Evaluation of Reference Evapotranspiration Estimation Methods for the Assessment of Hydrological Impacts of Photovoltaic Power Plants in Mediterranean Climates
Abstract
:1. Introduction
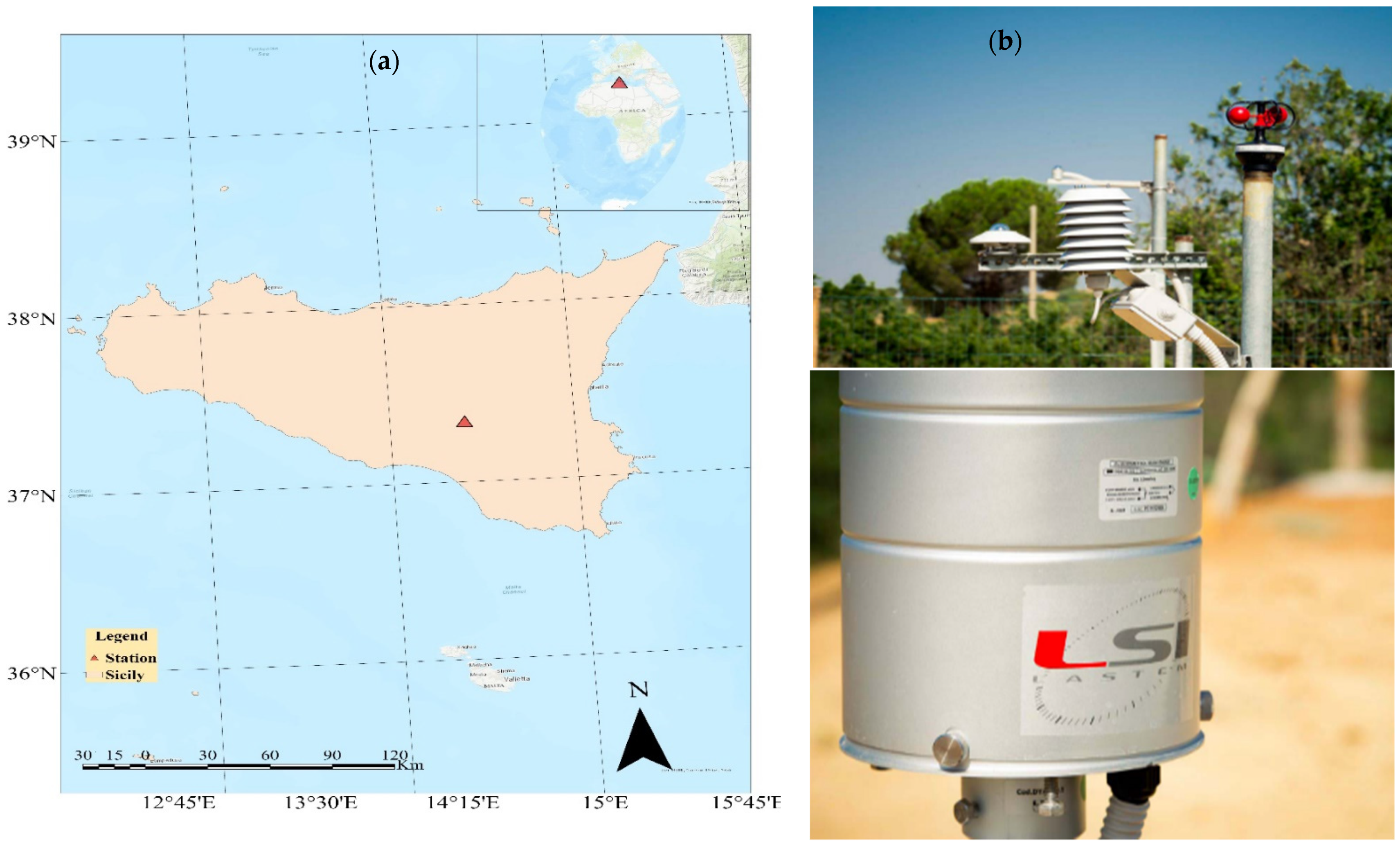
2. Study Area and Data
2.1. The Standardized ETo Estimation (FAO/Penman–Monteith) Method
2.2. Selected ETo Estimation Methods
2.3. Statistical Analysis
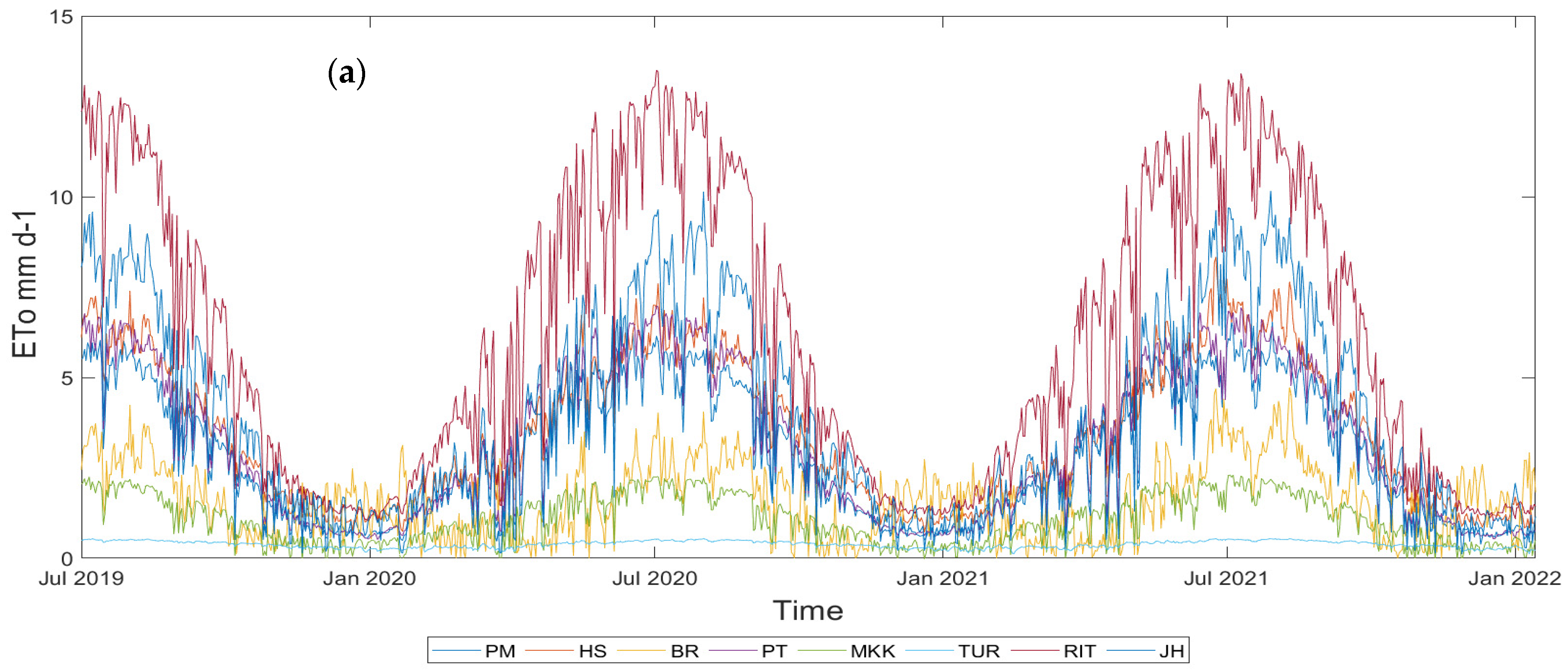
3. Results
4. Discussion
- A.
- Hargreaves and Samani (1985)
- B.
- Baier–Robertson (1965)
- C.
- Priestley–Taylor (1972)
- D.
- Makkink (1957)
- E.
- Turc (1961)
- F.
- Thornthwaite (1957)
- G.
- Blaney and Criddle (1950)
- H.
- Ritchie (1972)
- I.
- Jensen and Haise (1963)
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Edalat, M.M.; Stephen, H. Effects of two utility-scale solar energy plants on land-cover patterns using SMA of Thematic Mapper data. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 67, 1139–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grippo, M.; Hayse, J.W.; O’Connor, B.L. Solar Energy Development and Aquatic Ecosystems in the Southwestern United States: Potential Impacts, Mitigation, and Research Needs. Environ. Manag. 2014, 55, 244–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armstrong, A.; Ostle, N.J.; Whitaker, J. Solar park microclimate and vegetation management effects on grassland carbon cycling. Environ. Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 074016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Armstrong, A.; Waldron, S.; Whitaker, J.; Ostle, N. Wind farm and solar park effects on plant-soil carbon cycling: Uncertain impacts of changes in ground-level microclimate. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2014, 20, 1699–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cagle, A.; Armstrong, A.; Exley, G.; Grodsky, S.; Macknick, J.; Sherwin, J.; Hernandez, R. The Land Sparing, Water Surface Use Efficiency, and Water Surface Transformation of Floating Photovoltaic Solar Energy Installations. Sustainability 2020, 12, 8154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, R.R.; Armstrong, A.; Burney, J.; Ryan, G.; Moore-O’Leary, K.; Diédhiou, I.; Grodsky, S.M.; Saul-Gershenz, L.; Davis, R.; Macknick, J.; et al. Techno–ecological synergies of solar energy for global sustainability. Nat. Sustain. 2019, 2, 560–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barron-Gafford, G.A.; Minor, R.L.; Allen, N.A.; Cronin, A.D.; Brooks, A.E.; Pavao-Zuckerman, M.A. The photovoltaic heat island effect: Larger solar power plants increase local temperatures. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nemet, G.F. Net radiative forcing from widespread deployment of photovoltaics. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 2173–2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Gao, X.; Lv, F.; Hui, X.; Ma, L.; Hou, X. Study on the local climatic effects of large photovoltaic solar farms in desert areas. Solar Energy 2017, 144, 244–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broadbent, A.M.; Krayenhoff, E.S.; Georgescu, M.; Sailor, D.J. The observed effects of utility-scale photovoltaics on near-surface air temperature and energy balance. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2019, 58, 989–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Gao, P.; Mu, X. Influence of meteorological factors on the potential evapotranspiration in yanhe river basin, China. Water 2021, 13, 1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MÉszároš, I.; Miklánek, P. Calculation of potential evapotranspiration based on solar radiation income modeling in mountainous areas. Biologia 2006, 61, 284–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebler, S.; Franssen, H.-J.H.; Pütz, T.; Post, H.; Schmidt, M.; Vereecken, H. Actual evapotranspiration and precipitation measured by lysimeters: A comparison with eddy covariance and tipping bucket. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 19, 2145–2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moeletsi, M.E.; Walker, S.; Hamandawana, H. Comparison of the Hargreaves and Samani equation and the Thornthwaite equation for estimating dekadal evapotranspiration in the Free State Province, South Africa. Phys. Chem. Earth, Parts A/B/C 2013, 66, 4–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochoa-Sánchez, A.; Crespo, P.; Carrillo-Rojas, G.; Sucozhañay, A.; Célleri, R. Actual Evapotranspiration in the High Andean Grasslands: A Comparison of Measurement and Estimation Methods. Front. Earth Sci. 2019, 7, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pandey, P.K.; Dabral, P.P.; Pandey, V. Evaluation of reference evapotranspiration methods for the northeastern region of India. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2016, 4, 52–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alemu, H.; Kaptué, A.T.; Senay, G.B.; Wimberly, M.C.; Henebry, G.M. Evapotranspiration in the Nile Basin: Identifying dynamics and drivers, 2002–2011. Water 2015, 7, 4914–4931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, D. Methods of Evapotranspiration; CCS Haryana Agricultural University: Hisar, India, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharsallah, O.; Facchi, A.; Gandolfi, C. Comparison of six evapotranspiration models for a surface irrigated maize agro-ecosystem in Northern Italy. Agric. Water Manag. 2013, 130, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatfield, J.L.; Prueger, J.H.; Kustas, W.P.; Anderson, M.C.; Alfieri, J.G. Evapotranspiration: Evolution of Methods to Increase Spatial and Temporal Resolution. Advancesin 2016, 7, 159–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, D.; Singh, V.P. A Two-source Trapezoid Model for Evapotranspiration (TTME) from satellite imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 121, 370–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanner, C.B. Measurement of evapotranspiration. Irrig. Agric. Lands 1967, 11, 534–574. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, D.; Gao, G.; Xu, C.-Y.; Guo, J.; Ren, G. Comparison of the Thornthwaite method and pan data with the standard Penman-Monteith estimates of reference evapotranspiration in China. Clim. Res. 2005, 28, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.-Y.; Singh, V.P. Cross Comparison of Empirical Equations for Calculating Potential Evapotranspiration with Data from Switzerland. Water Resour. Manag. 2002, 16, 197–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingston, D.G.; Todd, M.C.; Taylor, R.G.; Thompson, J.R.; Arnell, N.W. Uncertainty in the estimation of potential evapotranspiration under climate change. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moorhead, J.E.; Marek, G.W.; Gowda, P.H.; Lin, X.; Colaizzi, P.D.; Evett, S.R.; Kutikoff, S. Evaluation of Evapotranspiration from Eddy Covariance Using Large Weighing Lysimeters. Agronomy 2019, 9, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Estévez, J.; Gavilán, P.; Berengena, J. Sensitivity analysis of a Penman–Monteith type equation to estimate reference evapotranspiration in southern Spain. Hydrol. Processes 2009, 23, 3342–3353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subedi, A.; Chávez, J.L. Crop Evapotranspiration (ET) Estimation Models: A Review and Discussion of the Applicability and Limitations of ET Methods. J. Agric. Sci. 2015, 7, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Utset, A.; Farré, I.; Martínez-Cob, A.; Cavero, J. Comparing Penman–Monteith and Priestley–Taylor approaches as reference-evapotranspiration inputs for modeling maize water-use under Mediterranean conditions. Agric. Water Manag. 2004, 66, 205–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rana, G.; Katerji, N. Measurement and estimation of actual evapotranspiration in the field under Mediterranean climate: A review. Eur. J. Agron. 2000, 13, 125–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agnese, C.; Cammalleri, C.; Mario, M.; Provenzano, G.; Rallo, G. Testing Approach to Estimate Hourly Reference Evapotranspiration with Scintillometer Measurements Under Mediterranean Climate, Nuovi Scenari Agroambientali: Fenologia, Produzioni Agrarie e Avversità. In Proceedings of the XV Convegno Nazionale Dell’associazione Italiana Di Agrometeorologia, Palermo, Italy, 5–7 June 2012; pp. 123–124. [Google Scholar]
- de Melo, G.L.; Fernandes, A.L.T. Evaluation of empirical methods to estimate reference evapotranspiration in Uberaba, State of Minas Gerais, Brazil. Eng. Agrícola 2012, 32, 875–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lang, D.; Zheng, J.; Shi, J.; Liao, F.; Ma, X.; Wang, W.; Chen, X.; Zhang, M. A Comparative Study of Potential Evapotranspiration Estimation by Eight Methods with FAO Penman–Monteith Method in Southwestern China. Water 2017, 9, 734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nikam, B.R.; Kumar, P.; Garg, V.; Thakur, P.K.; Aggarwal, S.P. Comparative evaluation of different potential evapotranspiration estimation approaches. Int. J. Res. Eng. Technol. 2014, 3, 544–552. [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigues, G.; Braga, R. Estimation of Reference Evapotranspiration during the Irrigation Season Using Nine Temperature-Based Methods in a Hot-Summer Mediterranean Climate. Agriculture 2021, 11, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaç, S.S.; Todorovic, M. Estimation of daily potato crop evapotranspiration using three different machine learning algorithms and four scenarios of available meteorological data. Agric. Water Manag. 2020, 228, 105875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tikhamarine, Y.; Malik, A.; Kumar, A.; Souag-Gamane, D.; Kisi, O. Estimation of monthly reference evapotranspiration using novel hybrid machine learning approaches. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2019, 64, 1824–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulualem, G.M.; Liou, Y.-A. Application of Artificial Neural Networks in Forecasting a Standardized Precipitation Evapotranspiration Index for the Upper Blue Nile Basin. Water 2020, 12, 643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tellen, V.A. A comparative analysis of reference evapotranspiration from the surface of rainfed grass in Yaounde, calculated by six empirical methods against the penman-monteith formula. Earth Perspect. 2017, 4, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Todorovic, M.; Karic, B.; Pereira, L.S. Reference evapotranspiration estimate with limited weather data across a range of Mediterranean climates. J. Hydrol. 2012, 481, 166–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goh, E.H.; Ng, J.L.; Huang, Y.F.; Yong, S.L.S. Performance of potential evapotranspiration models in Peninsular Malaysia. J. Water Clim. Change 2021, 12, 3170–3186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azhar, A.H.; Perera, B.J.C. Evaluation of Reference Evapotranspiration Estimation Methods under Southeast Australian Conditions. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2011, 137, 268–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazari, M.; Chaichi, M.R.; Kamel, H.; Grismer, M.; Sadeghi, S.M.M. Evaluation of Estimation Methods for Monthly Reference Evapotranspiration in Arid Climates. Arid. Ecosyst. 2020, 10, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndulue, E.; Ranjan, R.S. Performance of the FAO Penman-Monteith equation under limiting conditions and fourteen reference evapotranspiration models in southern Manitoba. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2021, 143, 1285–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minacapilli, M.; Cammalleri, C.; Ciraolo, G.; Rallo, G.; Provenzano, G. Using scintillometry to assess reference evapotranspiration methods and their impact on the water balance of olive groves. Agric. Water Manag. 2016, 170, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartholy, J. Global Climate Modells and Regional Climate Projections for the 21st Century; Eötvös Loránd University: Budapest, Hungary, 1997; pp. 189–199. [Google Scholar]
- Torina, A.; Khoury, C.; Caracappa, S.; Maroli, M. Ticks Infesting Livestock on Farms in Western Sicily, Italy. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2006, 38, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonaccorso, B.; Cancelliere, A.; Rossi, G. Probabilistic forecasting of drought class transitions in Sicily (Italy) using Standardized Precipitation Index and North Atlantic Oscillation Index. J. Hydrol. 2015, 526, 136–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandris, S.; Stricevic, R.; Petkovic, S. Comparative analysis of reference evapotranspiration from the surface of rainfed grass in central Serbia, calculated by six empirical methods against the Penman-Monteith formula. Eur. Water 2008, 21, 17–28. [Google Scholar]
- Almorox, J.; Senatore, A.; Quej, V.H.; Mendicino, G. Worldwide assessment of the Penman–Monteith temperature approach for the estimation of monthly reference evapotranspiration. Arch. Meteorol. Geophys. Bioclimatol. Ser. B 2016, 131, 693–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonopoulos, V.Z.; Antonopoulos, A.V. Evaluation of different methods to estimate monthly reference evapotranspiration in a Mediterranean area. Water Util. J. 2002, 18, 61–77. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, L.; Xu, C.-Y.; Chen, D.; Halldin, S.; Chen, Y.D. Sensitivity of the Penman–Monteith reference evapotranspiration to key climatic variables in the Changjiang (Yangtze River) basin. J. Hydrol. 2006, 329, 620–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seginer, I. The Penman—Monteith Evapotranspiration Equation as an Element in Greenhouse Ventilation Design. Biosyst. Eng. 2002, 82, 423–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Schrier, G.; Jones, P.D.; Briffa, K.R. The sensitivity of the PDSI to the Thornthwaite and Penman-Monteith parameterizations for potential evapotranspiration. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2011, 116, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCuen, R.H.; Knight, Z.; Cutter, A.G. Evaluation of the Nash–Sutcliffe Efficiency Index. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2006, 11, 597–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.; Li, Y.; Feng, H. The best alternative for estimating reference crop evapotranspiration in different sub-regions of mainland China. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 5458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gupta, H.V.; Kling, H. On typical range, sensitivity, and normalization of Mean Squared Error and Nash-Sutcliffe Efficiency type metrics. Water Resour. Res. 2011, 47, W10601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, S.K.; Sudheer, K.P. Fitting of Hydrologic Models: A Close Look at the Nash–Sutcliffe Index. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2008, 13, 981–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.X.; Thomas, A. Spatiotemporal variability of reference evapotranspiration and its contributing climatic factors in Yunnan Province, SW China, 1961–2004. Clim. Change 2013, 116, 309–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gul, S.; Ren, J.; Xiong, N.; Khan, M.A. Design and analysis of statistical probability distribution and nonparametric trend analysis for reference evapotranspiration. PeerJ 2021, 9, e11597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Traore, S.; Cui, Y.; Luo, Y.; Zhu, G.; Liu, B.; Fipps, G.; Karthikeyan, R.; Singh, V. Assessment of spatiotemporal variability of reference evapotranspiration and controlling climate factors over decades in China using geospatial techniques. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 213, 499–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valipour, M. Retracted: Comparative Evaluation of Radiation-Based Methods for Estimation of Potential Evapotranspiration. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2015, 20, 04014068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senatore, A.; Mendicino, G.; Cammalleri, C.; Ciraolo, G. Regional-Scale Modeling of Reference Evapotranspiration: Intercomparison of Two Simplified Temperature- and Radiation-Based Approaches. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2015, 141, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepaskhah, A.R.; Razzaghi, F. Evaluation of the adjusted Thornthwaite and Hargreaves-Samani methods for estimation of daily evapotranspiration in a semi-arid region of Iran. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2009, 55, 51–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quej, V.H.; Almorox, J.; Arnaldo, J.A.; Moratiel, R. Evaluation of Temperature-Based Methods for the Estimation of Reference Evapotranspiration in the Yucatán Peninsula, Mexico. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2019, 24, 1040–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čadro, S.; Uzunović, M.; Žurovec, J.; Žurovec, O. Validation and calibration of various reference evapotranspiration alternative methods under the climate conditions of Bosnia and Herzegovina. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2017, 5, 309–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Method | Model Type | Abbreviation | Formula | Timescale | Parameters |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hargreaves and Samani (1985) | Temp | HS | 0.0023Ra(Tavg + 17.8) (Tmax − Tmin)0.5 | Daily | Tmax, Tmin, φ |
| Baier and Robertson (1965) | Temp | BR | 0.157Tmax + 0.158(Tmax − Tmin) + 0.109 Ra − 5.39 | Daily | Tmax, Tmin, φ |
| Priestley and Taylor (1972), | Rad | PT | 1.26· | Daily | Tmax, Tmin, φ, Tavg |
| Makkink (1957) | Rad | MAK | 0.61 | Daily | Tavg, Rs |
| Turc (1961 | Rad | TUR | 0.013 | Daily | Tavg, Rs |
| Thornthwaite (1957) | Temp | THN | 16·(10)a | Monthly | Tmax, Tmin, φ |
| Blaney and Criddle (1950) | Temp | BG | p (0.457Tavg + 8.128) | Monthly | Tavg and p (FAO document) |
| Ritchie (1972) | Rad | RT | Daily | Rs | |
| Jensen and Haise (1963) | Rad | JH | (0.0252Tavg + 0.078) | Daily | Tavg, Rs |
| PM | HS | BR | PT | MKK | TUR | RIT | JH | THN | BG | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| average | 2.32 | 2.88 | 1.65 | 2.39 | 2.86 | 1.26 | 4.61 | 3.68 | 65.36 | 4.39 |
| NSE | 0.51 | −1.01 | 0.91 | −0.51 | −0.49 | −4.42 | −4.58 | −1.74 | −6.44 | |
| RMSE (mm/d) | 0.80 | 1.63 | 0.34 | 1.41 | 1.41 | 2.68 | 2.72 | 41.50 | 2.22 | |
| AIC | −681.4 | 1537.6 | −3363.02 | 1435.9 | 1474.8 | 2902.02 | 3285.2 | 90.32 | 19.42 | |
| BIC | −674.04 | 1544.94 | −3355.7 | 1443.3 | 1482.14 | 2909.4 | 3292.6 | 92.8 | 21.91 | |
| Willmott index | 0.651 | 0.318 | 0.865 | 0.499 | 0.37 | 0.18 | 0.034 | 0.577 | 0.4514 | |
| MAE (mm/d) | 0.66 | 1.30 | 0.26 | 0.95 | 1.20 | 2.32 | 1.84 | 36.34 | 1.94 | |
| MBE (mm/d) | 0.56 | −0.67 | 0.06 | 0.54 | −1.06 | 2.29 | 1.36 | −9.23 | 1.94 | |
| R2 | 0.75 | 0.01 | 0.94 | 0.40 | 0.35 | 0.94 | 0.29 | 0.18 | 0.42 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aschale, T.M.; Sciuto, G.; Peres, D.J.; Gullotta, A.; Cancelliere, A. Evaluation of Reference Evapotranspiration Estimation Methods for the Assessment of Hydrological Impacts of Photovoltaic Power Plants in Mediterranean Climates. Water 2022, 14, 2268. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14142268
Aschale TM, Sciuto G, Peres DJ, Gullotta A, Cancelliere A. Evaluation of Reference Evapotranspiration Estimation Methods for the Assessment of Hydrological Impacts of Photovoltaic Power Plants in Mediterranean Climates. Water. 2022; 14(14):2268. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14142268
Chicago/Turabian StyleAschale, Tagele Mossie, Guido Sciuto, David J. Peres, Aurora Gullotta, and Antonino Cancelliere. 2022. "Evaluation of Reference Evapotranspiration Estimation Methods for the Assessment of Hydrological Impacts of Photovoltaic Power Plants in Mediterranean Climates" Water 14, no. 14: 2268. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14142268
APA StyleAschale, T. M., Sciuto, G., Peres, D. J., Gullotta, A., & Cancelliere, A. (2022). Evaluation of Reference Evapotranspiration Estimation Methods for the Assessment of Hydrological Impacts of Photovoltaic Power Plants in Mediterranean Climates. Water, 14(14), 2268. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14142268








