Responses of Net Anthropogenic N Inputs and Export Fluxes in the Megacity of Chengdu, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
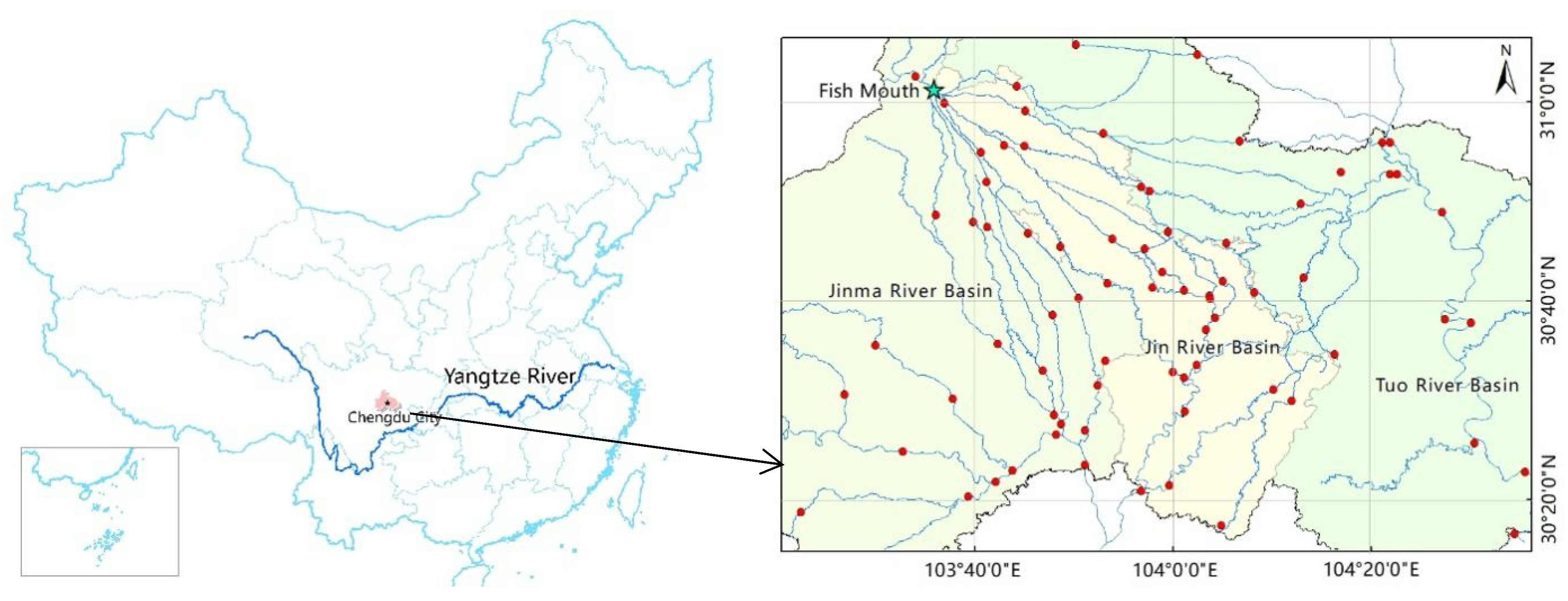
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Calculation of the NANI
2.2.1. Calculation of
2.2.2. Calculation of
2.2.3. Calculation of
2.2.4. Calculation of
2.3. River N Export Fluxes
2.4. Sample Collection and Analysis
2.5. Bayesian Model in R (SIAR) Mixing Model Estimation
3. Results
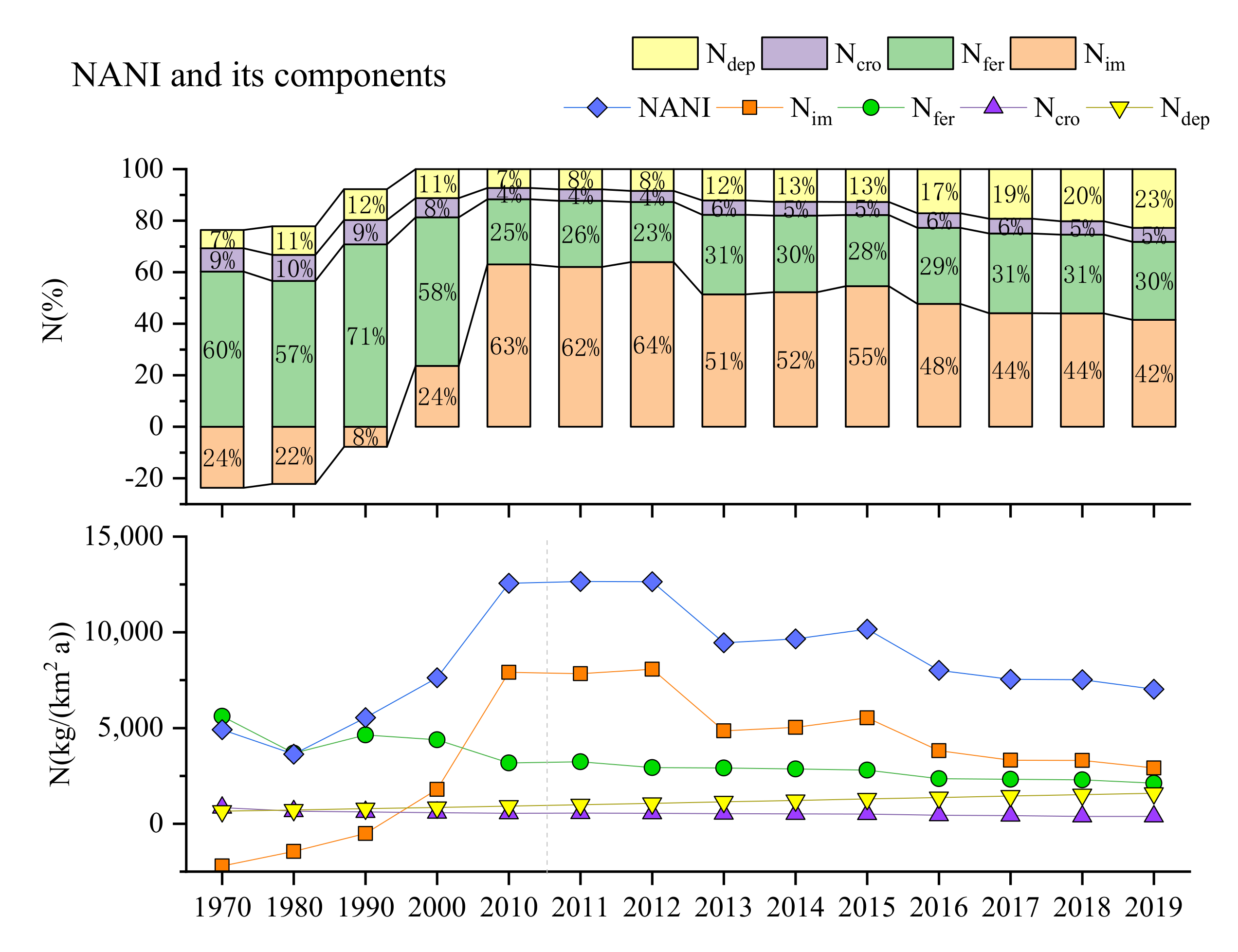
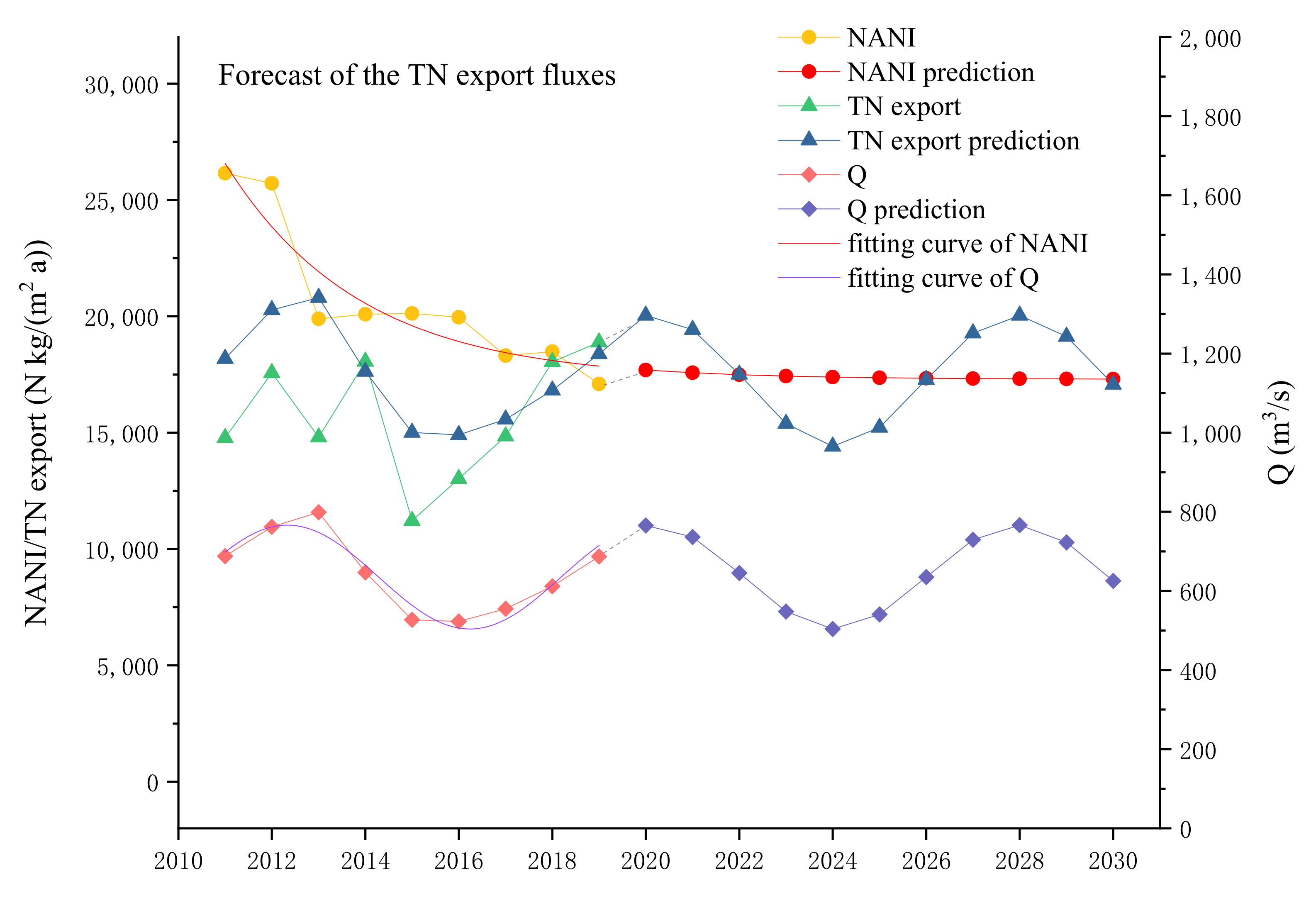
3.1. Variation of the NANI in Chengdu between 1970 and 2019
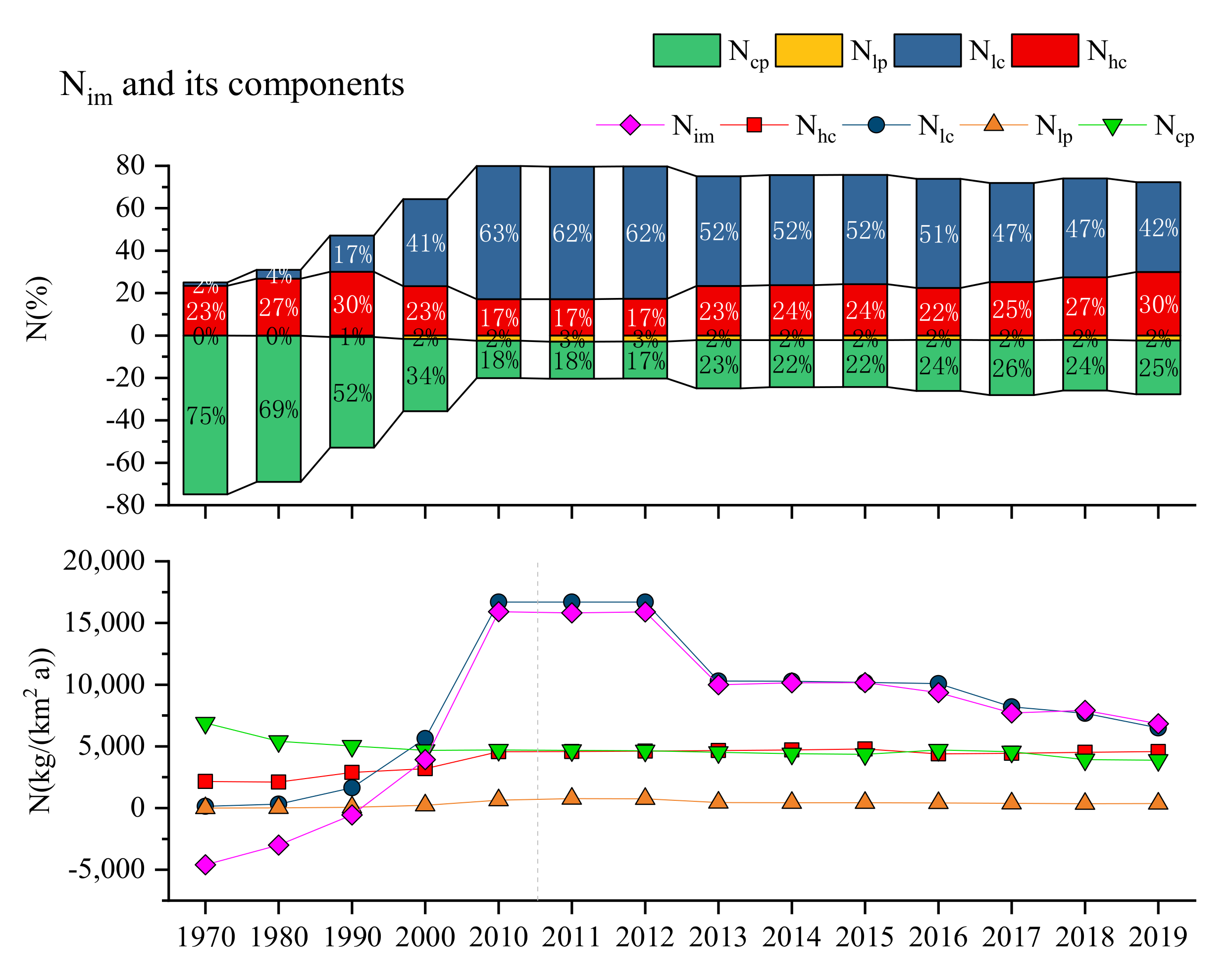
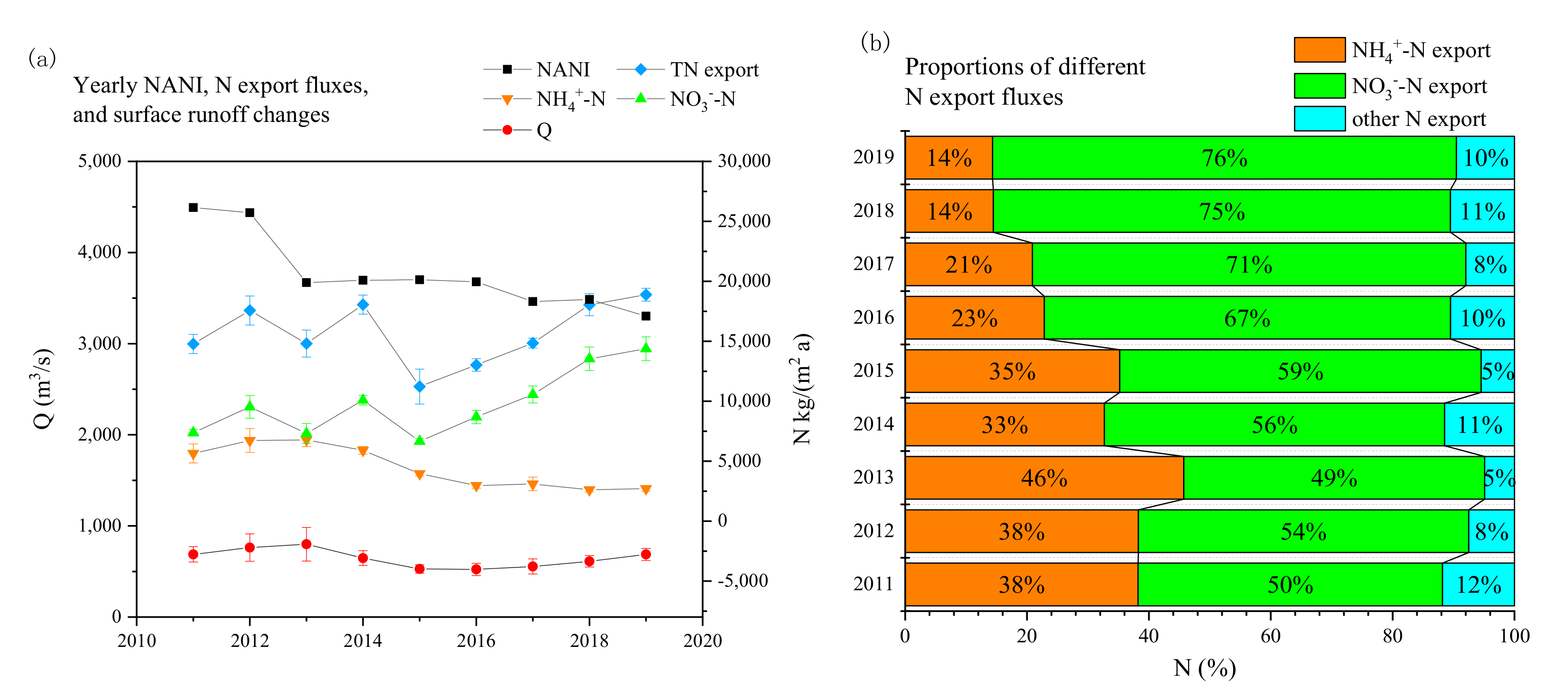
3.2. Variations in the Riverine TN Export Fluxes between 2011 and 2019
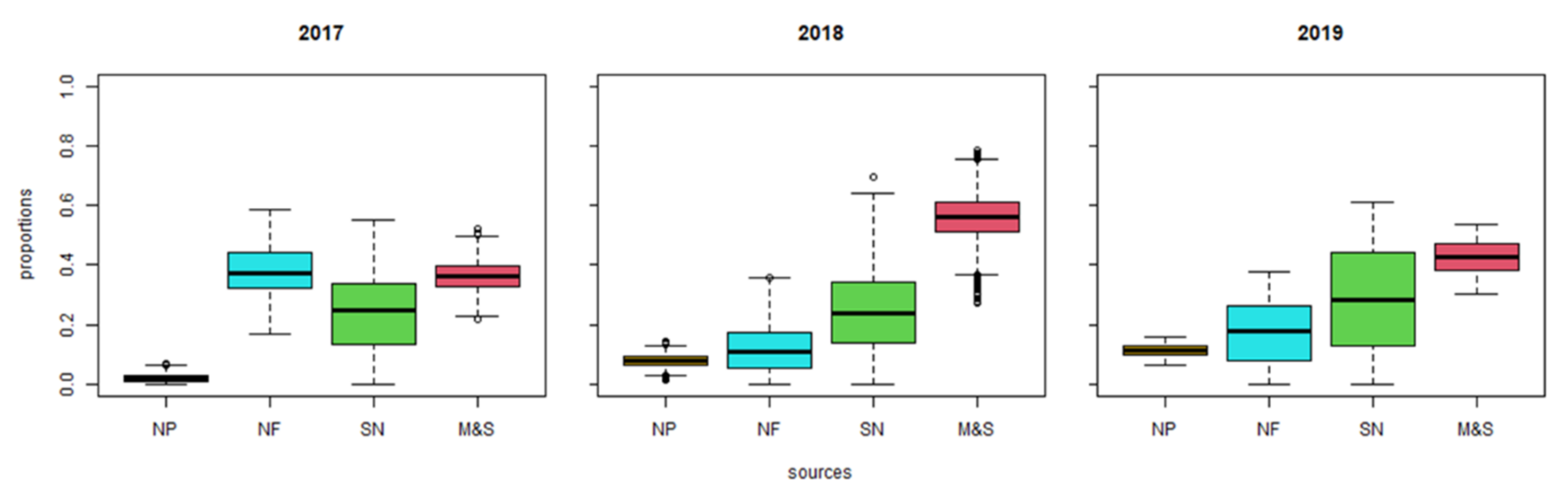
3.3. Identifying the -N Pollution Sources Using Data from 2017–2019
4. Discussion
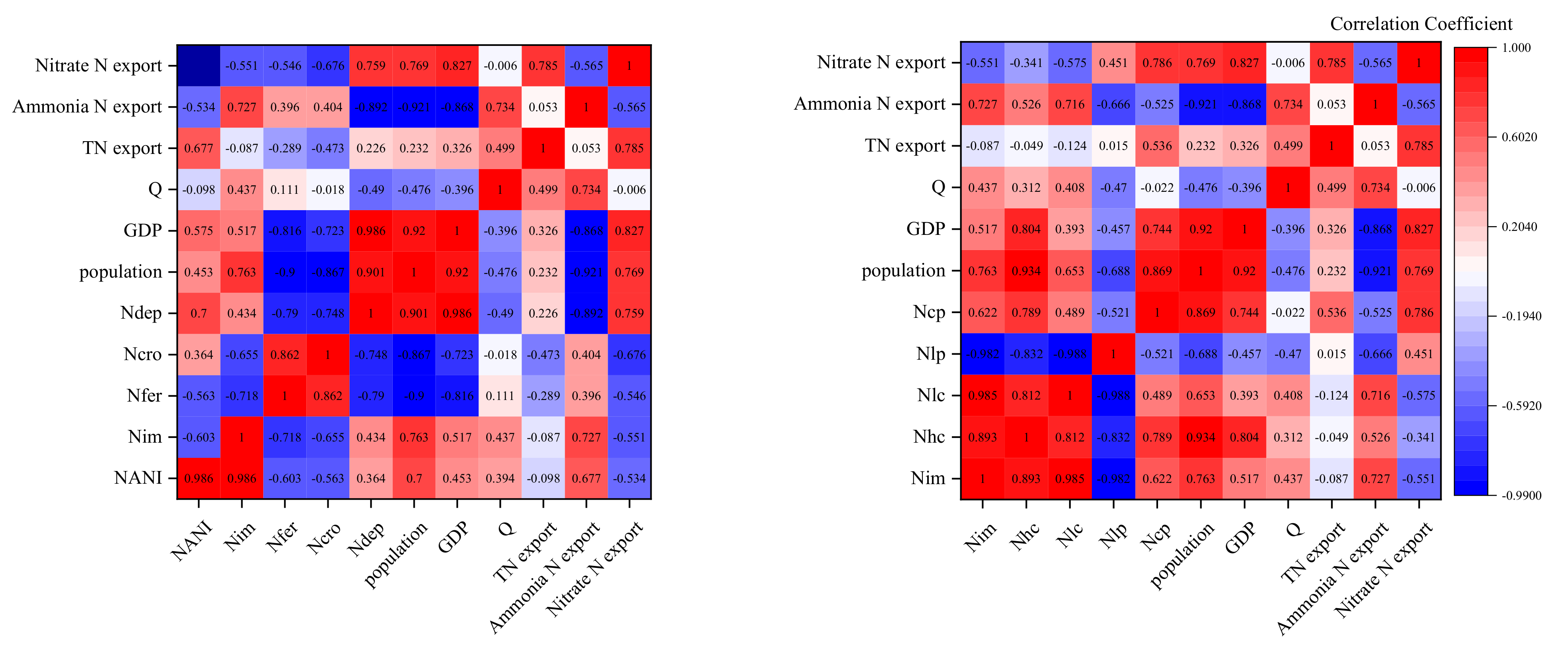
4.1. Relationships between N Budgets in the Chengdu City River Systems
4.2. Changes in N Inputs, Outputs, and Sources in Response to Urban Development and Management
4.3. Key Conversion of River N
4.4. Prediction of N Retention
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| NANI | net anthropogenic N input |
| SIAR | bayesian model |
| GDP | gross domestic product |
| JM | Jinma River Basin |
| J | Jin River Basin |
| T | Tuo River Basin |
| TN | total N |
| -N | ammonia-N |
| nitrate | |
| nitrite | |
| DO | dissolved oxygen |
| represents the food/feed N inputs | |
| the fertilizer N inputs | |
| the N from crop fixation | |
| the N from atmospheric deposition | |
| the N from aquaculture | |
| the food N consumption | |
| the feed N consumption | |
| the N content of livestock/poultry products | |
| the N content of agricultural crop products | |
| NP | atmospheric deposition |
| NF | chemical fertilizers |
| SN | soil organic N nitrification |
| M & S | manure and sewage |
| Q | the runoff |
References
- Liu, Y.; Yang, L.; Jiang, W. Coupling Coordination and Spatiotemporal Dynamic Evolution between Social Economy and Water Environmental Quality—A Case Study from Nansi Lake Catchment, China. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 119, 106870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhu, Z.; Fan, Y. The Impact of Environmental Regulation on the Coordinated Development of Environment and Economy in China. Nat. Hazards 2018, 91, 473–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Fang, C.; Liu, H.; Liu, X. Assessing Sustainability of Urbanization by a Coordinated Development Index for an Urbanization-Resources-Environment Complex System: A Case Study of Jing-Jin-Ji Region, China. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 96, 383–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Yang, J.; Li, H.; Jin, S.; Pang, M.; Lu, C. Research on the Spatial-Temporal Synthetic Measurement of the Coordinated Development of Population-Economy-Society-Resource-Environment (PESRE) Systems in China Based on Geographic Information Systems (GIS). Sustainability 2019, 11, 2877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Puppim De Oliveira, J.A.; Doll, C.N.H.; Kurniawan, T.A.; Geng, Y.; Kapshe, M.; Huisingh, D. Promoting Win-Win Situations in Climate Change Mitigation, Local Environmental Quality and Development in Asian Cities through Co-Benefits. J. Clean. Prod. 2013, 58, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinelli, L.A.; Howarth, R.W.; Cuevas, E.; Filoso, S.; Austin, A.M.Y.T.; Donoso, L.; Huszar, V.; Keeney, D.; Lara, L.L.; Llerena, C.; et al. Sources of Reactive Nitrogen Affecting Ecosystems in Latin America and the Caribbean: Current Trends and Future Perspectives. Biodegradation 2006, 79, 3–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, B.; Dong, X.; Peng, C.; Luo, W.; Chang, J.; Ge, Y. The Long-Term Impact of Urbanization on Nitrogen Patterns and Dynamics in Shanghai, China. Environ. Pollut. 2012, 171, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, C.; Wang, Q.; Zou, C.; Hayashi, Y.; Yasunari, T. Recent Trends in Nitrogen Flows with Urbanization in the Shanghai Megacity and the Effects on the Water Environment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 3431–3440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.S.; Swaney, D.P.; Li, X.Y.; Hong, B.; Howarth, R.W.; Ding, S.H. Anthropogenic Point-Source and Non-Point-Source Nitrogen Inputs into Huai River Basin and Their Impacts on Riverine Ammonia-Nitrogen Flux. Biogeosciences 2015, 12, 4275–4289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pickett, S.T.A.; Cadenasso, M.L.; Grove, J.M.; Boone, C.G.; Groffman, P.M.; Irwin, E.; Kaushal, S.S.; Marshall, V.; McGrath, B.P.; Nilon, C.H.; et al. Urban Ecological Systems: Scientific Foundations and a Decade of Progress. J. Environ. Manag. 2011, 92, 331–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Yuan, M.; Strokal, M.; Wu, H.C.; Liu, X.; Murk, A.; Kroeze, C.; Osinga, R. Impacts of Nitrogen Pollution on Corals in the Context of Global Climate Change and Potential Strategies to Conserve Coral Reefs. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 774, 145017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.; Peng, C.; Zhu, G.; Chen, L.; Liu, Y.; Shangguan, Z. Positive Responses of Belowground C Dynamics to Nitrogen Enrichment in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 616–617, 1035–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitousek, P.M.; Aber, J.D.; Howarth, R.W.; Likens, G.E.; Matson, P.A.; Schindler, D.W.; Schlesinger, W.H.; Tilman, D.G. Human Alteration of the Global Nitrogen Cycle: Sources and Consequences. Ecol. Appl. 1997, 7, 737–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Divers, M.T.; Elliott, E.M.; Bain, D.J. Quantification of Nitrate Sources to an Urban Stream Using Dual Nitrate Isotopes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 10580–10587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, H.; Song, X.; Zhang, Y.; Meng, W. Sources and Fate of Nitrate in the Haicheng River Basin in Northeast China Using Stable Isotopes of Nitrate. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 98, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, P.; Bi, Z.; Shan, Z.; Ren, L. The Deep Challenge of Nitrate Pollution in River Water of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 770, 144674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danni, S.O.; Bouchaou, L.; Elmouden, A.; Brahim, Y.A.; N’da, B. Assessment of Water Quality and Nitrate Source in the Massa Catchment (Morocco) Using δ 15N and δ 18O Tracers. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2019, 154, 108859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joossens, J.V.; Hill, M.J.; Elliott, P.; Stamler, R.; Stamler, J.; Lesaffre, E.; Dyer, A.; Nichols, R.; Kesteloot, H. Dietary Salt, Nitrate and Stomach Cancer Mortality in 24 Countries. Int. J. Epidemiol. 1996, 25, 494–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santamaria, P. Nitrate in Vegetables: Toxicity, Content, Intake and EC Regulation. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2006, 86, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knobeloch, L.; Salna, B.; Hogan, A.; Postle, J.; Anderson, H. Blue babies and nitrate-contaminated well water. Environ. Health Perspect. 2000, 7, 675–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fewtrell, L. Drinking-Water Nitrate, Methemoglobinemia, and Global Burden of Disease: A Discussion. Environ. Health Perspect. 2004, 112, 1371–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rassam, D.W.; Pagendam, D.E.; Hunter, H.M. Conceptualisation and Application of Models for Groundwater-Surface Water Interactions and Nitrate Attenuation Potential in Riparian Zones. Environ. Model. Softw. 2008, 23, 859–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Shi, P.; Song, J.; Li, Q. Application of Nitrogen and Oxygen Isotopes for Source and Fate Identification of Nitrate Pollution in Surfacewater: A Review. Appl. Sci. 2018, 9, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, H.; Xiao, Q.; Miao, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Q. Sources and Transformations of Nitrate Constrained by Nitrate Isotopes and Bayesian Model in Karst Surface Water, Guilin, Southwest China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 21299–21310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, C. Tracing Nitrogen Sources and Cycling in Catchments; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Kelly, B.; Mtiti, E.; McIntyre, P.B.; Vadeboncoeur, Y. Stable Isotopes Reveal Nitrogen Loading to Lake Tanganyika from Remote Shoreline Villages. Environ. Manag. 2017, 59, 264–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, C.; Yang, H.; Wang, J.; Guo, J.; Tang, X.; Chen, J. Combined Use of Stable Nitrogen and Oxygen Isotopes to Constrain the Nitrate Sources in a Karst Lake. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2020, 303, 107089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onodera, T.; Komatsu, K.; Kohzu, A.; Kanaya, G.; Mizuochi, M.; Syutsubo, K. Evaluation of Stable Isotope Ratios (δ15N and δ18O) of Nitrate in Advanced Sewage Treatment Processes: Isotopic Signature in Four Process Types. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 762, 144120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, D.; Botte, J.; de Baets, B.; Accoe, F.; Nestler, A.; Taylor, P.; van Cleemput, O.; Berglund, M.; Boeckx, P. Present Limitations and Future Prospects of Stable Isotope Methods for Nitrate Source Identification in Surface- and Groundwater. Water Res. 2009, 43, 1159–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Kang, P.; Sun, Y. A Stable Isotope Approach and Its Application for Identifying Nitrate Source and Transformation Process in Water. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 1133–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabb, K.C.; Ding, S.; Ning, X.; Liu, S.M.; Qian, B. Characterizing the impact of Three Gorges Dam on the Changjiang (Yangtze River): A story of nitrogen biogeochemical cycling through the lens of nitrogen stable isotopes. Environ. Res. 2021, 195, 110759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, W.; Wang, S.; Dong, Y.; Ni, Z.; Fan, Y.; Wu, D. Trends of the Response-Relationship between Net Anthropogenic Nitrogen and Phosphorus Inputs (NANI/NAPI) and TN/TP Export Fluxes in Raohe Basin, China. Chemosphere 2022, 286, 131662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.; Feng, G.; Swaney, D.P.; Dentener, F.; Koeble, R.; Ouyang, Y.; Gao, W. Global and Regional Estimation of Net Anthropogenic Nitrogen Inputs (NANI). Geoderma 2020, 361, 114066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Hou, L.; Liu, M.; Zheng, Y.; Yin, G.; Lin, X.; Li, X.; Zong, H.; Deng, F.; Gao, J.; et al. Net Anthropogenic Nitrogen Inputs (NANI) into the Yangtze River Basin and the Relationship with Riverine Nitrogen Export. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2016, 121, 451–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weigand, M.A.; Foriel, J.; Barnett, B.; Oleynik, S.; Sigman, D.M. Updates to Instrumentation and Protocols for Isotopic Analysis of Nitrate by the Denitrifier Method. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2016, 30, 1365–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mcilvin, M.R.; Casciotti, K.L. Technical Updates to the Bacterial Method for Nitrate Isotopic Analyses. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 1850–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kou, X.; Ding, J.; Li, Y.; Li, Q.; Mao, L.; Xu, C.; Zheng, Q.; Zhuang, S. Tracing Nitrate Sources in the Groundwater of an Intensive Agricultural Region. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 250, 106826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parnell, A.C.; Inger, R.; Bearhop, S.; Jackson, A.L. Source Partitioning Using Stable Isotopes: Coping with Too Much Variation. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e9672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.L.; Han, G.; Zeng, J.; Liu, M.; Li, X.Q.; Boeckx, P. Identifying the Sources of Nitrate Contamination Using a Combined Dual Isotope, Chemical and Bayesian Model Approach in a Tropical Agricultural River: Case Study in the Mun River, Thailand. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 760, 143938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Liu, W.; Xing, M.; Li, Y. Using a Nitrogen and Oxygen Isotopic Approach to Identify Nitrate Sources and Cycling in the Wei River of Northwestern China. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. 2019, 25, 755–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Xi, B.; Gao, R.; He, L.; Liu, H.; Dai, X.; Yu, Y. Identifying Diffused Nitrate Sources in a Stream in an Agricultural Field Using a Dual Isotopic Approach. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 484, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Cheng, H.; Pu, X.; Liu, X.; Cheng, Q. Nitrate Behaviors and Source Apportionment in an Aquatic System from a Watershed with Intensive Agricultural Activities. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2015, 17, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, C.; Elliott, E.M.; Wankel, S.D. Tracing anthropogenic inputs of nitrogen to ecosystems. In Stable Isotopes in Ecology and Environmental Science, 2nd ed.; Blackwell Publishing Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 2007; pp. 375–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, A.S.; Waring, S.A. The Natural Abundance of 15n in the Soil-Water System of a Small Catchment Area. Aust. J. Soil Res. 1977, 15, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widory, D.; Kloppmann, W.; Chery, L.; Bonnin, J.; Rochdi, H.; Guinamant, J.L. Nitrate in Groundwater: An Isotopic Multi-Tracer Approach. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2004, 72, 165–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellman, L.M. A Study of Tile Drain Nitrate—δ15N Values as a Tool for Assessing Nitrate Sources in an Agricultural Region. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2005, 71, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Shen, Z.; Yan, T.; Yang, Y. Source Identification and Impact of Landscape Pattern on Riverine Nitrogen Pollution in a Typical Urbanized Watershed, Beijing, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 628–629, 1296–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, P.; Liu, S.; Yu, Q.; Li, X.; Han, X. Sources and Transformations of Anthropogenic Nitrogen in the Highly Disturbed Huai River Basin, Eastern China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 11153–11169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Yang, Y.; Zou, J.; Wen, Y.; Gao, C. The Sources and Dispersal of Nitrate in Multiple Waters, Constrained by Multiple Isotopes, in the Wudalianchi Region, Northeast China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 24348–24361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böttcher, J.; Strebel, O.; Voerkelius, S.; Schmidt, H.L. Using Isotope Fractionation of Nitrate-Nitrogen and Nitrate-Oxygen for Evaluation of Microbial Denitrification in a Sandy Aquifer. J. Hydrol. 1990, 114, 413–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMahon, P.B.; Böhlke, J.K. Regional Patterns in the Isotopic Composition of Natural and Anthropogenic Nitrate in Groundwater, High Plains, U.S.A. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 2965–2970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, Y.; Liu, G.D.; Meng, Y.C.; Zhang, W.J.; Xia, C.C. Analysis of Stable Hydrogen and Oxygen Isotope Characteristics and Vapor Sources of Event-Based Precipitation in Chengdu. Huanjing Kexue Environ. Sci. 2019, 40, 1179–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, Y.; Tang, C.; Cao, Y. Mechanisms of Nitrate Accumulation in Highly Urbanized Rivers: Evidence from Multi-Isotopes in the Pearl River Delta, China. J. Hydrol. 2020, 587, 124924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soto, D.X.; Koehler, G.; Wassenaar, L.I.; Hobson, K.A. Spatio-Temporal Variation of Nitrate Sources to Lake Winnipeg Using N and O Isotope (δ15N, δ18O) Analyses. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 647, 486–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
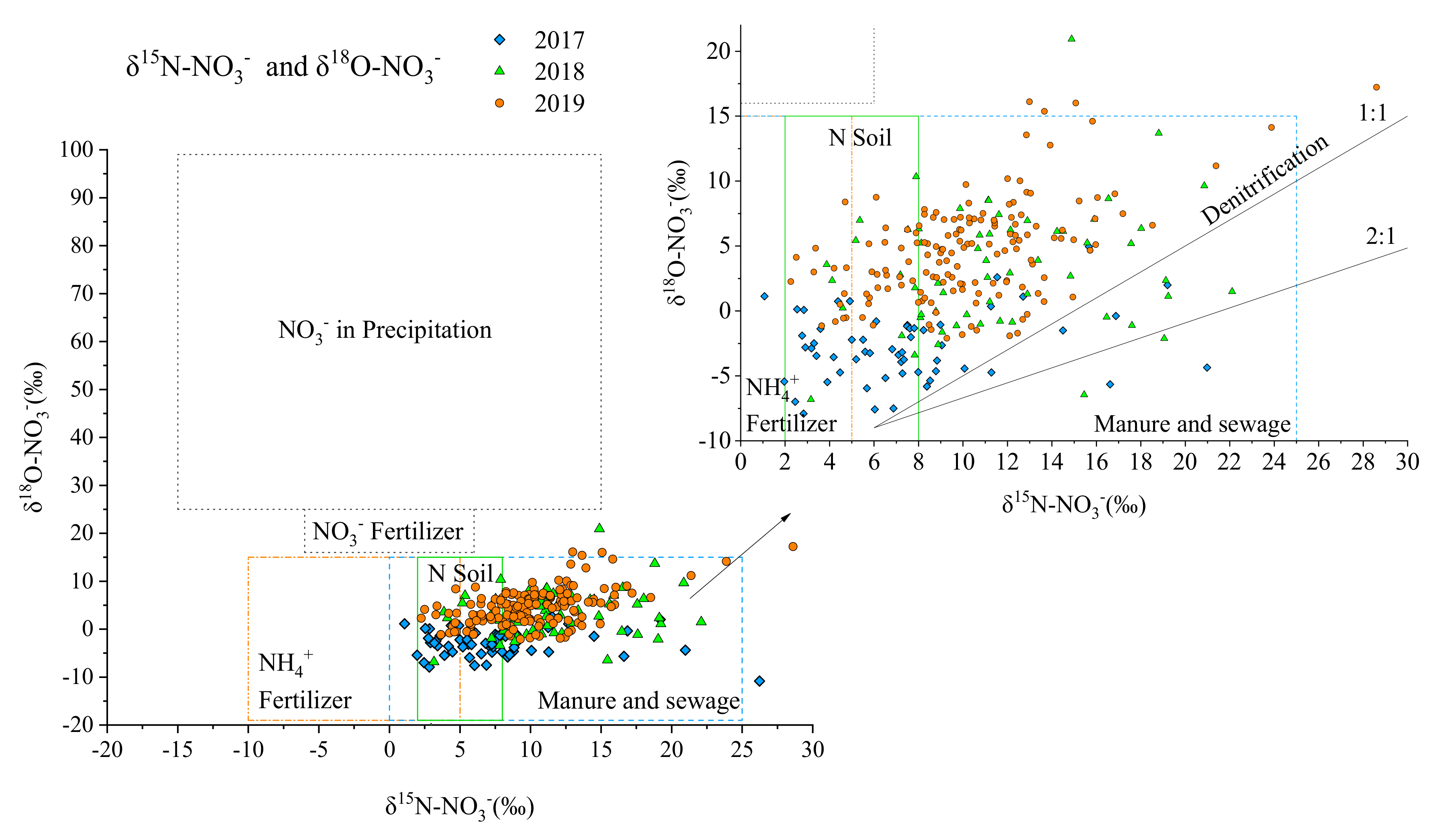
| Sources | n | - (‰) | - (‰) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | |||
| in precipitation (NP) | 26 | 2.3 | 5.4 | 30.9 | 9.4 | |
| Fertilizer N (NF) | 12 | −3.5 | 9.1 | −1.1 | 2.1 | |
| Soil N (SN) a | - | 4.6 | 4.4 | −0.3 | 6.8 | |
| Manure and sewage (M & S) | Manure | 8 | 22.9 | 8.4 | 3.1 | 5.0 |
| Sewage | 50 | 14.4 | 7.8 | −1.9 | 4.7 | |
| Total | 58 | 15.58 | 8.4 | −1.3 | 4.9 | |
| Year | Category | NP | NF | SN | M & S |
| 2017 | Low 95% hdr | 0.00 | 0.27 | 0.01 | 0.27 |
| High 95% hdr | 0.05 | 0.52 | 0.43 | 0.45 | |
| mode | 0.01 | 0.33 | 0.31 | 0.35 | |
| mean | 0.02 | 0.38 | 0.23 | 0.36 | |
| 2018 | Low 95% hdr | 0.04 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.42 |
| High 95% hdr | 0.12 | 0.25 | 0.45 | 0.70 | |
| mode | 0.08 | 0.03 | 0.22 | 0.57 | |
| mean | 0.08 | 0.12 | 0.24 | 0.56 | |
| 2019 | Low 95% hdr | 0.08 | 0.00 | 0.04 | 0.33 |
| High 95% hdr | 0.14 | 0.32 | 0.57 | 0.50 | |
| mode | 0.09 | 0.05 | 0.50 | 0.37 | |
| mean | 0.11 | 0.15 | 0.33 | 0.41 | |
| 2017–2019 | Low 95% hdr | 0.05 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.34 |
| High 95% hdr | 0.11 | 0.35 | 0.57 | 0.53 | |
| mode | 0.08 | 0.16 | 0.35 | 0.44 | |
| mean | 0.08 | 0.19 | 0.29 | 0.43 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ding, Y.; Lai, C.; Shi, Q.; Ouyang, L.; Wang, Z.; Yao, G.; Jia, B. Responses of Net Anthropogenic N Inputs and Export Fluxes in the Megacity of Chengdu, China. Water 2021, 13, 3543. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13243543
Ding Y, Lai C, Shi Q, Ouyang L, Wang Z, Yao G, Jia B. Responses of Net Anthropogenic N Inputs and Export Fluxes in the Megacity of Chengdu, China. Water. 2021; 13(24):3543. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13243543
Chicago/Turabian StyleDing, Yao, Chengyue Lai, Qing Shi, Lili Ouyang, Zhaoli Wang, Gang Yao, and Binyang Jia. 2021. "Responses of Net Anthropogenic N Inputs and Export Fluxes in the Megacity of Chengdu, China" Water 13, no. 24: 3543. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13243543
APA StyleDing, Y., Lai, C., Shi, Q., Ouyang, L., Wang, Z., Yao, G., & Jia, B. (2021). Responses of Net Anthropogenic N Inputs and Export Fluxes in the Megacity of Chengdu, China. Water, 13(24), 3543. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13243543






