Effective Removal of Humic Acid by Zr-MOFs with Surface Modification
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Zr-MOFs
2.3. Characterization
2.4. HA Adsorption Test of Zr-MOFs
2.5. Adsorption Kinetics and Isotherms
3. Results
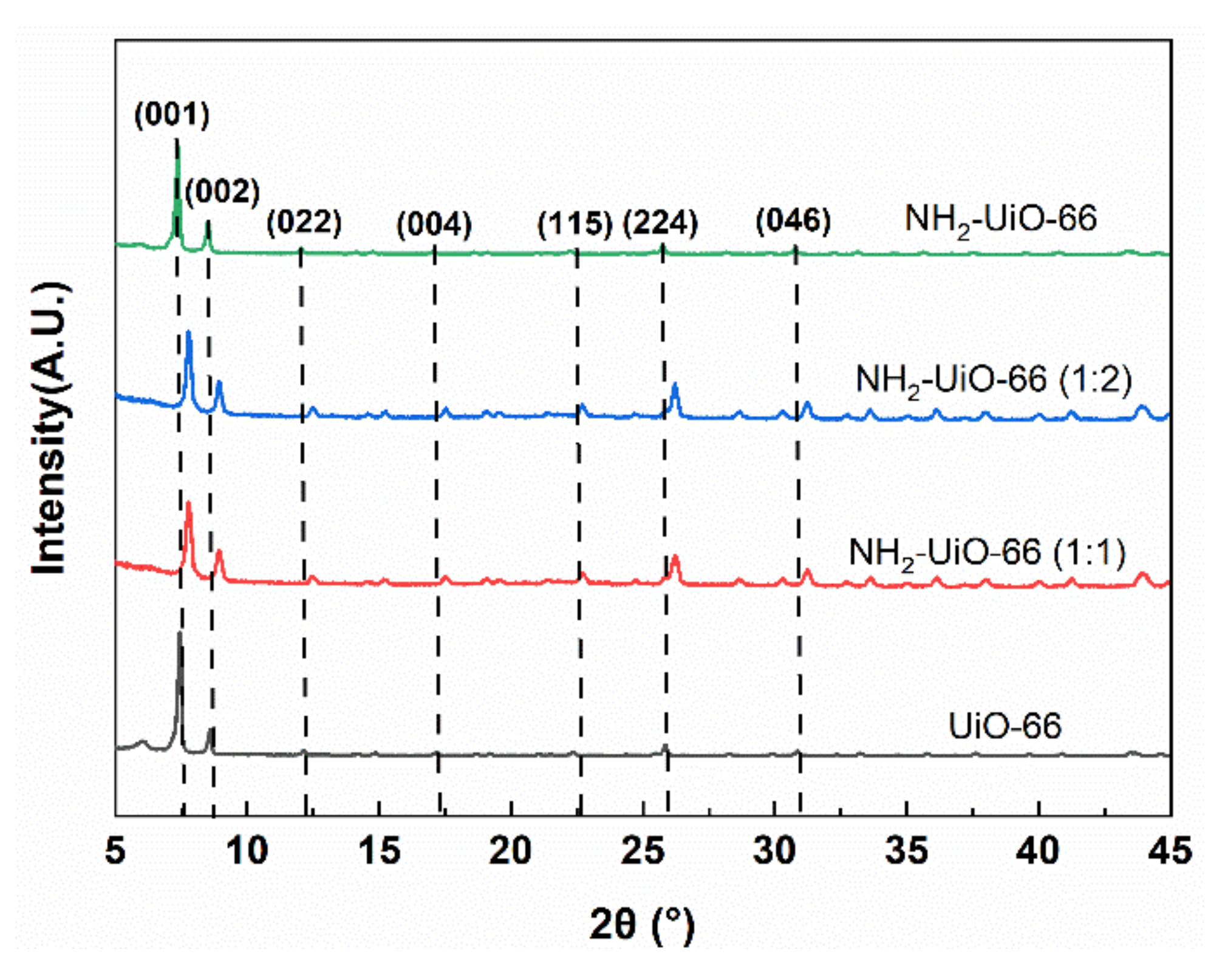
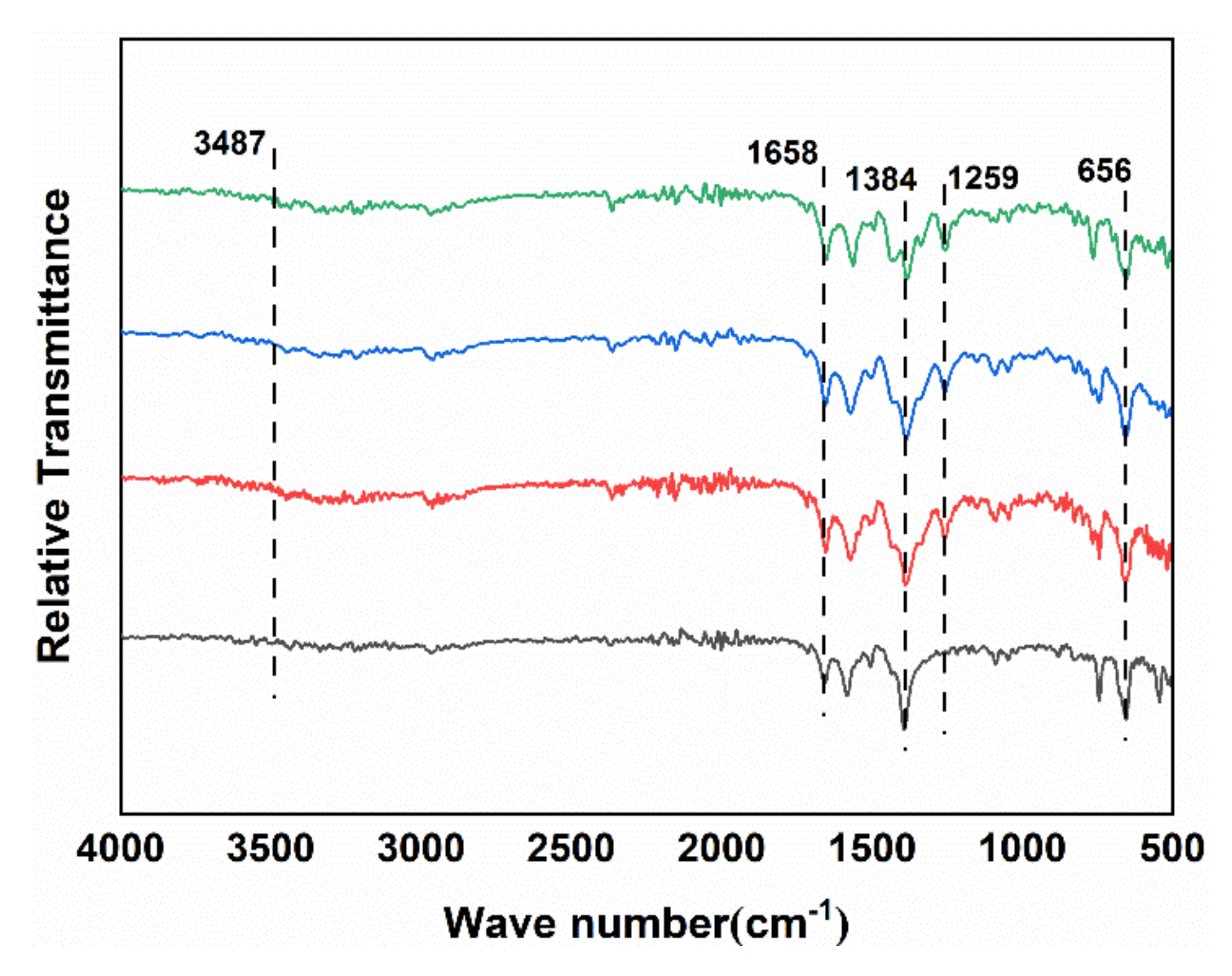
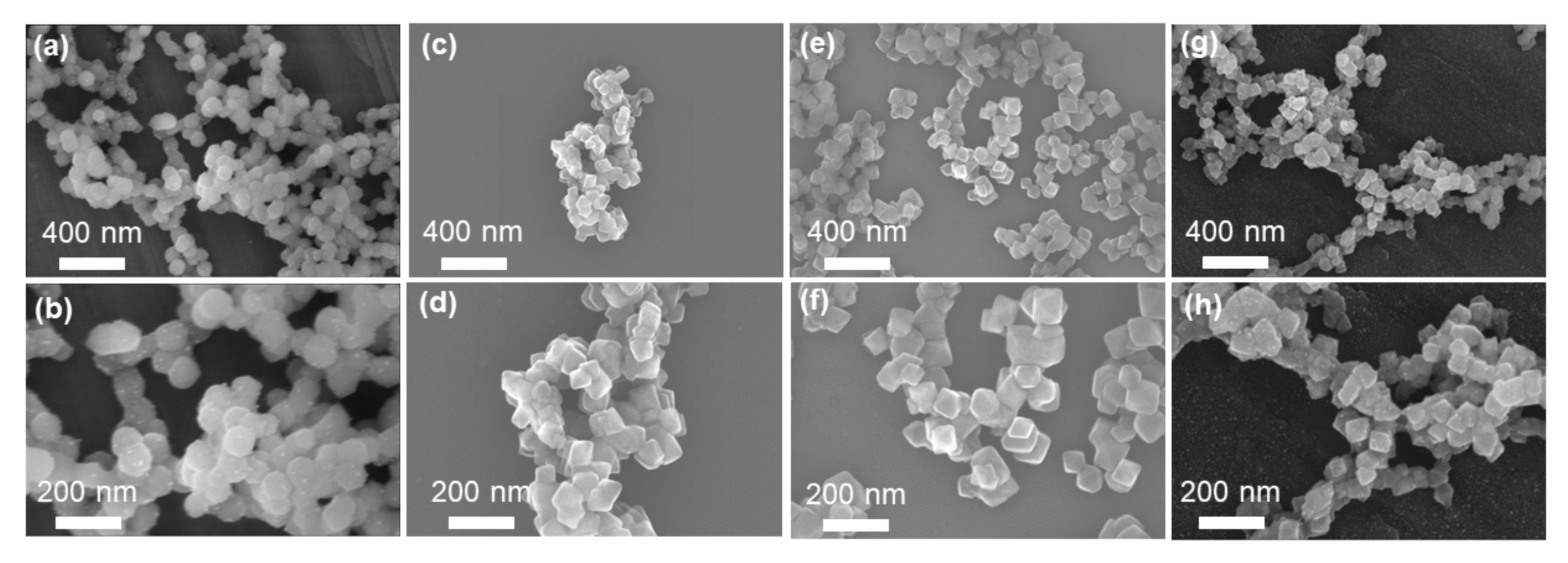
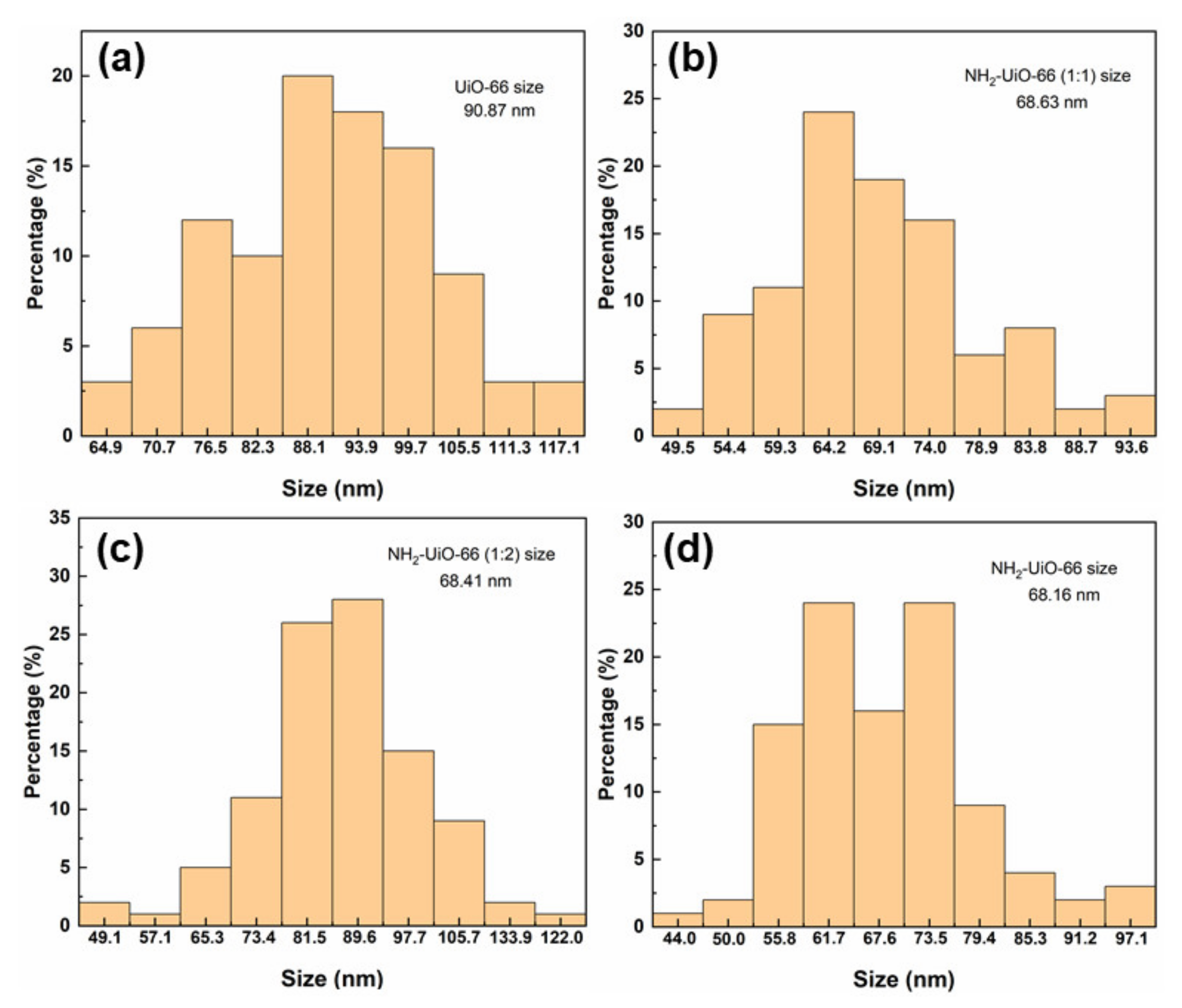
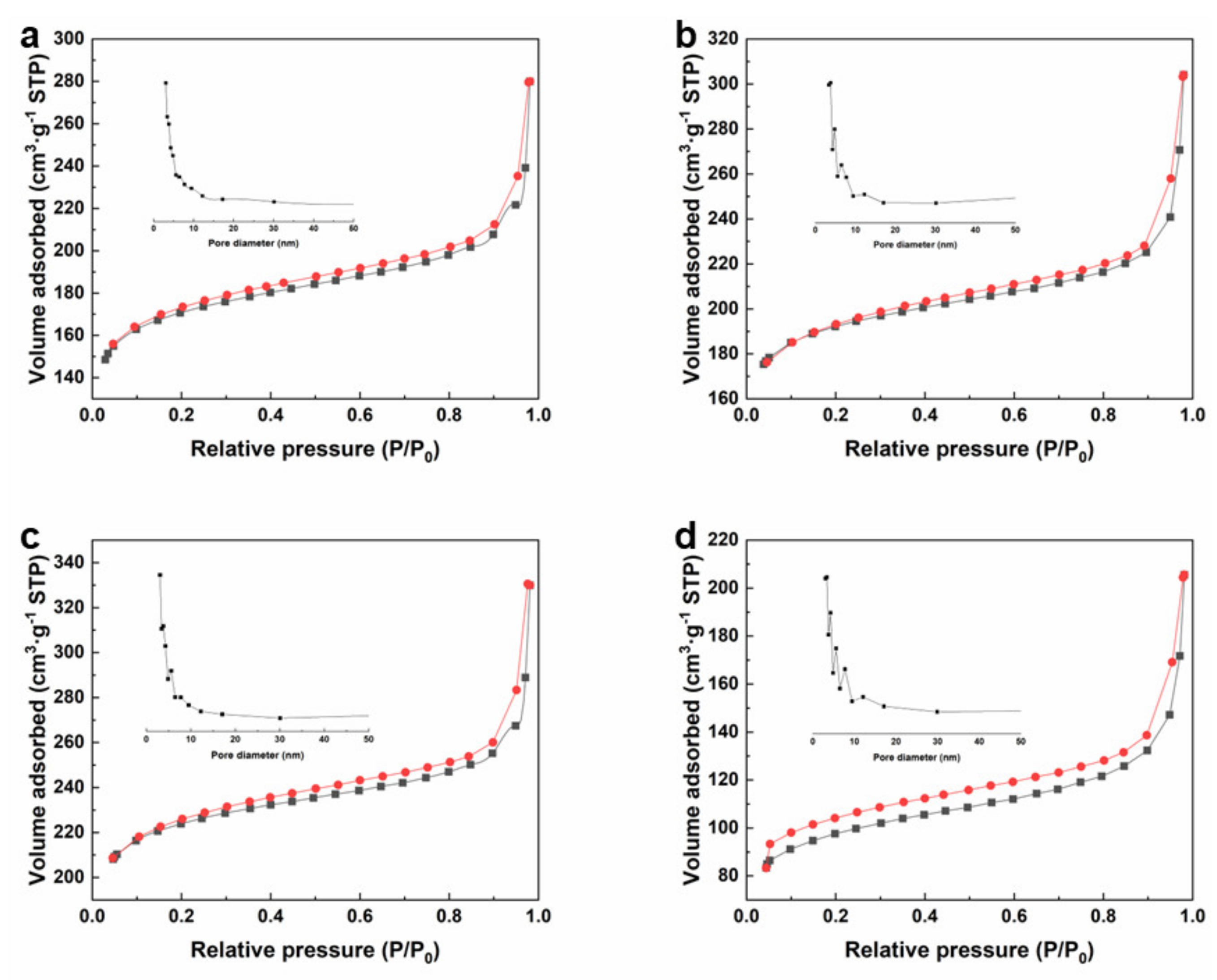
3.1. Morphology and Structure of Zr-MOFs
3.2. Kinetics Studies
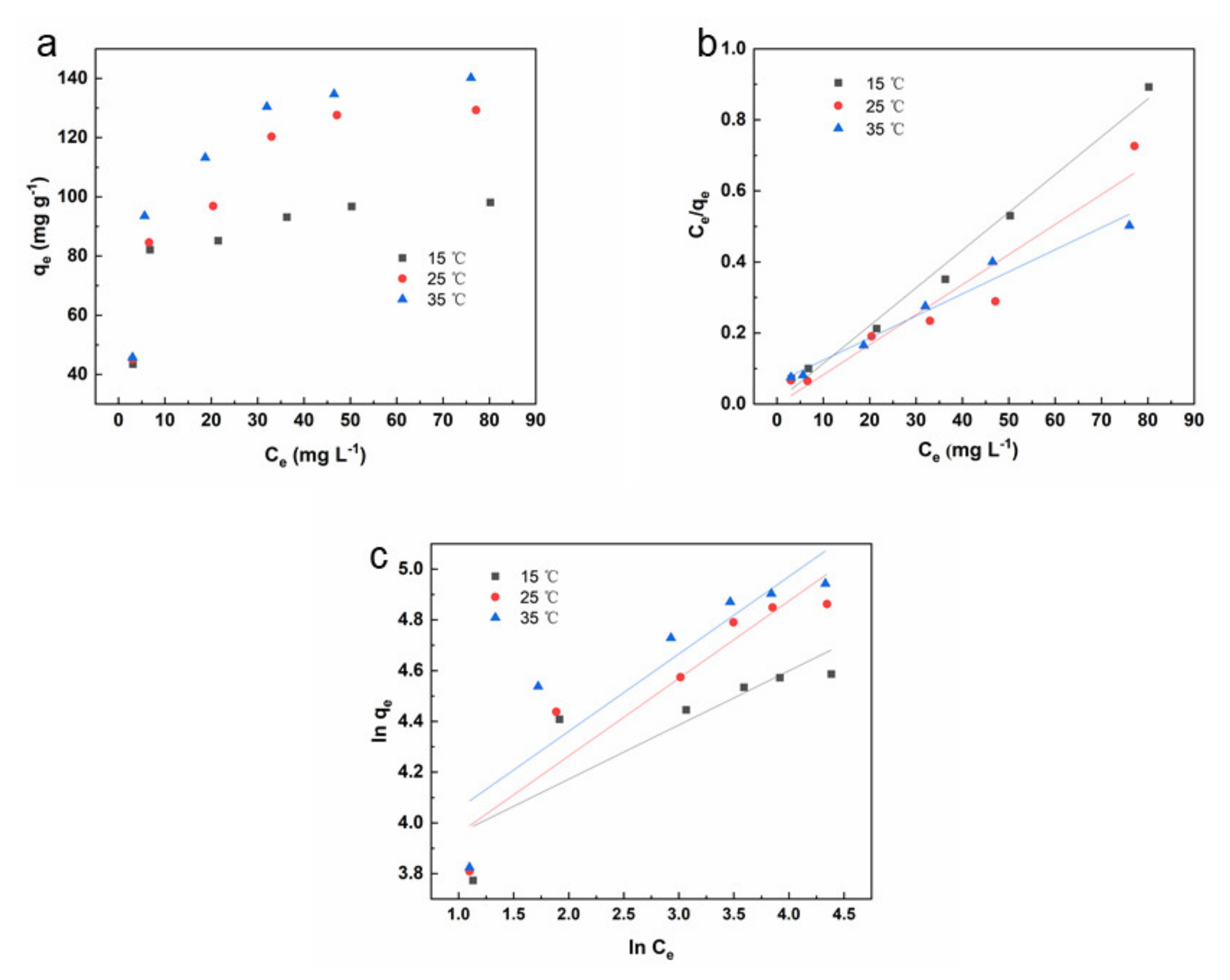
3.3. Isotherm and Thermodynamics Studies
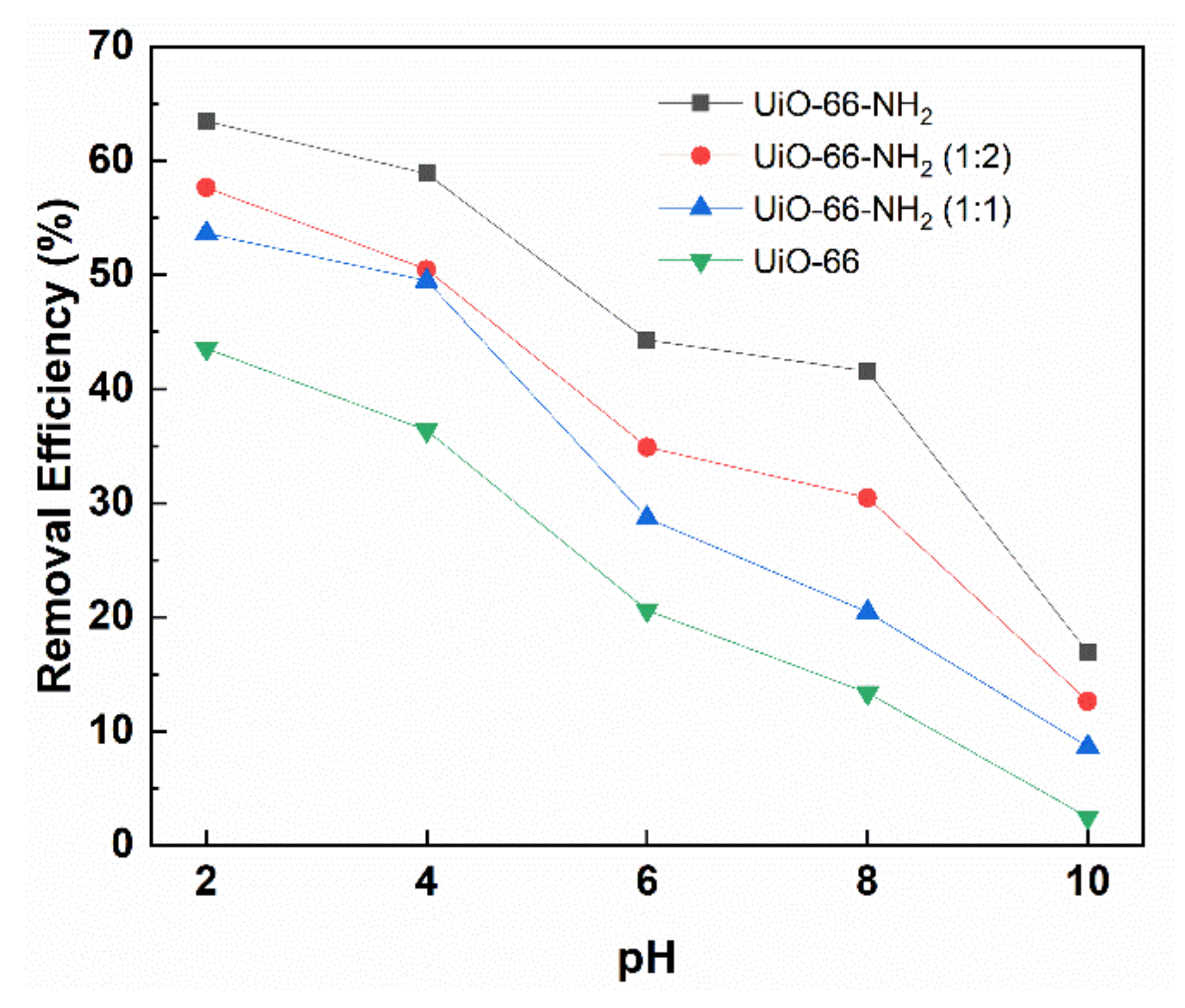
3.4. The Effect of pH on Adsorption
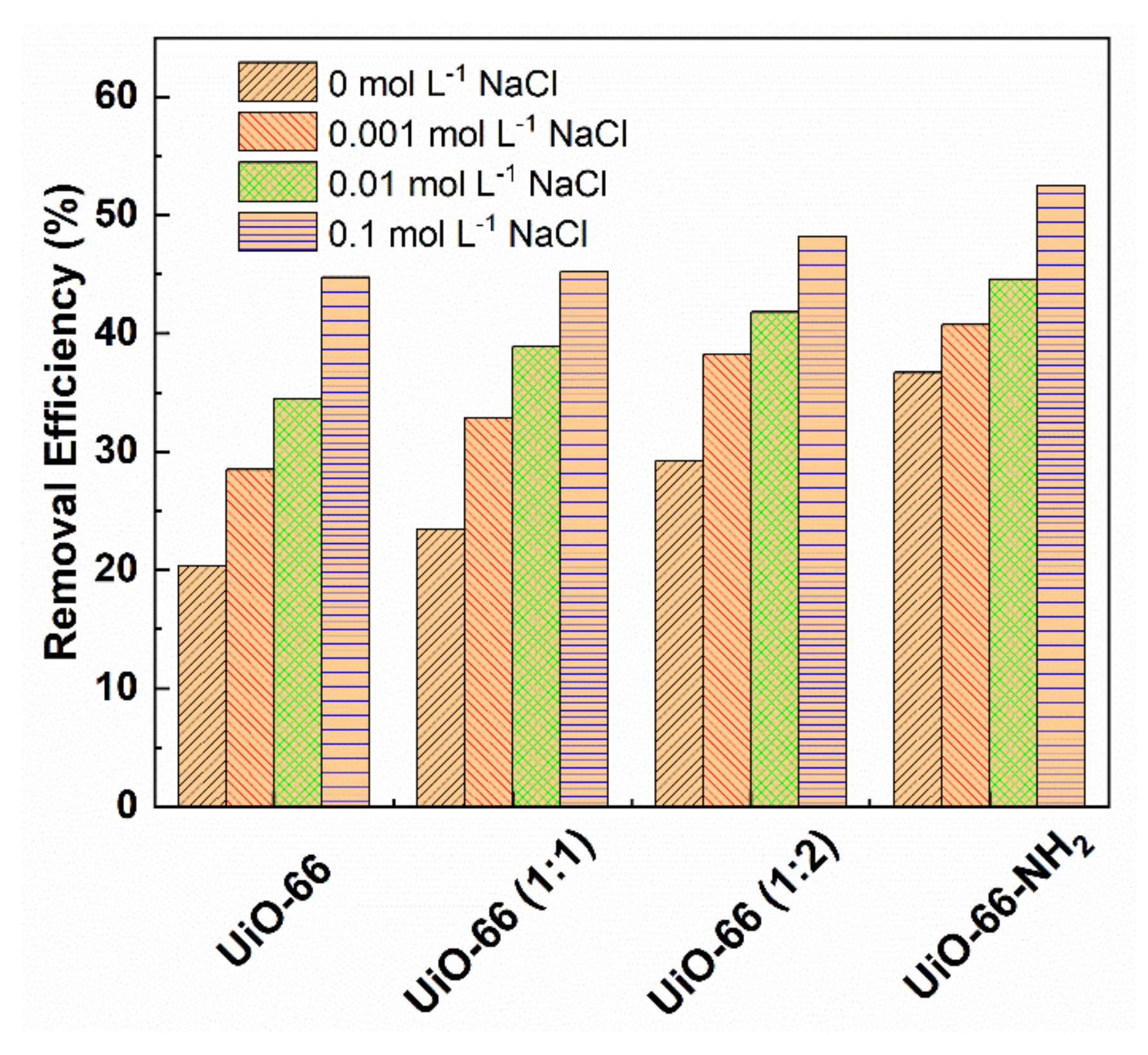
3.5. The Effect of Salt Concentration on Adsorption
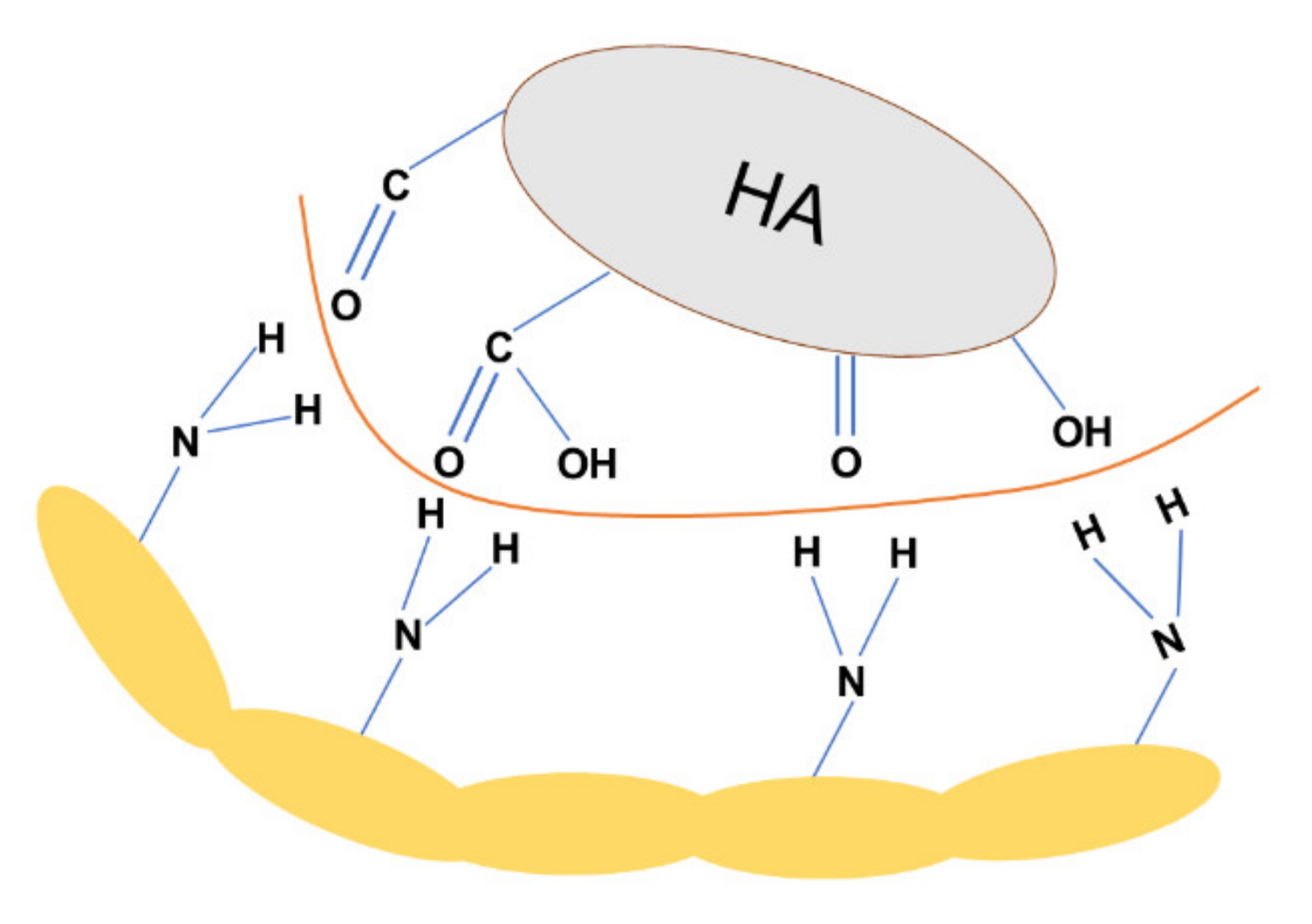
3.6. The mechanism of Adsorption
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Piccolo, A. The supramolecular structure of humic substances: A novel understanding of humus chemistry and implications in soil science. In Advances in Agronomy; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2002; pp. 57–134. [Google Scholar]
- Anjum, T.; Tamime, R.; Khan, A.L. Mixed-Matrix Membranes Comprising of Polysulfone and Porous UiO-66, Zeolite 4A, and Their Combination: Preparation, Removal of Humic Acid, and Antifouling Properties. Membranes 2020, 10, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowe, J.; Hossain, M.M. Application of ultrafiltration membranes for removal of humic acid from drinking water. Desalination 2008, 218, 343–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levchuk, I.; Marquez, J.J.R.; Sillanpaa, M. Removal of natural organic matter (NOM) from water by ion exchange—A review. Chemosphere 2018, 192, 90–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Z.P.; Qiao, Y.; Wang, N.N.; Cao, J. Decomposition characteristics of humic acid in boiler make-up water in power plants. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2018, 128, 1159–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansha, M.; Kazi, I.W.; Manzar, M.S.; Ahmed, T.; Waheed, A.; Ullah, N.; Blaisi, N.I. Ultrahigh removal of methyl orange, acid blue-92 and malachite green by a novel triazine-based polyamine resin: Synthesis, isotherm and kinetic studies. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2020, 8, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoudi, E.; Ng, L.Y.; Ang, W.L.; Chung, Y.T.; Rohani, R.; Mohammad, A.W. Enhancing Morphology and Separation Performance of Polyamide 6,6 Membranes By Minimal Incorporation of Silver Decorated Graphene Oxide Nanoparticles. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Xu, Y.H.; Sun, Y.J. Combination of Coagulation and Ozone Catalytic Oxidation for Pretreating Coking Wastewater. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, Y.J.; Zhao, C.F.; Sun, L.; Wang, X.K.; Liang, L.J. Coagulation mechanisms of humic acid in metal ions solution under different pH conditions: A molecular dynamics simulation. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 702, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zazouli, M.A.; Roohafzaee, M.; Shahamat, Y.D.; Yousefi, M. Application of magnetic activated carbon as a catalyst in catalytic ozonation process (COP) for removal and mineralization of humic acid from aqueous solution. Desalin. Water Treat. 2021, 220, 316–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohtar, S.S.; Aziz, F.; Nor, A.R.M.; Mohammed, A.M.; Mhamad, S.A.; Jaafar, J.; Yusof, N.; Salleh, W.N.W.; Ismail, A.F.J.J.o.E.C.E. Photocatalytic degradation of humic acid using a novel visible-light active α-Fe2O3/NiS2 composite photocatalyst. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseinzehi, M.; Ehrampoush, M.H.; Tamaddon, F.; Mokhtari, M.; Dalvand, A. Eco-environmental preparation of magnetic activated carbon modified with 3-aminopropyltrimethoxysilane (APTMS) from sawdust waste as a novel efficient adsorbent for humic acid removal: Characterisation, modelling, optimisation and equilibrium studies. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2021, 20, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llado, J.; Lao-Luque, C.; Sole-Sardans, M.; Montemurro, N.; Perez, S.; Fuente, E.; Ruiz, B. Elimination of persistent anthropogenic pollutants by micro-mesoporous carbon xerogels. Natural organic matter on surface water and textural properties influences. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.P.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, Q.H. Preparation of polyurethane foam/carbon nanotube composites and adsorption properties for humic acid. J. Chang. Univ. Ence Technol. 2009, 31, 1293–1303. [Google Scholar]
- Summers, R.S.; Roberts, P.V. Activated carbon adsorption of humic substances: II. Size exclusion and electrostatic interactions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1988, 122, 382–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Graham, N.; Yu, W.Z. Evaluation of a novel composite chitosan-graphene oxide membrane for NOM removal during water treatment. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazri, M.M.; Barbeau, B.; Mohseni, M. Evaluation of Weak and Strong Basic Anion Exchange Resins for NOM Removal. J. Environ. Eng. 2016, 142, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derakhshani, E.; Naghizadeh, A. Optimization of humic acid removal by adsorption onto bentonite and montmorillonite nanoparticles. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 259, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heikal, G.E. A Comparison between Kaolin, Montmorillonite fe-Modified Montmorillonite as Candidate of Upflow Column Media Filter for Humic Acid Removal from SSAS. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2021, 30, 2553–2560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.L.; Dionysiou, D.D.; Lin, J.M.; Huang, Y.X.; Xie, X.L. Removal of humic acid and Cr(VI) from water using ZnO-30N-zeolite. Chemosphere 2021, 279, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tipping, E. The adsorption of aquatic humic substances by iron oxides. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1981, 45, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Ou, T.; Su, M.; Peng, H.; Chen, D. U(VI) sequestration by Al-rich minerals: Mechanism on phase dependence and the influence of natural organic matter. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 415, 128858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Wang, T.; Du, G.; Zheng, M.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, X.; Gao, Z. Effective Removal of Humic Acid from Aqueous Solution in an Al-Based Metal–Organic Framework. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2019, 64, 3624–3631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, K.-Y.A.; Chang, H.-A. Efficient adsorptive removal of humic acid from water using zeolitic imidazole framework-8 (ZIF-8). Water Air Soil Pollut. 2015, 226, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Seo, P.W.; Song, J.Y.; Jhung, S.H. Adsorptive removal of hazardous organics from water with metal-organic frameworks. Appl. Chem. Eng. 2016, 27, 358–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lin, R.B.; Xiang, S.; Zhou, W.; Chen, B. Microporous Metal-Organic Framework Materials for Gas Separation. Chem. Aisan J. 2020, 6, 337–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Zhang, H.; Song, F.; Huang, T.; Ji, J.; Zhong, Q.; Chu, W.; Xu, Q. UiO-66-NH2/GO composite: Synthesis, characterization and CO2 adsorption performance. Materials 2018, 11, 589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilduff, J.E.; Karanfil, T. Trichloroethylene adsorption by activated carbon preloaded with humic substances: Effects of solution chemistry. Water Res. 2002, 36, 1685–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Zhan, Y. Adsorption of humic acid from aqueous solution onto unmodified and surfactant-modified chitosan/zeolite composites. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 200, 202–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.F.; Zhang, H.J.; Ge, S.T.; Song, J.B.; Wang, J.K.; Zhang, S.W. Synthesis of Carbon Nanotube Arrays with High Aspect Ratio via Ni-Catalyzed Pyrolysis of Waste Polyethylene. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Song, W.; Wang, M.; Ji, H. Controlling the size of a Zn-MOF through ligand exchange and pore-tailored ZnO assemblies for size-selective gas sensing. CrystEngComm 2019, 21, 6414–6422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mckinstry, C.; Cussen, E.J.; Fletcher, A.J.; Patwardhan, S.V.; Sefcik, J. Effect of Synthesis Conditions on Formation Pathways of Metal Organic Framework (MOF-5) Crystals. Cryst. Growth Des. 2013, 13, 5481–5486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, L.; Ge, L.; Liu, H.; Jiang, Z.; Jia, Y.; Li, Z.; Yang, D.; Hocking, R.K.; Li, M.; Zhang, L. A surfactant-free and scalable general strategy for synthesizing ultrathin two-dimensional metal–organic framework nanosheets for the oxygen evolution reaction. Angew. Chem. 2019, 131, 13699–13706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.-N.; Li, J.-L.; Zhao, Y.-M.; Pang, J.; Li, B.; Zhang, T.-L.; Zhou, H.-C. Structural tuning of zinc–porphyrin frameworks via auxiliary nitrogen-containing ligands towards selective adsorption of cationic dyes. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 6527–6530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katz, M.; Brown, Z.; Colón, Y.; Siu, P.; Scheidt, K.A.; Snurr, R.Q.; Hupp, J.T.; Farha, O.K. A Facile Synthesis of UiO-66, UiO-67 and Their Derivatives. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 9449–9451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, Q.; Zhao, H.; Dang, J.; Jin, R.; Zhao, W.; Li, Y. Wheat straws and corn straws as adsorbents for the removal of Cr (VI) and Cr (III) from aqueous solution: Kinetics, isotherm, and mechanism. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 6003–6009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karoyo, A.H.; Dehabadi, L.; Alabi, W.; Simonson, C.J.; Wilson, L.D. Hydration and sorption properties of raw and milled flax fibers. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 6113–6121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghaddam, F.M.; Jarahiyan, A.; Heidarian Haris, M.; Pourjavadi, A. An advancement in the synthesis of nano Pd@ magnetic amine-Functionalized UiO-66-NH2 catalyst for cyanation and O-arylation reactions. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Islamoglu, T.; Farha, O.K. Toward base heterogenization: A zirconium metal–organic framework/dendrimer or polymer mixture for rapid hydrolysis of a nerve-agent simulant. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2019, 2, 1005–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.-T.; Liu, Y.-M.; Wang, T.; Wu, Y.-L.; He, Y.-L.; Yang, R.; Zheng, S.-R. Regulation of the surface area and surface charge property of MOFs by multivariate strategy: Synthesis, characterization, selective dye adsorption and separation. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2018, 272, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, N.; Gan, C.; Liu, Y.; Chen, L.; Zhang, C.; Fang, Y. Synthesis of In2S3/UiO-66 hybrid with enhanced photocatalytic activity towards methyl orange and tetracycline hydrochloride degradation under visible-light irradiation. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Processing 2019, 91, 212–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vakili, R.; Xu, S.J.; Al-Janabi, N.; Gorgojo, P.; Holmes, S.M.; Fan, X.L. Microwave-assisted synthesis of zirconium-based metal organic frameworks (MOFs): Optimization and gas adsorption. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2018, 260, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doulia, D.; Leodopoulos, C.; Gimouhopoulos, K.; Rigas, F. Adsorption of humic acid on acid-activated Greek bentonite. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 340, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rauthula, M.S.; Srivastava, V.C. Studies on adsorption/desorption of nitrobenzene and humic acid onto/from activated carbon. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 168, 35–43. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Bi, L.; Ji, Y.; Ma, H.; Yin, X. Removal of humic acid from aqueous solution by magnetically separable polyaniline: Adsorption behavior and mechanism. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 430, 140–146. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Yue, D.; Cui, D.; Zhang, L.; Dong, X. Insights into adsorption of humic substances on graphitic carbon nitride. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 7910–7919. [Google Scholar]

| Pseudo-First-Order | Pseudo-Second-Order | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zr-MOFs | k1/min−1 | R2 | k2/min · g · mg−1 | R2 |
| UiO-66 | 1.021 × 10−3 | 0.968 | 2.475 × 10−4 | 0.991 |
| UiO-66-NH2 (1:1) | 2.30 × 10−4 | 0.542 | 6.376 × 10−4 | 0.999 |
| UiO-66-NH2 (1:2) | 3.69 × 10−4 | 0.683 | 1.518 × 10−4 | 0.999 |
| UiO-66-NH2 | 8.16 × 10−4 | 0.729 | 2.365 × 10−4 | 0.999 |
| Zr-MOFs | ki1 (mg g−1 min0.5) | ki2 (mg g−1 min0.5) | ki3 (mg g−1 min0.5) | Ci1 | Ci2 | Ci3 | R12 | R22 | R32 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UiO-66 | 3.088 | 1.380 | 0.589 | 1.888 | 18.351 | 38.150 | 0.989 | 0.982 | 0.934 |
| UiO-66-NH2 (1:1) | 7.468 | 1.113 | 0.151 | 3.088 | 58.189 | 79.958 | 0.993 | 0.888 | 0.978 |
| UiO-66-NH2 (1:2) | 7.189 | 2.223 | 0.376 | 6.635 | 46.888 | 89.219 | 0.997 | 0.918 | 0.980 |
| UiO-66-NH2 | 11.232 | 1.838 | 0.225 | 6.028 | 86.182 | 122.03 | 0.995 | 0.892 | 0.978 |
| Model | Parameters | Temperature) (°C) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15 | 25 | 35 | |||
| NH2- UiO-66 | Langmuir | qm/mg · g−1 | 102.15 | 140.25 | 150.15 |
| KL/L · mg−1 | 0.302 | 0.165 | 0.188 | ||
| R2 | 0.989 | 0.928 | 0.973 | ||
| Freundlich | KF/L1/n · mg−1−1/n · g−1 | 42.31 | 38.55 | 42.56 | |
| R2 | 0.744 | 0.882 | 0.770 | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, Z.; He, M.; Zhou, P. Effective Removal of Humic Acid by Zr-MOFs with Surface Modification. Water 2022, 14, 1800. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14111800
Jiang Y, Wang Z, Zhu Z, He M, Zhou P. Effective Removal of Humic Acid by Zr-MOFs with Surface Modification. Water. 2022; 14(11):1800. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14111800
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Yuankang, Zhenggang Wang, Zhiping Zhu, Mingpeng He, and Pan Zhou. 2022. "Effective Removal of Humic Acid by Zr-MOFs with Surface Modification" Water 14, no. 11: 1800. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14111800
APA StyleJiang, Y., Wang, Z., Zhu, Z., He, M., & Zhou, P. (2022). Effective Removal of Humic Acid by Zr-MOFs with Surface Modification. Water, 14(11), 1800. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14111800





