Modeling Monthly Nitrate Concentration in a Karst Spring with and without Discrete Conduit Flow
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Methods
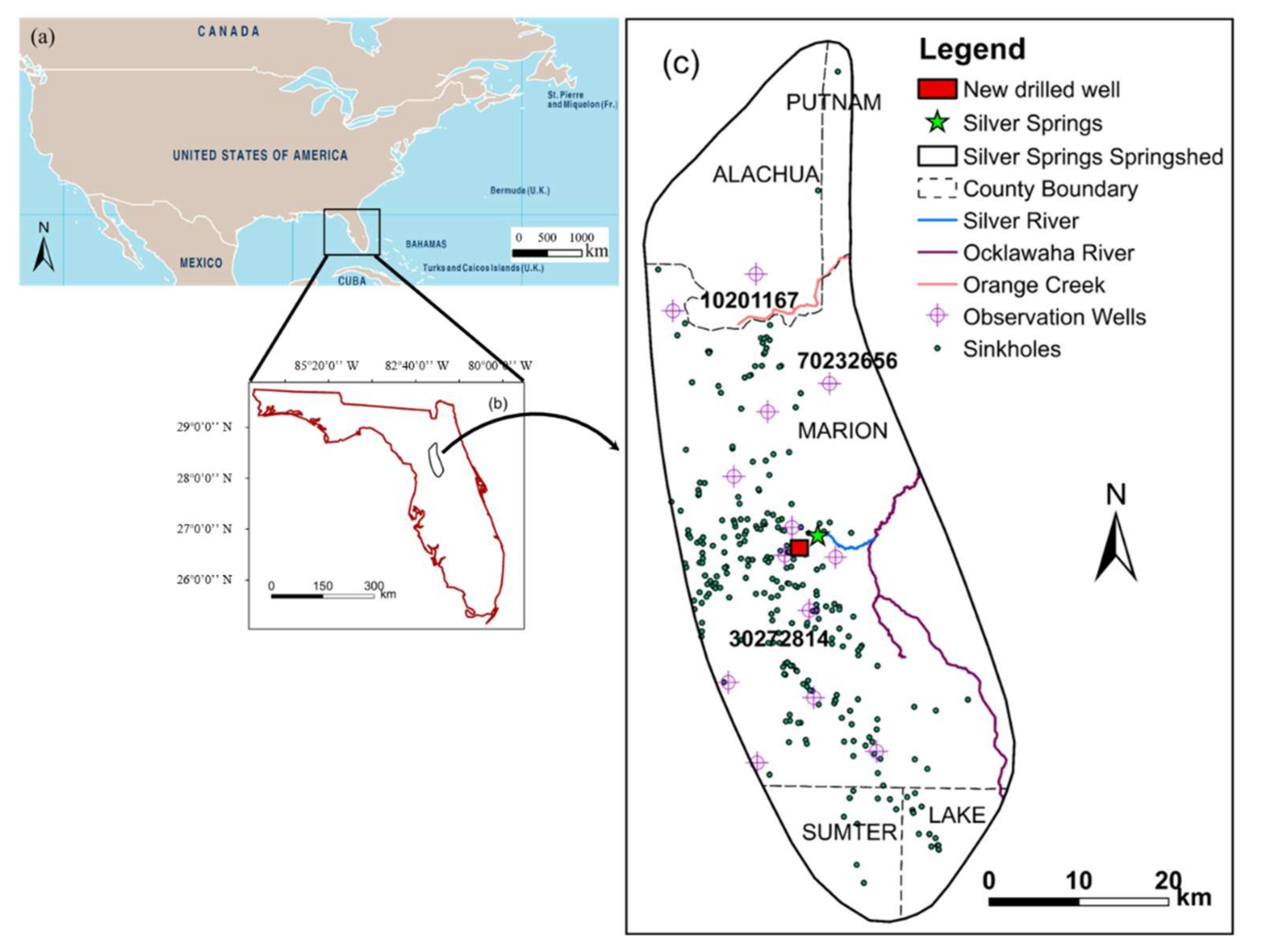
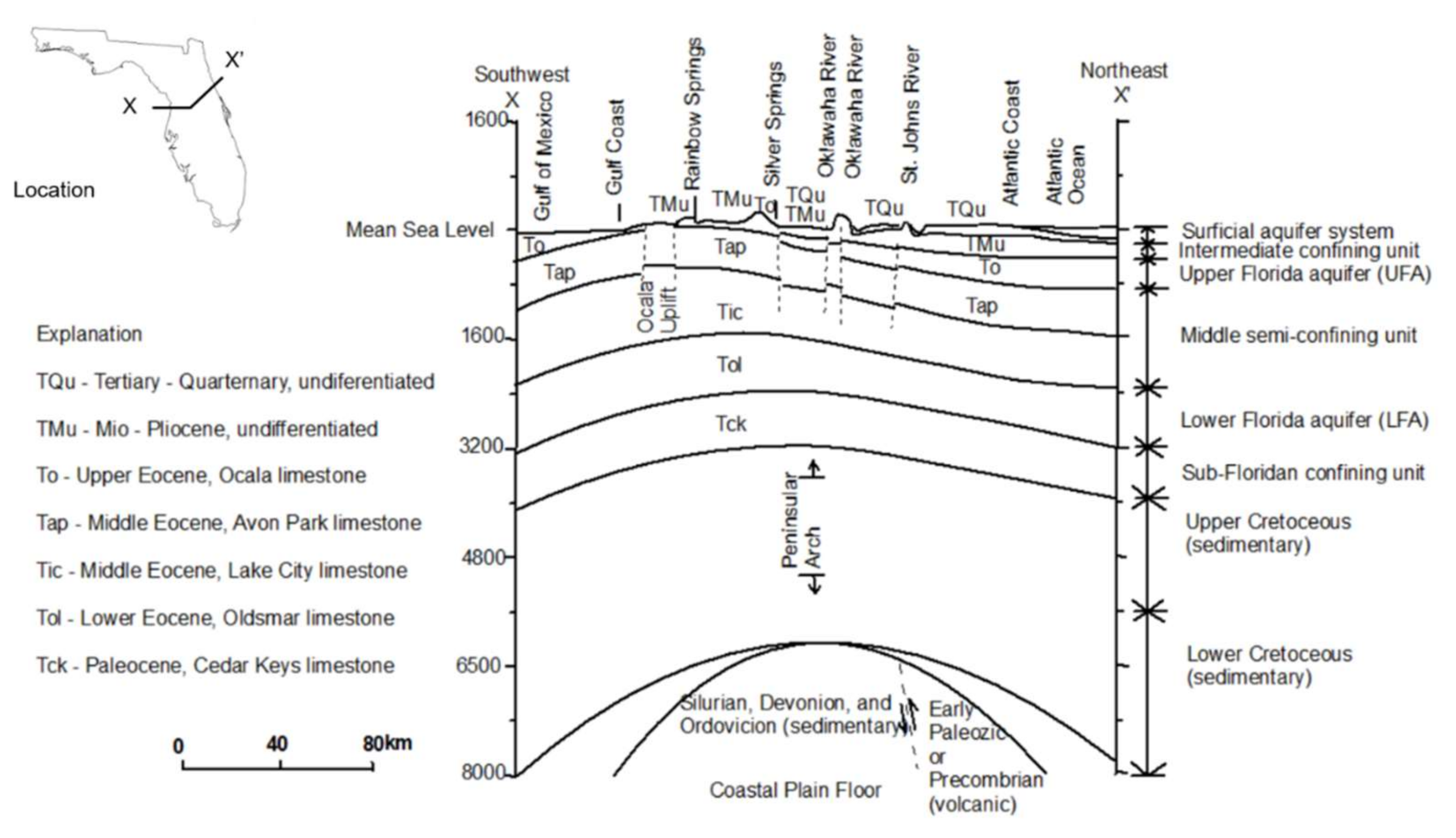
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Nitrate Contamination to Silver Springs
2.3. Datasets
2.4. Methods
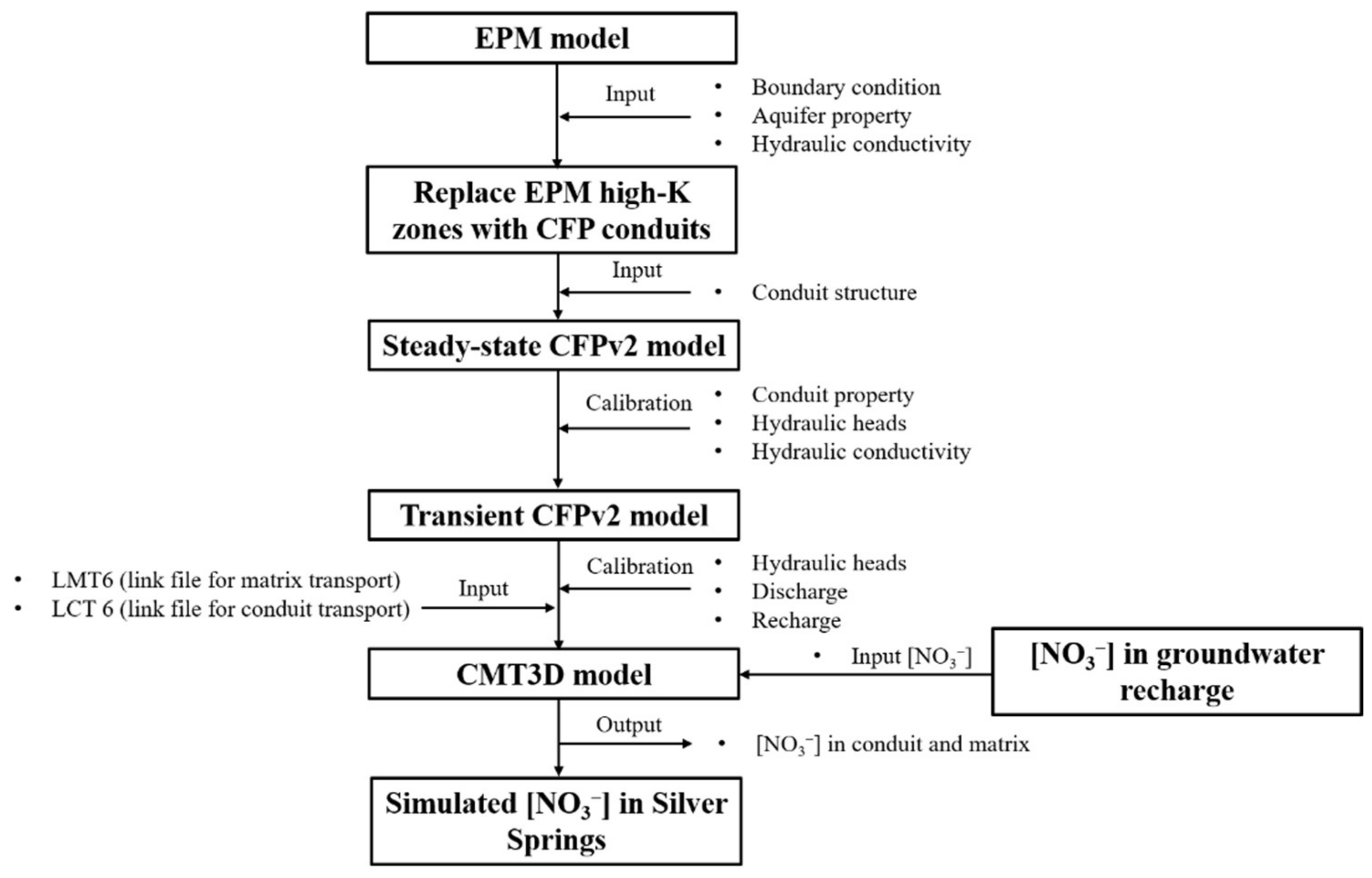
2.4.1. Model Development
2.4.2. The EPM Model
2.4.3. The CFPv2 Flow Modeling
2.4.4. The CMT3D Modeling
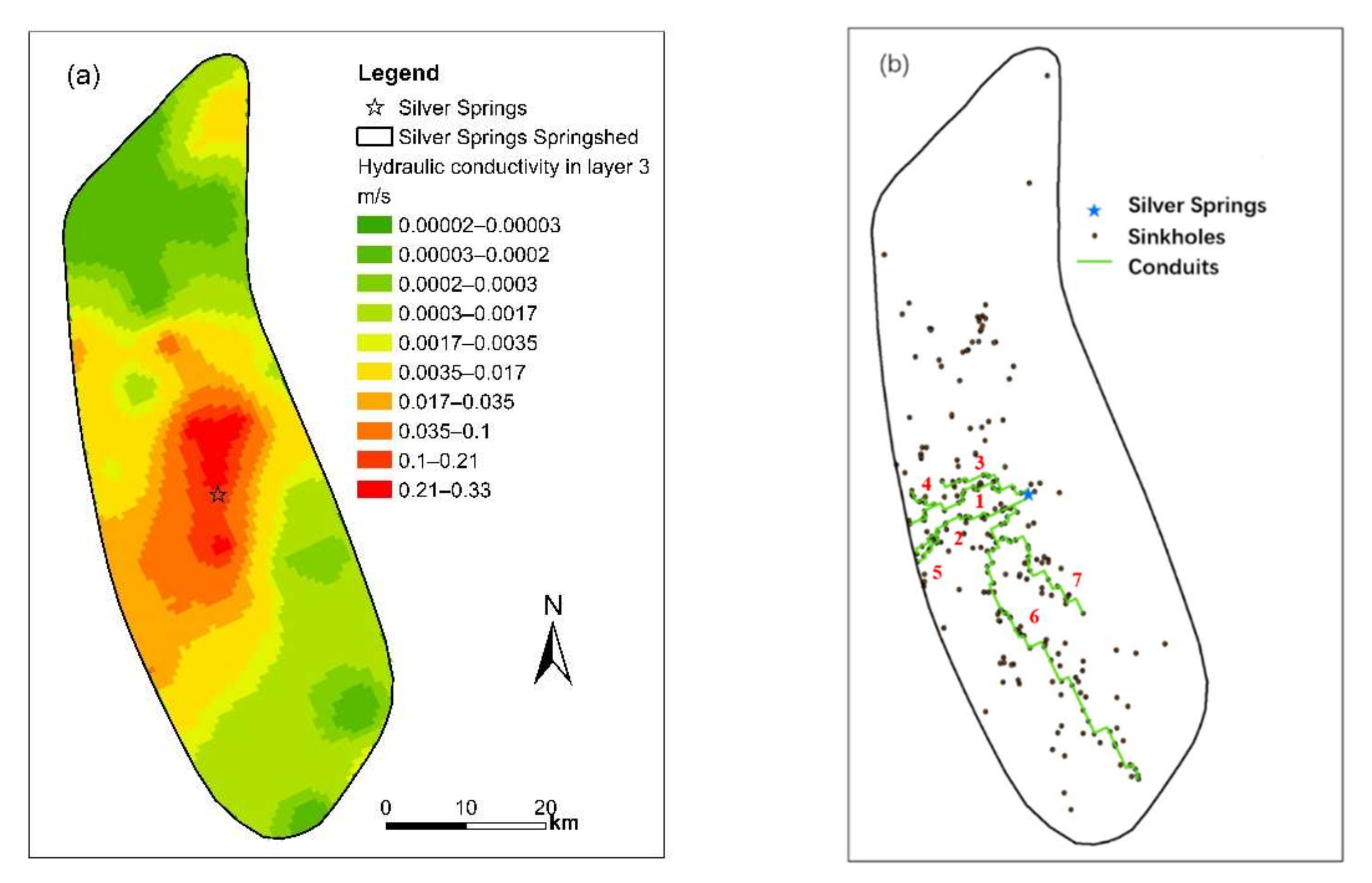
2.4.5. Conversion of EPM to CFPv2
2.4.6. Development of CMT3D Model
2.4.7. Nitrate Concentration in Groundwater Recharge
2.4.8. Model Calibration and Validation
3. Results
3.1. Groundwater Flow
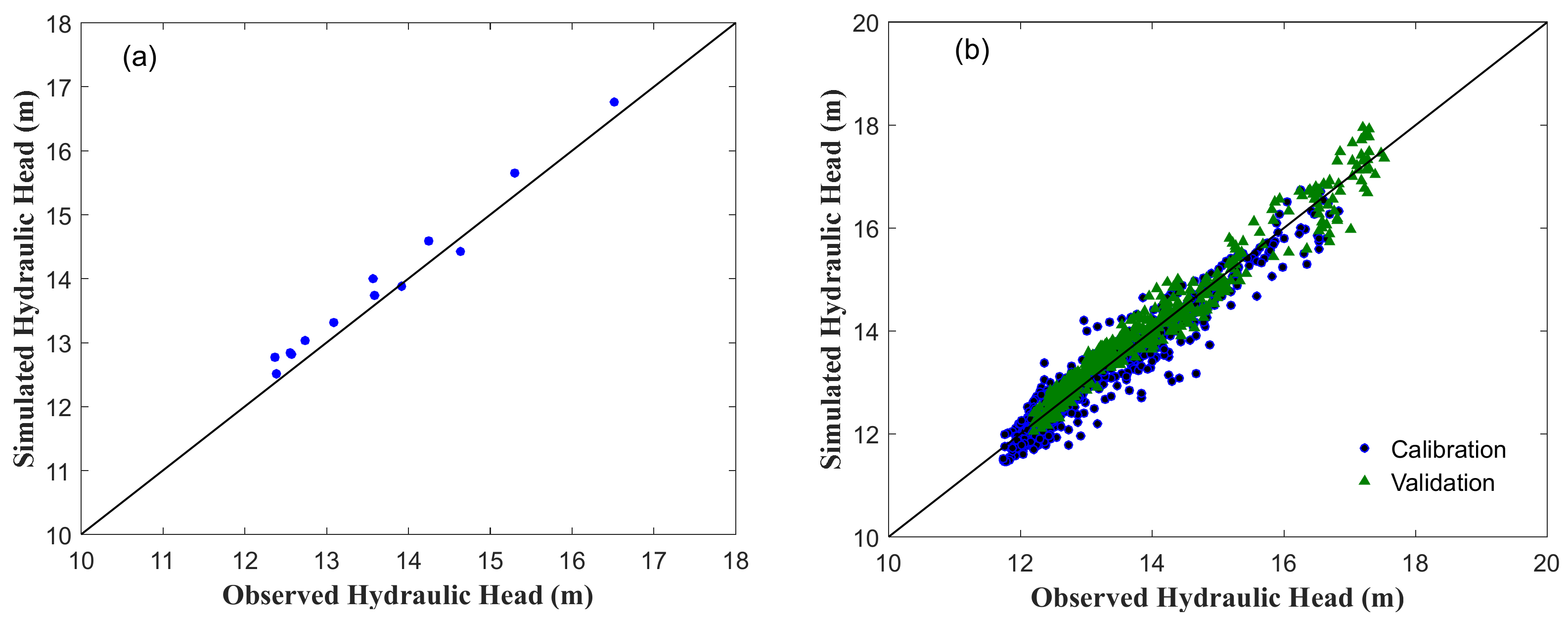
3.1.1. Steady-State Models
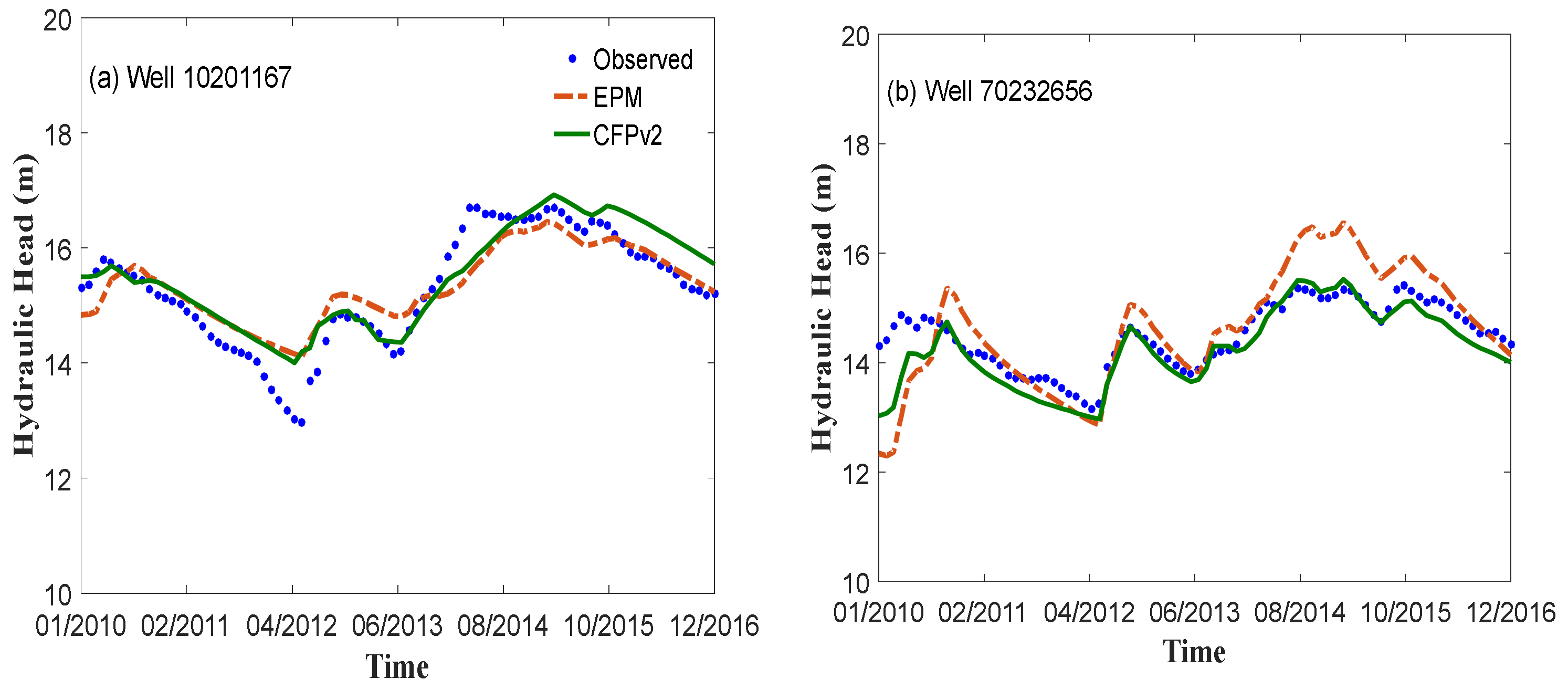
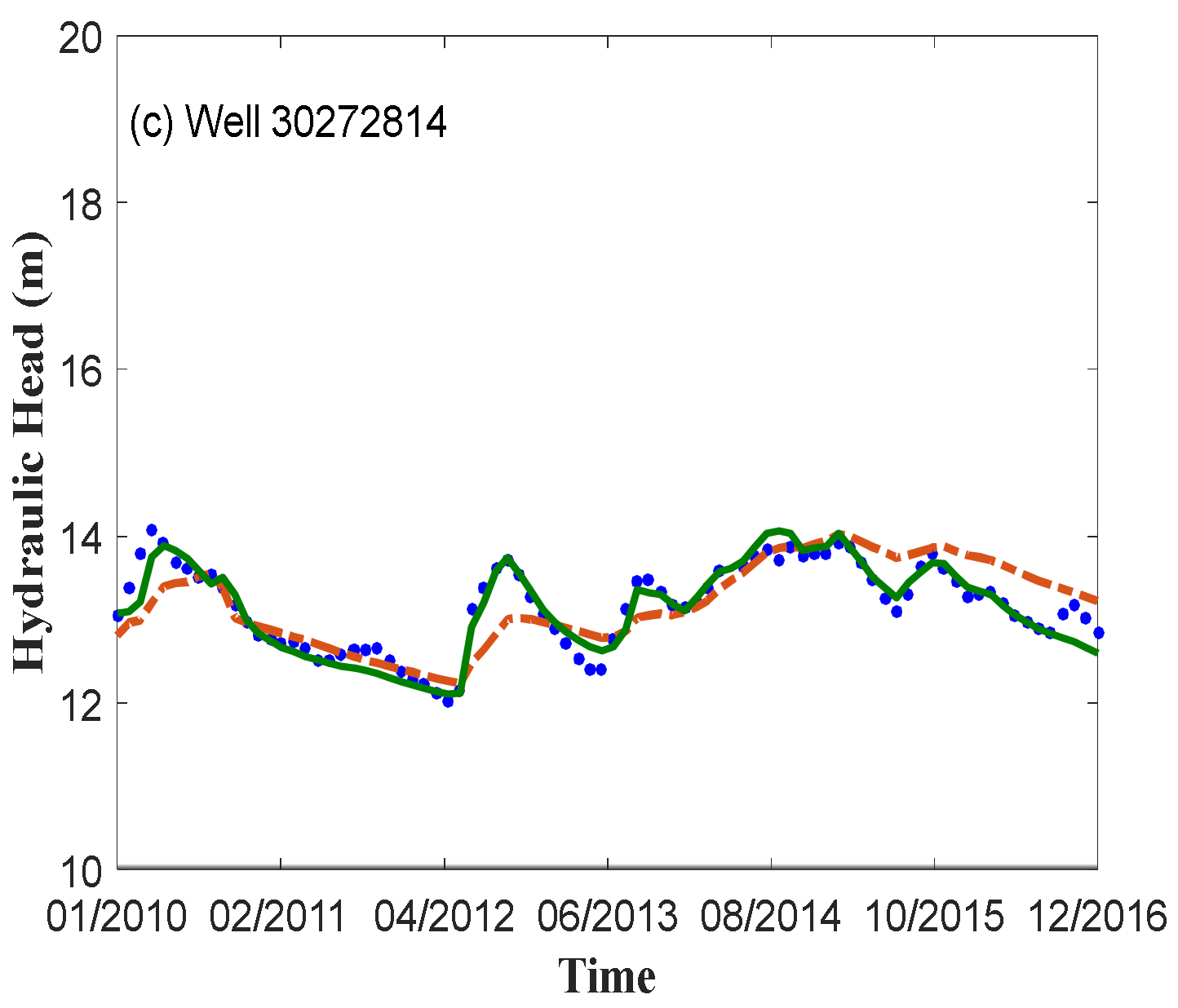
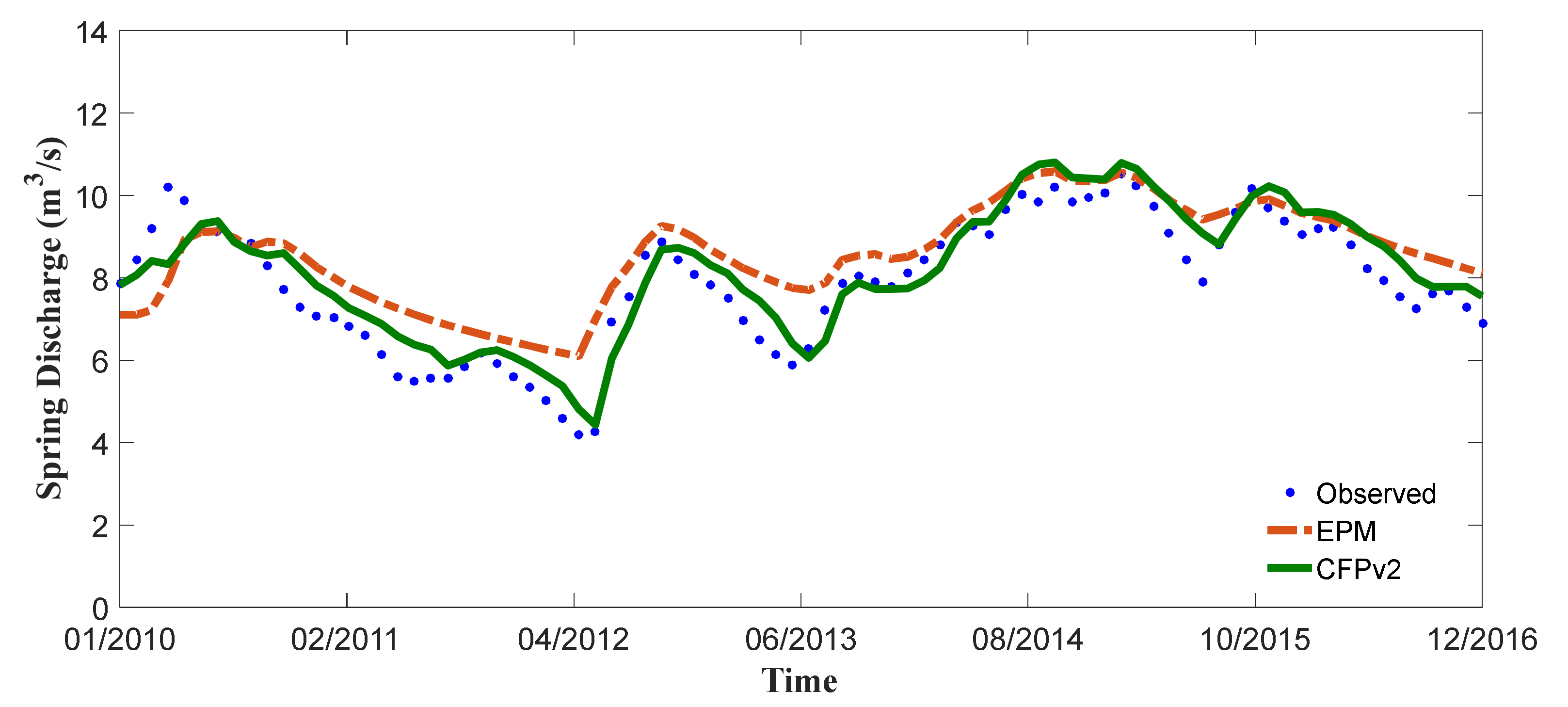
3.1.2. Transient Models
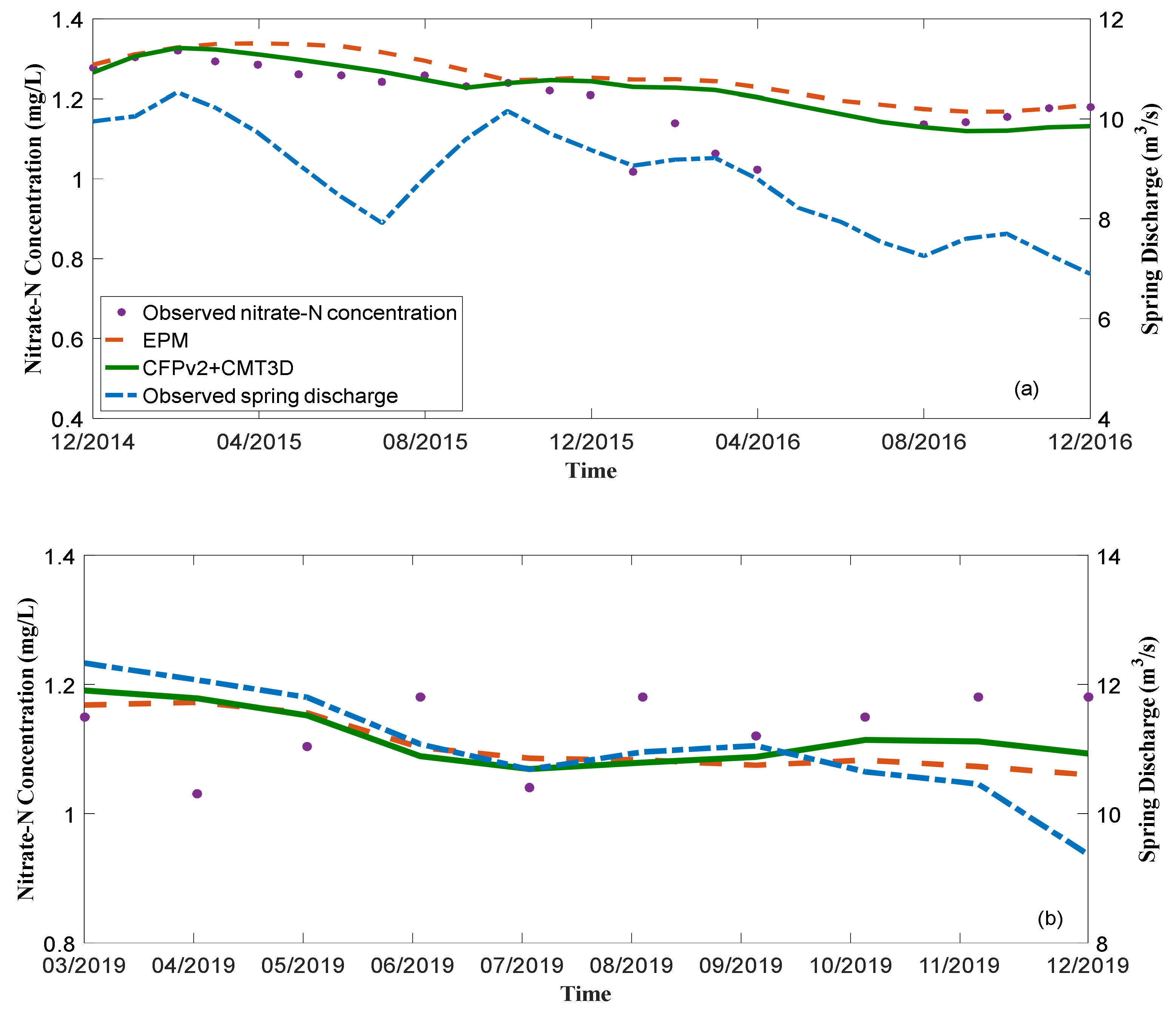
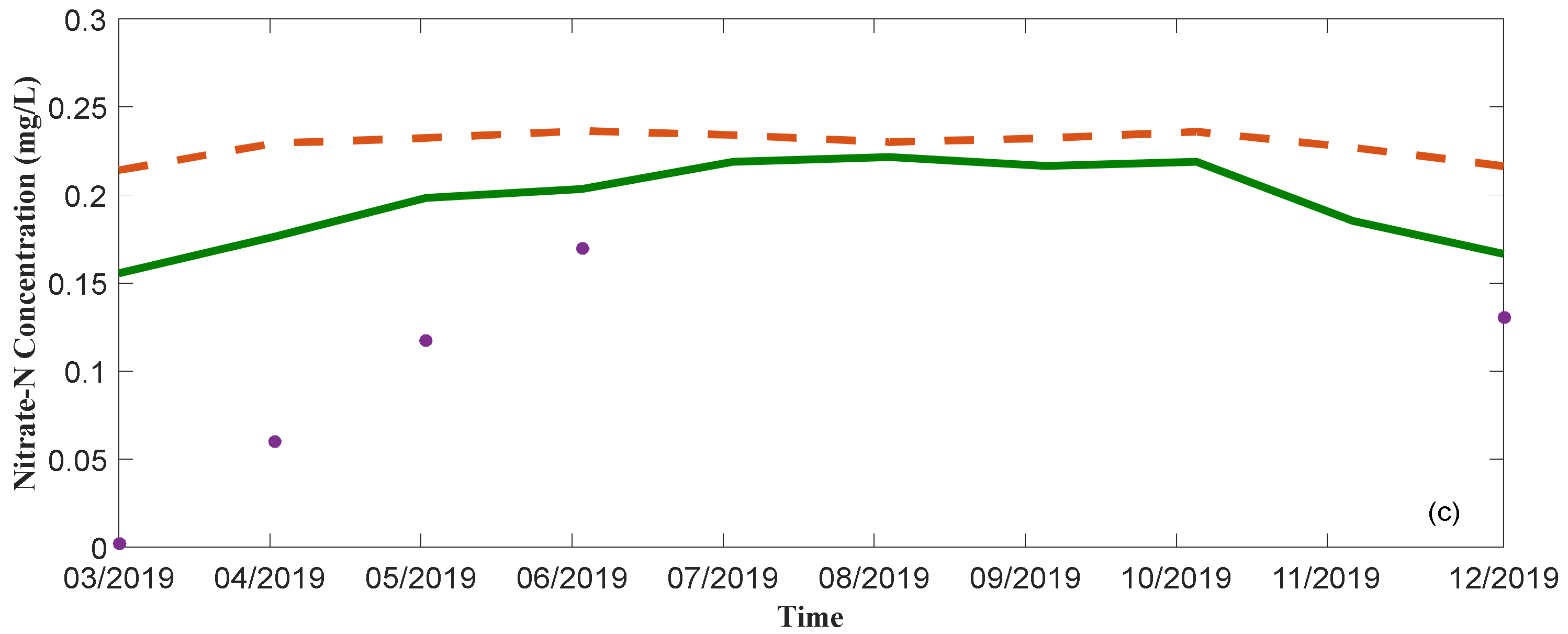
3.2. Nitrate Transport
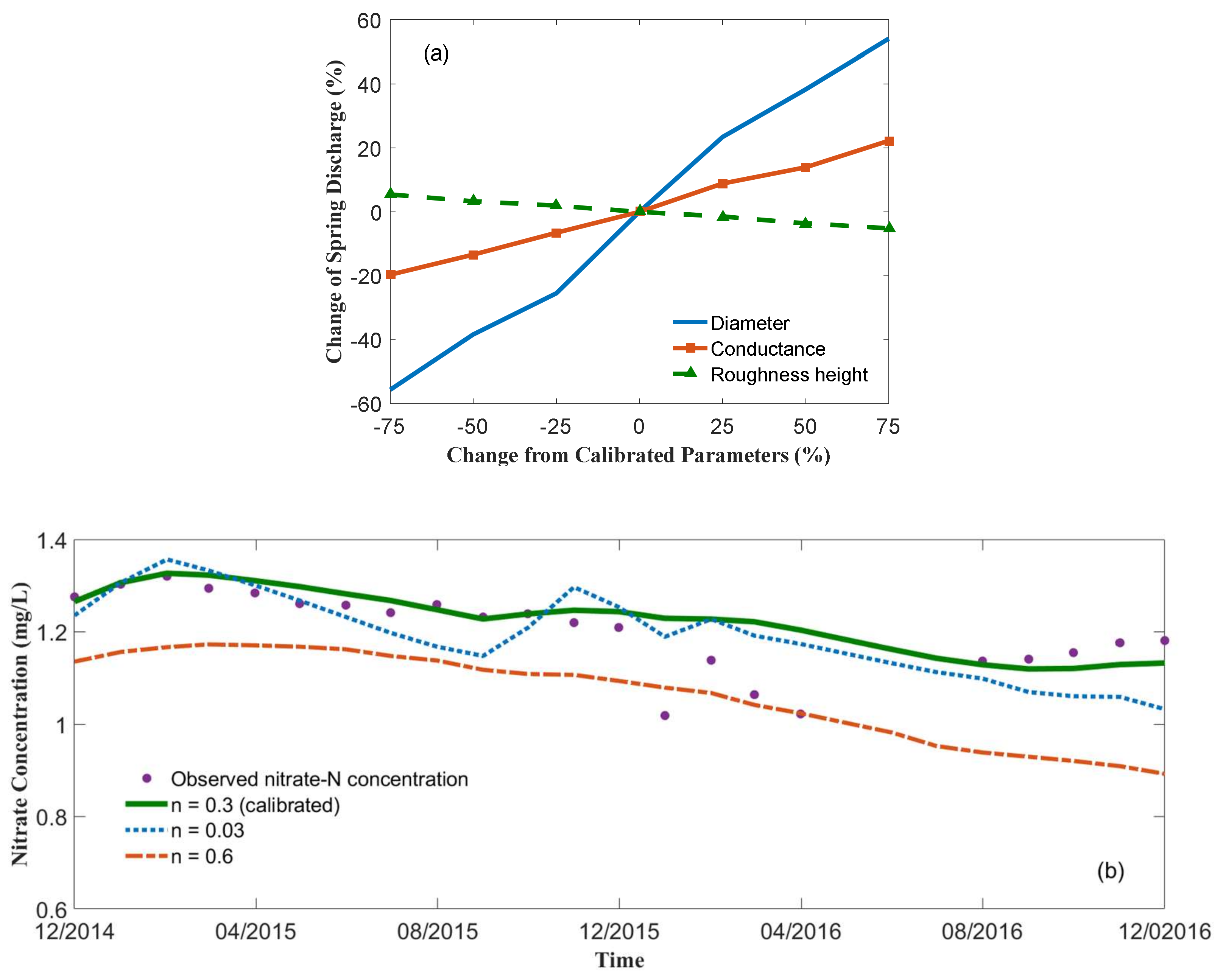
3.3. Sensitivity Anaysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Molenat, J.; Gascuel-Odoux, C. Modelling flow and nitrate transport in groundwater for the prediction of water travel times and of consequences of land use evolution on water quality. Hydrol. Processes 2002, 16, 479–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almasri, M.N.; Kaluarachchi, J.J. Modeling nitrate contamination of groundwater in agriculture watersheds. J. Hydrol. 2007, 343, 211–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Tang, C.; Song, X.; Yuan, R.; Han, Z.; Pan, Y. Factors contributing to nitrate contamination in a groundwater recharge area of the North China Plain. Hydrol. Processes 2016, 30, 2271–2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Bailey, R.T.; Records, R.M.; Wible, T.C.; Arabi, M. Comprehensive simulation of nitrate transport in coupled surface-subsurface hydrologic systems using the linked SWAT-MODFLOW-RT3D model. Environ. Model. Softw. 2019, 122, 1364–8152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevanovic, Z. Karst waters in potable water supply: A global scale overview. Environ. Earth Sci. 2019, 78, 662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldscheider, N.; Chen, Z.; Auler, A.S.; Bakalowicz, M.; Broda, S.; Drew, D.; Hartmann, J.; Jiang, G.; Moosdorf, N.; Stevanovic, Z.; et al. Global distribution of carbonate rocks and karst water resources. Hydrogeol. J. 2020, 28, 1661–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ritter, A.; Munoz-Carpena, R.; Bosch, D.D.; Schaffer, B.; Potter, T.L. Agricultural land use and hydrology affect variability of shallow groundwater nitrate concentration in south Florida. Hydrol. Processes Int. J. 2007, 21, 2464–2473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemizadeh, R.; Hellweger, F.; Butscher, C.; Padilla, I.; Vesper, D.; Field, M.; Alshawabkeh, A. Review: Groundwater flow and transport modeling of karst aquifers, with particular reference to the North Coast Limestone aquifer system of Puerto Rico. Hydrogeol. J. 2012, 20, 1441–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coinly, H.H. Cyanosis in infants caused by nitrates in well water. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 1945, 129, 112–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, K.K.; Vogel, R.M. Predicting ground water nitrate concentration from land use. Groundwater 2005, 43, 343–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Campbell, C.; Sullivan, S.M. Simulating time-varying cave flow and water levels using the storm water management model. Eng. Geol. 2002, 65, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, E.W.; Wicks, C.M. Assessing the importance of conduit geometry and physical parameters in karst systems using the storm water management model (SWMM). J. Hydrol. 2006, 329, 294–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Goldscheider, N. Modeling spatially and temporally varied hydraulic behavior of a folded karst system with dominant conduit drainage at catchment scale, Hochifen–Gottesacker, Alps. J. Hydrol. 2014, 514, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoemaker, W.B.; Kuniansky, E.L.; Birk, S.; Bauer, S.; Swain, E.D. Documentation of a Conduit Flow Process (CFP) for MODFLOW-2005: U.S. In Geological Survey Techniques and Methods; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2008; 50p, Book 6, Chapter A24. [Google Scholar]
- Hill, M.; Stewart, M.; Martin, A. Evaluation of the MODFLOW-2005 conduit flow process. Groundwater 2010, 48, 549–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reimann, T.; Liedl, R.; Birk, S.; Bauer, S. MODFLOW-CFPV2; Dresden Technical University: Dresden, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Reimann, T.; Liedl, R.; Birk, S.; Bauer, S. Modifications and Enhancements to CFPM1 Flow Subroutines and Addition of Transport Subroutines. 2013. Available online: http://tudresden.de/die_tu_dresden/fakultaeten/fakultaet_forst_geo_und_hydrowissenschaften/fachrichtung_wasserwesen/igw/forschung/downloads/cfpv2 (accessed on 12 July 2020).
- Reimann, T.; Giese, M.; Geyer, T.; Liedl, R.; Maréchal, J.C.; Shoemaker, W.B. Representation of water abstraction from a karst conduit with numerical discrete-continuum models. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2014, 18, 227–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.; Wang, P.P. MT3DMS: A Modular Three-dimensional Multispecies Transport Model for Simulation of Advection, Dispersion, and Chemical Reactions of Contaminants in Groundwater Systems; Documentation and User’s Guide; USA Contract Rep. SERDP-99–1; U.S. Army Engineer Research and Development Center: Vicksburg, MS, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Spiessl, S.M. Development and Evaluation of a Reactive Hybrid Transport Model (RUMT3D). Ph.D. Thesis, Hydrogeologic, Georg-August-University, Gottingen, Germany, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Spiessl, S.M.; Prommer, H.; Licha, T.; Sauter, M.; Zheng, C. A process-based reactive hybrid transport model for coupled discrete conduit–continuum systems. J. Hydrol. 2007, 347, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Hu, B.X.; Davis, H.; Cao, J. Simulating long term nitrate-N contamination processes in the Woodville Karst Plain using CFPv2 with UMT3D. J. Hydrol. 2015, 524, 72–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, T.P.; Gao, Y.; Reimann, T. Nitrate transport in a karst aquifer Numerical model development and source evaluation. J. Hydrol. 2019, 573, 432–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putnam, L.D.; Long, A.J. Numerical Groundwater-Flow Model of the Minnelusa and Madison Hydrogeologic Units in the Rapid City Area, South Dakota; Sci Invest. Rep. 2009-5205; US Geologival Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2009; 81p.
- Sepulveda, N. Simulation of Ground-Water Flow in the Intermediate and Floridan Aquifer System in Peninsular Florida; United States Geological Survey: Tallahassee, FL, USA, 2002.
- Canion, A.; McCloud, L.; Dobberfuhl, D. Predictive modeling of elevated groundwater nitrate in a karstic spring-contributing area using random forests and regression-kriging. Environ. Earth Sci. 2019, 78, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faulkner, G.L. Geohydrology of the Cross-Florida Barge Canal Area with Special Reference to the Ocala Vicinity; United States Geological Survey: Tallahassee, FL, USA, 1973.
- Phelps, G.G. Chemistry of Ground Water in the Silver Springs Basin, Florida, with an Emphasis on Nitrate; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2004.
- FDEP. Nutrient TMDL for Silver Springs, Silver Springs Group, and Upper Silver River (WBIDs 2772A, 2772C, and 2772E); Florida Department of Environmental Protection: Tallahassee, FL, USA, 2012.
- FDEP. Fifty-Year Retrospective Study of the Ecology of Silver Springs, Florida; Florida Department of Environmental Protection: Tallahassee, FL, USA, 2006.
- Durden, D.; Cera, T.; Johnson, N. North Florida Southeast Georgia (NFSEG) Groundwater Flow Model Conceptualization; St. Johns River Water Management District: Palatka, FL, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Y.; Libera, D.; Kibler, K.; Wang, D.; Chang, N.B. Evaluating the performance of BAM-based blanket filter on nitrate reduction in a karst spring. J. Hydrol. 2020, 591, 125491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harbaugh, A.W. MODFLOW-2005, the U.S. Geological Survey Modular Ground-Water Model: The Ground-Water Flow Process, Techniques and Methods 6–A16; United States Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2005. Available online: https://pubs.usgs.gov/tm/2005/tm6A16/PDF.htm (accessed on 12 February 2020).
- Clark, M.M. Transport Modeling for Environmental Engineers and Scientists; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Fandel, C.; Ferre, T.; Chen, Z.; Renard, P.; Goldscheider, N. A model ensemble generator to explore structure uncertainty in karst systems with unmapped conduits. Hydrogeol. J. 2020, 29, 229–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Hartmann, A.; Goldscheider, N. A new approach to evaluate spatiotemporal dynamics of controlling parameters in distributed environmental models. Environ. Model. Softw. 2017, 87, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiessl, S.M.; Sauter, M.; Zheng, C.; Liu, G. Comparison of Two Numerical Methods for Advection in a Pipe Network Coupled to a Continuum Transport Model; IAHS Press Centre for Ecology and Hydrology: Wallingford, Oxfordshire, UK, 2002; pp. 9–68. [Google Scholar]
- Henson, W.R.; Huang, L.; Graham, W.D.; Ogram, A. Nitrate reduction mechanisms and rates in an unconfined eogenetic karst aquifer in two sites with different redox potential. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2017, 122, 1062–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz, B. Sources and Chronology of Nitrate Contamination in Spring Waters, Suwannee River Basin, Florida; Water Resour. Invest. Rep. 1999; U.S. Geological Survey: Tallahassee, FL, USA, 1999; pp. 99–4252.
- Katz, B.G. Sources of nitrate contamination and age of water in large karstic springs of Florida. Environ. Geol. 2004, 46, 689–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz, B.G.; Böhlke, J.K.; Hornsby, H.D. Timescales for nitrate contamination of spring waters, northern Florida, USA. Chem. Geol. 2001, 179, 167–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, M.; Lamsal, J.; Kohrnak, S.L.V. Sources, Transport and Transformations of Nitrate-N in the Florida Environment; Special Publication SJ2007-SP10; St. Johns River Water Management District: Gainesville, FL, USA, 2007; pp. 1–128. [Google Scholar]
- Heffernan, J.B.; Albertin, A.R.; Fork, M.L.; Katz, B.G.; Cohen, M.J. Denitrification and inference of nitrogen sources in the karstic Floridan Aquifer. Biogeosciences 2012, 9, 1671–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Toride, N.; Leu, F.J.; van Genuchten, M.T. The CXTFIT Code for Estimating Transport Parameters from Laboratory or Field Tracer Experiments; Research Report 137; US Salinity Laboratory, USDA, ARS: Riverside, CA, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Schilling, O.S.; Cook, P.G.; Brunner, P. Beyond classical observations in hydrogeology: The advantages of including exchange flux, temperature, tracer concentration, residence time, and soil moisture observations in groundwater model calibration. Rev. Geophys. 2019, 57, 146–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hovorka, S.; Mace, R.E.; Collins, E.W. Regional Distribution of Permeability in the Edwards Aquifer; Edwards Underground Water District: San Antonio, TX, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Worthington, S.R.H. Characteristics of channel networks in unconfined carbonate aquifers. Bulletin 2015, 127, 759–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assari, A.; Mohammadi, Z. Assessing flow paths in a karst aquifer based on multiple dye tracing tests using stochastic simulation and the MODFLOW-CFP code. Hydrogeol. J. 2017, 25, 1679–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, E.M.; Wang, D.; Duranceau, S.J. Modeling anthropogenic boron in groundwater flow and discharge at Volusia Blue Spring (Florida, USA). Hydrogeol. J. 2017, 25, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; Wang, D.; Hagen, S.C.; Medeiros, S.C.; Hall, C.R. Assessing the impacts of sea-level rise and precipitation change on the surficial aquifer in the low-lying coastal alluvial plains and barrier islands, east-central Florida (USA). Hydrogeol. J. 2016, 24, 1791–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, J.M.; Welty, C.; Kemper, J.T.; Groffman, P.M.; Band, L.E. Dynamics of nitrate concentration-discharge patterns in an urban watershed. Water Resour. Res. 2017, 53, 7349–7365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huebsch, M.; Fenton, O.; Horan, B.; Hennessy, D.; Richards, K.G.; Jordan, P.; Goldscheider, N.; Butscher, C.; Blum, P. Mobilization or dilution? Nitrate response of karst springs to high rainfall events. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2014, 18, 4423–4435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harper, H.H. Florida fertilizer ordinances-the good, the bad, and the ugly. In Proceedings of the Florida Stormwater Association 2014 Annual Conference, Fort Myers, FL, USA, 11–13 June 2014. [Google Scholar]
- FDEP. Basin Management Action Plan for the Implementation of Total Maximum Daily Loads Adopted by the Florida Department of Environmental Protection in the Silver Springs Basin Management Area for Silver Springs, Silver Springs Group, and Upper Silver River; Florida Department of Environmental Protection: Tallahassee, FL, USA, 2015.
- Fountain, A.G.; Jacobel, R.W.; Schlichting, R.; Jansson, P. Fractures as the main pathways of water flow in temperature glaciers. Nature 2005, 433, 618–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Parameters | Conduit Index | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | |
| Diameter (m) | 6.0 | 6.0 | 3.0 | 3.0 | 1.5 | 6.0 | 6.0 |
| Conductance (m2/day) | 0.45 | 0.45 | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.20 | 0.45 | 0.45 |
| Roughness height (m) | 0.05 | ||||||
| Tortuosity | 1.5 | ||||||
| EPM Steady-State | CFPv2 Steady-State | EPM Transient | CFPv2 Transient | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Calibration | Validation | Calibration | Validation | |||
| Head RMSE (m) | 0.36 | 0.28 | 0.52 | 0.53 | 0.33 | 0.29 |
| Relative error of head | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.028 | 0.031 | 0.018 | 0.016 |
| Relative error of spring discharge | 0.014 | 0.011 | 0.16 | 0.07 | 0.08 | 0.06 |
| NSE | N/A | N/A | 0.59 | 0.77 | 0.85 | 0.84 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, Y.; Xu, Z.; Li, S.; Yu, W. Modeling Monthly Nitrate Concentration in a Karst Spring with and without Discrete Conduit Flow. Water 2022, 14, 1622. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14101622
Gao Y, Xu Z, Li S, Yu W. Modeling Monthly Nitrate Concentration in a Karst Spring with and without Discrete Conduit Flow. Water. 2022; 14(10):1622. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14101622
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Yuan, Zexuan Xu, Shen Li, and Wenjie Yu. 2022. "Modeling Monthly Nitrate Concentration in a Karst Spring with and without Discrete Conduit Flow" Water 14, no. 10: 1622. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14101622
APA StyleGao, Y., Xu, Z., Li, S., & Yu, W. (2022). Modeling Monthly Nitrate Concentration in a Karst Spring with and without Discrete Conduit Flow. Water, 14(10), 1622. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14101622





