How to Assess the Ecological Status of Highly Humic Lakes? Development of a New Method Based on Benthic Invertebrates
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
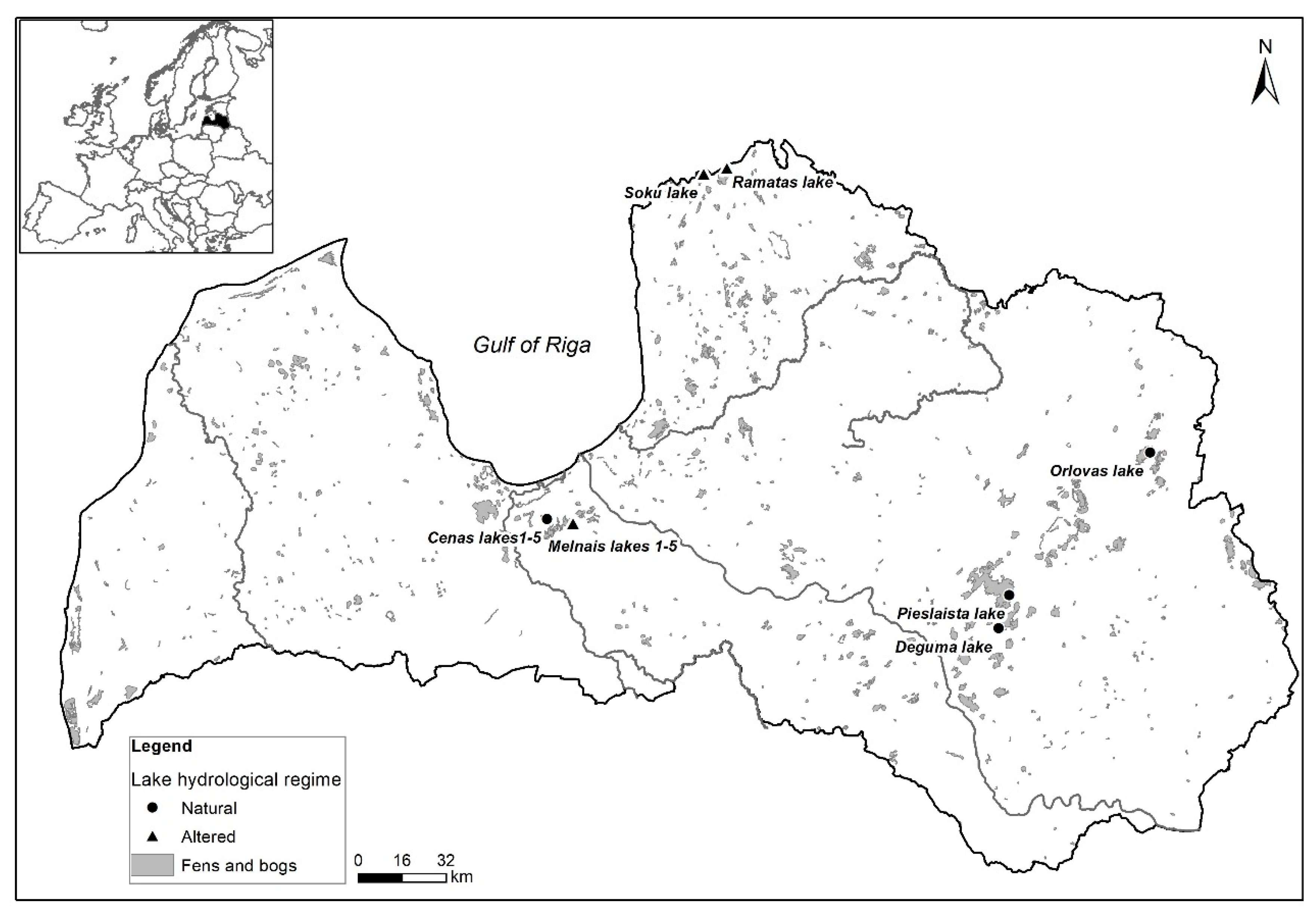
2.1. Study Sites
2.2. Physical and Chemical Parameters
2.3. Macroinvertebrate Sampling and Sample Processing
2.4. Data Analysis
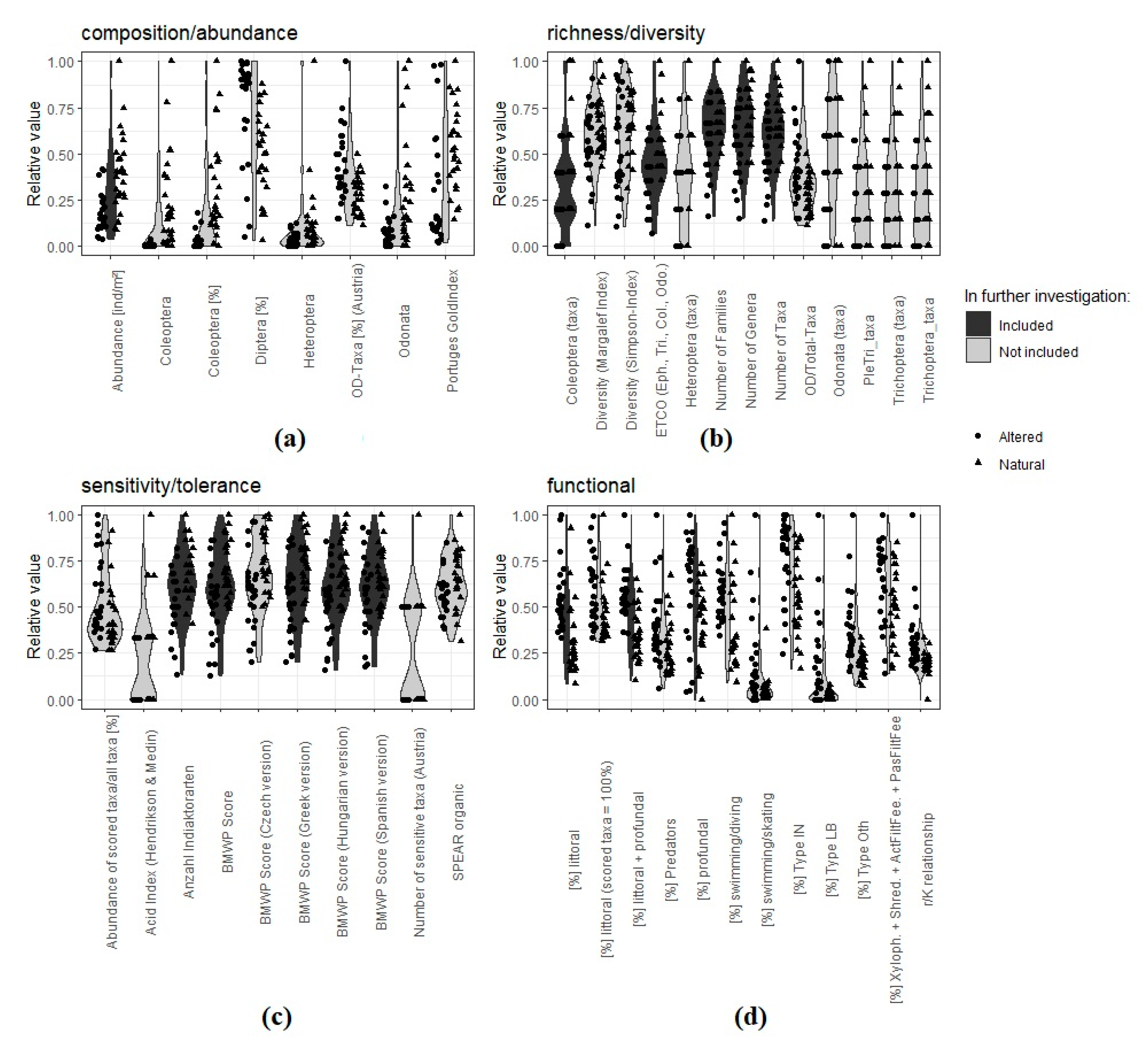
2.4.1. Selection of Metrics
2.4.2. Sensitivity to Stressor
2.4.3. Numerical Suitability
2.4.4. Ecological Relevance
2.4.5. Correlations
- For composition/abundance: abundance [ind/m2];
- For richness/diversity: Coleoptera (taxa);
- For sensitivity/tolerance: BMWP (Biological Monitoring Working Party) Score;
- For functional metrics: (%) littoral, (%) littoral + profundal, (%) profundal.
- (%) littoral;
- (%) littoral + profundal;
- (%) profundal.
2.4.6. Scaling
- 5th percentile and 95th percentile;
- 10th percentile and 90th percentile;
- 10th percentile and 80th percentile;
- Each of the previous with prespecified values for “Coleoptera (taxa)” as 0 for lower and 4 for upper.
2.4.7. Quality Classification
- Reference ≥0.8;
- Good ≥0.6 < 0.8;
- Moderate ≥0.4 < 0.6;
- Poor ≥0.2 < 0.4;
- Bad <0.2.
3. Results
3.1. Characterisation of Chemical and Environmental Variables
3.2. Benthic Invertebrate Taxa
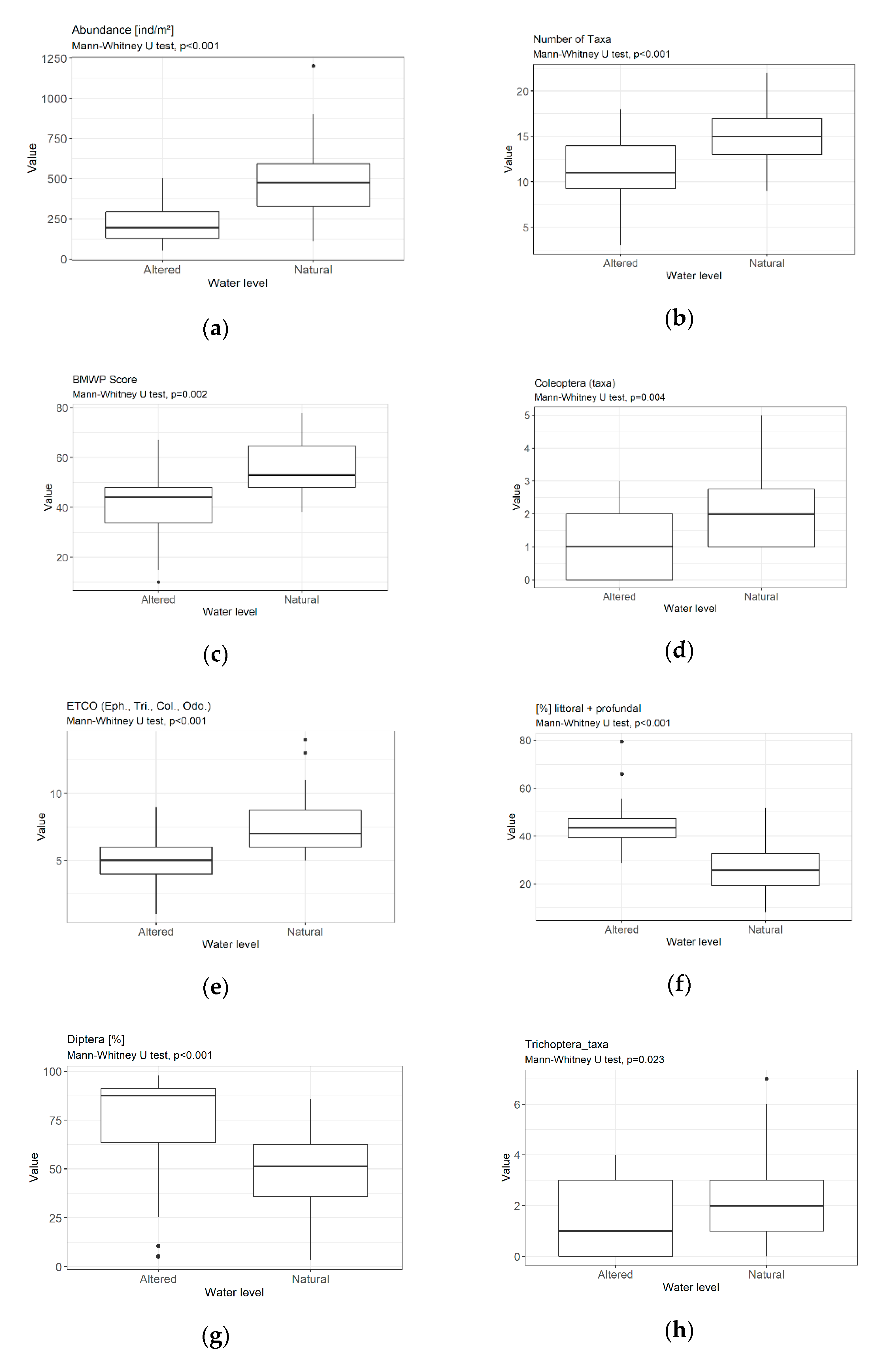
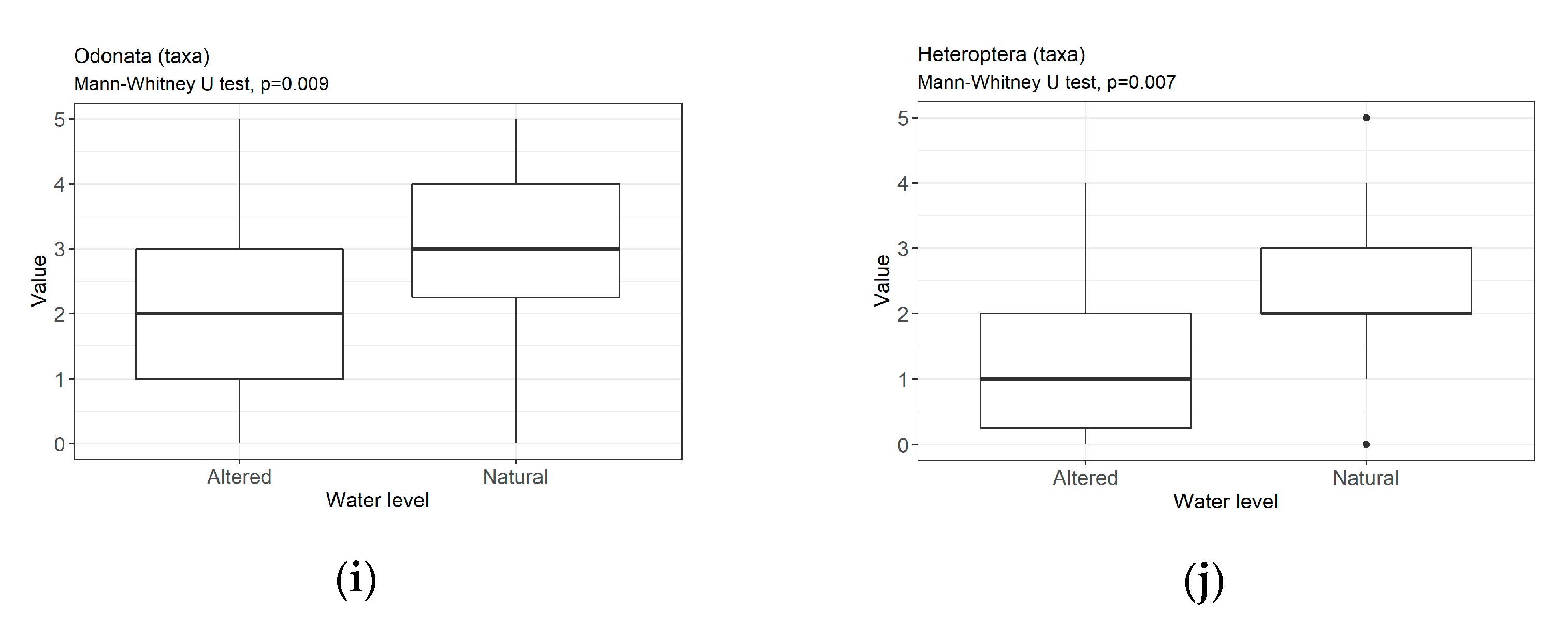
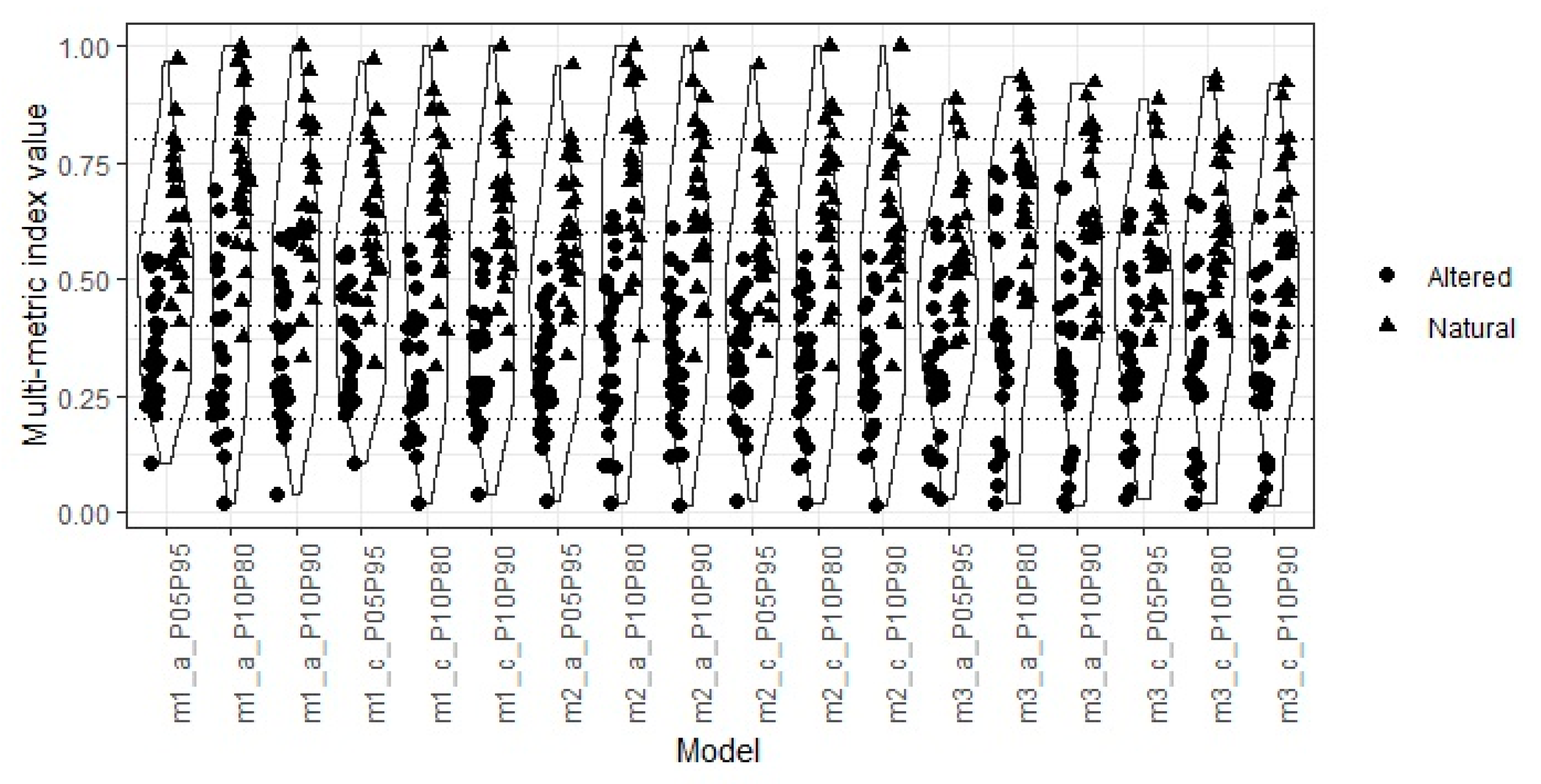
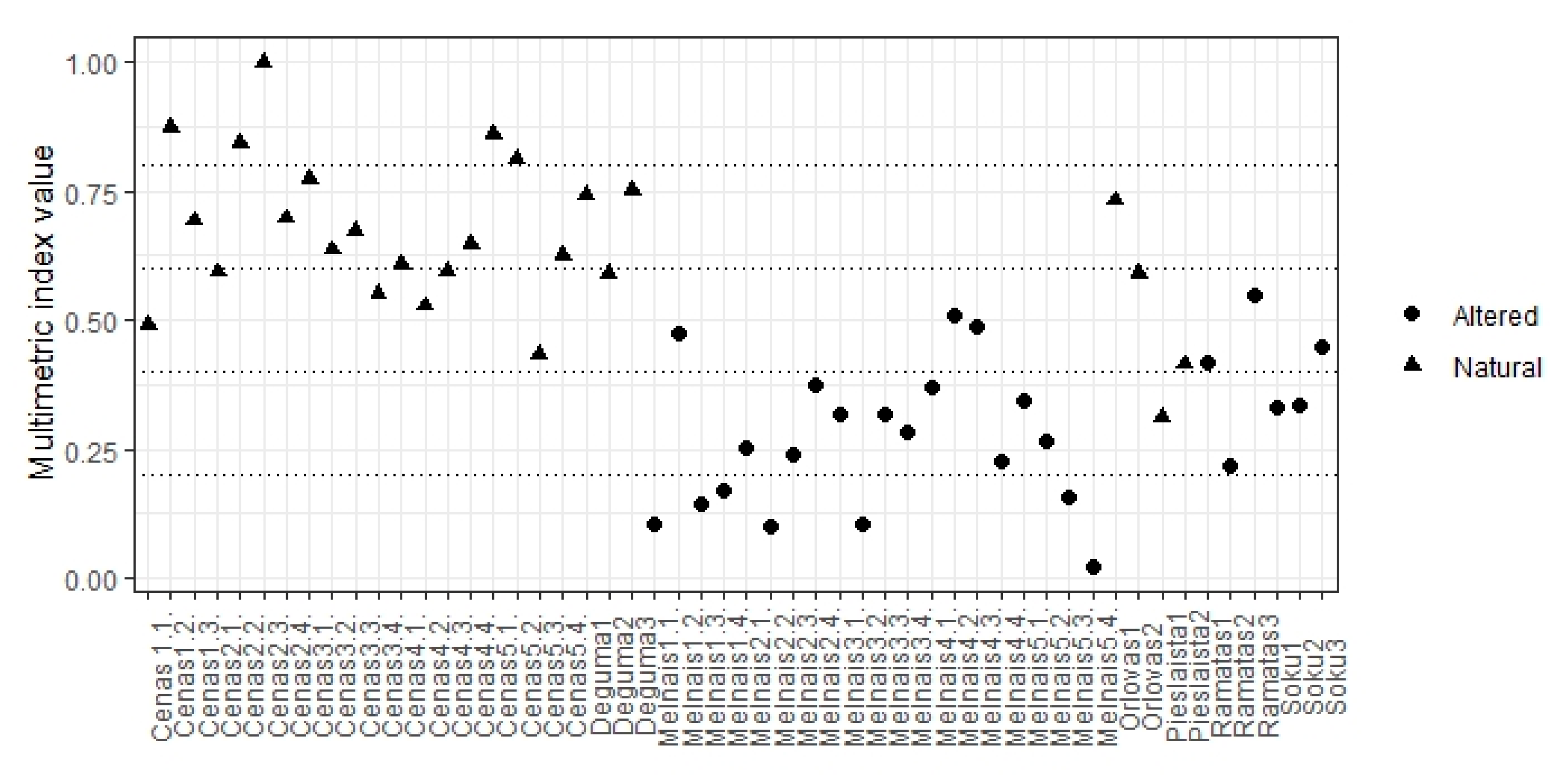
3.3. Metrics
3.4. Multimetric Index
4. Discussion
4.1. Use of Benthic Invertebrates in Lake Ecological Assessment
4.1.1. Sensitivity/Tolerance Metrics
4.1.2. Richness/Diversity Metrics
4.1.3. Composition/Abundance Metrics
4.1.4. Functional Metrics
4.2. Assessment of Hydrological Modifications
4.3. Assessment of Highly Humic Lakes
- (i)
- Classified reference lakes as impacted;
- (ii)
- Did not differentiate between reference and impacted lakes [17].
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Keskitalo, J.; Eloranta, P. (Eds.) Limnology of Humic Waters; Backhuys Publishers: Leiden, The Netherlands, 1999; p. 284. [Google Scholar]
- Wetzel, R.G. Limnology: Lake and River Ecosystems, 3rd ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2001; p. 1006. [Google Scholar]
- Salonen, K.; Arvola, L.; Tulonen, T.; Hammar, T.; Metsälä, T.R.; Kankaala, P.; Münster, U. Planktonic food chains of a highly humic lake. I. A mesocosm experiment during the spring primary production maximum. Hydrobiology 1992, 229, 125–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, R.I. The influence of humic substances on lacustrine planktonic food-chains. Hydrobiology 1992, 229, 73–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, C.T.; Jones, S.E.; Weidel, B.C.; Buffam, I.; Fork, M.L.; Karlsson, J.; Larsen, S.; Lennon, J.T.; Read, J.S.; Sadro, S.; et al. Ecosystem consequences of changing inputs of terrestrial dissolved organic matter to lakes: Current knowledge and future challenges. Ecosystem 2015, 18, 376–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinberg, C.E.W.; Kamara, S.; Prokhotskaya, V.Y.; Manusadzianas, L.; Karasyova, T.A.; Timofeyev, M.A.; Jie, Z.; Paul, A.; Meinelt, T.; Farjalla, V.F.; et al. Dissolved humic substances—Ecological driving forces from the individual to the ecosystem level? Freshw. Biol. 2006, 51, 1189–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepistö, L.; Holopainen, A.L.; Vuoristo, H. Type-specific and indicator taxa of phytoplankton as a quality criterion for assessing the ecological status of Finnish boreal lakes. Limnology 2004, 34, 236–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toivonen, H.; Huttunen, P. Aquatic macrophytes and ecological gradients in 57 small lakes in southern Finland. Aquat. Bot. 1995, 51, 197–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vesterinen, J.; Devlin, S.P.; Syväranta, J.; Jones, R.I. Influence of littoral periphyton on whole-lake metabolism relates to littoral vegetation in humic lakes. Ecology 2017, 98, 3074–3085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarvala, J.; Kankaala, P.; Zingel, P.; Arvola, L. Zooplankton. In Limnology of Humic Waters; Keskitalo, J., Eloranta, P., Eds.; Backhuys Publishers: Leiden, The Netherlands, 1999; pp. 173–191. [Google Scholar]
- Rask, M.; Viljanen, M.; Sarval, J. Humic lakes as fish habitats. In Limnology of Humic Waters; Keskitalo, J., Eloranta, P., Eds.; Backhuys Publishers: Leiden, The Netherlands, 1999; pp. 209–224. [Google Scholar]
- Ptacnik, R.; Solimini, A.G.; Brettum, P. Performance of a new phytoplankton composition metric along a eutrophication gradient in Nordic lakes. Hydrobiology 2009, 633, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rask, M.; Vuori, K.-M.; Hämäläinen, H.; Järvinen, M.; Hellsten, S.; Mykrä, H.; Arvola, L.; Ruuhijärvi, J.; Jyväsjärvi, J.; Kolari, I.; et al. Ecological classification of large lakes in Finland: Comparison of classification approaches using multiple quality elements. Hydrobiology 2011, 660, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Søndergaard, M.; Phillips, G.; Hellsten, S.; Kolada, A.; Ecke, F.; Mäemets, H.; Mjelde, M.; Azzella, M.M.; Oggioni, A. Maximum growing depth of submerged macrophytes in European lakes. Hydrobiology 2013, 704, 165–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepistö, L.; Holopainen, A.L.; Vuoristo, H.; Rekolainen, S. Phytoplankton assemblages as a criterion in the ecological classification of lakes in Finland. Boreal Environ. Res. 2006, 11, 35–44. [Google Scholar]
- Birk, S.; Ecke, F. The potential of remote sensing in ecological status assessment of coloured lakes using aquatic plants. Ecol. Indic. 2014, 46, 398–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alahuhta, J.; Vuori, K.M.; Hellsten, S.; Järvinen, M.; Olin, M.; Rask, M.; Palomäki, A. Defining the ecological status of small forest lakes using multiple biological quality elements and palaeolimnological analysis. Fund. Appl. Limnol. 2009, 175, 203–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baars, J.R.; Murray, D.A.; Hannigan, E.; Kelly-Quinn, M. Macroinvertebrate assemblages of small upland peatland lakes in Ireland. Biol. Environ. 2014, 114, 233–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, A.; Holden, J.; Kay, P.; Francis, B.; Foulger, M.; Gledhill, S.; McDonald, A.T.; Walker, A. The impact of peatland drain-blocking on dissolved organic carbon loss and discolouration of water; results from a national survey. J. Hydrol. 2010, 381, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beadle, J.M.; Brown, L.E.; Holden, J. Biodiversity and ecosystem functioning in natural bog pools and those created by rewetting schemes. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Water 2015, 2, 65–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepistö, L.; Saura, M. Effects of forest fertilization on phytoplankton in a boreal brown-water lake. Boreal Environ. Res. 1998, 3, 33–43. [Google Scholar]
- Drinan, T.J.; Graham, C.T.; O’Halloran, J.; Harrison, S.S.C. The impact of conifer plantation forestry on the Chydoridae (Cladocera) communities of peatland lakes. Hydrobiology 2013, 700, 203–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deininger, A.; Jonsson, A.; Karlsson, J.; Bergström, A.K. Pelagic food webs of humic lakes show low short-term response to forest harvesting. Ecol. Appl. 2018, 29, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drinan, T.J.; Foster, G.N.; Nelson, B.H.; O’Halloran, J.; Harrison, S.S.C. Macroinvertebrate assemblages of peatland lakes: Assessment of conservation value with respect to anthropogenic land-cover change. Biol. Conserv. 2013, 158, 175–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, C.T.; Drinan, T.J.; Harrison, S.S.; O’Halloran, J. Relationship between plantation forest and brown trout growth, energetics and population structure in peatland lakes in western Ireland. For. Ecol. Manag. 2014, 321, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Council Directive. European Commission Directive 2000/60/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 23 October 2000 Establishing a Framework for Community Action in the Field of Water Policy. OJEC 2000, 327, 1–72. [Google Scholar]
- Poikane, S.; Salas Herrero, F.; Kelly, M.G.; Borja, A.; Birk, S.; van de Bund, W. European aquatic ecological assessment methods: A critical review of their sensitivity to key pressures. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 740, 140075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poikane, S.; Zampoukas, N.; Borja, A.; Davies, S.P.; van de Bund, W.; Birk, S. Intercalibration of aquatic ecological assessment methods in the European Union: Lessons learned and way forward. Environ. Sci. Policy 2014, 44, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poikane, S.; Birk, S.; Böhmer, J.; Carvalho, L.; de Hoyos, C.; Gassner, H.; Hellsten, S.; Kelly, M.; Solheim, A.L.; Olin, M.; et al. A hitchhiker’s guide to European lake ecological assessment and intercalibration. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 52, 533–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, L.; Poikane, S.; Solheim, A.L.; Phillips, G.; Borics, G.; Catalan, J.; De Hoyos, C.; Drakare, S.; Dudley, B.J.; Järvinen, M.; et al. Strength and uncertainty of phytoplankton metrics for assessing eutrophication impacts in lakes. Hydrobiology 2013, 704, 127–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, G.; Lyche-Solheim, A.; Skjelbred, B.; Mischke, U.; Drakare, S.; Free, G.; Järvinen, M.; de Hoyos, C.; Morabito, G.; Poikane, S.; et al. A phytoplankton trophic index to assess the status of lakes for the Water Framework Directive. Hydrobiology 2013, 704, 75–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penning, W.E.; Dudley, B.; Mjelde, M.; Hellsten, S.; Hanganu, J.; Kolada, A.; van den Berg, M.; Poikane, S.; Phillips, G.; Willby, N.; et al. Using aquatic macrophyte community indices to define the ecological status of European lakes. Aquat. Ecol. 2008, 42, 253–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poikane, S.; Portielje, R.; Denys, L.; Elferts, D.; Kelly, M.; Kolada, A.; Mäemets, H.; Phillips, G.; Søndergaard, M.; Willby, N.; et al. Macrophyte assessment in European lakes: Diverse approaches but convergent views of ‘good’ ecological status. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 94, 185–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, M.; Urbanic, G.; Acs, E.; Bennion, H.; Bertrin, V.; Burgess, A.; Denys, L.; Gottschalk, S.; Kahlert, M.; Karjalainen, S.M.; et al. Comparing aspirations: Intercalibration of ecological status concepts across European lakes for littoral diatoms. Hydrobiology 2014, 734, 125–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyche-Solheim, A.; Feld, C.K.; Birk, S.; Phillips, G.; Carvalho, L.; Morabito, G.; Mischke, U.; Willby, N.; Søndergaard, M.; Hellsten, S.; et al. Ecological status assessment of European lakes: A comparison of metrics for phytoplankton, macrophytes, benthic invertebrates and fish. Hydrobiology 2013, 704, 57–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poikane, S.; Johnson, R.K.; Sandin, L.; Schartau, A.K.; Solimini, A.G.; Urbanič, G.; Arbačiauskas, K.; Aroviita, J.; Gabriels, W.; Miler, O.; et al. Benthic macroinvertebrates in lake ecological assessment: A review of methods, intercalibration and practical recommendations. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 543, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EEA. European Waters—Assessment of Status and Pressures; EEA Report; European Environment Agency: København, Denmark, 2018; pp. 1–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbanič, G. A Littoral Fauna Index for assessing the impact of lakeshore alterations in Alpine lakes. Ecohydrology 2014, 7, 703–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mjelde, M.; Hellsten, S.; Ecke, F. A water level drawdown index for aquatic macrophytes in Nordic lakes. Hydrobiology 2013, 704, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olin, M.; Rask, M.; Ruuhijärvi, J.; Tammi, J. Development and evaluation of the Finnish fish-based lake classification method. Hydrobiology 2013, 713, 149–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Duinen, G.A.; Brock, A.M.; Kuper, J.T.; Leuven, R.S.E.W.; Peeters, T.M.J.; Roelofs, J.G.M.; van der Velde, G.; Verberk, W.C.E.P.; Esselink, H. Do restoration measures rehabilitate fauna diversity in raised bogs? A comparative study on aquatic macroinvertebrates. Wetl. Ecol. Manag. 2003, 11, 447–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannigan, E.; Kelly-Quinn, M. Composition and structure of macroinvertebrate communities in contrasting open-water habitats in Irish peatlands: Implications for biodiversity conservation. Hydrobiology 2012, 692, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, I.R.; Fernando, C.H.; Paterson, C.G. Associations of Chironomidae (Diptera) of shallow, acid, humic lakes and bog pools in Atlantic Canada, and a comparison with an earlier paleoecological investigation. Hydrobiology 1985, 120, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakulnicka, J.; Zawal, A. Model of disharmonic succession of dystrophic lakes based on aquatic beetle fauna (Coleoptera). Mar. Freshw. Res. 2019, 70, 195–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakalne, M.; Kalnina, L. Mire ecosystems in Latvia. Stapfia 2005, 85, 147–174. [Google Scholar]
- Montanarella, L.; Jones, R.J.A.; Hiederer, R. The distribution of peatland in Europe. Mires Peat 2006, 1, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- European Council Directive. Council Directive 92/43/EEC on the conservation of natural habitats and of wild fauna and flora. OJEC 1992, 206, 7–42. [Google Scholar]
- Pakalne, M.; Kalniņa, L. Mires in Latvia. Suo 2000, 51, 213–226. [Google Scholar]
- Klavins, M.; Kokorite, I.; Springe, G.; Skuja, A.; Parele, E.; Rodinov, V.; Druvietis, I.; Strāķe, S.; Urtans, A. Water quality in cutaway peatland lakes in Seda mire, Latvia. Ecohydrol. Hydrobiol. 2010, 10, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latvian Environment, Geology and Meteorology Centre. River Basin Management Plans 2016–2021. Available online: https://videscentrs.lvgmc.lv/lapas/udens-apsaimniekosana-un-pludu-parvaldiba (accessed on 7 December 2020).
- American Public Health Association; American Water Works Association; Water Environment Federation. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 21th ed.; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2005; p. 1496. [Google Scholar]
- AQEM European Stream Assessment Program. English Manual, Version 2.3. Available online: http://www.aqem.de/mains/products.php (accessed on 7 December 2020).
- Hering, D.; Feld, C.K.; Moog, O.; Ofenbock, T. Cook book for the development of a Multimetric Index for biological condition of aquatic ecosystems: Experiences from the European AQEM and STAR projects and related initiatives. Hydrobiology 2006, 566, 311–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokal, R.R.; Rohlf, F.J. Biometry: The Principles and Practice of Statistics in Biological Research, 3rd ed.; W.H. Freeman and Co: New York, NY, USA, 1995; p. 880. [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. 2020. Available online: http://www.r-project.org/index.html (accessed on 3 November 2020).
- Wickham, H.; Averick, M.; Bryan, J.; Chang, W.; McGowan, L.; François, R.; Grolemund, G.; Hayes, A.; Henry, L.; Hester, J.; et al. Welcome to the Tidyverse. J. Open Source Softw. 2019, 4, 1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Convention on the Conservation of European Wildlife and Natural Habitats (Bern, Switzerland). 1979. Available online: https://rm.coe.int/1680078aff (accessed on 12 January 2021).
- Desrochers, A.; van Duinen, G.J. Peatland fauna. In Boreal Peatland Ecosystems, Ecological Studies 188; Wieder, R.K., Vitt, D.H., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; pp. 67–100. [Google Scholar]
- Ewald, M.L.; Feminella, J.W.; Lenertz, K.K.; Henry, R.P. Acute physiological responses of the freshwater snail Elimia flava (Mollusca: Pleuroceridae) to environmental pH and calcium. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C: Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2009, 150, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mäkelä, T.P.; Oikari, A.O.J. The effects of low water pH on the ionic balance in freshwater mussel Anodonta anatina L. Ann. Zool. Fennici. 1992, 29, 169–175. [Google Scholar]
- Schartau, A.K.; Moe, S.J.; Sandin, L.; McFarland, B.; Raddum, G.G. Macroinvertebrate indicators of lake acidification: Analysis of monitoring data from UK, Norway and Sweden. Aquat. Ecol. 2008, 42, 293–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soldán, T.; Bojková, J.; Vrba, J.; Bitušík, P.; Chvojka, P.; Papáček, M.; Peltanová, J.; Sychra, J.; Tátosová, J. Aquatic insects of the Bohemian Forest glacial lakes: Diversity, long-term changes, and influence of acidification. Silva Gabreta 2012, 18, 123–283. [Google Scholar]
- Karr, J.R.; Chu, E.W. Biological Monitoring and Assessment: Using Multimetric Indexes Effectively; EPA 235-R97-001; US Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 1997; p. 149.
- Armitage, P.D.; Moss, D.; Wright, J.F.; Furse, M.T. The performance of a new biological water quality score system based on macroinvertebrates over a wide range of unpolluted running-water sites. Water Res. 1983, 17, 333–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davy-Bowker, J.; Murphy, J.F.; Rutt, G.P.; Steel, J.E.C.; Furse, M.T. The development and testing of a macroinvertebrate biotic index for detecting the impact of acidity on streams. Arch. Hydrobiol. 2005, 163, 383–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiederholm, T. Use of benthos in lake monitoring. J. Water Pollut. Con. Fed. 1980, 52, 537–547. [Google Scholar]
- Miler, O.; Porst, G.; McGoff, E.; Pilotto, F.; Donohue, L.; Jurca, T.; Solimini, A.G.; Sandin, L.; Irvin, K.; Aroviita, J.; et al. Morphological alterations of lake shores in Europe: A multimetric ecological assessment approach using benthic macroinvertebrates. Ecol. Indic. 2013, 34, 398–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkes, H.A. Origin and development of the biological monitoring working party score system. Water Res. 1998, 32, 964–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šidagytė, E.; Višinskienė, G.; Arbačiauskas, K. Macroinvertebrate metrics and their integration for assessing the ecological status and biocontamination of Lithuanian lakes. Limnologica 2013, 43, 308–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavromati, E.; Kemitzoglou, D.; Tsiaoussi, V.; Lazaridou, M. Report on the Development of the National Method for the Assessment of Ecological Status of Natural Lakes in Greece, with the Use of Littoral Benthic Invertebrates; Greek Biotope/Wetland Centre and Special Secretariat for the Natural Environment and Waters, Ministry of Environment and Energy: Thermi, Greece, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Wiberg-Larsen, P.; Rasmussen, J.J. Revised Danish Macroinvertebrate Index for Lakes—A Method to Assess Ecological Quality. Aarhus University, DCE—Danish Centre for Environment and Energy. 2020. Available online: http://dce2.au.dk/pub/SR373.pdf (accessed on 17 January 2020).
- Böhmer, J.; Chiriac, G.; Varbiro, G.; Wolfram, G.; Poikane, S. Intercalibrating the National Classifications of Ecological Status for Eastern Continental Lakes: Biological Quality Element: Benthic Invertebrates; EUR 29342 EN; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2018; p. 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbanič, G.; Petkovska, V.; Pavlin, M. The relationship between littoral benthic invertebrates and lakeshore modification pressure in two alpine lakes. Fundam. Appl. Limnol. 2012, 180, 157–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aroviita, J.; Hämäläinen, H. The impact of water-level regulation on littoral macroinvertebrate assemblages in boreal lakes. Hydrobiology 2008, 613, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friberg, N.; Bonada, N.; Bradley, D.C.; Dunbar, M.J.; Edwards, F.K.; Grey, J.; Hayes, R.B.; Hildrew, A.G.; Lamouroux, N.; Trimmer, M.; et al. Biomonitoring of human impacts in freshwater ecosystems. The good, the bad and the ugly. Adv. Ecol. Res. 2011, 44, 1–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyjol, Y.; Argillier, C.; Bonne, W.; Borja, A.; Buijse, A.D.; Cardoso, A.C.; Daufresne, M.; Kernan, M.; Ferreira, M.T.; Poikane, S.; et al. Assessing the ecological status in the context of the European Water Framework Directive: Where do we go now? Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 497, 332–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brucet, S.; Poikane, S.; Lyche-Solheim, A.; Birk, S. Biological assessment methods for European lakes: Ecological rationale and human impacts. Freshw. Biol. 2013, 58, 1106–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, R.K.; Goedkoop, W. Bedömningsgrunder för Bottenfauna i Sjöar Och Vattendrag: Användarmanual och Bakgrundsdokument; Sveriges lantbruksuniversitet: Uppsala, Sweden, 2007; p. 84. [Google Scholar]
- Kelly, M.G.; Birk, S.; Willby, N.J.; Denys, L.; Drakare, S.; Kahlert, M.; Karjalainen, S.M.; Marchetto, A.; Pitt, J.A.; Urbanič, G.; et al. Redundancy in the ecological assessment of lakes: Are phytoplankton, macrophytes and phytobenthos all necessary? Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 568, 594–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutela, T.; Vehanen, T.; Rask, M. Assessment of the ecological status of regulated lakes: Stressor-specific metrics from littoral fish assemblages. Hydrobiology 2011, 675, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutela, T.; Aroviita, J.; Keto, A. Assessing ecological status of regulated lakes with littoral macrophyte, macroinvertebrate and fish assemblages. Ecol. Indic. 2013, 24, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evtimova, V.V.; Donohue, I. Water-level fluctuations regulate the structure and functioning of natural lakes. Freshw. Biol. 2016, 61, 251–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastrantuono, L.; Pilotto, F.; Rossopinti, A.; Bazzanti, M.; Solimini, G. Response of littoral macroinvertebrates to morphological disturbances in Mediterranean lakes: The case of Lake Piediluco (Central Italy). Fund. Appl. Limnol. 2015, 186, 297–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brauns, M.; Garcia, X.F.; Pusch, M. Potential effects of water level fluctuations on littoral invertebrates in lowland lakes. Hydrobiology 2008, 613, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palomäki, R. Response by macrozoobenthos biomass to water level regulation in some Finnish lake littoral zones. Hydrobiology 1994, 286, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tikkanen, P.; Kantola, L.; Niva, T.; Hellsten, S.; Alasaarela, E. Ecological Aspects of Lake Regulation in Northern Finland. Part 3. Macrozoobenthos and Feeding of Fish; VTT Research Notes 987; Technical Research Centre of Finland: Espoo, Finland, 1989; (in Finnish with English). [Google Scholar]
- Jyväsjärvi, J.; Nyblom, J.; Hämäläinen, H. Palaeolimnological validation of estimated reference values for a lake profundal macroinvertebrate metric (Benthic Quality Index). J. Paleolimnol. 2010, 44, 253–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tammi, J.; Lappalainen, A.; Mannio, J.; Rask, M.; Vuorenmaa, J. Effects of eutrophication on fish and fisheries in Finnish lakes: A survey based on random sampling. Fish. Manag. Ecol. 1999, 6, 173–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skuja, A.; Ozoliņš, D. Fitting New Method—Latvian Lake Macroinvertebrate Multimetric Index (LLMMI) to Results of Central—Baltic Geographical Intercalibration Group (CB—GIG) Lake Benthic Macroinvertebrate Intercalibration; Report; Institute of Biology, University of Latvia: Salaspils, Latvia, 2016; p. 12. [Google Scholar]



| Lakes | Altered Water Level (+) | Year | pH | Cond μS/cm | Colour mg Pt/L | TN mg/L | TP mg/L |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cenas Mire Lake 1 | 2015 | 3.93 | 28 | 124 | 0.95 | 0.017 | |
| Cenas Mire Lake 2 | 2015 | 4.44 | 29 | 144 | 0.99 | 0.020 | |
| Cenas Mire Lake 3 | 2015 | 4.49 | 26 | 114 | 0.90 | 0.019 | |
| Cenas Mire Lake 4 | 2015 | 3.75 | 32 | 189 | 0.83 | 0.021 | |
| Cenas Mire Lake 5 | 2015 | 3.46 | 43 | 304 | 0.92 | 0.020 | |
| Melnais Lake Mire Lake 1 | + | 2015 | 3.68 | 65 | 393 | 1.31 | 0.019 |
| Melnais Lake Mire Lake 2 | + | 2015 | 3.53 | 49 | 402 | 1.25 | 0.022 |
| Melnais Lake Mire Lake 3 | + | 2015 | 3.58 | 44 | 365 | 1.17 | 0.022 |
| Melnais Lake Mire Lake 4 | + | 2015 | 3.43 | 45 | 505 | 1.36 | 0.017 |
| Melnais Lake Mire Lake 5 | + | 2015 | 3.35 | 48 | 666 | 1.68 | 0.028 |
| Deguma Lake | 2017 | 5.09 | 31 | 222 | 0.95 | 0.032 | |
| Orlovas Lake | 2017 | 5.42 | 21 | 205 | 0.87 | 0.037 | |
| Pieslaista Lake | 2017 | 5.02 | 36 | 238 | 0.65 | 0.061 | |
| Ramatas Lielezers Lake | + | 2017 | 6.09 | 23 | 134 | 0.65 | 0.032 |
| Soku Lake | + | 2017 | 5.88 | 25 | 130 | 0.43 | 0.035 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ozoliņš, D.; Skuja, A.; Jēkabsone, J.; Kokorite, I.; Avotins, A.; Poikane, S. How to Assess the Ecological Status of Highly Humic Lakes? Development of a New Method Based on Benthic Invertebrates. Water 2021, 13, 223. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13020223
Ozoliņš D, Skuja A, Jēkabsone J, Kokorite I, Avotins A, Poikane S. How to Assess the Ecological Status of Highly Humic Lakes? Development of a New Method Based on Benthic Invertebrates. Water. 2021; 13(2):223. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13020223
Chicago/Turabian StyleOzoliņš, Dāvis, Agnija Skuja, Jolanta Jēkabsone, Ilga Kokorite, Andris Avotins, and Sandra Poikane. 2021. "How to Assess the Ecological Status of Highly Humic Lakes? Development of a New Method Based on Benthic Invertebrates" Water 13, no. 2: 223. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13020223
APA StyleOzoliņš, D., Skuja, A., Jēkabsone, J., Kokorite, I., Avotins, A., & Poikane, S. (2021). How to Assess the Ecological Status of Highly Humic Lakes? Development of a New Method Based on Benthic Invertebrates. Water, 13(2), 223. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13020223






