | nd | 7 | nd | nd | nd | 108 | 176 | 141 | nd | nd | nd | [21] |
| Isonzo River (Italy) | <LOD-8.60 | nd | <LOD-300 | 190–2310 | <LOD-310 | 150–1770 | <LOD-57,900 | <LOD-810 | 1070–16,900 | <LOD-6640 | nd | [21] |
| Gulf of Trieste (Italy), 2012 | 1 | nd | nd | 1500 | 620 | 2610 | 4640 | 880 | 1540 | 12,500 | nd | [31] |
| Venice Lagoon, 1992 | nd | nd | 4–30 | nd | nd | 240–560 | nd | 380–1130 | 270–1530 | 80–630 | nd | [32] |
| Adriatic Sea, 1992–1995 | nd | nd | nd | nd | nd | nd | nd | 290–1170 | 1400–5660 | 280–1840 | nd | [33] |
| Krka River (Croatia), 1997–2000 | 0.50–1.10 | nd | nd | nd | nd | nd | nd | nd | nd | nd | nd | [34] |
| Zrmanja River | nd | nd | 54,300–127,000 | 250–1740 | 220–110 | <50–1040 | nd | 40–6360 | 130–3220 | 6140–10,100 | nd | [35] |
| Gulf of Trieste, 1990–1999 | <0.20–4.9 | nd | nd | nd | nd | nd | nd | nd | nd | nd | nd | [36] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Susmel, S.; Girolametti, F.; Fonti, V.; Figueredo, F.; Scognamiglio, V.; Antonacci, A.; Manna, V.; Bilić, J.; Soljan, V.; De Bortoli, N.; et al. The Interreg Project AdSWiM: Managed Use of Treated Wastewater for the Quality of the Adriatic Sea. Water 2022, 14, 2460. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14162460
Susmel S, Girolametti F, Fonti V, Figueredo F, Scognamiglio V, Antonacci A, Manna V, Bilić J, Soljan V, De Bortoli N, et al. The Interreg Project AdSWiM: Managed Use of Treated Wastewater for the Quality of the Adriatic Sea. Water. 2022; 14(16):2460. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14162460
Chicago/Turabian StyleSusmel, Sabina, Federico Girolametti, Viviana Fonti, Federico Figueredo, Viviana Scognamiglio, Amina Antonacci, Vincenzo Manna, Josipa Bilić, Vice Soljan, Nicola De Bortoli, and et al. 2022. "The Interreg Project AdSWiM: Managed Use of Treated Wastewater for the Quality of the Adriatic Sea" Water 14, no. 16: 2460. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14162460







