Probabilistic Minimum Night Flow Estimation in Water Distribution Networks and Comparison with the Water Balance Approach: Large-Scale Application to the City Center of Patras in Western Greece
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data
3. Methodology
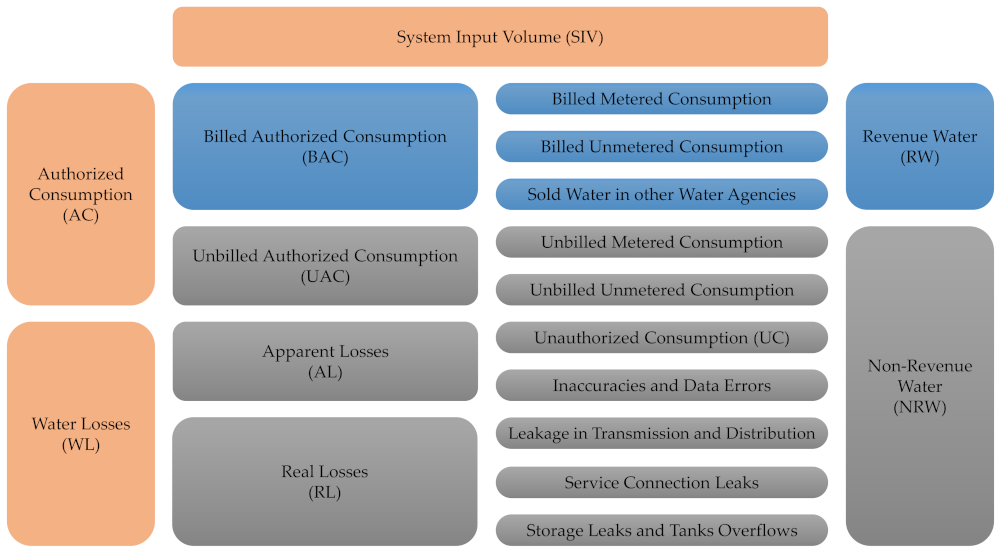
3.1. Water Balance (Top-Down) Approach
3.2. Minimum Night Flow (Bottom-Up) Approach
4. Application and Results
4.1. Water Balance (Top-Down) Approach
4.2. Minimum Night Flow (Bottom-Up) Approach
4.3. Comparison between Approaches
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AC | Authorized Consumption |
| AL | Apparent Losses |
| BABE | Bursts and Background Estimates |
| BAC | Billed Authorized Consumption |
| DEYAP | Municipal Enterprise of Water Supply and Sewerage of the City of Patras |
| DMA | District Metered Area |
| ePDF | empirical Probability Density Function |
| FRP | Fiber-Reinforced Polymer |
| HDPE | High Density Polyethylene |
| IWA | International Water Association |
| MNF | Minimum Night Flow |
| N1 | Leakage exponent |
| NDF | Night-Day Factor |
| NNF | Net Night Flow |
| NRW | Non-Revenue Water |
| Probability Density Function | |
| PE | Polyethylene |
| Pi | Mean pressure during each hour i of the day |
| PMA | Pressure Management Area |
| PMNF | Mean night pressure during the MNF estimation period |
| Ps,d | Pressure set point during day |
| Ps,n | Pressure set point during night |
| PVC | Polyvinyl Chloride |
| RL | Real Losses |
| RW | Revenue Water |
| SIV | System Input Volume |
| SWN | Smart Water Network |
| UAC | Unbilled Authorized Consumption |
| UARL | Unavoidable Annual Real Losses |
| UC | Unauthorized Consumption |
| UNC | Users’ Night Consumption |
| WB | Water Balance |
| WDN | Water Distribution Network |
| WL | Water Losses |
| μMN | Ensemble mean of the individual MNF estimates |
| σMNF | Standard deviation of the individual MNF estimates |
References
- Lambert, A.; Hirner, W. Losses from Water Supply Systems: A Standard Terminology and Recommended Performance Measures; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Lambert, A.; Charalambous, B.; Fantozzi, M.; Kovac, J.; Rizzo, A.; Galea, S. 14 years experience of using IWA best practice water balance and water loss performance indicators in Europe. In Proceedings of the IWA Specialized Conference: Water Loss, Vienna, Austria, 30 March–2 April 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter, T.; Lambert, A.; McKenzie, R. Applying the IWA approach to water loss performance indicators in Australia. Water Supply 2003, 3, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, R.; Marques, J.A.S.; Sousa, J. Estimation of the benefits yielded by pressure management in water distribution systems. Urban Water J. 2011, 8, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkasseh, J.M.A.; Adlan, M.N.; Abustan, I.; Aziz, H.A.; Hanif, A.B.M. Applying Minimum Night Flow to Estimate Water Loss Using Statistical Modeling: A Case Study in Kinta Valley, Malaysia. Water Resour. Manag. 2013, 27, 1439–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, W.; Suresh, M.A.; Smith, L.; Ostfeld, A.; Stoleru, R.; Rasekh, A.; Banks, M.K. Mobile sensor networks for optimal leak and backflow detection and localization in municipal water networks. Environ. Model. Softw. 2016, 80, 306–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adedeji, K.B.; Hamam, Y.; Abe, B.T.; Abu-Mahfouz, A.M. Towards Achieving a Reliable Leakage Detection and Localization Algorithm for Application in Water Piping Networks: An Overview. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 20272–20285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, A. International Report: Water losses management and techniques. Water Supply 2002, 2, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petroulias, N.; Foufeas, D.; Bougoulia, E. Estimating Water Losses and Assessing Network Management Intervention Scenarios: The Case Study of the Water Utility of the City of Drama in Greece. Procedia Eng. 2016, 162, 559–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beuken, R.H.S.; Lavooij, C.S.W.; Bosch, A.; Schaap, P.G. Low Leakage in the Netherlands Confirmed. In Proceedings of the Water Distribution Systems Analysis Symposium, Cincinnati, OH, USA, 27–30 August 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liemberger, R.; Wyatt, A. Quantifying the global non-revenue water problem. Water Supply 2018, 19, 831–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, A.; Lalonde, A. Using practical predictions of Economic Intervention Frequency to calculate Short-run Economic Leakage Level, with or without Pressure Management. In Proceedings of the IWA Specialised Conference ‘Leakage 2005’, Halifax, NS, Canada, 12–14 September 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Mazzolani, G.; Berardi, L.; Laucelli, D.; Martino, R.; Simone, A.; Giustolisi, O. A Methodology to Estimate Leakages in Water Distribution Networks Based on Inlet Flow Data Analysis. Procedia Eng. 2016, 162, 411–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ociepa, E.; Mrowiec, M.; Deska, I. Analysis of Water Losses and Assessment of Initiatives Aimed at Their Reduction in Selected Water Supply Systems. Water 2019, 11, 1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulos, P.F.; Aboujaoude, A.S. Managing leaks using flow step-testing, network modeling, and field measurement. J. Am. Water Work. Assoc. 2011, 103, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutikanga, H.E.; Sharma, S.K.; Vairavamoorthy, K. Methods and Tools for Managing Losses in Water Distribution Systems. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2013, 139, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosetlhe, T.C.; Hamam, Y.; Du, S.; Monacelli, E. Appraising the Impact of Pressure Control on Leakage Flow in Water Distribution Networks. Water 2021, 13, 2617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, D.; Trow, S. Calculating economic levels of leakage. In Proceedings of the IWA Water Loss 2005 Conference, Halifax, NS, Canada, 12–14 September 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Kanakoudis, V.; Tsitsifli, S.; Papadopoulou, A. Integrating the Carbon and Water Footprints’ Costs in the Water Framework Directive 2000/60/EC Full Water Cost Recovery Concept: Basic Principles Towards Their Reliable Calculation and Socially Just Allocation. Water 2012, 4, 45–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ávila, C.; Sánchez-Romero, F.-J.; López-Jiménez, P.; Pérez-Sánchez, M. Leakage Management and Pipe System Efficiency. Its Influence in the Improvement of the Efficiency Indexes. Water 2021, 13, 1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heryanto, T.; Sharma, S.; Daniel, D.; Kennedy, M. Estimating the Economic Level of Water Losses (ELWL) in the Water Distribution System of the City of Malang, Indonesia. Sustainability 2021, 13, 6604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashton, C.; Hope, V. Environmental valuation and the economic level of leakage. Urban. Water 2001, 3, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanakoudis, V.; Gonelas, K. The Optimal Balance Point between NRW Reduction Measures, Full Water Costing and Water Pricing in Water Distribution Systems. Alternative Scenarios Forecasting the Kozani’s WDS Optimal Balance Point. Procedia Eng. 2015, 119, 1278–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molinos-Senante, M.; Mocholí-Arce, M.; Sala-Garrido, R. Estimating the environmental and resource costs of leakage in water distribution systems: A shadow price approach. Sci. Total. Environ. 2016, 568, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pearson, D. Standard Definitions for Water Losses; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2019; ISBN 9781789060881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, S.; Charalambous, B. Leak Detection: Technology and Implementation; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2013; ISBN 9781780404707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberascher, M.; Möderl, M.; Sitzenfrei, R. Water Loss Management in Small Municipalities: The Situation in Tyrol. Water 2020, 12, 3446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, A. Accounting for Losses: The Bursts and Background Concept. Water Environ. J. 1994, 8, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farley, M.; Trow, S. Losses in Water Distribution Networks: A Practitioners’ Guide to Assessment, Monitoring and Control; Water Intelligence; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2005; Volume 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liemberger, R.; Farley, M. Developing a nonrevenue water reduction strategy Part 1: Investigating and assessing water losses. In Proceedings of the IWA WWC 2004 Conference, Marrakech, Morocco, 19–24 September 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Hunaidi, O.; Brothers, K. Night flow analysis of pilot DMAs in Ottawa. In Proceedings of the Water Loss Specialist Conference, International Water Association, Bucharest, Romania, 23 September 2007; pp. 32–46. [Google Scholar]
- Amoatey, P.K.; Minke, R.; Steinmetz, H. Leakage estimation in developing country water networks based on water balance, minimum night flow and component analysis methods. Water Pr. Technol. 2018, 13, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AWWA. Water Audits and Loss Control Programs Manual of Water Supply Practices, M36; American Water Works Association: Denver, CO, USA, 2009; ISBN 978–1-58321–631–6. [Google Scholar]
- Lambert, A.; Taylor, R. Water Loss Guidelines–Water New Zealand; Water New Zealand: Wellington, New Zealand, 2010; ISBN 978–0-9941243–2-6. [Google Scholar]
- Mutikanga, H.E.; Sharma, S.K.; Vairavamoorthy, K. Assessment of apparent losses in urban water systems. Water Environ. J. 2011, 25, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Washali, T.M.; Sharma, S.K.; Kennedy, M.D. Alternative Method for Nonrevenue Water Component Assessment. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2018, 144, 04018017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, A.; Brown, T.G.; Takizawa, M.; Weimer, D. A review of performance indicators for real losses from water supply systems. J. Water Supply Res. Technol.-Aqua 1999, 48, 227–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, A. Ten years experience in using the UARL formula to calculate infrastructure leakage index. In Proceedings of the IWA Specialized Conference: Water Loss 2009, Cape Town, South Africa, 26–29 April 2009; pp. 189–196. [Google Scholar]
- Bhagat, S.K.; Tiyasha; Welde, W.; Tesfaye, O.; Tung, T.M.; Al-Ansari, N.; Salih, S.Q.; Yaseen, Z.M. Evaluating Physical and Fiscal Water Leakage in Water Distribution System. Water 2019, 11, 2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Washali, T.; Sharma, S.; Kennedy, M. Methods of Assessment of Water Losses in Water Supply Systems: A Review. Water Resour. Manag. 2016, 30, 4985–5001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Washali, T.; Sharma, S.; Al-Nozaily, F.; Haidera, M.; Kennedy, M. Modelling the Leakage Rate and Reduction Using Minimum Night Flow Analysis in an Intermittent Supply System. Water 2019, 11, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serafeim, A.V.; Kokosalakis, G.; Deidda, R.; Karathanasi, I.; Langousis, A. Probabilistic estimation of minimum night flow in water distribution networks: Large-scale application to the city of Patras in western Greece. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2021, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsakiris, G.; Charalambous, B. Management of Water Supply Networks. In Hydraulic Works Design and Management; Urban Hydraulic Works, Tsakiris, G., Eds.; Symmetria: Athens, Greece, 2010; Volume 1, pp. 445–482. (In Greek) [Google Scholar]
- Al-Washali, T.; Sharma, S.; Lupoja, R.; Al-Nozaily, F.; Haidera, M.; Kennedy, M. Assessment of water losses in distribution networks: Methods, applications, uncertainties, and implications in intermittent supply. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2020, 152, 104515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, D.; Memon, F.A. Water Demand Management; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2005; p. 384. ISBN 1843390787. [Google Scholar]
- Adlan, M.N.; Aziz, H.A.; Razib, N.M.; Hanif, A.B.M. The effects of pressure reduction on Non-Revenue Water in water reticulation system. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Water Conservation in Arid Regions, Kingabdul Aziz University, Jeddah, Saudi Arabia, 28 April 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Tabesh, M.; Yekta, A.H.A.; Burrows, R. An Integrated Model to Evaluate Losses in Water Distribution Systems. Water Resour. Manag. 2009, 23, 477–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, P.B.; Girol, G.V.; Abe, N.; Propato, M. Night Flow Analysis and Modeling for Leakage Estimation in a Water Distribution System, Integrating Water Systems (CCWI 2010); Taylor & Francis Group: London, UK, 2010; ISBN 978–0-415–54851–9. [Google Scholar]
- Loureiro, D.; Borba, R.; Rebelo, M.; Alegre, H.; Coelho, S.; Covas, D.; Amado, C.; Pacheco, A.; Pina, A. Analysis of household night-time consumption, 10th international conference on computing and control for the water industry. In Proceedings of the CCWI 2009, Integrating Water Systems, Sheffield, UK, 1–3 September 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Brandt, M.J.; Johnson, K.M.; Jonhson, A.J.; Elphinston, D.; Ratnayaka, D.J. Twort’s Water Supply, 7th ed.; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makaya, E. Predictive Leakage Estimation using the Cumulative Minimum Night Flow Approach. Am. J. Water Resour. 2017, 5, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negharchi, S.M.; Shafaghat, R. Leakage estimation in water networks based on the BABE and MNF analyses: A case study in Gavankola village, Iran. Water Supply 2020, 20, 2296–2310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzola, I.; Alvisi, S.; Franchini, M. Analysis of MNF and FAVAD Model for Leakage Characterization by Exploiting Smart-Metered Data: The Case of the Gorino Ferrarese (FE-Italy) District. Water 2021, 13, 643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karathanasi, I.; Papageorgakopoulos, C. Development of a Leakage Control System at the Water Supply Network of the City of Patras. Procedia Eng. 2016, 162, 553–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serafeim, A.V. Statistical Estimation of Water Losses in the Water Distribution Network (WDN) of the City of Patras. Master’s Thesis, University of Patras, Patra, Greece, 2018. (In Greek). [Google Scholar]
- Bisselink, B.; Bernhard, J.; Gelati, E.; Adamovic, M.; Guenther, S.; Mentaschi, L.; De Roo, A. Impact of a Changing Climate, Land Use, and Water Usage on Europe’s Water Resources; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2018; ISBN 978–92–79–80287–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzanakakis, V.A.; Angelakis, A.N.; Paranychianakis, N.V.; Dialynas, Y.G.; Tchobanoglous, G. Challenges and Opportunities for Sustainable Management of Water Resources in the Island of Crete, Greece. Water 2020, 12, 1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seago, C.; Bhagwan, J.; McKenzie, R. Benchmarking leakage from water reticulation systems in South Africa. Water SA 2004, 30, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Arregui, F.; Cabrera, E.; Cobacho, R.; García-Serra, J. Reducing Apparent Losses Caused by Meters Inaccuracies. Water Pr. Technol. 2006, 1, wpt2006093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alegre, H.; Baptista, J.M.; Cabrera, E.; Cubillo, F.; Duarte, P.; Hirner, W.; Merkel, W.; Parena, R. Performance Indicators for Water Supply Services, 2nd ed.; Water Intelligence Online; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2013; Volume 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farley, M. Leakage management and control: A best practice training manual, World Health Organization, Water, Sanitation and Health Team & Water Supply and Sanitation Collaborative Council. 2001. Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/66893 (accessed on 2 November 2020).
- Hamilton, S.; McKenzie, R. Water Management and Water Loss; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2014; p. 250. ISBN 9781780406350. [Google Scholar]
- Morrison, J.; Tooms, S.; Rogers, D. DMA Management Guidance Notes; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- McKenzie, R.S.; Wegelin, W.A.; Meyer, N. Water Demand Management Cookbook; Rand Water: Johannesburg, South Africa, 2003; ISSN 062030734X. [Google Scholar]
- Fallis, P.; Hübschen, K.; Oertlé, E.; Ziegler, D.; Klingel, P.; Baader, A.J.; Trujillo, R.; Laures, C. Guidelines for Water Loss Reduction: A Focus on Pressure Management; Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ) GmbH: Eschborn, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Wyatt, A.S. Non-Revenue Water: Financial Model for Optimal Management in Developing Countries; RTI International Press: Research Triangle Park, NC, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
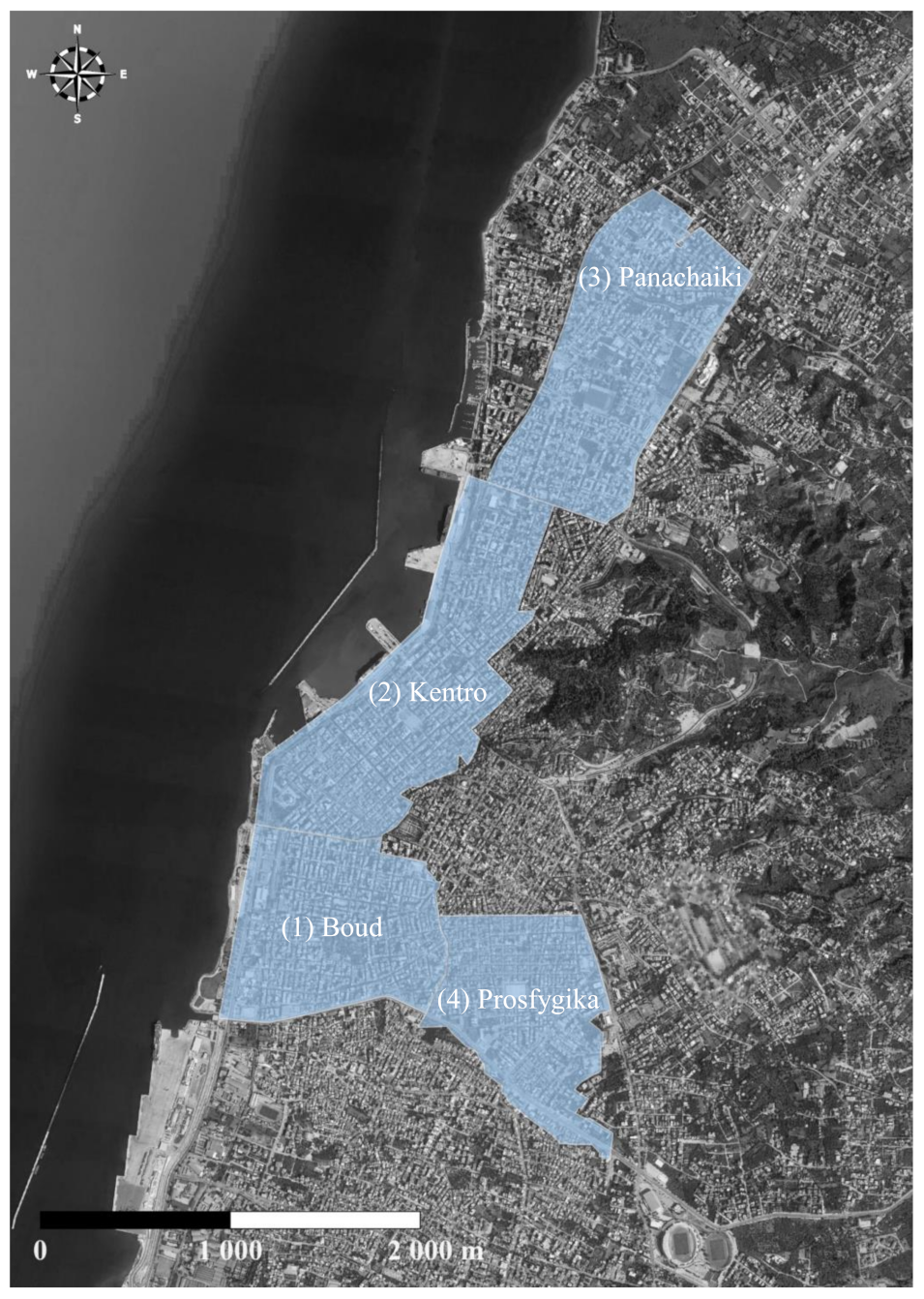

| PMA Number and Name | Area (m2) | Pipeline Length (m) | Population | Hydrometers |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1) Boud | 952,568 | 44,954 | 15,362 | 10,586 |
| (2) Kentro | 1,206,867 | 62,174 | 13,992 | 16,454 |
| (3) Panachaiki | 1,184,262 | 51,703 | 18,003 | 11,983 |
| (4) Prosfygika | 801,557 | 43,246 | 10,657 | 5206 |
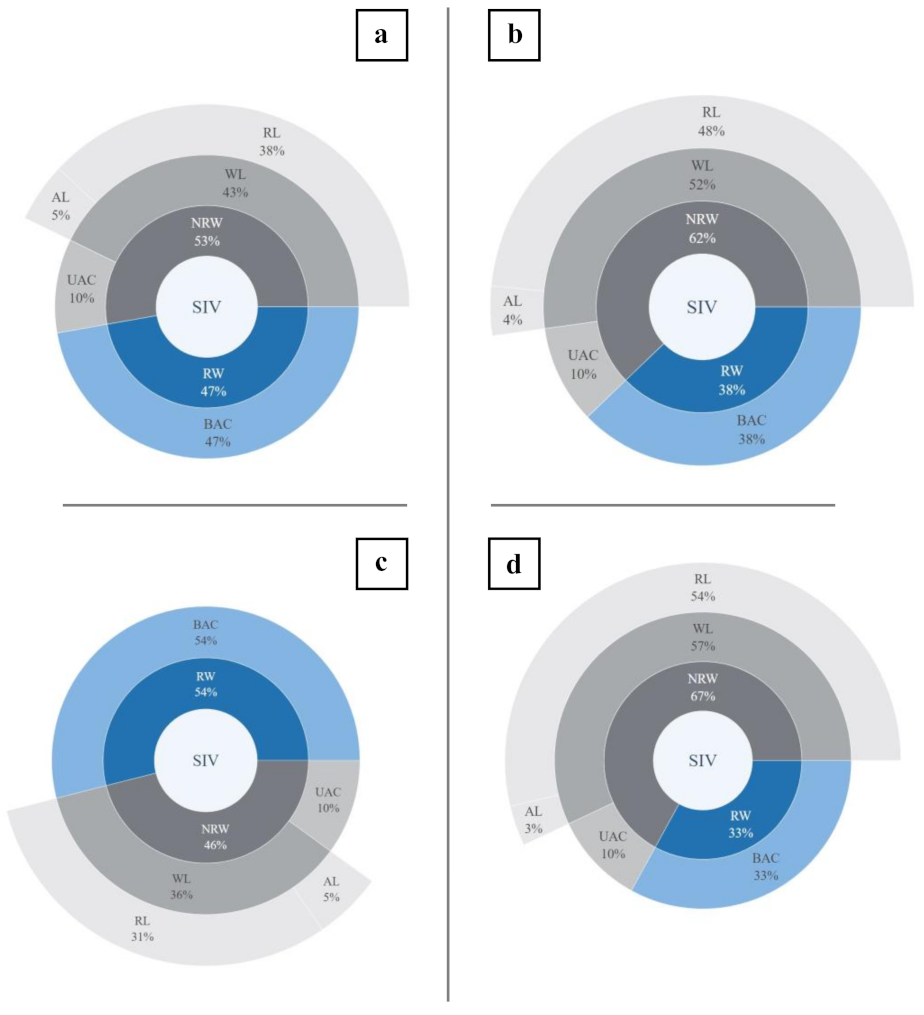
| PMA Number and Name | SIV (m3) | BAC (m3) | NRW (m3) | UAC (m3) | WL (m3) | AL (m3) | RL (m3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1) Boud | 638,400 | 344,379 | 294,020 | 63,840 | 230,180 | 34,438 | 195,742 |
| (2) Kentro | 467,134 | 154,056 | 313,078 | 46,713 | 266,365 | 15,406 | 250,959 |
| (3) Panachaiki | 1,210,274 | 457,614 | 752,660 | 121,027 | 631,632 | 45,761 | 585,871 |
| (4) Prosfygika | 555,293 | 262,232 | 293,062 | 55,529 | 237,532 | 26,223 | 211,309 |
| PMA Number and Name | μMNF (L/s) | σMNF (L/s) | 95% Confidence Intervals (L/s) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower Limit | Upper Limit | |||
| (1) Boud | 26.68 | 0.55 | 26.58 | 26.78 |
| (2) Kentro | 69.85 | 3.91 | 69.15 | 70.55 |
| (3) Panachaiki | 18.81 | 2.24 | 18.41 | 19.21 |
| (4) Prosfygika | 27.80 | 1.27 | 27.57 | 28.03 |
| PMA Number and Name | MNF 95% Lower [Upper] Limit (L/s) | UNC Lower [Upper] Limit (L/s) | NNF Lower [Upper] Limit (L/s) | NDF | RL Lower [Upper] Limit (m3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1) Boud | 26.58 [26.78] | 4.414 [4.444] | 22.18 [22.34] | 24.00 | 227,905 [229,653] |
| (2) Kentro | 69.15 [70.55] | 21.13 [21.55] | 48.02 [49.00] | 27.24 | 561,231 [572,685] |
| (3) Panachaiki | 18.41 [19.21] | 0.500 [0.500] | 17.91 [18.71] | 24.12 | 185,068 [193,334] |
| (4) Prosfygika | 27.57 [28.03] | 4.432 [4.500] | 23.14 [23.53] | 27.52 | 272,817 [277,427] |
| PMA Number and Name | Ps,d (atm) | Ps,n (atm) |
|---|---|---|
| (1) Boud | 2.30 | 2.30 |
| (2) Kentro | 3.06 | 3.54 |
| (3) Panachaiki | 6.87 | 6.91 |
| (4) Prosfygika | 3.39 | 3.96 |
| PMA Number and Name | WB RL (%) | MNF RL Low Limit (%) | MNF RL Upper Limit (%) | Absolute Relative Difference (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1) Boud | 38.05 | 41.04 | 41.36 | 7.28–7.99 |
| (2) Kentro | 48.41 | 46.37 | 47.32 | 2.30–4.39 |
| (3) Panachaiki | 30.66 | 28.99 | 30.28 | 1.25–5.77 |
| (4) Prosfygika | 53.72 | 58.40 | 59.39 | 8.01–9.54 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Serafeim, A.V.; Kokosalakis, G.; Deidda, R.; Karathanasi, I.; Langousis, A. Probabilistic Minimum Night Flow Estimation in Water Distribution Networks and Comparison with the Water Balance Approach: Large-Scale Application to the City Center of Patras in Western Greece. Water 2022, 14, 98. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14010098
Serafeim AV, Kokosalakis G, Deidda R, Karathanasi I, Langousis A. Probabilistic Minimum Night Flow Estimation in Water Distribution Networks and Comparison with the Water Balance Approach: Large-Scale Application to the City Center of Patras in Western Greece. Water. 2022; 14(1):98. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14010098
Chicago/Turabian StyleSerafeim, Athanasios V., George Kokosalakis, Roberto Deidda, Irene Karathanasi, and Andreas Langousis. 2022. "Probabilistic Minimum Night Flow Estimation in Water Distribution Networks and Comparison with the Water Balance Approach: Large-Scale Application to the City Center of Patras in Western Greece" Water 14, no. 1: 98. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14010098
APA StyleSerafeim, A. V., Kokosalakis, G., Deidda, R., Karathanasi, I., & Langousis, A. (2022). Probabilistic Minimum Night Flow Estimation in Water Distribution Networks and Comparison with the Water Balance Approach: Large-Scale Application to the City Center of Patras in Western Greece. Water, 14(1), 98. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14010098







