Estimation of Soil Erosion and Evaluation of Soil and Water Conservation Benefit in Terraces under Extreme Precipitation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
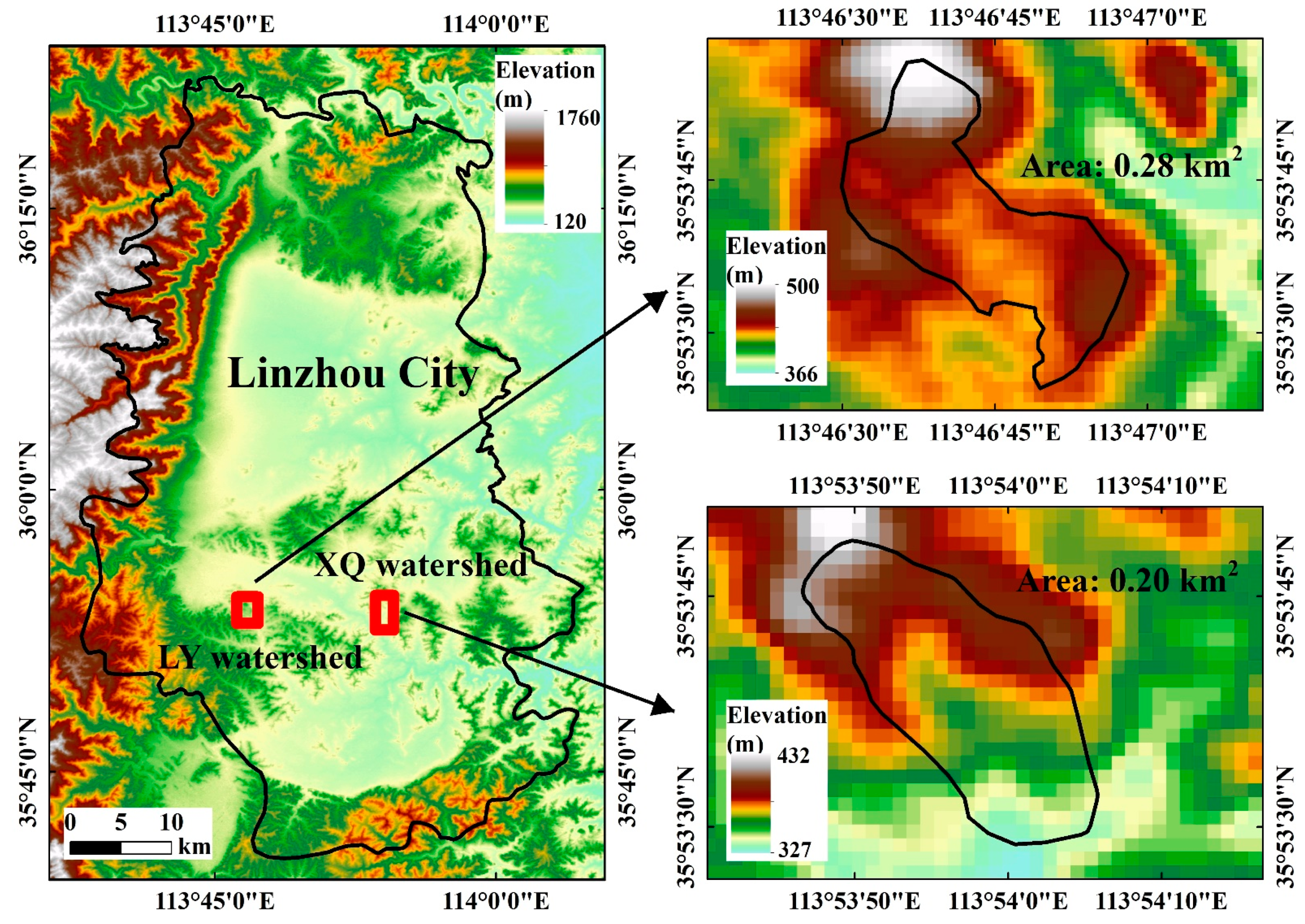
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Soil Erosion Modelling
2.3.1. Rainfall Erosivity Factor R
2.3.2. Soil Erodibility Factor K
2.3.3. Slope Length Factor L and Slope Gradient Factor S
2.3.4. Vegetation Cover and Biological-Practices Factor B
2.3.5. Engineering-Control in Water and Soil Conservation Factor E and Tillage Practices in Water and Soil Conservation Factor T
3. Results
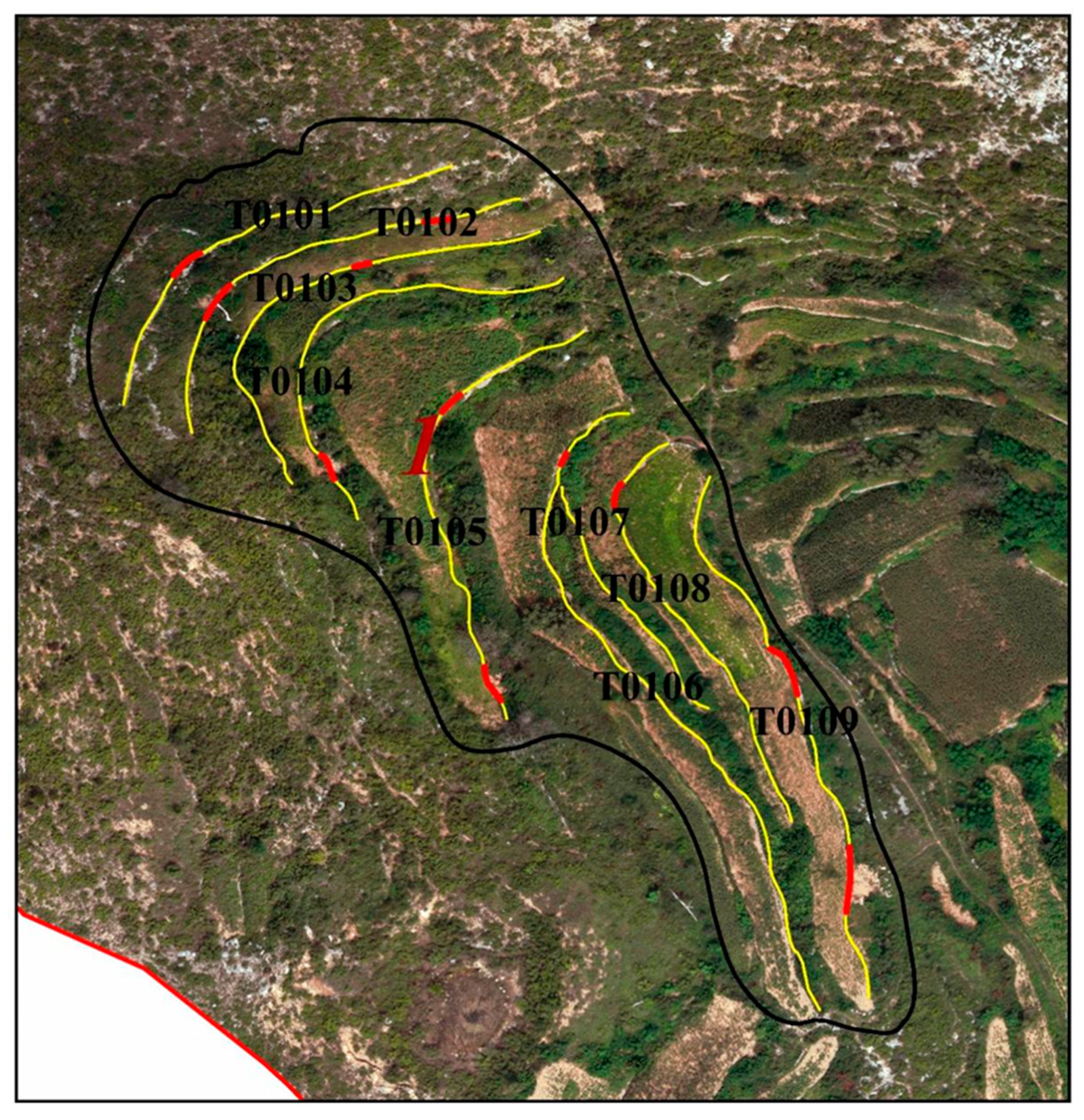
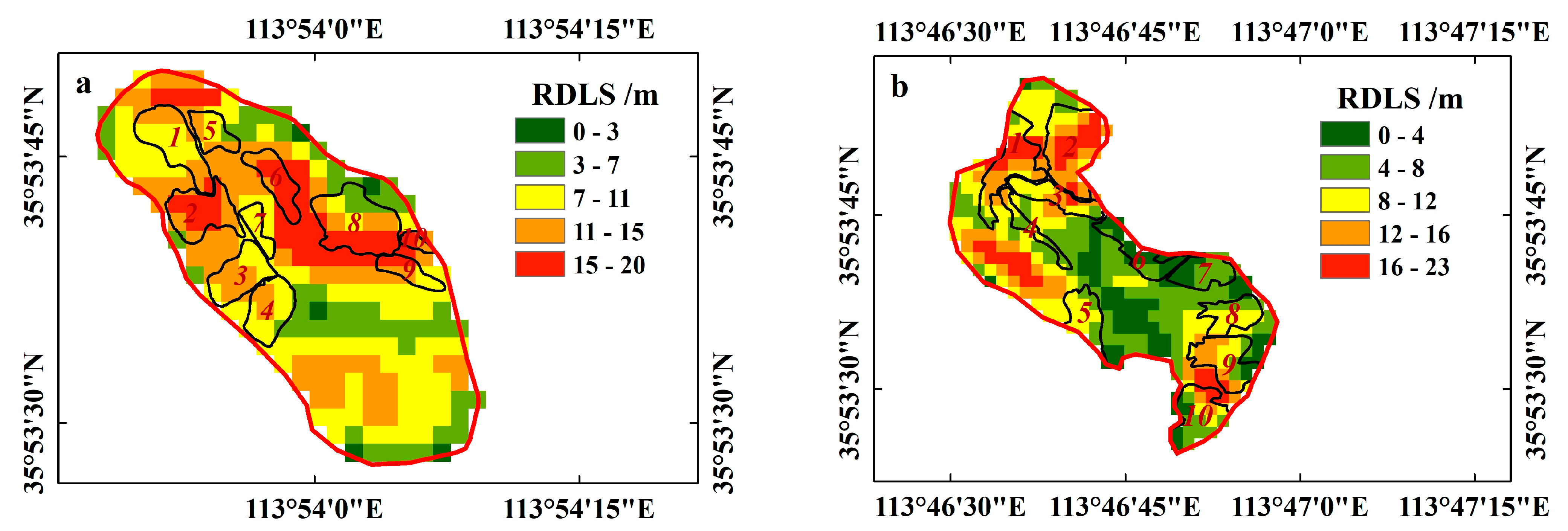
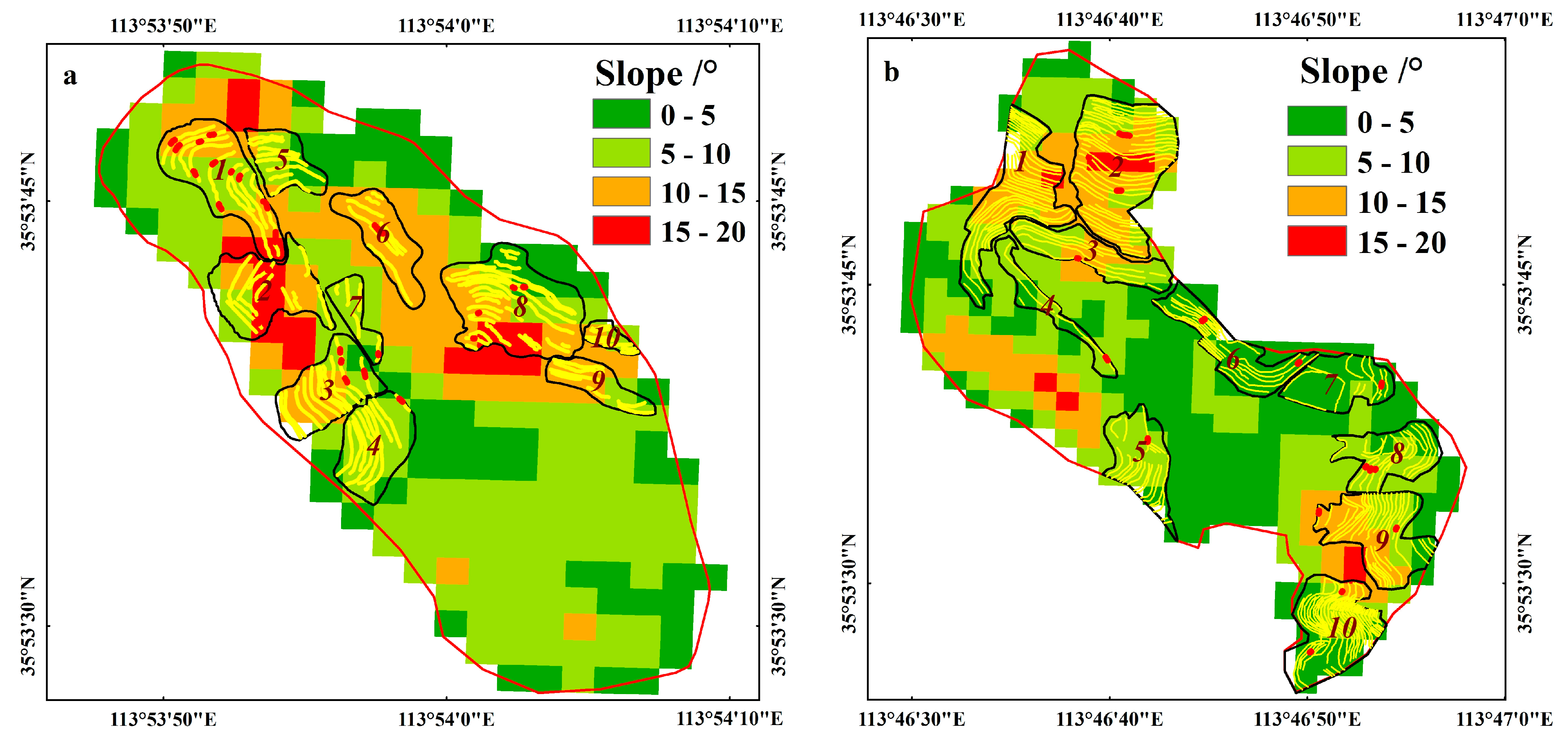
3.1. The Damaged of Terraces under Extreme Precipitation
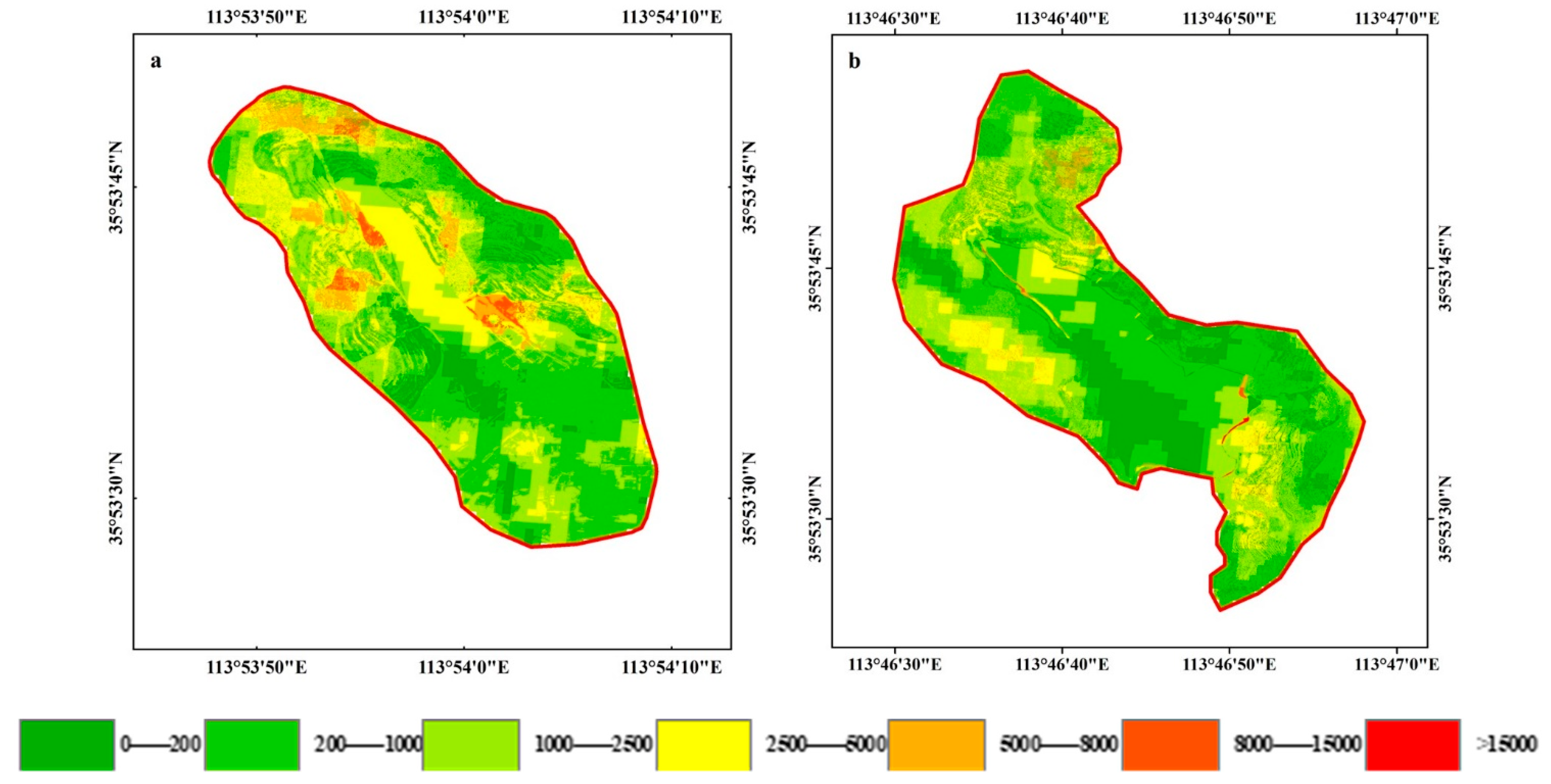
3.2. Soil Erosion under Extreme Precipitation
3.3. Benefits of Soil and Water Conservation Measures against Extreme Precipitations
4. Discussion
4.1. Application of UAV Remote Sensing Image in Gully Erosion Field Investigation
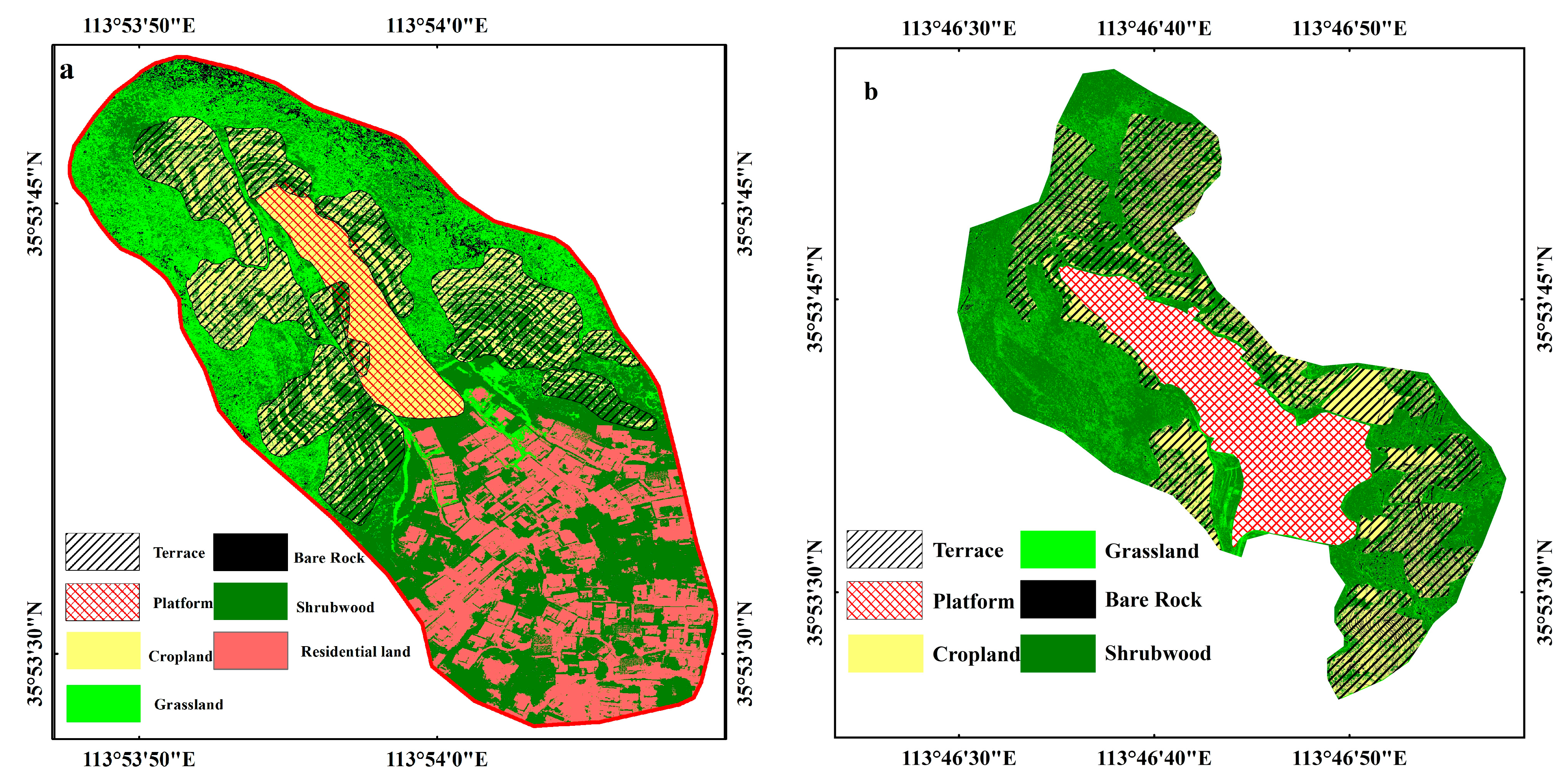
4.2. Influencing Factors of Terrace Damage in Two Small Watersheds
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Borrelli, P.; Robinson, D.A.; Fleischer, L.R.; Lugato, E.; Ballabio, C.; Alewell, C.; Meusburger, K.; Modugno, S.; Schuett, B.; Ferro, V.; et al. An Assessment of the Global Impact of 21st Century Land Use Change on Soil Erosion. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, L.; Cheng, H.; Pu, X.; Wang, J.; Cheng, Q.; Liu, X. Identifying Organic Matter Sources Using Isotopic Ratios in a Watershed Impacted by Intensive Agricultural Activities in Northeast China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2016, 222, 48–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meliho, M.; Nouira, A.; Benmansour, M.; Boulmane, M.; Khattabi, A.; Mhammdi, N.; Benkdad, A. Assessment of Soil Erosion Rates in a Mediterranean Cultivated and Uncultivated Soils Using Fallout 137Cs. J. Environ. Radioact. 2019, 208, 106021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanidis, S.; Alexandridis, V.; Ghosal, K. Assessment of Water-Induced Soil Erosion as a Threat to Natura 2000 Protected Areas in Crete Island, Greece. Sustainability 2022, 14, 2738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, V.; Shah, H.L. Hydroclimatological Perspective of the Kerala Flood of 2018. J. Geol. Soc. India 2018, 92, 645–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fekete, A.; Sandholz, S. Here Comes the Flood, but Not Failure? Lessons to Learn after the Heavy Rain and Pluvial Floods in Germany 2021. Water 2021, 13, 3016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crosta, G.B.; Frattini, P. Rainfall-Induced Landslides and Debris Flows—Preface. Hydrol. Process. 2008, 22, 473–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowler, H.J.; Lenderink, G.; Prein, A.F.; Westra, S.; Allan, R.P.; Ban, N.; Barbero, R.; Berg, P.; Blenkinsop, S.; Do, H.X.; et al. Anthropogenic Intensification of Short-Duration Rainfall Extremes. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2021, 2, 107–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santoso, A.M.; Phoon, K.-K.; Quek, S.-T. Effects of Soil Spatial Variability on Rainfall-Induced Landslides. Comput. Struct. 2011, 89, 893–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, R.; Lewis, S.C.; Arblaster, J.M.; Abram, N.J. A Review of Past and Projected Changes in Australia’s Rainfall. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev.-Clim. Change 2019, 10, e577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westra, S.; Fowler, H.J.; Evans, J.P.; Alexander, L.V.; Berg, P.; Johnson, F.; Kendon, E.J.; Lenderink, G.; Roberts, N.M. Future Changes to the Intensity and Frequency of Short-Duration Extreme Rainfall. Rev. Geophys. 2014, 52, 522–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, A.; Wasson, R.J.; Ziegler, A.D.; Chow, W.T.L.; Sundriyal, Y.P. Characteristics of Rain-Induced Landslides in the Indian Himalaya: A Case Study of the Mandakini Catchment during the 2013 Flood. Geomorphology 2019, 330, 100–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dezfuli, A. Rare Atmospheric River Caused Record Floods across the Middle East. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2020, 101, E394–E400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, R.; Tsuchida, T.; Moriwaki, T.; Kano, S. Hiroshima Prefecture Geo-Disasters Due to Western Japan Torrential Rainfall in July 2018. Soils Found. 2020, 60, 283–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanidis, S.; Alexandridis, V.; Chatzichristaki, C.; Stefanidis, P. Assessing Soil Loss by Water Erosion in a Typical Mediterranean Ecosystem of Northern Greece under Current and Future Rainfall Erosivity. Water 2021, 13, 2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagos, P.; Ballabio, C.; Himics, M.; Scarpa, S.; Matthews, F.; Bogonos, M.; Poesen, J.; Borrelli, P. Projections of Soil Loss by Water Erosion in Europe by 2050. Environ. Sci. Policy 2021, 124, 380–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Kateb, H.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, P.; Mosandl, R. Soil Erosion and Surface Runoff on Different Vegetation Covers and Slope Gradients: A Field Experiment in Southern Shaanxi Province, China. Catena 2013, 105, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartanto, H.; Prabhu, R.; Widayat, A.S.E.; Asdak, C. Factors Affecting Runoff and Soil Erosion: Plot-Level Soil Loss Monitoring for Assessing Sustainability of Forest Management. For. Ecol. Manag. 2003, 180, 361–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keesstra, S.; Pereira, P.; Novara, A.; Brevik, E.C.; Azorin-Molina, C.; Parras-Alcantara, L.; Jordan, A.; Cerda, A. Effects of Soil Management Techniques on Soil Water Erosion in Apricot Orchards. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 551, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, J.; Bai, Z.; Lv, C. Effects of Vegetation on Runoff and Soil Erosion on Reclaimed Land in an Opencast Coal-Mine Dump in a Loess Area. Catena 2015, 128, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddadchi, A.; Nosrati, K.; Ahmadi, F. Differences between the Source Contribution of Bed Material and Suspended Sediments in a Mountainous Agricultural Catchment of Western Iran. Catena 2014, 116, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, G.; Sena, D.R.; Patra, S.; Singh, D.; Kurothe, R.S.; Mishra, P.K.; Nyonand. Design and Development of a Low-Cost Automatic Runoff Sampler for Time Distributed Sampling. J. Hydrol. 2021, 592, 125845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mhiret, D.A.; Dagnew, D.C.; Guzman, C.D.; Alemie, T.C.; Zegeye, A.D.; Tebebu, T.Y.; Langendoen, E.J.; Zaitchik, B.F.; Tilahun, S.A.; Steenhuis, T.S. A Nine-Year Study on the Benefits and Risks of Soil and Water Conservation Practices in the Humid Highlands of Ethiopia: The Debre Mawi Watershed. J. Environ. Manage. 2020, 270, 110885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walling, D.E.; Russell, M.A.; Hodgkinson, R.A.; Zhang, Y. Establishing Sediment Budgets for Two Small Lowland Agricultural Catchments in the UK. Catena 2002, 47, 323–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Tian, G.; Mayer, A.L.; He, R. Risk Assessment of Soil Erosion by Application of Remote Sensing and GIS in Yanshan Reservoir Catchment, China. Nat. Hazards 2015, 79, 277–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Tian, Y.; Mu, X.; Zhai, J.; Gao, P.; Zhao, G. Loess Landslide Inventory Map Based on GF-1 Satellite Imagery. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vrieling, A. Satellite Remote Sensing for Water Erosion Assessment: A Review. Catena 2006, 65, 2–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Yang, S. Regional Characteristics of Long-Term Changes in Total and Extreme Precipitations over China and Their Links to Atmospheric-Oceanic Features. Int. J. Climatol. 2017, 37, 751–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duan, X.; Bai, Z.; Rong, L.; Li, Y.; Ding, J.; Tao, Y.; Li, J.; Li, J.; Wang, W. Investigation Method for Regional Soil Erosion Based on the Chinese Soil Loss Equation and High-Resolution Spatial Data: Case Study on the Mountainous Yunnan Province, China. Catena 2020, 184, 104237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamel, P.; Chaplin-Kramer, R.; Sim, S.; Mueller, C. A New Approach to Modeling the Sediment Retention Service (InVEST 3.0): Case Study of the Cape Fear Catchment, North Carolina, USA. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 524, 166–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Duan, Z.; Kono, Y.; Wang, M. Integration of Remotely Sensed C Factor into SWAT for Modelling Sediment Yield. Hydrol. Process. 2011, 25, 3387–3398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toumi, S.; Meddi, M.; Mahe, G.; Brou, Y.T. Remote sensing and GIS applied to the mapping of soil loss by erosion in the Wadi Mina catchment. Hydrol. Sci. J.-J. Sci. Hydrol. 2013, 58, 1542–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- AbdelRahman, M.A.E.; Natarajan, A.; Hegde, R.; Prakash, S.S. Assessment of Land Degradation Using Comprehensive Geostatistical Approach and Remote Sensing Data in GIS-Model Builder. Egypt. J. Remote Sens. Space Sci. 2019, 22, 323–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayat, F.; Monfared, A.B.; Jahansooz, M.R.; Terol Esparza, E.; Keshavarzi, A.; Gimenez Morera, A.; Pulido Fernandez, M.; Cerda, A. Analyzing Long-Term Soil Erosion in a Ridge-Shaped Persimmon Plantation in Eastern Spain by Means of ISUM Measurements. Catena 2019, 183, 104176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Degroote, J.; Wolter, C.; Sugumaran, R. Integration of Modified Universal Soil Loss Equation (Musle) into a Gis Framework to Assess Soil Erosion Risk. Land Degrad. Dev. 2009, 20, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.-G.; He, D.; Hu, J.-M.; Cao, J. Variability of Extreme Precipitation over Yunnan Province, China 1960–2012. Int. J. Climatol. 2015, 35, 245–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiong, W.; Mingjun, Z.; Shengjie, W.; Qian, M.; Meiping, S. Changes in Temperature Extremes in the Yangtze River Basin, 1962–2011. J. Geogr. Sci. 2014, 24, 59–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Mu, X.; Song, X.; Wu, D.; Cheng, A.; Qiu, B. Changes in Extreme Temperature and Precipitation Events in the Loess Plateau (China) during 1960–2013 under Global Warming. Atmospheric Res. 2016, 168, 33–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.; Wang, W.; Song, S.; Ma, J. Spatial and Temporal Variations of Precipitation Extremes and Seasonality over China from 1961–2013. Water 2018, 10, 719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- You, Q.; Kang, S.; Aguilar, E.; Pepin, N.; Fluegel, W.-A.; Yan, Y.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, J. Changes in Daily Climate Extremes in China and Their Connection to the Large Scale Atmospheric Circulation during 1961–2003. Clim. Dyn. 2011, 36, 2399–2417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xukai, Z.; Fumin, R. Changes in Regional Heavy Rainfall Events in China during 1961–2012. Adv. Atmospheric Sci. 2015, 32, 704–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Wei, W.; Fu, B.; Lu, Y. Soil and Water Conservation on the Loess Plateau in China: Review and Perspective. Prog. Phys. Geogr.-Earth Environ. 2007, 31, 389–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, T.; Li, J.; Yang, J.; Luo, M. Have Anthropogenic Factors Mitigated or Intensified Soil Erosion over the Past Three Decades in South China? J. Environ. Manage. 2022, 302, 114093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Liu, H. Soil Erosion Changes during the Last 30 Years and Contributions of Gully Erosion to Sediment Yield in a Small Catchment, Southern China. Geomorphology 2020, 368, 107357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Huang, M.; Barbour, S.L. Storm-Based CSLE That Incorporates the Estimated Runoff for Soil Loss Prediction on the Chinese Loess Plateau. Soil Tillage Res. 2018, 180, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Liu, X.; Ma, X. Application of a Modified Distributed-Dynamic Erosion and Sediment Yield Model in a Typical Watershed of a Hilly and Gully Region, Chinese Loess Plateau. Solid Earth 2016, 7, 1577–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yin, S.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, L.; Liu, B.; Xie, Y.; Wang, G.; Li, Y. Regional Soil Erosion Assessment Based on a Sample Survey and Geostatistics. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2018, 22, 1695–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wischmeier, W.H.; Smith, D.D. Predicting Rainfall Erosion Losses—A Guide to Conservation Planning; Agriculture Handbook No. 537; Department of Agriculture, Science and Education Administration: Washington, DC, USA, 1978; pp. 285–291. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; McDermid, G.J.; Castilla, G.; Linke, J. Measuring Vegetation Height in Linear Disturbances in the Boreal Forest with UAV Photogrammetry. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moe, K.T.; Owari, T.; Furuya, N.; Hiroshima, T. Comparing Individual Tree Height Information Derived from Field Surveys, LiDAR and UAV-DAP for High-Value Timber Species in Northern Japan. Forests 2020, 11, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roeder, M.; Latifi, H.; Hill, S.; Wild, J.; Svoboda, M.; Bruna, J.; Macek, M.; Novakova, M.H.; Guelch, E.; Heurich, M. Application of Optical Unmanned Aerial Vehicle-Based Imagery for the Inventory of Natural Regeneration and Standing Deadwood in Post-Disturbed Spruce Forests. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2018, 39, 5288–5309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebastian, D.O.; Irene, M.; Klaus, P.; Johannes, R. Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) for Monitoring Soil Erosion in Morocco. Remote Sens. 2012, 4, 3390–3416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yuan, M.; Yang, M.; Deng, J. Estimation of Initiation Thresholds and Soil Loss from Gully Erosion on Unpaved Roads on China’s Loess Plateau. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2021, 46, 1713–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santo, A.; Santangelo, N.; Forte, G.; De Falco, M. Post Flash Flood Survey: The 14th and 15th October 2015 Event in the Paupisi-Solopaca Area (Southern Italy). J. Maps 2017, 13, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


| The Primary Classification | The Secondary Classification | The Three-Level Classification | Factor Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Engineering Measures | Terrace | Earth Ridge Terrace | 0.084 |
| Stone Ridge Terrace | 0.121 | ||
| Slope Terrace | 0.414 | ||
| Broad-Base Terrace | 0.414 | ||
| Rverse Slope Terrace | 0.151 | ||
| Parallel Ditch | 0.335 | ||
| Fish Scale Pits | 0.249 | ||
| Tillage Measures | Contour Tillage | 0.431 | |
| Ridge Tillage and Pitting Field | 0.152 | ||
| Contour Furrow | 0.425 | ||
| Lea Farming | 0.225 | ||
| Intercropping | 0.225 | ||
| Green Manure | 0.225 | ||
| Minimum Tillage | 0.212 | ||
| No-Tillage | 0.136 | ||
| Crop Rotation | 0.392 |
| Watershed Name | Proportion of Soil Erosion Intensity in Each Area | Average Soil Loss Modulus (t/km2) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0–200 | 200–1000 | 1000–2500 | 2500–5000 | 5000–8000 | 8000–15,000 | >15,000 | ||
| XQ Watershed | 8.74 | 40.53 | 24.31 | 20.41 | 4.58 | 1.43 | 0.00 | 1778.2 |
| LY Watershed | 20.90 | 41.07 | 23.52 | 12.90 | 1.44 | 0.09 | 0.07 | 1175.4 |
| Number | Width (m) | Height (m) | The Slope of Terrace (°) | Land Utilization | The Type of Terrace | The Length of Damaged (m) | The Length of the Terrace (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T0101 | 7.5 | 1.2 | 3.2 | Grassland | Horizontal Terraces | 4.9 | 64.3 |
| T0102 | 6.9 | 2.7 | 2.1 | Grassland | Horizontal Terraces | 5.7 | 70.5 |
| T0103 | 5.1 | 1.68 | 1.9 | Grassland | Horizontal Terraces | 4 | 75.5 |
| T0104 | 6.6 | 2.7 | 2.3 | Grassland | Horizontal Terraces | 6.6 | 70.2 |
| T0105 | 16 | 2.65 | 2.4 | Farmland | Horizontal Terraces | 6.1 | 80.1 |
| T0106 | 12 | 2.4 | 2.7 | Farmland and Grassland | Horizontal Terraces | 2.7 | 107.9 |
| T0107 | 5.6 | 1.58 | 1.9 | Farmland | Horizontal Terraces | 0 | 50.1 |
| T0108 | 6.1 | 1.2 | 3.0 | Farmland | Horizontal Terraces | 4.1 | 70 |
| T0109 | 12.1 | 1.85 | 2.0 | Farmland | Horizontal Terraces | 6.9 | 106.6 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jia, H.; Wang, X.; Sun, W.; Mu, X.; Gao, P.; Zhao, G.; Li, Z. Estimation of Soil Erosion and Evaluation of Soil and Water Conservation Benefit in Terraces under Extreme Precipitation. Water 2022, 14, 1675. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14111675
Jia H, Wang X, Sun W, Mu X, Gao P, Zhao G, Li Z. Estimation of Soil Erosion and Evaluation of Soil and Water Conservation Benefit in Terraces under Extreme Precipitation. Water. 2022; 14(11):1675. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14111675
Chicago/Turabian StyleJia, Hao, Xidong Wang, Wenyi Sun, Xingmin Mu, Peng Gao, Guangju Zhao, and Zixuan Li. 2022. "Estimation of Soil Erosion and Evaluation of Soil and Water Conservation Benefit in Terraces under Extreme Precipitation" Water 14, no. 11: 1675. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14111675
APA StyleJia, H., Wang, X., Sun, W., Mu, X., Gao, P., Zhao, G., & Li, Z. (2022). Estimation of Soil Erosion and Evaluation of Soil and Water Conservation Benefit in Terraces under Extreme Precipitation. Water, 14(11), 1675. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14111675








