Abstract
This study evaluated the effect of the addition of green iron microparticles (Fe-MPs) as a three-dimensional electrode on efficiency of the electrochemical oxidation process. Polyphenols present in green tea extract act as a reducing and capping agent during green synthesis of the Fe-MPs. Scanning electron microscopy and energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy analysis indicates that the average size of particles is 100 µm, with about ~47 wt % of Fe in oxide form. The addition of Fe-MPs as a third electrode in the conventional electro-oxidation (EO) process converts it into a three-dimensional (3D) catalytic EO process to enhance the decolorization efficiency. Green synthesized Fe-MPs function as several microelectrodes in the process. Adsorption study indicated that only 12% of decolorization is due to adsorption on the Fe-MPs surface. Moreover, improvement in generation of hydroxyl radicals was validated by applying dimethyl sulfoxide as scavenger, and it was observed that generation of hydroxyl radicals decreased with the addition of DMSO. Results showed that decolorization efficiency increased in the 3D EO process with Fe-MPs by about 24% compared to the conventional 2D process without the Fe-MPs dosing, and initial pH as well as the Fe-MPs dose has a significant effect on decolorization efficiency during the 3D process. It is observed that reaction works better at highly acidic pH (2-4), and decolorization efficiency improved with higher doses of Fe-MPs.
1. Introduction
Researchers are empathizing more towards dye wastewater treatment on the grounds of numerous adverse effects. Dye wastewater is a tremendous source of highly toxic, carcinogenic and non-biodegradable organic and inorganic compounds. Dye wastewater contributes to eutrophication and demotes the transparency of water bodies, which is an aesthetic disadvantage. Discharge of dye wastewater into natural water bodies has various demerits, including reduced light penetration that acts on photosynthesis and decreased gas solubility that abates dissolved oxygen [1,2,3].
Conventionally, coagulation, membrane filtration, adsorption, ion exchange, chemical oxidation, ozonation, bio-sorption, aerobic and anaerobic digestion and some other biological processes are practiced to deal with dye wastewater [4,5,6]. Each of these treatment technologies has certain limitations of sludge production and formulation of secondary pollutants that are causing greater threats than the primary pollutant itself. Advanced oxidation processes (AOP) have great potential to conquer these limitations. AOPs such as Fenton, electro Fenton, Ozonation are designed as destructive methods to decompose pollutants into less harmful compounds and terminate production of secondary pollutants. These technologies incorporate powerful oxidant hydroxyl radical (OH•) generation [7,8]. Various studies with modifications in AOPs have been done to abate pollutants from wastewater. Iron-based metal organic frameworks (MOFs) were modified to improve their catalytic function during ozonation [9]. The combination or series of different AOPs is considered as an effective approach to degrade pollutant efficiently in less time. It was observed that degradation and mineralization of 4-nitrophenol increased with photocatalytic ozonation while adding Fe-based MOF as catalyst compared to photocatalysis or catalytic ozonation individually [10].
Electrochemical advanced oxidation processes (EAOPs) are exploited successfully to oxidize persistent organics and dyes into harmless compounds. In the course of the electrolysis procedure, electrically originated hydroxyl radicals support mineralization of pollutants. EAOPs are generally bisected into the following stages: direct and indirect oxidation. During direct oxidation, hydroxyl radicals are generated upon the exterior surface of the anode, corresponding to Equations (1) and (2) [11,12,13].
Application of mixed-metal-oxides-coated titanium plate as anode is effectively practiced for pollutant mineralization in electrolysis [14]. A wide range of metal oxides such as PbO2, SnO2, IrO2, RuO2, TiO2 have been employed as coating material [15,16]. In this work, titanium plate coated with IrO2, RuO2, TiO2 was utilized as anode material in the electrochemical oxidation process.
On the other hand, in indirect oxidation, intermediate oxidizing agents are produced in the liquid according to the present electrolyte. If NaCl is present as supporting electrolyte, chlorine (Cl2) and hypochlorites (OCl− and HOCl) are generated, as shown in Equations (3)–(5). These chlorine compounds are strong oxidative species, while with Na2SO4 as a supporting electrolyte, weak oxidative species like ozone and peroxodisulphate (S2O8−2) ion are produced by oxidation of SO4−2 according to Equations (6) and (7) [17,18,19].
In our previous study, experiments were performed using the electrolytes NaCl and Na2SO4 during electrochemical oxidation (EO) for decolorization of Rhodamine-B dye. Results showed a lower efficiency of EO with Na2SO4 [14]. A longer time was required with Na2SO4. This was due to little or no indirect oxidation process at anode and poor oxidation potential of the peroxodisulphate group in comparison to chloride species [20,21]. Therefore, there is a requirement to advance the efficiency of EO with Na2SO4. The catalytic electro-oxidation process was recently developed as an innovative and environmentally benign advanced oxidation technology. Since this operation is straightforward with high degradation efficiency for most compounds, this ecofriendly approach has drawn the interest of scientists lately. Directly or indirectly produced hydroxyl radicals can degrade nonbiodegradable contaminants through the reactions on the catalytical activity electrode efficiently under normal temperature and pressure [22,23,24]. Employment of three-dimensional (3D) electrochemical reactions for removal of recalcitrant contaminants is a recent advancement in the catalytic EO process. The 3D EO system is analogous to the usual two-electrode method. However, it involves a particle third electrode that predominately acts as a heterogeneous catalyst [25]. Usually, a granular material that may include metal oxides is utilized as a particle electrode and loaded between anode and cathode. The particle electrodes get polarized throughout the electrolysis process. As a result of the polarization, the particles turn into a plethora of charged microelectrodes by means of cathode on one side and anode on another side [26]. Additional microelectrodes shoot up the ionic strength of the electrolytic system by providing supplementary ion species in the cell and also remove the pollutant by means of the sorption method. Owing to its advanced mass transfer and hefty surface for reaction on microelectrodes, the degradation efficiency achieved during three-dimensional EO arrangement is elevated compared to the typical EO arrangement [27].
Few researchers have used the 3D EO process for dye removal. Zhang et al. 2014 employed zero-valent nanoscale iron/activated carbon in the 3D electro-Fenton system that acts as a heterogeneous Fenton catalyst and observed that degradation efficiency of methyl orange improved by 30% [28]. Steel slag derivative particle electrodes and manganese-loaded particle electrodes were applied as catalyst by Wang et al. 2014 [29]. An ultrasound impregnation calcination approach was utilized during the 3D process using stainless steel plate as cathode with Pt plate as anode for the elimination of Rh-B from the wastewater sample. Observations show that dye is totally removed in 50 min reaction time. Wang et al. 2008 conducted an electrolysis study to decompose real dyeing wastewater with the help of graphite rings particle electrode to achieve 70.6% decolorization. Electrolysis for the removal of Rh-B was conducted using particle electrode made from steel slag and reported 82.4% of Rh-B removal efficiency [25].
To our knowledge, no study was found for the synthesis and subsequent use of a green catalyst as a third electrode in the EO process. In the present study, iron microparticles (Fe-MPs) were synthesized by a biosynthetic method that is novel, quick, and a one-step synthesis method. Aqueous extract of green tea was utilized as both the reducing and capping agent. Biosynthesis of nanoparticles can be defined as a type of bottom-up approach in which the core reaction taking place is oxidation or reduction. The polyol elements available in the extracts of plants are accountable for the green synthesis of metallic particles during the bioreduction, while the created microparticles are stabilized by the water-soluble heterocyclic components. The green synthesis process is ecofriendly, cost-efficient and can be scaled up for large-scale production effortlessly. This process does not require energy, high pressure and high temperature, which also opens plausibility of easy and improved process control and offers better manipulation. Further, biosynthesis provides good control over crystal growth and stabilization. Green synthesis is attracting significant attention because of easy availability of plant resources and their pharmacological importance [30,31,32,33]. In the current study, green synthesized iron microparticles were used as a three-dimensional electrode along with EO to analyze its effect on the efficiency of the EO process.
2. Material and Methodology
2.1. Chemicals Used during the Process
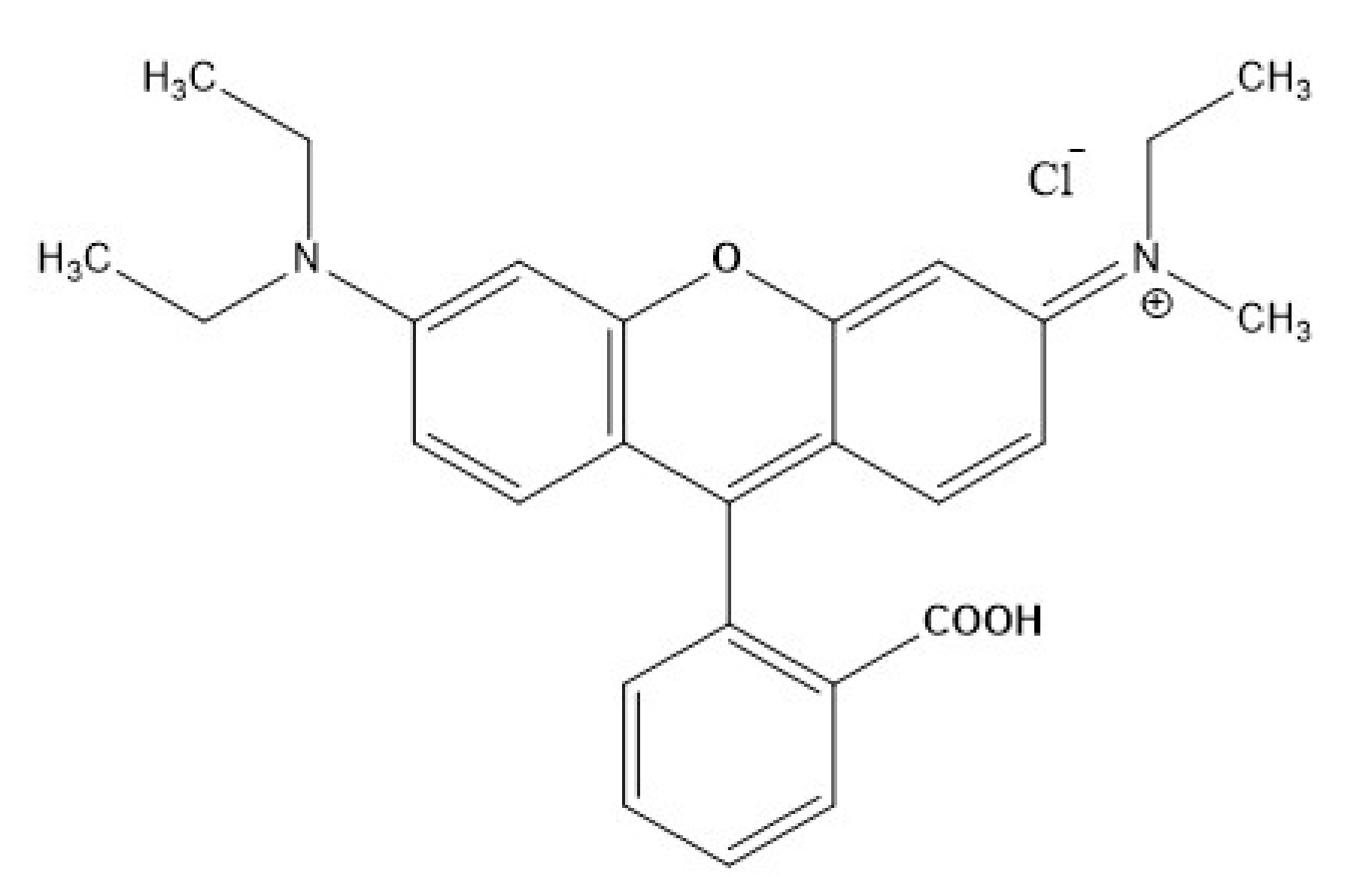
The synthetic dye solution containing Rhodamine-B is used as model pollutant. Rhodamine-B is recalcitrant dye that is mostly used in the food and cosmetic industries. Rhodamine-B dye with 99% purity (C28H30N2O3, Molecular weight = 479.02 g/mol & 15 gm/L solubility in water) having maximum adsorption at 554 nm was purchased from a chemical laboratory in India. The molecular structure of Rh-B is depicted in Figure 1. Sodium sulphate (Na2SO4, Loba Chemie) and sodium chloride (NaCl, Loba Chemie) are used as supporting electrolyte, sulphuric acid (H2SO4, Sulab Laboratory) and sodium hydroxide (NaOH) solution are used to adjust the pH of the sample. Mixed-metal oxide (MMO) is used as anode and stainless steel as cathode. Other chemicals used are ferric chloride anhydrous (FeCl3·6H2O, Sulab Laboratory) as the metal precursor and dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO, Loba Chemie). The green tea leaves (Tetley green tea) were purchased from a local super market. All the abovementioned chemicals were analytical grade reagents without further purification. For dilution and preparation purposes, distilled water was used.
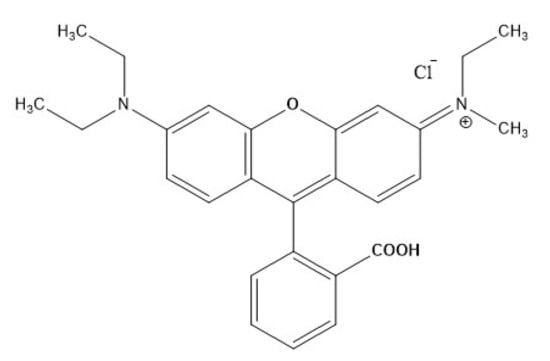
Figure 1.
Structure of Rhodamine-B.
2.2. Production of Iron Microparticles (Fe-MPs)
The first step in the production of iron microparticles is preparation of the reducing agent—green tea extract. The mixture was formulated by adding 20 g of green tea leaves in 1 L of distilled water and heated at 80 °C for 20 min. The solution was cooled and filtered using Whatman filter paper. The collected and filtered extract (solution-1) was stored at 4 °C for further application. Next, for the synthesis of iron microparticles, 500 mL of 0.01 M ferric chloride (solution-2) were added drop-wise in the 500 mL of the earlier-prepared solution-1 in the cleaned and dried flasks. Immediate color change took place by mixing both the solutions. The resulting solution was of black color. The immediate color change was indicative of synthesis of iron microparticles. The supernatant was discarded once the solution was centrifuged at 10,000 RPM for 15 min. The pellets were washed several times using distilled water and then dried at (100 ± 5) °C in water bath. The microparticles, in dried powder form, were obtained and stored in a clean dry container for further use [34]. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM, Jeol JSM 500F, Tokyo, Japan), energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS, Oxford instruments, Abingdon, Oxfordshire, UK), and X-ray diffraction spectroscopy (XRD, PANalytical, Almelo, The Netherlands) analysis were performed to examine the size, structure, and crystalline phase of synthesized Fe-MPs.
2.3. Electrochemical Experimentsin 3D Approach
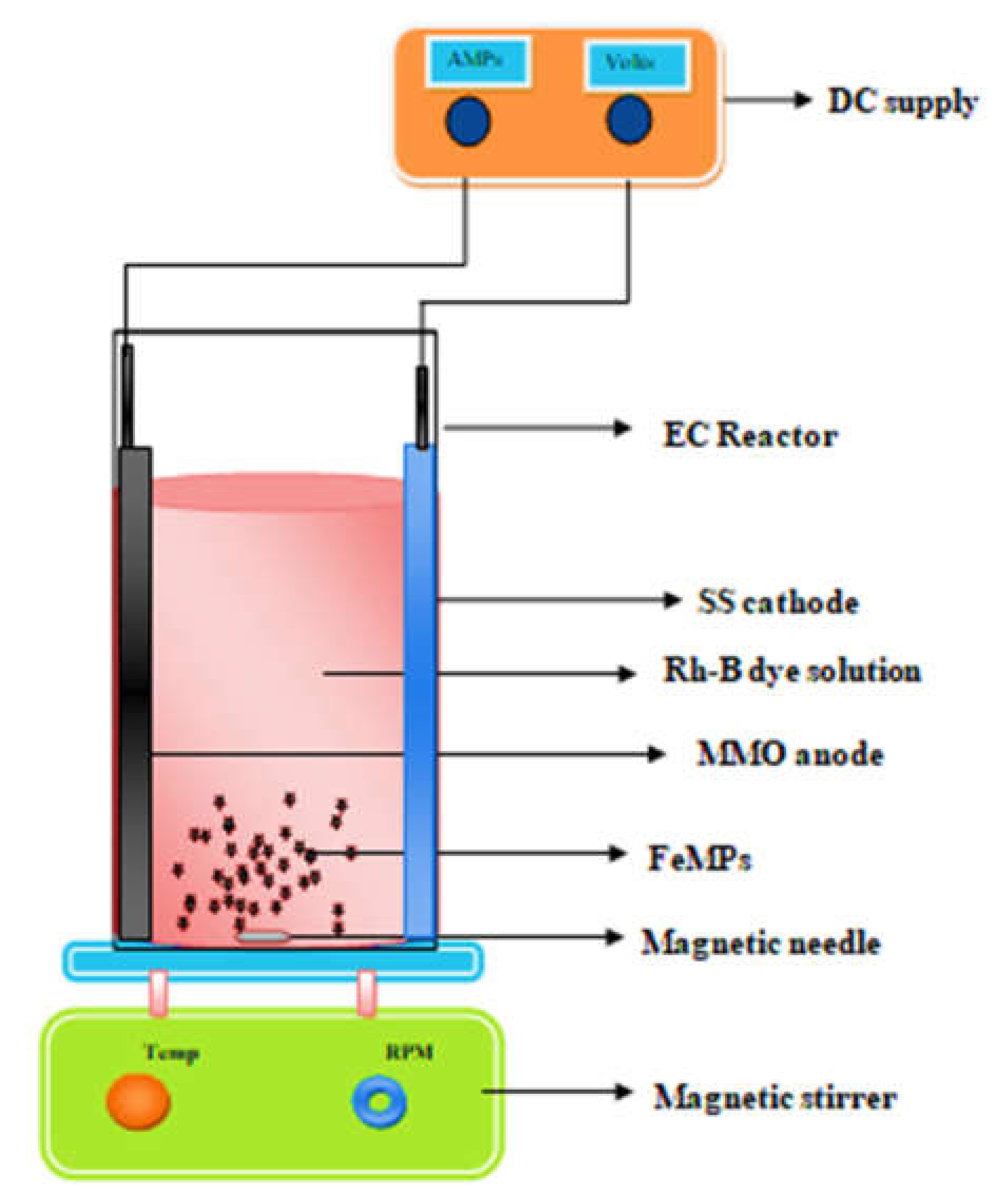
The 250 mL of undivided polyacrylic electrochemical with measurements of 7 cm × 6.5 cm × 13 cm were used to conduct experiments. Commercially available mixed-metal-oxide (TiO2, IrO2, RuO2)-coated titanium plate was employed as anode and a stainless steel plate was employed as cathode. Both the electrodes were of the same size of 5 cm × 5 cm and placed vertical and parallel to one another at 6 cm apart in a bench-scale batch process, as shown in Figure 2. Rhodamine-B dye solution with concentration of 100 mg/L was prepared using distilled water. Prepared synthetic dye was transferred into the reactor. The anode and cathode were connected to the respective nodes of the DC current meter. Current was applied using DC power supply having a range of 0–2 A and 0–32 V. A magnetic stirrer was used to keep the solution well mixed. During the 3D electrochemical process, 1 gm/L of Fe-MP was added in dried powder form in the reactor containing 250 mL of 100 mg/L of Rh-B dye. The solution was aerated at the rate of 2 LPM and mixing was provided at 500 RPM. The 3D EO process occurred in the presence of 0.1 M Na2SO4 electrolyte, 10mA/cm2 current density, 25 °C temperature, and pH 4 (solution pH). To verify whether decolorization was achieved due to the in situ generation of hydroxyl radicals, experiments were carried out by adding radical scavengers as 2.4 mM of DMSO for hydroxyl radicals in 2D and 3D electrode reactors.
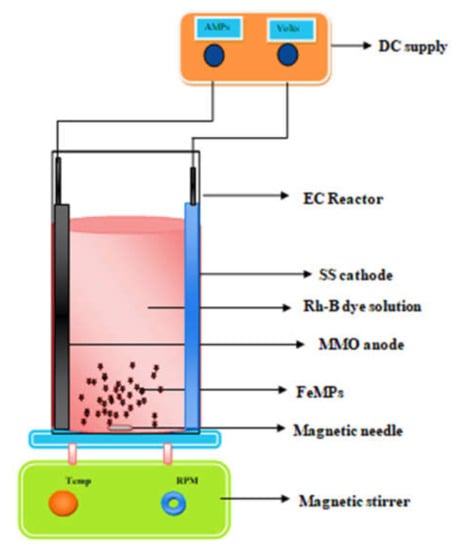
Figure 2.
Experimental set-up in the 3D EO process.
The UV-Vis spectrophotometer (UV-1800, Shimadzu, Tokyo, Japan) was utilized to record UV-Vis spectra between 200 and 900 nm for the samples. While using Fe-MP as particle electrodes, samples were withdrawn at fixed time intervals, centrifuged at 10,000 RPM for 10 min, and supernatant was collected and analyzed for color removal. The concentration of Rhodamine-B was evaluated by determining the absorbance before and after treatment at 554 nm wavelength. Percentage of color removal is evaluated by the following Equation:
where ABS0 and ABSt are the absorbency of sample before electrolysis and absorbency of sample after electrolysis at time t, respectively.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of Synthesized Iron Microparticles
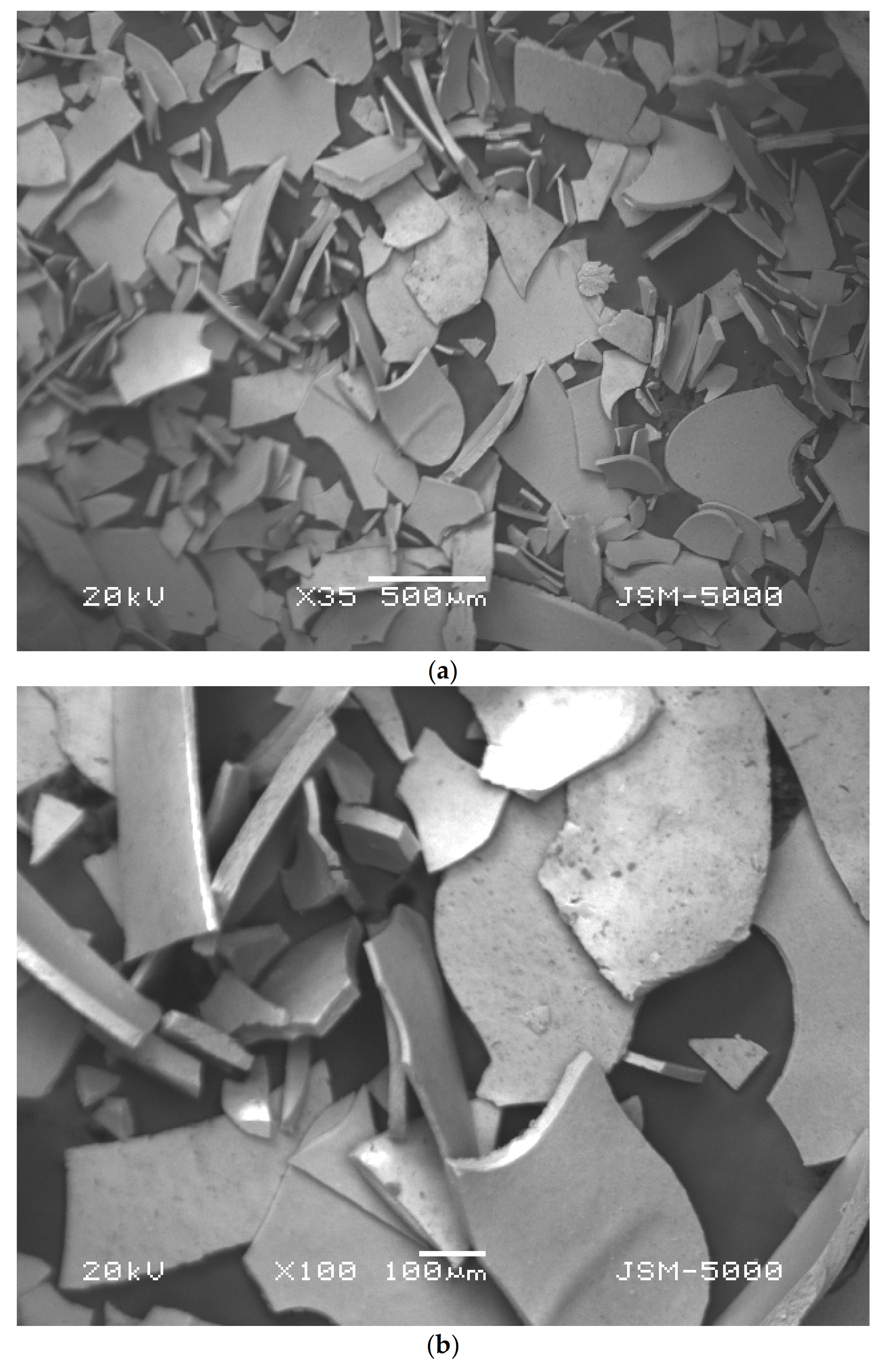
Characterization of the iron microparticles was done by SEM analysis to verify the morphology, shape, and size of synthesized particles, and EDS evaluation was carried out to study the functional groups of the microparticles [35]. The samples were observed by scanning electron microscopy, SEM (Jeol JSM 500F, Tokyo, Japan). Initially, the powdered samples were attached onto adhesive tapes reinforced on metallic disks and then secured with a thin, electric conductive gold film. Micrographs of samples were produced at two different resolution of Figure 3a 500 µm and Figure 3b 100 µm at voltage of 20 kV. Iron microparticles were found to be of average diameter of about 100 µm. The shape of the particles is irregular because of the agglomeration and drying process.
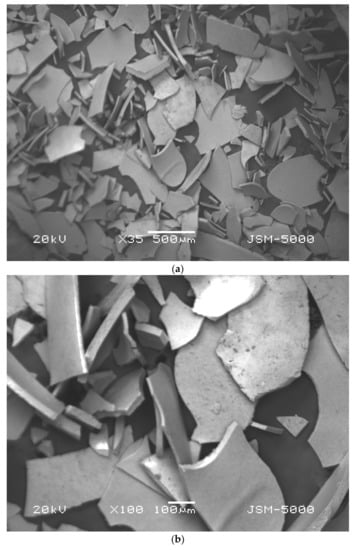
Figure 3.
(a) SEM image of synthesized iron microparticles at 500 µm resolution, (b) SEM image of synthesized iron microparticles at 100 µm resolution.
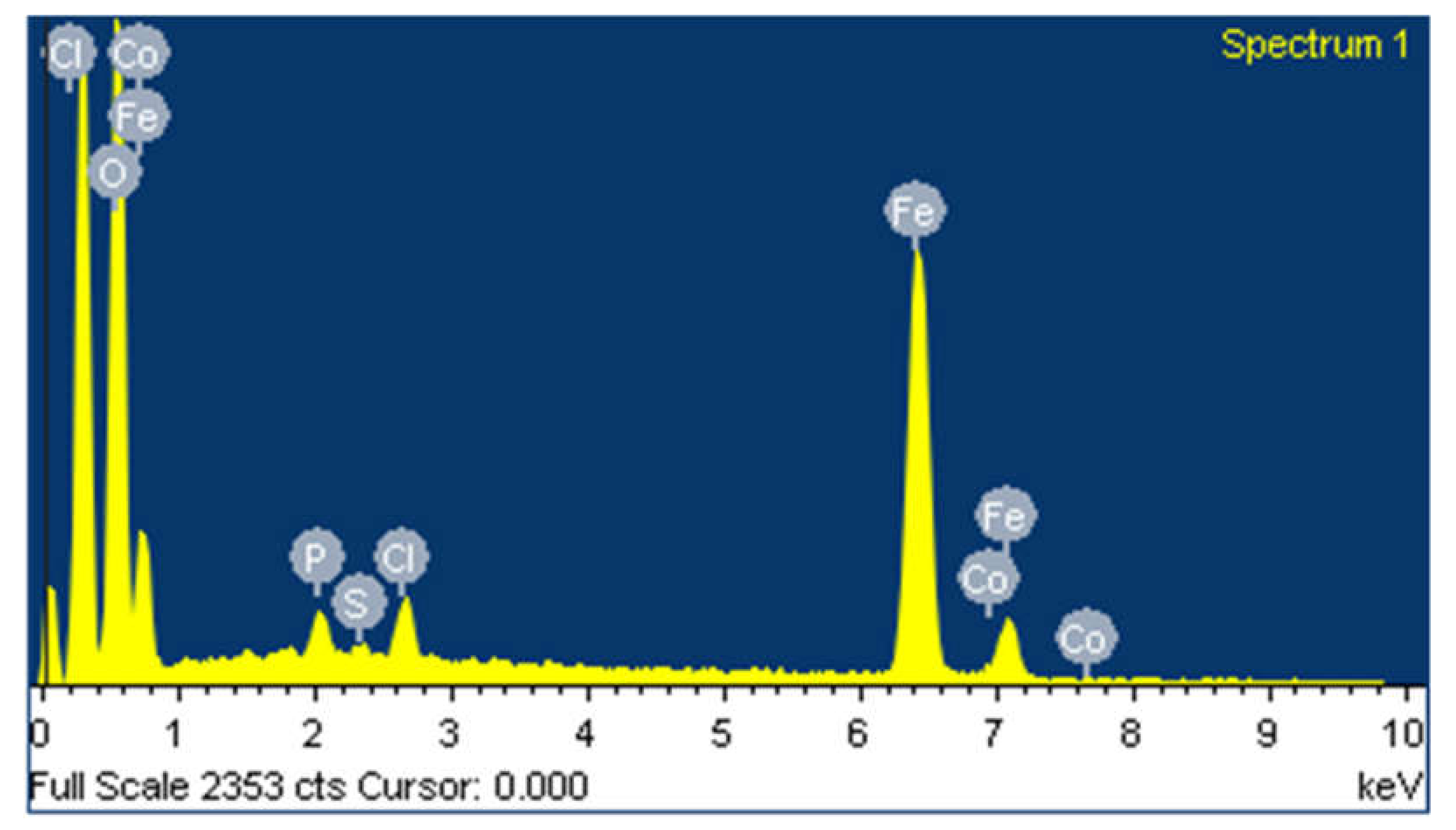
EDS is performed to evaluate the content of every single component in the sample of synthesized iron particles. Figure 4 shows EDS analysis of synthesized iron particles. The image clearly demonstrated strong peaks for iron atoms. The high signal peaks were observed at 0.7 KeV and between 6 KeV and 7 KeV near to 6.3 KeV as a result of absorption of iron crystals, which reveals the presence of iron microparticles. EDS spectrum recorded high peaks for 47.77% iron and 47.34% oxygen, which suggest that iron is in oxide form. Various peaks of other elements are reported such as 2.31% chlorine, 1.74% phosphate, 0.42% sulfur, and 0.42% cobalt. These compounds from plant extract are also present on the surface of Fe-MPs.
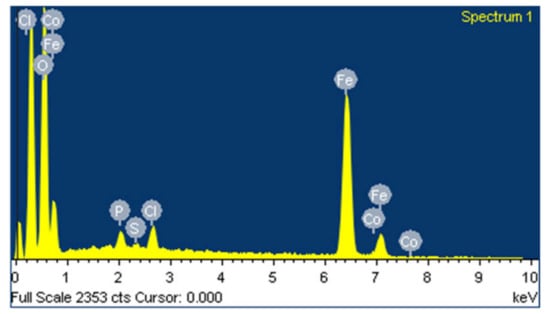
Figure 4.
EDS spectrum of synthesized iron microparticles.
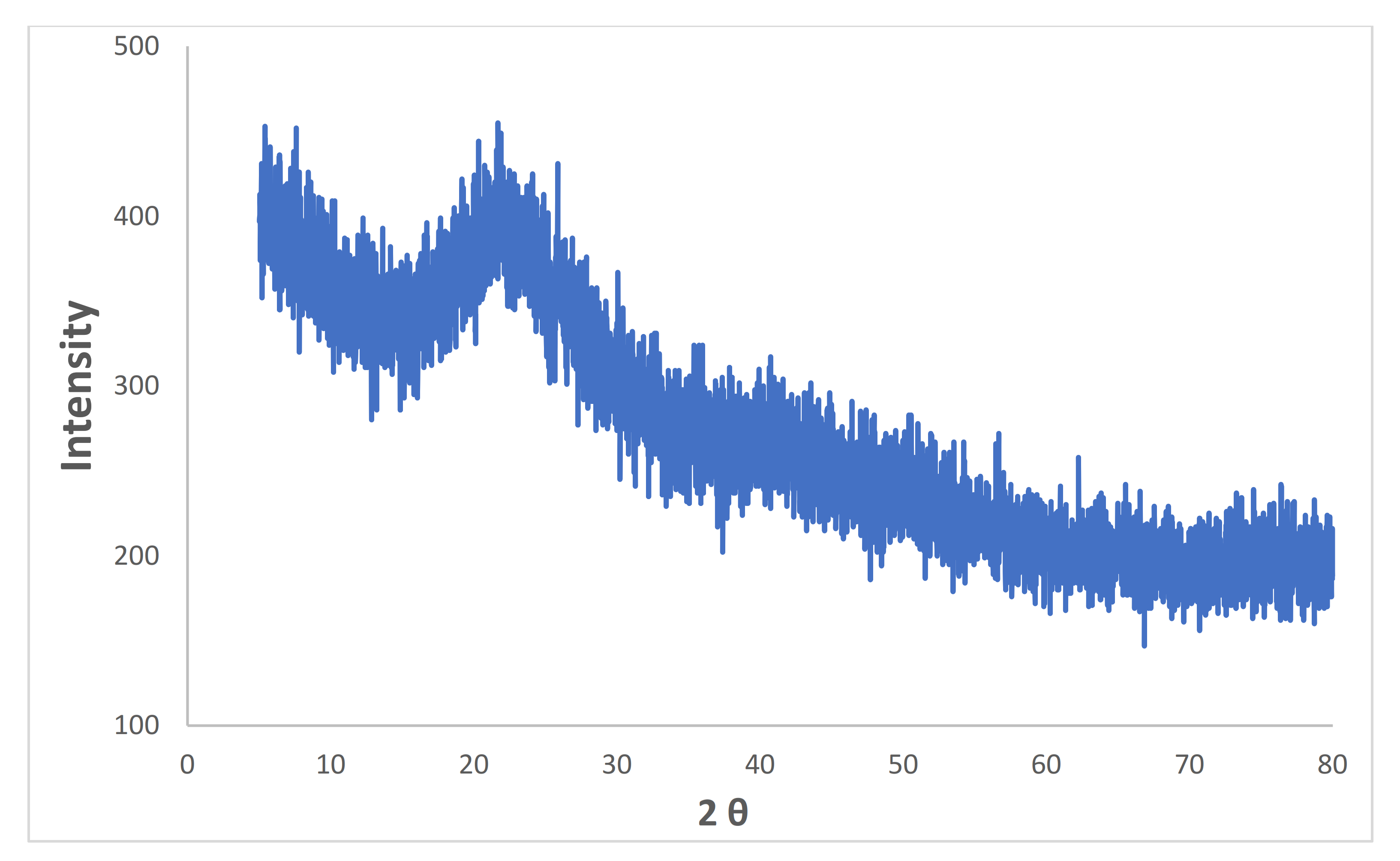
X-ray diffraction (XRD) spectroscopy was performed using X-ray diffraction (XRD)-PANalytical equipped with a Cu-anode to the phase and crystalline nature of prepared iron microparticles. The pattern obtained, as shown in Figure 5, is lacking distinctive diffraction peaks, which suggests that the structure of iron microparticles is amorphous. The results are in agreement with the other previously reported studies [36,37]. A broad peak observed at around 2θ of 15−25° is possibly due to organic materials present in green tea extract that play a role of capping agent during the synthesis of iron microparticles.
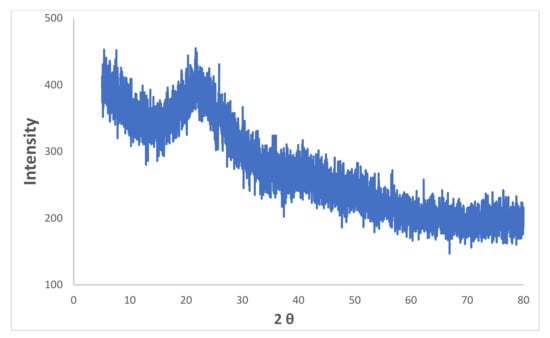
Figure 5.
XRD spectrum of synthesized iron microparticles.
3.2. Results of 3D Electrochemical Process
3.2.1. Evaluation of Catalytic Effect of Fe-MP as Third Electrode
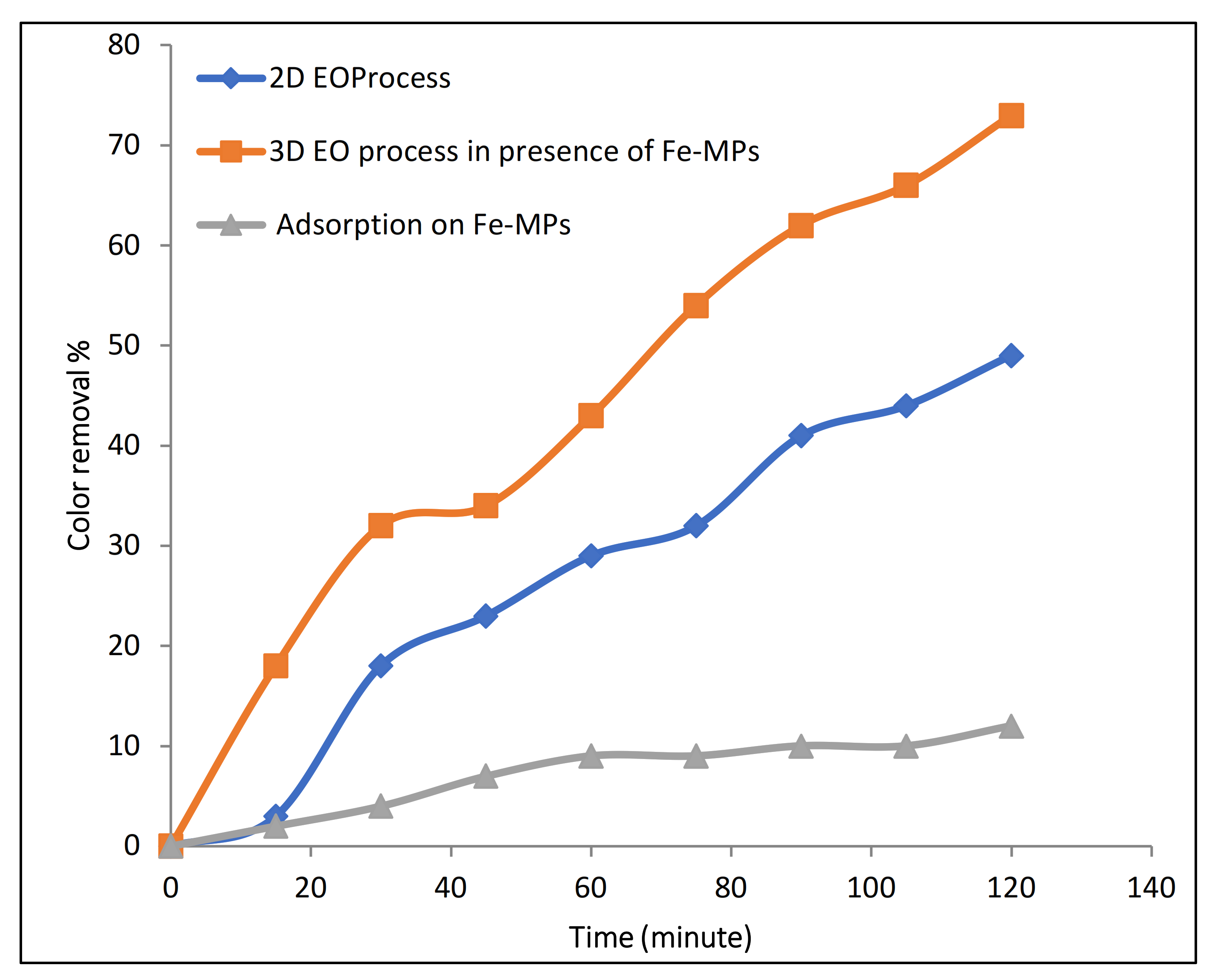
During our previous studies, 2D electrochemical oxidation results showed lower removal efficiency while using Na2SO4 as electrolyte [14]. Hence, to improve the efficiency of electrochemical oxidation with Na2SO4, synthesized Fe microparticles were used as a three-dimensional particle electrode/catalyst in this study. Figure 6 indicates that, in the presence of Na2SO4, in the 2D EO process, 49% color removal was observed in 120 min of reaction time. On the other hand, during the 3D EO treatment, 73% color removal was observed in the same period of 120 min of electrolysis time. This clearly shows that the addition of Fe-MP as third electrode has a catalytic effect on the electro-oxidation process. For the investigation of adsorption on Fe-MPs, the solution of 100 ppm Rh-B with 1 g/L dose of Fe-MPs was continuously stirred at 500 RPM for two hours. The samples were taken at predetermined time intervals, centrifuged, and analyzed by UV-spectroscopy. A result of UV-spectrophotometers revealed that only 12% adsorption of Rh-B dye occurs on Fe-MPs in 120 min.
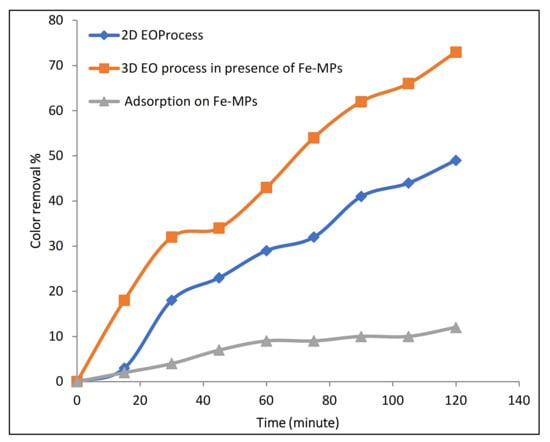
Figure 6.
Effect of addition of Fe-MPs on the electro-oxidation process.
There can be possibly two mechanisms present during the 3D process. One is electrosorption, as the adsorption of dye on particle electrode is unavoidable due to elevated porosity and the large specific surface area of particle electrode. As soon as an external electrostatic field is introduced, positive charges and negative charges will accumulate at two sides of the particle. The charged pollutant dye ions are compelled to reallocate to the counter-charged side of microparticle electrodes, producing the mechanism of electrosorption. The blend of adsorption and electrosorption successfully improves the removal mechanism [38,39,40]. The other mechanism can be catalytic degradation since every particle of Fe-MPs converts into a micro-electrolytic cell by means of the polarization. Electro-Fenton or electro-Fenton-like reactions occurs whenever any solid catalysts comprising iron groups are utilized as the supply of iron for a replacement of ferrous salt. Hydrogen peroxide, which is formed at the cathode surface, reacts with released iron species from the heterogeneous catalyst in the mixture same as in the usual Fenton process. Occasionally, with no iron content dissolution in solution, the Fenton reactions possibly take place at the surface of catalyst. Efficient mixing should be provided in these situations to keep the catalyst in suspension for sound contact between particle electrodes and pollutant particles. These oxidation and catalytic behaviors of microparticles promote the removal of pollutants [26,41,42].
3.2.2. Analysis of Free Radicals
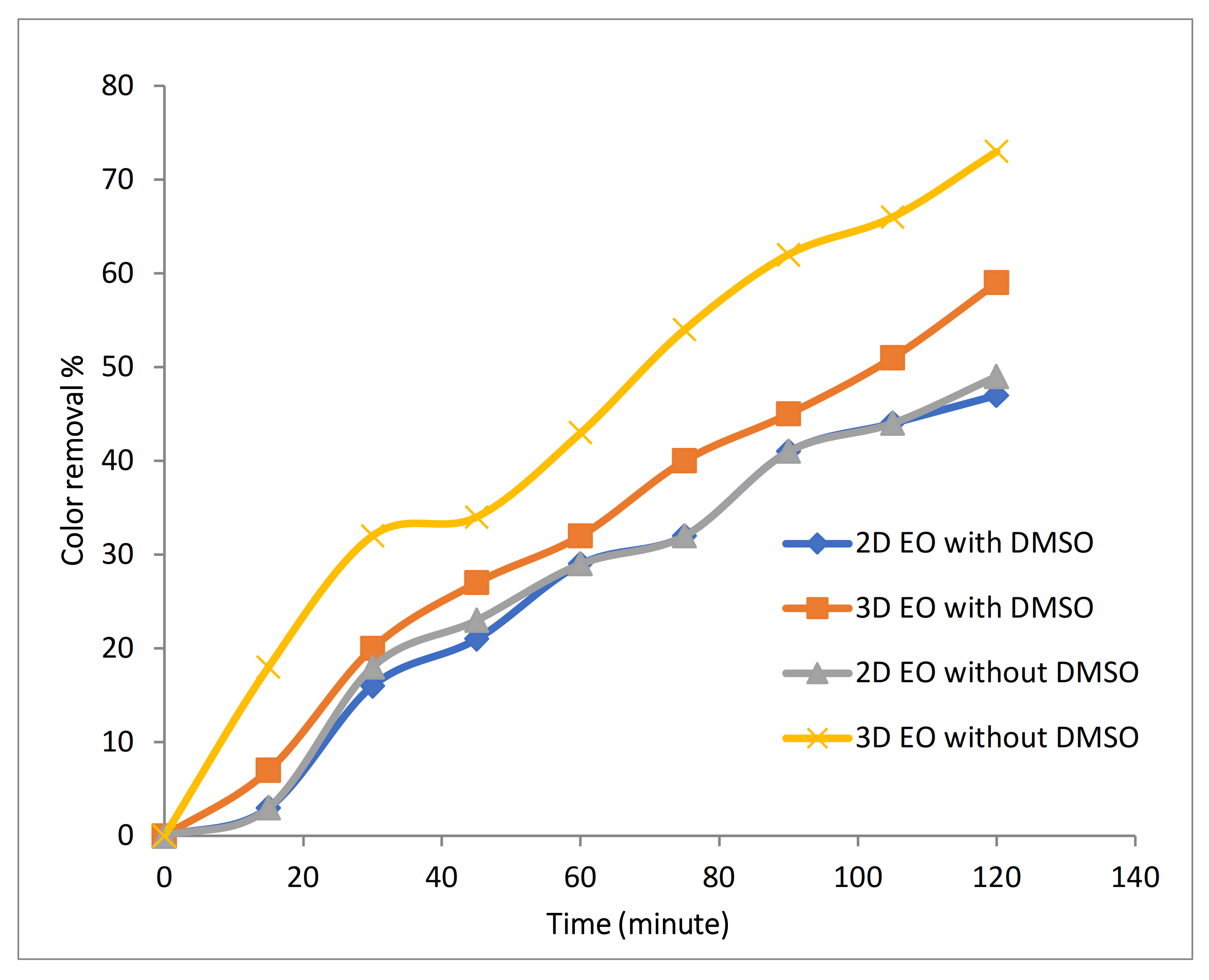
To detect whether formation of free radicals increased with the use of Fe-MPs, radical scavenger DMSO was used. Affinity of DMSO towards hydroxyl radical is higher than dye molecules, thus DMSO associates with hydroxyl radical and methane sulfinic acid to form methyl radical. Detection of hydroxyl radicals was carried out using 2.4 mM of DMSO in 100 mg/L of Rh-B dye with 0.1 M of Na2SO4 at 10 mA/cm2 with initial temperature of 25 °C, 500 RPM and at pH 4 in 2D, and during the 3D EO process, 2 LPM air flow with 1 g/L of Fe-MP were added. DMSO was used for scavenging hydroxyl radicals, and therefore, reduction in the rate of decolorization should occur if hydroxyl radicals are present. During 2D EO, slight reduction in decolorization efficiency was observed, as shown in Figure 7, indicating the presence of hydroxyl radicals in small quantity, because during the 2D EO process in the presence of Na2SO4, degradation of pollutant mainly occurs due to direct oxidation at the anode; detection or formation of hydroxyl radicals in large quantity did not take place. During 3D EO, a major reduction in decolorization process was observed after the addition of DMSO, indicating that a higher amount of hydroxyl radicals was produced in the 3D EO process. As the Fe-MPs showed catalytic effect during the 3D electro-oxidation process, further investigation has been done to analyze the effect of pH and Fe-MPs dose on the process.
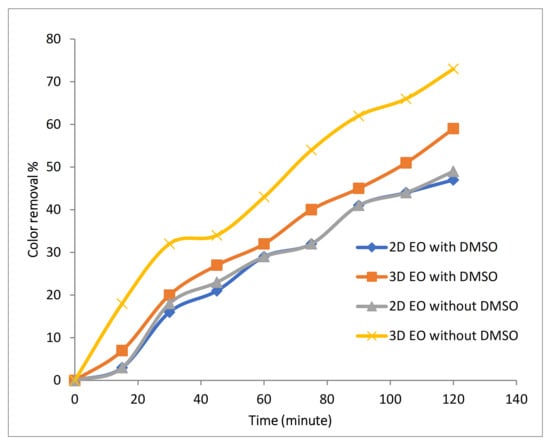
Figure 7.
Effect of addition of DMSO on color removal during 2D and 3D approaches.
3.2.3. Effect of pH on 3D EO Process
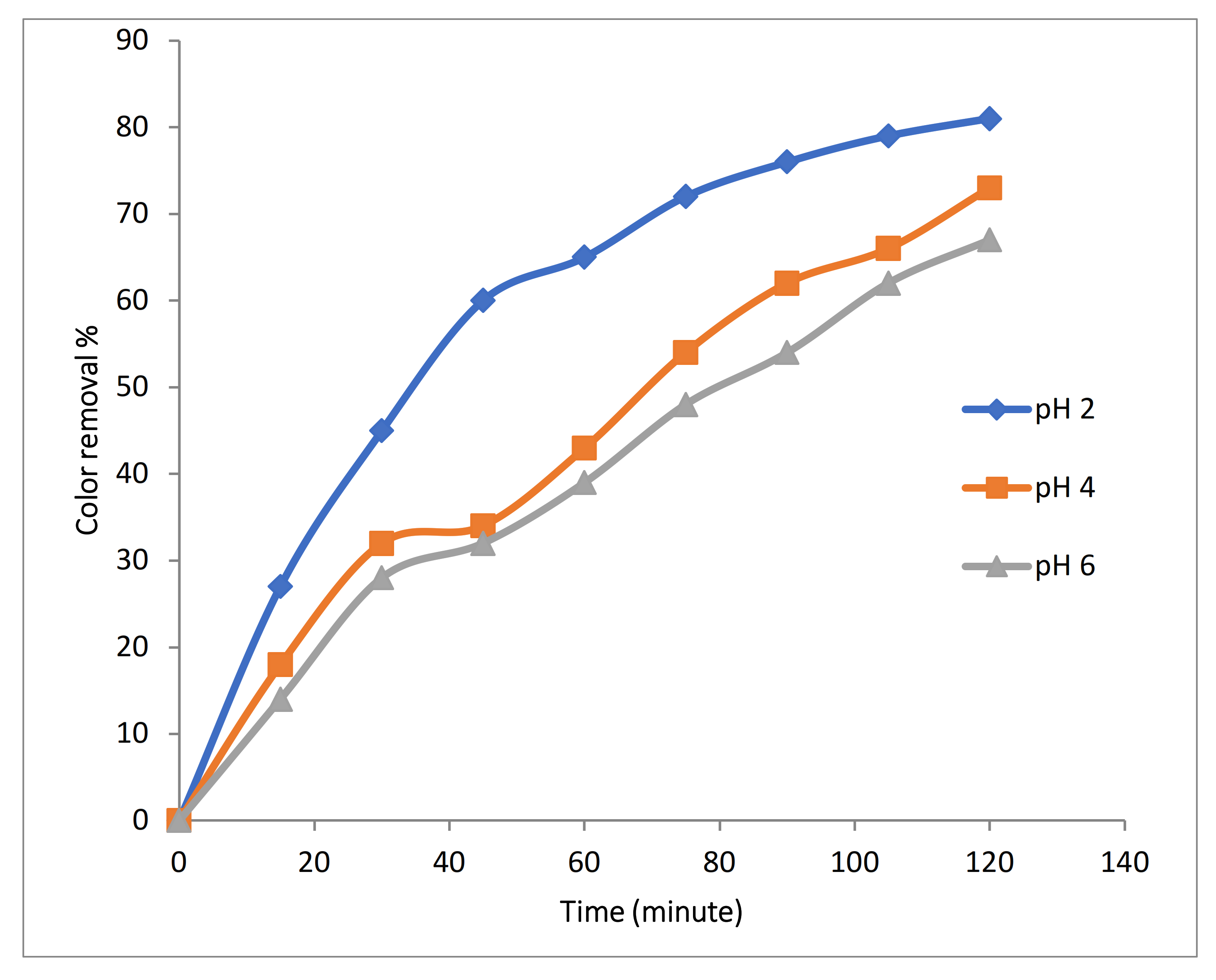
Experiments were conducted using 100 mg/L Rh-B dye along with 1 gm/L Fe-MP dose, 3.55 g/L (0.1 M) of Na2SO4 at 10 mA/cm2 with initial temperature of 25 °C and 500 RPM, 2 LPM air flow with varying pH (2, 4 and 6). Results in Figure 8 show that pH produced the significant effects on the efficiency of color removal. At pH above 4, decomposition rate decreases, because the oxidation potential of hydroxyl (OH•) radicals and dissolved portion of iron species decreases when pH increases. Optimum pH range for electro-Fenton reaction is also 2 to 4. At lower pH value, hydrogen peroxide is converted to H3O2 that is more stable and also reduces its reactivity with ferrous ions, which reduces production of hydroxyl (OH•) radicals.
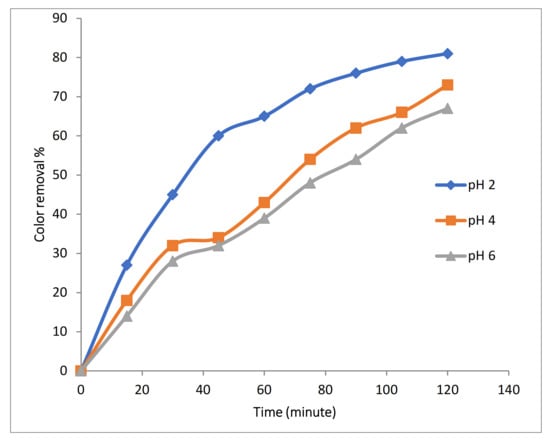
Figure 8.
Effect of initial pH on color removal during 3D approach.
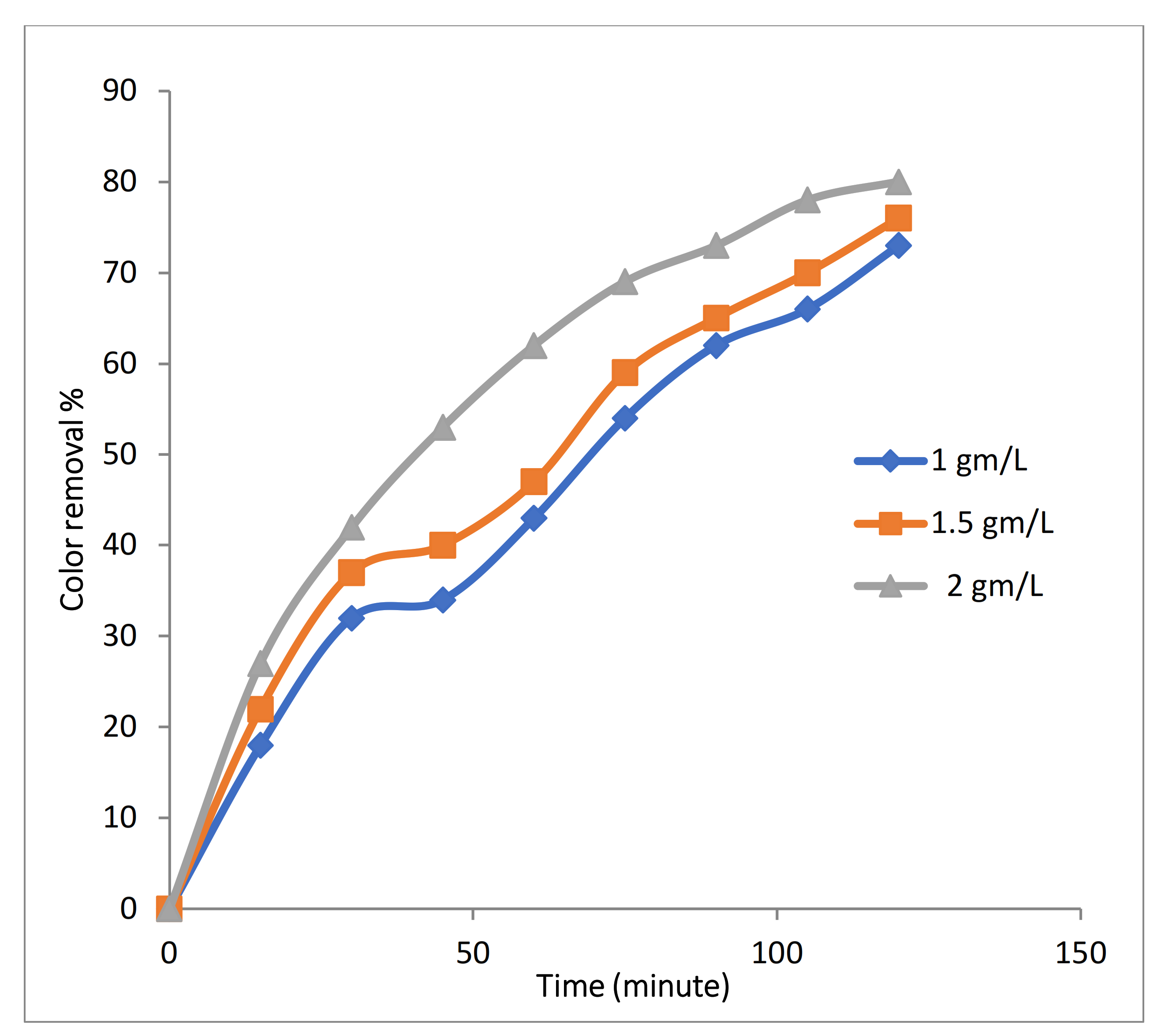
3.2.4. Effect of Fe-MP Dose on 3D EO Process
Experiments were conducted with 100 mg/L of Rh-B dye along with 3.55 g/L (0.1 M) of Na2SO4 at 10 mA/cm2 with initial temperature of 25 °C and 500 RPM, 2 LPM air flow at pH 4 with varying Fe-MP dose, (1, 1.5, and 2 g/L). Figure 9 clearly shows that with increases in dose of Fe-MPs, color removal efficiency and decolorization rate increased. This is because of obvious reasons that the concentration of Fe2+ ion and numbers of microelectrodes increases with an increase in dose of Fe-MPs, which leads to a higher decolorization rate and color removal efficiency.
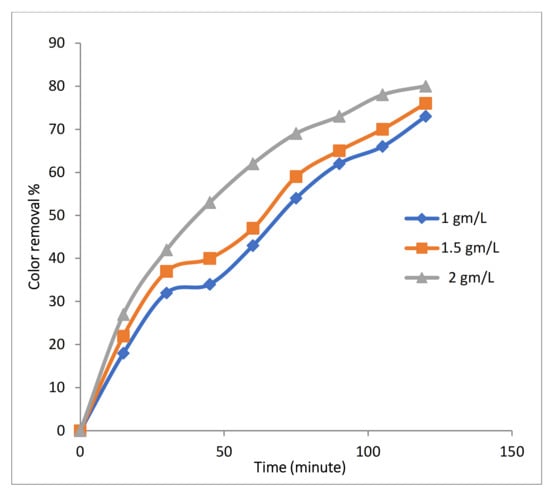
Figure 9.
Effect of Fe-MPs dose on color removal during 3D approach.
4. Conclusions
The study evaluates decolorization of Rhodamine-B dye from artificially prepared wastewater in a bench-scale reactor consisting of anode made up of Ti plate covered with mixed-metal oxide (TiO2, RuO2, IrO2) with cathode prepared of stainless steel plate. Excellent oxidation capacity of MMO anode was observed for decolorization of Rhodamine-B dye from artificially prepared wastewater. The novel microelectrodes were added to improve the efficiency of EO with Na2SO4 as electrolyte. The green synthesis approach was utilized for synthesis of iron microparticles where green tea extract was used as reducing and capping agent. Due to agglomeration, particles of micro size are produced. All the Fe-MPs were found stable with an average size less than 100 µm. XRD analysis suggested that prepared microparticles are amorphous in nature. Addition of Fe-MP as third electrode has a catalytic effect on the electro-oxidation process. Apart from key electrodes, Fe-MPs particle electrode play a significant role in enhancing the removal efficiency. The merits of third-electrode Fe-MPs include high specific area for adsorption, greater electro-catalytic activity, and excellent conductivity, enhancing the current efficiency. Initial pH and Fe-MP dose play a dynamic role in achieving decolorization using Fe-MPs as third electrode in the 3D EO process. The addition of DMSO confirmed the formation of hydroxyl radicals and as observed, production of hydroxyl radicals was increased during the use of Fe-MPs as particle electrode. It can, therefore, be concluded that green synthesized Fe-MPs can be used as third electrode in the EO process for its catalytic effect.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, method development and formal analysis was done by M.S.K. and supervised by K.A.S. and A.A.H. All authors discussed the results and contributed to the final manuscript; writing—original draft preparation by M.S.K. and K.A.S.; writing—review and editing by A.A.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Martinez-Huitle, C.A.; Brillas, E. Decontamination of wastewaters containing synthetic organic dyes by electrochemical methods: A general review. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2009, 87, 105–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forgacs, E.; Cserhati, T.; Oros, G. Removal of synthetic dyes from wastewaters: A review. Environ. Int. 2004, 30, 953–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, T.; McMullan, G.; Marchant, R.; Nigam, P. Remediation of dyes in textile effluent: A critical review on current treatment technologies with a proposed alternative. Bioresour. Technol. 2001, 77, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez, M.C.; Crespi, M. A review of electrochemical treatments for colour elimination. Color. Technol. 1999, 115, 342–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naim, M.M.; El Abd, Y.M. Removal and recovery of dyestuffs from dyeing wastewaters. Sep. Purif. Methods 2002, 31, 171–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, O.J.; Kim, H.; Chiang, P.-C. Decolorization of wastewater. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2000, 30, 449–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simond, O.; Schaller, V.; Comninellis, C. Theoretical model for the anodic oxidation of organics on metal oxide electrodes. Electrochim. Acta 1997, 42, 2009–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotz, R.; Stucki, S.; Carcer, B. Electrochemical waste water treatment using high overvoltage anodes. Part I: Physical and electrochemical properties of SnO2 anodes. J. Appl. Electrochem. 1991, 21, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.; Wang, L.; Yang, T.; Yang, G.; Wang, D.; Huagang, N.; Wu, M. Tuning Lewis acidity of iron-based metal-organic frameworks for enhanced catalytic ozonation. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 404, 127075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Yu, D.; Wang, D.; Yang, T.; Li, Z.; Wu, M.; Crittenden, J. Accelerating Fe (III) / Fe (II) cycle via Fe (II) substitution for enhancing Fenton-like performance of Fe-MOFs. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2021, 286, 119859. [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigo, M.A.; Canizares, P.; Sanchez-Carretero, A.; Saez, C. Use of conductive-diamond electrochemical oxidation for wastewater treatment. Catal. Today 2010, 151, 173–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canizares, P.; Saez, C.; Sanchez-Carretero, A.; Rodrigo, M.A. Influence of the characteristics of p-Si BDD anodes on the efficiency of peroxodi phosphate electrosynthesis process. Electrochem. Commun. 2008, 10, 602–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brillas, E.; Sirés, I.; Arias, C.; Cabot, P.L.; Centellas, F.; Rodríguez, R.M.; Garrido, J.A. Mineralization of paracetamol in aqueous medium by anodic oxidation with a boron-doped diamond electrode. Chemosphere 2005, 58, 399–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kothari, M.S.; Shah, K.A. Electrochemical oxidation for decolorization of Rhodamine-B dye using mixed metal oxide electrode: Modeling and optimization. Water Sci. Technol. 2020, 81, 720–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajeshwar, K.; Ibanez, J.G. Environmental Electrochemistry: Fundamentals and Applications in Pollution Sensors and Abatement; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Mohan, N.; Balasubramanian, N.; Subramanian, V. Electrochemical treatment of simulated textile effluent. Chem. Eng. Technol. Ind. Chem. Plant Equip. Process Eng. Biotechnol. 2001, 24, 749–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panizza, M.; Cerisola, G. Removal of colour and COD from wastewater containing acid blue 22 by electrochemical oxidation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 153, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, N.; Balasubramanian, N. In situ electrocatalytic oxidation of acid violet 12 dye effluent. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 136, 239–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isarain-Chávez, E.; Baró, M.D.; Rossinyol, E.; Morales-Ortiz, U.; Sort, J.; Brillas, E.; Pellicer, E. Comparative electrochemical oxidation of methyl orange azo dye using Ti/Ir-Pb, Ti/Ir-Sn, Ti/Ru-Pb, Ti/Pt-Pd and Ti/RuO2 anodes. Electrochim. Acta 2017, 244, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rajkumar, D.; Kim, J.G. Oxidation of various reactive dyes with in situ electro-generated active chlorine for textile dyeing industry wastewater treatment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 136, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajkumar, K.; Muthukumar, M. Optimization of electro-oxidation process for the treatment of Reactive Orange 107 using response surface methodology. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2012, 19, 148–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nidheesh, P.V.; Gandhimathi, R.; Velmathi, S.; Sanjini, N.S. Magnetite as a heterogeneous electro Fenton catalyst for the removal of Rhodamine B from aqueous solution. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 5698–5708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, L.; Wang, K.; Guo, J.; Yang, J.; Luo, X.; Lian, J.; Wang, L. Enhanced electrochemical oxidation of dye wastewater with Fe2O3 supported catalyst. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2014, 20, 725–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosales, E.; Iglesias, O.; Pazos, M.; Sanroman, M.A. Decolourisation of dyes under electro-Fenton process using Fe alginate gel beads. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 213, 369–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Qi, J.; Feng, Y.; Li, K.; Li, X. Fabrication and electrocatalytic performance of a novel particle electrode. Catal. Commun. 2014, 46, 165–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Jiang, Y.; Li, Y.; Hu, Z.; Zhou, L.; Zhou, M. Three-dimensional electrochemical process for wastewater treatment: A general review. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 228, 455–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.-T.; Hu, J.-L.; Chou, W.-L.; Kuo, Y.-M. Removal of color from real dyeing wastewater by Electro-Fenton technology using a three-dimensional graphite cathode. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 152, 601–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhou, L.; Yang, J.; Yu, X.; Jiang, Y.; Zhou, M. Nanoscale zero-valent iron/AC as heterogeneous Fenton catalysts in three-dimensional electrode system. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 8398–8405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Qi, J.; Feng, Y.; Li, K.; Li, X. Preparation of catalytic particle electrodes from steel slag and its performance in a three-dimensional electrochemical oxidation system. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2014, 20, 3672–3677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanpuria, P.; Rana, N.K.; Yadav, S.K. Biosynthesis of nanoparticles: Technological concepts and future applications. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2008, 10, 507–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shobha, G.; Moses, V.; Ananda, S. Biological synthesis of copper nanoparticles and its impact. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Inven. 2014, 3, 6–28. [Google Scholar]
- Latha, N.; Gowri, M. Bio synthesis and characterisation of Fe3O4 nanoparticles using Caricaya Papaya leaves extract. Synthesis 2014, 3, 1551–1556. [Google Scholar]
- Pattanayak, M.; Nayak, P.L. Green synthesis and characterization of zero valent iron nanoparticles from the leaf extract of Azadirachta indica (Neem). World J. Nano Sci. Technol. 2013, 2, 6–9. [Google Scholar]
- Gottimukkala, K.S.V.; Harika, R.P.; Zamare, D. Green synthesis of iron nanoparticles using green tea leaves extract. J. Nanomed. Biother. Discov. 2017, 7, 151. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, V.; Sharma, J. Electron microscopy study of green synthesized zero valent Iron nanoparticle. Int. J. Eng. Technol. Sci. Res. 2017, 4, 654–658. [Google Scholar]
- Kouhbanani, M.A.J.; Beheshtkhoo, N.; Taghizadeh, S.; Amani, A.M.; Alimardani, V. One-step green synthesis and characterization of iron oxide nanoparticles using aqueous leaf extract of Teucrium polium and their catalytic application in dye degradation. Adv. Nat. Sci. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2019, 10, 015007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z.; Yuan, M.; Yang, B.; Liu, Z.; Huang, J.; Sun, D. Plant-mediated synthesis of highly active iron nanoparticles for Cr (VI) removal: Investigation of the leading biomolecules. Chemosphere 2016, 150, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ban, A.; Schafer, A.; Wendt, H. Fundamentals of electrosorption on activated carbon for wastewater treatment of industrial effluents. J. Appl. Electrochem. 1998, 28, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Cong, Y.; Zhou, M.; Tan, T. p-Nitrophenol abatement by the combination of electrocatalysis and activated carbon. Chem. Eng. J. 2005, 106, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navalon, S.; Dhakshinamoorthy, A.; Alvaro, M.; Garcia, H. Heterogeneous Fenton catalysts based on activated carbon and related materials. ChemSusChem 2011, 4, 1712–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Guo, S.; Yan, G.; Chen, C.; Jiang, X. Electrochemical pretreatment of heavy oil refinery wastewater using a three-dimensional electrode reactor. Electrochim. Acta 2010, 55, 8615–8620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Lei, L. The role of activated carbon on the removal of p-nitrophenol in an integrated three-phase electrochemical reactor. Chemosphere 2006, 65, 1197–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).