Vertical Motion of Air over the Indian Ocean and the Climate in East Asia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
2.1. Data
2.2. Methodology
3. Vertical Motion of Air over the Indian Ocean
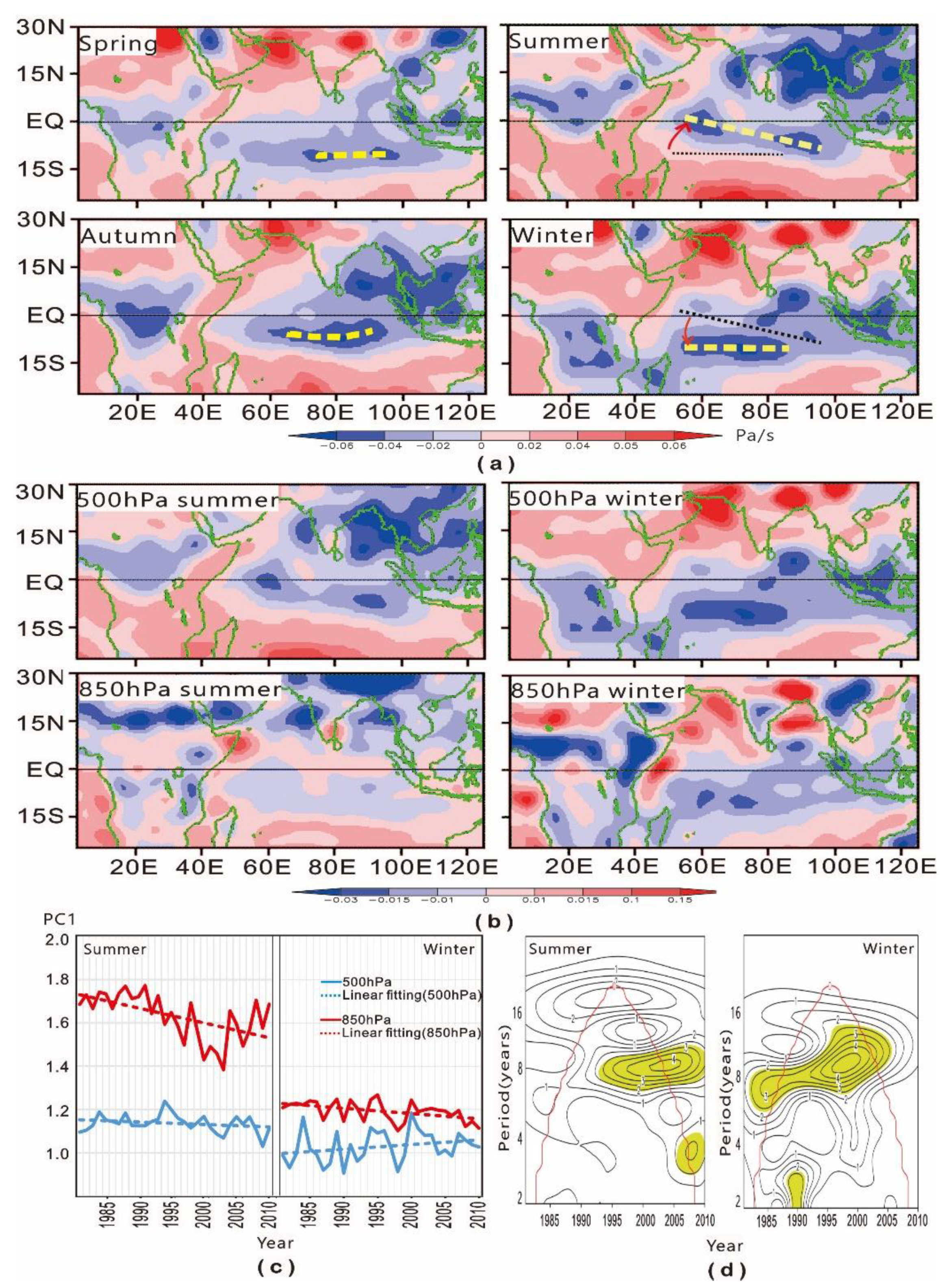
3.1. Distribution of the Vertical Velocity of Air
3.2. Distribution Characteristics of Atmospheric Vertical Motion over the Indian Ocean
3.3. Period of Vertical Motion of Air
4. Relationship between the Vertical Motion of Air and the Climate in East Asia
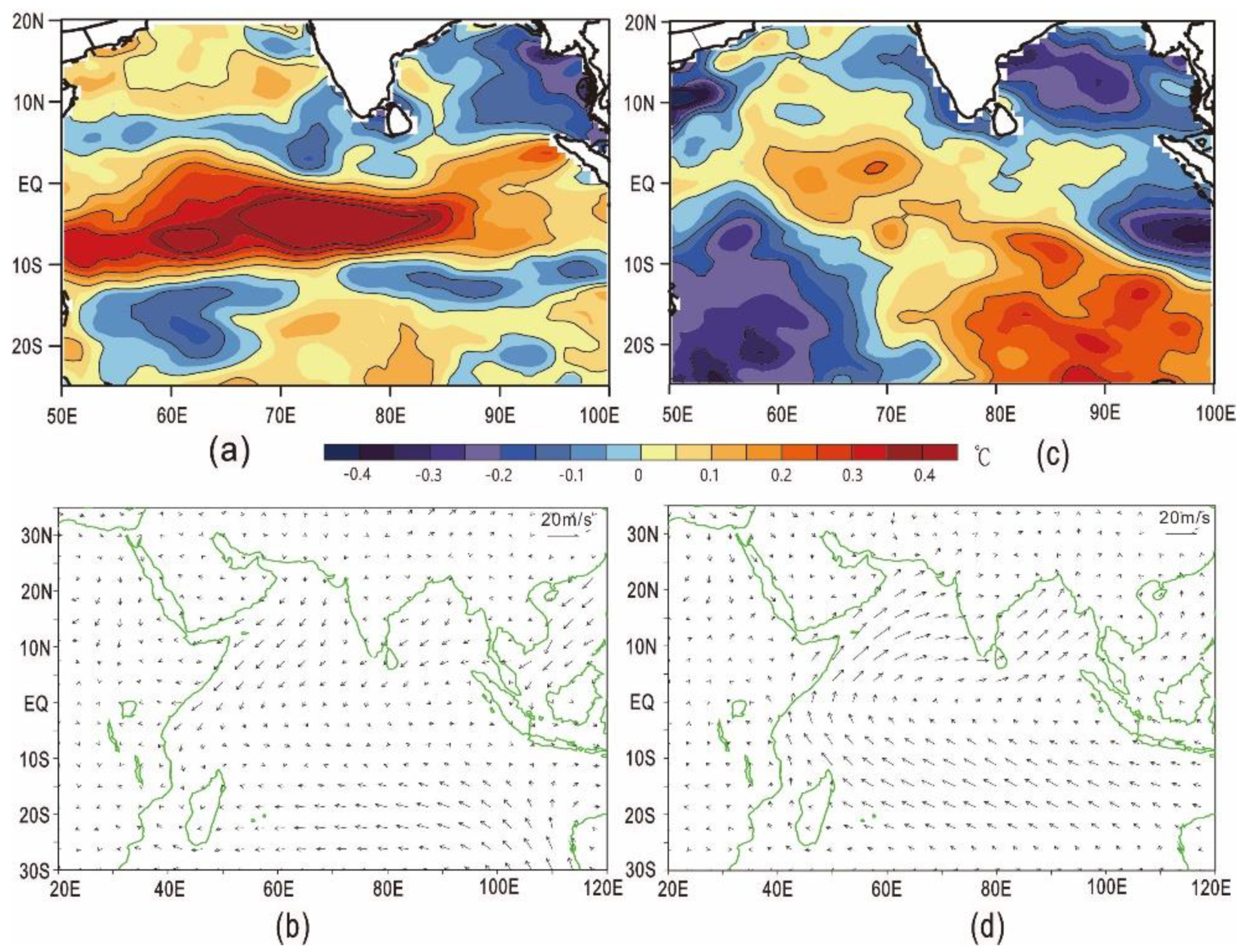
4.1. Vertical Motion of Air over the Indian Ocean and the East Asian Climate in Summer
4.1.1. Vertical Motion and Precipitation in June
4.1.2. Surface Air Temperature, Pressure and the Vertical Motion of Air in June
4.2. Vertical Motion of Air over the Indian Ocean and the East Asian Climate in Winter
4.2.1. Vertical Motion of Air and Precipitation in January
4.2.2. Surface Air Temperature, Pressure and Vertical Motion of Air in January
5. Discussion
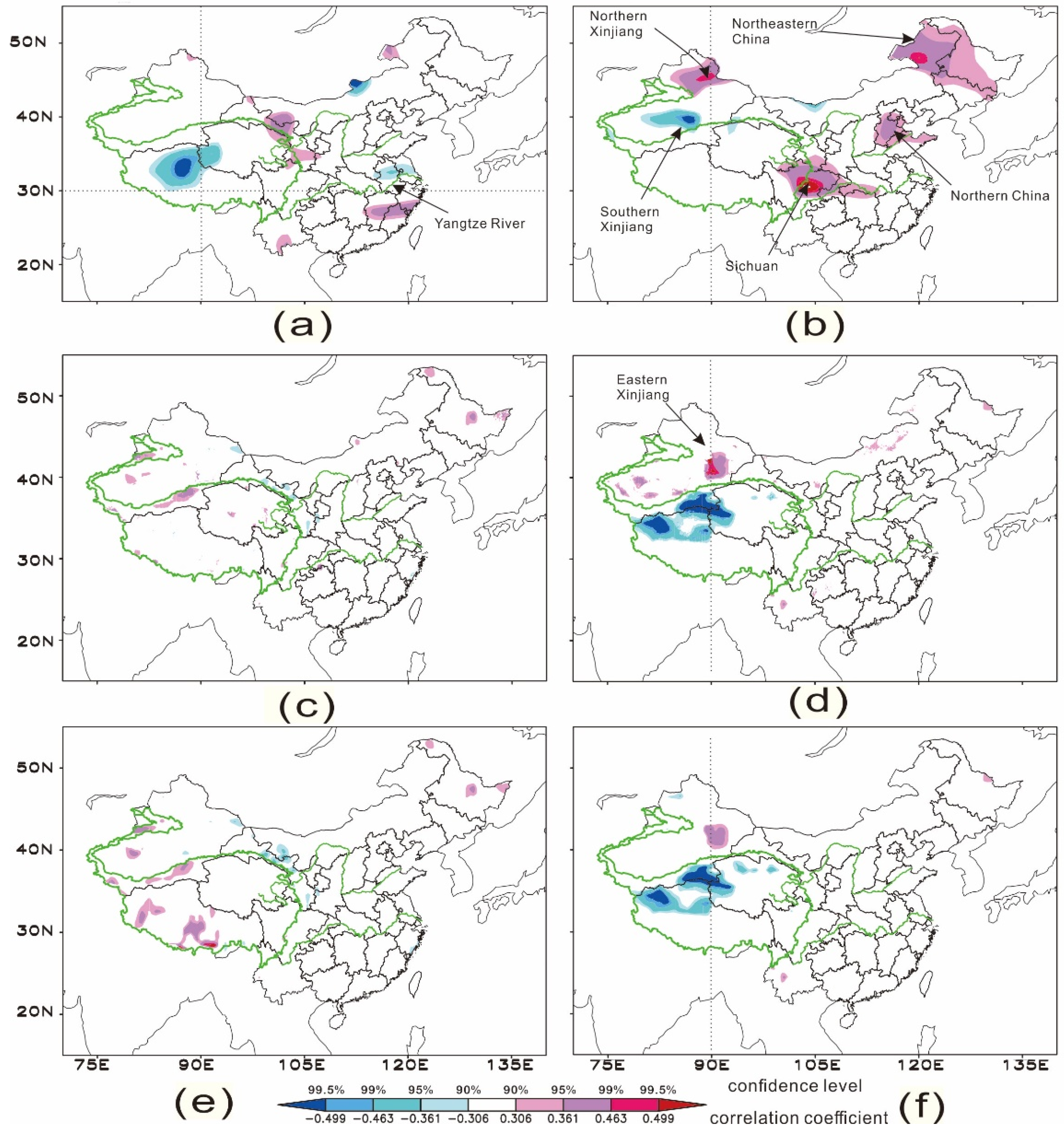
5.1. Relevance to Precipitation
5.2. Correlation between Vertical Motion over the Indian Ocean and Surface Temperature and Pressure in China in Winter
5.3. Turning of the Axis of Vertical Motion Center
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schott, F.A.; McCreary, J.P., Jr. The monsoon circulation of the Indian Ocean. Prog. Oceanogr. 2001, 51, 1–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Yanai, M. The Onset and Interannual variability of the Asian Summer Monsoon in relation to land-sea thermal contrast. J. Clim. 1996, 9, 358–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, K.M.; Wu, H.T.; Bony, S. The role of large-scale atmospheric circulation in the relationship between tropical convection and sea surface temperature. J. Clim. 1997, 10, 381–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Wu, R.; Li, T. Atmosphere–warm ocean interaction and its impacts on Asian–Australian monsoon variation. J. Clim. 2003, 16, 1195–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Z.C. Analysis and calculation of large-scale vertical movement. Acta Meteorol. Sin. 1954, 25, 3–20. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Sreelekha, P.N.; Babu, C.A. Organized convection over southwest peninsular India during the pre-monsoon season. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2019, 135, 1279–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadley, G. Concerning the Cause of the General Trade-Winds. Philos. Trans. 1735, 39, 58–62. [Google Scholar]
- Mathew, S.S.; Kumar, K.K. Characterization of the long-term changes in moisture, clouds and precipitation in the ascending and descending branches of the Hadley Circulation. J. Hydrol. 2019, 570, 366–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjerknes, J. Atmospheric teleconnections from the equatorial. Mon. Weather. Rev. 1969, 97, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyrtki, K.; Eldyn, G. Equatorial upwelling events in the central pacific. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 1982, 12, 984–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peixoto, J.P.; Oort, A.H. Physics of Climate; American Institute of Physics: New York, NY, USA, 1992; p. 520. [Google Scholar]
- Saha, K. Zonal anomaly of sea surface temperature in equatorial Indian Ocean and its possible effect upon monsoon circulation. Tellus 1970, 22, 403–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjerknes, P.V.F. Synoptical representation of atmospheric motions. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1910, 36, 267–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidson, J.W. African rainfall and its relation to upper air circulation. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1977, 103, 441–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, M.; Entekhabi, D.; Nicholson, S.E. Interannual variability in rainfall, water vapor flux, and vertical motion over West Africa. J. Clim. 2000, 13, 3827–3841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.Y.; Ding, Y.H. Teleconnection between the indian summer monsoon onset and the meiyu over the yangtze river valley. Sci. China Ser. D Earth Sci. 2008, 51, 1021–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.G. Relationship between Indian and East Asian Summer Rainfall Variations. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2017, 34, 4–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalnay, E.; Kanamitsu, M.; Kistler, R.; Collins, W.; Deaven, D.; Gandin, L.; Joseph, D. The NCEP/NCAR 40-year reanalysis project. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1996, 77, 437–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Wu, R.; Fu, X. Pacific–East Asian teleconnection: How does ENSO affect East Asian climate? J. Clim. 2000, 13, 1517–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swain, M.; Sinha, P.; Mohanty, U.C.; Pattnaik, S. Dominant large-scale parameters responsible for diverse extreme rainfall events over vulnerable Odisha state in India. Clim. Dyn. 2020, 54, 2221–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Z.G.; Chao, J.P. Teleconnections of the sea surface temperature in the Indian ocean with sea surface temperature in the eastern equatorial pacific, and with the 500 hPa geopotential height field in the Northern Hemisphere. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 1987, 4, 343–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.L.; Li, C.Y. Dipole Oscillation in the Southern Indian Ocean and Its Impacts on Climate. Chin. J. Geophys. 2005, 48, 1323–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parthasarathy, B.; Munot, A.A.; Kothawale, D.R. All-India Monthly and Seasonal Rainfall Series 1871–1993. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 1994, 49, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.Y.; Tian, R.X.; Feng, S. Comparison of Atmospheric Vertical Motion over China in ERA-Interim, JRA-55, and NCEP/NCAR Reanalysis Datasets. Asia-Pac. J. Atmos. Sci. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenz, E.N. Statistical forecasting program: Empirical orthogonal functions and statistical weather prediction. Sci. Rep. 1956, 409, 997–999. [Google Scholar]
- North, G.R.; Bell, T.L.; Cahalan, R.F. Sampling errors in the estimation of empirical orthogonal functions. Mon. Weather Rev. 1982, 110, 699–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrence, C.; Compo, G.P.A. Practical guide to wavelet analysis. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1998, 79, 61–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grinsted, A.; Moore, J.C.; Jevrejeva, S. Application of the cross wavelet transform and wavelet coherence to geophysical time series. Nonlinear Process. Geophys. 2004, 11, 561–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furon, A.C.; Wagner-Riddle, C.; Smith, C.R.; Warland, J.S. Wavelet analysis of wintertime and spring thaw CO2 and N2O fluxes from agricultural fields. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2008, 148, 1305–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrence, C.; Webster, P.J. Interdecadal Changes in the ENSO-Monsoon system. J. Clim. 1999, 12, 2679–2690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freire, S.L.M. Application of singular value decomposition to vertical seismic profiling. Geophysics 1988, 53, 778–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, E.; Hofrichter, J. Singular value decomposition-application to analysis of experimental-data. Methods Enzymol. 1992, 210, 129–192. [Google Scholar]
- Stork, C. Singular value decomposition of the velocity-reflector depth tradeoff, Part 2: High-resolution analysis of a generic model. Geophysics 1992, 57, 927–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wallace, J.M.; Smith, C.; Bretherton, C.S. Singular value decomposition of wintertime sea surface temperature and 500-mb height anomalies. J. Clim. 1992, 5, 561–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreimer, N.; Sacchi, M.D. A tensor higher-order singular value decomposition for prestack seismic data noise reduction and interpolation. Geophysics 2012, 77, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kjellsson, J. Weakening of the global atmospheric circulation with global warming. Clim. Dyn. 2015, 45, 975–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.G.; Lin, J.R.; Shou, S.W.; Tang, D.S. Principles and Methods of Synoptic Meteorology; China Meteorological Press: Beijing, China, 2007; pp. 168–213. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, W.Y.; Xu, X.D.; Sun, J.H. An investigation into the surface energy balance on the southeast edge of the Tibetan Plateau and the cloud’s impact. Acta Meteorol. Sin. 2012, 70, 837–846. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]

| Cold Air from the High Latitude | Vertical Motion over the Indian Ocean | Precipitation in Southern/Northern Xinjiang | Upward Motion of Air in Eastern Xinjiang | Temperature/Pressure in the Eastern Xinjiang | Sinks in the North of the Tibetan Plateau | Temperature/Pressure in the Tibetan Plateau |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strengthen (+) | Weaken (−) | Increase/decrease (+/−) | Increase (+) | Decrease/decrease (−/−) | Increase (+) | Increase/increase (+/+) |
| Weaken (−) | Strengthen (+) | Increase/decrease (−/+) | Decrease (−) | Increase/increase (+/+) | Decrease (+) | Decrease/decrease (−/−) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tian, R.; Ma, Y.; Ma, W. Vertical Motion of Air over the Indian Ocean and the Climate in East Asia. Water 2021, 13, 2641. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13192641
Tian R, Ma Y, Ma W. Vertical Motion of Air over the Indian Ocean and the Climate in East Asia. Water. 2021; 13(19):2641. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13192641
Chicago/Turabian StyleTian, Rongxiang, Yaoming Ma, and Weiqiang Ma. 2021. "Vertical Motion of Air over the Indian Ocean and the Climate in East Asia" Water 13, no. 19: 2641. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13192641
APA StyleTian, R., Ma, Y., & Ma, W. (2021). Vertical Motion of Air over the Indian Ocean and the Climate in East Asia. Water, 13(19), 2641. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13192641








