Abstract
Nowadays, plant invasion has become a global ecological threat to local biodiversity and ecosystem stability. Spartina alterniflora encroaches on the ecological niches of local species and changes the soil’s nutrient cycle. However, few comprehensive assessments focus on the effects of S. alterniflora invasion. Here, we investigated how soil sulfur changed with spatiotemporal variation and life forms of native species after S. alterniflora invasion and speculated the possible mechanism of the sulfur increase based on the references. The invasion of S. alterniflora increased soil total sulfur by 57.29% and phytotoxic sulfide by 193.29%. In general, the invasion of S. alterniflora enhanced the total plant biomass and soil nutrients, e.g., soil organic carbon, total nitrogen, and soil microbial biomass carbon, further increasing soil sulfur content. The sulfur accumulation caused by S. alterniflora might result in the poisoning of native species. Thus, we hypothesized that the success of S. alterniflora invasion was closely connected with soil sulfur, especially toxic sulfide. Our study suggests that researchers should give more attention to the correlation between S. alterniflora invasion and the soil sulfur increase. More research is needed to investigate the mechanisms of the successful invasion by accumulating phytotoxic sulfide.
1. Introduction
Coastal wetlands are of great importance to ecosystem biodiversity, stability, and sustainability, playing a vital role in global carbon sequestration [1], wetland hydrology [2], and biodiversity protection [3]. Ecological communities are complex, with dynamic interactions among organisms [4]. Alien plant invasion is a major threat to coastal ecosystems, which may cause biodiversity loss, affecting marine ecosystem services across temporal and spatial scales [5].
Originally, Spartina alterniflora lived in the Atlantic Coast area of North America, providing food sources and nursery areas for animals [6]. For erosion control, soil amelioration, and dike protection, S. alterniflora has been widely introduced in northern and coastal Europe, Africa, Australia, New Zealand, and China. S. alterniflora was first introduced to China in 1979, behaving well in soil stabilization, heavy metal removal, and carbon dioxide sequestration with high primary productivity [7]. However, its significant negative impacts on coastal native species and ecosystems gradually emerged, and its distribution area continued to expand [8]. The invasion of S. alterniflora reduces local biodiversity and affects large-scale ecosystems such as animal migration due to the change of habitats of migratory birds and further shapes insular mutualistic networks [9]. There was an explosive growth of S. alterniflora in China with the area increasing by 50,204 ha between 1990 and 2015 [10]. To date, the distribution of S. alterniflora in China is concentrated in the eastern coastal area, covering the temperate monsoon climate and subtropical monsoon climate from the Leizhou Peninsula in the south to the Duliujian River in the north with the latitudinal range of 20° N–39° N. Zhanjiang, Zhangjiang, Minjiang, Yangtze River, and Yellow River basin are all contained [11].
Sulfur is a necessary macronutrient for the synthesis of many metabolites, participating in essential biochemical reactions of plants and responding to environmental changes [12]. In the soil of coastal wetlands, sulfur mainly comes from seawater. It can be divided into inorganic sulfur and organic sulfur [13], and the proportions are closely related to soil type, pH, drainage status, organic matter content, mineral composition, and depth [14]. The sulfur cycle in the soil of coastal wetlands is complex since tidal flooding periodically changes the soil redox conditions, thus changing the proportions of sulfate and sulfide by affecting the redox process in the sulfur cycle [15]. Sulfates can be absorbed by roots and transported through membranes by proton–sulfate cotransporters [16], while the reductive sulfide usually causes ecological toxicity in the ecosystem, including plants, animals, and microorganisms [17]. Reduced sulfur compound is a potent phytotoxin that inhibits the activity of cytochrome c oxidase in mitochondria, thereby inhibiting energy production [18]. The biological toxicity of sulfide depends on the ability of the species to metabolize sulfide into mercaptan [19]. Strong evidence was reported in the defining effect of sulfide on species distribution in salt marshes [20]. However, S. alterniflora with high sulfide tolerance was reported to survive in high sulfide concentrations up to 8 mM, which was much higher than other species in salt marshes [19], resulting from the ability to absorb sulfide and divert energy from metabolism to oxidize sulfide [21].
S. alterniflora was reported to increase the soil sulfur content after the invasion in previous studies [22,23,24]. The reduction of sulfate in the flooded and anaerobic environment will lead to a large amount of toxic sulfide accumulation [25], which may have adverse effects on organisms with weak sulfur tolerance in the ecosystem. Meanwhile, the invasion of S. alterniflora changed the abundance, composition, and structure of the soil microbial community [26], especially sulfur-reducing bacteria (SRB) and sulfur-oxidizing bacteria (SOB) [27]. SRB use sulfate as an electron acceptor for organic matter to reduce sulfate to sulfide [28]. The reduction of organic matter by SRB is considered the most important degradation pathway in the soil of the intertidal zone [29,30]. It was reported that S. alterniflora might have unique detoxification mechanisms, oxidizing sulfide through aerenchyma to reduce the sulfide content around the rhizosphere in flooded soil [31]. In addition, there is a feedback mechanism between plants and soil. Therefore, more biogenic elements, especially sulfur, can be circulated in the soil–plant system after S. alterniflora invades with high primary productivity [32].
Most previous studies found that S. alterniflora invasion in communities with Phragmites australis, Suaeda salsa, Scirpus mariqueter, and Cyperus malaccensis mainly increased soil sulfur content [22,23,24,33]. However, according to the published data, we found that there was also a decrease in soil sulfur content in mangroves and other communities after S. alterniflora invasion [34,35,36]. S. alterniflora invasion in mangroves can affect the soil biochemical process by reducing carbon and nitrogen storage and heterogeneity of biogenic elements [37]. The effects of S. alterniflora invasion on soil sulfur content and distribution vary in regions with different environmental conditions. However, there is no comprehensive analysis to discuss and summarize the effects of S. alterniflora invasion on soil sulfur content and distribution with spatiotemporal variation and life forms of native species.
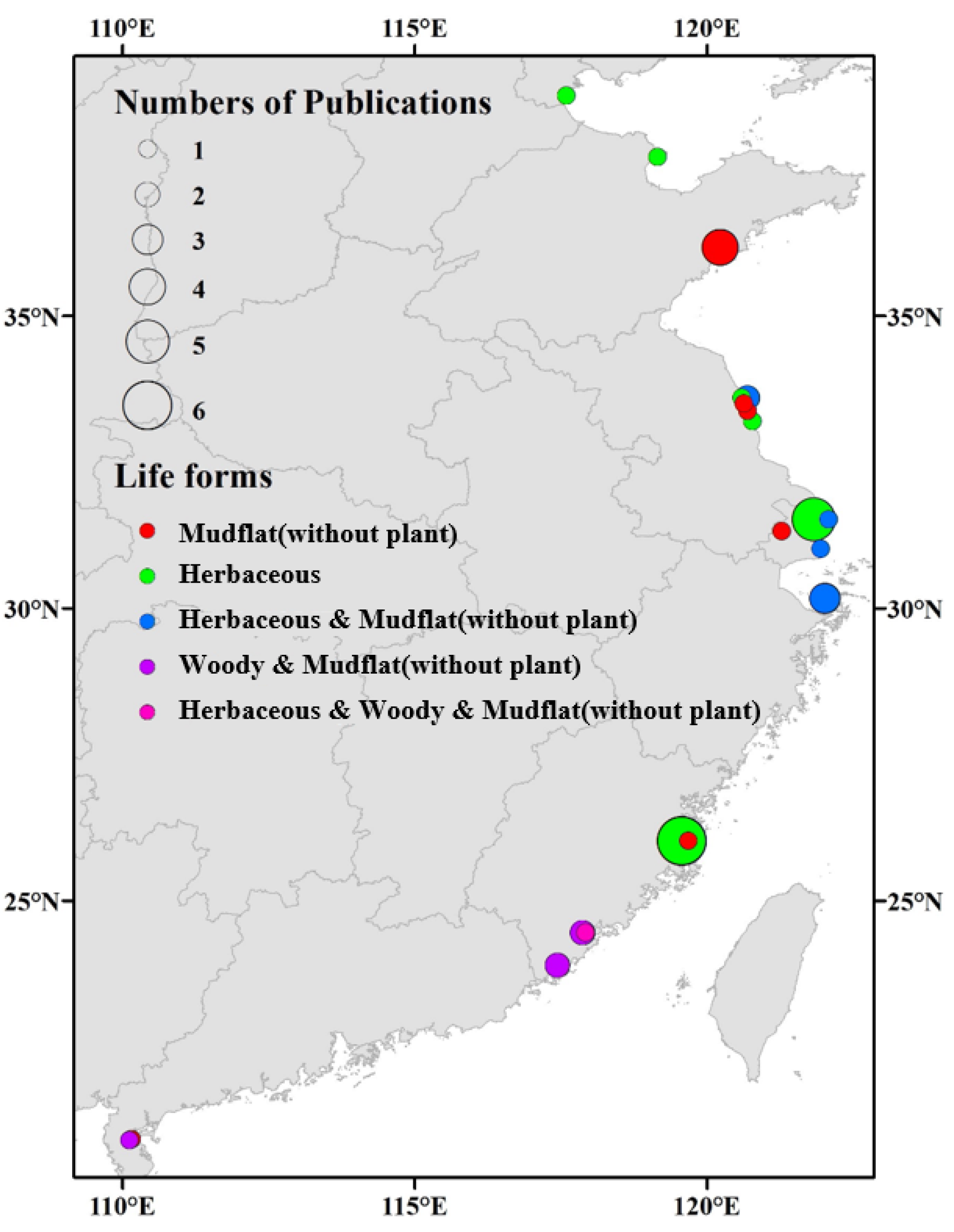
We undertook a synthesis to assess the effects of S. alterniflora invasion on soil sulfur using meta-analysis. Our analysis covered 38 studies of S. alterniflora invasion located along the eastern coast of China with a latitudinal range of 20.9° N–39.7° N and a longitudinal range of 110.1° E–112.1° E and included 2501 data items (Figure 1). The native plants in the invaded areas are mainly S. mariqueter, P. australis, S. salsa, C. compressus, Aegiceras corniculatum, Avicennia marina, Kandelia obovate, and Kandelia candel. Specifically, we measured the effect size of S. alterniflora invasion on soil total sulfur, sulfate (SO42−), and sulfide (S2−). We conducted subgroup analyses with the data obtained according to the seasons, invasion stages, soil depths, and life forms of native species using meta-analysis. We attempted to answer two questions: (a) What are the effects of S. alterniflora invasion on soil sulfur content and distribution? (b) What are the changes in soil nutrients and physicochemical properties caused by S. alterniflora invasion, and how do they impact soil sulfur? The results of our previous studies and many other studies showed that the increase in biomass brought by S. alterniflora was accompanied by an increase in soil sulfur content [23,24,38], because sulfur could accumulate and be stored in tissues of S. alterniflora [39]. Therefore, we hypothesized that (a) the introduction of S. alterniflora increased soil total sulfur, SO42-, and S2- contents; (b) soil nutrients and physicochemical properties were influenced by S. alterniflora invasion and further increased soil sulfur content through indirect approaches. Our analysis provides the first comprehensive assessment of the effects on soil sulfur content after S. alterniflora invasion, and a new perspective on the mechanisms of global plant invasion related to soil sulfur is proposed.
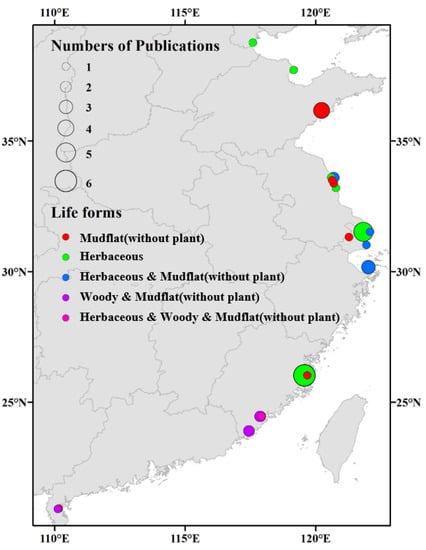
Figure 1.
A distribution map of S. alterniflora invasion sites with soil sulfur data. The different colors of circles indicate various life forms of native species, and the sizes of circles represent the number of studies.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Literature Research and Data Collection
To identify quantitative evidence of the impacts of S. alterniflora invasion on soil sulfur content and distribution, we conducted a systematic search of the scientific literature. On 2 March 2020, we searched for articles reporting soil sulfur content before and after S. alterniflora invasion using the Web of Science and the China National Knowledge Internet (CNKI), with a restriction on the year of publication from 1979 to 2020. The following search combination was used: (Spartina alterniflora OR Spartina-alterniflora OR Smooth Cordgrass OR Smooth-Cordgrass OR Sporobolus alterniflorus) AND (invasi* OR invad* OR exotic OR alien OR encroach OR introduced OR allochthonous OR non-indigenous OR nonindigenous OR non-native) AND (sulfur OR sulfate OR sulfide OR sulphide OR sulphate OR sulphur OR S), and the keyword combination in the Chinese literature search was the same.
Through literature retrieval, we obtained 830 references from the Web of Science and 180 references from CNKI. Then, we screened the reference lists of all obtained articles to further select publications related to our research topic. The references obtained from the literature search were evaluated according to the following steps by scanning the titles and abstracts of articles to exclude articles that were completely unrelated to our topic. Then, we searched for data from the publications we found by reading the full texts and Supplementary Materials. The inclusion and exclusion criteria were as follows: (1) at least one kind of soil sulfur content, such as total sulfur, SO42−, and S2− was reported; (2) the research contained duplications with data of both native communities and invasive S. alterniflora communities; (3) the means and standard deviations of the data were reported; and (4) studies with other artificial interventions or without replication were excluded (Figure S1). Although the keywords in the literature search did not impose geographical restrictions, the study sites of the publications that met the requirements after screening were all in China, which might lead to unavoidable geographical limitations of our study.
For each study, we extracted the basic characteristics of each study, including publication year, journal, location, temperature, precipitation, type of invasive species, the biomass of invasive plants and native plants, and soil properties (Table S1). The study sites were marked on a map and were mostly located on the eastern coast of China (Figure 1). Following the above criteria, 1339 observations of sulfur-related variables were extracted from 38 publications. The variables we chose were related to plant biomass and soil physicochemical properties, including aboveground and underground biomass, soil pH, electrical conductivity, bulk density, salinity, water content, total carbon, soil organic carbon, soil microbial biomass carbon, organic matter, total nitrogen, ammonium (NH4+), nitrate (NO3−), carbon–nitrogen ratio (C/N), total phosphorus, total sulfur, available sulfur, SO42−, S2−, H2O-S, adsorbed-S, HCl-soluble-S, and HCl-volatile-S. For each variable included, means, standard deviations/standard errors/confidence intervals, and sample sizes (n) were extracted from native communities and the communities invaded by S. alterniflora. If the sample size was lacking, it was defined as 3. Each observation was regrouped for subgroup meta-analysis according to the differences in season species, invasion stages, soil depths, and life forms of the native species. The invasion stages were divided into an earlier stage (invaded for 0–5 years) and a later stage (invaded for more than 5 years). The soil depths were divided into three groups: 0–20 cm, 20–50 cm, and 50–100 cm. The life forms of native species were grouped into herbaceous and woody communities, and mudflats without vegetation served as a control. Part of the data was directly obtained from the article. When the data were presented in a bar chart or line chart, GetData Graph Digitizer (http://www.getda ta-graph-digitizer.com/ (accessed on 2 March 2020)) was used to extract the data in the graphic.
2.2. Statistical Analysis
The method of Hedges was followed to conduct the meta-analysis [40]. Hedges’ g was used to measure the unbiased, standardized mean difference between the experimental group (S. alterniflora invasion) and the control group (the native communities). The invasion of S. alterniflora was considered the only treatment in the two groups. Hedges’ g was estimated as
We chose random-effect models to analyze our data, as the data we collected were from field sampling, which might be largely heterogeneous [41]. A negative effect size indicates a negative effect on the native community after S. alterniflora invasion, while a positive effect size indicates a positive impact. Hedges’ g and a 95% confidence interval (CI) were used to present the effect of each factor.
Funnel plots were used to assess the publication bias of effect size standard errors against residuals [42]. The appearance of asymmetry reflects large residuals and high variances. When the funnel plot was asymmetric, we removed the data with large residual values and high variances to adjust for potential publication bias [43,44]. If there was no change in the outcomes of the analysis after adjustment, our results were not severely influenced by potential publication bias. If the direction of effects was changed, publication bias might severely affect the results. I2 was used to represent the heterogeneity of each factor. Stata 12.0 was used to conduct the above analysis. (eRR++ − 1) × 100% was calculated with R software to indicate the percentage change [45]. In addition, to identify the effects of S. alterniflora invasion on soil total sulfur, SO42−, and S2−, scatter diagrams and box charts were created for more intuitive analysis. All figures were created using Origin 9.0 software.
3. Results
3.1. Effects of S. alterniflora Invasion on Soil Sulfur
Although there were asymmetries in some funnel plots (Figures S2–S7), the direction of the response did not change after removing the data with large residuals, so we considered that there was no significant effect on our study caused by publication bias [44].
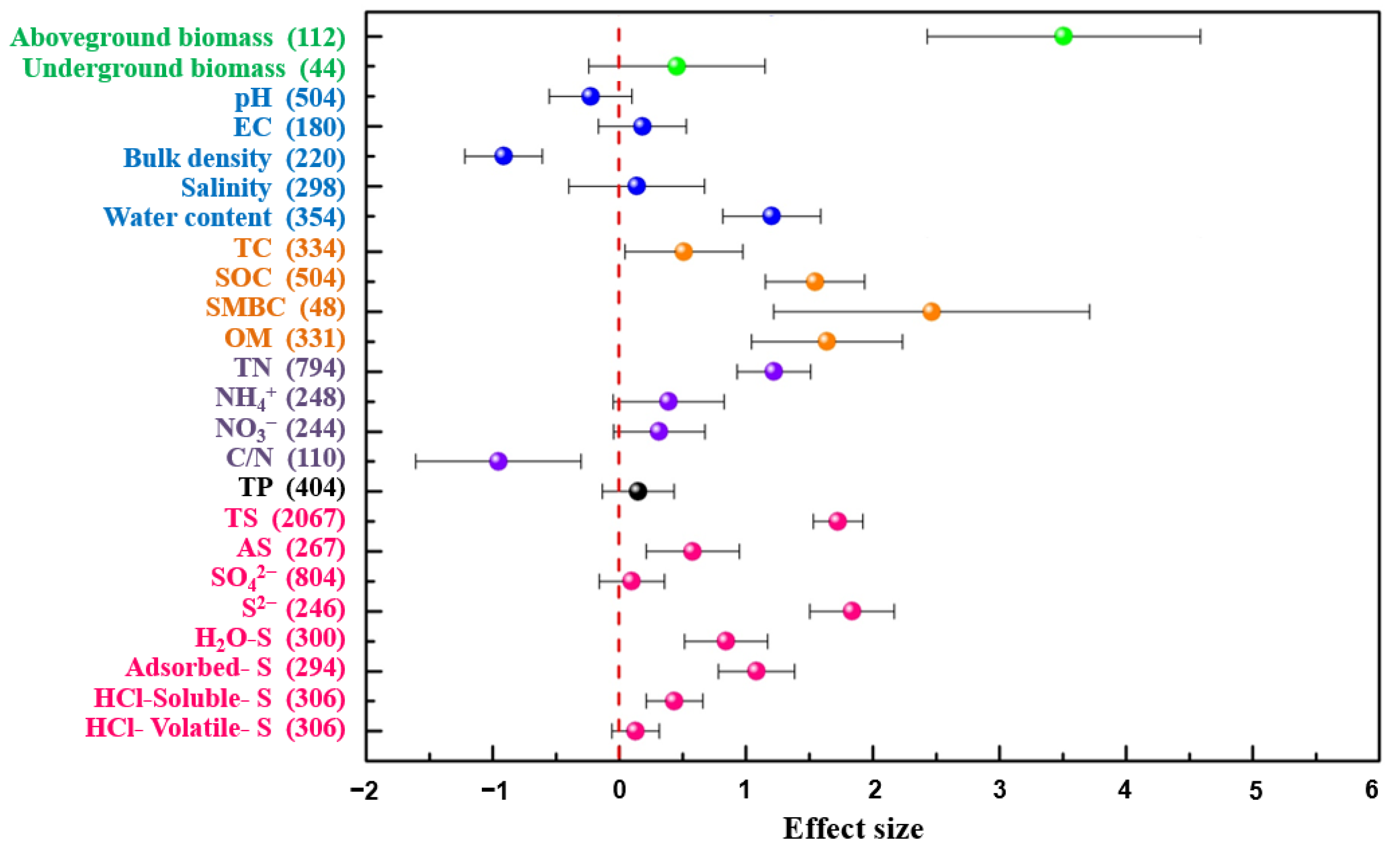
Significant increases in soil total sulfur (standard mean difference: 1.72, CI: 1.53/1.92), available sulfur (SMD: 0.58, CI: 0.21/0.95), and S2− (SMD: 1.84, CI: 1.50/2.17) were found according to the results of the meta-analysis (Figure 2). H2O-S (SMD: 0.84, CI: 0.51/1.17), adsorbed-S (SMD: 1.08, CI: 0.78/1.39), HCl-soluble-S (SMD: 0.44, CI: 0.21/0.66), and HCl-volatile-S (SMD: 0.13, CI: −0.06/0.31) are four different inorganic sulfur forms, and the effect sizes showed positive effects (Figure 2).
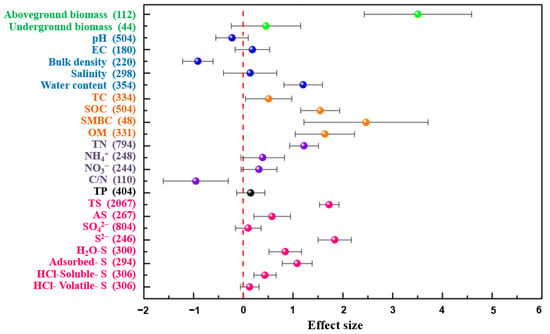
Figure 2.
Effects of S. alterniflora invasion on soil properties. The x-axis is the SMD of each variable in invaded vs. native areas. The vertical line was drawn at SMD = 0. The numbers of observations are shown in parentheses. EC, electrical conductivity; TC, total carbon; SOC, soil organic carbon; SMBC, soil microbial biomass carbon; OM, organic matter; TN, total nitrogen; TP, total phosphorus; TS, total sulfur; AS, available sulfur.
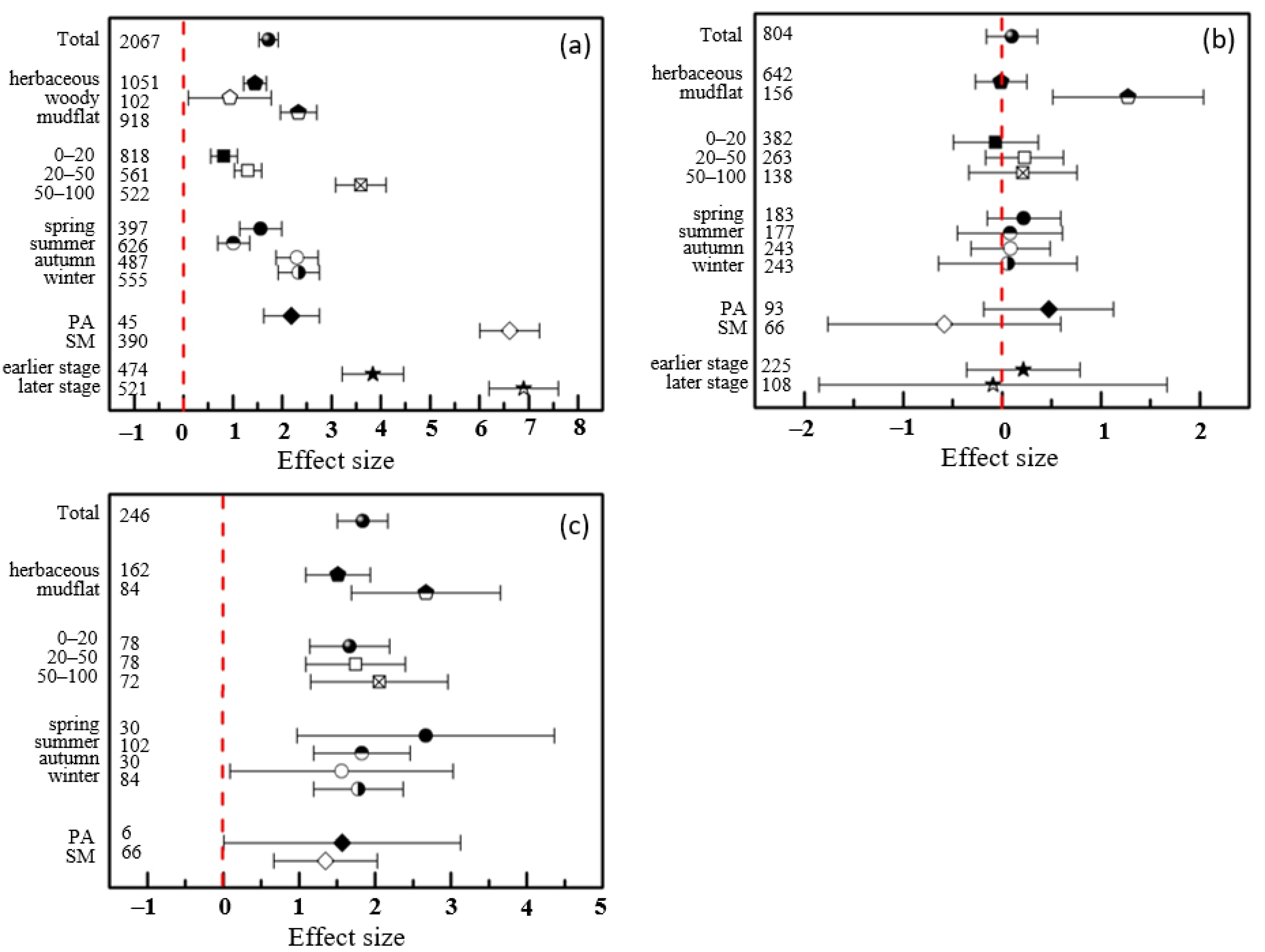
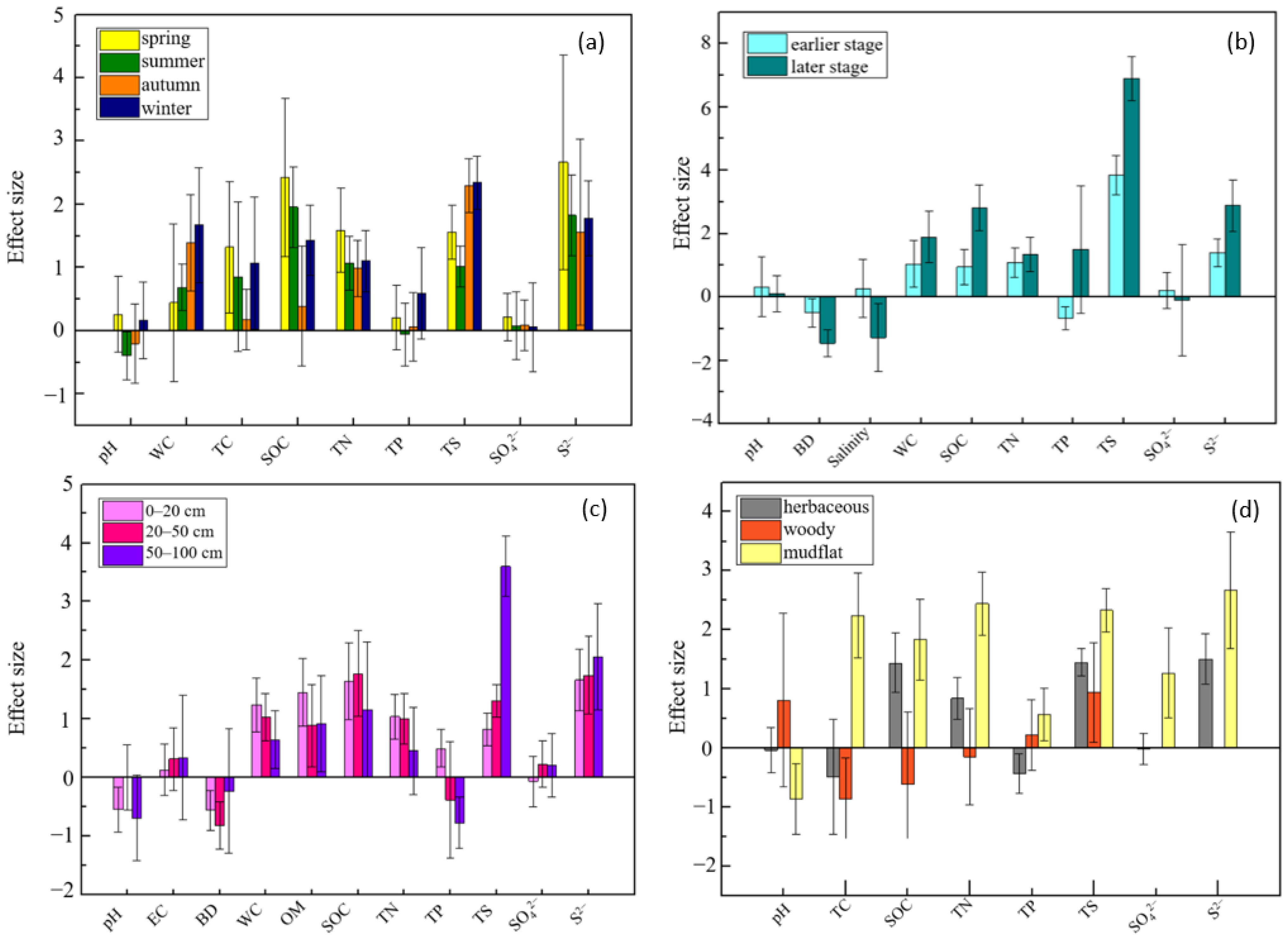
According to the results of subgroup analysis, the effects of S. alterniflora invasion on soil total sulfur, sulfate, and sulfide all showed increasing trends with increasing depths, especially total sulfur, with effect sizes of 0.82 at 0–20 cm, 1.31 at 20–50 cm, and 3.60 at 50–100 cm (Figure 3a). Considering the lack of data on soil sulfate and sulfide in woody communities invaded by S. alterniflora, these indicators were compared only in herbaceous communities and mudflats. A lower effect of S. alterniflora invasion on soil total sulfur was found in the woody communities with an SMD of 0.94, and it was higher in the herbaceous communities and mudflats with SMDs of 1.45 and 2.33 (Figure 3a). Except for the slightly negative effect on soil sulfate in the invasion of S. alterniflora in herbaceous communities (SMD: −0.01), the concentrations of soil sulfide and sulfate in the herbaceous communities and sulfate in mudflats increased after S. alterniflora invasion (Figure 3b,c). In the subgroup analysis by season, we found no conspicuous or regular change in soil sulfur (Figure 3a).
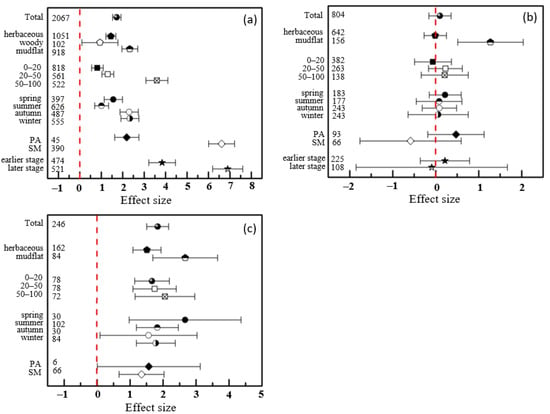
Figure 3.
Effects of impacts of S. alterniflora invasion on soil total sulfur (a), sulfate (b), and sulfide (c) contents. The vertical line was drawn at SMD = 0.
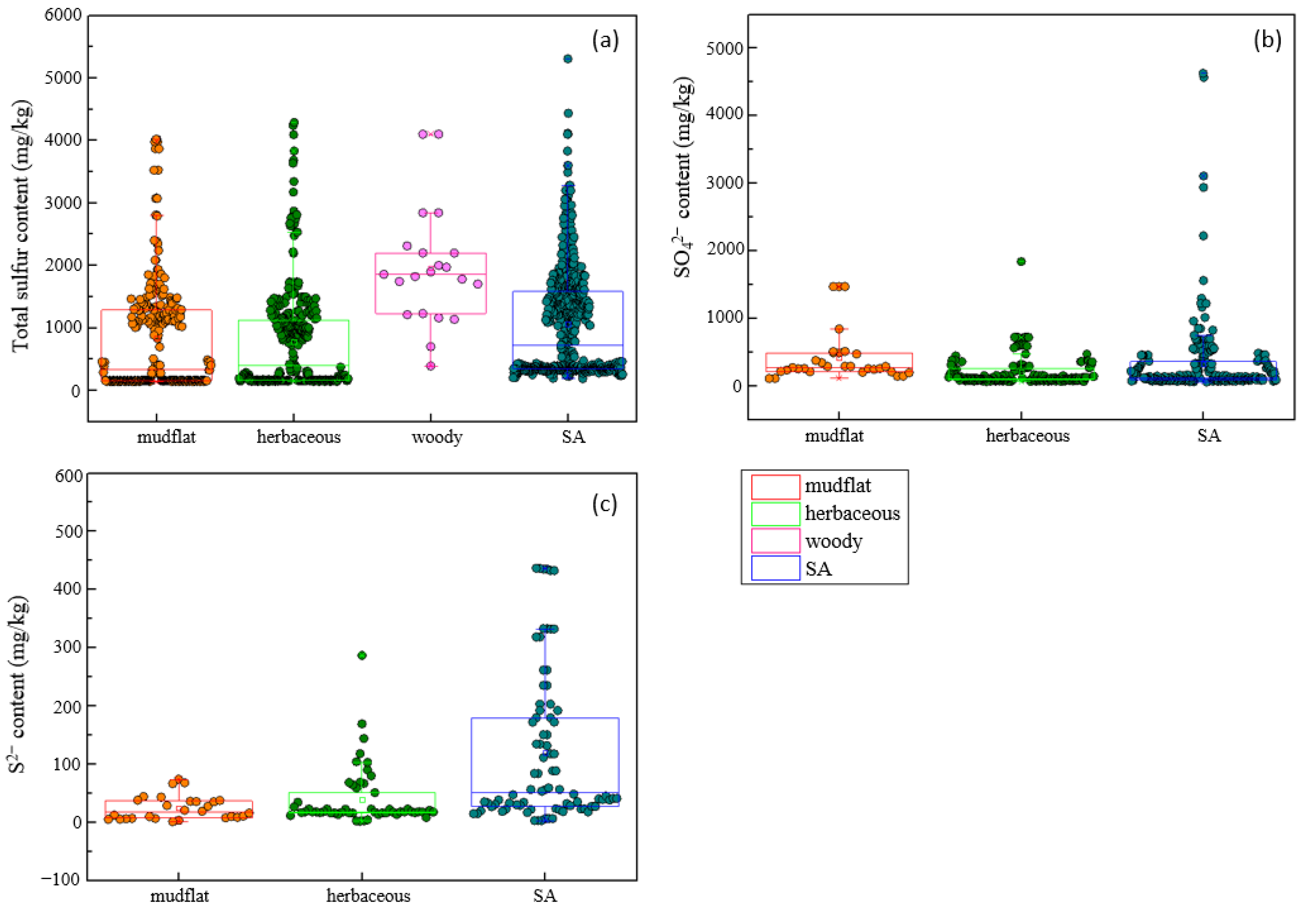
Compared with soil total sulfur content, sulfate and sulfide content responded differently in four seasons to the invasion of S. alterniflora (Figure 3). It is worth mentioning that the effects on soil total sulfur after S. alterniflora invasion in autumn (SMD: 2.30) and winter (SMD: 2.34) were more significant than those in spring (SMD: 1.56) and summer (SMD: 1.02) (Figure 3a), while the effect sizes of sulfate and sulfide in spring were greater than those in the other three seasons (Figure 3b,c). To observe the changes more intuitively and visually in soil sulfur content after S. alterniflora invasion, three scatter diagrams and box charts are shown in Figure 4. The content of soil total sulfur with S. alterniflora was generally higher than that in mudflats and herbaceous communities except in woody communities (Figure 4a). We chose not to show scatter plots or box charts of the soil sulfide and sulfate contents in the woody communities due to a lack of data in mangrove communities in previous literature.
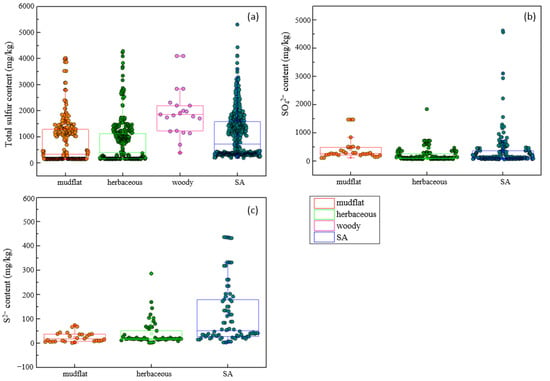
Figure 4.
Soil total sulfur contents (a), sulfate contents (b), and sulfide contents (c) in invasive S. alterniflora communities, and three different life forms of native communities.
3.2. Effects of S. alterniflora Invasion on Soil Physicochemical Properties
The analysis revealed that after S. alterniflora invasion, plant biomass and 22 soil properties, including physical and chemical properties and nutrients, changed significantly compared with the native areas (Figure 2). The invasion of S. alterniflora had a positive direct effect on plant biomass, the effect size of aboveground biomass was 3.51, and the effect size of underground biomass was 0.453 (Figure 2). Similarly, other soil biogenic elements, including soil total carbon (SMD: 0.51, CI: 0.05/0.98), organic carbon (SMD: 1.54, CI: 1.15/1.94), microbial biomass carbon (SMD: 2.47, CI: 1.22/3.71), organic matter (SMD: 1.64, CI: 1.04/2.23), total nitrogen (SMD: 1.22, CI: 0.93/1.51), and total phosphorus (SMD: 0.15, CI: −0.13/0.43), all showed different degrees of positive effects after S. alterniflora invasion (Figure 2). The effect size of NH4+ (SMD: 0.39, CI: −0.05/0.83) and NO3- (SMD: 0.31, CI: −0.05/0.68) were both positive, and the effect size of C/N was −0.96 with a CI from −0.30 to −0.61.
Unlike positive effects on C, N, P, and S, different directions of effects appeared in soil physical properties. Negative effects were found in soil pH (SMD: −0.23, CI: −0.56/0.10) and bulk density (SMD: −0.915, CI: −1.222/−0.608), while positive effects appeared for electrical conductivity (SMD: 0.18, CI: −0.17/0.53), salinity (SMD: 0.14, CI: −0.40/0.67), and water content (SMD: 1.20, CI: 0.82/1.59) (Figure 2).
3.3. Effects Differed in Various Spatiotemporal Conditions and Life Forms of Native Species
The results of the subgroup analysis of soil properties showed that the range of changes after S. alterniflora invasion also varied among seasons, invasion stages, soil depths, and life forms of native species (Figure 5). In the four seasons, soil organic carbon and total nitrogen increased, and the highest effect size appeared in spring, while the lowest was in autumn (Figure 5a). In all subgroups of soil depths, the invasion of S. alterniflora enhanced soil organic carbon and total nitrogen contents more in 0–50 cm soil layer than in the 50–100 cm layer (Figure 5c). After S. alterniflora invasion, soil organic carbon and total nitrogen increased in the herbaceous communities and mudflats but decreased in the woody communities (Figure 5d). The contents of soil total phosphorus in the herbaceous communities decreased after S. alterniflora invasion (SMD: −0.43), but that in the woody communities increased (SMD: 0.22) compared with an SMD of 0.57 in mudflat (Figure 5d). In addition, soil total phosphorus contents in the earlier stage of S. alterniflora invasion decreased (SMD: −0.66), while it increased in the later stage (SMD: 1.50) (Figure 5b).
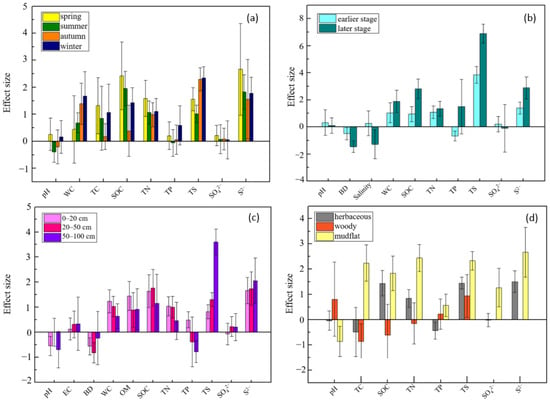
Figure 5.
Effects of S. alterniflora invasion on soil properties in different subgroups. The y-axis is the SMD of soil properties in invaded vs. native areas, grouped by (a) seasons, (b) invading stages, (c) depths, and (d) life forms of native species. The parallel line was at SMD = 0. EC, electrical conductivity; TC, total carbon; SOC, soil organic carbon; OM, organic matter; TN, total nitrogen; TP, total phosphorus; TS, total sulfur.
The effects of S. alterniflora invasion on soil pH differed among seasons, with negative effects in summer and autumn and positive effects in spring and winter (Figure 5a). The soil pH in the invaded woody communities displayed significant positive effects with an SMD of 0.81. In contrast, the effect sizes of soil pH in herbaceous communities and mudflats were all negative, with SMDs of −0.03 and −0.86, respectively (Figure 5d). S. alterniflora invasion had a more significant impact on soil pH in the earlier invasion stage than in the later stage (Figure 5b), and the effect size of soil pH increased with depth (Figure 5c). The effect size of water content increased in the seasons according to the ranked order of spring (SMD: 0.44), summer (SMD: 0.69), autumn (SMD: 1.39), and winter (SMD: 1.67) (Figure 5a), which was also more obvious in the surface layer than in the deeper layers (Figure 5c). In the process of S. alterniflora invasion, soil water content increased more during the later invasion stage (SMD: 1.90) than during the earlier stage (SMD: 1.04). Soil bulk density decreased more during the later invasion stage (SMD: −1.46) than during the earlier stage (SMD: −0.50) (Figure 5b). After S. alterniflora invasion, soil bulk density decreased in all depths suffering a more significant impact in the 0–20 cm (SMD: −0.56) and 20–50 cm (SMD: −0.82) layers than in the 50–100 cm (SMD: −0.23) layer (Figure 5c). Soil salinity increased slightly in the earlier invasion stage (SMD: 0.27) while decreased in the later stage (SMD: −1.28) (Figure 5b).
4. Discussion
4.1. S. alterniflora Invasion Increased Soil Sulfur Contents
The results confirmed our first hypothesis that S. alterniflora invasion tended to increase soil sulfur content caused by the addition of sulfur sources from primary production [24]. The increase in sulfur content could promote the growth of S. alterniflora in return and enhance its tolerance to metal, and the increase in sulfide could threaten the growth of native species (Figure 2), further promoting S. alterniflora expansion. It was reported that sulfide could limit root hair development and nutrient uptake, inhibit respiratory metallo-enzyme activities, and reduce polyphenol oxidase and external phosphatase activity in different species [46]. However, the high tolerance to the phytotoxic sulfide of S. alterniflora was verified [19].
The effects of S. alterniflora invasion on soil sulfur content also varied across seasons (Figure 5a) with different temperature, tide, and precipitation, affecting plant growth status, microbial activity, and soil properties [47,48]. S. alterniflora can uptake sulfate dissolved in pore water directly to grow new tissue, decreasing the response of soil sulfur significantly in summer compared with that in spring (Figure 5a). Plants grow most vigorously in spring, absorbing abundant nutrients from the soil, while the roots need to accumulate large amounts of sulfur for winter consumption [49]. Therefore, decomposition of a large amount of litter entering the soil leads to a significant increase in soil total sulfur content in autumn and winter (Figure 5a) [50]. In addition, the abundance and activities of soil microorganisms vary in different climatic conditions, affecting the sulfur cycle mediated by microbial communities after S. alterniflora invasion [51]. Sulfate is mainly believed to mainly come from seawater because sulfate is the second most abundant ion in seawater [19]. The irregular and inconspicuous response of soil sulfate after S. alterniflora invasion was in agreement with previous studies [52], which can be explained by the material exchange through frequent tidal flooding (Figure 3b). S. alterniflora was reported to release oxygen through aerenchyma to oxidize toxic sulfide to sulfate in the rhizosphere [53]. Therefore, the seasonal variation in soil sulfide is similar to sulfate (Figure 5a), since they are interchangeable [19].
The more significant response of soil total sulfur and sulfide contents in the later stage of invasion (longer than 6 years) (Figure 5b) was consistent with the sulfur enrichment effect and accumulation with the increase in invasion time proposed by Wang et al. (2019b) [24]. The return of plant sulfur to the soil through the litter pathway leads to the accumulation of soil sulfur, so S. alterniflora behaves as a sulfur pump to constantly import sulfur to the soil [50].
The effect sizes of S. alterniflora on soil total sulfur, sulfate, and sulfide contents increasing with soil depths (Figure 5c) were closely associated with the length of roots, the transport capacity of soil, and the microbial activities in different layers [33]. The roots of S. alterniflora were mainly distributed in the soil of 0–25 cm, while the roots of mangroves and herbaceous species were distributed in deeper and shallower layers, respectively [54]. In addition, the increase of soil water content and decrease in bulk density after S. alterniflora invasion led to water-soluble ions such as sulfate vertically leaching into the deep soil. Since the roots of S. alterniflora cannot penetrate the deepest layer of soil, the bulk density and water content cannot be changed there [55]. Furthermore, the ecological niches and nutrient sources of microorganisms were changed dissimilarly in different layers (Figure 5c); thus, the biological driver also altered soil sulfur content and distribution indirectly [19].
The differences in the magnitude of the increase of soil total sulfur, sulfate, and sulfide after S. alterniflora invasion in different life forms (Figure 4) are mainly because the diverse root activities and living characteristics of plants lead to various soil properties after invasion [56]. The introduction of S. alterniflora accelerated the biogeochemical cycle of soil sulfur by accelerating root activity and litter decomposition; thus, the maximum effect was found in mudflats that were originally unvegetated (Figure 5d). Herbaceous and woody species are the main native plants disrupted by the invasion of S. alterniflora on the eastern coast of China. Herbaceous species are distributed in a wide latitude from 24.3°N to 37.5°N with hot, humid summer but cold, dry winter [35], while woody species are mainly distributed in the Jiulong River Estuary, Leizhou Peninsula, and Zhangjiang Estuary with a humid subtropical climate [34,37,57]. Mangroves are composed of tropical intertidal halophytic arbors and shrubs with complex food webs, high diversity of species, and high net primary productivity [58]. In addition, it has been reported that mangrove wetlands maintain a high level of organic carbon, which is three times the average carbon density of natural soil, while the organic carbon content of S. alterniflora soil is much lower [59,60]. Compared with herbaceous communities and unvegetated mudflats, woody communities have the largest aboveground and underground biomass with high levels of salinity, redox potential, organic matter content, and sulfur sources [61]. The high aboveground biomass might reduce the quantity of light obtained by S. alterniflora and limit its growth. In turn, S. alterniflora invasion also weakens the relationship between light use efficiency and photochemical reflectance index in mangrove communities [62]. Stable litter decomposing communities were also found in mangroves to withstand the environmental changes and disturbances [63]. Therefore, mangroves have better resistance to the S. alterniflora invasion in the slight change of soil sulfur.
4.2. Invasive Plant Biomass Promotes Soil Nutrient Contents, Changes Physicochemical Properties, and Increases Soil S Contents
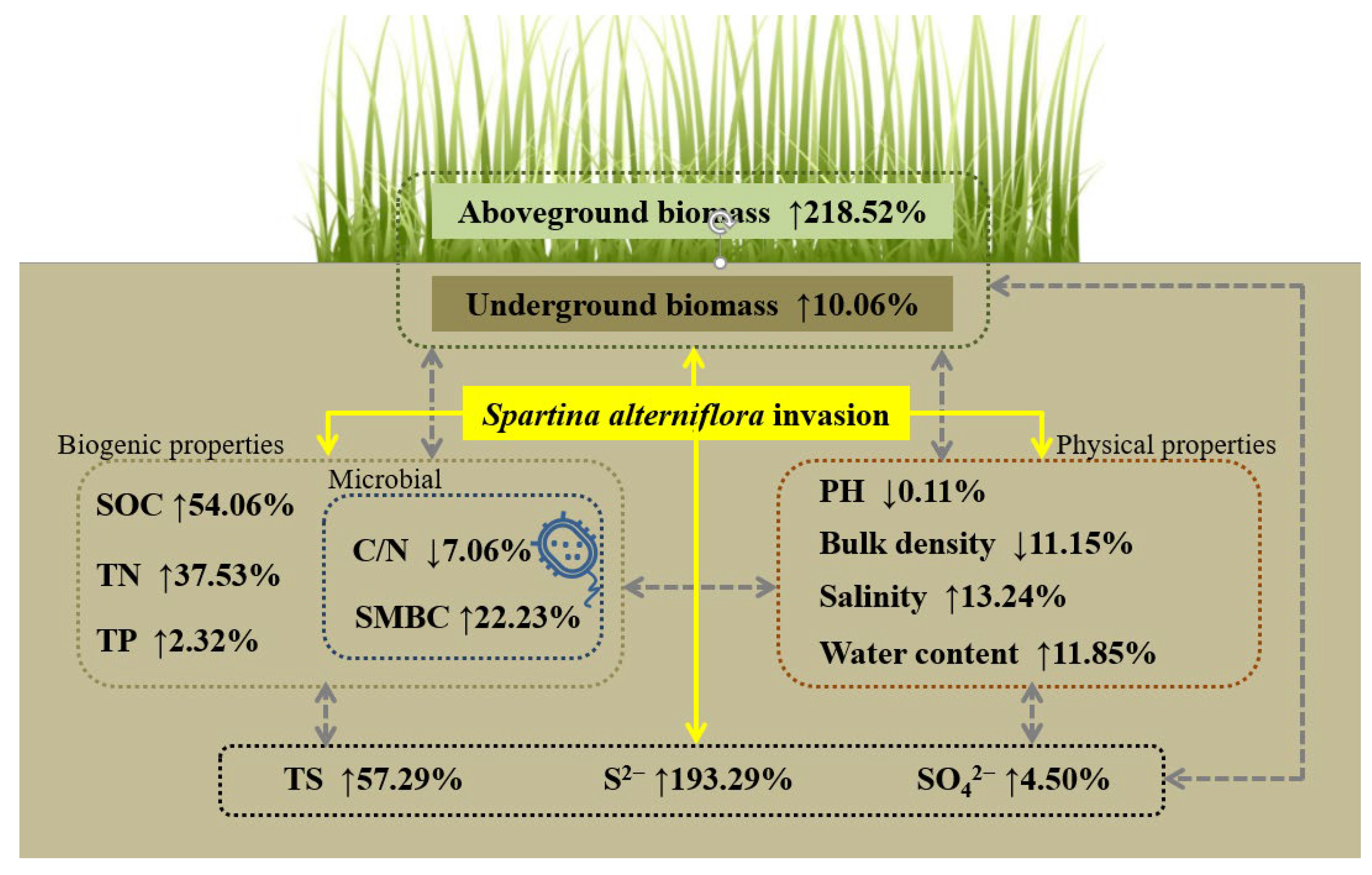
The results showed that the invasion of S. alterniflora stimulated the contents of soil sulfur, including total sulfur, S2−, and SO42−, by 57.29%, 193.29%, and 4.50%, respectively (Figure 6). All results of the meta-analysis support the conceptual framework (Figure 6), which might be an illustration of the pivotal role of sulfur in the success of S. alterniflora invasion. After the invasion of S. alterniflora, the distinct increase in aboveground biomass and underground biomass (Figure 2) led to direct enhancement in net primary production and decomposition of litters [64].
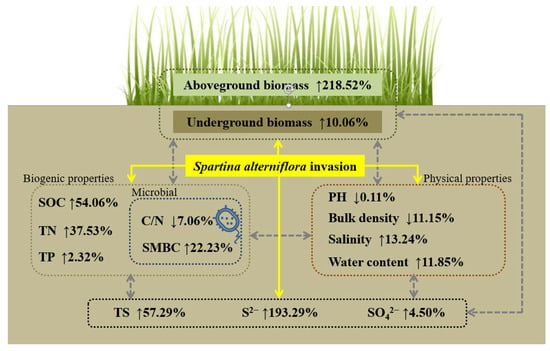
Figure 6.
A conceptual framework illustrating how S. alterniflora invasion affects soil sulfur contents and other soil properties. “↑” means positive effect; “↓” means negative effect. Solid and dashed arrows, respectively, represent direct effects of S. alterniflora invasion and indirect effects speculated. SOC, soil organic carbon; TN, total nitrogen; TP, total phosphorus; SMBC, soil microbial biomass carbon; TS, total sulfur.
The residues of S. alterniflora may stimulate soil sulfur accumulation by supporting more nutrients and abundant decomposers [14]. The growth of microorganisms is closely related to carbon and nitrogen sources, and a low C/N is conducive to the reproduction of microorganisms that might participate in the sulfur cycle [65,66]. More abundant available resources generated from S. alterniflora support more decomposers (C/N raised by 7.06% and soil microbial biomass carbon raised by 22.23%), promoting more plant-available nutrients through faster nutrient cycling (soil organic carbon raised by 54.06%, total nitrogen raised by 37.53%, and total phosphorus raised by 2.32%) [55]. In turn, more nutrients stimulate the activity and reproduction of soil microbes, including those participating in the sulfur cycle [27]. According to previous studies, the invasion of S. alterniflora changes the abundance, composition, and community structure of sulfur-related bacterium, especially SRB and SOB [32,38,51]. In addition, the increase in microbial activity further changes soil physicochemical properties as well as plant biomass [67].
After S. alterniflora invasion, soil physical properties were changed, further affecting the contents and distribution of sulfur (Figure 6) [68]. The slight decrease in soil pH derived from organic acids secreted by root activities could lead to a higher proportion of H2S among sulfide compounds (Figure 6), because pH could greatly affect the chemical speciation of sulfide (H2S, HS−, and S2−) [19]. Although S. alterniflora could change soil pH by organic acids and ammonium nitrogen assimilation, no significant change in pH was found because of the exchange of substances between water and salt with frequent tides [52]. The woody mangroves invaded by S. alterniflora were mostly located in Fujian and Guangdong provinces and were severely affected by acid rain, leading to a soil pH between 6.52 and 7.63 [69]. In addition, the various buffering capacities of woody communities and herbaceous communities result in the different directions of the response in soil pH after S. alterniflora invasion (Figure 5d), which are correlated with soil clay, texture, and organic matter [70].
Bulk density can reflect the density of the solid soil matrix in its natural configuration, which is strongly associated with a series of soil and hydrological processes [71]. With the decrease in soil bulk density (Figure 2), sulfate could be vertically transferred into deeper layers by improving the leaching capacity along the vertical direction, changing the spatial distribution of sulfur. Furthermore, S. alterniflora can absorb salt from soil and returned through salt-secreting glands [23], while salts can affect the decomposition and mineralization rates of litter [72,73]. Therefore, the accumulation of salt by S. alterniflora results in the retention of salt from the tide to the soil, indirectly leading to the increase of soil sulfur [74]. At last, the positive impact on soil water content after S. alterniflora invasion (Figure 6) affects sulfur content directly through the migration of soluble ions [75] and indirectly by accelerating organism synthesis and litter decomposition [23]. The large leaf area index, plant density, and biomass of S. alterniflora provide shade and reduce water loss for soil [76,77]. Meanwhile, more organic matters introduced by S. alterniflora improve the soil structure and colloid conditions, strengthening the capacity of adsorption and water retention [49].
Numerous hypotheses explain the successful invasion with characteristics of the invaders or the invaded ecosystems [78]. In this study, we focus on the invader S. alterniflora. One of the invasion theories of S. alterniflora is allelopathy, e.g., reporting that the root exudates of S. alterniflora inhibit offspring of S. mariqueter [79]. Our results suggest that S. alterniflora might successfully invade by increasing the phytotoxic sulfide content in the soil, and the mechanism of sulfide increase might be closely related to other invasion theories. Therefore, the important role of sulfur in the invasion of S. alterniflora needs to be studied further.
5. Conclusions
Based on a meta-analysis and conceptual framework, the effects of S. alterniflora invasion on soil sulfur were uncovered. The invasion of S. alterniflora significantly increased the sulfur content with high plant biomass in direct ways. Enhancing ecosystem nutrient pools, promoting abundant decomposers, and altering the soil physical properties also indirectly increase the soil sulfur content. Although the response of soil sulfur content after S. alterniflora invasion varied with seasons, invasion stages, soil depths, and native communities, positive feedbacks were still found. Sulfide is phytotoxic to most plants except for S. alterniflora; thus, the accumulation of soil sulfur after S. alterniflora invasion might place native plants in danger, accelerating the process of invasion and community succession. Overall, our findings indicate that the importance of soil sulfur in the successful invasion of S. alterniflora needs more thorough studies in the future.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/w14101633/s1, Figure S1: (a) The screening process used in the meta-analysis; (b) evidence on the response of soil sulfur content after S. alterniflora invasion was synthesized in our database of researches published between 2012 and 2019.; Table S1: Basic information including literature source, site location, native species, native species life form, temperature, precipitation, sample years, and soil properties extracted from the articles used in the meta-analysis; references for analysis.; Figure S2–S7: Funnel plots of the meta-analysis.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Z.Z. and C.H.; methodology, X.C. and D.W.; software, F.W.; validation, J.L. and Z.Z.; formal analysis, L.C.; investigation, L.C.; resources, Y.L.; data curation, Y.L. and G.L.; writing—original draft preparation, L.C.; writing—review and editing, D.W. and Z.Z.; visualization, X.L.; supervision, C.H. and D.W.; project administration, C.H.; funding acquisition, Z.Z. and C.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by National Natural Science Foundation of China (41907270, 41971055), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2020M671069), State’s Key Project of Research and Development Plan (2016YFA0601003).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to express the sincere gratitude to the reviewers and editors for their time and effort. Also, we are grateful to all of the researchers whose work contributed data to this analysis.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Macreadie, P.I.; Anton, A.; Raven, J.A.; Beaumont, N.; Connolly, R.M.; Friess, D.A.; Kelleway, J.J.; Kennedy, H.; Kuwae, T.; Lavery, P.S.; et al. The future of Blue Carbon science. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- O’Connell, J.L.; Mishra, D.R.; Alber, M.; Byrd, K.B. BERM: A Belowground Ecosystem Resiliency Model for estimating Spartina alterniflora belowground biomass. New Phytol. 2021, 232, 425–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sievers, M.; Brown, C.J.; Tulloch, V.J.D.; Pearson, R.M.; Haig, J.A.; Turschwell, M.P.; Connolly, R.M. The Role of Vegetated Coastal Wetlands for Marine Megafauna Conservation. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2019, 34, 807–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latombe, G.; Richardson, D.M.; McGeoch, M.A.; Altwegg, R.; Catford, J.A.; Chase, J.M.; Courchamp, F.; Esler, K.J.; Jeschke, J.M.; Landi, P.; et al. Mechanistic reconciliation of community and invasion ecology. Ecosphere 2021, 12, e03359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worm, B.; Barbier, E.B.; Beaumont, N.; Duffy, J.E.; Folke, C.; Halpern, B.S.; Jackson, J.B.C.; Lotze, H.K.; Micheli, F.; Palumbi, S.R.; et al. Impacts of biodiversity loss on ocean ecosystem services. Science 2006, 314, 787–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wails, C.N.; Baker, K.; Blackburn, R.; Del Vallé, A.; Heise, J.; Herakovich, H.; Holthuijzen, W.A.; Nissenbaum, M.P.; Rankin, L.; Savage, K.; et al. Assessing changes to ecosystem structure and function following invasion by Spartina alterniflora and Phragmites australis: A meta-analysis. Biol. Invasions 2021, 23, 2695–2709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syed, S.; Xu, M.; Wang, Z.; Yu, C.; Lian, B. Invasive Spartina alterniflora in controlled cultivation: Environmental implications of converging future technologies. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 130, 108027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Liao, C.H.; Zhang, X.D.; Chen, H.L.; Wang, Q.; Chen, Z.Y.; Gan, X.J.; Wu, J.H.; Zhao, B.; Ma, Z.J.; et al. Spartina alterniflora invasions in the Yangtze River estuary, China: An overview of current status and ecosystem effects. Ecol. Eng. 2009, 35, 511–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, C. Introduced species shape insular mutualistic networks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2026396118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, D.; Liu, M.; Wang, Z.; Li, L.; Man, W.; Jia, M.; Zhang, Y. Rapid invasion of Spartina alterniflora in the coastal zone of mainland China: Spatiotemporal patterns and human prevention. Sensors 2019, 19, 2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Xiao, X.; Qiu, S.; Xu, X.; Wang, X.; Chang, Q.; Wu, J.; Li, B. Quantifying latitudinal variation in land surface phenology of Spartina alterniflora saltmarshes across coastal wetlands in China by Landsat 7/8 and Sentinel-2 images. Remote Sens. Environ. 2022, 269, 112810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gigolashvili, T.; Kopriva, S. Transporters in plant sulfur metabolism. Front. Plant Sci. 2014, 5, 442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moran, M.A.; Durham, B.P. Sulfur metabolites in the pelagic ocean. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2019, 17, 665–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blum, S.C.; Lehmann, J.; Solomon, D.; Caires, E.F.; Alleoni, L.R.F. Sulfur forms in organic substrates affecting S mineralization in soil. Geoderma 2013, 200, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jørgensen, B.B.; Findlay, A.J.; Pellerin, A. The biogeochemical sulfur cycle of marine sediments. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zhao, P.X.; Miao, Z.Q.; Qi, G.F.; Wang, Z.; Yuan, Y.; Ahmad, N.; Cao, M.J.; Hell, R.; Wirtz, M.; et al. SULTR3s function in chloroplast sulfate uptake and affect ABA biosynthesis and the stress response. Plant Physiol. 2019, 180, 593–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagarinao, T. Sulfide as an environmental factor and toxicant: Tolerance and adaptations in aquatic organisms. Aquat. Toxicol. 1992, 24, 21–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raven, J.A.; Scrimgeour, C.M. The influence of anoxia on plants of saline habitats with special reference to the sulphur cycle. Ann. Bot. 1997, 79, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamers, L.P.M.; Govers, L.L.; Janssen, I.C.J.M.; Geurts, J.J.M.; Van der Welle, M.E.W.; Van Katwijk, M.M.; Van der Heid, T.; Roelofs, J.G.M.; Smolders, A.J.P. Sulfide as a soil phytotoxin—A review. Front. Plant Sci. 2013, 4, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bradley, P.M.; Dunn, E.L. Effects of sulfide on the growth of three salt marsh halophytes of the southeastern United States. Am. J. Bot. 1989, 76, 1707–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, P.R.; Forrest, J. Uptake of dissolved sulfide by Spartina alterniflora: Evidence from natural sulfur isotope abundance ratios. Science 1982, 216, 633–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, T.; Sun, Z.; Li, J.; Gao, H.; Wang, H.; Wang, J.; Chen, B. Distributions characteristics and influencing factors of inorganic sulfur forms in soil of Spartina alterniflora marsh and Cyperus malaccensis marsh in the Min River Estuary. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 2017, 37, 4747–4756. [Google Scholar]
- Li, P.; Xie, W.; Wang, Z.; Yan, Q. Effects of Spartina alterniflora invasion on sulfur content temporal and spatial variation in tidal flat wetland of Jiaozhou Bay. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 2019, 39, 870–879. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, H.; He, C.; Liu, C.; Liang, X.; Chen, X. Spatiotemporal variability in soil sulfur storage is changed by exotic Spartina alterniflora in the Jiuduansha Wetland, China. Ecol. Eng. 2019, 133, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, T.; Sun, Z.; Li, J.; Gao, H.; Zhu, H.; Ren, P. Spatial Distribution of total sulfur contents in plant-soil systems of the typical marshes with different flooding regimes in the Min River Estuary. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2016, 30, 246–254. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, S.; Luo, M.; Liu, Y.; Bai, J.; Yang, Y.; Zhai, Z.; Huang, J. Rhizosphere effect and its associated soil-microbe interactions drive iron fraction dynamics in tidal wetland soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 756, 144056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Bu, N.S.; Long, X.E.; Sun, J.; He, C.Q.; Liu, X.Y.; Cui, J.; Liu, D.X.; Chen, X.P. Sulfate reducer and sulfur oxidizer respond differentially to the invasion of Spartina alterniflora in estuarine salt marsh of China. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 99, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenzuela, E.I.; Prieto-Davó, A.; López-Lozano, N.E.; Hernández-Eligio, A.; Vega-Alvarado, L.; Juárez, K.; García-González, A.S.; López, M.G.; Cervantes, F.J. Anaerobic methane oxidation driven by microbial reduction of natural organic matter in a tropical wetland. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 83, e00645-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pallud, C.; Van Cappellen, P. Kinetics of microbial sulfate reduction in estuarine sediments. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2006, 70, 1148–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pester, M.; Knorr, K.H.; Friedrich, M.W.; Wagner, M.; Loy, A. Sulfate-reducing microorganisms in wetlands—fameless actors in carbon cycling and climate change. Front. Microbiol. 2012, 3, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maricle, B.R.; Lee, R.W. Aerenchyma development and oxygen transport in the estuarine cordgrasses Spartina alterniflora and S. anglica. Aquat. Bot. 2002, 74, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, S.; Liu, X.; Mou, X.; Zhao, Y. Comparison of Carbon, Nitrogen, and Sulfur in Coastal Wetlands Dominated by Native and Invasive Plants in the Yancheng National Nature Reserve, China. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2020, 30, 202–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, X.; Sun, Z.; Zeng, A.; Chen, B.; Wang, H. Effects of Spartina alterniflora invasion in a seaward direction on variations of inorganic sulfur forms in marsh soils of the Minjiang River estuary, China. J. Appl. Ecol. 2019, 30, 3518–3526. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, S.; Li, J.; He, Z.; Van Nostrand, J.D.; Tian, Y.; Lin, G.; Zhou, J.; Zheng, T. GeoChip-based analysis of the functional gene diversity and metabolic potential of soil microbial communities of mangroves. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 97, 7035–7048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.P.; Sun, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.Y.; He, C.Q.; Liu, X.Y.; Bu, N.S.; Long, X.E. Temporal and spatial impact of Spartina alterniflora invasion on methanogens community in Chongming Island, China. J. Microbiol. 2018, 56, 507–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.L.; Wang, Y.H.; Whitt, A.A.; Wang, H.D.; Ma, C.C.; Guo, H.Y. Belowground responses of Phragmites australis and Suaeda salsa to salinity and water depth changes. Pakistan J. Bot. 2018, 50, 853–861. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Liao, G.; D’Souza, M.; Yu, X.; Yang, J.; Yang, X.; Zheng, T. Temporal and spatial variations of greenhouse gas fluxes from a tidal mangrove wetland in Southeast China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 1873–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Cheng, L.; Wang, D.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, Z.; Wang, F.; Wang, X.; Zhang, P.; Chen, X.; Liu, X. Spartina alterniflora raised soil sulfide content by regulating sulfur cycle-associated bacteria in the Jiuduansha Wetland of China. Plant Soil 2021, 469, 107–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, L.; Yang, W.; Zhao, H.; Xiao, Y.; Qing, H.; Zhou, C.; An, S. High Soil Sulfur Promotes Invasion of Exotic Spartina alterniflora into Native Phragmites australis Marsh. Clean Soil Air Water 2015, 43, 1666–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedges, L.V.; Gurevitch, J.; Curtis, P.S. The meta-analysis of response ratios in experimental ecology. Ecology 1999, 80, 1150–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borenstein, M.; Hedges, L.V.; Higgins, J.P.T.; Rothstein, H.R. A basic introduction to fixed-effect and random-effects models for meta-analysis. Res. Synth. Methods 2010, 1, 97–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duval, S.; Tweedie, R. A Nonparametric “Trim and Fill” Method of Accounting for Publication Bias in Meta-Analysis. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 2000, 95, 89–98. [Google Scholar]
- He, Q.; Bertness, M.D.; Altieri, A.H. Global shifts towards positive species interactions with increasing environmental stress. Ecol. Lett. 2013, 16, 695–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maggi, E.; Benedetti-Cecchi, L.; Castelli, A.; Chatzinikolaou, E.; Crowe, T.P.; Ghedini, G.; Kotta, J.; Lyons, D.A.; Ravaglioli, C.; Rilov, G.; et al. Ecological impacts of invading seaweeds: A meta-analysis of their effects at different trophic levels. Divers. Distrib. 2015, 21, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, I.C.; Cott, G.M.; Devaney, J.L.; Simkanin, C. Differential effects of biological invasions on coastal blue carbon: A global review and meta-analysis. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2018, 24, 5218–5230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, M.S.; Mendelssohn, I.A. Sulphide as a Soil Phytotoxin: Differential Responses in Two Marsh Species. J. Ecol. 1989, 77, 565–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeleke, J.; Sheng, Q.; Wang, J.G.; Huang, M.Y.; Xia, F.; Wu, J.H.; Quan, Z.X. Effects of Spartina alterniflora invasion on the communities of methanogens and sulfate-reducing bacteria in estuarine marsh sediments. Front. Microbiol. 2013, 4, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, J.; Wu, Y.; Kang, Q.; Zhang, J. Spatial variations of carbon, nitrogen, phosphorous and sulfur in the salt marsh sediments of the Yangtze Estuary in China. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2007, 71, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, D.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, Z. The range expansion patterns of Spartina alterniflora on salt marshes in the Yangtze Estuary, China. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2010, 88, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Li, B.; Wu, J.; Hu, S. Invasive plants differentially affect soil biota through litter and rhizosphere pathways: A meta-analysis. Ecol. Lett. 2019, 22, 200–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cui, J.; Chen, X.; Nie, M.; Fang, S.; Tang, B.; Quan, Z.; Li, B.; Fang, C. Effects of Spartina alterniflora Invasion on the Abundance, Diversity, and Community Structure of Sulfate Reducing Bacteria along a Successional Gradient of Coastal Salt Marshes in China. Wetlands 2017, 37, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, N.; Hu, Y.; Yang, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J.; Li, B.; Fang, C.; Song, Y. Effects of Spartina alterniflora invasion on soil physical and chemical properties in wetlands of the Yangtze River. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2017, 26, 100–109. [Google Scholar]
- Kraus, D.W.; Doeller, J.E. Oxidation of sulfide by Spartina alterniflora roots. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1999, 44, 1155–1159. [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira, T.O.; Otero, X.L.; Vidal-Torrado, P.; Macías, F. Effects of bioturbation by root and crab activity on iron and sulfur biogeochemistry in mangrove substrate. Geoderma 2007, 142, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Luo, Y.; Chen, J.; Lin, G.; Chen, J.; Li, B. Short-term C4 plant Spartina alterniflora invasions change the soil carbon in C3 plant-dominated tidal wetlands on a growing estuarine Island. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2006, 38, 3380–3386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhu, L.; Liu, N. C, N, and P Concentrations and Their Stoichiometry of Leaves and Roots with Different Life Forms in Hainan Province. J. Trop. Subtrop. Bot. 2020, 28, 131–135. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Q.; Jian, S.; Ma, K.; Chen, P. Differences in macrobenthic faunal communities in mangrove wetland habitats (Zhanjiang, China) invaded and non-invaded by exotic cordgrass Spartina alterniflora. Ecol. Res. 2018, 33, 1113–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Yang, J.; Liu, L.; Tian, Y.; Yu, Z. Effects of Spartina alterniflora invasion on biogenic elements in a subtropical coastal mangrove wetland. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 3107–3115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, D.; He, D.; Hong, W.; You, W.; Wu, L.; Ji, Z.; Xiao, S. Influence of Invasive Spartina alterniflora on Soil Ecosystem in Coastal Wetland. Wetl. Sci Manag. 2015, 11, 67–72. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Guo, Z.; Li, Z. Carbon storage and carbon sink of mangrove wetland: Research progress. J. Appl. Ecol. 2013, 24, 1153–1159. [Google Scholar]
- Varon-Lopez, M.; Dias, A.C.F.; Fasanella, C.C.; Durrer, A.; Melo, I.S.; Kuramae, E.E.; Andreote, F.D. Sulphur-oxidizing and sulphate-reducing communities in Brazilian mangrove sediments. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 16, 845–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Wang, L.; Shi, C.; Lu, Y. Evaluating the relationship between the photochemical reflectance index and light use efficiency in a mangrove forest with Spartina alterniflora invasion. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2018, 73, 778–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taketani, R.G.; Moitinho, M.A.; Mauchline, T.H.; Melo, I.S. Co-occurrence patterns of litter decomposing communities in mangroves indicate a robust community resistant to disturbances. PeerJ 2018, 6, e5710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, C.; Luo, Y.; Jiang, L.; Zhou, X.; Wu, X.; Fang, C.; Chen, J.; Li, B. Invasion of Spartina alterniflora enhanced ecosystem carbon and nitrogen stocks in the Yangtze Estuary, China. Ecosystems 2007, 10, 1351–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Hua, Z.S.; Lu, H.; Oehmen, A.; Guo, J. Elucidating functional microorganisms and metabolic mechanisms in a novel engineered ecosystem integrating C, N, P and S biotransformation by metagenomics. Water Res. 2019, 148, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, N.; Li, H.; Tang, Z.; Li, Z.; Li, G.; Jiang, Y.; Hu, X.; Lou, Y. Community size, activity and C: N stoichiometry of soil microorganisms following reforestation in a Karst region. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2016, 73, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Wang, C.; Luo, Y. Meta-analysis of the impacts of global change factors on soil microbial diversity and functionality. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guimarães, R.M.L.; Ball, B.C.; Tormena, C.A.; Giarola, N.F.B.; da Silva, Á.P. Relating visual evaluation of soil structure to other physical properties in soils of contrasting texture and management. Soil Tillage Res. 2013, 127, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Lin, C.; Qiu, P.; Song, Y.; Yang, W.; Xu, G.; Feng, X.; Yang, Q.; Yang, X.; Niu, A. Tungsten- and cobalt-dominated heavy metal contamination of mangrove sediments in Shenzhen, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 100, 562–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weaver, A.R.; Kissel, D.E.; Chen, F.; West, L.T.; Adkins, W.; Rickman, D.; Luvall, J.C. Mapping Soil pH Buffering Capacity of Selected Fields in the Coastal Plain. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2004, 68, 662–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Si, B.; Li, H.; Biswas, A. Elucidating controls of the variability of deep soil bulk density. Geoderma 2019, 348, 146–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Li, H.; Wu, H.; Yan, B. Unraveling bacterial community structure and function and their links with natural salinity gradient in the Yellow River Delta. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 773, 145673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Q.; Bai, J.; Gao, Z.; Wang, J.; Zhao, Q. Effects of Water Level and Salinity on Total Sulfur Contents in Salt Marsh Soils of the Yellow River Delta, China. Wetlands 2016, 36, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Song, J.; Feng, G.; Zhao, M.; Liu, J. Species, types, distribution, and economic potential of halophytes in China. Plant Soil 2011, 342, 495–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Zhang, Q.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, X. Inner-annual variation of soil water content and groundwater level in a typical islet wetland of Lake Poyang. J. Lake Sci. 2014, 26, 260–268. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, L.F.; Luo, Y.Q.; Chen, J.K.; Li, B. Ecophysiological characteristics of invasive Spartina alterniflora and native species in salt marshes of Yangtze River estuary, China. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2009, 81, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, C.Z.; Luo, Y.Q.; Fang, C.M.; Chen, J.K.; Li, B. Litter pool sizes, decomposition, and nitrogen dynamics in Spartina alterniflora-invaded and native coastal marshlands of the Yangtze Estuary. Oecologia 2008, 156, 589–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catford, J.A.; Jansson, R.; Nilsson, C. Reducing redundancy in invasion ecology by integrating hypotheses into a single theoretical framework. Divers. Distrib. 2009, 15, 22–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liang, X.; Zheng, H.; He, C.Q.; Xu, Q.Y.; Zhan, Y.W.; Lei, Y.R.; Du, W.; Yang, J.N. Allelopathic effects of invasive Spartina alterniflora root exudates in soil on the offspring (seeds) of Scirpus mariqueter. Allelopath. J. 2012, 29, 251–262. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).