From Waste to Biosorbent: Removal of Congo Red from Water by Waste Wood Biomass
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
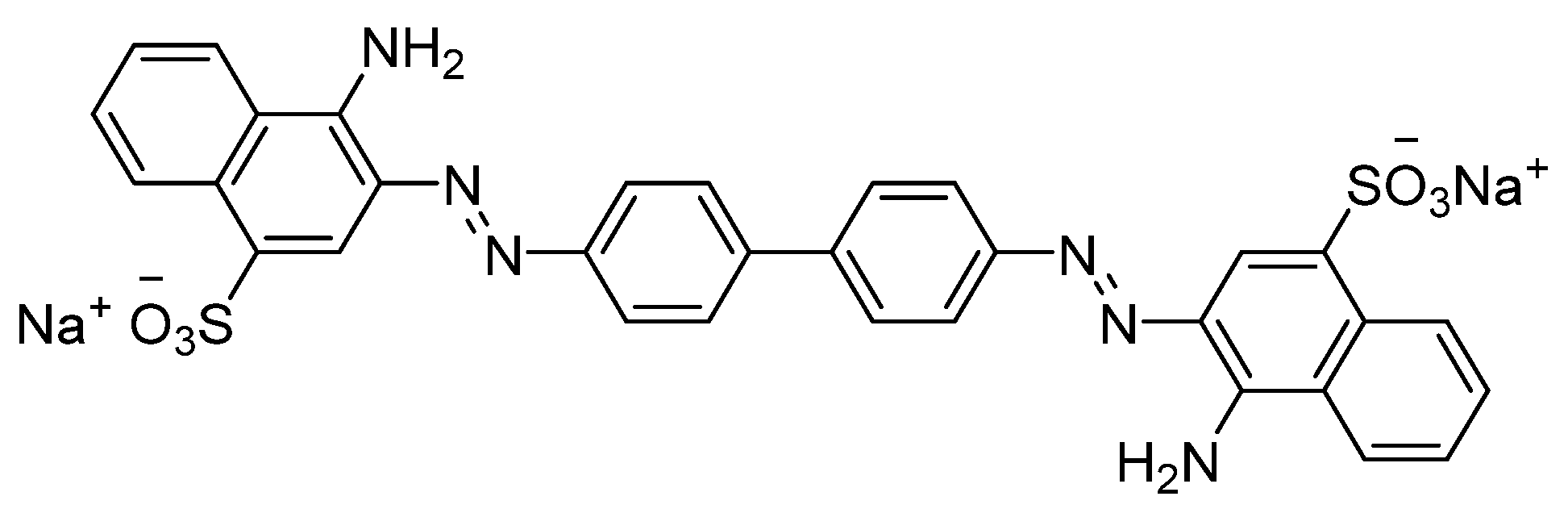
2.1. Biosorbents and Adsorbate
2.2. Model Congo Red (CR) Solutions and Synthetic Wastewater Preparation
2.3. Biosorbent Characterization
2.4. Batch Biosorption Studies
Biosorption Studies Using EP as Biosorbent
3. Results and Discussion
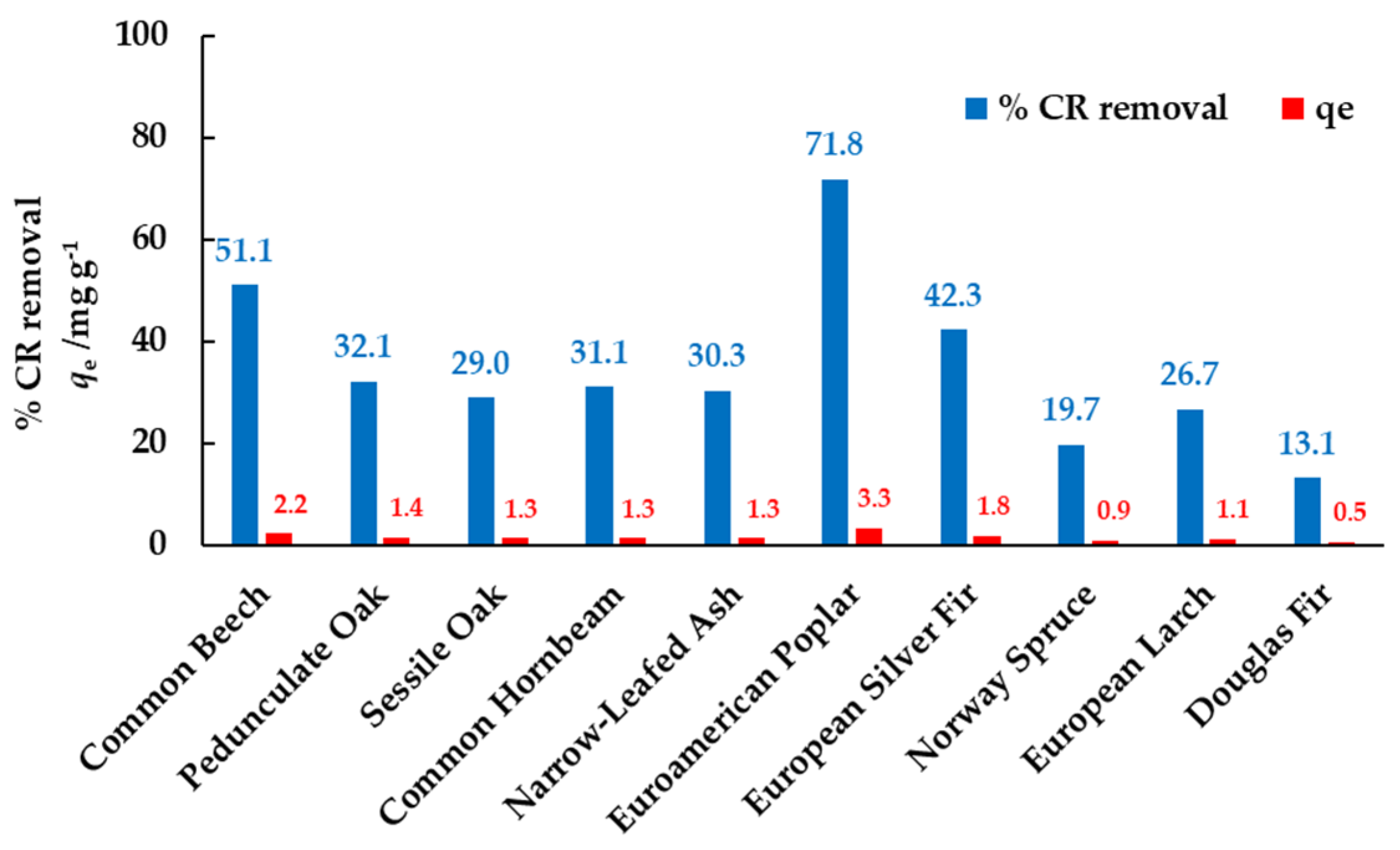
3.1. Screening of Waste Biomass of Different Wood Species as Biosorbents for CR Removal
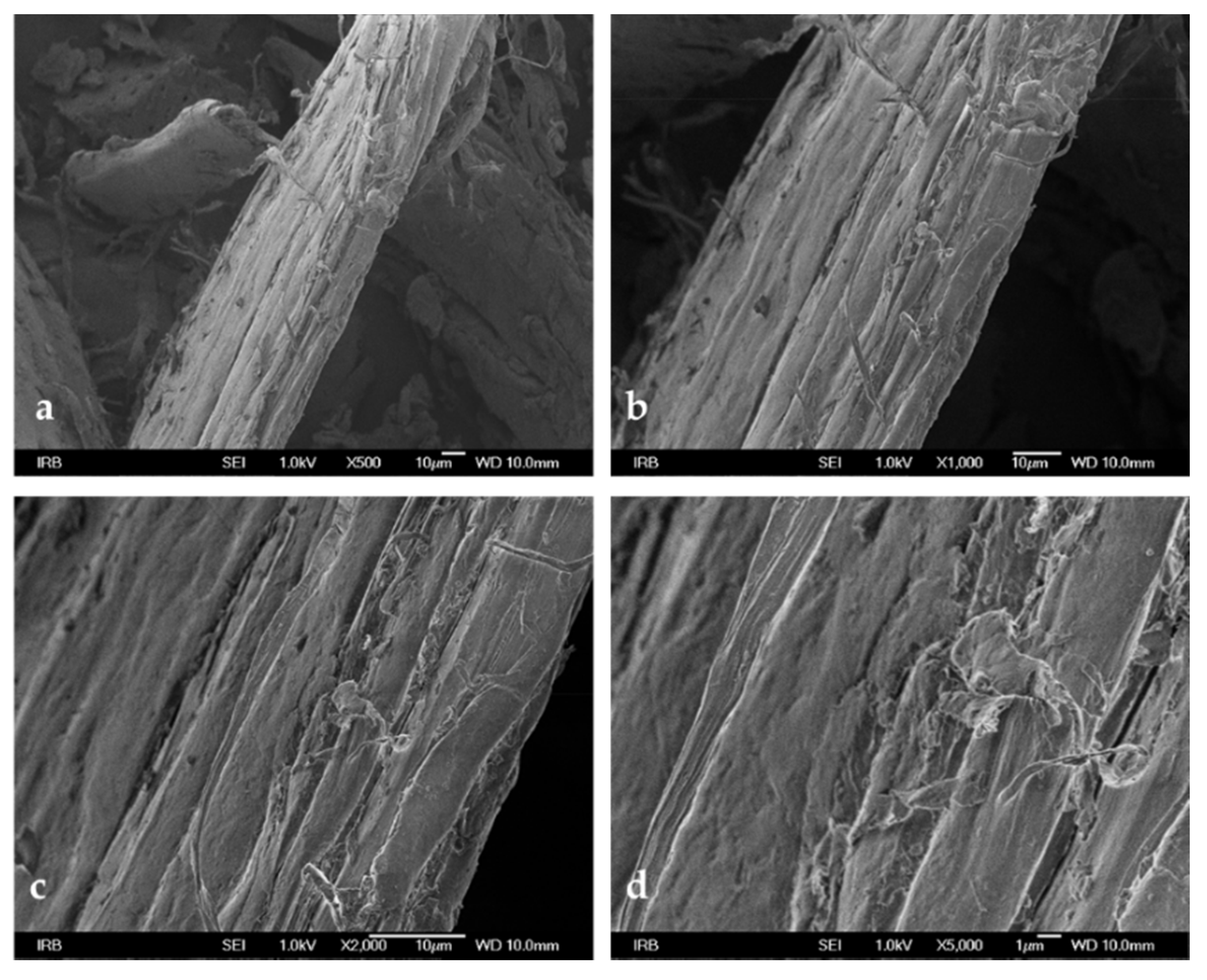
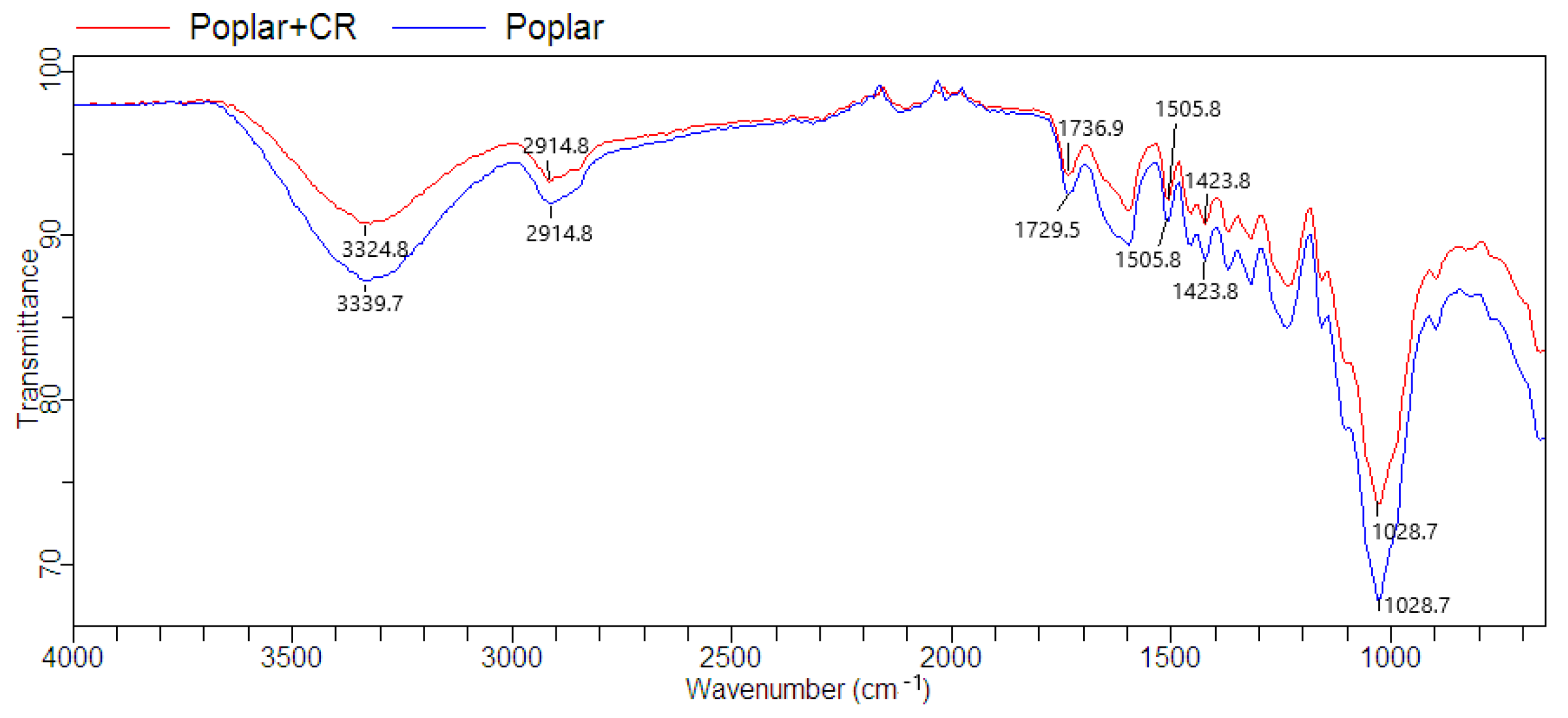
3.2. Euroamerican Poplar (EP) Characterization
3.3. Biosorption Studies Using EP as Biosorbent
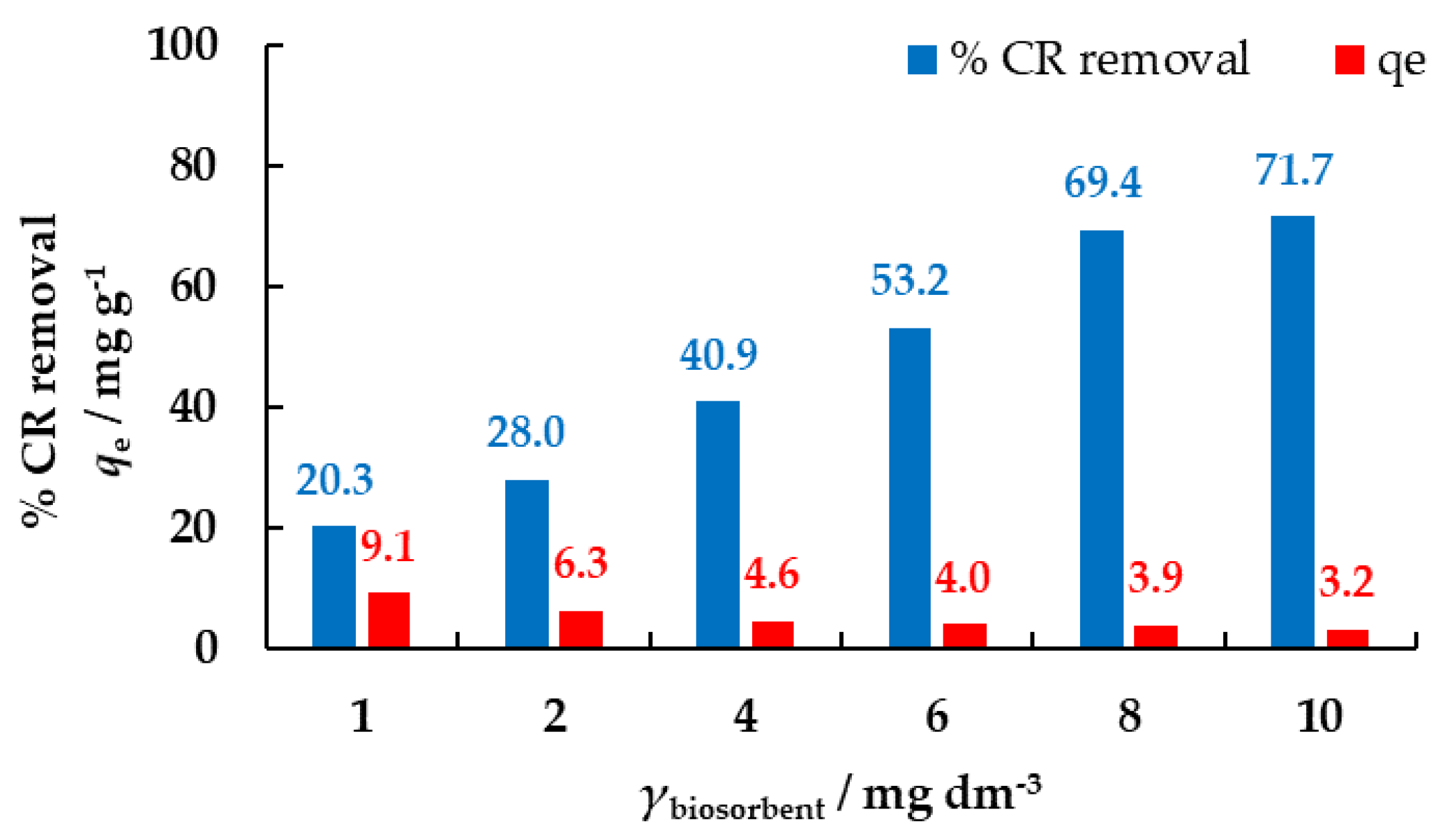
3.3.1. The Effect of Biosorbent Concentration
3.3.2. The Effect of Contact Time
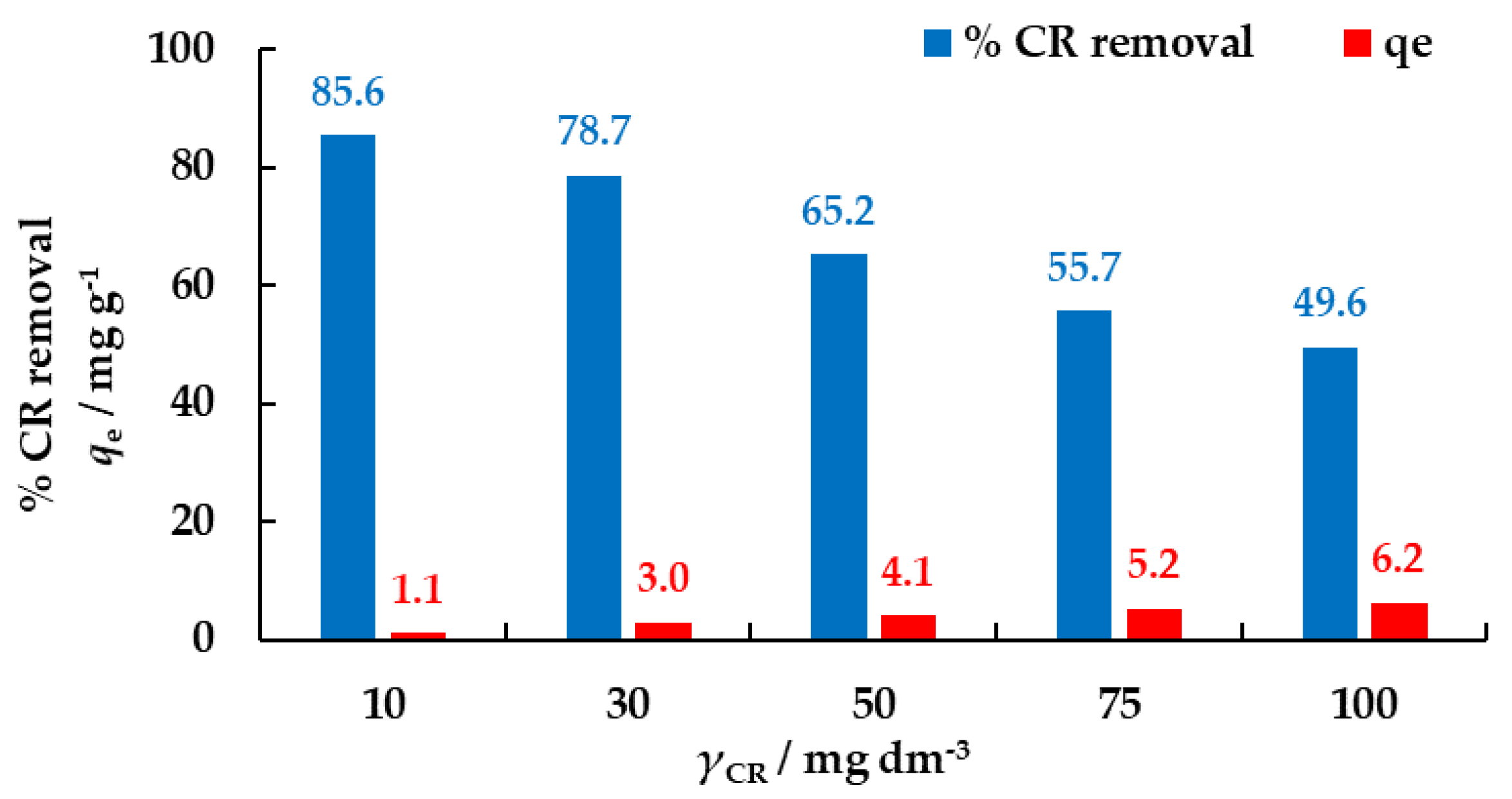
3.3.3. The Effect of Initial CR Concentration
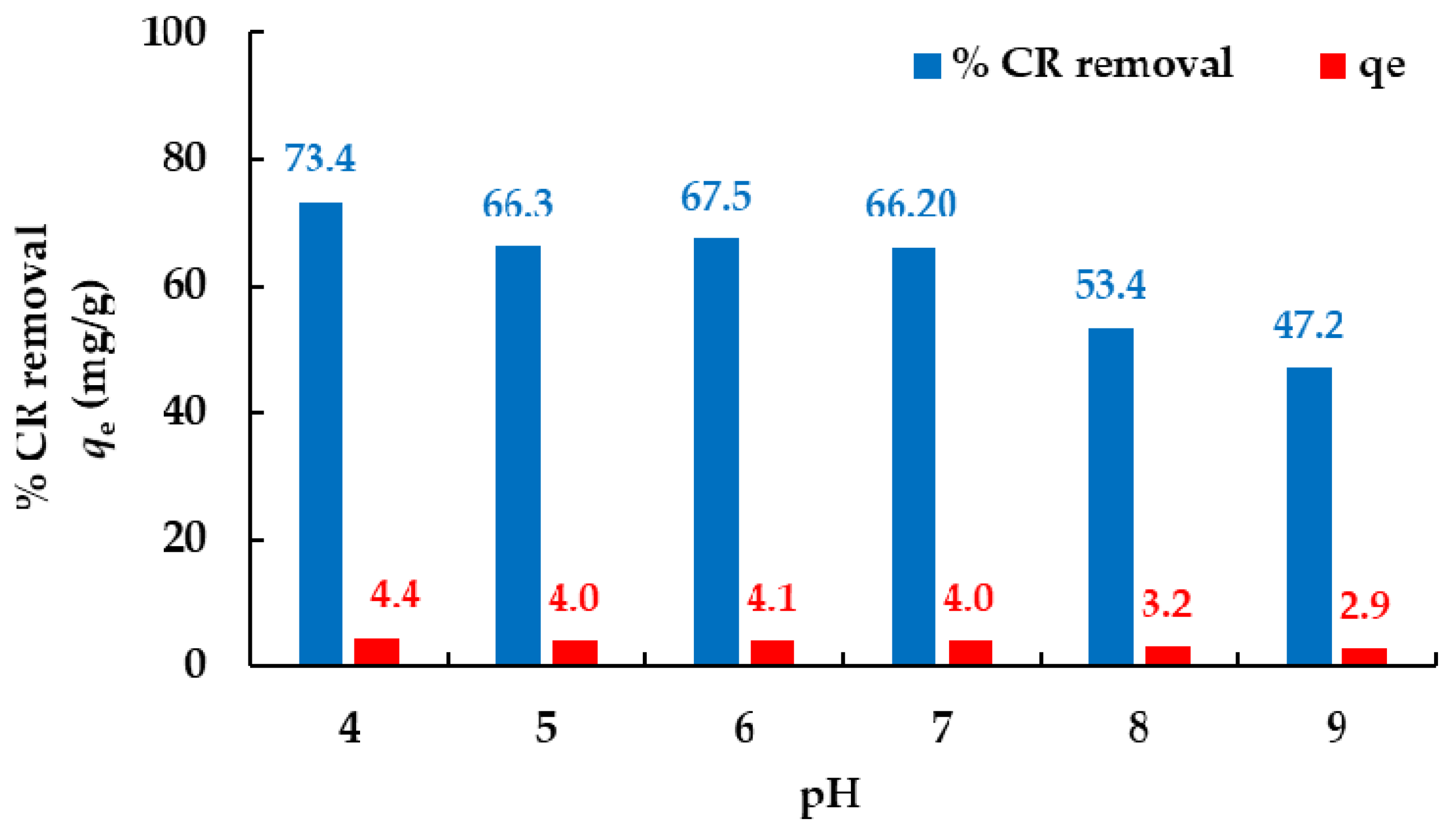
3.3.4. The Effect of pH
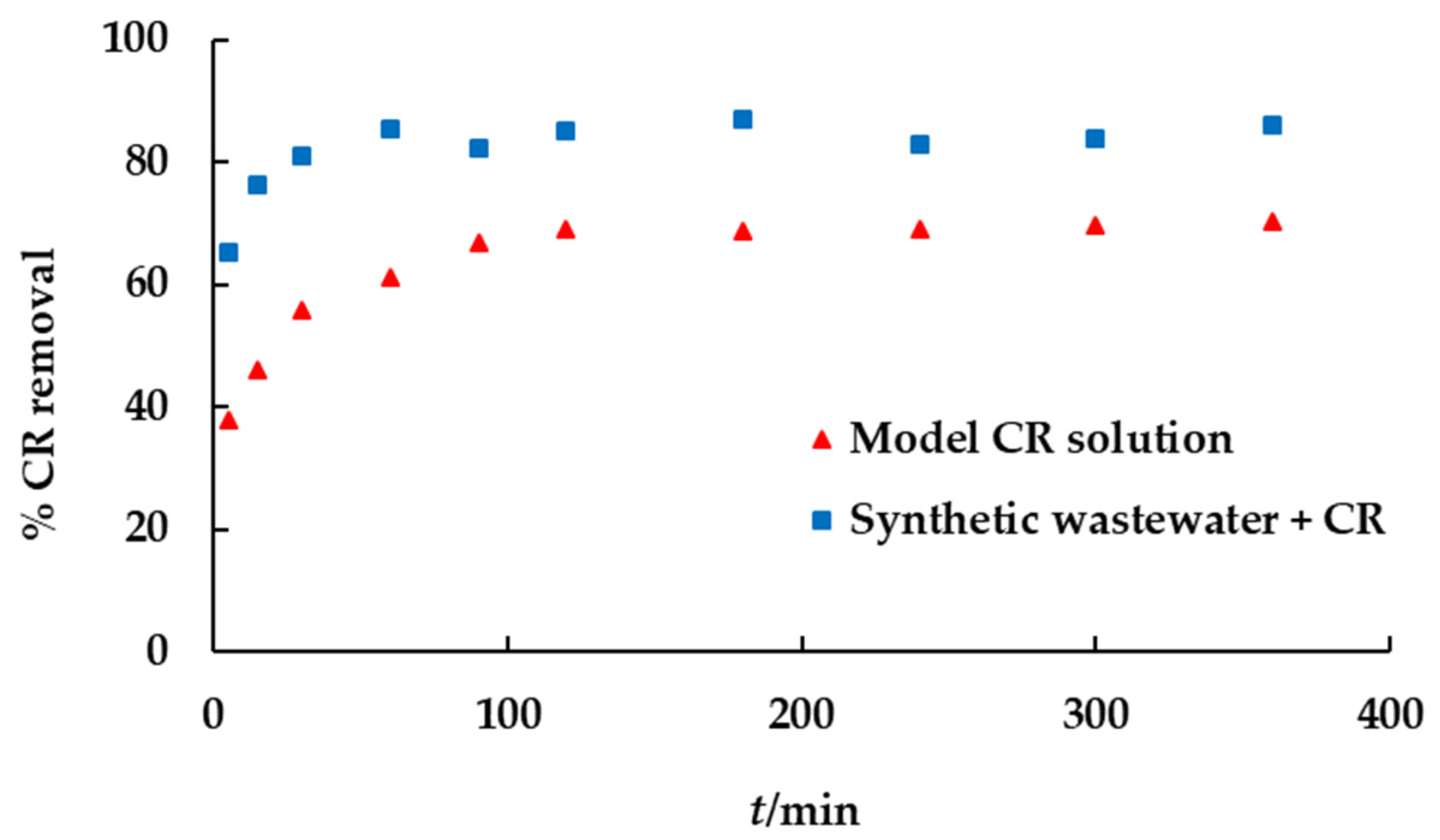
3.3.5. Biosorption of CR to EP from Synthetic Wastewater
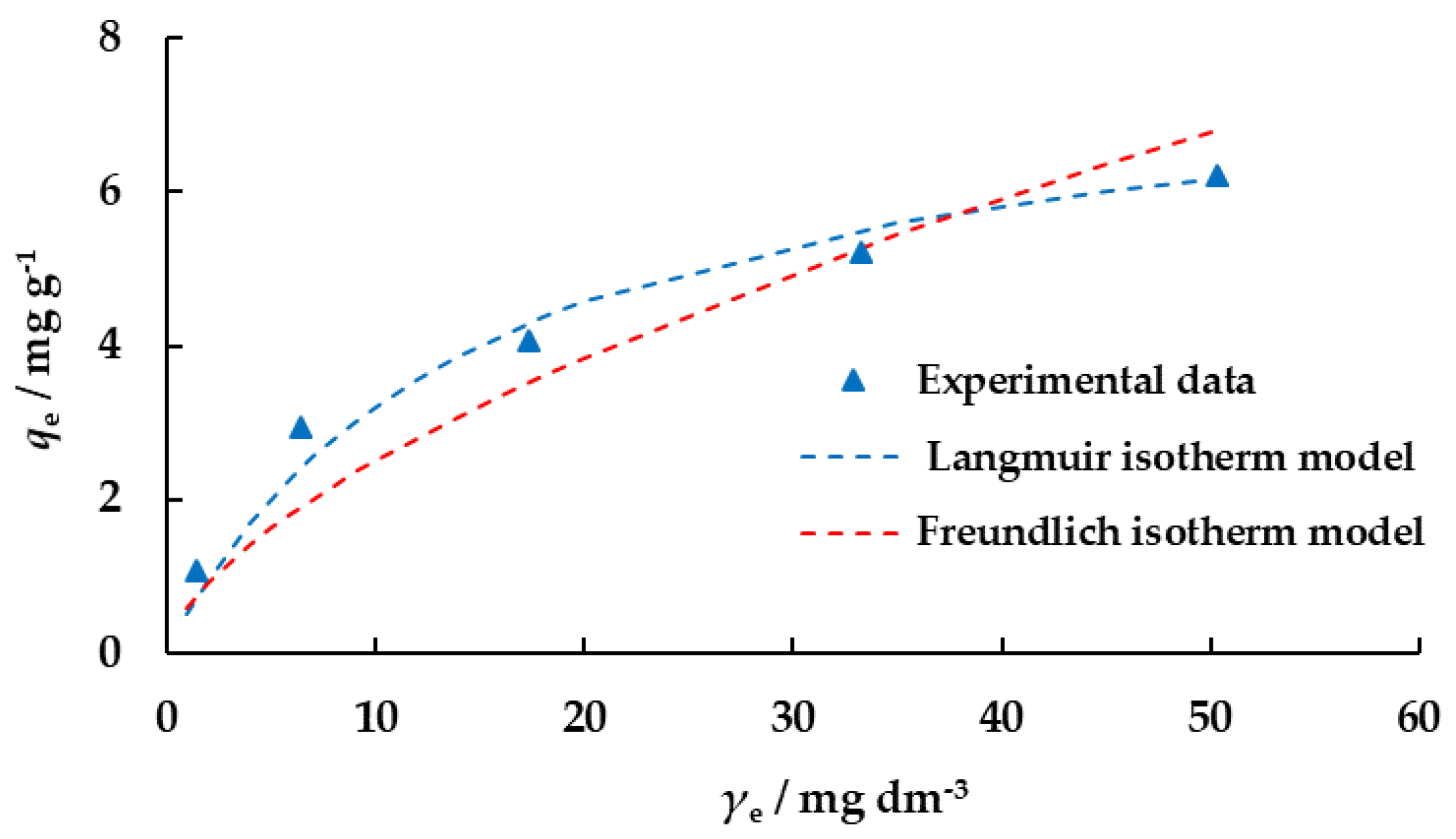
3.3.6. Adsorption Isotherms
3.3.7. Adsorption Kinetics
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Uasuf, A.; Becker, G. Wood pellets production costs and energy consumption under different framework conditions in Northeast Argentina. Biomass Bioenerg. 2011, 35, 1357–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ejder-Korucu, M.; Gürses, A.; Doğar, Ç.; Sharma, S.K.; Açıkyıldız, M. Removal of Organic Dyes from Industrial Effluents: An Overview of Physical and Biotechnological Applications. In Green Chemistry for Dyes Removal from Wastewater, 1st ed.; Sharma, S.K., Ed.; Scrivener Publishing: Beverly, MA, USA, 2015; pp. 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- Mathur, N.; Bhatnagar, P.; Bakre, P. Assessing mutagenicity of textile dyes from Pali (Rajasthan) using ames bioassay. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2006, 4, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puvaneswari, N.; Muthukrishnan, J.; Gunasekaran, P. Toxicity assessment and microbial degradation of azo dyes. Indian J. Exp. Biol. 2006, 44, 618–626. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yesilada, O.; Asma, D.; Cing, S. Decolorization of textile dyes by fungal pellets. Process Biochem. 2003, 38, 933–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crini, G. Non-conventional low-cost adsorbents for dye removal: A review. Bioresor. Technol. 2006, 97, 1061–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michalak, I.; Chojnacka, K.; Witek-Krowiak, A. State of the art for the biosorption process—A review. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2013, 170, 1389–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sjostrom, E. Wood Chemistry. Fundamentals and Applications, 2nd ed.; Academic press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1993; p. 292. [Google Scholar]
- Litefti, K.; Freire, M.S.; Stitou, M.; González-Álvarez, J. Adsorption of an anionic dye (Congo red) from aqueous solutions by pine bark. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, A.V.F.N.; da Silva, A.R.; Pereira, M.G.; Licinio, M.V.V.J.; Ribeiro, J.N. Wood sawdust powder from Corimbya citriodora to congo red toxic dye adsorption. Indian J. Appl. Res. 2018, 8, 29–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burcă, S.; Indolean, C.; Măicăneanu, A. Isotherms study of congo red biosorption equilibrium using FIR (Abies Nordmanniana) sawdust biomass. Rev. Roum. Chim. 2017, 62, 381–389. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, T.A.; Sharma, S.; Khan, E.A.; Mukhlif, A.A. Removal of congo red and basic violet 1 by chir pine (Pinus roxburghii) sawdust, a saw mill waste: Batch and column studies. Toxicol. Environ. Chem. 2014, 96, 555–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mane, V.S.; Vijay Babu, P.V. Kinetic and equilibrium studies on the removal of Congo red from aqueous solution using Eucalyptus wood (Eucalyptus globulus) sawdust. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2013, 44, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardazi, S.M.H.; Shah, J.A.; Ashfag, T.; Sherazi, T.A.; Ali, M.A.; Pervez, A.; Rashid, N. Equilibrium, kinetics and thermodynamic study of the adsorptive removal of methylene blue from industrial wastewater by white cedar sawdust. Environ. Prot. Eng. 2019, 45, 5–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velić, N.; Stjepanović, M.; Begović, L.; Habuda-Stanić, M.; Velić, D.; Jakovljević, T. Valorisation of waste wood biomass as biosorbent for the removal of synthetic dye methylene blue from aqueous solutions. South-East Eur. For. 2018, 9, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salazar-Rabago, J.J.; Leyva-Ramos, R.; Rivera-Utrilla, J.; Ocampo-Perez, R.; Cerino-Cordova, F.J. Biosorption mechanism of Methylene Blue from aqueous solution onto White Pine (Pinus durangensis) sawdust: Effect of operating conditions. Sustain. Environ. Res. 2017, 27, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdaoui, O. Batch study of liquid-phase adsorption of methylene blue using cedar sawdust and crushed brick. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 135, 264–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tezcan Un, U.; Ates, F. Low-cost adsorbent prepared from poplar sawdust for removal of disperse orange 30 dye from aqueous solutions. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 16, 899–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhouairi, S.; Ouachtak, H.; Addi, A.A.; Jada, A.; Douch, J. Natural Sawdust as Adsorbent for the Eriochrome Black T Dye Removal from Aqueous Solution. Water Air Soil Poll. 2019, 230, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, T.K.; Bishwas, R.K.; Karmaker, S.; Islam, Z. Adsorption Characteristics of Allura Red AC onto Sawdust and Hexadecylpyridinium Bromide-Treated Sawdust in Aqueous Solution. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 13358–13374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saroha, A.; Ghosh, A. Biosorption of Safranine O Dye by SawDust. In Advances in Water Pollution Monitoring and Control; Springer Transactions in Civil and Environmental Engineering; Siddiqui, N., Tauseef, S., Dobhal, R., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asses, N.; Ayed, L.; Hkiri, N.; Hamdi, M. Congo Red Decolorization and Detoxification by Aspergillus niger: Removal Mechanisms and Dye Degradation Pathway. BioMed Res. Int. 2018, 3049686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clement, C.G.; Truong, L.D. An evaluation of Congo red fluorescence for the diagnosis of amyloidosis. Hum. Pathol. 2014, 45, 1766–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD. Guideline for Testing of Chemicals; Test Guidline 302 B; OECD: Paris, France, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Jewiarz, M.; Wróbel, M.; Mudryk, K.; Szufa, S. Impact of the Drying Temperature and Grinding Technique on Biomass Grindability. Energies 2020, 13, 3392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niemczyk, M.; Kaliszewski, A.; Jewiarz, M.; Wróbel, M.; Mudryk, K. Productivity and biomass characteristics of selected poplar (Populus spp.) cultivars under the climatic conditions of northern Poland. Biomass Bioenergy 2018, 111, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karbowniczak, A.; Hamerska, J.; Wróbel, M.; Jewiarz, M.; Nęcka, K. Evaluation of Selected Species of Woody Plants in Terms of Suitability for Energy Production. In Renewable Energy Sources: Engineering, Technology, Innovation; Springer Proceedings in Energy; Mudryk, K., Werle, S., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 735–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nacu, G. Studies on the Use of Cellulosic Waste to Reduce Environmental Pollution. Ph.D. Thesis, Technical University “Gheorghe Asachi” of Iaşi, Iaşi, Romania, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Da Silva, B.C.; Zanutto, A.; Pietrobelli, M.T.A.J. Biosorption of reactive yellow dye by malt bagasse. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2019, 37, 236–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.; Rafatullah, M.; Sulaiman, O.; Ibrahim, M.H.; Hashim, R. Scavenging behaviour of meranti sawdust in the removal of methylene blue from aqueous solution. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 170, 357–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pistorius, A.M.A.; DeGrip, W.J.; Egorova-Zachernyuk, T.A. Monitoring of Biomass Composition from Microbiological Sources by Means of FT-IR Spectroscopy. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2009, 103, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adegoke, K.A.; Bello, O.S. Dye sequestration using agricultural wastes as adsorbents. Water Resour. Ind. 2015, 12, 8–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, E.W.; Karthikeyan, K.G.; Tshabalala, M.A. Adsorption mechanism of cadmium on juniper bark and wood. Bioresour. Technol. 2007, 98, 588–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suteu, D.; Rusu, G.; Zaharia, C. Removal of reactive dye Orange 16 from aqueous solution by sorption onto sawdust. Chem. Bull. Politeh. Univ. 2011, 56, 24–28. [Google Scholar]
- Bulut, Y.; Aydin, H. A kinetics and thermodynamics study of methylene blue adsorption on wheat shells. Desalination 2006, 194, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagub, M.T.; Sen, T.K.; Afroze, S.; Ang, H.M. Dye and its removal from aqueous solution by adsorption: A review. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 209, 172–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanyonyi, W.; Onyari, J.; Shiundu, P. Adsorption of Congo Red Dye from Aqueous Solutions Using Roots of Eichhornia crassipes: Kinetic and Equilibrium Studies. Energy Procedia 2014, 50, 862–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Chen, H.; Ji, F.; Yuan, S. Removal of Congo Red from Aqueous Solution by Cattail Root. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 173, 292–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abu-El-Halawa, R.; Zabin, S.A.; Abu-Sittah, H.H. Investigation of Methylene Blue Dye Adsorption from Polluted Water Using Oleander Plant (Al Defla) Tissues as Sorbent. Am. J. Environ. Sci. 2016, 12, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crini, G.; Peindy, H.N.; Gimbert, F.; Robert, C. Removal of C.I. Basic Green (Malachite Green) from aqueous solutions by adsorption using cyclodextrin-based adsorbent: Kinetic and equilibrium studies. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2007, 53, 97–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiol, N.; Villaescusa, I. Determination of sorbent point zero charge:usefulness in sorption studies. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2009, 7, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanzu, H.A.; Onyari, J.M.; Shiundu, P.M. Brewers’ spent grain in adsorption of aqueous Congo Red and Malachite Green dyes: Batch and continuous flow systems. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 380, 120897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.X.; Zhang, R.J.; Tang, L.; Zhang, J.H.; Mao, Z.G. Use of cassava residue for the removal of Congo red from aqueous solution by a novel process incorporating adsorption and in vivo decolorization. BioResources 2014, 9, 6682–6698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, R.; Sikawar, S. Adsorption and desorption studies of Congo red using low-costadsorbent: Activated de-oiled mustard. Desalination Water Treat. 2013, 52, 7400–7411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hameed, B.H.; Ahmad, A.A. Batch adsorption of methylene blue from aqueous solution by garlic peel, an agricultural waste biomass. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 164, 870–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharathi, K.S.; Ramesh, S.T. Removal of dyes using agricultural waste as low-cost adsorbents: A review. Appl. Water Sci. 2013, 3, 773–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmuir, I. The adsorption of gases on plane surfaces of glass, mica and platinum. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1918, 40, 1361–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freundlich, H.M.F. Over the Adsorption in Solution. J. Phys. Chem. 1906, 57, 385–471. [Google Scholar]
- Sadaf, S.; Bhatti, H.N.; Nausheen, S.; Noreen, S. Potential Use of Low-Cost Lignocellulosic Waste for the Removal of Direct Violet 51 from Aqueous Solution: Equilibrium and Breakthrough Studies. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2014, 66, 557–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.S.; Bhattacharyya, K.G. Kinetics of adsorption of metal ions on inorganic materials: A review. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 162, 39–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lagergren, S. About the theory of so-called adsorption of soluble substances, Zur theorie der sogenannten adsorption gel?ster stoffe. Kungliga Svenska Vetenskapsakademiens Handlingar Band 1898, 24, 1–39. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, R.M.; Hamad, H.A.; Hussein, M.M.; Malash, G.F. Potential of using green adsorbent of heavy metal removal from aqueous solutions: Adsorption kinetics, isotherm, thermodynamic, mechanism and economic analysis. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 91, 317–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, Y.S.; McKay, G. Sorption of dye from aqueous solution by peat. Chem. Eng. J. 1998, 70, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pap, S.; Radonić, J.; Trifunović, S.; Adamović, D.; Mihajlović, I.; Vojinović Miloradov, M.; Turk Sekulić, M. Evaluation of the adsorption potential of eco-friendly activated carbon prepared from cherry kernels for the removal of Pb2+, Cd2+ and Ni2+ from aqueous wastes. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 184, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojedokun, A.T.; Bello, O.S. Kinetic modeling of liquid-phase adsorption of Congo red dye using guava leaf-based activated carbon. Appl. Water Sci. 2017, 7, 1965–1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olgun, A.; Atar, N.; Wang, S. Batch and column studies of phosphate and nitrate removal adsorption on waste solids containing boron impurity. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 222, 108–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, W.J.; Morris, J.C. Advances in water pollution research: Removal of biologically resistant pollutant from wastewater by adsorption. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Water Pollution Symposium 2, London, UK, 3–7 September 1962; Pergamon: Oxford, UK, 1962; pp. 231–266. [Google Scholar]


| Dye | Biosorbent | qmax/mg g−1 (Langmuir) | % Removal | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Congo Red | Pine bark | 1.6 | 100 | [9] |
| Lemon-scented gum sawdust | 0.523 | >80 | [10] | |
| Fir (Abies nordmanniana) sawdust | 28.1 | 86 | [11] | |
| Chir pine (Pinus roxburghii) sawdust | 5.8 | 72 | [12] | |
| Eucalyptus (Eucalyptus globulus) sawdust | - | >80 | [13] | |
| Methylene Blue | White cedar sawdust | 55.15 | - | [14] |
| Poplar waste biomass | 21.9 | 98.50 | [15] | |
| Pine sawdust (Pinus strobus) | 10.3 | 99.94 | [16] | |
| Cedar tree sawdust | 142.36 | - | [17] | |
| Basic Violet 1 | Chir pine (Pinus roxburghii) sawdust | 11.3 | 96 | [12] |
| Disperse Orange 30 | Poplar sawdust | 0.089 | 83.4 | [18] |
| Eriochrome Black T | Sawdust unspecified | 40.96 | 80 | [19] |
| Allura Red AS | Sawdust unspecified | 50.98 | - | [20] |
| Safranine O | Sawdust unspecified | - | 98 | [21] |
| Isotherm Model | CR |
|---|---|
| qm exp./mg g−1 | 6.21 |
| Langmuir | |
| qm cal./mg g−1 | 8.00 |
| KL/dm3 mg−1 | 0.067 |
| RL | 0.130 |
| se | 0.441 |
| Freundlich | |
| KF/(mg/g (dm3/mg)1/n) | 0.60 |
| n | 1.61 |
| se | 0.794 |
| Pseudo-First Order | Pseudo-Second Order | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter | |||||||
| γ0/mg dm−3 | qe exp/mg g−1 | k1/min−1 | qe cal/mg g−1 | R2 | k2/g mg−1 min−1 | qe cal./mg g−1 | R2 |
| 50 | 3.95 | 0.061 | 1.063 | 0.837 | 0.035 | 4.023 | 0.9998 |
| Intraparticle Diffusion Model | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter | |||||||||
| γ0/ mg dm−3 | ki1 * | C1 | R12 | ki2 * | C2 | R22 | ki3 * | C3 | R32 |
| 50 | 0.3089 | 14.329 | 0.9974 | 0.1419 | 23.678 | 0.9651 | 0.0143 | 36.758 | 0.9636 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stjepanović, M.; Velić, N.; Galić, A.; Kosović, I.; Jakovljević, T.; Habuda-Stanić, M. From Waste to Biosorbent: Removal of Congo Red from Water by Waste Wood Biomass. Water 2021, 13, 279. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13030279
Stjepanović M, Velić N, Galić A, Kosović I, Jakovljević T, Habuda-Stanić M. From Waste to Biosorbent: Removal of Congo Red from Water by Waste Wood Biomass. Water. 2021; 13(3):279. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13030279
Chicago/Turabian StyleStjepanović, Marija, Natalija Velić, Antonela Galić, Indira Kosović, Tamara Jakovljević, and Mirna Habuda-Stanić. 2021. "From Waste to Biosorbent: Removal of Congo Red from Water by Waste Wood Biomass" Water 13, no. 3: 279. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13030279
APA StyleStjepanović, M., Velić, N., Galić, A., Kosović, I., Jakovljević, T., & Habuda-Stanić, M. (2021). From Waste to Biosorbent: Removal of Congo Red from Water by Waste Wood Biomass. Water, 13(3), 279. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13030279









