Degradation of Reactive Yellow 18 Using Ionizing Radiation Based Advanced Oxidation Processes: Cytotoxicity, Mutagenicity and By-Product Distribution
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Determination of λmax of RY-18
2.3. Preparation of Sample Solution
2.4. Gamma Treatment of Sample
2.5. FTIR Analysis
2.6. LCMS Analysis
2.7. Toxicity Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Reactive Yellow 18 Analysis
3.2. Effect of Dye Concentration
3.3. Effect of Hydrogen Peroxide
3.4. Effect of pH
3.5. Identification of By-Products
3.6. Effect of Gamma Radiation Treatment on Toxicity
3.6.1. Cytotoxicity
3.6.2. Mutagenicity
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Grillini, V.; Verlicchi, P.; Zanni, G. SWOT-SOR analysis of activated carbon-based technologies and O3/UV process as polishing treatments for hospital effluent. Water 2022, 14, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starkl, M.; Brunner, N.; Das, S.; Singh, A. Sustainability assessment for wastewater treatment systems in developing countries. Water 2022, 14, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, T.P.; Babcock, R.W.; Uekawa, T.; Schneider, J.; Hu, B. Effects of waste activated sludge extracellular polymeric substances on biosorption. Water 2022, 14, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.-C.; Liu, G.-Q.; Xu, Z.-H.; Tao, W.-Y. Decolorization of a dye industry effluent by Aspergillus fumigatus XC6. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2007, 74, 239–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, C.; Hawkes, F.R.; Hawkes, D.L.; Lourenço, N.D.; Pinheiro, H.M.; Delée, W. Colour in textile effluents–sources, measurement, discharge consents and simulation: A review. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. Int. Res. Process Environ. Clean Technol. 1999, 74, 1009–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqua, U.H.; Ali, S.; Iqbal, M.; Hussain, T. Relationship between structure and dyeing properties of reactive dyes for cotton dyeing. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 241, 839–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinta, S.; VijayKumar, S. Technical facts & figures of reactive dyes used in textiles. Int. J. Eng. Manag. Sci. 2013, 4, 308–312. [Google Scholar]
- Gowri, R.S.; Vijayaraghavan, R.; Meenambigai, P. Microbial degradation of reactive dyes—A review. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci. 2014, 3, 421–436. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, D.M. Developments in the chemistry of reactive dyes and their application processes. Coloration Technol. 2014, 130, 382–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fartode, A.P.; Fartode, S.A.; Shelke, T.R.; Parwate, D.V. Synergistic effect of H2O2 Addition on Gamma Radiolytic Decoloration of Some commercial Dye Solutions. In IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Okoro, H.K.; Tella, A.C.; Ajibola, O.A.; Zvinowanda, C.; Ngila, J.C. Adsorptive removal of naphthalene and anthracene from aqueous solution with zinc and copper-terephthalate metal-organic frameworks. Bull. Chem. Soc. Ethiop. 2019, 33, 229–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shah, L.A.; Haleem, A.; Sayed, M.; Siddiq, M. Synthesis of sensitive hybrid polymer microgels for catalytic reduction of organic pollutants. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 3492–3497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohtani, B.; Ogawa, Y.; Nishimoto, S.I. Photocatalytic activity of amorphous—Anatase mixture of titanium (IV) oxide particles suspended in aqueous solutions. J. Phys. Chem. B 1997, 101, 3746–3752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, X.; Mao, S.S. Titanium dioxide nanomaterials: Synthesis, properties, modifications, and applications. Chem. Rev. 2007, 107, 2891–2959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saquib, M.; Abu Tariq, M.; Faisal, M.; Muneer, M. Photocatalytic degradation of two selected dye derivatives in aqueous suspensions of titanium dioxide. Desalination 2008, 219, 301–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modirshahla, N.; Behnajady, M.A. Photooxidative degradation of Malachite Green (MG) by UV/H2O2: Influence of operational parameters and kinetic modeling. Dye. Pigment. 2006, 70, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrank, S.G.; dos Santos, J.N.R.; Souza, D.S.; Souza, E.E.S. Decolourisation effects of Vat Green 01 textile dye and textile wastewater using H2O2/UV process. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2007, 186, 125–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Ma, W.; He, J.; Zhao, J.; Jimmy, C.Y. Photooxidation of azo dye in aqueous dispersions of H2O2/α-FeOOH. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2002, 39, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, F.H.; Rauf, M.; Ashraf, S.S. Photolytic oxidation of Safranin-O with H2O2. Dye. Pigment. 2007, 72, 349–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barakat, M.; El-Banna, M. Radiolytic studies on some organic dyes in aqueous solutions. Int. J. Low Radiat. 2007, 4, 286–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleboyeh, A.; Kasiri, M.; Olya, M. Prediction of azo dye decolorization by UV/H2O2 using artificial neural networks. Dye. Pigment. 2008, 77, 288–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauf, M.; Ashraf, S.S. Radiation induced degradation of dyes—An overview. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 166, 6–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Yang, R.; Wang, W.; Shen, Z.; Bian, S.; Zhu, Z. Radiation-induced decomposition and decoloration of reactive dyes in the presence of H2O2. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2006, 75, 286–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arshad, R.; Bokhari, T.H.; Khosa, K.K.; Bhatti, I.A.; Munir, M.; Iqbal, M.; Iqbal, D.N.; Khan, M.; Iqbal, M.; Nazir, A. Gamma radiation induced degradation of anthraquinone Reactive Blue-19 dye using hydrogen peroxide as oxidizing agent. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2020, 168, 108637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arshad, R.; Bokhari, T.H.; Javed, T.; Bhatti, I.A.; Rasheed, S.; Iqbal, M.; Nazir, A.; Naz, S.; Khan, M.I.; Khosa, M.K.K.; et al. Degradation product distribution of Reactive Red-147 dye treated by UV/H2O2/TiO2 advanced oxidation process. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 3168–3178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, T.; An, J.; Gao, Y.; Li, G.; Fang, H.; Song, W. Photocatalytic degradation and mineralization mechanism and toxicity assessment of antivirus drug acyclovir: Experimental and theoretical studies. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2015, 164, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maron, D.M.; Ames, B.N. Revised methods for the Salmonella mutagenicity test. Mutat. Res. Environ. Mutagenesis Relat. Subj. 1983, 113, 173–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilal, M.; Rasheed, T.; Iqbal, H.M.; Li, C.; Wang, H.; Hu, H.; Wang, W.; Zhang, X. Photocatalytic degradation, toxicological assessment and degradation pathway of CI Reactive Blue 19 dye. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2018, 129, 384–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, M.; Abbas, M.; Arshad, M.; Hussain, T.; Ullah Khan, A.; Masood, N.; Tahir, M.A.; Hussain, S.M.; Bokhari, T.H.; Ahmad Khera, R. Short communication gamma radiation treatment for reducing cytotoxicity and mutagenicity in industrial wastewater. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2015, 24, 2745–2750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.-J.; Yu, H.-Q.; Li, Q.-R. Radiolytic degradation of Acid Orange 7: A mechanistic study. Chemosphere 2005, 61, 1003–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şolpan, D.; Güven, O.; Takács, E.; Wojnárovits, L.; Dajka, K. High-energy irradiation treatment of aqueous solutions of azo dyes: Steady-state gamma radiolysis experiments. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2003, 67, 531–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muneer, M.; Kanjal, M.I.; Saeed, M.; Javed, T.; Haq, A.U.; Ud Den, N.Z.; Jamal, M.A.; Ali, S.; Iqbal, M. High energy radiation induced degradation of reactive yellow 145 dye: A mechanistic study. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2020, 177, 109115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muneer, M.; Hafiz, N.; Usman, M.; Rehman, F.U.; Saeed, M.; Bhatti, H.; Kanjal, M.I. Environmentally friendly oxidative degradation of reactive orange dye by high energy radiation. Oxid. Commun. 2015, 38, 2091–2099. [Google Scholar]
- Iqbal, M.; Bhatti, I.A. Gamma radiation/H2O2 treatment of a nonylphenol ethoxylates: Degradation, cytotoxicity, and mutagenicity evaluation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 299, 351–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbas, M.; Hafiz, N.; Usman, M.; Rehman, F.U.; Saeed, M.; Bhatti, H.; Kanjal, M.I. Vibrio fischeri bioluminescence inhibition assay for ecotoxicity assessment: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 626, 1295–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, M.; Khera, R.A.; Hussain, T.; Sadia, H.; Abbas, M.; Nazir, A.; Younas, U. Cytotoxicity and bioactivity evaluation of pygmy date palm extracts. Cur. Sci. Perspect 2017, 3, 106. [Google Scholar]
- Arshad, M.; Hussain, T.; Chaudhry, N.; Sadia, H.; Aslam, B.; Tahir, U.; Abbas, M.; Qureshi, N.; Nazir, A.; Rajoka, M.I.; et al. Enhancing profitability of ethanol fermentation through gamma ray mutagenesis of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2019, 28, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Name of DyeReactive Yellow 18 | |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C25H16ClN9Na4O13S4 |
| Molecular weight (g/mole) | 906.12 |
| Chemical nature | Anionic yellow 18 |
| Class | Single azo |
| Color index name | Yellow |
| Color index number | 13245 |
| λmax (nm) | 410 |
| Sr. No | Structural Formula | Molecular Weight | m/z Value | Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |  | 180.16 | 179.0 | Detected |
| 2 | 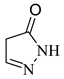 | 84.08 | 84.0 | Not detected |
| 3 |  | 130.54 | 130 | Detected |
| 4 |  | 90.51 | 90.0 | Detected |
| 5 |  | 242.62 | 241.95 | Detected |
| 6 | 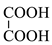 | 90 | 90.03 | Detected |
| 7 | 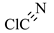 | 61.47 | 60.0 | Not detected |
| 8 |  | 297.22 | 296.17 | Detected |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shahzadi, M.; Bokhari, T.H.; Nazish, N.; Usman, M.; Ezzine, S.; Alwadai, N.; Iqbal, M.; Alfryyan, N.; Iqbal, M.; Khosa, M.K.; et al. Degradation of Reactive Yellow 18 Using Ionizing Radiation Based Advanced Oxidation Processes: Cytotoxicity, Mutagenicity and By-Product Distribution. Water 2022, 14, 1688. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14111688
Shahzadi M, Bokhari TH, Nazish N, Usman M, Ezzine S, Alwadai N, Iqbal M, Alfryyan N, Iqbal M, Khosa MK, et al. Degradation of Reactive Yellow 18 Using Ionizing Radiation Based Advanced Oxidation Processes: Cytotoxicity, Mutagenicity and By-Product Distribution. Water. 2022; 14(11):1688. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14111688
Chicago/Turabian StyleShahzadi, Maryam, Tanveer Hussain Bokhari, Nadia Nazish, Muhammad Usman, Safa Ezzine, Norah Alwadai, Munawar Iqbal, Nada Alfryyan, Mazhar Iqbal, Muhammad Kaleem Khosa, and et al. 2022. "Degradation of Reactive Yellow 18 Using Ionizing Radiation Based Advanced Oxidation Processes: Cytotoxicity, Mutagenicity and By-Product Distribution" Water 14, no. 11: 1688. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14111688
APA StyleShahzadi, M., Bokhari, T. H., Nazish, N., Usman, M., Ezzine, S., Alwadai, N., Iqbal, M., Alfryyan, N., Iqbal, M., Khosa, M. K., & Abbas, M. (2022). Degradation of Reactive Yellow 18 Using Ionizing Radiation Based Advanced Oxidation Processes: Cytotoxicity, Mutagenicity and By-Product Distribution. Water, 14(11), 1688. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14111688






