Applicability Study of Hydrological Period Identification Methods: Application to Huayuankou and Lijin in the Yellow River Basin, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (i)
- The conditions under which such methods are applicable and;
- (ii)
- How the consequences of such methods vary.
2. Study Area and Data
3. Methodology
3.1. The Mann–Kendall Test
3.2. Fourier Methods
3.2.1. Periodogram
3.2.2. Autocorrelation Analysis (AA)
3.2.3. Maximum Entropy Spectral Analysis (MESA)
3.3. Wavelet Analysis
3.4. The Hilbert–Huang Transform
4. Results
4.1. Period Identification Results
- (i)
- Periods of less than 24 months (which are recorded directly) and;
- (ii)
- Periods of 24 months or more.
- (i)
- The results of periods identification obtained from HHS are relatively consistent to those obtained from LHS and
- (ii)
- The second-category periods (24 months or more) in the monthly series correspond reasonably well with those in the annual series.
4.2. Period Validation
5. Discussion
5.1. Performance of Five Methods
5.2. Theoretical Analysis
5.3. Artificial Influences
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Oki, T.; Kanae, S. Global hydrological cycles and world water resources. Science 2006, 313, 1068–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, T.; Xiong, L.H.; Xu, C.Y.; Gippel, C.J.; Guo, S.L.; Liu, P. Return period and risk analysis of nonstationary low–flow series under climate change. J. Hydrol. 2015, 527, 234–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.; You, Y.; Kim, S.; Kim, K.T.; Kim, H.S. Decomposition of Water Level Time Series of a Tidal River into Tide, Wave and Rainfall–Runoff Components. Water 2018, 10, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jukić, D.; Denić–Jukić, V. Partial spectral analysis of hydrological time series. J. Hydrol. 2011, 400, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.L.; Wang, C.Y.; Liang, G.X.; Cui, Y.L.; Zhang, Q.L. Influence of Land Use Change on Hydrological Cycle: Application of SWAT to Su–Mi–Huai Area in Beijing, China. Water 2020, 12, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worqlul, A.W.; Taddele, Y.D.; Ayana, E.K.; Jeong, J.; Adem, A.A.; Gerik, T. Impact of Climate Change on Streamflow Hydrology in Headwater Catchments of the Upper Blue Nile Basin, Ethiopia. Water 2018, 10, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Hessel, R.; Mu, X.M.; Maroulis, J.; Zhao, G.J.; Geissen, V.; Ritsema, C. Distinguishing the impacts of human activities and climate variability on runoff and sediment load change based on paired periods with similar weather conditions: A case in the Yan River, China. J. Hydrol. 2015, 527, 884–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.; Huang, B.S.; Liu, K.S.; Chen, H.; Liu, F.; Qiu, J.; Yang, J.X. Using the wavelet transform to detect temporal variations in hydrological processes in the Pearl River, China. Quat. Int. 2017, 440, 52–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, R.T.; Newhouse, M.W.; Dettinger, M.D. A methodology to asess relations between climatic variability and variations in hydrologic time series in the southwestern United States. J. Hydrol. 2004, 287, 252–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.H.; Mei, Y.; She, D.X.; Li, J.Q. Chaotic Bayesian optimal prediction method and its application in hydrological time series. Comput. Math. Appl. 2011, 61, 1975–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.Y.; Huang, Q.; Chang, J.X.; Liu, S.Y.; Wang, Y.M. Period analysis of hydrologic series through moving–window correlation analysis method. J. Hydrol. 2016, 538, 278–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stojković, M.; Plavšić, J.; Prohaska, S. Annual and seasonal discharge prediction in the middle Danube River basin based on a modified TIPS (Tendency, Intermittency, Periodicity, Stochasticity) methodology. J. Hydrol. Hydromech. 2017, 65, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danandeh Mehr, A.; Kahya, E. A Pareto–optimal moving average multigene genetic programming model for daily streamflow prediction. J. Hydrol. 2017, 549, 603–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, Y.F.; Wang, Z.G.; Liu, C.M. Period identification in hydrologic time series using empirical mode decomposition and maximum entropy spectral analysis. J. Hydrol. 2012, 424–425, 154–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Deng, Y.R. Stochastic Hydrology; Chengdu University of Science and Technology: Chengdu, China, 1988. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Huang, N.E.; Wu, Z.H.; Long, S.R.; Arnold, K.C.; Chen, X.Y.; Blank, K. On instantaneous frequency. Adv. Adapt. Data Anal. 2009, 1, 177–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kay, S.M.; Marple, S.L. Spectrum analysis—A modern perspective. Proc. IEEE 1981, 69, 1380–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padmanabhan, G.; Ramachandra Rao, A. Maximum entropy spectral analysis of hydrologic data. Water Resour. Res. 1988, 24, 1519–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Übeyli, E.D.; Güler, İ. Spectral analysis of internal carotid arterial Doppler signals using FFT, AR, MA, and ARMA methods. Comput. Biol. Med. 2004, 34, 293–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Amico, K.H. Practical utilization of power spectrum estimation techniques. In Proceedings of the IEEE Region 5 Conference, Colorado Springs, CO, USA, 21–23 March 1988; pp. 107–111. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, V.P. The use of entropy in hydrology and water resources. Hydrol. Processes 1997, 11, 587–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herring, R.W. The cause of line splitting in burg maximum–entropy spectral analysis. IEEE Trans. Acoust. 1980, 28, 692–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigozo, N.R.; Echer, E.; Nordemann, D.J.R.; Vieira, L.E.A.; De Faria, H.H. Comparative study between four classical spectral analysis methods. Appl. Math. Comput. 2005, 168, 411–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, Y.F.; Wang, D. New method for estimating periods in hydrologic series data. In Proceedings of the 2008 Fifth International Conference on Fuzzy Systems and Knowledge Discovery, Jinan, China, 18–20 October 2008; pp. 645–649. [Google Scholar]
- Andreo, B.; Jiménez, P.; Durán, J.J.; Carrasco, F.; Vadillo, I.; Mangin, A. Climatic and hydrological variations during the last 117–166 years in the south of the Iberian Peninsula, from spectral and correlation analyses and continuous wavelet analyses. J. Hydrol. 2006, 324, 24–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, G. Time series, periodograms, and significance. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 1999, 104, 10355–10368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, Y.F.; Wang, D.; Wu, J.C.; Zhu, Q.P.; Wang, L. The relation between periods’ identification and noises in hydrologic series data. J. Hydrol. 2009, 368, 165–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Partal, T.; Kişi, Ö. Wavelet and neuro–fuzzy conjunction model for precipitation forecasting. J. Hydrol. 2007, 342, 199–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labat, D. Wavelet analysis of the annual discharge records of the world’s largest rivers. Adv. Water Resour. 2008, 31, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labat, D. Recent advances in wavelet analyses: Part 1. A review of concepts. J. Hydrol. 2005, 314, 275–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altunkaynak, A.; Nigussie, T.A. Monthly water consumption prediction using season algorithm and wavelet transform–based models. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2017, 143, 4017011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maheswaran, R.; Khosa, R. Comparative study of different wavelets for hydrologic forecasting. Comput. Geosci. 2012, 46, 284–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nourani, V.; Hosseini Baghanam, A.; Adamowski, J.; Kisi, O. Applications of hybrid wavelet–Artificial Intelligence models in hydrology: A review. J. Hydrol. 2014, 514, 358–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, N.E.; Shen, Z.; Long, S.R.; Wu, M.C.; Shih, H.H.; Zheng, Q.; Yen, N.C.; Tung, C.C.; Liu, H.H. The empirical mode decomposition and the Hilbert spectrum for nonlinear and non–stationary time series analysis. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 1998, 454, 903–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.C.; Wang, Y.H.; You, G.J.Y.; Wei, C.C. Comparison of methods for non–stationary hydrologic frequency analysis: Case study using annual maximum daily precipitation in Taiwan. J. Hydrol. 2017, 545, 197–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castino, F.; Bookhagen, B.; Strecker, M.R. Oscillations and trends of river discharge in the southern Central Andes and linkages with climate variability. J. Hydrol. 2017, 555, 108–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Qiu, X.; Luo, J.P.; Gu, P.Q.; Liu, Y.L. Analysis of temperature time series based on Hilbert–Huang Transform. J. Hydrodyn. Ser. B 2015, 27, 587–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.H.; Huang, N.E. Ensemble empirical mode decomposition: A noise–assisted data analysis method. Adv. Adapt. Data Anal. 2009, 1, 1–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Yang, J.; Liu, G.; Yao, R.; Wang, X. Improvement for the multi–scale periodic characteristics revealing of precipitation signals and its impact assessment on soil hydrological process by combining HHT and CWT approaches. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 15, 393–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.S.; Jin, J.L.; Li, Y.Q. Advances in stochastic simulation of Hydrology. Adv. Water Sci. 2007, 18, 768–775, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Ishak, E.H.; Rahman, A.; Westra, S.; Sharma, A.; Kuczera, G. Evaluating the non–stationarity of Australian annual maximum flood. J. Hydrol. 2013, 494, 134–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamed, K.H. Trend detection in hydrologic data: The Mann–Kendall trend test under the scaling hypothesis. J. Hydrol. 2008, 349, 350–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuster, A. On the investigation of hidden periodicities with application to a supposed 26 day period of meteorological phenomena. Terr. Magn. 1898, 3, 13–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuster, A. On the periodicities of sunspots. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A Contain. Pap. Math. Phys. Character 1906, 206, 69–100. [Google Scholar]
- Gadiyar, H.G.; Padma, R. Ramanujan–Fourier series, the Wiener–Khintchine formula and the distribution of prime pairs. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 1999, 269, 503–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, L.; Miao, C.Y.; Borthwick, A.G.L.; Duan, Q.Y. Wavelet–based variability of Yellow River discharge at 500-, 100-, and 50-year timescales. Gondwana Res. 2017, 49, 94–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrence, C.; Compo, G.P. A practical guide to wavelet analysis. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1998, 79, 61–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, N.E.; Wu, Z.H. A review on Hilbert–Huang transform: Method and its applications to geophysical studies. Rev. Geophys. 2008, 46, RG2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, Y.F.; Wang, D.; Wu, J.C.; Zhu, Q.P. Wavelet cross–correlation method for hydrologic time series analysis. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2010, 41, 1272–1279, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Zhu, Y.S. Research on cryptic period of hydrologic time series based on MEM1 spectral analysis. Hydrology 2002, 22, 19–23, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Hao, Z.X.; Zheng, J.Y.; Ge, Q.S. Precipitation cycles in the middle and lower Yellow River. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2007, 62, 537–544, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.N.; Meng, W.G.; Wang, A.Y.; Liu, L.M.; Feng, R.Q.; Hou, E.B. Climatic characteristics of the intensity and position of the subtropical high in the Western Pacific. Trop. Geogr. 2003, 23, 35–39. [Google Scholar]
- Han, Y.Z.; Ma, L.H.; Yin, Z.Q. Time variation of periodic components of polar motion amplitude. Prog. Geophys. 2006, 21, 798–801, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Stager, J.C.; Ruzmaikin, A.; Conway, D.; Verburg, P.; Mason, P.J. Sunspots, El Niño, and the levels of Lake Victoria, East Africa. J. Geophys. Res. 2007, 112, D15106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narasimha, R.; Bhattacharyya, S. A wavelet cross–spectral analysis of solar–ENSO–rainfall connections in the Indian monsoons. Appl. Comput. Harmon. Anal. 2010, 28, 285–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, A.; Massei, N.; Laignel, B. A synthesis of the time–scale variability of commonly used climate indices using continuous wavelet transform. Glob. Planet. Change 2010, 78, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.G.; Cheng, B.Y.; Li, R. Multitime scale correlations between runoff and regional climate variations in the source region of the Yellow River. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2009, 64, 117–127, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Groth, A.; Ghil, M. Monte Carlo singular spectrum analysis (SSA) revisited: Detecting oscillator clusters in multivariate datasets. J. Clim. 2015, 28, 7873–7893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, M.E.; Lees, J.M. Robust estimation of background noise and signal detection in climatic time series. Clim. Chang. 1996, 33, 409–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, Y.F.; Xie, P.; Gu, H.T.; Li, X.X. Discussion on several major issues in the studies of hydrological nonstationarity. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2017, 62, 254–261, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Liavas, A.P.; Regalia, P.A. On the behavior of information theoretic criteria for model order selection. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2001, 49, 1689–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
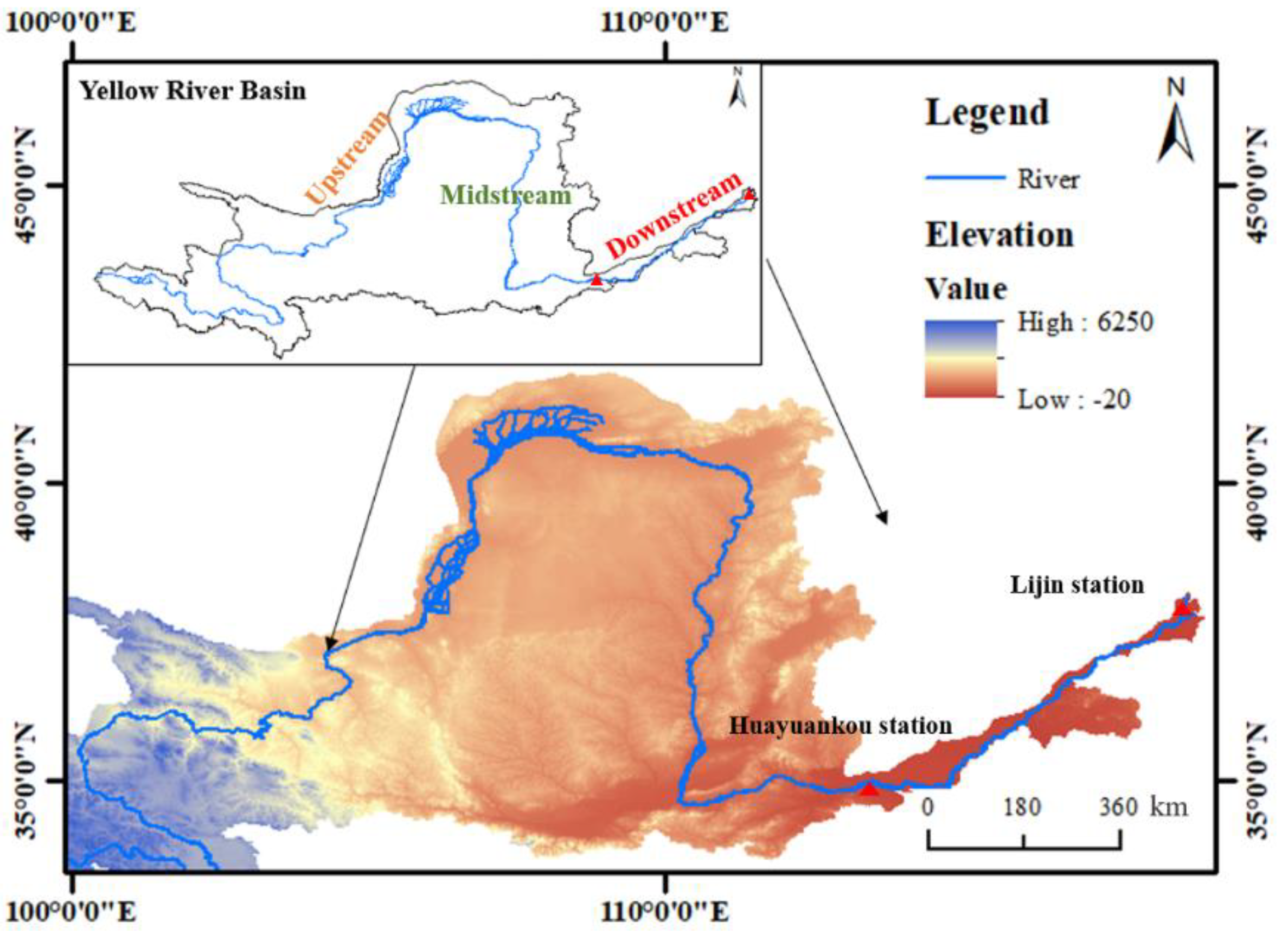
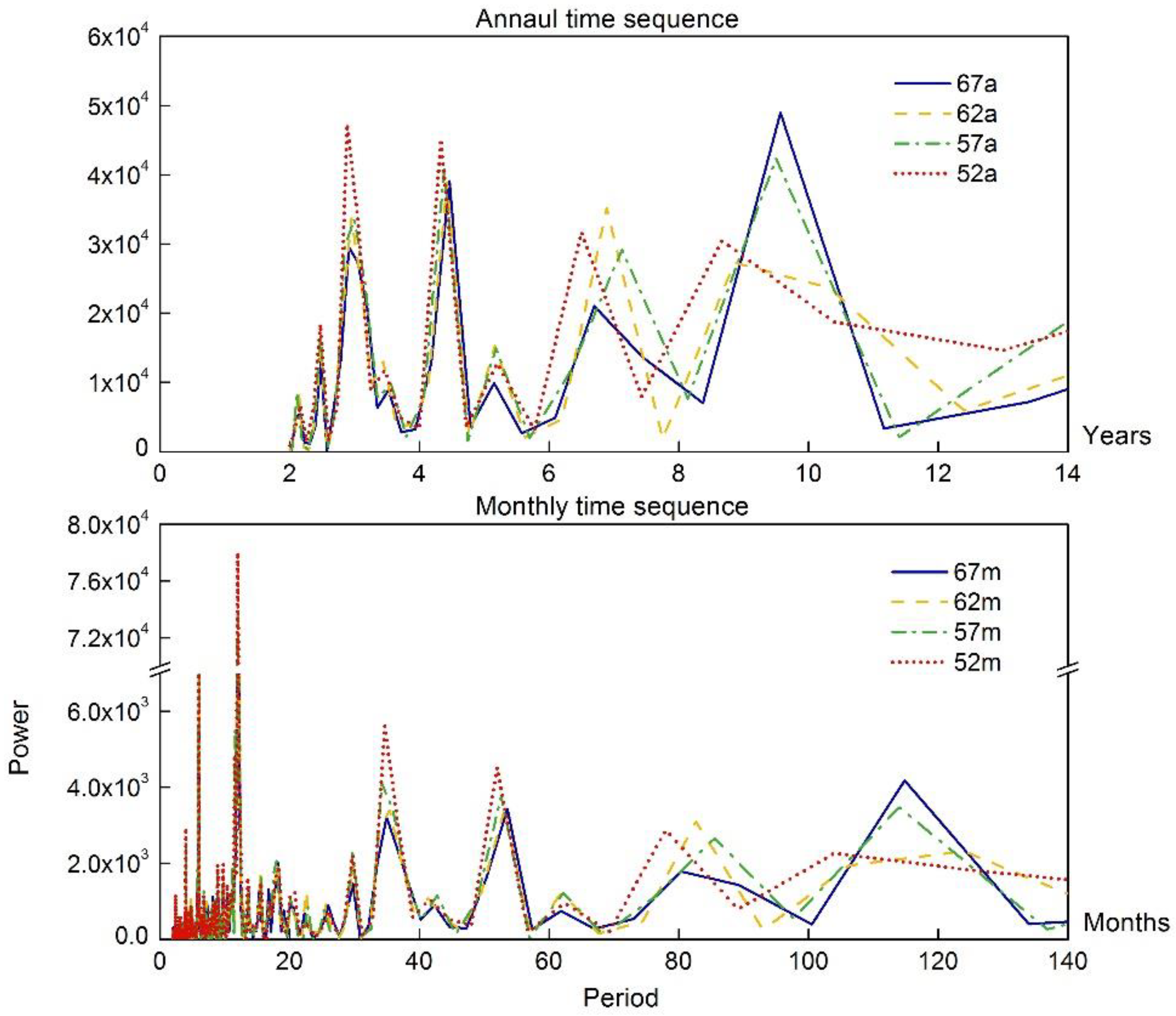
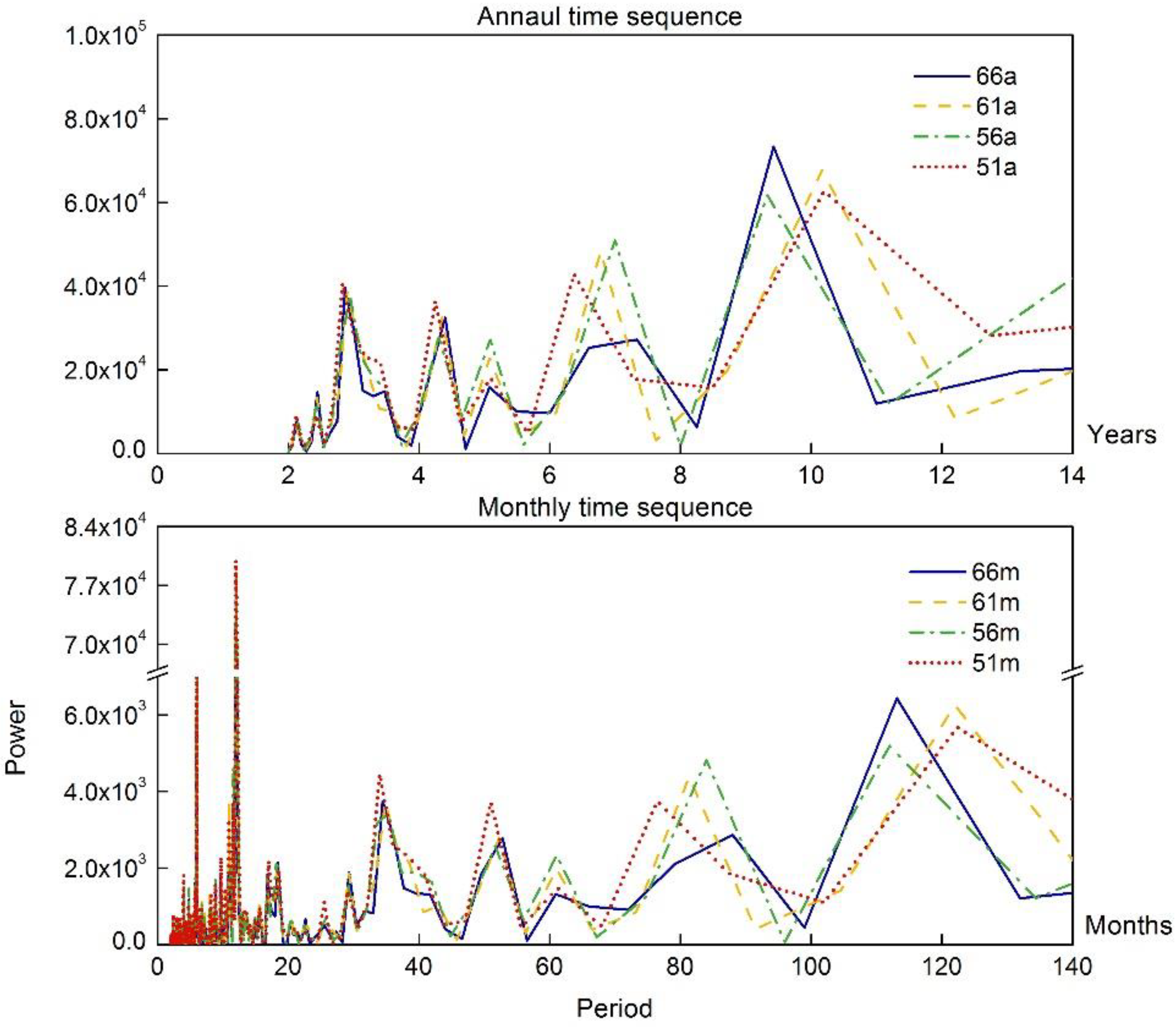
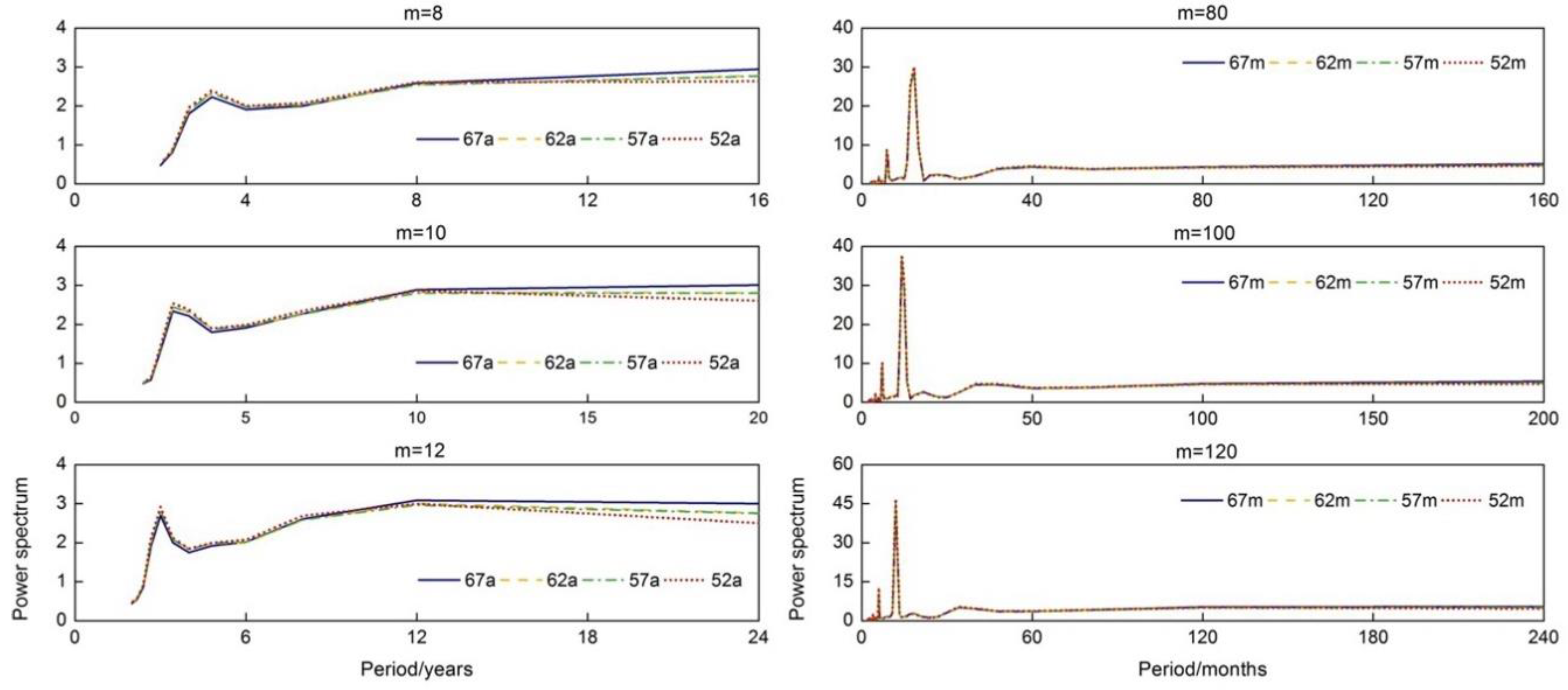
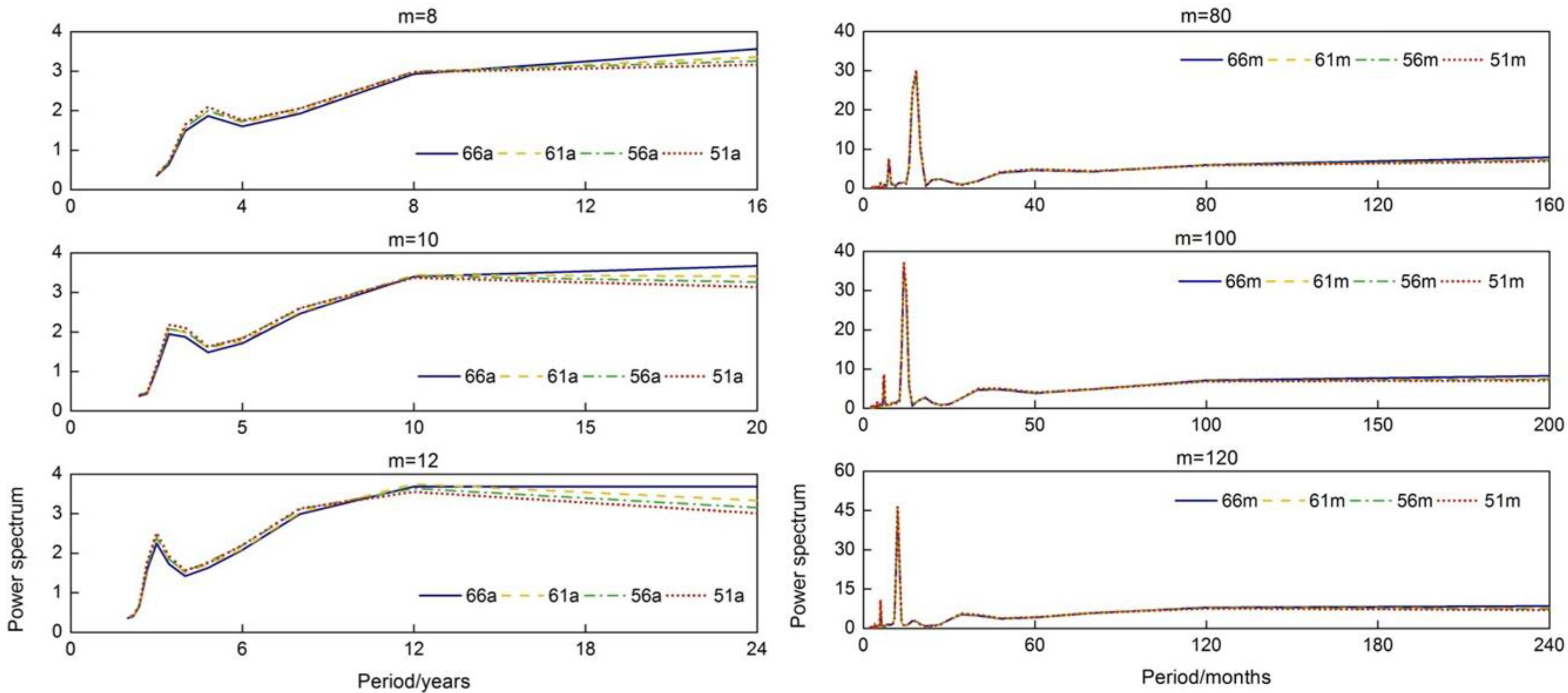

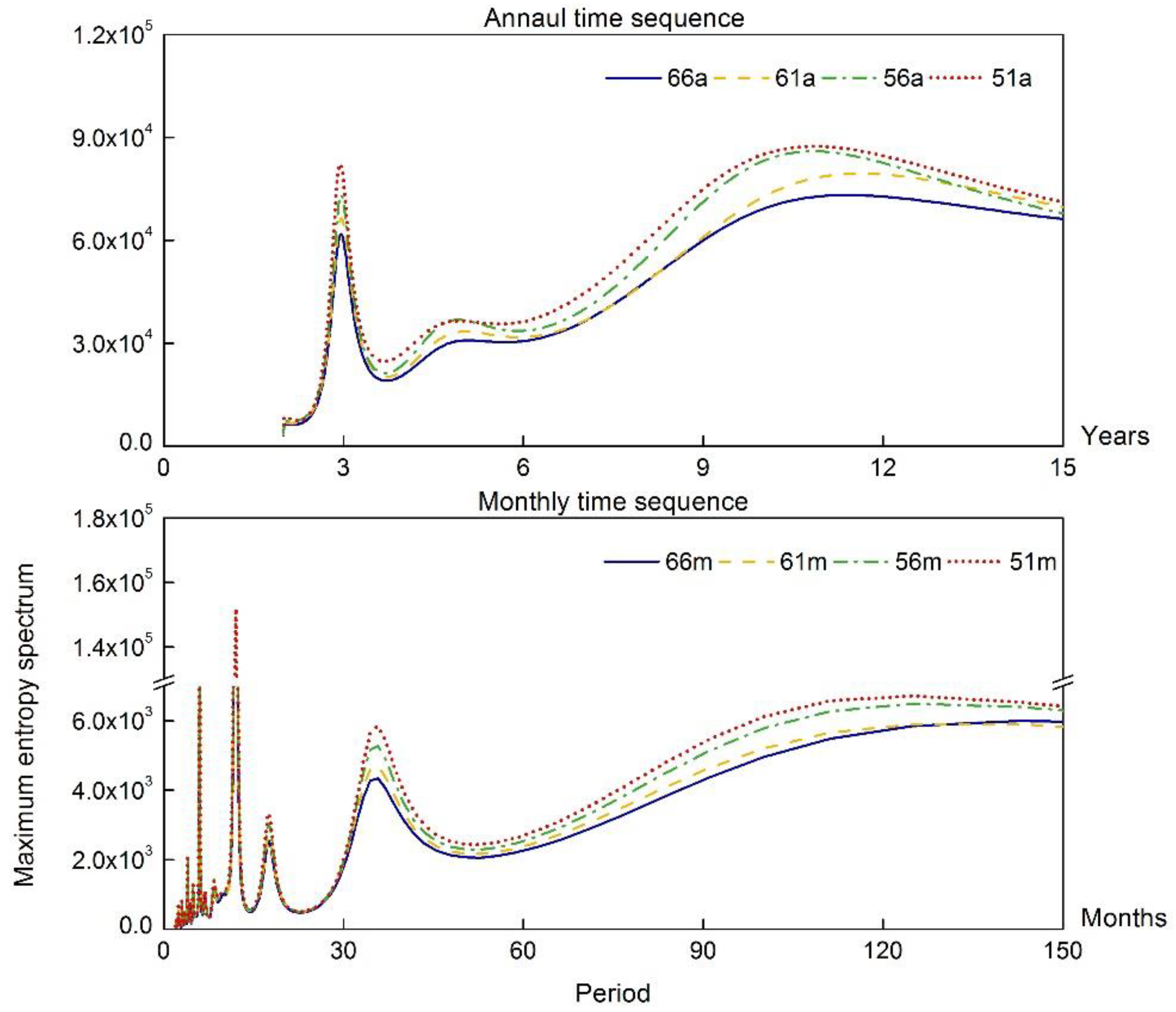
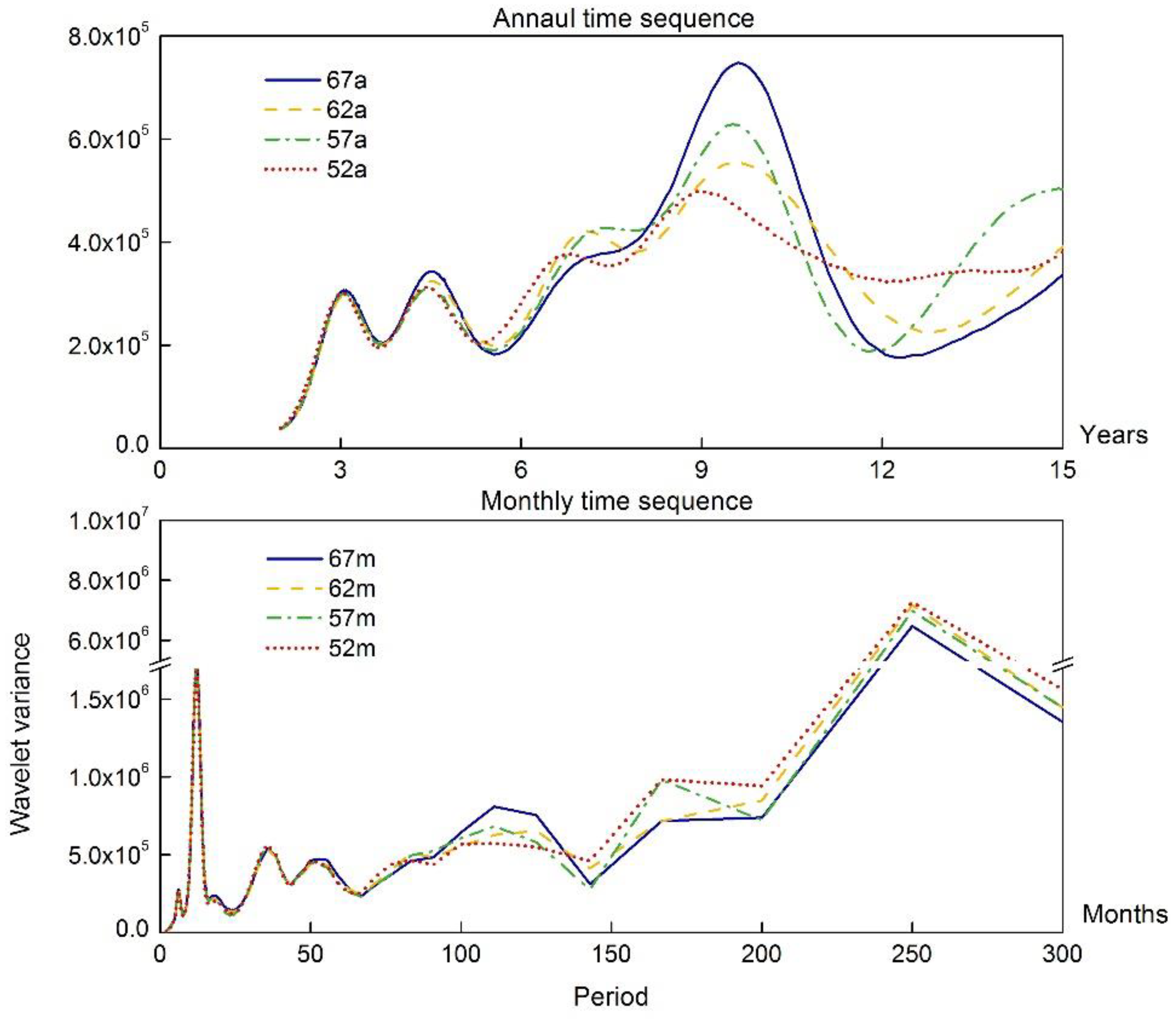
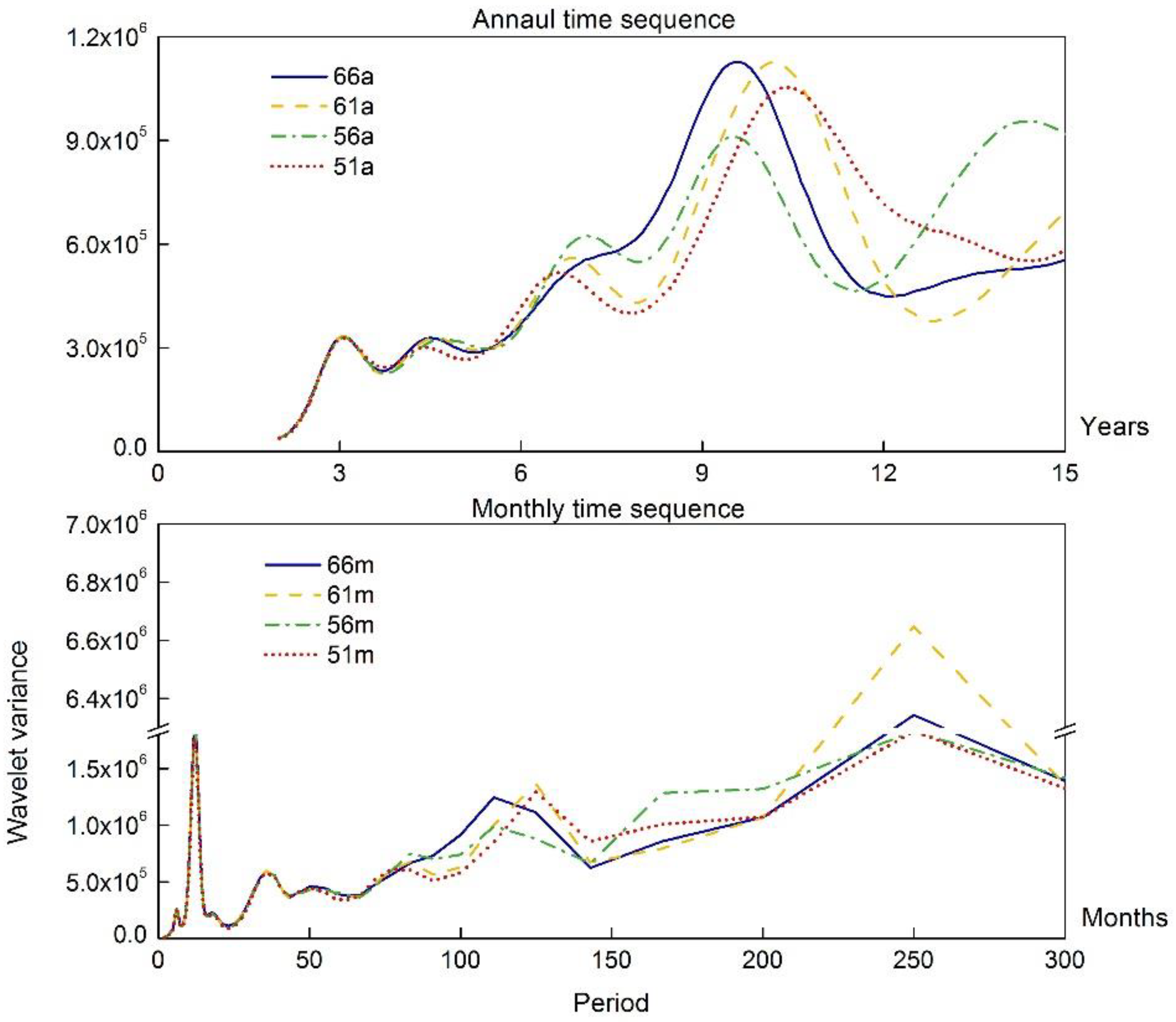
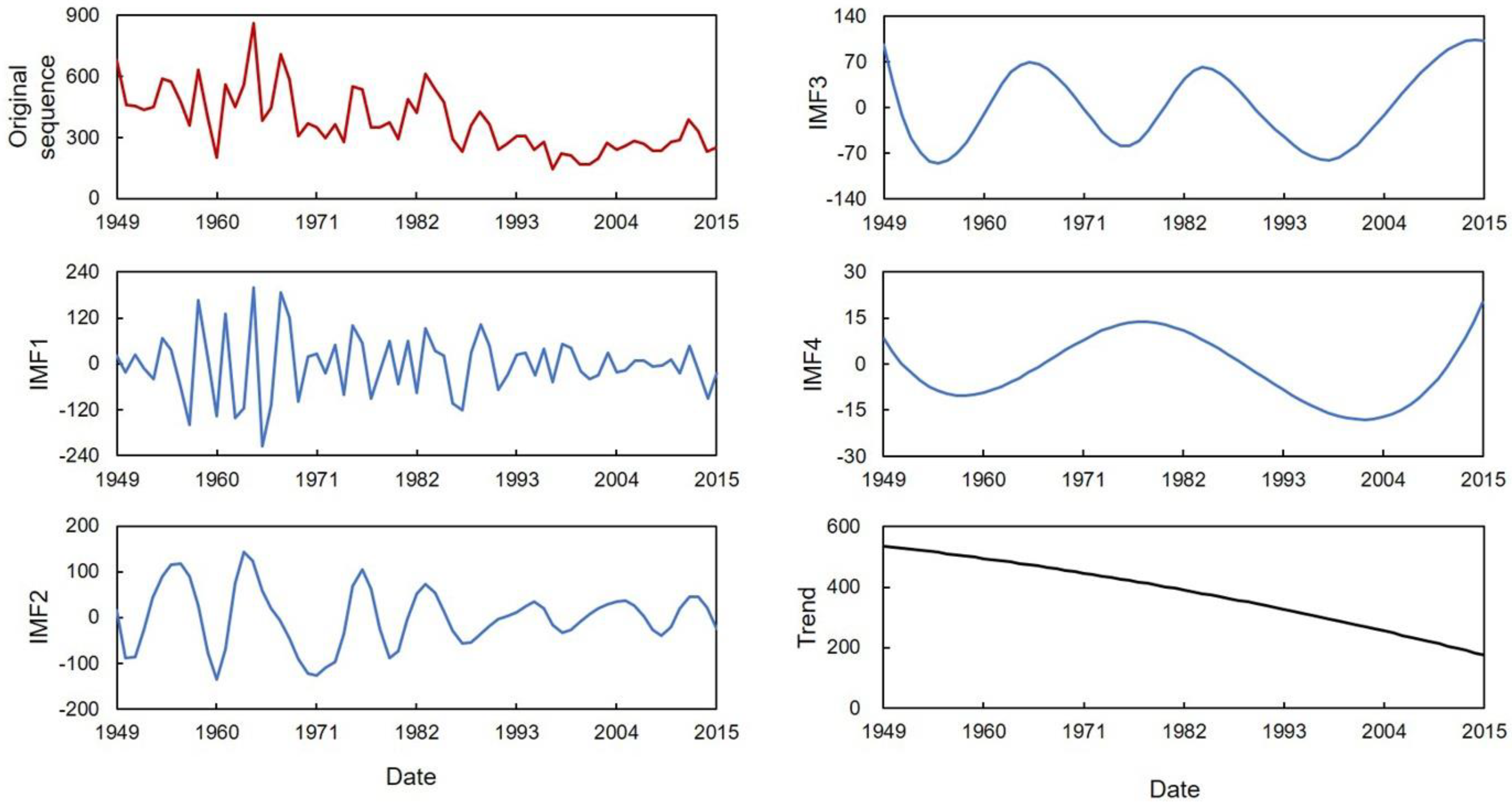
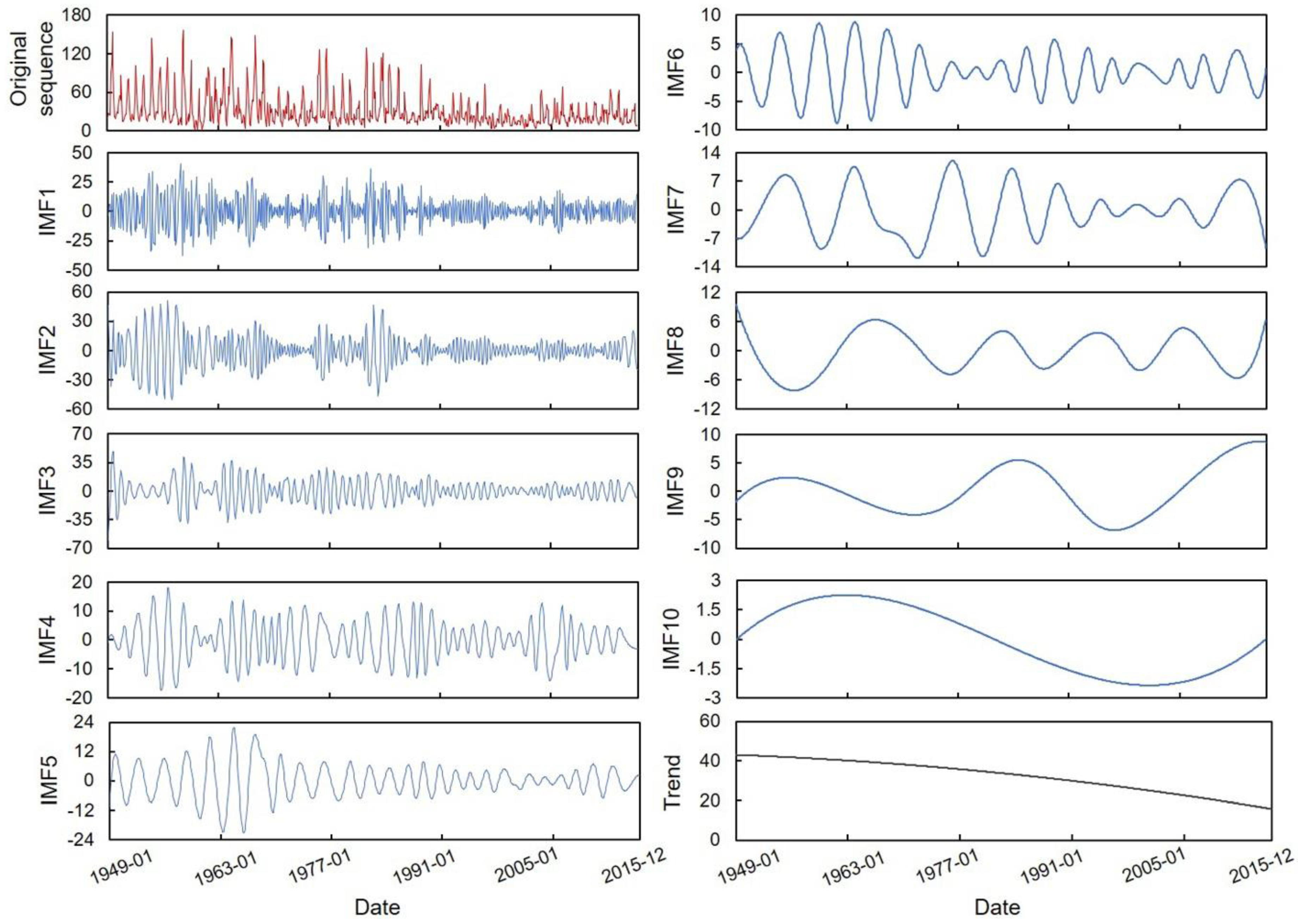

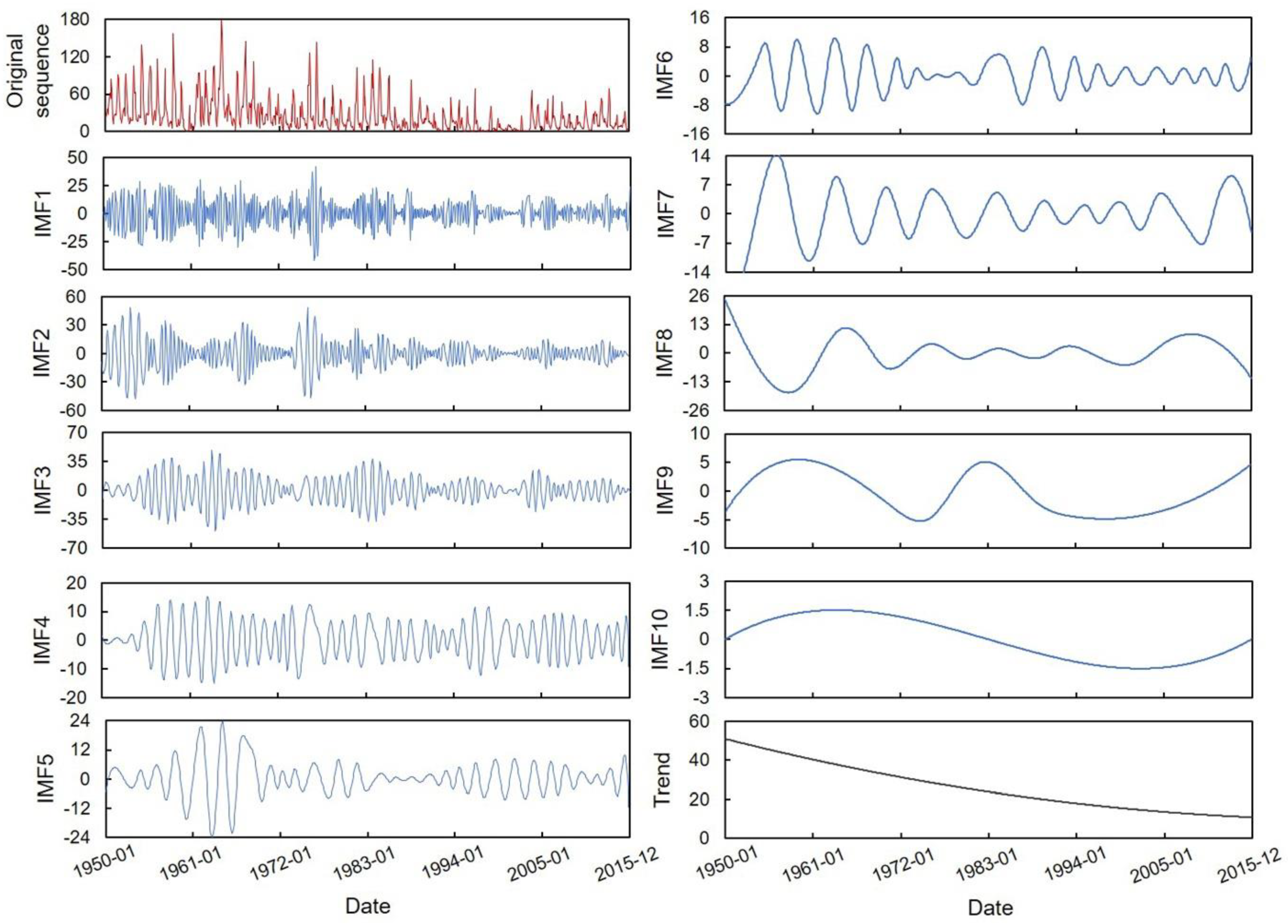



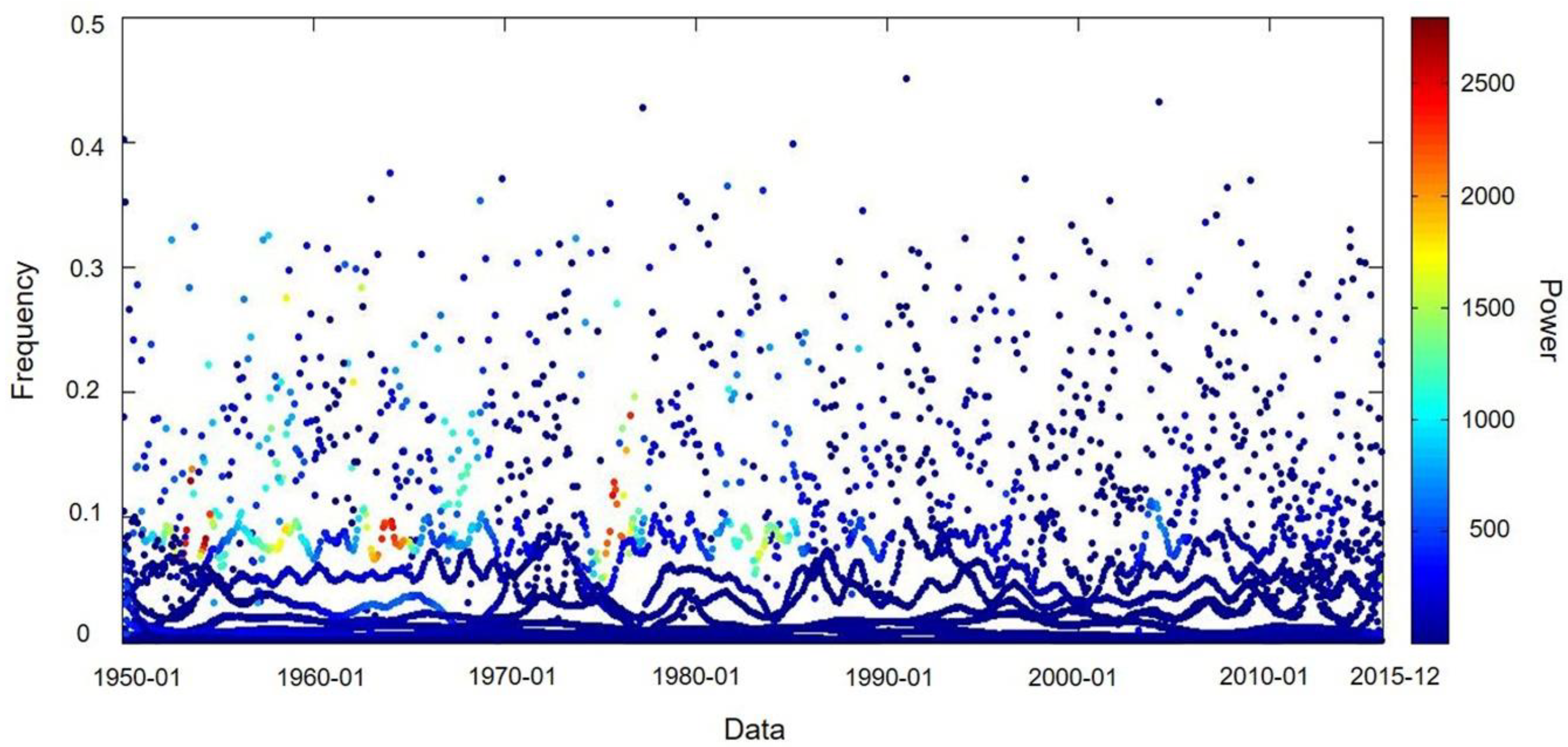
| Station | Series I | Series II | Years |
|---|---|---|---|
| HHS | 67a | 67m | 1949–2015 |
| 62a | 62m | 1949–2010 | |
| 57a | 57m | 1949–2005 | |
| 52a | 52m | 1949–2000 | |
| LHS | 66a | 66m | 1950–2015 |
| 61a | 61m | 1950–2010 | |
| 56a | 56m | 1950–2005 | |
| 51a | 51m | 1950–2000 |
| Series | Intrinsic Mode Functions | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IMF1 | IMF2 | IMF3 | IMF4 | |||||
| f (1/a) | T (a) | f (1/a) | T (a) | f (1/a) | T (a) | f (1/a) | T (a) | |
| 67a | 0.2639 | 3.79 | 0.1027 | 9.74 | 0.0437 | 22.88 | 0.0262 | 38.16 |
| 62a | 0.2667 | 3.75 | 0.0982 | 10.18 | 0.0468 | 21.37 | 0.0279 | 35.8 |
| 57a | 0.2717 | 3.68 | 0.1049 | 9.53 | 0.0491 | 20.35 | 0.0174 | 57.31 |
| 52a | 0.2584 | 3.87 | 0.0987 | 10.13 | 0.0476 | 20.99 | 0.0193 | 51.68 |
| Series | Intrinsic Mode Functions | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IMF1 | IMF2 | IMF3 | IMF4 | IMF5 | ||||||
| f (1/m) | T (m) | f (1/m) | T (m) | f (1/m) | T (m) | f (1/m) | T (m) | f (1/m) | T (m) | |
| 67m | 0.1842 | 5.43 | 0.1366 | 7.32 | 0.0831 | 12.04 | 0.0527 | 18.96 | 0.0327 | 30.59 |
| 62m | 0.1848 | 5.41 | 0.1372 | 7.29 | 0.0855 | 11.69 | 0.0592 | 16.9 | 0.0371 | 26.99 |
| 57m | 0.1862 | 5.37 | 0.1346 | 7.43 | 0.0833 | 12.01 | 0.0542 | 18.44 | 0.0343 | 29.16 |
| 52m | 0.1842 | 5.43 | 0.1312 | 7.62 | 0.0811 | 12.33 | 0.0546 | 18.33 | 0.0341 | 29.34 |
| Series | IMF6 | IMF7 | IMF8 | IMF9 | IMF10 | |||||
| f (1/m) | T (m) | f (1/m) | T (m) | f (1/m) | T (m) | f (1/m) | T (m) | f (1/m) | T (m) | |
| 67m | 0.0210 | 47.54 | 0.0112 | 89.39 | 0.0061 | 163.36 | 0.0029 | 346.2 | 0.0012 | 802.92 |
| 62m | 0.0234 | 42.74 | 0.0131 | 76.26 | 0.0072 | 138.15 | 0.0027 | 372.49 | 0.0013 | 743.67 |
| 57m | 0.0225 | 44.47 | 0.0134 | 74.47 | 0.0088 | 113.93 | 0.0034 | 293.58 | 0.0015 | 683.29 |
| 52m | 0.0183 | 54.53 | 0.0119 | 83.98 | 0.0081 | 123.39 | 0.0040 | 252.57 | 0.0016 | 623.53 |
| Series | Intrinsic Mode Functions | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IMF1 | IMF2 | IMF3 | IMF4 | |||||
| f (1/a) | T (a) | f (1/a) | T (a) | f (1/a) | T (a) | f (1/a) | T (a) | |
| 66a | 0.2159 | 4.63 | 0.1029 | 9.72 | 0.0453 | 22.06 | 0.0211 | 47.29 |
| 61a | 0.2392 | 4.18 | 0.0980 | 10.20 | 0.0499 | 20.06 | 0.0235 | 42.53 |
| 56a | 0.2193 | 4.56 | 0.0990 | 10.10 | 0.0484 | 20.68 | 0.0256 | 39.11 |
| 51a | 0.2280 | 4.39 | 0.0979 | 10.21 | 0.0479 | 20.86 | 0.0303 | 33.01 |
| Series | Intrinsic Mode Functions | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IMF1 | IMF2 | IMF3 | IMF4 | IMF5 | ||||||
| f (1/m) | T (m) | f (1/m) | T (m) | f (1/m) | T (m) | f (1/m) | T (m) | f (1/m) | T (m) | |
| 67m | 0.1861 | 5.37 | 0.1398 | 7.15 | 0.0850 | 11.77 | 0.0546 | 18.33 | 0.0360 | 27.80 |
| 62m | 0.1809 | 5.53 | 0.1344 | 7.44 | 0.0828 | 12.07 | 0.0542 | 18.46 | 0.0338 | 29.56 |
| 57m | 0.1771 | 5.65 | 0.1275 | 7.84 | 0.0783 | 12.78 | 0.0521 | 19.19 | 0.0306 | 32.72 |
| 52m | 0.1851 | 5.40 | 0.1310 | 7.63 | 0.0789 | 12.68 | 0.0527 | 18.96 | 0.0324 | 30.85 |
| Series | IMF6 | IMF7 | IMF8 | IMF9 | IMF10 | |||||
| f (1/m) | T (m) | f (1/m) | T (m) | f (1/m) | T (m) | f (1/m) | T (m) | f (1/m) | T (m) | |
| 67m | 0.0216 | 46.37 | 0.0125 | 79.77 | 0.0070 | 142.70 | 0.0030 | 328.95 | 0.0013 | 790.91 |
| 62m | 0.0185 | 54.11 | 0.0131 | 76.11 | 0.0075 | 132.81 | 0.0032 | 316.41 | 0.0014 | 730.91 |
| 57m | 0.0167 | 59.72 | 0.0105 | 95.51 | 0.0055 | 180.54 | 0.0041 | 244.47 | 0.0015 | 670.91 |
| 52m | 0.0190 | 52.54 | 0.0121 | 82.68 | 0.0080 | 125.10 | 0.0038 | 260.29 | 0.0016 | 610.91 |
| Methods | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Periodogram | AA | MESA | WA | HHT |
| 4–5 | 3 | 3 | 9–10 | 3–4 |
| 3 | 10–11 | 6–7 | 9–10 | |
| 9–10 | 4–5 | 4–5 | 20–21 | |
| 6–7 | 3 |
| Methods | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Periodogram | AA | MESA | WA | HHT | |||||
| I | II | I | II | I | II | I | II | I | II |
| 12 | 2–3 | 12 | 3 | 12 | 3 | 12 | 21 | 5–6 | 2–3 |
| 6 | 4–5 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 9–10 | 7–8 | 3–4 | ||
| 4 | 8–10 | 18 | 4 | 18–19 | 3 | 12 | 6–7 | ||
| 18 | 6–7 | 4 | 18–19 | 4–5 | 18–19 | ||||
| 9–10 | |||||||||
| Methods | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Periodogram | AA | MESA | WA | HHT |
| 9–10 | 3 | 11 | 9–10 | 4–5 |
| 6–7 | 3 | 6–7 | 9–10 | |
| 3 | 5 | 3 | 20–22 | |
| 4 | 4–5 |
| Methods | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Periodogram | AA | MESA | WA | HHT | |||||
| I | II | I | II | I | II | I | II | I | II |
| 12 | 9–10 | 12 | 3 | 12 | 3 | 12 | 20–21 | 5–6 | 2–3 |
| 6 | 6–7 | 6 | 6 | 10–12 | 6 | 9–11 | 7–8 | 4–5 | |
| 9–11 | 5 | 17–18 | 17–18 | 18 | 6–7 | 12–13 | 6–7 | ||
| 17–18 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 18–19 | 10–12 | |||
| 3 | 3 | ||||||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, X.; Wang, X.; Lian, J. Applicability Study of Hydrological Period Identification Methods: Application to Huayuankou and Lijin in the Yellow River Basin, China. Water 2021, 13, 1265. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13091265
Chen X, Wang X, Lian J. Applicability Study of Hydrological Period Identification Methods: Application to Huayuankou and Lijin in the Yellow River Basin, China. Water. 2021; 13(9):1265. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13091265
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Xingtong, Xiujie Wang, and Jijian Lian. 2021. "Applicability Study of Hydrological Period Identification Methods: Application to Huayuankou and Lijin in the Yellow River Basin, China" Water 13, no. 9: 1265. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13091265
APA StyleChen, X., Wang, X., & Lian, J. (2021). Applicability Study of Hydrological Period Identification Methods: Application to Huayuankou and Lijin in the Yellow River Basin, China. Water, 13(9), 1265. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13091265






