Size Characteristics of Sediments Eroded under Different Masson Pine Litter Covers in South China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site and Soil Samples
2.2. Soil Tank Filling Test
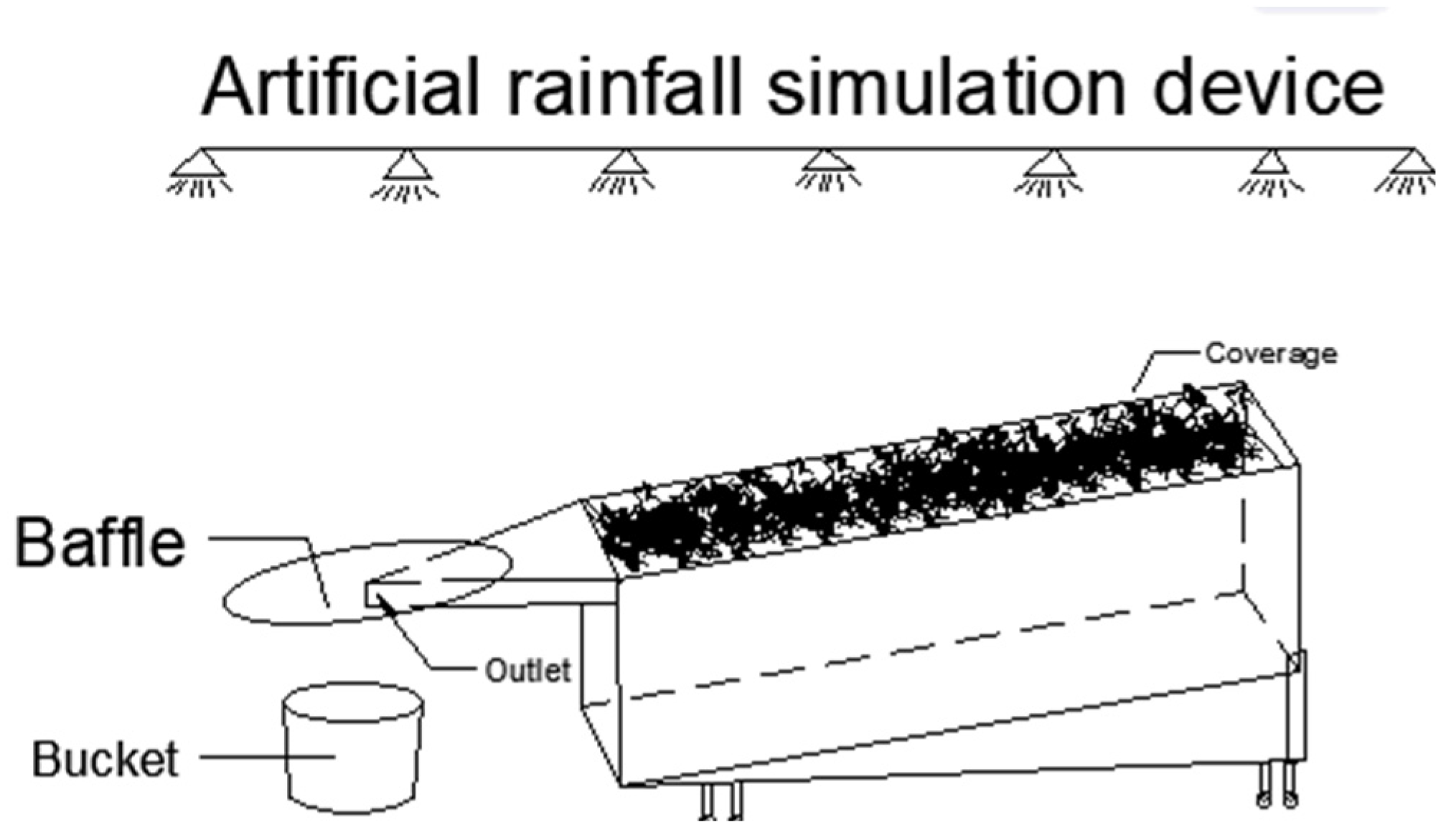
2.3. Rainfall Simulation Experiment
2.4. Particle Size Analysis Experiment
2.5. Data Collection and Analysis
3. Results
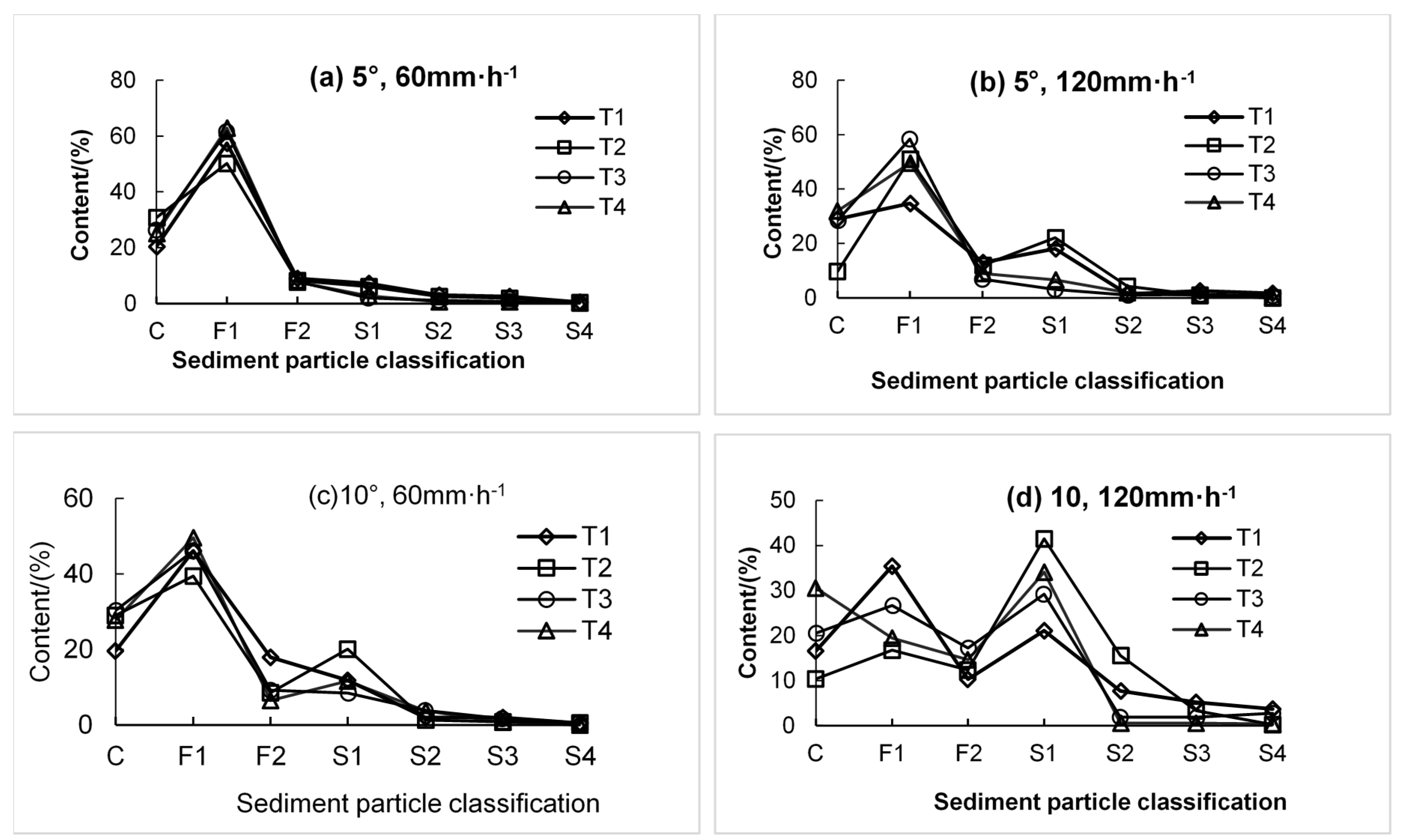
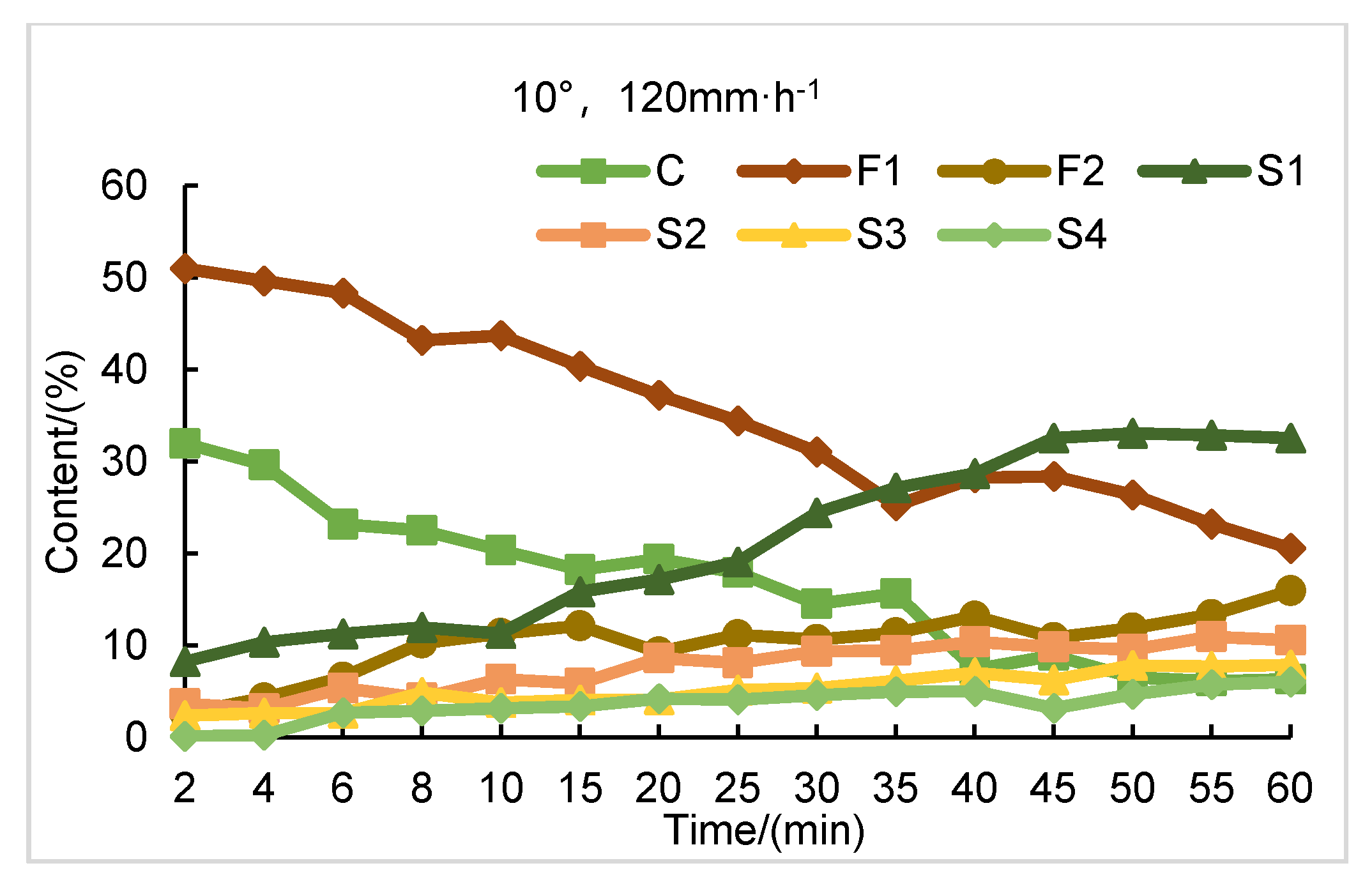
3.1. Characteristics of Sediment Size Change under Litter Coverage
3.2. Separation Characteristics of Eroded Sediment Particles under Different Litter Coverages
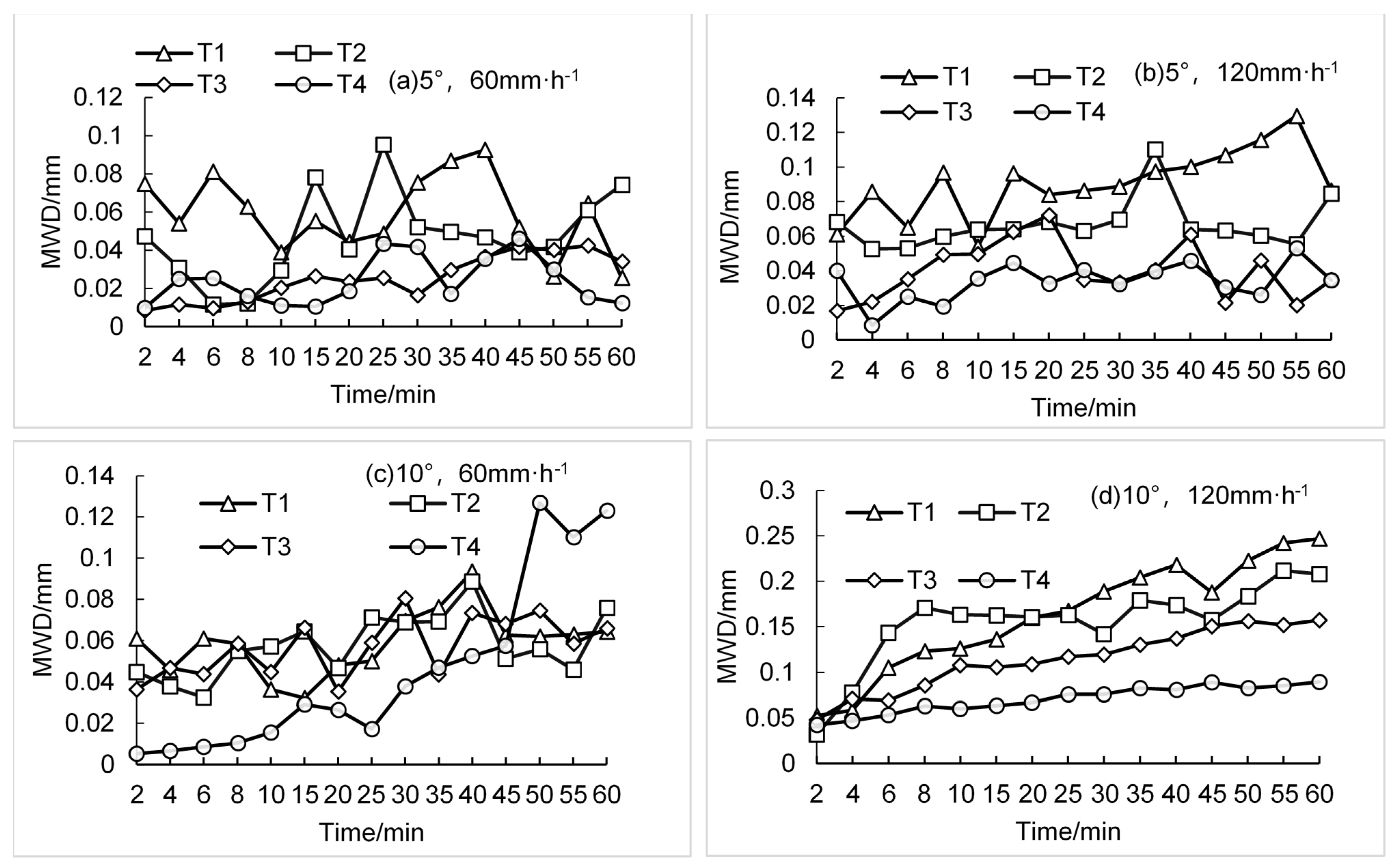
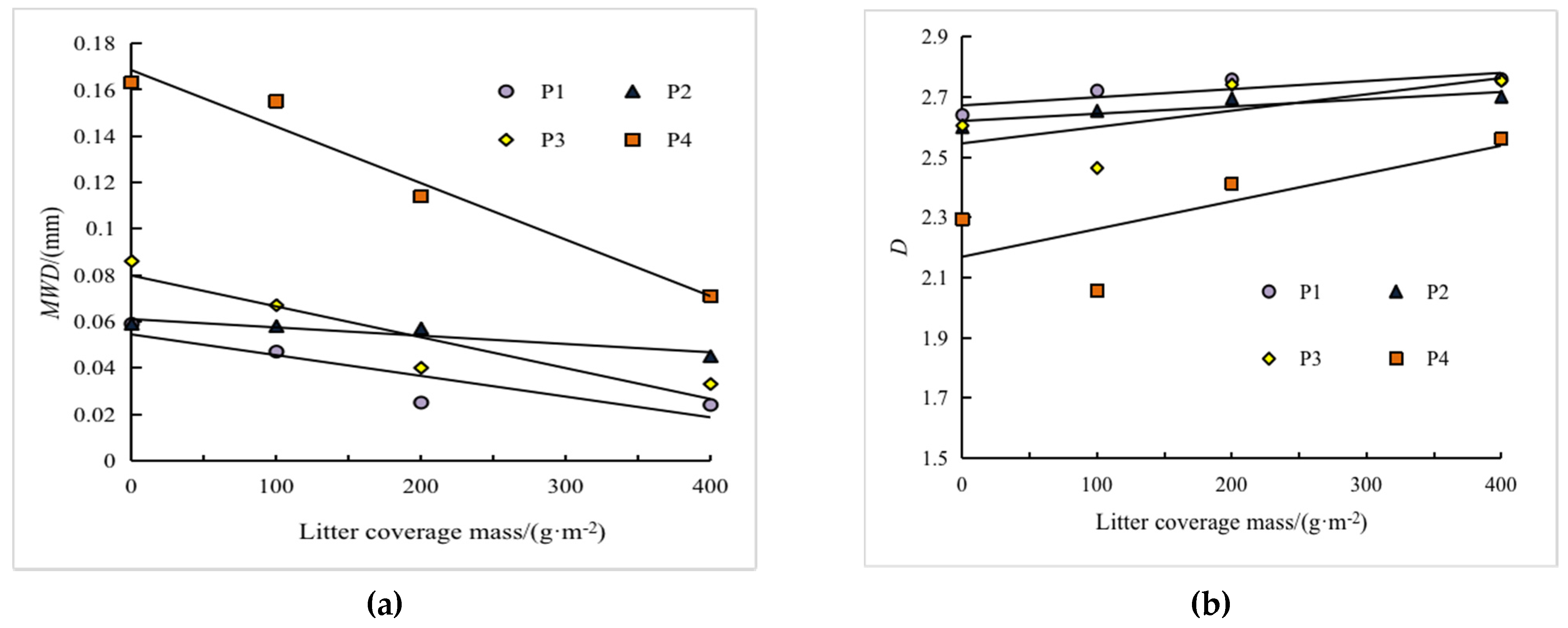
3.2.1. Mean Weight Diameter of Eroded Soil Particle Size under Litter Coverage
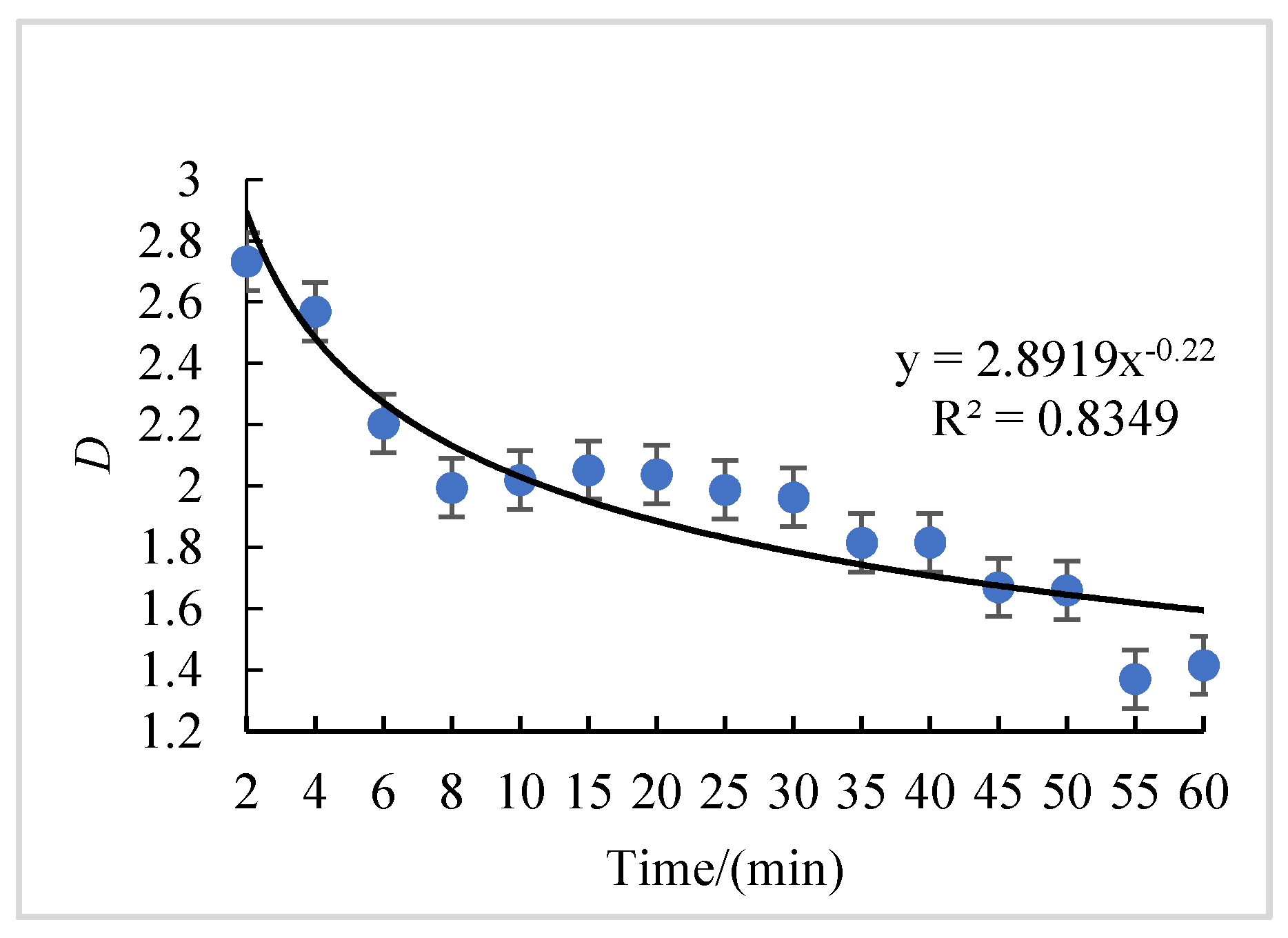
3.2.2. The Fractal Dimension D of Eroded Soil Particle Size under Litter Coverage
3.2.3. Particle Enrichment Ratio of Eroded Sediment
3.3. Quantitative Relationship between Litter Coverage Mass and Eroded Sediment Particle Separation Characteristic Parameters
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lu, J.; Sun, B.; Ren, F.; Li, H.; Jiao, X. Effect of Freeze-Thaw Cycles on Soil Detachment Capacities of Three Loamy Soils on the Loess Plateau of China. Water 2021, 13, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, W.S.d.; Seitz, S.; Oliveira, L.F.C.d.; Carvalho, D.F.d. Duration and intensity of rainfall events with the same erosivity change sediment yield and runoff rates. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2021, 9, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piacentini, T.; Galli, A.; Marsala, V.; Miccadei, E. Analysis of Soil Erosion Induced by Heavy Rainfall: A Case Study from the NE Abruzzo Hills Area in Central Italy. Water 2018, 10, 1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, B.; Walter, M.T.; Steenhuis, T.S.; Parlange, J.Y.; Richards, B.K.; Hogarth, W.L.; Rose, C.W. Investigating raindrop effects on transport of sediment and non-sorbed chemicals from soil to surface runoff. J. Hydrol. 2005, 308, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinnell, P.I.A. Raindrop-impact-induced erosion processes and prediction: A review. Hydrol. Process. 2005, 19, 2815–2844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.M.; Li, Z.X.; Cai, C.F.; Wang, J.-G. The dynamic response of splash erosion to aggregate mechanical breakdown through rainfall simulation events in Ultisols (subtropical China). Catena 2014, 121, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiani-Harchegani, M.; Sadeghi, S.H.; Singh, V.P.; Asadi, H.; Abedi, M. Effect of rainfall intensity and slope on sediment particle size distribution during erosion using partial eta squared. Catena 2019, 176, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nearing, M.A.; Bradford, J.M. Single Waterdrop Splash Detachment and Mechanical Properties of Soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1985, 49, 547–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsons, A.J.; Abrahams, A.D.; Wainwright, J. Rainsplash and erosion rates in an interrill area on semi-arid grassland, Southern Arizona. Catena 1994, 22, 215–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.C. Determining and Modeling Dominant Processes of Interrill Soil Erosion. Water Resour. Res. 2019, 55, 4–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wirtz, S.; Seeger, M.; Ries, J.B. Field experiments for understanding and quantification of rill erosion processes. Catena 2012, 91, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, V.J. Retardance coefficients for low flow in channels lined with vegetation. Eos. Trans. Amer. Geophys. Union 1946, 27, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Wei, Y.; Cai, C.; Yuan, Z.; Liao, Y.; Li, D. Effects of erosion-induced land degradation on effective sediment size characteristics in sheet erosion. Catena 2020, 195, 104843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Zheng, F.; Li, G.; Bian, F.; An, J. The effects of raindrop impact and runoff detachment on hillslope soil erosion and soil aggregate loss in the Mollisol region of Northeast China. Soil Tillage Res. 2016, 161, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Descheemaeker, K.; Nyssen, J.; Poesen, J.; Raes, D.; Haile, M.; Muys, B.; Deckers, S. Runoff on slopes with restoring vegetation: A case study from the Tigray highlands, Ethiopia. J. Hydrol. 2006, 331, 219–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Jia, G.; Yu, X. Effects of the undecomposed layer and semi-decomposed layer of Quercus variabilis litter on the soil erosion process and the eroded sediment particle size distribution. Hydrol. Process. 2021, 35, e14195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Zhang, G.h.; Luan, L.l.; Liu, F. Temporal variation in soil resistance to flowing water erosion for soil incorporated with plant litters in the Loess Plateau of China. Catena 2016, 145, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, G.; Zhu, P.; Wang, X. Comparison of the effects of litter covering and incorporation on infiltration and soil erosion under simulated rainfall. Hydrol. Process. 2020, 34, 2911–2922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Niu, J.; Xie, B. Study on Hydrological Functions of Litter Layers in North China. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e70328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Z.H.; Yue, B.J.; Wang, L.; Fang, N.F.; Wang, D.; Wu, F.Z. Effects of Mulch Cover Rate on Interrill Erosion Processes and the Size Selectivity of Eroded Sediment on Steep Slopes. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2012, 77, 257–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marzen, M.; Iserloh, T.; Casper, M.C.; Ries, J.B. Quantification of particle detachment by rain splash and wind-driven rain splash. Catena 2015, 127, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, R.P.C.; Quinton, J.N.; Smith, R.E.; Govers, G.; Poesen, J.W.A.; Auerswald, K.; Chisci, G.; Torri, D.; Styczen, M.E. The European Soil Erosion Model (EUROSEM): A dynamic approach for predicting sediment transport from fields and small catchments. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 1998, 23, 527–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streeter, M.T.; Schilling, K.E.; Burras, C.L.; Wolter, C.F. Erosion and sediment delivery in southern Iowa watersheds: Implications for conservation planning. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2021, 76, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, S.H.; Kiani Harchegani, M.; Asadi, H. Variability of particle size distributions of upward/downward splashed materials in different rainfall intensities and slopes. Geoderma 2017, 290, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieri, L.; Bittelli, M.; Hanuskova, M.; Ventura, F.; Vicari, A.; Pisa, P.R. Characteristics of eroded sediments from soil under wheat and maize in the North Italian Apennines. Geoderma 2009, 154, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durnford, D.; King, J.P. Experimental Study of Processes and Particle-Size Distributions of Eroded Soil. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 1993, 119, 383–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Shi, Z.H.; Wang, J.; Fang, N.F.; Wu, G.L.; Zhang, H.Y. Rainfall kinetic energy controlling erosion processes and sediment sorting on steep hillslopes: A case study of clay loam soil from the Loess Plateau, China. J. Hydrol. 2014, 512, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutherland, R.A.; Wan, Y.; Lee, C.T.; Ziegler, A.D. Aggregate enrichment ratios for splash and wash transported sediment from an Oxisol. Catena 1996, 26, 187–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beuselinck, L.; Steegen, A.; Govers, G.; Nachtergaele, J.; Takken, I.; Poesen, J. Characteristics of sediment deposits formed by intense rainfall events in small catchments in the Belgian Loam Belt. Geomorphology 2000, 32, 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wendroth, O.; Walton, R.J. Field-Scale Bromide Leaching as Affected by Land Use and Rain Characteristics. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2013, 77, 1157–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Yang, Y.; Liu, B.; Liu, Y.; Gao, X.; Guo, Q. Size characteristics of sediments eroded from three soils in China under natural rainfall. J. Soils Sediments 2016, 16, 2153–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.Z.; Cheng, H.J.; Zhou, Z.D. The Sediment Particles Characteristics of Splash and Sheetwash in Rocky Mountain Area of Northern China. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2016, 3, 71–77. [Google Scholar]
- Proffitt, A.P.B.; Rose, C.W.; Hairsine, P.B. Rainfall Detachment and Deposition: Experiments with Low Slopes and Significant Water Depths. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1991, 55, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, W.R. Representation of Soil Aggregate-Size Distribution by a Logarithmic-Normal Distribution. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1956, 20, 151–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moss, A.J.; Walker, P.H.; Hutka, J. Raindrop-stimulated transportation in shallow water flows: An experimental study. Sediment. Geol. 1979, 22, 165–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Litter Species | Length/ (cm·g−1) | Projected Area/ (cm2·g−1) | Surface Area/ (cm2·g−1) | Average Diameter/ mm | Litter Density/ (g·cm−3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pinus massoniana | 29.26 | 6.06 | 147.62 | 0.84 | 0.45 |
| Treatment Number | T1 | T2 | T3 | T4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Litter mass coverage/(g·m−2) | 0 | 100 | 200 | 400 |
| Treatment (Slope-Coverage Mass-Rainfall Intensity)/(°—mm·h−1) | MWD/(mm) | D | Q/(mL) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5°T1-60 | 0.059 ± 0.021 | 2.640 ± 0.017 | 438.933 ± 80.368 |
| 5°T2-60 | 0.047 ± 0.02 | 2.721 ± 0.014 | 316.133 ± 72.796 |
| 5°T3-60 | 0.025 ± 0.011 | 2.758 ± 0.008 | 264.433 ± 68.551 |
| 5°T4-60 | 0.024 ± 0.012 | 2.759 ± 0.010 | 185.200 ± 14.338 |
| 10°T1-60 | 0.0590 ± 0.016 | 2.600 ± 0.031 | 920.533 ± 41.815 |
| 10°T2-60 | 0.058 ± 0.015 | 2.654 ± 0.034 | 674.510 ± 32.179 |
| 10°T3-60 | 0.057 ± 0.014 | 2.695 ± 0.020 | 590.069 ± 26.571 |
| 10°T4-60 | 0.045 ± 0.042 | 2.701 ± 0.024 | 373.999 ± 34.078 |
| 5°T1-120 | 0.086 ± 0.021 | 2.605 ± 0.034 | 763.698 ± 44.152 |
| 5°T2-120 | 0.067 ± 0.015 | 2.464 ± 0.047 | 462.533 ± 44.071 |
| 5°T3-120 | 0.040 ± 0.016 | 2.741 ± 0.007 | 369.867 ± 95.027 |
| 5°T4-120 | 0.033 ± 0.011 | 2.754 ± 0.016 | 293.667 ± 55.978 |
| 10°T1-120 | 0.163 ± 0.055 | 2.295 ± 0.036 | 1791.000 ± 579.379 |
| 10°T2-120 | 0.155 ± 0.016 | 2.055 ± 0.123 | 1627.357 ± 108.354 |
| 10°T3-120 | 0.114 ± 0.030 | 2.411 ± 0.057 | 1428.186 ± 217.291 |
| 10°T4-120 | 0.071 ± 0.014 | 2.561 ± 0.068 | 1030.629 ± 25.739 |
| Treatment (Slope-Coverage Mass-Rainfall Intensity)/(°—mm·h−1) | Clay <0.002 mm | Fine Silt 0.002–0.02 mm | Coarse Silt 0.02–0.05 mm | Fine Sand 0.05–0.25 mm | Medium Sand 0.25–0.5 mm | Coarse 0.5–1 mm | Very Coarse Sand 1–2 mm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5° T1-60 | 0.618 | 0.874 | 1.762 | 6.224 | 2.228 | 1.540 | 0.528 |
| 5° T2-60 | 0.914 | 0.748 | 0.841 | 10.602 | 1.486 | 0.687 | 0.582 |
| 5° T3-60 | 0.953 | 0.875 | 0.907 | 4.444 | 4.303 | 1.312 | 0.623 |
| 5° T4-60 | 0.874 | 0.941 | 0.638 | 6.116 | 4.185 | 0.581 | 0.001 |
| 10° T1-60 | 0.642 | 1.089 | 0.879 | 3.795 | 3.419 | 2.012 | 0.552 |
| 10° T2-60 | 0.967 | 0.952 | 0.802 | 3.165 | 2.897 | 1.514 | 0.389 |
| 10° T3-60 | 0.830 | 1.167 | 0.765 | 1.092 | 1.292 | 0.549 | 0.206 |
| 10° T4-60 | 0.791 | 1.191 | 0.761 | 1.476 | 0.743 | 0.452 | 0.211 |
| 5° T1-120 | 0.838 | 0.659 | 1.276 | 9.541 | 1.664 | 2.005 | 1.815 |
| 5° T2-120 | 0.306 | 0.966 | 1.175 | 11.631 | 4.739 | 0.777 | 0.030 |
| 5° T3-120 | 0.896 | 1.107 | 0.673 | 1.627 | 1.141 | 1.064 | 0.864 |
| 5° T4-120 | 1.005 | 0.939 | 0.886 | 3.467 | 2.112 | 0.685 | 0.133 |
| 10° T1-120 | 0.522 | 0.671 | 1.013 | 11.105 | 8.667 | 4.107 | 3.880 |
| 10° T2-120 | 0.325 | 0.317 | 1.215 | 21.805 | 17.500 | 2.607 | 0.250 |
| 10° T3-120 | 0.645 | 0.506 | 1.687 | 15.368 | 2.121 | 1.456 | 2.844 |
| 10° T4-120 | 0.959 | 0.368 | 1.432 | 17.926 | 0.577 | 0.412 | 0.425 |
| Slope | 60 mm·h−1 | 120 mm·h−1 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| F(x) | R2 | F(x) | R2 | |
| 5° | MWD= −0.00009x + 0.0544 | 0.7909 | MWD = −0.0001x + 0.0798 | 0.8593 |
| 10° | MWD = −0.00004x + 0.061 | 0.8669 | MWD = −0.0002x + 0.1684 | 0.9662 |
| 5° | D = 0.0003x + 2.6722 | 0.6826 | D = 0.0002x + 2.6204 | 0.7770 |
| 10° | D = 0.0005x + 2.546 | 0.4655 | D = 0.0009x + 2.169 | 0.5449 |
| Functional Relation F(x) | R2 |
|---|---|
| D = 100.022SA0.148AD−0.272Q0.908 | 0.6625 |
| MWD = 102.821SA0.097AD−0.032Q−0.876 | 0.8015 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, F.; Li, Y.; Cheng, J. Size Characteristics of Sediments Eroded under Different Masson Pine Litter Covers in South China. Water 2021, 13, 2190. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13162190
Zhu F, Li Y, Cheng J. Size Characteristics of Sediments Eroded under Different Masson Pine Litter Covers in South China. Water. 2021; 13(16):2190. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13162190
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Fangfang, Yuchen Li, and Jinhua Cheng. 2021. "Size Characteristics of Sediments Eroded under Different Masson Pine Litter Covers in South China" Water 13, no. 16: 2190. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13162190
APA StyleZhu, F., Li, Y., & Cheng, J. (2021). Size Characteristics of Sediments Eroded under Different Masson Pine Litter Covers in South China. Water, 13(16), 2190. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13162190






