Microbial Community Structure and Its Driving Environmental Factors in Black Carp (Mylopharyngodon piceus) Aquaculture Pond
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Experimental Design and Sampling Procedure
2.2. Physicochemical Measurements
2.3. Water DNA Extraction and 16S rRNA Gene Amplification
2.4. Sequencing Data Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
2.6. Nucleotide Sequence Accession Number
3. Results
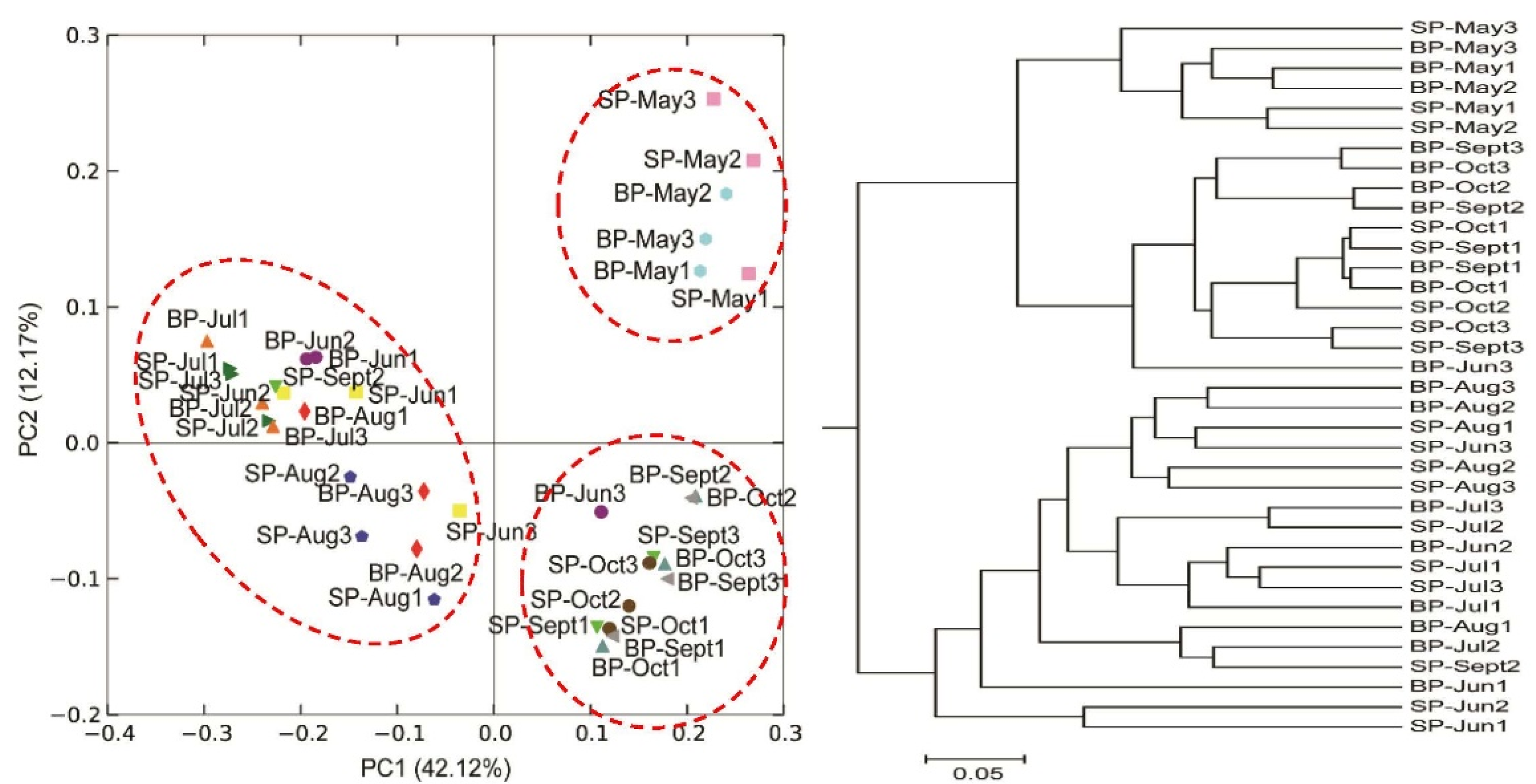
3.1. Microbiota Diversity and Richness in the Pond Water Column
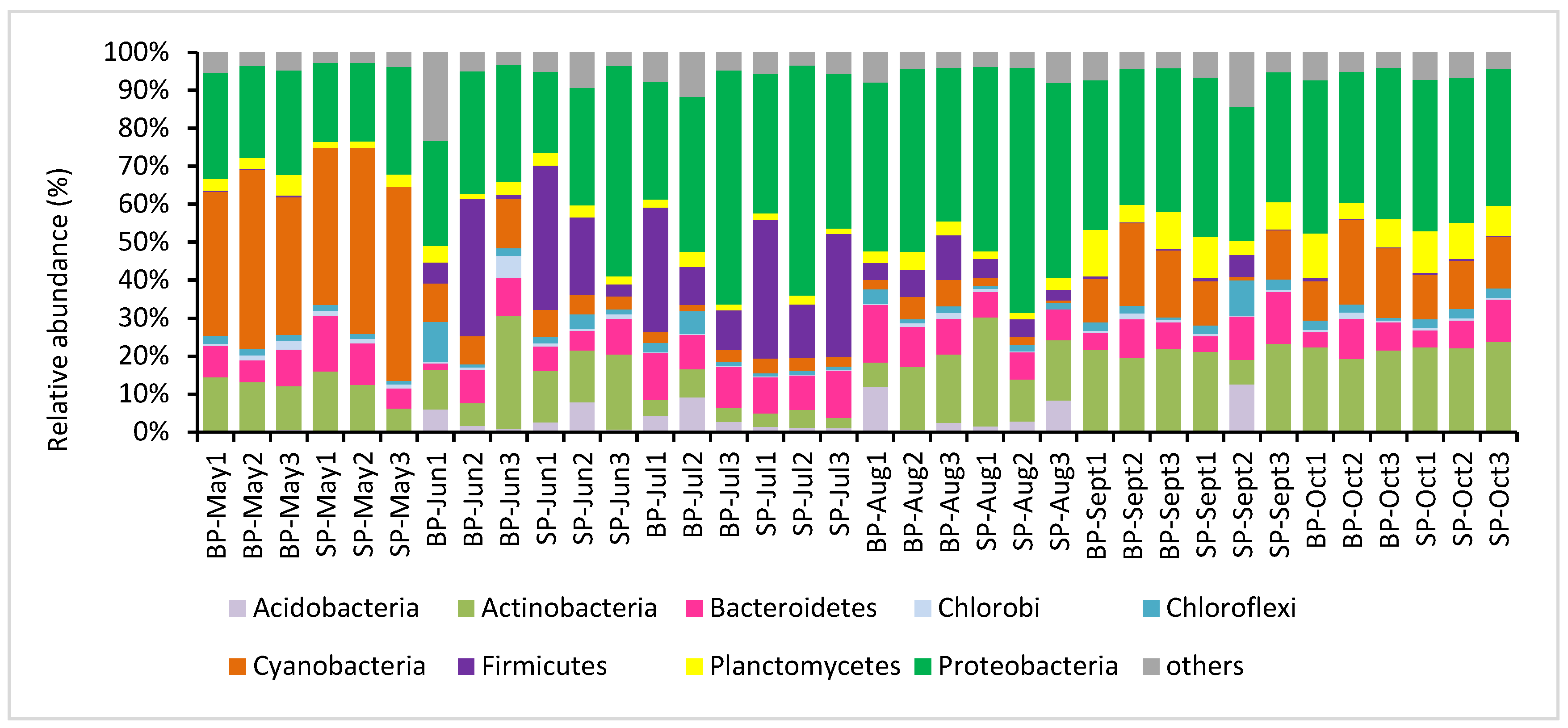
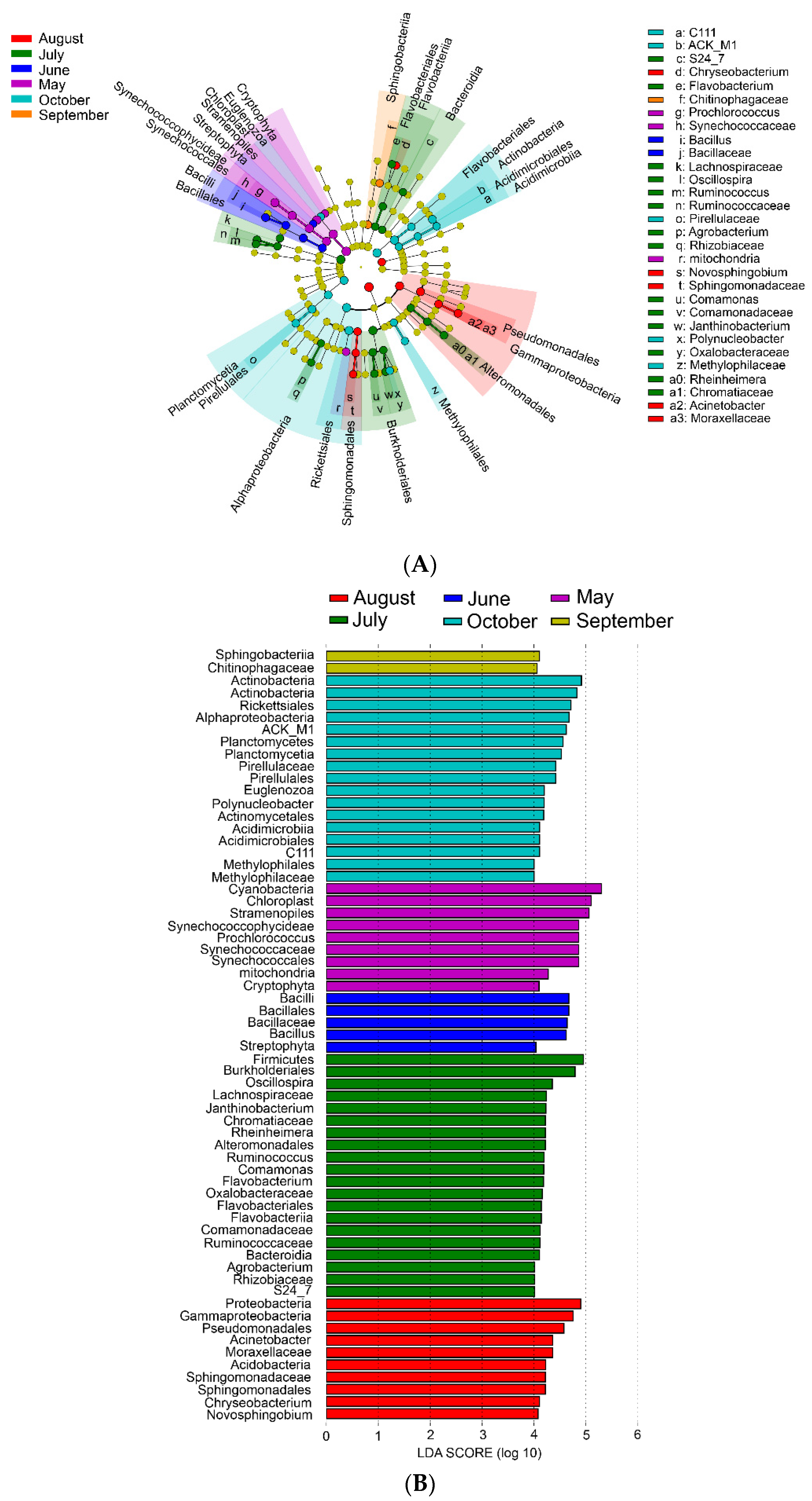
3.2. Microbial Composition and Community Structure in the Pond Water Column
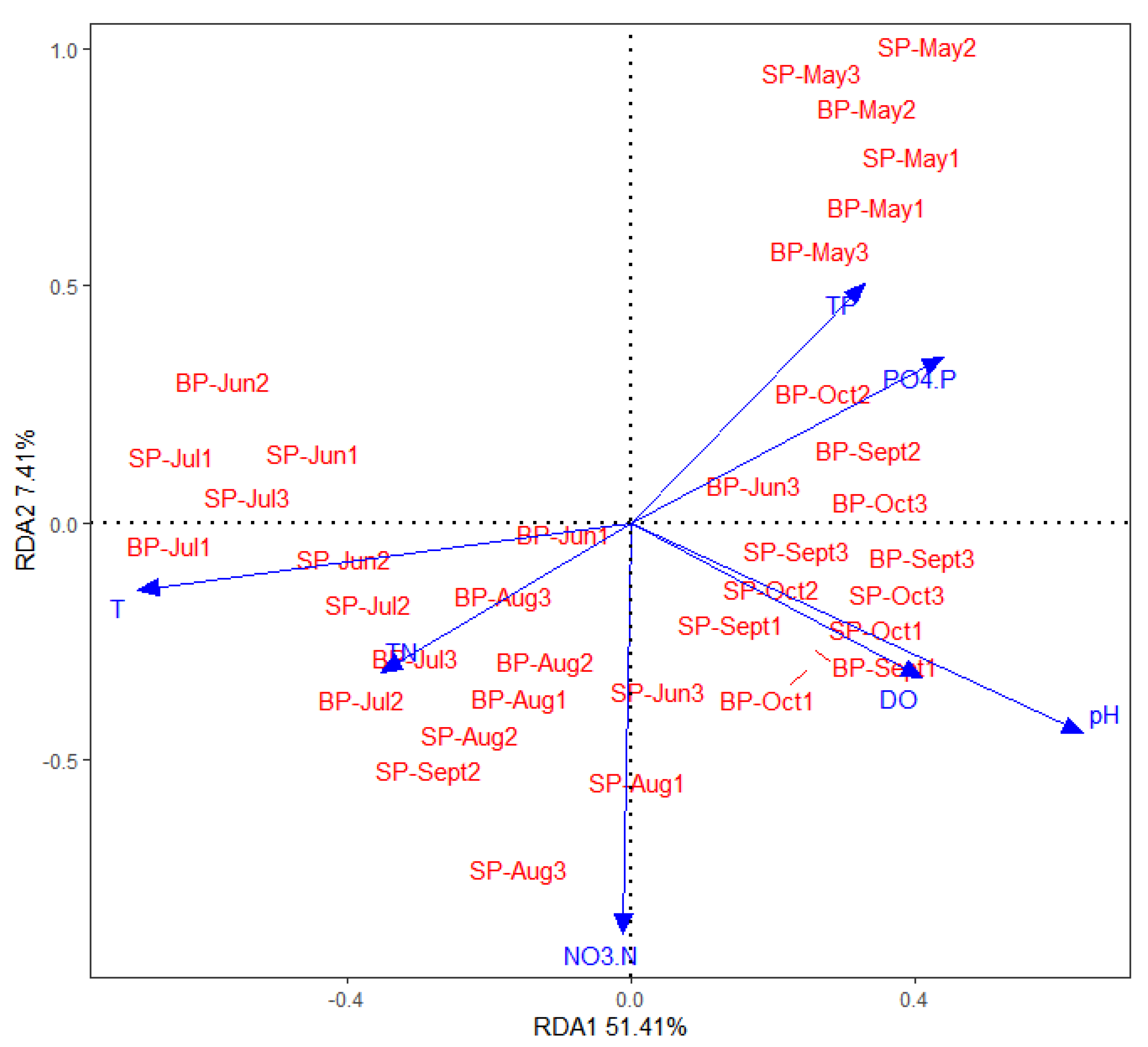
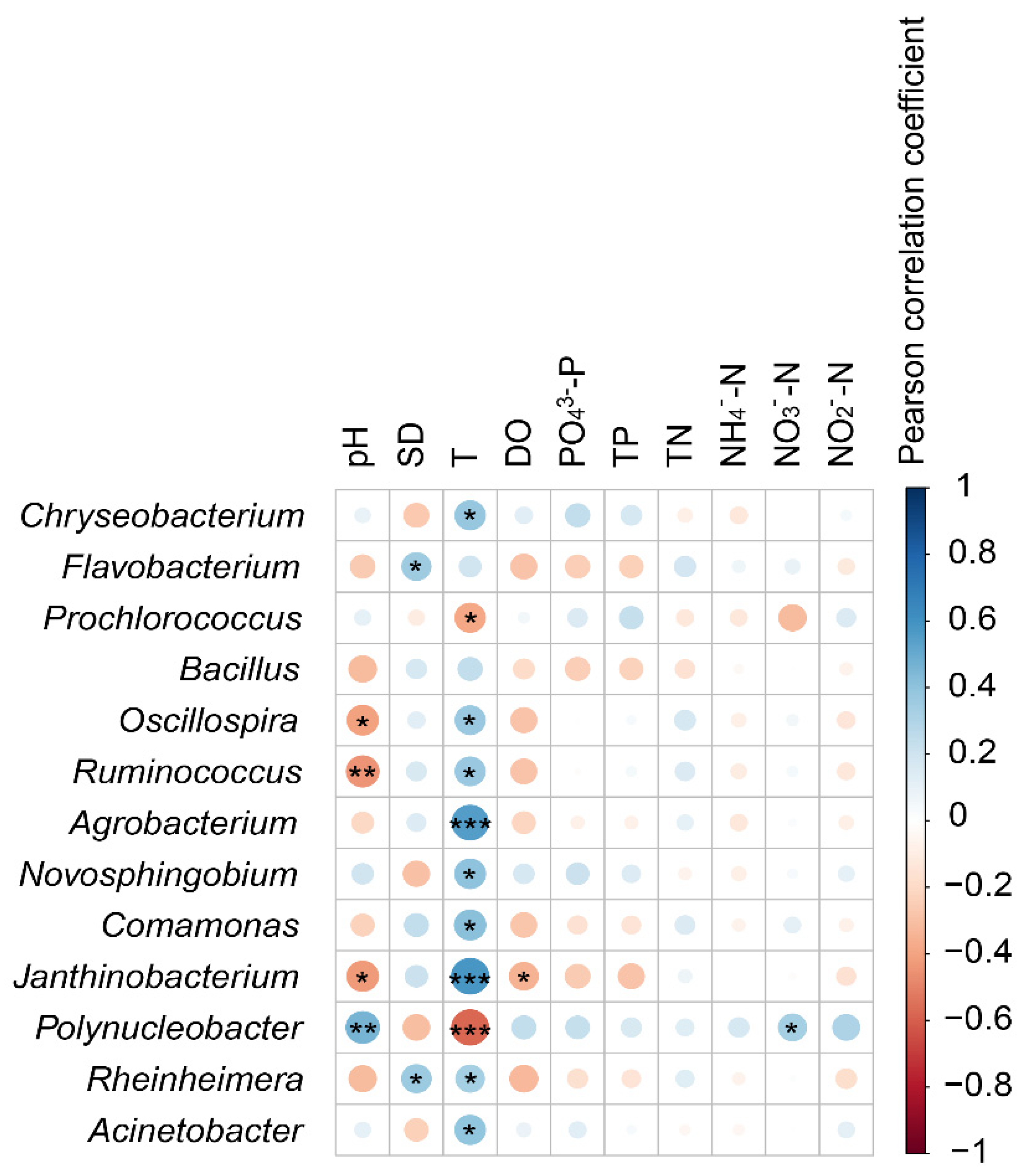
3.3. Key Factors Affecting Microbial Community Composition in the Pond Water Column
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Naylor, R.L.; Goldburg, R.J.; Primavera, J.H.; Kautsky, N.; Beveridge, M.C.M.; Clay, J.; Folke, C.; Lubchenco, J.; Mooney, H.; Troell, M. Effect of aquaculture on world fish supplies. Nature 2000, 405, 1017–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shen, L.; Wu, H.; Gao, Z.; Ruan, Y.; Xu, X.; Li, J.; Ma, S.; Zheng, P. Evidence for anaerobic ammonium oxidation process in freshwater sediments of aquaculture ponds. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 1344–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Beusen, A.H.W.; Liu, X.; Bouwman, A.F. Aquaculture production is a large, spatially concentrated source of nutrients in Chinese freshwater and coastal seas. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 54, 1464–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MAFBC. 2020 China Fishery Statistical Yearbook; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2020. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Lu, S.; Liao, M.; Xie, C.; He, X.; Li, D.; He, L.; Chen, J. Seasonal dynamics of ammonia-oxidizing microorganisms in freshwater aquaculture ponds. Ann. Microbiol. 2014, 65, 651–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, O.; Sereti, V.; Eding, E.H. Analysis of nutrient flows in integrated intensive aquaculture systems. Aquac. Eng. 2005, 32, 379–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brune, D.E.; Schwartz, G.; Eversole, A.G.; Collier, J.A.; Schwedler, T.E. Intensification of pond aquaculture and high rate photosynthetic systems. Aquac. Eng. 2003, 28, 65–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuypers, M.M.M.; Marchant, H.K.; Kartal, B. The microbial nitrogen-cycling network. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 16, 263–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueroa, I.A.; Coates, J.D. Microbial phosphite oxidation and its potential role in the global phosphorus and carbon cycles. Adv. Appl. Microbiol. 2017, 98, 93–117. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Merbt, S.N.; Stahl, D.A.; Casamayor, E.O.; Marti, E.; Nicol, G.W.; Prosser, J.I. Differential photoinhibition of bacterial and archaeal ammonia oxidation. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2012, 327, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ni, J.J.; Li, X.J.; Chen, F.; Wu, H.H.; Xu, M.Y. Community structure and potential nitrogen metabolism of subtropical aquaculture pond microbiota. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2018, 16, 7687–7697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, M.; Hou, J.; Song, K.; Chen, J.; Gou, J.; Li, D.; He, X. Community metagenomic assembly reveals microbes that contribute to the vertical stratification of nitrogen cycling in an aquaculture pond. Aquaculture 2020, 520, 734911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Hu, S.; Chen, D. The trends of aquacultural nitrogen budget and its environmental implications in China. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 10877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Tong, J.; Wang, J.; Yu, X. Development of microsatellite markers and genetic diversity in wild and cultured populations of black carp (Mylopharyngodon piceus) along the Yangtze River. Aquac. Int. 2020, 28, 1867–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haag, W.R. Black carp: Biological synopsis and risk assessment of an introduced fish. J. N. Am. Benthol. Soc. 2008, 27, 800–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Pan, L.; Huang, F.; Gao, S.; Su, C.; Zhang, M.; He, Z. Metagenomic analysis of composition, function and cycling processes of microbial community in water, sediment and effluent of Litopenaeus vannamei farming environments under different culture modes. Aquaculture 2019, 506, 280–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Kuczynski, J.; Stombaugh, J.; Bittinger, K.; Bushman, F.D.; Costello, E.K.; Fierer, N.; Peña, A.G.; Goodrich, J.K.; Gordon, J.I.; et al. QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 335–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Edgar, R.C.; Haas, B.J.; Clemente, J.C.; Quince, C.; Knight, R. UCHIME improves sensitivity and speed of chimera detection. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2194–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Q.; Garrity, G.M.; Tiedje, J.M.; Cole, J.R. Naïve Bayesian classifier for rapid assignment of rRNA sequences into the new bacterial taxonomy. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 5261–5267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pouil, S.; Samsudin, R.; Slembrouck, J.; Sihabuddin, A.; Sundari, G.; Khazaidan, K.; Kristanto, A.H.; Pantjara, B.; Caruso, D. Nutrient budgets in a small-scale freshwater fish pond system in Indonesia. Aquaculture 2019, 504, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Deng, Q.; Wan, L.; Cao, X.; Song, C. Bacterial Communities and enzymatic activities in sediments of long-term fish and crab aquaculture ponds. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.; Liu, C.; Peng, L.; Song, C.; Li, G. Different distribution patterns of microorganisms between aquaculture pond sediment and water. J. Microbiol. 2021, 59, 376–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, T.; Wang, Y.; Tang, J.; Dai, Y. Bacterial communities in Chinese grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus) farming ponds. Aquac. Res. 2013, 45, 138–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Jiang, J.; Pan, Y.; Dong, Y.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, G.; Gao, S.; Sun, H.; Guan, X.; Wang, B.; et al. Temporal dynamics of bacterial communities in the water and sediments of sea cucumber (Apostichopus japonicus) culture ponds. Aquaculture 2020, 528, 735498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klase, G.; Lee, S.; Liang, S.; Kim, J.; Zo, Y.-G.; Lee, J. The microbiome and antibiotic resistance in integrated fishfarm water: Implications of environmental public health. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 649, 1491–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernal, M.G.; Campa-Córdova, Á.I.; Saucedo, P.E.; González, M.C.; Marrero, R.M.; MazónSuástegui, J.M. Isolation and in vitro selection of actinomycetes strains as potential probiotics for aquaculture. Vet. World 2015, 8, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Keulen, G.; Dyson, P.J. Production of specialized metabolites by Streptomyces coelicolor A3. Adv. Appl. Microbiol. 2014, 89, 217–266. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Qin, Y.; Hou, J.; Deng, M.; Wu, C.; Ji, Y.; He, X. Bacterial abundance and diversity in pond water supplied with different feeds. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 35232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sunagawa, S.; Coelho, L.P.; Chaffron, S.; Kultima, J.R.; Labadie, K.; Salazar, G.; Djahanschiri, B.; Zeller, G.; Mende, D.R.; Alberti, A.; et al. Ocean plankton. Structure and function of the global ocean microbiome. Science 2015, 348, 1261359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duarte, L.N.; Coelho, F.J.R.C.; Cleary, D.F.R.; Bonifácio, D.; Martins, P.; Gomes, N.C.M. Bacterial and microeukaryotic plankton communities in a semi-intensive aquaculture system of sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax): A seasonal survey. Aquaculture 2019, 503, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, X.; Wang, B.; Duan, P.; Tian, J.; Dong, Y.; Jiang, J.; Sun, B.; Zhou, Z. The dynamics of bacterial community in a polyculture aquaculture system of Penaeus chinensis, Rhopilema esculenta and Sinonovacula constricta. Aquac. Res. 2020, 51, 1789–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Xu, Y.; Peng, L.; Liu, G.; Wan, X.; Hua, Y.; Zhu, D.; Hamilton, D.P. Diversity of anammox bacteria and abundance of functional genes for nitrogen cycling in the rhizosphere of submerged macrophytes in a freshwater lake in summer. J. Soils Sediments 2019, 19, 3648–3656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masayoshi, U.; Kiyokuni, M. Fish-pathogenic bacteria isolated from diseased ayu, eel and carp cultured in ponds in aichi prefecture. Fish Pathol. 2010, 8, 165–170. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, L.; Wang, Z.; Chen, M.; Qu, Y.; Li, J.; Zhou, A.; Xie, S.; Zeng, F.; Zou, J. Microbiota comparison of pacific white shrimp intestine and sediment at freshwater and marine cultured environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 657, 1194–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, F.; Zhu, W.; Yu, Y.; He, Z.; Wu, B.; Wang, C.; Shu, L.; Li, X.; Yin, H.; Wang, J.; et al. Host development overwhelms environmental dispersal in governing the ecological succession of zebrafish gut microbiota. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes 2021, 7, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, F.; Liao, L.; Xu, Q.; He, Z.; Xiao, T.; Wang, J.; Huang, J.; Yu, Y.; Wu, B.; Yan, Q. Host-microbiota interactions and responses to grass carp reovirus infection in Ctenopharyngodon idellus. Environ. Microbiol. 2021, 23, 431–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, M.W.; Hoetzinger, M. Polynucleobacter. In Bergey’s Manual of Systematics of Archaea and Bacteria; Trujillo, M.E., Dedysh, S., DeVos, P., Hedlund, B., Kämpfer, P., Rainey, F.A., Whitman, W.B., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2019; in Association with Bergey’s Manual Trust. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.; Liu, L.; Zhu, Y.; Zhu, T.; Wu, X.; Yang, D. Microbial Community Structure and Its Driving Environmental Factors in Black Carp (Mylopharyngodon piceus) Aquaculture Pond. Water 2021, 13, 3089. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13213089
Li X, Liu L, Zhu Y, Zhu T, Wu X, Yang D. Microbial Community Structure and Its Driving Environmental Factors in Black Carp (Mylopharyngodon piceus) Aquaculture Pond. Water. 2021; 13(21):3089. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13213089
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xuemei, Lu Liu, Yongjiu Zhu, Tingbing Zhu, Xingbing Wu, and Deguo Yang. 2021. "Microbial Community Structure and Its Driving Environmental Factors in Black Carp (Mylopharyngodon piceus) Aquaculture Pond" Water 13, no. 21: 3089. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13213089
APA StyleLi, X., Liu, L., Zhu, Y., Zhu, T., Wu, X., & Yang, D. (2021). Microbial Community Structure and Its Driving Environmental Factors in Black Carp (Mylopharyngodon piceus) Aquaculture Pond. Water, 13(21), 3089. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13213089





