Examining How a Smart Rainwater Harvesting System Connected to a Green Roof Can Improve Urban Stormwater Management
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Green Roof
2.2. Cistern with Real-Time Control
2.3. Analysis
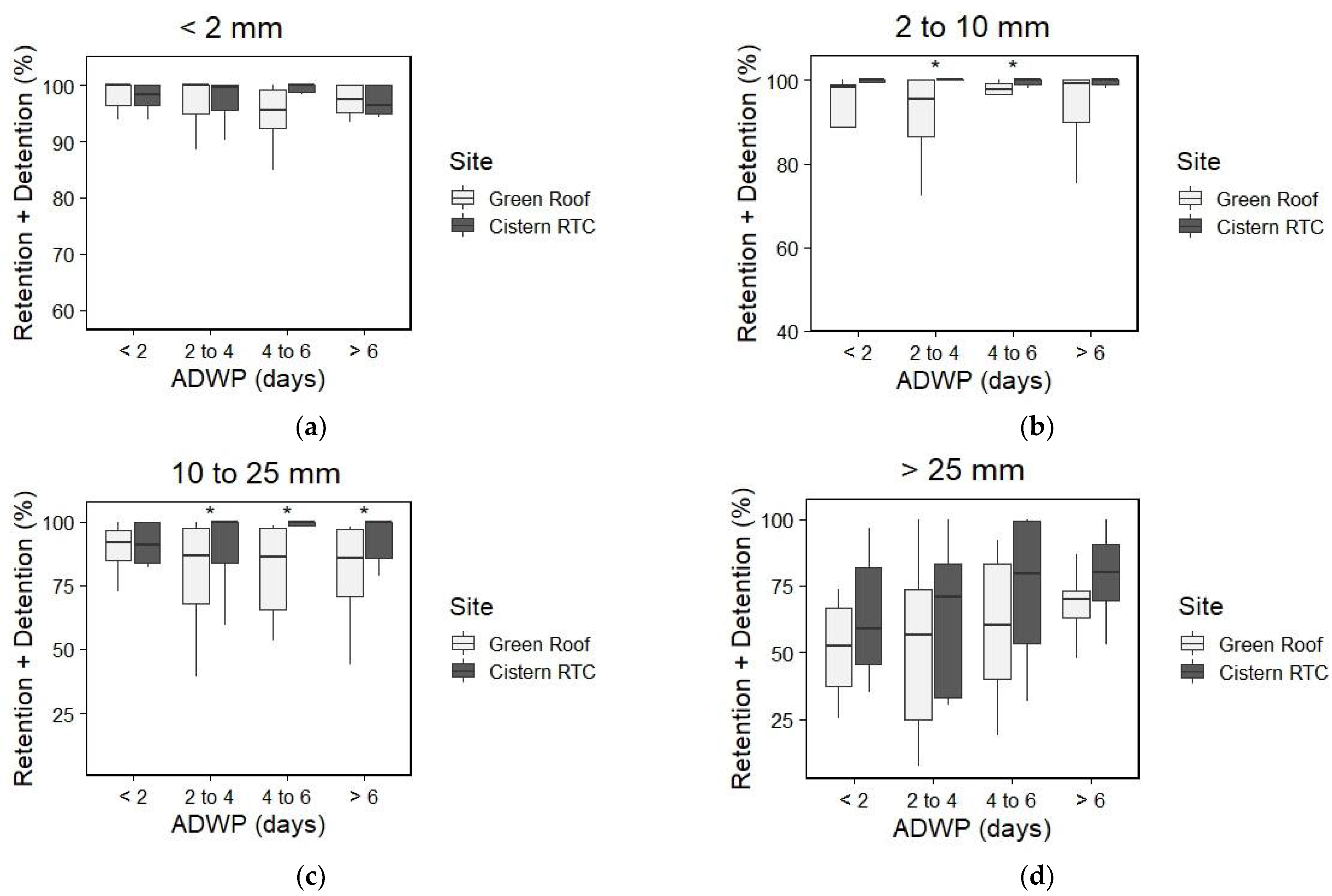
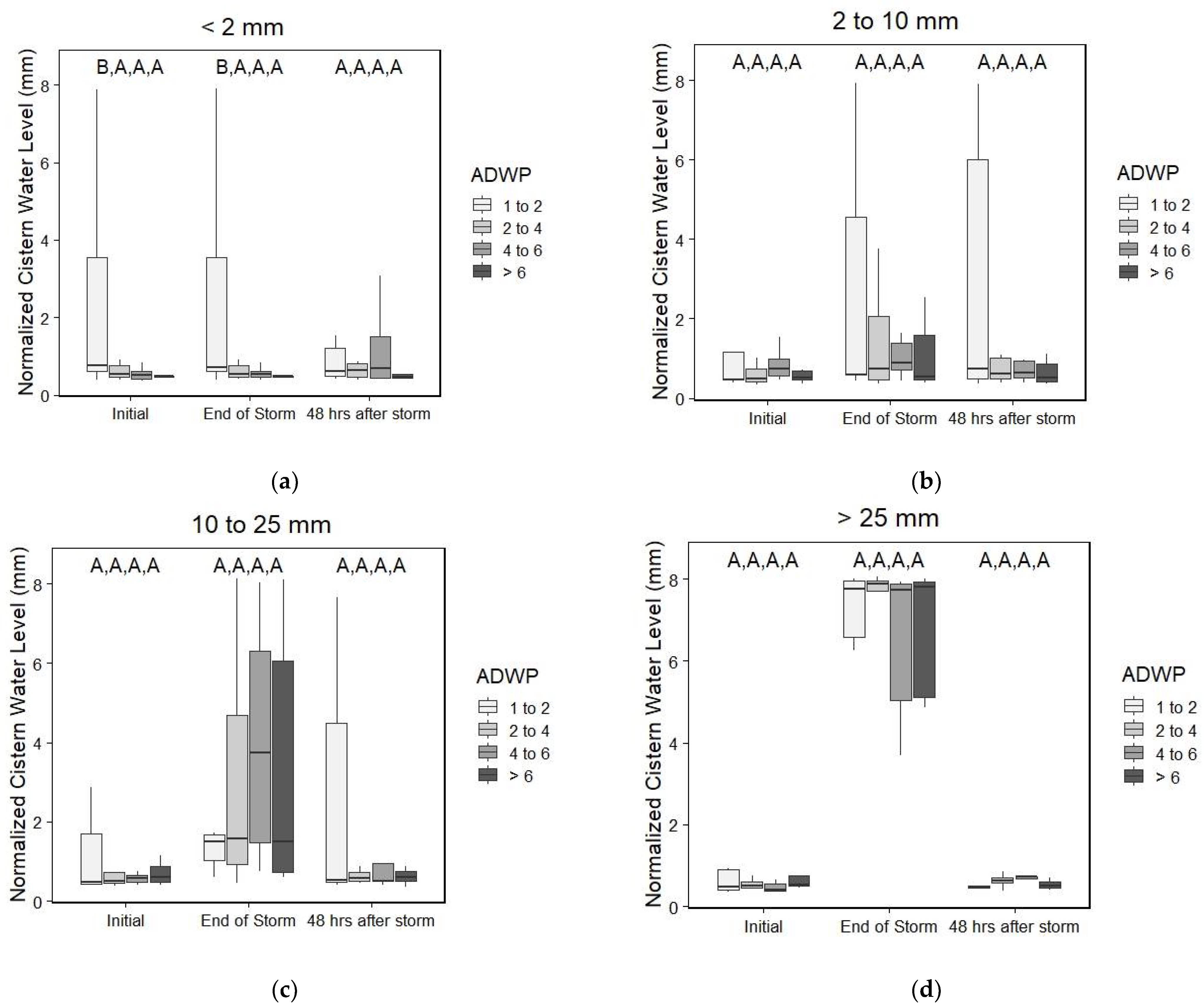
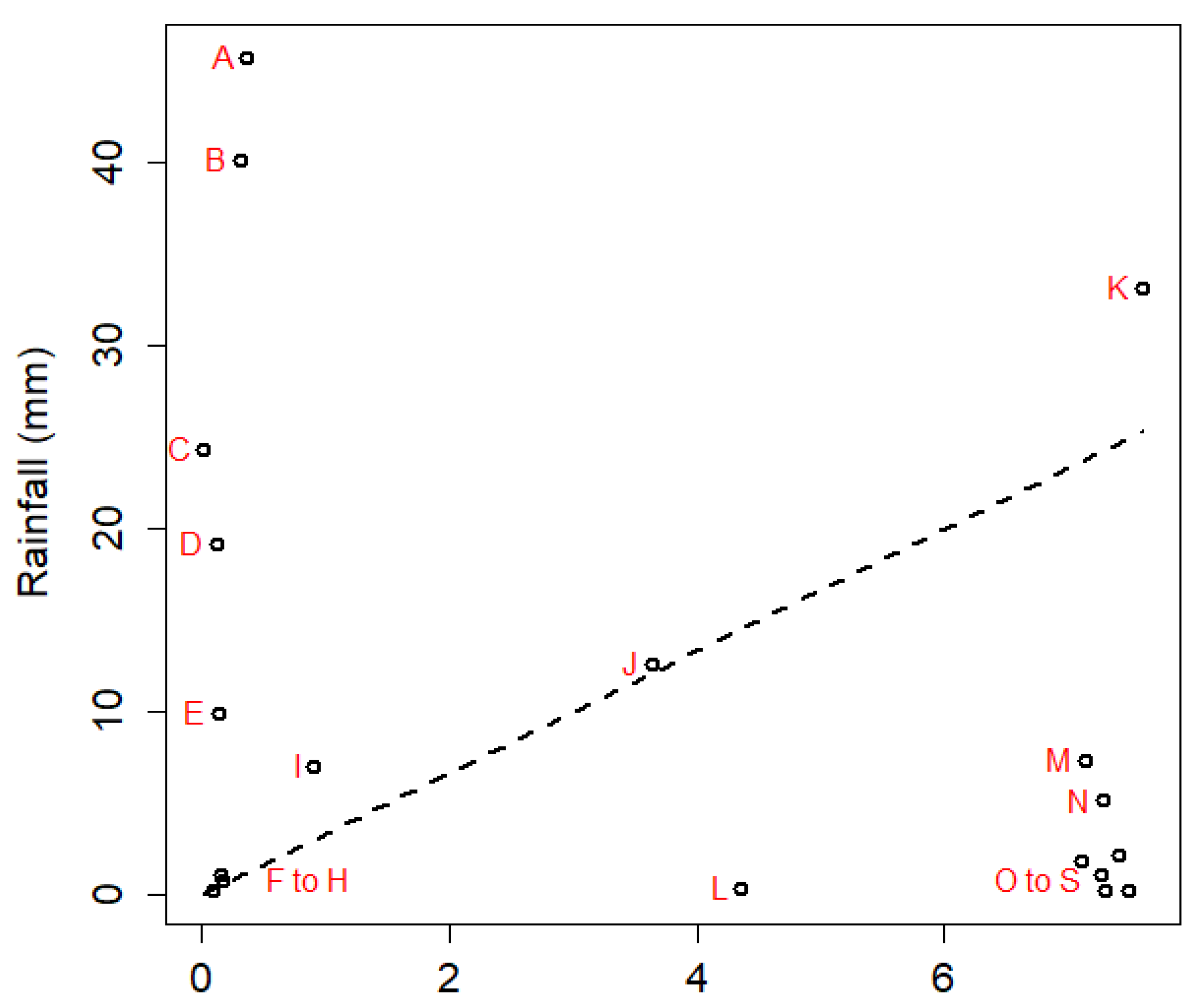
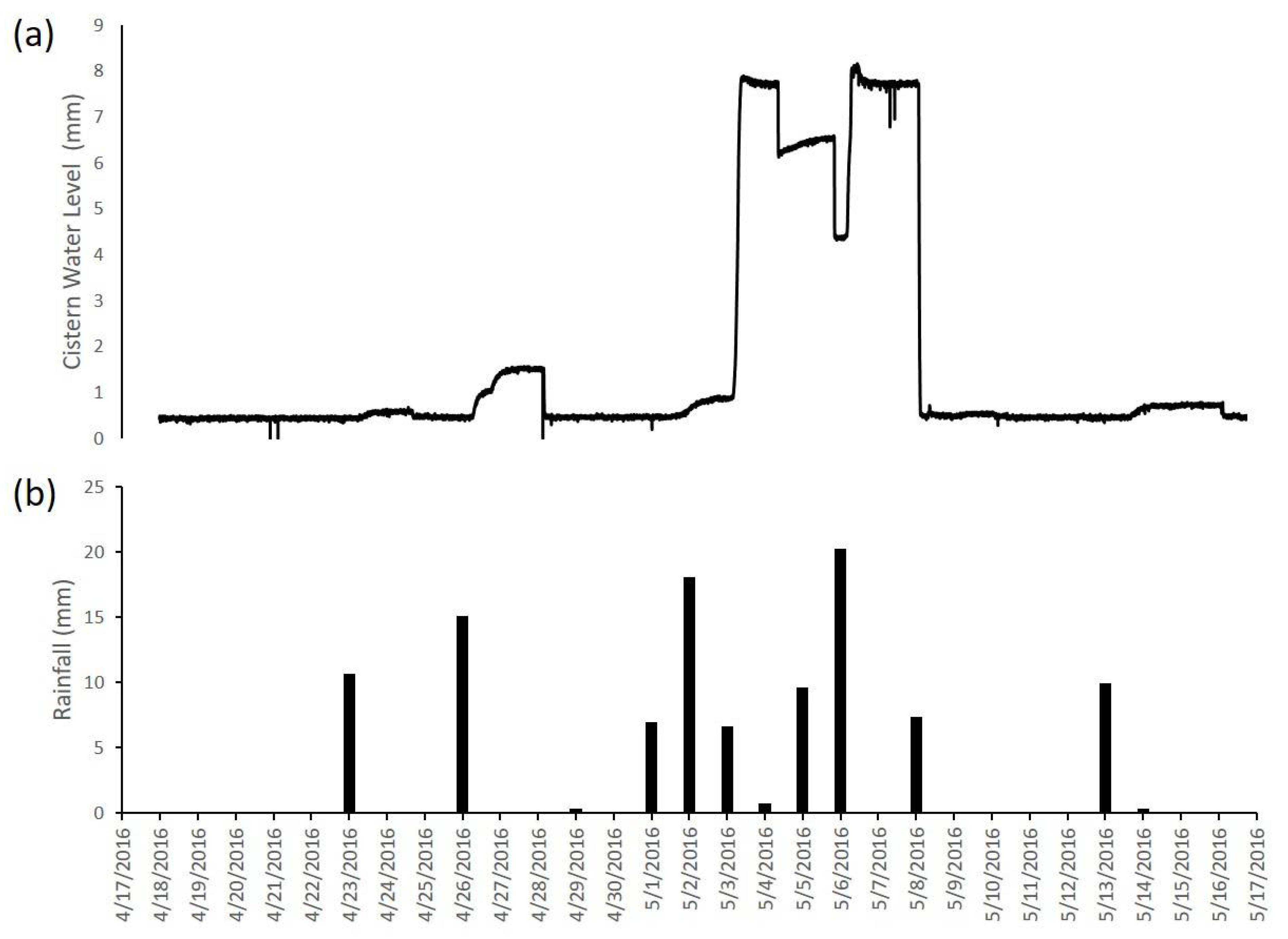
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Percentage of Water Detained by Cistern Affected by Rain Depth and by Length of Antecedent Dry-Weather Period
3.2. Smart Sensor’s Weather Forecasts
3.3. An Example of the Storm Sensor Handling Back-to-Back Storm Events
3.4. Our Study Compared to Other Findings
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- US EPA Combined Sewer Overflows (CSOs). Available online: https:/www.epa.gov/npdes/combined-sewer-overflows-csos (accessed on 8 March 2021).
- Montalto, F.; Behr, C.; Alfredo, K.; Wolf, M.; Arye, M.; Walsh, M. Rapid assessment of the cost-effectiveness of low impact development for CSO control. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2007, 82, 117–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Babcock, R.W. Green roof hydrologic performance and modeling: A review. Water Sci. Technol. 2014, 69, 727–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campisano, A.; Modica, C. Rainwater harvesting as source control option to reduce roof runoff peaks to downstream drainage systems. J. Hydroinform. 2016, 18, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Velasco-Munoz, J.F.; Aznar-Sanchez, J.A.; Batiles-delaFuente, A.; Fidelibus, M.D. Rainwater harvesting for agricultural irrigation: An analysis of global research. Water 2019, 11, 1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Semaan, M.; Day, S.D.; Garvin, M.; Ramakrishnan, N.; Pearce, A. Optimal sizing of rainwater harvesting systems for domestic water usages: A systematic literature review. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2020, 6, 100033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberascher, M.; Kinzel, C.; Kastlunger, U.; Kleidorfer, M.; Zingerle, C.; Rauch, W.; Sitzenfrei, R. Integrated urban water management with micro storages developed as an IoT-based solution—The smart rain barrel. Environ. Model. Softw. 2021, 139, 105028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannak, S.A.; Jaber, F.H.; Lesikar, B.J. Modeling the effect of cistern size, soil type, and irrigation scheduling on rainwater harvesting as a stormwater control measure. Water Resour. Manag. 2014, 28, 4219–4235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debusk, K.M.; Hunt, W.; Quigley, M.; Jeray, J.; Bedig, A. Rainwater harvesting: Integrating water conservation and stormwater management. World Environ. Water Resour. Congr. 2012, 3703–3710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roman, D.; Braga, A.; Shetty, N.; Culligan, P. Design and modeling of an adaptively controlled rainwater harvesting system. Water 2017, 9, 974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, W.D.; Fletcher, T.D.; Duncan, H.P.; Bergmann, D.J.; Breman, J.; Burns, J.M. Improving the multi-objective performance of rainwater harvestign systems using real-time control technology. Water 2018, 10, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Muschalla, D.; Vallet, V.; Anctil, F.; Lessard, P.; Pelletier, G.; Vanrolleghem, P.A. Ecohydraulic-driven real-time control of stormwater basins. J. Hydrol. 2014, 511, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Quinn, R.; Melville-Shreeve, P.; Butler, D.; Stovin, V. A critical evaluation of the water supply and stormwater management performance of retrofittable domestic rainwater harvesting systems. Water 2020, 12, 1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Burns, M.J.; Fletcher, T.D.; Duncan, H.P.; Hatt, B.E.; Ladson, A.R.; Walsh, C.J. The performance of rainwater tanks for stormwater retention and water supply at the household scale: An empirical study. Hydrol. Process. 2015, 160, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardin, M.; Wanielista, M.; Chopra, M. A mass balance model for designing green roof systems that: Incorporate a cistern for re-use. Water 2012, 4, 914–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerkez, B.; Gruden, C.; Lewis, M.; Montestruque, L.; Quigley, M.; Wong, B.; Bedig, A.; Kertesz, R.; Braun, T.; Cadwalader, O.; et al. Smarter stormwater systems. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 7267–7273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shetty, N.H.; Elliott, R.M.; Wang, M.; Palmer, M.I.; Culligan, P.J. Comparing the hydrological performance of an irrigated native vegetation green roof with a conventional Sedum spp. green roof in New York City. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shetty, N.H. New York City’s Green Infrastructure: Impacts on Nutrient Cycling and Improvements in Performance. Ph.D. Thesis, Columbia University, New York, NY, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Helsel, D.R.; Hirsch, R.M. Statistical Methods in Water Resources; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 2002; Volume 4. [Google Scholar]
- Carson, T.B.; Marasco, D.E.; Culligan, P.J.; McGillis, W.R. Hydrological performance of extensive green roofs in New York City: Observations and multi-year modeling of three full-scale systems. Environ. Res. Lett. 2013, 8, 024036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, P.; Deletic, A.; Bratieres, K.; McCarthy, D.T. Real time control of biofilters delivers stormwater suitable for harvesting and reuse. Water Res. 2020, 169, 115257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.D.; Fletcher, T.D.; Burns, M.J.; Cherqui, F. Real time control of rainwater harvesting systems: The benefits of increasing rainfall forecast window. Water Resour. Res. 2020, 56, e2020WR027856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gainguly, A.R. A hybrid approach to improving rainfall forecasts. Comput. Sci. Eng. 2002, 4, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braga, A.; O’Grady, H.; Dabak, T.; Lane, C. Performance of two advanced rainwater harvesting systems in Washington DC. Water 2018, 10, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Behera, P.K.; Adams, B.J.; Li, J.Y. Runoff quality analysis of urban catchments with analytical probabilistic models. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2005, 132, 4–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Antecedent Dry-Weather Period (Days) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 to 2 | 2 to 4 | 4 to 6 | >6 | Total | |
| <2 mm | 17 | 19 | 10 | 5 | 51 |
| From 2 to 10 mm | 9 | 23 | 19 | 19 | 70 |
| From 10 to 25 mm | 7 | 16 | 9 | 9 | 41 |
| >25 mm | 10 | 13 | 6 | 12 | 41 |
| Total | 43 | 71 | 44 | 45 | 203 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shetty, N.; Wang, M.; Elliott, R.; Culligan, P. Examining How a Smart Rainwater Harvesting System Connected to a Green Roof Can Improve Urban Stormwater Management. Water 2022, 14, 2216. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14142216
Shetty N, Wang M, Elliott R, Culligan P. Examining How a Smart Rainwater Harvesting System Connected to a Green Roof Can Improve Urban Stormwater Management. Water. 2022; 14(14):2216. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14142216
Chicago/Turabian StyleShetty, Nandan, Mark Wang, Robert Elliott, and Patricia Culligan. 2022. "Examining How a Smart Rainwater Harvesting System Connected to a Green Roof Can Improve Urban Stormwater Management" Water 14, no. 14: 2216. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14142216





