Abstract
The potential impact of controlled drainage (CD), which limits drainage outflow, and subirrigation (SI), which provides supplemental water through drain tile, on surface water quality are not well known in the Red River Valley (RRV). In this study, water samples were collected and analyzed for chemical concentrations from a tile-drained field that also has controlled drainage and subirrigation modes in the RRV of southeastern North Dakota from 2012–2018. A decreasing trend in overall nutrient load loss was observed because of reduced drainage outflow, though some chemical concentrations were found to be above the recommended surface water quality standards in this region. For example, sulfate was recommended to be below 750 mg/L but was reported at a mean value of 1971 mg/L during spring free drainage. The chemical composition of the subirrigation water was shown to have an impact on drainage water and the soil, specifically on salinity-related parameters, and the impact varied between years. This variation largely depended on the amount of subirrigation applied, soil moisture, and soil properties. Overall, the results of this study show the benefits of controlled drainage on nutrient loss reduction from agricultural fields.
1. Introduction
Agricultural drainage is often required to bring moisture levels in a field to a point where crop growth and equipment traffic is possible. Despite the many benefits of drainage, issues related to surface water contamination are often associated with the practice. Subsurface drainage (SSD) is a specific type of drainage drawing criticism because of the amount of nitrate and phosphate that may leave a field through SSD outlets [1,2]. The SSD practice has become popular in the Red River Valley (RRV) due to recent wet years, fields with little variation in topography, and soil impacted by salinity. For example, the number of hectares approved for SSD permits by the North Dakota State Water Commission in Richland County, North Dakota rose from 536 in 2005 to 3141 in 2015, an increase of approximately 586% [3]. The introduction of SSD into a field improves trafficability for equipment by lowering the amount of moisture in the soil, which increases soil penetration resistance [4].
Controlled drainage (CD) has been presented as a management practice that limits the nutrient loss out of SSD outlets through a reduction in drain flow. This is in contrast with the conventional free drainage (FD) without any regulation at the drainage outlet. The practice of CD is defined as a “regulation of the soil water table by means of pumps, control dams, or check drains, or a combination of these, for maintaining the water table at a depth favorable to crop growth and/or for minimizing the effects of drainage during the fallow season to prevent nutrient loss” [5].
For a CD field with a pump station outlet, the pump station is turned on prior to planting and harvest to remove moisture from the field, increasing trafficability, the ability of equipment to maneuver through the field, which saves time for farmers and decreases rutting in the field. During the growing season, the CD status is recommended to be manipulated to best provide optimal soil conditions in terms of aeration and water content [6]. Crop yields have been shown to improve when grown where the water table depth is controlled by the combination of subirrigation (SI) and CD [7,8].
Along with the positive impact on crop yield, CD has also been shown to reduce nutrient losses from agricultural fields in a variety of studies. Wesström et al. [9] found a correlation between reduction in drainage outflow and reduction in nitrate and phosphate loss because the highest nitrate concentrations were found during the periods of highest drainage outflow. A 25% reduction in nitrate concentration was reported by Drury et al. [10] between conventional drainage and CD, with most nutrient losses from the CD field occurring during the non-cropping period. Feser et al. [11] also concluded that the reduction in nitrate-nitrogen was due to a reduction in drainage outflow.
SI is defined as an “application of irrigation water below the ground surface by raising the water table to within or near the root zone” [5] and can increase the amount of moisture in a field when desired while still implementing SSD. Despite the benefits of additional moisture through the application of SI, the use of a water source with marginal quality can have deleterious impacts on the surrounding soils. Much of the research published on the use of sodic water for irrigation has taken place in arid environments with sandy soils [12,13]. Because of their tendency to swell and disperse during drying and wetting, smectitic soils may be more prone to permeability issues caused by irrigation water quality compared to soils with different mineralogy [14]. Irrigation water guidelines indicate the potential for a severe reduction in infiltration with a sodium adsorption ratio (SAR) value between 3–6 and an electrical conductivity (EC) below 0.3 dS/m, though a slight risk is possible at as high as 1.2 dS/m [15]. Site characteristics such as soil minerology are encouraged to be taken into consideration when using these values to interpret data.
Despite the rise in popularity of CD and SI practices, little research has been done in the RRV to determine the impact of CD and SI on surface water and soil quality. This study used the water quality data from a field with CD and SI to analyze the impacts of these management practices on nearby surface water quality. The impact of SI with water of marginal quality on soil quality was also assessed. The resulting data provide insight into the applicability and environmental benefit of these practices in the RRV. The objectives were to analyze the rainfall and drainage outflow patterns; to compare and evaluate drainage water quality parameters during periods of FD, SI, and CD; to estimate the daily chemical loads during the different water management periods; and to assess the impact of SI with a marginal water source on soil quality.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Site
The field site is located approximately 4.2 km south of Fairmount in Richland County, ND. The geographic location is 46°00′45′′ N and 96°35′47′′ W, with an elevation of 296 m above sea level. The area of the field is about 44 ha, with 802 m in the west-east and 548 in the north-south directions. The original field layout, installed in 2002, was half undrained (north half) and half drained (south half), with 18.2 m spacing [16,17]. In 2011, the entire field was converted to SI with 9.1 m spacing. The SI water source is groundwater located at a depth of 23 m to 40 m below the ground. The SI water is pumped for application near the east sump pump and comprised of a mixture of surface seepage and groundwater. The SI water is delivered to the sump via buried PVC pipes along the north edge of the field. The depth of tile varies from 1.0 m to 1.5 m below the soil surface. Soil series within the project area are Clearwater-Reis silty clay (Clearwater series, Fine, smectitic, frigid Typic Epiaquerts; Reis series, Fine, smectitic, frigid Typic Calciaquerts), Antler-Mustinka silty clay loam (Mustinka series, fine, smectitic, frigid Typic Argiaquolls), Antler silty clay loam (Fine-loamy, mixed, superactive, frigid Aeric Calciaquolls), and Doran clay loam (Doran series, Fine, smectitic, frigid Aquertic Argiudolls) [18]. These soils were formed in clayey and clayey, calcareous till on lake plains, and specifically prehistoric Lake Agassiz. These soils would have World Reference Base classifications of “Chernozems” or “Kastanozems” [19]. Other than 2012, when sugarbeets (Beta vulgaris) were planted, a corn (Zea mays) and soybean (Glycine max) rotation has been used with tillage after harvest each year.
Southeastern North Dakota has a humid continental climate with an average temperature of 6.5 °C. According to weather data at the Wahpeton North Dakota Agricultural Weather Network (NDAWN) station, approximately 26 km north of the field site, the average maximum temperature of 28.8 °C occurs in July while the average minimum temperature of −17.9 °C occurs in January. Average annual precipitation from 2012–2018 was 567 mm. During the study period of this project (2012–2018), the driest year was in 2012, with only 336 mm of rainfall. The wettest years were in 2013 and 2016, with approximately 521 mm of rainfall [20].
2.2. Instrumentation
A transducer (Water Level Loggers U20L-04, Onset HOBO, Bourne, MA, USA) was installed in the two sump structures in order to monitor the water level changes. A conductance sensor (Conductivity Loggers U24-002-C, Onset HOBO, Bourne, MA, USA) was also installed to monitor the water quality [21]. The drainage flow was monitored by a current switch sensor (CSV-A8, Onset, Bourne, MA, USA) and recorded by a state datalogger (UX90-001, Onset, Bourne, MA, USA). The current sensor was installed on the electrical board of the sump pump.
Near each of the sump pump stations, paired manual and automatic rain gauges were installed at about 1.5 m above the ground without any obstacles. The manual rain gauges were read every 2 weeks during field visits. The automatic rain gauges (Stratus RG202, Stratus, Fergus Falls, MN, USA) used a datalogger (WatchDog data Logger Model 115 Spectrum Technologies, Inc., Aurora, IL, USA) to record the data every 10 min. Two rain gauges were used to prevent the inclusion of inaccurate data.
2.3. Precipitation
During the study period from 2012 to 2018, the rainfall amounts were measured in the field, and the snowfall in terms of snow water equivalent (SWE) amounts were obtained from an NDAWN station in Breckenridge, MN, approximately 38 km north of the field. The SWE values were recorded between November and March or April of the current year depending on precipitation characteristics. Total precipitation was calculated as the sum of SWE and rainfall.
2.4. Water Sampling
Water samples were taken from the sump structures and ditches using a bailer every other week from approximately May to October every year since 2008 (excluding 2011), or when water was not frozen. The water samples were preserved according to the instruction by the North Dakota Department of Environmental Quality (DEQ) Chemistry Laboratory [22]. Each water sample was immediately filtrated with a filter (0.45-micron High-Capacity dispos-a-filters™, Geotech Environmental Equipment, Inc., Denver, CO, USA). For nutrient analysis, 2 mL of sulfuric acid was added to the filtered water in a 500 mL plastic bottle. For trace metal analysis, 2 mL of nitric acid was added to the filtered water in a 250 mL plastic bottle [23]. Samples were later grouped by management practice period for comparison purposes. Periods of FD were defined as when the sump pump was turned on, usually before planting and harvesting. Periods of CD occurred when the sump pump was turned off, usually after crop emergence, and SI was applied when water was pumped into the sump and back into the field through the same drain tile [24].
2.5. Water Sample Chemical Analysis
The water samples were sent to the ND DEQ for chemical analysis. Flow injection analysis and Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) method 353.2 were used for nitrite and nitrate-nitrogen (NOx-N) analysis, and method P4500-P B.5 was used for orthophosphate (PO4-P) analysis [16]. Total dissolved solids and conductivity were determined by Method 1030 E and by Conductivity Method 2510, respectively [16]. EPA method 200.7 was used for sodium, calcium, magnesium, and potassium ion analysis. EPA method 300.0 was used for chloride and sulfate ion analysis J. Quarnstrom [25]. Temperature and electrical conductivity (EC) were measured manually in the field by a transducer (Model 107 TLC Meter, Solinst Canada Ltd., Georgetown, ON, CA, USA). A pH sensor (Low-Range pH/Conductivity/TDS Tester, Hanna Instruments, Smithfield, RI, USA) was connected to a data logger and used for the pH measurement in the field after calibration. These field measurements provided a comparison between the laboratory-analyzed data and the field data.
Since 2016, a duplicated water sample has been collected and sent to a laboratory at the North Dakota State University (NDSU) campus for nitrate, ammonium (NH4), PO4-P, potassium, EC, and pH analysis. This data provided a means for comparison and validation of the North Dakota Department of Health data. At the NDSU laboratory, EPA method 365.1 Revision 2.0 was used for dissolved phosphorus analysis. The Berthelot, or Indophenol Reaction, along with a segmented flow analyzer (SEAL AutoAnalyzer, SEAL Analytical, Mequon, IL, USA), was used for NH4-N analysis. Nitrate-nitrogen was measured through the trans-nitration of salicylic acid method, and an atomic adsorption device (210VGP Atomic Adsorption Spectrophotometer, Buck Scientific, East Norwalk, CT, USA) was used for potassium analysis S. Mathews [26].
2.6. Soil Sampling
To observe the impact of SI application with water of marginal quality on soil quality, soil samples were taken around drain tiles within the field and analyzed in 2014, 2015, and 2017. The samples were obtained by excavation of the soil above the drain tiles followed by the collection of soil samples at distances of 0 cm, 20 cm, 41 cm, and 81 cm above the drain tile at three locations, with three replicates. Samples were then sent to the NDSU Soil Testing Lab for analysis. The locations of the soil sampling points are given in Figure 1. The ammonium acetate method with an atomic adsorption device (210VGP Atomic Adsorption Spectrophotometer, Buck Scientific, East Norwalk, CT, USA) was used for potassium, calcium, magnesium, and sodium ion analysis S. Mathews [26]. Percent sodium was calculated using Equation (1).
where units of cations are cmol(+)/kg.

Figure 1.
Experimental layout, where A2, B1, and C2 are soil sampling locations and the curved lines identify the soil map units, with I236A for Clearwater-Reis silty clays, I243A for Doran clay loam, I405A for Antler clay loam, and I397A for Antler-Mustinka complex, respectively.
To calculate the sodium adsorption ratio (SAR) from the percent sodium, Equation (2) was adapted from DeSutter et al. [27]:
A 1:1 slurry was used for the EC measurement along with an electrochemistry meter (Orion™ Versa Star Pro™, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). A 1:1 slurry and an electronic pH meter (Accumet AB15 Basic, Fisher Scientific, Hampton, NH, USA) were used for the pH measurement (S. Mathews, personal communication, 4 February 2020).
2.7. Flow and Nutrient Load Calculations
To determine daily tile flow, the following equation (Equation (3)) was incorporated from Scherer and Jia [28]:
where Qp is average pump flow rate over one pump duty cycle, Vs is sump storage volume, Ton is the time interval when the pump is running, and Qi is average flow rate from the tile into the sump.
Input values for determining daily flow, as well as the time of pumping and the dimensions of the sump pump structure, were recorded by the event logger [28]. Daily nutrient loads were calculated from the daily flow rates, nutrient concentrations, and drainage area.
Since the chemical concentrations were measured every 2 weeks and drainage flow was measured continuously and calculated daily, the daily chemical load was estimated through linear interpolation of the chemical concentrations.
Due to concerns regarding the quality of the water used for subirrigation, specifically in terms of salinity, the SAR was calculated for the east sump pump and ditch water samples (Equation (4)).
where [ ] is the concentration in milliequivalents/liter (meq/L)
Percent sodium was calculated using Equation (5) (J. Quarnstrom, personal communication, 3 February 2020):
where hardness total refers to the amount of dissolved calcium and magnesium.
2.8. Statistical Analysis
To determine if statistically significant differences were present between the chemical concentration data, a two-factor analysis of variance without replication was performed with a Tukey’s honestly significant difference post hoc test. An alpha value of 0.05 was used. Descriptive statistics were used to summarize the chemical concentration data and simple regression was used to compare chemical load and drainage outflow volume.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Precipitation and Drainage Outflow
Both the amount of rainfall during the growing season and the snowfall over the winter period affected the drainage outflow and varied between each year and season. The amount of SI applied, which was determined by the landowner, also varied from year to year. Yearly totals of total precipitation, SWE, rainfall, SI, and drainage outflow are listed in Table 1.

Table 1.
Total annual precipitation, snow water equivalent from November to April, rainfall amount from May to October, subirrigation, and drainage outflow from the east sump pump at the Richland County, ND site.
With a higher SWE of 199 mm from fall 2012 to spring 2013, the highest drainage flow (107 mm) was found in spring 2013. The lowest SWE of 57 mm occurred from fall 2015 to spring 2016, so the least amount of drainage flow was expected to occur in spring 2016. However, the direct correlation was not found in the results (Table 1) due to a higher average daily drainage outflow influenced by SI and rainfall in 2016 (0.5 mm/day) compared to 2017 (0.2 mm/day) and 2018 (0.14 mm/day).
The variation in rainfall and SWE directly affected the drainage outflow. In fact, the drainage outflow in the springtime was affected primarily by the SWE, but the drainage outflow in the summer and the fall season followed with the rainfall distribution (Figure 2). Data from 2014–2016 provide an example of how SWE impacted the total drainage outflow. The total precipitation (479 mm) in 2014 was lower than the total precipitation in 2015 and 2016, but more drainage outflow occurred in 2014. This was likely because of the higher SWE in 2014 compared to those in 2015 and 2016. The majority of drainage outflow in 2014 occurred in the spring, when snowmelt contributed more to the drainage flow.
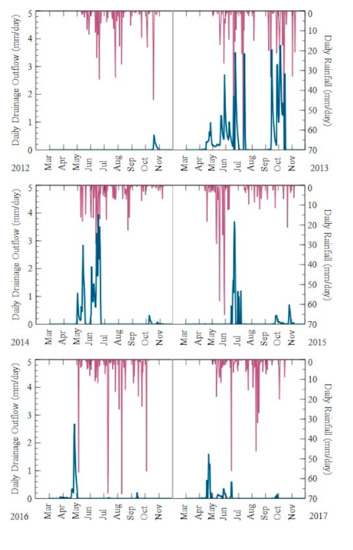
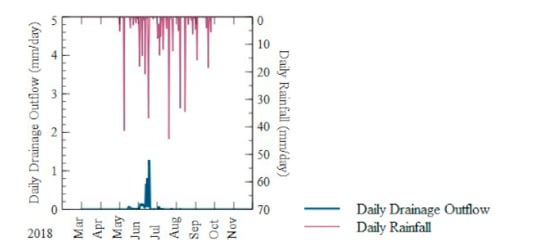
Figure 2.
Daily rainfall and drainage outflow in 2012–2018 at the east sump of the study site in Richland County, ND.
The predominate trend in Figure 2 consisted of two periods of drainage flow, one in the spring and the other one in the fall, which corresponded to the recommended CD practices, where drainage was turned on before planting and harvest in order to allow the soil to dry enough for equipment traffic. The relationship between the total amounts of rainfall and the drainage flow was positive. The highest drainage outflow occurred in 2013, which was the wettest year. The amount of snowfall in terms of SWE in the previous winter impacted the amount of drainage outflow in the spring. When little flow occurred in the spring or fall, it was likely because there was insufficient rainfall or SWE that could be infiltrated into the field and eventually generate drainage outflow. This positive relationship between rainfall and drainage outflow was typical and can be found in other studies [9,29,30].
3.2. Chemical Concentrations
To see how different water management practices including FD, CD, and SI impacted water quality, the chemical concentrations from water samples at the east sump of the site were grouped according to the management practices when the water samples were taken (Table 2).

Table 2.
The mean values for percent sodium, sodium adsorption ratio (SAR), total dissolved solids (TDS), electrical conductivity (EC), and chemical concentrations for sodium, potassium, calcium, magnesium, chloride, sulfate, nitrite + nitrate nitrogen (NOx-N), and orthophosphate (PO4-P) from the water samples at the east sump from 2012–2018 during periods of free drainage (FD), controlled drainage (CD), and subirrigation (SI). Standard values were obtained from the North Dakota Standards of Quality for Waters of the State when listed. Significant differences as determined by Tukey’s honestly significant difference post hoc test with an alpha value of 0.05 are shown by different letters. Sample size (n) is given below each column title and standard deviations are listed for each value.
There were chemical concentration differences during the periods with different management practices, though the only statistically significant difference occurred between the CD-spring and SI practices. Calcium, magnesium, sulfate, NOx-N, and PO4-P were found in much smaller concentrations in the SI samples compared to those in the CD and FD samples, which was mainly due to the difference in water sources. The water in the east sump during CD and FD is mainly influenced by rainfall, horizontal seepage, upward contributions from the water table, and the soil parent materials [16,31]. The water source for the SI samples, however, is confined to the irrigation water source. As stated by Jia et al. [16], the irrigation water is from groundwater, which has a distinct water quality than the drainage water from the cultivated farm field. One distinguishing attribute of the groundwater source is a higher PO4-P concentration that was reported in Jia et al. [16], where samples taken from the east sump pump outlet during SI had PO4-P concentrations ranging from 0.33 1 mg/L to 1 mg/L. However, during CD, PO4-P concentrations averaged 0.068 mg/L. Less significant variances were found in this study compared to what Jia et al. [16] reported, but PO4-P concentrations were found to be the highest during the SI application at 0.58 mg/L. Two other parameters found to be higher in the SI samples compared to the samples in CD and FD were percent sodium and the SAR. This was also expected because of the composition of the SI water. Previous research has indicated no expected differences between NOx-N and PO4-P concentrations between the FD and CD samples [32,33]. However, the results in this study showed greater differences between the FD and CD samples, especially for the NOx-N and sulfate values. This was possibly caused by the difference in water sources. The water samples from the FD period were from soil, but the water samples from the CD period were a mixture of drainage and SI water.
Compared to the water quality standard for surface waters, there are six mean concentration values in Table 2 that were above the North Dakota Standards of Quality for Waters of the State [34]. Among these five parameters, however, only three, PO4-P, NOx-N, and sulfate, impacted the surface water because they occurred during the FD period. The other two parameters, percent sodium in the SI samples and sulfate in every CD and SI sample, had little or no direct effect on the surface water since drainage outflow was not occurring at the time of collection. The only value calculated from the SI samples in violation of the standards was the percent sodium, which is required not to be above 50%, but was found to be 63.6% in this study. This is attributed from the quality of the groundwater used for the SI application. The mean sulfate concentrations in FD-spring, FD-fall, and CD-spring samples were all above the recommended value of 750 mg/L at 1971 mg/L, 1643 mg/L, and 2048 mg/L, respectively. Sulfate is known to predominate in North Dakota soils, so high levels were expected [35]. However, a sulfate concentration above 1000 mg/L in drinking water can have a laxative effect on humans. Therefore, direct consumption of the surface water is not recommended [36]. The exact value at which negative impacts are experienced by consumers of water high in sulfate has varied between studies, though the United States EPA recommends against consuming water with a sulfate concentration higher than 500 mg/L. The average NOx-N value during the FD-spring exceeded the recommended value of 10 mg/L at 17.7 mg/L. Samples taken during 2012 increased the mean NOx-N, which was likely due to a variety of reasons, such as new tile drainage installation in the fall of 2011, spring fertilization, dry weather conditions, etc. Excluding the 2012 samples, the NOx-N mean concentration in the FD samples was below the 10 mg/L threshold.
3.3. Comparison between the Surface and Subsurface Water Samples
Along with comparison between management practices, water quality samples from the surface water in the two locations (east and west of the field) along the same ditch were also compared to the subsurface water samples from the east sump. It was assumed that drainage water exiting the field would only influence the ditch samples during the FD period. However, surface runoff and horizontal seepage after substantial rainfall events and during snowmelt might have occurred during the SI and CD periods and may have contributed to the chemistry of the ditch water samples. However, it is unlikely that any contribution from the field through these processes would have caused significant changes to the water in the ditch because the volume of water added would have been insignificant. The chemical concentrations at the upstream of the field in the west sampling location and the downstream of the field in the east sampling location along the same ditch are summarized in Table 3 and Table 4, respectively.

Table 3.
Upstream ditch water mean values for percent sodium, sodium adsorption ratio (SAR), total dissolved solids (TDS), electrical conductivity (EC), and chemical concentrations for sodium, potassium, calcium, magnesium, chloride, sulfate, nitrite + nitrate nitrogen NOx-N, and orthophosphate (PO4-P) in 2012–2018 during free drainage (FD), controlled drainage (CD), and subirrigation (SI) periods. Significant differences as determined by Tukey’s honestly significant difference post hoc test with an alpha value of 0.05 are shown by different letters. Sample size (n) is given below each column title and standard deviations are listed for each value.

Table 4.
Downstream ditch water mean values for percent sodium, sodium adsorption ratio (SAR), total dissolved solids (TDS), electrical conductivity (EC), and chemical concentrations for sodium, potassium, calcium, magnesium, chloride, sulfate, nitrite + nitrate nitrogen NOx-N, and orthophosphate (PO4-P) in 2012–2018 during free drainage (FD), controlled drainage (CD), and subirrigation (SI) periods. Significant differences as determined by Tukey’s Honestly significant difference post hoc test with an alpha value of 0.05 are shown by different letters. Sample size (n) is given below each column title and standard deviations are listed for each value.
The flow in this ditch occurs from the west to the east. For the purposes of this study, differences in nutrient concentrations during the FD period were considered to be attributed to this field. For most of the parameters measured, chemical concentrations were found to be higher in the downstream samples compared to the upper stream samples during FD-spring and FD-fall. NOx-N had the largest increase in concentration from the upper stream to downstream at 26% in FD-spring and 52% in FD-fall. These increases in chemical concentrations are indicative of the impact drained water from the field had on nearby surface water, but these increases did not lead to chemical concentrations that exceeded recommended values.
The water samples from the ditch displayed less variation among the five management practice periods compared to the samples from the subsurface outlet in the east sump. In contrast to samples from the east sump, significant differences were not present between samples from the west end of the ditch (upper stream) and samples from the east side of the ditch (downstream). Major differences were seen for the salt-related parameters, including SAR, percent sodium, and EC values, between the SI ditch samples (Table 3 and Table 4) and the east sump SI samples (Table 2). Samples from the east sump during the SI period were found to be statistically different from the samples from the ditch during the same period. This is once again attributed to the different water source for the SI application. Another difference in chemical concentrations between the sampling locations was the seasonality of calcium and magnesium concentration. Samples from the east sump showed higher calcium and magnesium concentrations during the spring, while the ditch water samples showed fairly consistent concentrations of calcium and magnesium throughout the year. The seasonality of calcium and magnesium concentrations in the east sump may be attributed to the transition to and from the SI water source. The only statistically significant difference between the samples from the east sump and those from both ends of the ditches were samples in the sump during the SI period and samples in the ditch at both ends during the CD-spring, SI, and FD-fall periods. Since water in the east sump during SI does not contribute to drainage outflow, these differences are not of environmental concern to nearby bodies of water. Because of the overall similarity between the two sampling locations (upstream and downstream), the results indicate a similar chemical composition of the water in the study field compared to the water drained by nearby fields.
The only nutrient concentrations from the ditch (surface) water samples that were above the recommended values in North Dakota were the mean sulfate concentrations, which were all significantly greater than the recommended 750 mg/L. This is once again expected in this region because of the soil minerology. Sulfate is expected to be found in the soil and water of this field because it is often the anion found in salts in this region, usually in the form of sodium or magnesium sulfate [33]. To avoid the contribution of sulfate to the surface water in areas impacted by excess sulfate, CD is an effective strategy and may be required to limit negative impacts to surface water.
3.4. Chemical Loads
The chemical load is a valuable assessment on the impact of the tile drainage water to the surface water system. Three parameters, NOx-N, PO4-P, and TDS, were selected for the chemical load analysis. The two water quality contaminants of the most concern are NOx-N and PO4-P because of their contributions to eutrophication in bodies of water, such as the Gulf of Mexico [37]. The inclusion of TDS data allowed for the analysis of the amount of dissolved substances present in the water samples. Even though the TDS value is not specific to any component of a water sample, it is typically assumed as an indicator of water quality [21]. Bodies of water with elevated TDS values may have aesthetic issues, such as an abnormal color or taste [38]. The chemical load comparison for the three parameters in 2012 to 2018 is shown in Figure 3.
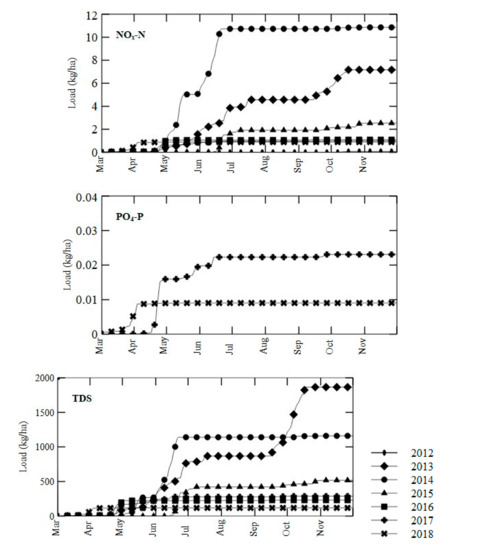
Figure 3.
Cumulative nitrite + nitrate nitrogen (NOx-N), orthophosphate (PO4-P), and total dissolved solids (TDS) loads from the east sump. Orthophosphate concentration data were not collected prior to September 2016, so only data from 2017 and 2018 are shown.
The largest amounts of load were lost in the spring for all three parameters. The high amounts of NOx-N load in the spring compared to that in the fall corresponds with relatively high NOx-N concentrations and relatively large amounts of drainage outflow. Since nitrate is more soluble in water than PO4-P, a higher proportion of nitrate loss is expected in the spring, when more water is lost through drainage outflow compared to that in the fall. The highest total NOx-N load was lost in 2014, when the second highest drainage outflow occurred, with a value of 10.9 kg/ha/year. This correlation provides further evidence that a greater drainage outflow has a greater impact on the loss of nutrient load than the nutrient concentration, similar to what has been previously reported [39]. The lowest NOx-N load occurred in 2012 and was equal to 0.08 kg/ha/year. Concentrations of NOx-N were high in samples during this year, but the extremely low amount of outflow in 2012 did not allow for substantial nutrient loss. Data from nearby Manitoba had a total nitrate load of 10 kg/ha/year when drainage outflow averaged over three replications was equal to 53 mm [40]. A similar drainage outflow of 56 mm occurred in 2013, but NOx-N load was approximately 7 kg/ha/year, much lower than that found in the Manitoba study.
In 2017, the highest PO4-P load of 0.023 kg/ha/year occurred. The lowest PO4-P load of 0.009 kg/ha/year occurred in 2018. Data from 2012–2016 were unavailable because PO4-P concentrations were not measured. Results from the same Manitoba study that was discussed in relation to NOx-N load showed an orthophosphate load of 0.08 kg/ha/year when drainage outflow equaled 53 mm [40]. Higher PO4-P loads may have occurred from 2012–2016 because of more drainage outflow, although the exact values are unknown. Since smectite is the dominant clay mineral in the soil in the research field, soil cracking was common, which created multiple macropores during dry periods. Previous research has indicated PO4-P loss from tile-drained fields most commonly occurs through macropores, so relatively high PO4-P loads were expected in this area, but may have been reduced by the small amounts of drainage outflow via CD practice [31].
The TDS loads appeared to occur more often in the spring compared to that in the fall, similar to the NOx-N and PO4-P loads. In 2013, the TDS was different from other years, because TDS increased in October during the FD-fall period. The highest load once again occurred in 2013, which was also the wettest year during the study periods. The lowest cumulative TDS load occurred in 2012, the driest year with the least drainage outflow. The coefficient of determination (R2) value between cumulative load and cumulative drainage outflow was above 0.95 for PO4-P and TDS, but only 0.62 for NOx-N.
3.5. Soil Quality
Since the water quality for the SI application is marginal with an EC ranging from 1 dS/m to 2 dS/m and an SAR ranging from 4 to 6 [16], the impact of the SI water on soil quality has been a concern from the beginning of the project, especially in terms of an increase in soil sodicity. When present in high amounts, soil sodicity can lead to further consequences such as decreased soil permeability [41] and reduced yield [42]. To observe the impact, soil sampling around a tile drainage pipe was planned for every year immediately after harvest. However, this has not been done every year due to weather and funding limitations. The average values and standard deviations for the three replicates at the three locations in the field (Figure 1) are described in Table 5 according to the distance above the tile.

Table 5.
Mean pH, electroconductivity (EC), and sodium adsorption ratio (SAR) in relation to the tile position in 2014, 2015, and 2017. Sample size (n) is given next to each row title and standard deviations are listed for each value.
The highest EC of 1.40 dS/m occurred in 2014, and the highest SAR of 4.04 occurred in 2017. The highest pH value of 8.36 occurred in 2014, while the lowest pH value of 7.82 occurred in 2015. Compared to previously reported soil pH data collected in North Dakota, the range of values between 7.5 and 8 is typical for Richland County [43]. Because of the buffering capabilities of calcium carbonate and organic matter, which were very prevalent in the soil, drastic changes in pH were not expected during the study period [44]. The lowest EC value of 0.77 dS/m was recorded in 2015, and the lowest SAR value of 1.04 was recorded in 2014. Assuming the initial soil conditions were the same at any distance from the tile, changes to pH, EC, and SAR over time are likely attributed to drainage and SI practices in the field.
The four samples taken each year showed no significant patterns of salt reduction. Additional years of extensive drainage may have been needed to produce noticeable salt reduction in the field associated with SSD. As time goes on, the range of EC values in relation to tile position is expected to become lesser due to the leaching of salts from the soil profile through drainage, eventually leading to a homogenous distribution of salts less prevalent than conditions prior to drainage. For this to occur, there needs to be enough precipitation to allow for the downward movement of salts.
The SAR values in 2014 were the lowest out of the 3 years of data. Also, 2014 was the only year that showed increases in the SAR values as the distance above the tile increased. The results from 2015 and 2017 showed significantly higher SAR values near the tile compared to 81 cm from the tile. Despite having a percentage of total precipitation in the form of SI comparable to that of 2015, the cumulative effects of SI with water of marginal quality may not have been evident in 2014, causing much lower SAR values than those in 2015. Considerably less of the total precipitation in 2017 occurred as SI, but the high SAR values may have been a cumulative SI impact from the earlier years. Despite the range of SAR values found in this study, the soil was still well below recommended maximum SAR values. To be classified as a sodic soil, the SAR should be above 13, while the values found in this study fell well below [45]. If SI was the main source of water for the field, then the SAR may have been negatively impacted, but this scenario has not yet occurred and is unlikely to due to high magnesium and calcium concentrations in the soil.
4. Conclusions
Because the water source was different for the SI application than that from the drainage, differences in chemical concentrations were expected between the water samples from the field throughout the growing season. A major factor impacting these differences was the SAR of the SI water, which was higher than those of the CD and FD water sources. Along with water samples, soil samples were also taken during the study period. Soil samples above the drain tiles were used to assess the impact of drainage and SI on soil quality. An increase in SAR near the drain tiles was found, possibly due to the higher SAR in the SI water.
The results showed that there were differences related to salinity parameters between the water samples during the SI period compared to the water samples during other times in the growing season. This is likely attributed to the differences in water sources between the SI and CD/FD. The differences in NOx-N concentration may have been due to difference in fertilizer timing and the amount of drainage outflow. Because of less drainage outflow in North Dakota compared to other regions in the United States, nutrient loads in this study were much lower than those reported in studies elsewhere. Soil sample results showed significant spatial differences in SAR in 2015 and 2017, although these values were well below those found in sodic soils. Because of the marginal quality of the SI water, SAR is expected to be lower in the soil when less of the total precipitation in the field is from SI.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, K.A. and X.J.; Methodology, K.A. and X.J.; Investigation, K.A. and X.J.; Resources, X.J.; Writing—Original draft preparation, K.A.; Writing—Review and editing, X.J., T.D. and T.S.; Data analysis, M.L.; Supervision, X.J.; Funding acquisition, X.J. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by USDA National Institute of Food and Agriculture project 2015-68007-23193, NASA ROSES Project NNX15AC47G, USDA Sustainable Agriculture Research and Education project LNC11-332, ND State Water Commission, ND Soybean Council, ND Water Resources Research Institute, ND Agricultural Experimental Station, and USDA Hatch project ND01482.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank James Moos, Dongqing Lin, and Talon Mack for their technical support and help with field work.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Jaynes, D.B.; Colvin, T.S.; Karlen, D.L.; Cambardella, C.A.; Meek, D.W. Nitrate loss in subsurface drainage as affected by nitrogen fertilizer rate. J. Environ. Qual. 2001, 30, 1305–1314. [Google Scholar]
- Gentry, L.E.; David, M.B.; Royer, T.V.; Mitchell, C.A.; Starks, K.M. Phosphorus transport pathways to streams in tile-drained agricultural watersheds. J. Environ. Qual. 2007, 36, 408–415. [Google Scholar]
- Finocchiaro, R.G. Agricultural Subsurface Drainage Tile Locations by Permits in North Dakota [Data Set]; U.S. Geological Survey: Jamestown, ND, USA,, 2014.
- Kandel, H.J.; Brodshaug, J.A.; Steele, D.D.; Ransom, J.K.; DeSutter, T.M.; Sands, G.R. Subsurface drainage effects on soil penetration resistance and water table depth on a clay soil in the Red River of the North Valley, USA. Agric. Eng. Int. CIGR J. 2013, 15, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- ASABE Standards. S526.4: Soil and Water Terminology; ASABE: St. Joseph, MI, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- ASAE Standards. EP479.1: Operation of Controlled Drainage Systems in Humid Regions; ASABE: St. Joseph, MI, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Madramootoo, C.A.; Dodds, G.T.; Papadopoulos, A. Agronomic and environmental benefits of water-table management. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 1993, 119, 1052–1065. [Google Scholar]
- Niaghi, A.R.; Jia, X.; Steele, D.D.; Scherer, T.F. Drainage water management effects on energy flux partitioning, evapotranspiration, and crop coefficients of corn. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 225, 105760. [Google Scholar]
- Wesström, I.; Messing, I.; Linner, H.; Lindström, J. Controlled drainage—Effects on drain outflow and water quality. Agric. Water Manag. 2001, 47, 85–100. [Google Scholar]
- Drury, C.F.; Tan, C.S.; Gaynor, J.D.; Oloya, T.O.; Welacky, T.W. Influence of controlled drainage-subirrigation on surface and tile drainage nitrate loss. J. Environ. Qual. 1996, 25, 317–324. [Google Scholar]
- Feser, S.E.; Strock, J.S.; Sands, G.R.; Birr, A.S. Controlled drainage to improve edge of-field water quality in southwest Minnesota, USA. In Proceedings of the Drainage IX: Ninth International Drainage Symposium, Quebec City, QC, Canada, 13–16 June 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Choudhary, O.P.; Ghuman, B.S.; Josan, A.S.; Bajwa, M.S. Effect of alternating irrigation with sodic and non-sodic waters on soil properties and sunflower yield. Agric. Water Manag. 2006, 85, 151–156. [Google Scholar]
- Jalali, M.; Ranjbar, F. Effects of sodic water on soil sodicity and nutrient leaching in poultry and sheep manure amended soils. Geoderma. Reg. 2009, 153, 194–204. [Google Scholar]
- Bauder, J.W. Rainfall Induced Dispersion and Hydraulic Conductivity Reduction under Low SAR × EC Combinations in Smectite-Dominated Soils of Eastern Montana. Report to Montana Department of Environmental Quality (DEQ Contract# 207066). 2009; 62p. Available online: http://deq.mt.gov/Portals/112/Energy/CoalbedMethane/Documents/MuggliFinalReportwithoutline.pdf (accessed on 18 October 2010).
- Ayers, R.S.; Westcot, D.W. Water Quality for Agriculture. FAO Irrigation and Drainage Paper Vol 29 Rev. 1; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, X.; DeSutter, T.M.; Lin, Z.; Schuh, W.M.; Steele, D.D. Subsurface drainage and subirrigation effects on water quality in southeast North Dakota. Trans. ASABE 2012, 55, 1757–1769. [Google Scholar]
- Rijal, I.; Jia, X.; Zhang, X.; Steele, D.D.; Scherer, T.F.; Akyuz, A. Effects of subsurface drainage on evapotranspiration for corn and soybean crops in southeastern North Dakota. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2012, 138, 1060–1067. [Google Scholar]
- NRCS. Web Soil Survey. 2020. Available online: http://websoilsurvey.nrcs.usda.gov/app/WebSoilSurvey.aspx/ (accessed on 22 December 2020).
- IUSS Working Group WRB. World Reference Base for Soil Resources 2014, Update 2015 International Soil Classification System for Naming Soils and Creating Legends for Soil Maps; World Soil Resources Reports No. 106; FAO: Roma, Italy, 2015; 192p. [Google Scholar]
- NDAWN. North Dakota Agriculture Weather Network. Available online: https://ndawn.ndsu.nodak.edu/ (accessed on 21 December 2020).
- Jia, X.; Scherer, T.F. Reducing cost of water quality monitoring in tile drainage outflow using electrical conductivity as a surrogate. In Using 21st Century Technology to Better Manage Irrigation Water Supplies, Proceedings of the Seventh International Conference on Irrigation and Drainage, Phoenix, AZ USA, 16–19 April 2013; Wallin, B.T., Anderson, S.S., Wallin, B.T., Anderson, S.S., Eds.; U.S. Committee on Irrigation and Drainage: Denver, CO, USA, 2013; pp. 213–225. [Google Scholar]
- NDDEQ. Standard Operating Procedures for the Collection and Preservation of Stream and River Grab Samples for Chemical and Biological Analysis. Section 7.08. Revision 2; 2011. Available online: https://deq.nd.gov/publications/WQ/3_WM/SOPs/7.08_StreamOrRiverGrabSampleSOP.pdf (accessed on 22 December 2020).
- Pang, X. Impact of Subsurface Drainage on Water Availability in the Red River Basin. Master’s Thesis, Department of Agricultural and Biosystems Engineering North Dakota State University, Fargo, ND, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, X.; Scherer, T.F.; Steele, D.D.; DeSutter, T.M. Subirrigation system performance and evaluation in the Red River Valley of the North. Appl. Eng. Agric. 2017, 33, 811–818. [Google Scholar]
- Quarnstrom, J.; (NDDEQ, Bismarck, ND, USA). Personal communication, 2020.
- Mathews, S.; (NDSU Soil Testing Lab, Fargo, ND, USA). Personal communication, 2020.
- DeSutter, T.; Franzen, D.; He, Y.; Wick, A.; Lee, J.; Deutsch, B.; Clay, D. Relating sodium percentage to sodium adsorption ratio and its utility in the northern Great Plains. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2015, 79, 1261–1264. [Google Scholar]
- Scherer, T.F.; Jia, X. A simple method to measure the flow rate and volume from tile drainage pump stations. Appl. Eng. Agric. 2010, 26, 79–83. [Google Scholar]
- Helmers, M.; Christianson, R.; Brenneman, G.; Lockett, D.; Pederson, C. Water table, drainage, and yield response to drainage water management in southeast Iowa. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2012, 67, 495–501. [Google Scholar]
- Carstensen, M.V.; Børgesen, C.D.; Ovesen, N.B.; Poulsen, J.R.; Hvid, S.K.; Kronvang, B. Controlled drainage as a targeted mitigation measure for nitrogen and phosphorus. J. Environ. Qual. 2019, 48, 677–685. [Google Scholar]
- Vidon, P.; Cuadra, P.E. Phosphorus dynamics in tile-drain flow during storms in the US Midwest. Agric. Water Manag. 2011, 98, 532–540. [Google Scholar]
- Skaggs, R.W.; Fausey, N.R.; Evans, R.O. Drainage water management. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2012, 67, 167A–172A. [Google Scholar]
- Wesström, I.; Messing, I. Effects of controlled drainage on N and P losses and N dynamics in a loamy sand with spring crops. Agric. Water Manag. 2007, 87, 229–240. [Google Scholar]
- North Dakota Century Code. Chapter 33.1-16-02.1 Standards of Quality for Waters of the State. Available online: https://www.legis.nd.gov/information/acdata/pdf/33.1-16-02.1.pdf (accessed on 21 December 2020).
- Keller, L.P.; McCarthy, G.J.; Richardson, J.L. Mineralogy and stability of soil evaporites in North Dakota. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1986, 50, 1069–1071. [Google Scholar]
- USEPA. Drinking Water Advisory: Consumer Acceptability Advice and Health Effects Analysis on Sulfate. EPA-822-R-03-007; Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2003.
- Turner, R.E.; Rabalais, N.N. Linking landscape and water quality in the Mississippi River Basin for 200 years. Bioscience 2003, 53, 563. [Google Scholar]
- Sibanda, T.; Chigor, V.N.; Koba, S.; Obi, C.L.; Okoh, A.I. Characterisation of the physicochemical qualities of a typical rural-based river: Ecological and public health implications. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 11, 1771–1780. [Google Scholar]
- Bjorneberg, D.L.; Kanwar, R.S.; Melvin, S.W. Seasonal changes in flow and nitrate-N loss from subsurface drains. Trans. ASAE 1996, 39, 961–967. [Google Scholar]
- Cordeiro, M.R.; Ranjan, R.S.; Ferguson, I.J.; Cicek, N. Nitrate, phosphorus, and salt export through subsurface drainage from corn fields in the Canadian Prairies. Trans. ASABE 2014, 57, 43–50. [Google Scholar]
- Sumner, M. Sodic soils—New perspectives. Soil Res. 1993, 31, 683. [Google Scholar]
- Rengasamy, P. Soil processes affecting crop production in salt-affected soils. Funct. Plant Biol. 2010, 37, 613–620. [Google Scholar]
- Franzen, D.W.; Nanna, T.; Norvell, W.A. A survey of soil attributes in North Dakota by landscape position. Agron. J. 2006, 98, 1015–1022. [Google Scholar]
- Magdoff, F.R.; Bartlett, R.J. Soil pH buffering revisited. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1985, 49, 145–148. [Google Scholar]
- Richards, L.A. Diagnosis and Improvement of Saline and Alkali Soils; Agriculture Handbook; USDA: Washington, DC, USA, 1954; Volume 60.
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).