An Artificial Oasis in a Deadly Desert: Practices and Enlightenments
Abstract
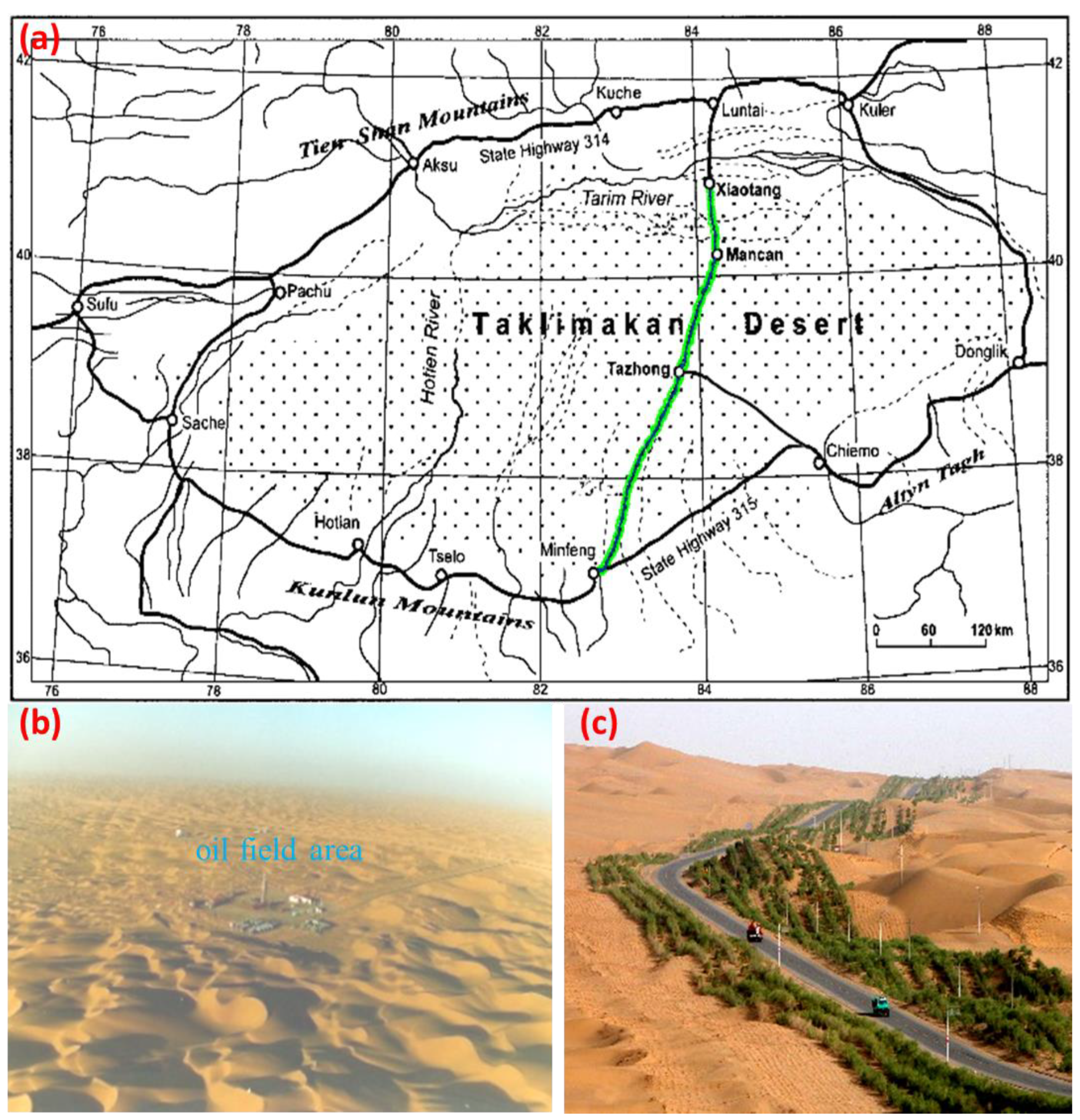
:1. Introduction
2. Overview of TDHS
3. Soil Hydrological Processes under Irrigation in the Desert
3.1. Saline Water Irrigation for Shelterbelt Engineering in Desert
3.2. Dominant Soil Hydrological Processes under Irrigation Conditions
4. Implications of the TDHS Project
4.1. Underlying Mechanisms to Maintain an Artificial Ecosystem in the Desert
4.2. Implications from China’s “Green Wall”
5. Sustainable Evaluation of the TDHS
6. Technology Transfer
7. Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xu, X.; Li, B.; Wang, X. Progress in study on irrigation practice with saline groundwater on sand lands of Taklimakan Desert hinterland. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2006, 51 (Suppl. I), 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scanlon, B.R.; Bongers, F.; Lambin, E.F. Ecological controls on water-cycle response to climate variability in deserts. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 6033–6038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Eggenberger, S.; Gobet, E.; van Leeuwen, J.F.N. Millennial multi-proxy reconstruction of oasis dynamics in Jordan, by the Dead Sea. Veget. Hist. Archaeobot. 2018, 27, 649–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations. Transforming Our World: The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, B.; Smith, D.M.S.; Lambin, E.F. The Global-DEP conceptual framework—Research on dryland ecosystems to promote sustainability. Cur. Opin. Env. Sus. 2021, 48, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Bao, W.K.; Bongers, F.; Chen, B.; Chen, G.K.; Guo, K.; Jiang, M.X.; Lai, J.S.; Lin, D.M.; Liu, C.J.; et al. Drivers of tree carbon storage in subtropical forests. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 654, 684–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, J.Q.; Li, S.Y.; Jin, Z.Z.; Fan, J.L.; Wang, H.F.; Fan, D.D.; Zhou, H.W.; Gu, F.; Qiu, Y.Z.; Xu, B. Comprehensive eco-environmental effects of the shelter-forest ecological engineering along the Tarim Desert Highway. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2008, 53 (Suppl. II), 190–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Xu, X.; Lei, J.; Sun, S.; Fan, J.; Li, S.; Gu, F.; Qiu, Y.; Xu, B. The salt accumulation at the shifting aeolian sandy soil surface with high salinity groundwater drip irrigation in the hinterland of the Taklimakan Desert. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2009, 53, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.G.; Lei, J.Q.; Wang, Y.D.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, X.X. Survival and growth of three afforestation species under high saline drip irrigation in the Taklimakan Desert, China. Ecosphere 2016, 7, e01285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.J.; Lei, J.Q.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, X.W.; Li, S.Y. Effect of saline water irrigation on soil development and plant growth in the Taklimakan Desert Highway Shelterbelt. Soil Till. Res. 2014, 146, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danin, A.; Bar-Or, Y.; Dor, I.; Yisraeli, T. The role of cyanobacteria in stabilization of sand dunes in Southern Israel. Ecol. Medit. 1989, XV, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Hu, Q.; Xue, J. Effects of Irrigation Regimes on Soil Water Dynamics of Two Typical Woody Halophyte Species in Taklimakan Desert Highway Shelterbelt. Water 2022, 14, 1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Xu, X.; Li, S.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, A.; Zhang, T. Is the Taklimakan Desert Highway Shelterbelt sustainable to long-term drip irrigation with high saline groundwater? PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0164106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, W.; Cao, L.; Yimit, H.; Xu, X.W.; Zhang, J.G. Optimization of the saline groundwater irrigation system along the Tarim Desert highway ecological shelterbelt project in China. Ecol. Eng. 2012, 40, 108–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qadir, M.; Steffens, D.; Yan, F.; Schubert, S. Proton release by N2-fixing plant roots: A possible contribution to phytoremediation of calcareous sodic soils. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2013, 166, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Shi, W. Cotton/halophytes intercropping decreases salt accumulation and improves soil physicochemical properties and crop productivity in saline-alkali soils under mulched drip irrigation: A three-year field experiment. Field Crop. Res. 2020, 262, 108027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhao, Y.; Sial, T.A.; Liu, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J. Photosynthetic responses of two woody halophyte species to saline groundwater irrigation in the Taklimakan Desert. Water 2022, 14, 1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.D.; Zhao, Y.; Li, S.Y.; Shen, F.Y.; Jia, M.M.; Zhang, J.G.; Xu, X.W.; Lei, J.Q. Soil aggregation formation in relation to planting time, water salinity, and species in the Taklimakan Desert Highway shelterbelt. J. Soil Sed. 2017, 18, 1466–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, I.M.; Crawford, J.W. Interactions and self-organization in the soil-microbe complex. Science 2004, 304, 1634–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Z.J.; Zhao, C.H. Desert “Soilization”: An ecomechanical solution to desertification. Engineering 2016, 2, 270–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xi, Y.Q.; Zhao, Y.; Li, S.Y. Effects of Three Kinds of Soil Amendments on Shear Strength of Aeolian Soil. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2018, 55, 1401–1410. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, J.; Gui, D.; Lei, J.; Sun, H.; Liu, Y. Oasification: An unable evasive process in fighting against desertification for the sustainable development of arid and semiarid regions of China. Catena 2019, 179, 197–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlesinger, W.H.; Raikes, J.A.; Hartley, A.E.; Cross, A.F. On the spatial pattern of soil nutrients in desert ecosystems. Ecology 1996, 77, 364–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, X.; Hill, R.; Lei, J. Litter decomposition and nutrient dynamics of three woody halophytes under surface and buried treatment in the Taklimakan Desert. Arid. Land Man. 2017, 4, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, Z.; Li, C.; Li, S.; Lei, J.; Zhao, Y.; Umut, H. Stoichiometric features of C, N, and P in soil and litter of Tamarix cones and their relationship with environmental factors in the Taklimakan Desert, China. J. Soils Sed. 2019, 20, 690–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatichi, S.; Pappas, C. Constrained variability of modeled T:ET ratio across biomes. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 6795–6803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Li, S.; Zhao, Y.; Lei, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, C. Stable oxygen-hydrogen isotopes reveal water use strategies of Tamarix taklamakanensis in the Taklimakan Desert, China. J. Arid Land. 2020, 12, 115–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Safriel, U.; Adeel, Z. Development paths of drylands: Thresholds and sustainability. Sustain. Sci. 2008, 3, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.X.; Zhong, B.L.; Yue, H.; Zeng, H.S.; Zeng, J.H. Development and testing of a sustainable environmental restoration policy on eradicating the poverty trap in China’s Changting County. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 106, 10712–10716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bryan, B.A.; Smith, D.M.S.; Lambin, E.F. China’s response to a national land-system sustainability emergency. Nature 2018, 559, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Venkatesan, K.; Balakrishnan, V. Revegetation in China’s Loess Plateau is approaching sustainable water resource limits. Nat. Clim. Change 2016, 6, 1019–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.X.; Lei, J.Q.; Xu, X.W. Excessive reliance on afforestation in China’s arid and semi-arid regions: Lessons in ecological restoration. Earth Sci. Rev. 2011, 104, 240–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharji, P. Uighurs and China’s Xinjiang Region. Washington Post, 1 August 2008; 1–2. Available online: http://www.washingtonpost.com/wp-dyn/content/article/2008/08/01/AR2008080100933.html (accessed on 1 June 2022).
- Seckler, D.; Barker, R.; Amarasinghe, U. Water scarcity in the twenty-first century. Int. J. Water Res. Dev. 1999, 15, 29–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.L.; Xu, B.W.; Xu, X.W.; Li, S.Y. Technology Progress of Sand Industry Based on Desertification Control Engineering by Revegetation: Case Study on Cistanche Plantation. Bull. Chin. Acad. Sci. 2020, 35, 717–723. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.J.; Wang, Y.D.; Lei, J.Q.; Xu, X.W.; Wang, S.J.; Fan, J.L.; Li, S.Y. Damage by wind-blown sand and its control measures along the Taklimakan Desert Highway in China. J. Arid Land. 2021, 13, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Li, Y.; Fu, C.; Chen, F.; Fu, Q.; Dai, A.; Rozema, J.; Flowers, T. Dryland climate change: Recent progress and challenges. Rev. Geophys. 2017, 55, 719–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravindran, K.C.; Venkatesan, K.; Balakrishnan, V.; Chellappan, K.P.; Balasubramanian, T. Restoration of saline land by halophytes for Indian soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2007, 39, 2661–2664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozema, J.; Flowers, T. Crops for a salinized world. Science 2008, 322, 1478–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhao, Z.Y.; Zhang, K.; Tian, C.Y. Reclamation and utilization of saline soils in arid northwestern China: A promising halophyte drip-irrigation system. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 5518–5519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, J.F.; Smith, D.M.S.; Lambin, E.F.; Rozema, J.; Flowers, T. Global desertification: Building a science for dryland development. Science 2007, 316, 847–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Delgado-Baquerizo, M.; Reich, P.B.; Bardgett, R.D. The influence of soil age on ecosystem structure and function across biomes. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Control Measures | Effects of Sand Prevention | Input (USD km−1 a−1) | Ecological Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mechanical measures | More than 70% of the control measures were ineffective | ~0.1 million | No |
| Biological measures | More than 90% of the artificial shelterbelts were effective | ~0.2 million | Improve the eco-environment and increase biodiversity |
| Chemical measures | Ineffective | ~0.15 million | Bring chemical materials to the desert and damage the eco-environment |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, Y.; Xue, J.; Wu, N.; Hill, R.L. An Artificial Oasis in a Deadly Desert: Practices and Enlightenments. Water 2022, 14, 2237. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14142237
Zhao Y, Xue J, Wu N, Hill RL. An Artificial Oasis in a Deadly Desert: Practices and Enlightenments. Water. 2022; 14(14):2237. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14142237
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Ying, Jie Xue, Nan Wu, and Robert Lee Hill. 2022. "An Artificial Oasis in a Deadly Desert: Practices and Enlightenments" Water 14, no. 14: 2237. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14142237






