Responses of Different Submerged Macrophytes to the Application of Lanthanum-Modified Bentonite (LMB): A Mesocosm Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Design
2.2. Sampling
2.3. Statistical Analysis
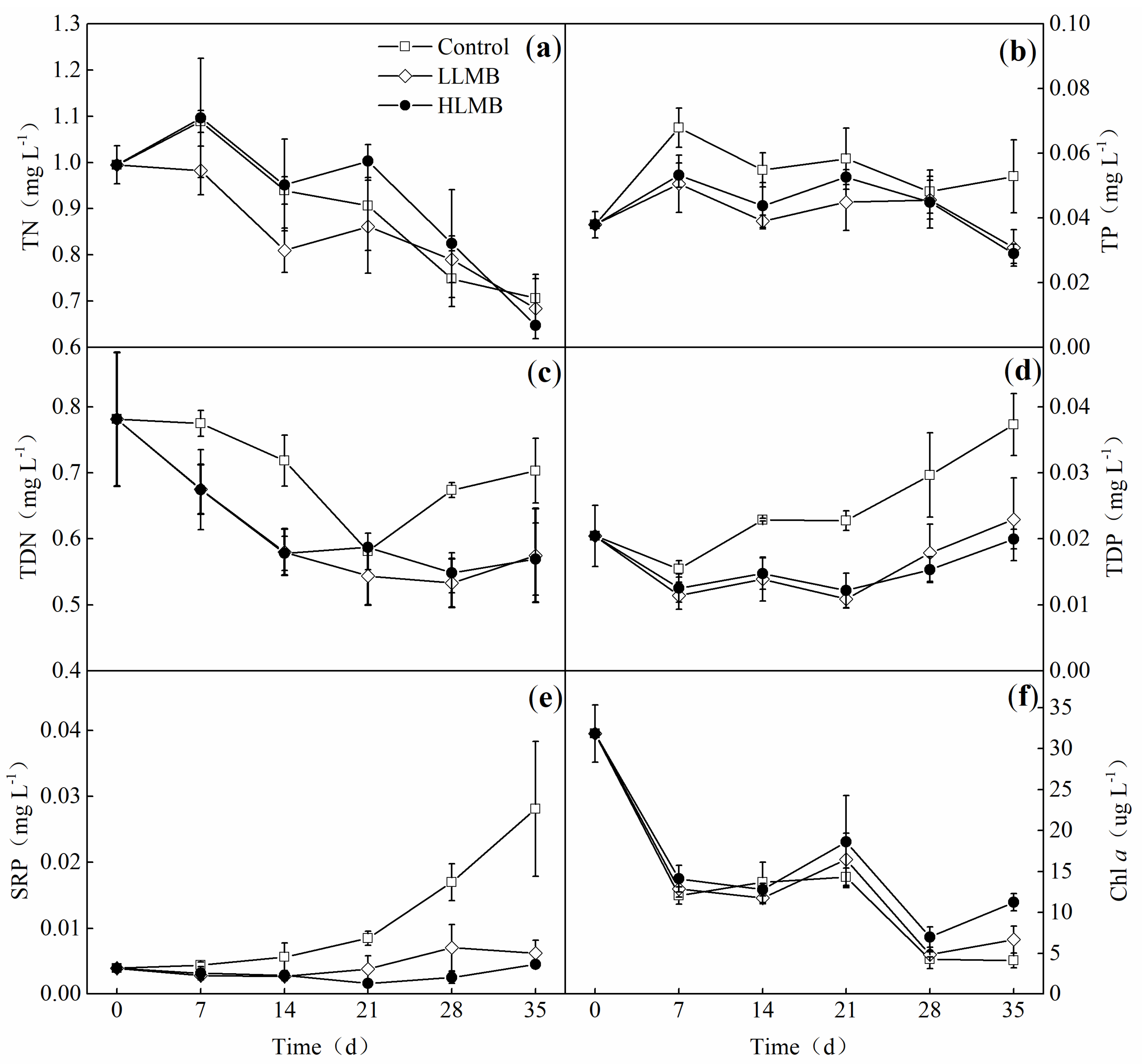
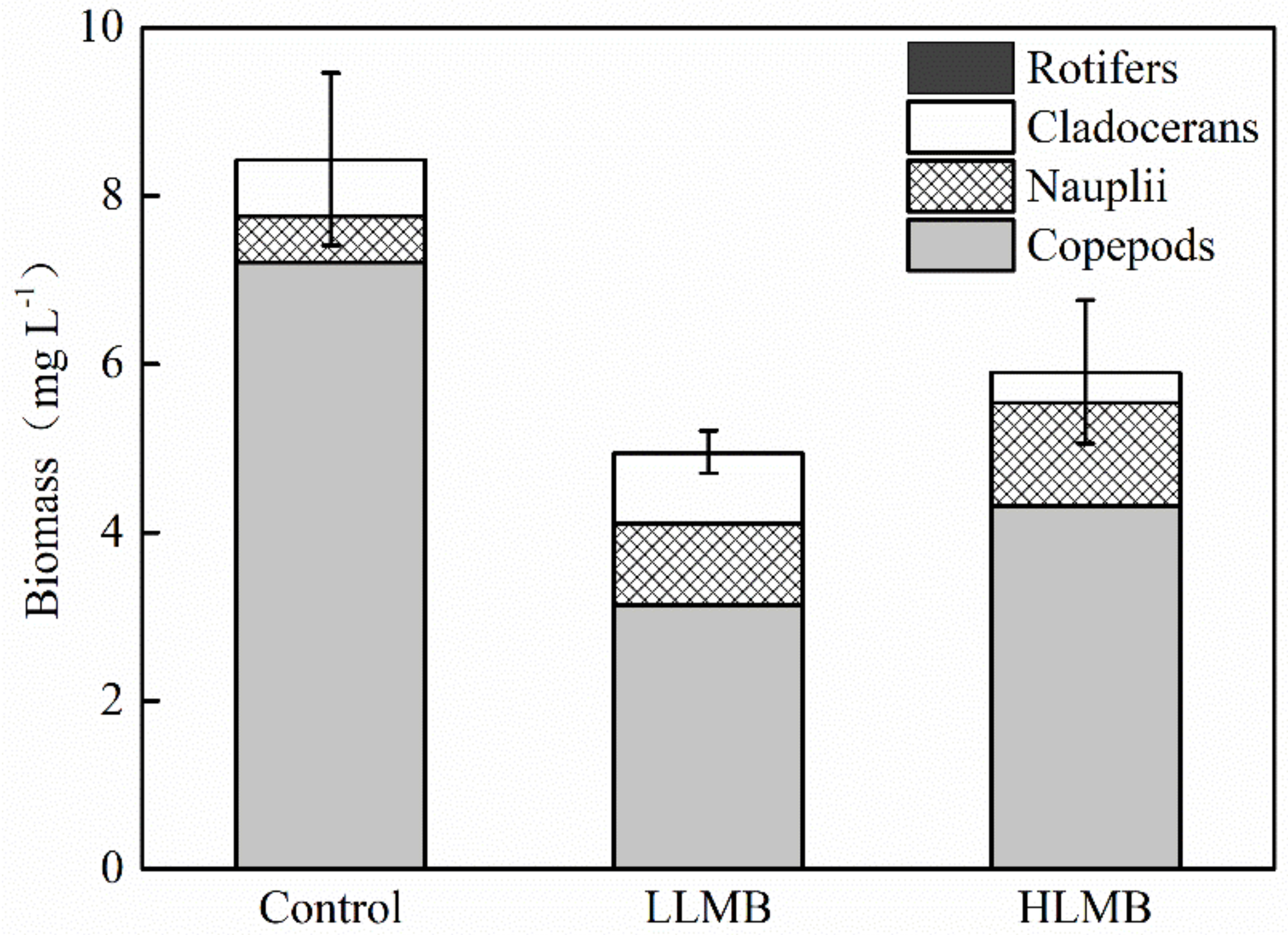
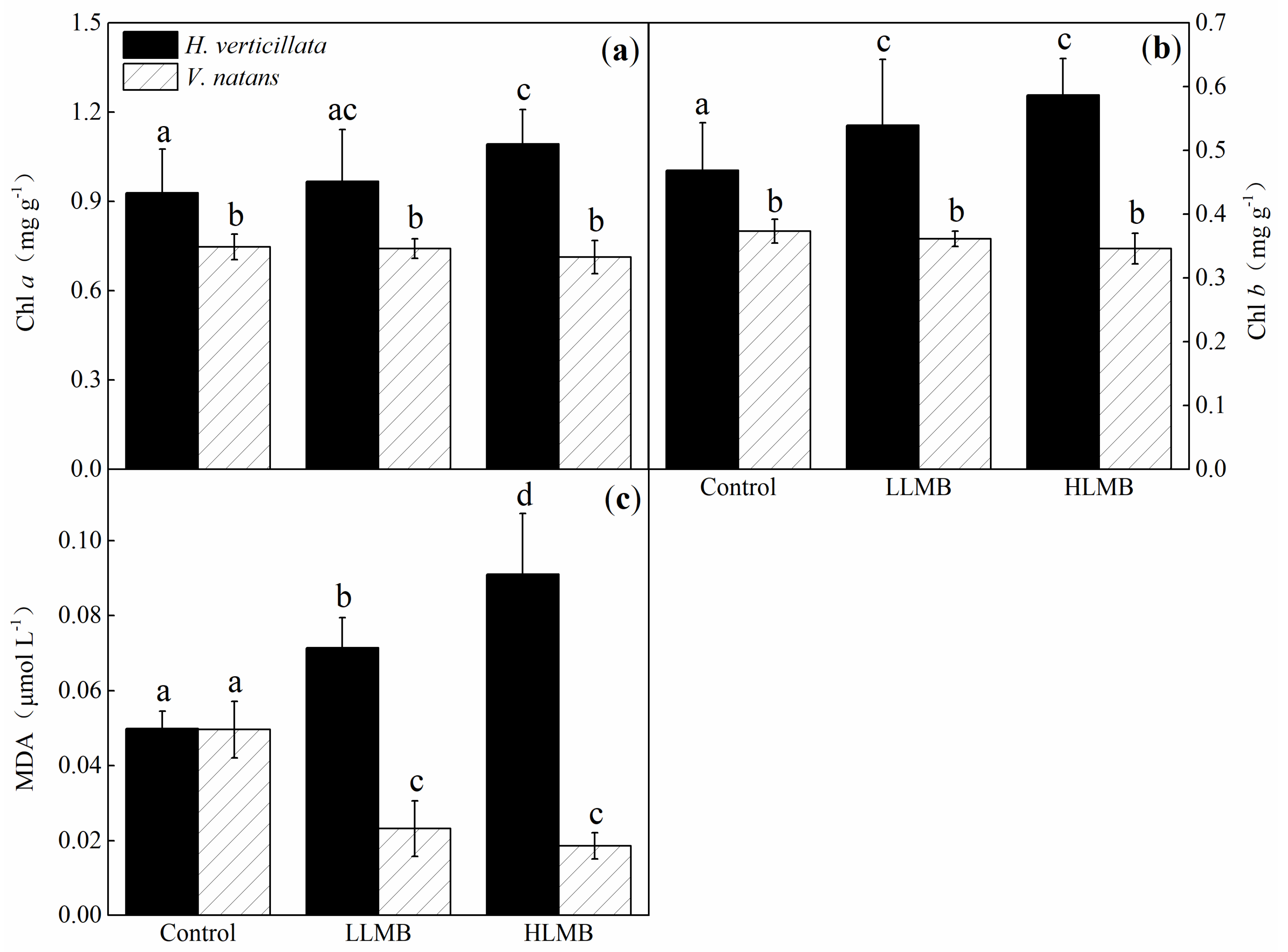
3. Results
3.1. Physicochemical Parameters in the Overlying Water
3.2. Zooplankton
3.3. Macrophytes
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of LMB on Hydrilla verticillata and Vallisneria natans
4.2. Effects of LMB on the Water Purification Ability of Submerged Macrophytes
4.3. Implications for the Restoration of Subtropical Lakes
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Smith, V.H.; Schindler, D.W. Eutrophication science: Where do we go from here? Trends Ecol. Evol. 2009, 24, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conley, D.J.; Paerl, H.W.; Howarth, R.W.; Boesch, D.F.; Seitzinger, S.P.; Havens, K.E.; Lancelot, C.; Likens, G.E. Controlling eutrophication by reducing both nitrogen and phosphorus. Science 2009, 323, 1014–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindler, D.W.; Hecky, R.E.; Findlay, D.L.; Stainton, M.P.; Parker, B.R.; Paterson, M.J.; Beaty, K.G.; Lyng, M.; Kasian, S.E. Eutrophication of lakes cannot be controlled by reducing nitrogen input: Results of a 37-year whole-ecosystem experiment. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 11254–11258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schindler, D.W.; Carpenter, S.R.; Chapra, S.C.; Hecky, R.E.; Orihel, D.M. Reducing phosphorus to curb lake eutrophication is a success. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 8923–8929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeppesen, E.; Søndergaard, M.; Jensen, J.P.; Havens, K.; Anneville, O.; Carvalho, L.; Coveney, M.F.; Deneke, R.; Dokulil, M.T.; Foy, B.; et al. Lake responses to reduced nutrient loading–An analysis of contemporary long-term data from 35 case studies. Freshw. Biol. 2005, 50, 1747–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooke, G.D.; Welch, E.B.; Peterson, S.; Nichols, S.A. Restoration and Management of Lakes and Reservoirs, 3rd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Sharpley, A.; Jarvie, H.P.; Buda, A.; May, L.; Spears, B.M.; Kleinman, P. Phosphorus legacy: Overcoming the effects of past management practices to mitigate future water quality impairment. J. Environ. Qual. 2013, 42, 1308–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Søndergaard, M.; Bjerring, R.; Jeppesen, E. Persistent internal loading during summer in shallow lakes. Hydrobiologia 2012, 710, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spears, B.M.; Carvalho, L.; Perkins, R.; Kirika, A.; Paterson, D.M. Long-term variation and regulation of internal phosphorus loading in Loch Leven. Hydrobiologia 2012, 681, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lürling, M.; Faassen, E.J. Controlling toxic cyanobacteria: Effects of dredging and phosphorus-binding clay on cyanobacteria and microcystins. Water Res. 2012, 46, 1447–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, G.B.; Lurling, M.; Spears, B.M. Assessment of changes in potential nutrient limitation in an impounded river after application of lanthanum-modified bentonite. Water Res. 2016, 97, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, C.; Liu, Z.S.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, B.Y.; Zhou, Q.H.; Zeng, L.; He, F.; Wu, Z.B. Synergistic removal effect of P in sediment of all fractions by combining the modified bentonite granules and submerged macrophyte. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 626, 458–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.W.; Hu, J.R.; Zhong, P.; Zhang, X.F.; Ning, J.J.; Larsen, S.E.; Chen, D.Y.; Gao, Y.M.; He, H.; Jeppesen, E. Successful restoration of a tropical shallow eutrophic lake: Strong bottom-up but weak top-down effects recorded. Water Res. 2018, 146, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lürling, M.; Waajen, G.; Van Oosterhout, F. Humic substances interfere with phosphate removal by lanthanum modified clay in controlling eutrophication. Water Res. 2014, 54, 78–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.B.; Kong, M.; Han, M.X.; Fan, C.X. Influence of sediment resuspension on the efficacy of geoengineering materials in the control of internal phosphorous loading from shallow eutrophic lakes. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 219, 568–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dithmer, L.; Nielsen, U.G.; Lundberg, D.; Reitzel, K. Influence of dissolved organic carbon on the efficiency of P sequestration by a lanthanum modified clay. Water Res. 2016, 97, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mucci, M.; Maliaka, V.; Noyma, N.P.; Marinho, M.M.; Lürling, M. Assessment of possible solid-phase phosphate sorbents to mitigate eutrophication: Influence of pH and anoxia. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 619–620, 1431–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copetti, D.; Finsterle, K.; Marziali, L.; Stefani, F.; Tartari, G.; Douglas, G.; Reitzel, K.; Spears, B.M.; Winfield, I.J.; Crosa, G.; et al. Eutrophication management in surface waters using lanthanum modified bentonite: A review. Water Res. 2016, 97, 162–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Spears, B.M.; Mackay, E.; Yasseri, S.; Gunn, I.D.M.; Waters, K.E.; Andrews, C.; Cole, S.; Ville, M.D.; Kelly, A.; Meis, S.; et al. A meta-analysis of water quality and aquatic macrophyte responses in 18 lakes treated with lanthanum modified bentonite (Phoslock®). Water Res. 2016, 97, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kong, M.; Liu, F.F.; Tao, Y.; Wang, P.F.; Wang, C.; Zhang, Y.M. First attempt for in situ capping with lanthanum modified bentonite (LMB) on the immobilization and transformation of organic phosphorus at the sediment-water interface. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 741, 140342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.D.; Chen, J.B.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Kuang, Y.; Yang, R.J.; Wu, D.Y. Interactions of phosphate and dissolved organic carbon with lanthanum modified bentonite: Implications for the inactivation of phosphorus in lakes. Water Res. 2020, 181, 115941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.M.; Zhen, W.; Jensen, H.S.; Reitzel, K.; Jeppesen, E.; Liu, Z.W. The combined effects of macrophytes (Vallisneria denseserrulata) and a lanthanum-modified bentonite on water quality of shallow eutrophic lakes: A mesocosm study. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 277, 116720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeppesen, E.; Søndergaard, M.; Søndergaard, M.; Christoffersen, K. The Structuring Role of Submerged Macrophytes in Lakes; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Wang, L.G.; Chao, C.X.; Yu, H.W.; Yu, D.; Liu, C.H. Submerged macrophytes successfully restored a subtropical aquacultural lake by controlling its internal phosphorus loading. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 268, 115949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Donk, E.; Bund, W.J.V.D. Impact of submerged macrophytes including charophytes on phyto- and zooplankton communities: Allelopathy versus other mechanisms. Aquat. Bot. 2002, 72, 261–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauridsen, T.L.; Jensen, J.P.; Jeppesen, E.; Søndergaard, M. Response of submerged macrophytes in Danish lakes to nutrient loading reductions and biomanipulation. Hydrobiologia 2003, 506, 641–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levi, P.S.; Riis, T.; Alnøe, A.B.; Peipoch, M.; Maetzke, K. Macrophyte complexity controls nutrient uptake in Lowland Streams. Ecosystems 2015, 18, 914–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhou, W.; Li, X.W.; Chu, Q.S.; Tang, N.; Shu, B.; Liu, G.; Xing, W. How many submerged macrophyte species are needed to improve water clarity and quality in Yangtze floodplain lakes? Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 724, 138267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waajen, G.; Van Oosterhout, F.; Douglas, G.; Lürling, M. Geo-engineering experiments in two urban ponds to control eutrophication. Water Res. 2016, 97, 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, H.; Qian, X.; Wu, H.; Li, H.; Pan, H.; Han, C. Combined effects of submerged macrophytes and aquatic animals on the restoration of a eutrophic water body—A case study of Gonghu Bay, Lake Taihu. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 102, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.H.; He, R.; Wu, Y.; Lürling, M.; Cai, H.Y.; Jiang, H.L.; Liu, X. Bioavailable phosphorus (P) reduction is less than mobile P immobilization in lake sediment for eutrophication control by inactivating agents. Water Res. 2017, 109, 196–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Zhong, Y.F.; Fan, H.; Song, C.F.; Yu, C.; Gao, Y.; Xiong, X.; Wu, C.X.; Liu, J.T. Chemical treatment of contaminated sediment for phosphorus control and subsequent effects on ammonia-oxidizing and ammonia-denitrifying microorganisms and on submerged macrophyte revegetation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 1007–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.F.; Su, H.J.; Zhou, G.A.; Dai, Y.Y.; Hu, J.; Zhao, Y.H.; Liu, Z.G.; Cao, T.; Ni, L.Y.; Zhang, M.; et al. Effects of benthivorous fish disturbance and snail herbivory on water quality and two submersed macrophytes. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 713, 136734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.Q.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Q.S.; Lürling, M.; Li, W.; He, H.; Gu, J.; Li, K.Y. Submerged macrophytes benefit from lanthanum modified bentonite treatment under juvenile omni-benthivorous fish disturbance: Implications for shallow lake restoration. Freshw. Biol. 2022, 67, 672–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowes, G.; Rao, S.K.; Estavillo, G.M.; Reiskind, J.B. C4 mechanisms in aquatic angiosperms: Comparisons with terrestrial C4 systems. Funct. Plant Biol. 2002, 29, 379–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, D.R.; Wu, Z.B.; Liu, B.Y.; Deng, J.Q.; Fu, G.P.; He, F. The restoration of aquatic macrophytes for improving water quality in a hypertrophic shallow lake in Hubei Province, China. Ecol. Eng. 2001, 18, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, B.L.; Qin, B.Q.; Gao, G.; Cai, X.L. Submerged macrophyte communities and the controlling factors in large, shallow Lake Taihu (China): Sediment distribution and water depth. J. Great Lakes Res. 2014, 40, 646–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.H.; An, S.Q.; Wu, B.F.; Wang, W.W. Density-dependent root morphology and root distribution in the submerged plant Vallisneria natan. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2006, 57, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.F.; Liu, Z.W. Interspecific competition effects on phosphorus accumulation by Hydrilla verticillata and Vallisneria natans. J. Environ. Sci. 2011, 23, 1274–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langeland, K.A. Hydrilla verticillata (L.f.) Royle (Hydrocharataceae), the perfect aquatic weed. Castanea 1996, 61, 293–304. [Google Scholar]
- Shearer, J.F.; Grodowitz, M.J.; McFarland, D.G. Nutritional quality of Hydrilla verticillata (L.f.) Royle and its effects on a fungal pathogen Mycoleptodiscus terrestris (Gerd.) Ostazeski. Biol. Control. 2007, 41, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.C.; Tu, Q. The Standard Methods for Observation and Analysis in Lake Eutrophication, 2nd ed.; Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 1990. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.J. Fauna Sinica; Rotifer; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1961. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Shen, J.R.; Du, N.S. Fauna Sinica, Crustacea, Freshwater Copepoda; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1979. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chiang, S.C.; Du, N.S. Fauna Sinica, Crustacea, Freshwater Cladocera; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1979. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X.F. Survey Observation and Analysis of Lake Ecology; Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 1999. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.K.; Huang, J.L. Experimental Principles and Techniques of Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 2nd ed.; Higher Education Press: Beijing, China, 2006. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Litchtenthaler, H.K.; Wellburn, A.R. Determinations of total carotenoids and chlorophylls a and b of leaf extracts in different solvents. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 1983, 11, 591–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiao, K.; Yu, D.; Wang, J. Habitat selection in spatially heterogeneous environments: A test of foraging behavior in the clonal submerged macrophyte Vallisneria spiralis L. Freshw. Biol. 2006, 51, 1552–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, S.H.; Wang, P.F.; Hou, J.; Li, W.; Zhang, W.J. Metabolic adaptations to ammonia-induced oxidative stress in leaves of the submerged macrophyte Vallisneria natans (Lour.) Hara. Aquat. Toxicol. 2008, 87, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van, T.K.; Wheeler, G.S.; Center, T.D. Competition between Hydrilla verticillata and Vallisneria americana as influenced by soil fertility. Aquat. Bot. 1999, 62, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, M.J. Analysis of the relationship between submerged aquatic vegetation (SAV) and water trophic status of Lakes Clustered in Northwestern Hillsborough county, Florida. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2010, 214, 539–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sim, D.Z.H.; Mowe, M.A.D.; Song, Y.; Lu, J.; Tan, H.T.W.; Mitrovic, S.M.; Roelke, D.L.; Yeo, D.C.J. Tropical macrophytes promote phytoplankton community shifts in lake mesocosms: Relevance for lake restoration in warm climates. Hydrobiologia 2021, 848, 4861–4884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Oosterhout, F.; Lürling, M. Effects of the novel ‘flock & lock’ lake restoration technique on Daphnia in Lake Rauwbraken (The Netherlands). J. Plankton Res. 2011, 33, 255–263. [Google Scholar]
- Van Oosterhout, F.; Lürling, M. The effect of phosphorus binding clay (Phoslock®) in mitigating cyanobacterial nuisance: A laboratory study on the effects on water quality variables and plankton. Hydrobiologia 2013, 710, 265–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamada-Ferraz, T.M.; Sueitt, A.P.E.; Oliveira, A.F.; Botta, C.M.R.; Fadini, P.S.; Nascimento, M.R.L.; Faria, B.M.; Mozeto, A.A. Assessment of Phoslock® application in a tropical eutrophic reservoir: An integrated evaluation from laboratory to field experiments. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2015, 4, 194–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Donk, E.; Gulati, R.D.; Grimm, M.P. Restoration by biomanipulation in a small hypertrophic lake: First-year results. Hydrobiologia 1990, 191, 285–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- DeBoom, C.S.; Wahl, D.H. Piscivore enhancement effects on food webs depend on planktivore body size and species composition in replicated whole lake experiments. Hydrobiologia 2014, 736, 31–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Jin, H.; Erik, J.; Li, K.Y.; Liu, Z.W.; Zhang, Y.D. Fish-mediated plankton responses to increased temperature in subtropical aquatic mesocosm ecosystems: Implications for lake management. Water Res. 2018, 144, 304–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeppesen, E.; Jensen, J.P.; Søndergaard, M.; Lauridsen, T.; Landkildehus, F. Trophic structure, species richness and biodiversity in Danish lakes: Changes along a phosphorus gradient. Freshw. Biol. 2000, 45, 201–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; He, F.; Xia, S.; Zhou, Q.H.; Wu, Z.B. Studies on the treatment efficiency of sediment phosphorus with a combined technology of PCFM and submerged macrophytes. Environ. Pollut. 2015, 206, 705–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, T.S.; Cao, T.; Ni, L.Y.; He, L.; Yi, C.L.; Yuan, C.B.; Xie, P. Improvement of water quality by sediment capping and re-vegetation with Vallisneria natans L.: A short-term investigation using an in situ enclosure experiment in Lake Erhai, China. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 86, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.S.; Zhang, Y.; Yan, P.; Luo, J.; Kong, L.W.; Chang, J.J.; Liu, B.Y.; Xu, D.; He, F.; Wu, Z.B. Synergistic control of internal phosphorus loading from eutrophic lake sediment using MMF coupled with submerged macrophytes. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 731, 138697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egemose, S.; Reitzel, K.; Andersen, F.Ø.; Flindt, M.R. Chemical lake restoration products: Sediment stability and phosphorus dynamics. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 985–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| df | pH | DO | Conductivity | Turbidity | Chl a | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | Pr > F | F | Pr > F | F | Pr > F | F | Pr > F | F | Pr > F | ||
| L | 2 | 3.32 | n.s. | 2.70 | n.s. | 39.10 | ** | 53.37 | ** | 21.65 | ** |
| T | 5 | 53.86 | ** | 150.11 | ** | 94.65 | ** | 18.39 | ** | 133.65 | ** |
| L × T | 10 | 0.89 | n.s. | 3.34 | n.s. | 9.03 | * | 6.03 | * | 1.66 | n.s. |
| TN | TP | TDN | TDP | SRP | TN | TP | TDN | TDP | SRP | ||
| L | 2 | 4.23 | n.s. | 13.52 | * | 21.79 | * | 17.33 | * | 99.30 | ** |
| T | 5 | 59.14 | ** | 23.18 | ** | 10.86 | * | 57.36 | ** | 18.90 | * |
| L × T | 10 | 1.63 | n.s. | 2.24 | n.s. | 5.81 | * | 3.62 | n.s. | 13.42 | * |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, Y.; Zou, X.; Li, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Li, K. Responses of Different Submerged Macrophytes to the Application of Lanthanum-Modified Bentonite (LMB): A Mesocosm Study. Water 2022, 14, 1783. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14111783
Han Y, Zou X, Li Q, Zhang Y, Li K. Responses of Different Submerged Macrophytes to the Application of Lanthanum-Modified Bentonite (LMB): A Mesocosm Study. Water. 2022; 14(11):1783. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14111783
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Yanqing, Xiaojuan Zou, Qisheng Li, You Zhang, and Kuanyi Li. 2022. "Responses of Different Submerged Macrophytes to the Application of Lanthanum-Modified Bentonite (LMB): A Mesocosm Study" Water 14, no. 11: 1783. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14111783
APA StyleHan, Y., Zou, X., Li, Q., Zhang, Y., & Li, K. (2022). Responses of Different Submerged Macrophytes to the Application of Lanthanum-Modified Bentonite (LMB): A Mesocosm Study. Water, 14(11), 1783. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14111783






