What Is the Suitable Sampling Frequency for Water Quality Monitoring in Full-Scale Constructed Wetlands Treating Tail Water?
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
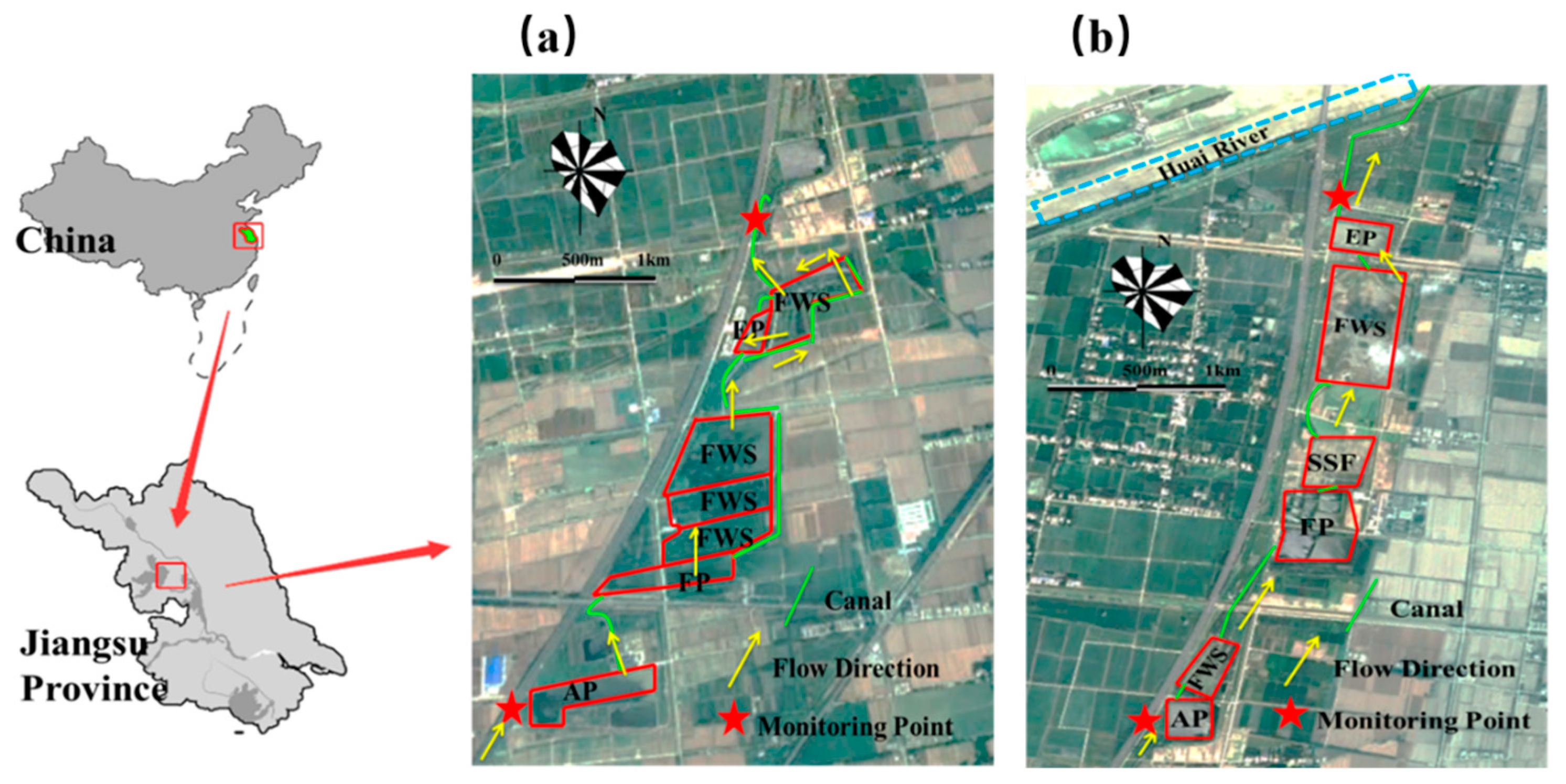
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Online Water Quality Monitoring
2.3. Data Evaluation Method
3. Results and Discussion
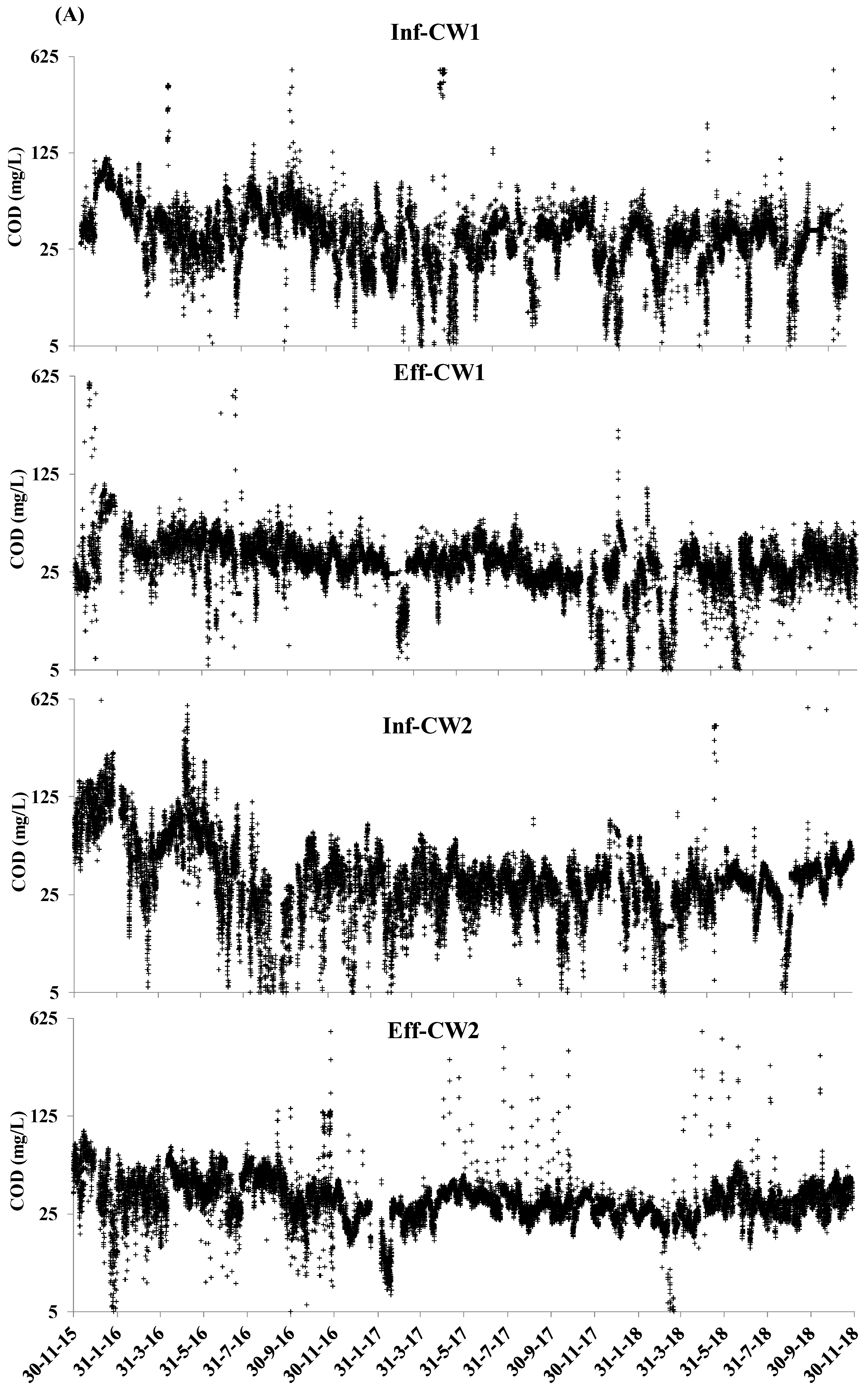
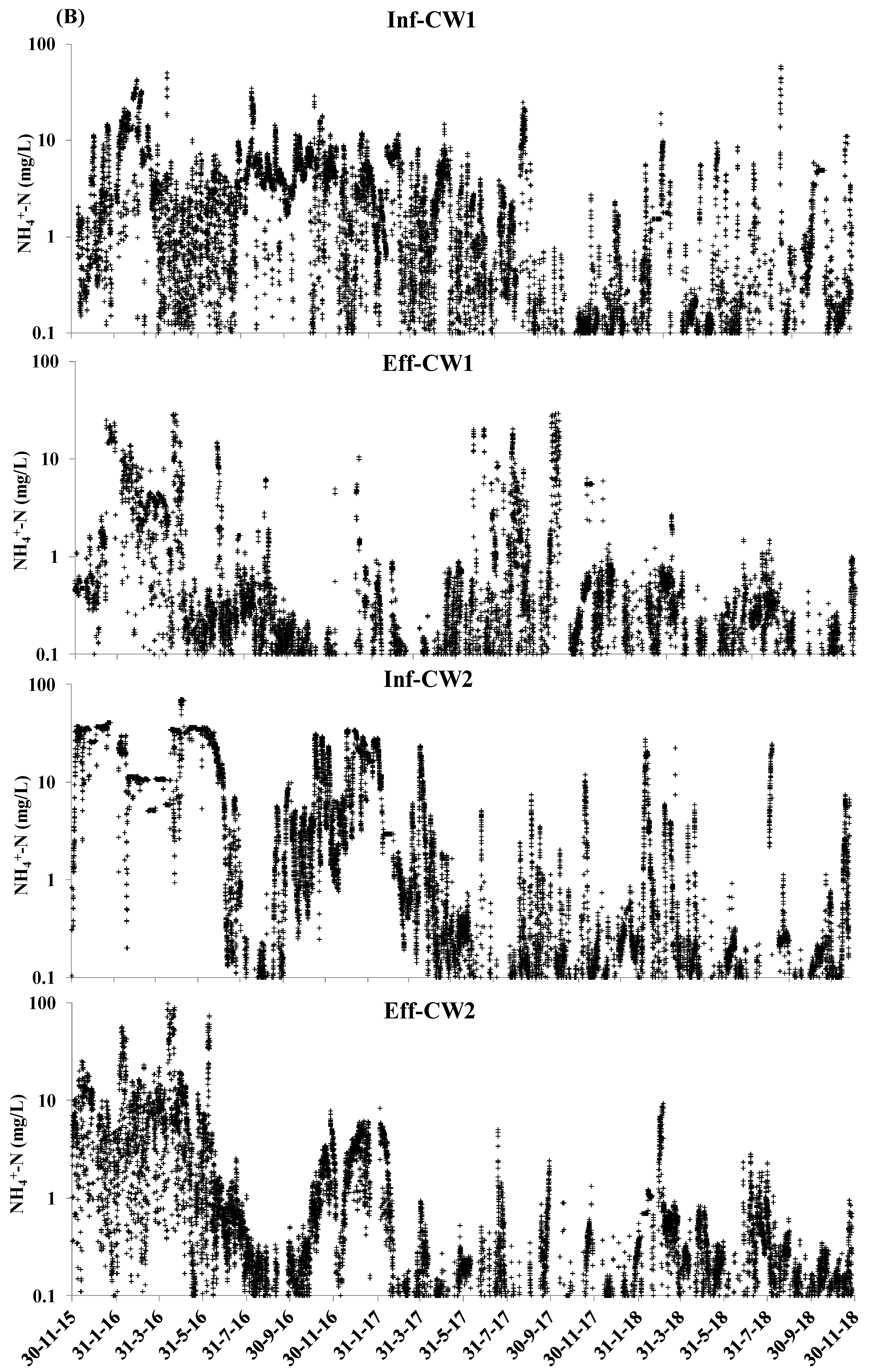
3.1. The Average Value and Coefficient of Variation of COD and NH4+-N
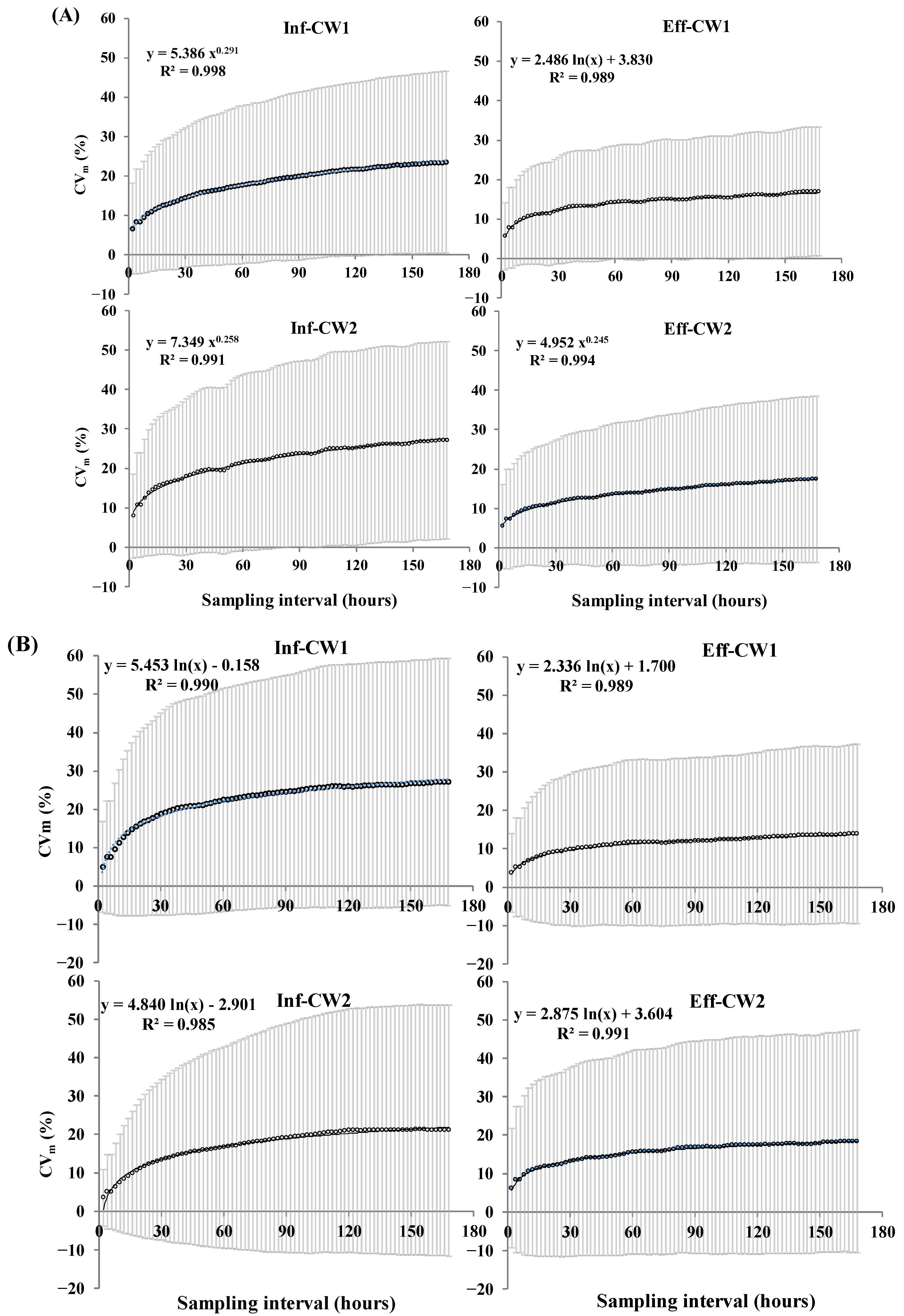
3.2. The Suitable Sampling Frequency in Modified Coefficient of Variation
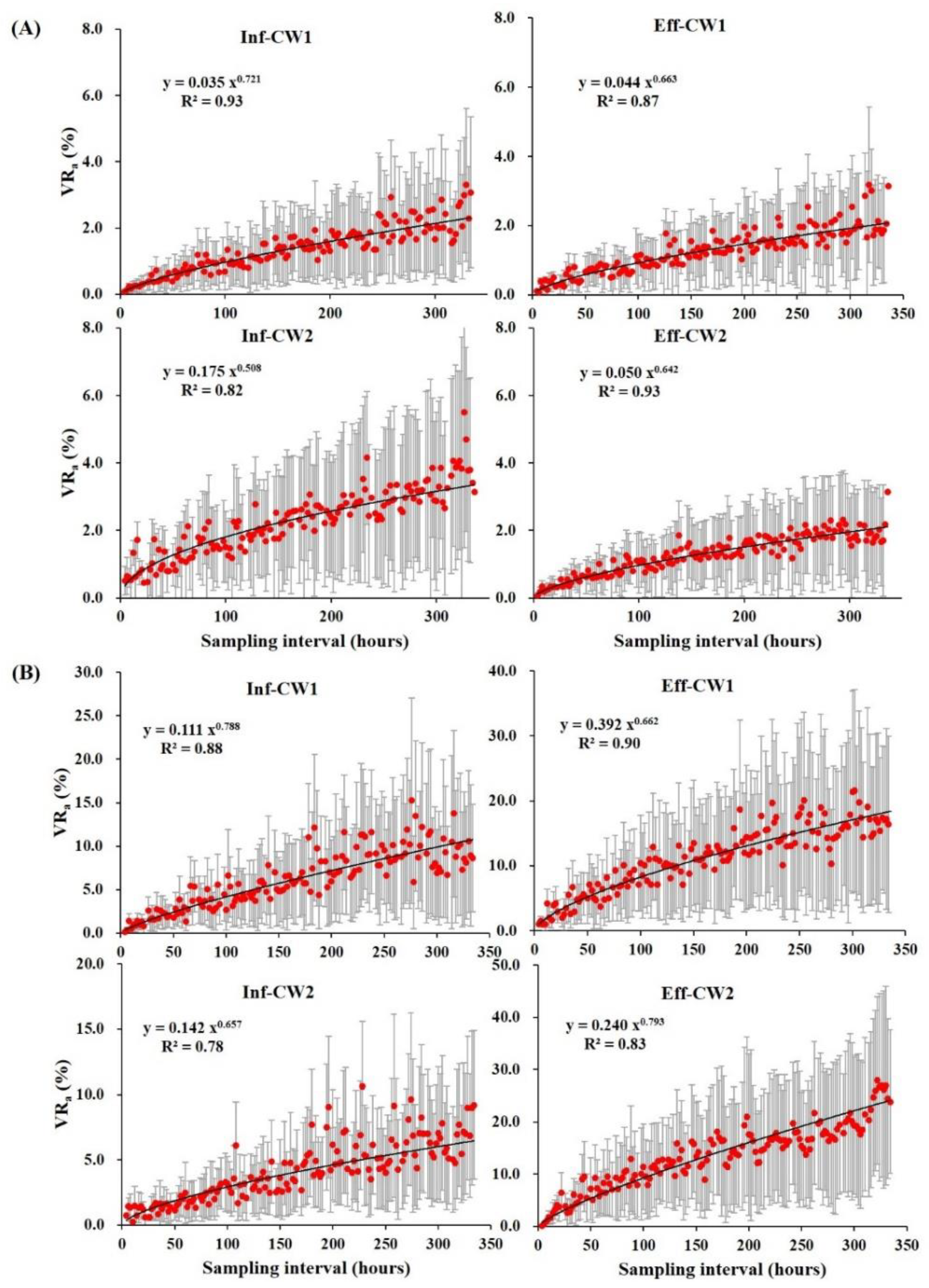
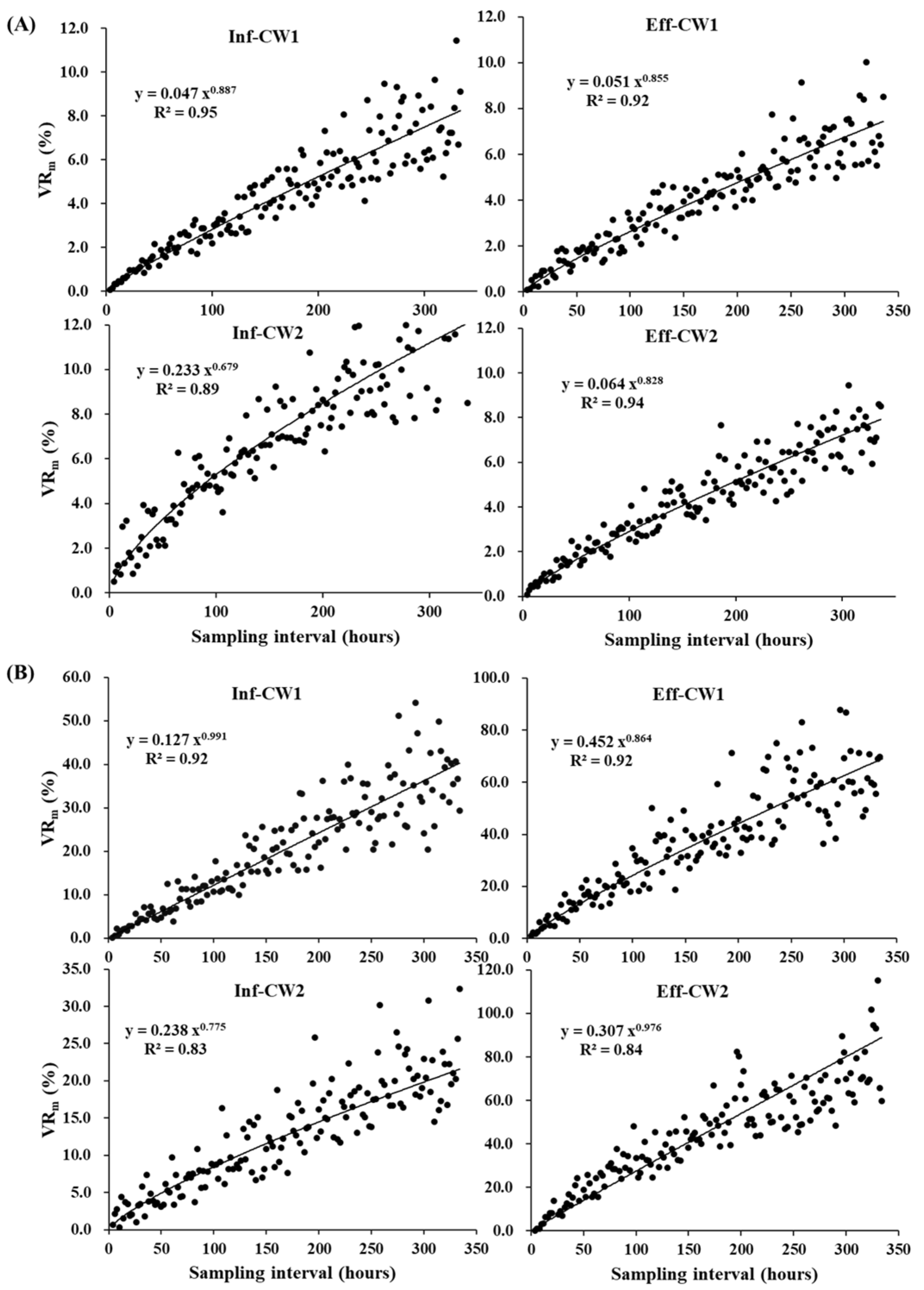
3.3. The Proper Sampling Interval in Average Variation Rate and the Maximum Variation Rate
3.3.1. Average Variation Rate (VRa)
3.3.2. The Maximum Average Variation Rate (VRm)
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ji, M.; Hu, Z.; Hou, C.; Liu, H.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W.; Lu, S.; Zhang, J. New insights for enhancing the performance of constructed wetlands at low temperatures. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 301, 122722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, M.; Rousseau, D.P.L.; Ahmed, S. A full-scale comparison of two hybrid constructed wetlands treating domestic wastewater in Pakistan. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 210, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Engel, B.A.; Flanagan, D.C.; Gitau, M.W.; McMillan, S.K.; Chaubey, I. A review on effectiveness of best management practices in improving hydrology and water quality: Needs and opportunities. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 601–602, 580–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matamoros, V.; Rodriguez, Y.; Bayona, J.M. Mitigation of emerging contaminants by full-scale horizontal flow constructed wetlands fed with secondary treated wastewater. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 99, 222–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelissari, C.; Ávila, C.; Trein, C.M.; García, J.; de Armas, R.D.; Sezerino, P.H. Nitrogen transforming bacteria within a full-scale partially saturated vertical subsurface flow constructed wetland treating urban wastewater. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 574, 390–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, H.; Fan, J.; Zhang, J.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W. Large-scale multi-stage constructed wetlands for secondary effluents treatment in northern China: Carbon dynamics. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 233, 933–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Drake, C.; Jones, C.; Schilling, K.; Amado, A.A.; Weber, L. Estimating nitrate-nitrogen retention in a large constructed wetland using high-frequency, continuous monitoring and hydrologic modeling. Ecol. Eng. 2018, 117, 69–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rode, M.; Wade, A.J.; Cohen, M.J.; Hensley, R.; Bowes, M.; Kirchner, J.W.; Arhonditsis, G.; Jordan, P.; Kronvang, B.; Halliday, S.; et al. Sensors in the Stream: The High-Frequency Wave of the Present. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 10297–10307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Valkama, P.; Mäkinen, E.; Ojala, A.; Vahtera, H.; Lahti, K.; Rantakokko, K.; Vasander, H.; Nikinmaa, E.; Wahlroos, O. Seasonal variation in nutrient removal efficiency of a boreal wetland detected by high-frequency on-line monitoring. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 98, 307–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chappell, N.A.; Jones, T.D.; Tych, W. Sampling frequency for water quality variables in streams: Systems analysis to quantify minimum monitoring rates. Water Res. 2017, 123, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Cai, Y.; Jiang, H.; Xu, D.; Zhang, W.; An, S. Estimation of water clarity in Taihu Lake and surrounding rivers using Landsat imagery. Adv. Water Resour. 2011, 34, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brauer, N.; O’Geen, A.T.; Dahlgren, R.A. Temporal variability in water quality of agricultural tailwaters: Implications for water quality monitoring. Agric. Water Manag. 2009, 96, 1001–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, A.S.; Horsburgh, J.S.; Mesner, N.O.; Ryel, R.J.; Stevens, D.K. Influence of sampling frequency on estimation of annual total phosphorus and total suspended solids loads. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2012, 48, 1258–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreo-Martínez, P.; García-Martínez, N.; Quesada-Medina, J.; Almela, L. Domestic wastewaters reuse reclaimed by an improved horizontal subsurface-flow constructed wetland: A case study in the southeast of Spain. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 233, 236–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ávila, C.; Salas, J.J.; Martín, I.; Aragón, C.; García, J. Integrated treatment of combined sewer wastewater and stormwater in a hybrid constructed wetland system in southern Spain and its further reuse. Ecol. Eng. 2013, 50, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilmin, L.; Flipo, N.; Escoffier, N.; Groleau, A. Estimation of the water quality of a large urbanized river as defined by the European WFD: What is the optimal sampling frequency? Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 23485–23501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, S.; Liu, B.; Zhang, W.; Wang, P.; Qiao, Y.; Zhao, D.; Yang, T.; An, S.; Leng, X. Performance of a large-scale wetland treatment system in treating tailwater from a sewage treatment plant. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2018, 69, 833–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Zhang, M.; Liu, Z.; Sheng, J.; An, S. Can cold-season macrophytes at the senescence stage improve nitrogen removal in integrated constructed wetland systems treating low carbon/nitrogen effluent? Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 265, 380–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wen, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Vymazal, J. Effects of plant biomass on nitrogen transformation in subsurface-batch constructed wetlands: A stable isotope and mass balance assessment. Water Res. 2014, 63, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Yin, Q.; Wen, Y.; Guo, W.; Liu, C.; Zhou, Q. Enhanced nitrate removal in self-supplying carbon source constructed wetlands treating secondary effluent: The roles of plants and plant fermentation broth. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 91, 310–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dunne, E.J.; Coveney, M.F.; Marzolf, E.R.; Hoge, V.R.; Conrow, R.; Naleway, R.; Lowe, E.F.; Battoe, L.E.; Inglett, P.W. Nitrogen dynamics of a large-scale constructed wetland used to remove excess nitrogen from eutrophic lake water. Ecol. Eng. 2013, 61, 224–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilley, D.R.; Badrinarayanan, H.; Rosati, R.; Son, J. Constructed wetlands as recirculation filters in large-scale shrimp aquaculture. Aquac. Eng. 2002, 26, 81–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Zhang, J.; Guo, W.; Liang, S.; Fan, J. Secondary effluent purification by a large-scale multi-stage surface-flow constructed wetland: A case study in northern China. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 249, 1092–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jóźwiakowski, K.; Bugajski, P.; Kurek, K.; Cáceres, R.; Siwiec, T.; Jucherski, A.; Czekała, W.; Kozłowski, K. Technological reliability of pollutant removal in different seasons in one-stage constructed wetland system with horizontal flow operating in the moderate climate. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 238, 116439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Wallace, S.; Brix, H.; Kuschk, P.; Kirui, W.K.; Masi, F.; Dong, R. Treatment of industrial effluents in constructed wetlands: Challenges, operational strategies and overall performance. Environ. Pollut. 2015, 201, 107–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaen, P.J.; Khamis, K.; Lloyd, C.E.; Bradley, C.; Hannah, D.; Krause, S. Real-time monitoring of nutrients and dissolved organic matter in rivers: Capturing event dynamics, technological opportunities and future directions. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 569–570, 647–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rizzo, A.; Langergraber, G. Novel insights on the response of horizontal flow constructed wetlands to sudden changes of influent organic load: A modeling study. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 93, 242–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvao, A.; Matos, J. Response of horizontal sub-surface flow constructed wetlands to sudden organic load changes. Ecol. Eng. 2012, 49, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, J.; Green, B.; Lundquist, T.; Mujeriego, R.; Hernández-Mariné, M.; Oswald, W. Long term diurnal variations in contaminant removal in high rate ponds treating urban wastewater. Bioresour. Technol. 2006, 97, 1709–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahl, S.; Nivala, J.; van Afferden, M.; Müller, R.A.; Reemtsma, T. Effect of design and operational conditions on the performance of subsurface flow treatment wetlands: Emerging organic contaminants as indicators. Water Res. 2017, 125, 490–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fauvel, B.; Cauchie, H.-M.; Gantzer, C.; Ogorzaly, L. Contribution of hydrological data to the understanding of the spatio-temporal dynamics of F-specific RNA bacteriophages in river water during rainfall-runoff events. Water Res. 2016, 94, 328–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Site | COD | NH4+-N | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean (mg L−1) | CV (%) | Mean (mg L−1) | CV (%) | |
| Inf-CW1 | 34.7 | 82.3 | 2.41 | 182.9 |
| Eff-CW1 | 31.3 | 100.6 | 0.92 | 302.2 |
| Inf-CW2 | 40.4 | 100.0 | 6.21 | 183.9 |
| Eff-CW2 | 33.1 | 46.1 | 1.83 | 316.0 |
| Site | Season | COD | NH4+-N | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5% | 10% | 15% | 5% | 10% | 15% | ||
| Inf-CW1 | Spring | 0.3 | 4.0 | 17.8 | 1.3 | 3.3 | 8.2 |
| Summer | 1.4 | 13.6 | 51.9 | 3.0 | 8.0 | 21.5 | |
| Autumn | 1.1 | 12.7 | 53.7 | 4.3 | 12.8 | 38.2 | |
| Winter | 0.9 | 8.3 | 29.8 | 3.6 | 6.9 | 13.5 | |
| Overall | 0.8 | 8.4 | 33.9 | 2.7 | 6.6 | 16.3 | |
| Eff-CW1 | Spring | 1.1 | 8.9 | 72.6 | 4.2 | 50.6 | 611.4 |
| Summer | 1.0 | 11.2 | 121.3 | 2.9 | 17.1 | 100.4 | |
| Autumn | 1.4 | 24.4 | 413.5 | 22.1 | 204.0 | 748.0 | |
| Winter | 1.3 | 12.4 | 47.3 | 2.9 | 15.9 | 86.0 | |
| Overall | 1.7 | 12.2 | 89.0 | 4.2 | 35.1 | 291.6 | |
| Inf-CW2 | Spring | 1.4 | 4.7 | 15.9 | 4.6 | 12.7 | 35.4 |
| Summer | 1.1 | 12.7 | 53.7 | 10.5 | 88.4 | 744.8 | |
| Autumn | 0.4 | 4.9 | 21.2 | 4.0 | 9.2 | 21.0 | |
| Winter | 1.8 | 4.1 | 9.5 | 3.6 | 15.0 | 34.2 | |
| Overall | 0.2 | 3.4 | 16.0 | 5.3 | 14.7 | 40.7 | |
| Eff-CW2 | Spring | 2.2 | 21.6 | 81.7 | 1.5 | 6.2 | 26.5 |
| Summer | 3.4 | 28.8 | 247.4 | 5.5 | 65.5 | 775.6 | |
| Autumn | 0.3 | 9.6 | 66.6 | 1.6 | 30.6 | 170.6 | |
| Winter | 0.9 | 14.6 | 75.5 | 0.7 | 2.5 | 8.1 | |
| Overall | 1.1 | 17.8 | 92.3 | 1.7 | 9.4 | 52.8 | |
| Site | COD | NH4+-N | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5% | 10% | 5% | 10% | ||
| Inf-CW1 | 2018 | 450.0 | 1124.3 | 21.6 | 51.1 |
| 2017 | 342.7 | 811.4 | 94.7 | 179.8 | |
| 2016 | 427.4 | 1019.9 | 102.8 | 193.9 | |
| Eff-CW1 | 2018 | 379.5 | 1083.7 | 44.4 | 88.5 |
| 2017 | 817.6 | 2234.8 | 10.8 | 28.4 | |
| 2016 | 451.4 | 1020.3 | 53.9 | 129.4 | |
| Inf-CW2 | 2018 | 459.9 | 1131.7 | 30.5 | 63.1 |
| 2017 | 261.6 | 530.1 | 96.2 | 177.3 | |
| 2016 | 232.1 | 665.8 | 200.9 | 421.8 | |
| Eff-CW2 | 2018 | 822.1 | 2175.4 | 34.7 | 84.7 |
| 2017 | 1255.6 | 3753.9 | 62.9 | 160.7 | |
| 2016 | 417.9 | 1269.3 | 41.8 | 92.3 | |
| Site | COD | NH4+-N | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5% | 10% | 5% | 10% | ||
| Inf-CW1 | 2018 | 107.0 | 215.2 | 11.6 | 20.8 |
| 2017 | 88.4 | 179.2 | 40.8 | 72.4 | |
| 2016 | 108.9 | 221.3 | 44.3 | 76.0 | |
| Eff-CW1 | 2018 | 79.7 | 181.3 | 20.7 | 39.3 |
| 2017 | 161.6 | 357.0 | 6.1 | 12.4 | |
| 2016 | 125.0 | 248.8 | 19.3 | 40.2 | |
| Inf-CW2 | 2018 | 109.7 | 228.8 | 12.0 | 23.0 |
| 2017 | 91.6 | 171.4 | 42.7 | 77.2 | |
| 2016 | 53.8 | 123.6 | 70.0 | 134.4 | |
| Eff-CW2 | 2018 | 156.1 | 338.1 | 14.8 | 30.6 |
| 2017 | 163.9 | 361.6 | 21.5 | 45.5 | |
| 2016 | 75.3 | 175.3 | 18.2 | 34.5 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, S.; Sheng, S.; Xu, J.; Zhao, D. What Is the Suitable Sampling Frequency for Water Quality Monitoring in Full-Scale Constructed Wetlands Treating Tail Water? Water 2022, 14, 2431. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14152431
Song S, Sheng S, Xu J, Zhao D. What Is the Suitable Sampling Frequency for Water Quality Monitoring in Full-Scale Constructed Wetlands Treating Tail Water? Water. 2022; 14(15):2431. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14152431
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Siyuan, Sheng Sheng, Jianqiang Xu, and Dehua Zhao. 2022. "What Is the Suitable Sampling Frequency for Water Quality Monitoring in Full-Scale Constructed Wetlands Treating Tail Water?" Water 14, no. 15: 2431. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14152431
APA StyleSong, S., Sheng, S., Xu, J., & Zhao, D. (2022). What Is the Suitable Sampling Frequency for Water Quality Monitoring in Full-Scale Constructed Wetlands Treating Tail Water? Water, 14(15), 2431. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14152431





