Anthropogenic Organic Pollutants in Groundwater Increase Releases of Fe and Mn from Aquifer Sediments: Impacts of Pollution Degree, Mineral Content, and pH
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
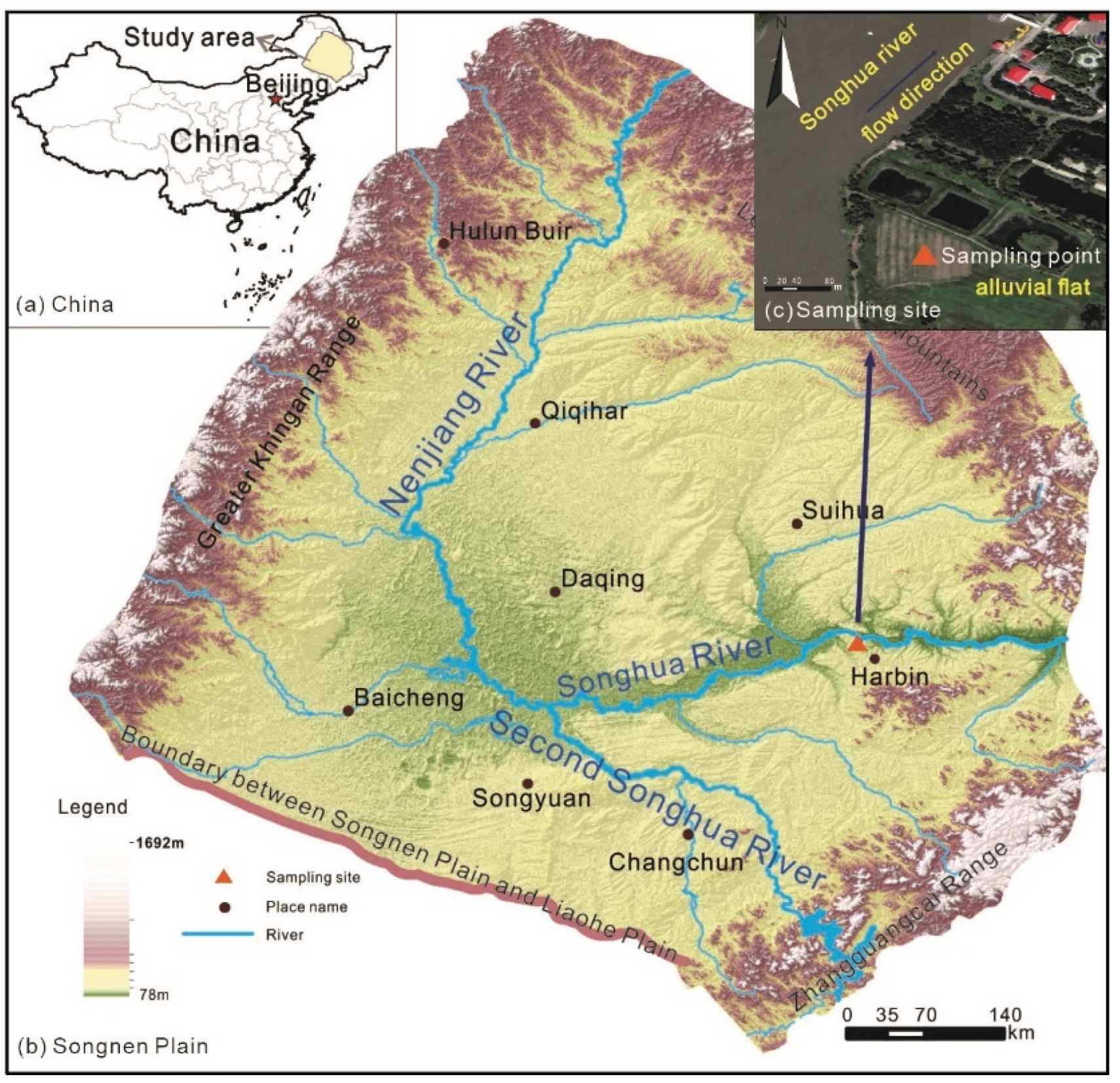
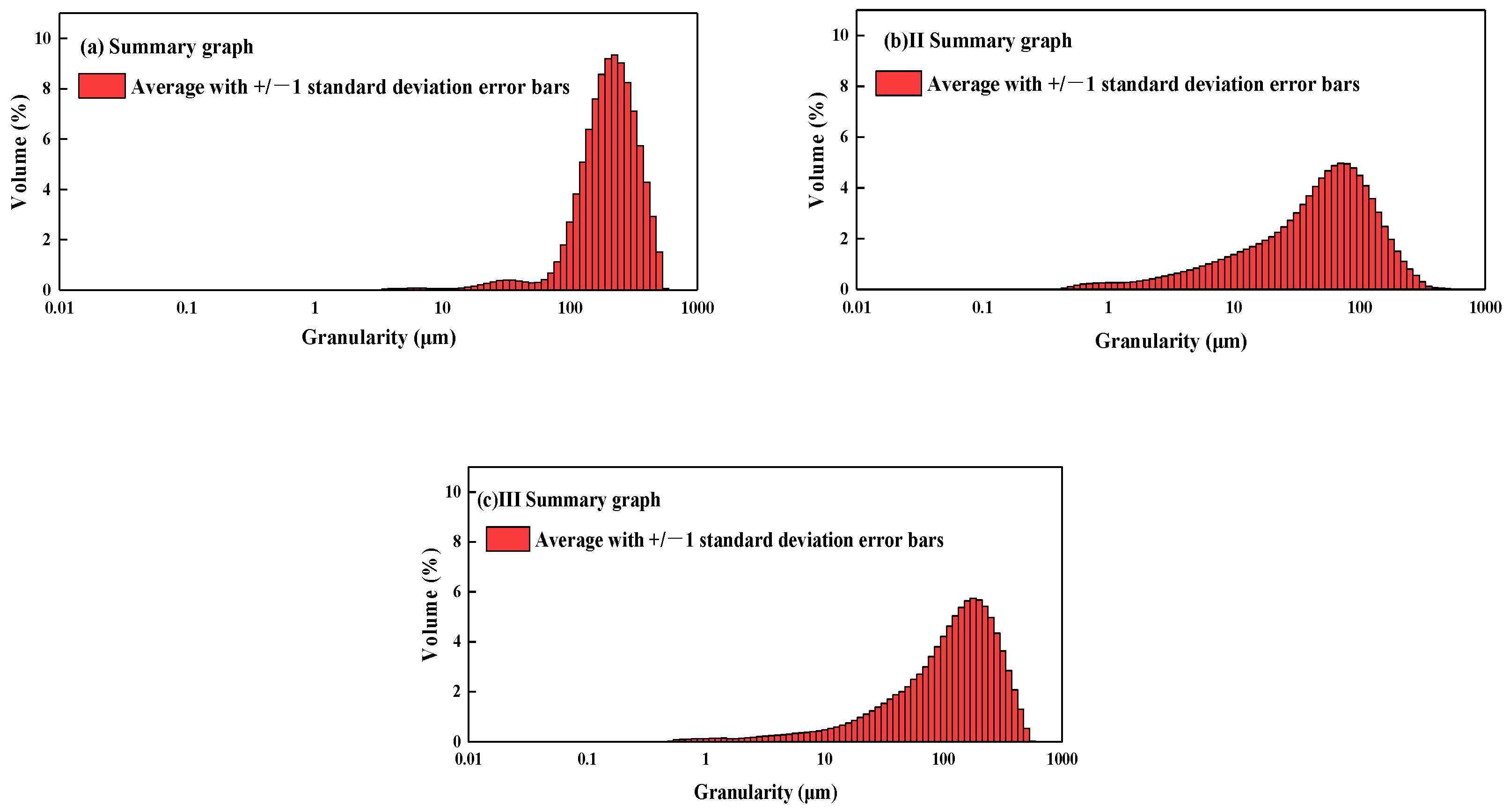
2.1. In Situ Sediments Sampling and Characterization
2.2. Artificial Polluted Groundwater with Organics
2.3. Chemicals and Utensils
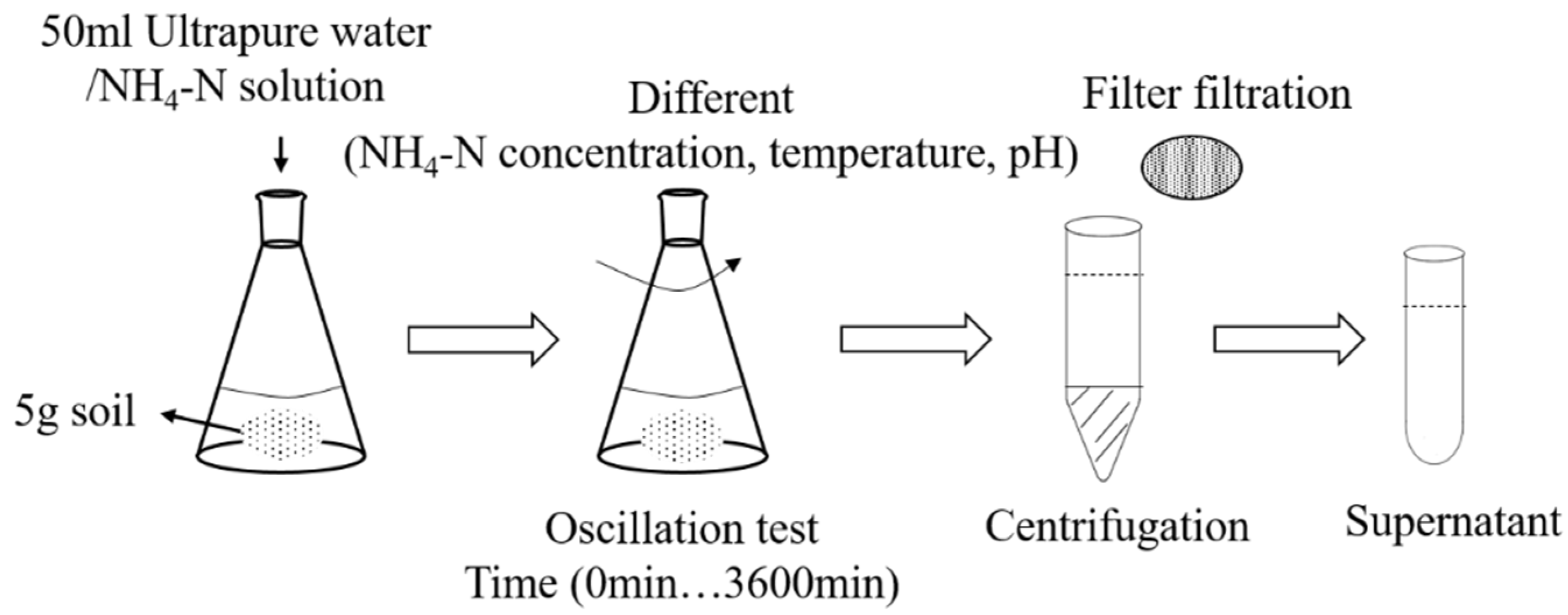
2.4. Leaching Test Procedures
2.5. Leachate Measurements
3. Results
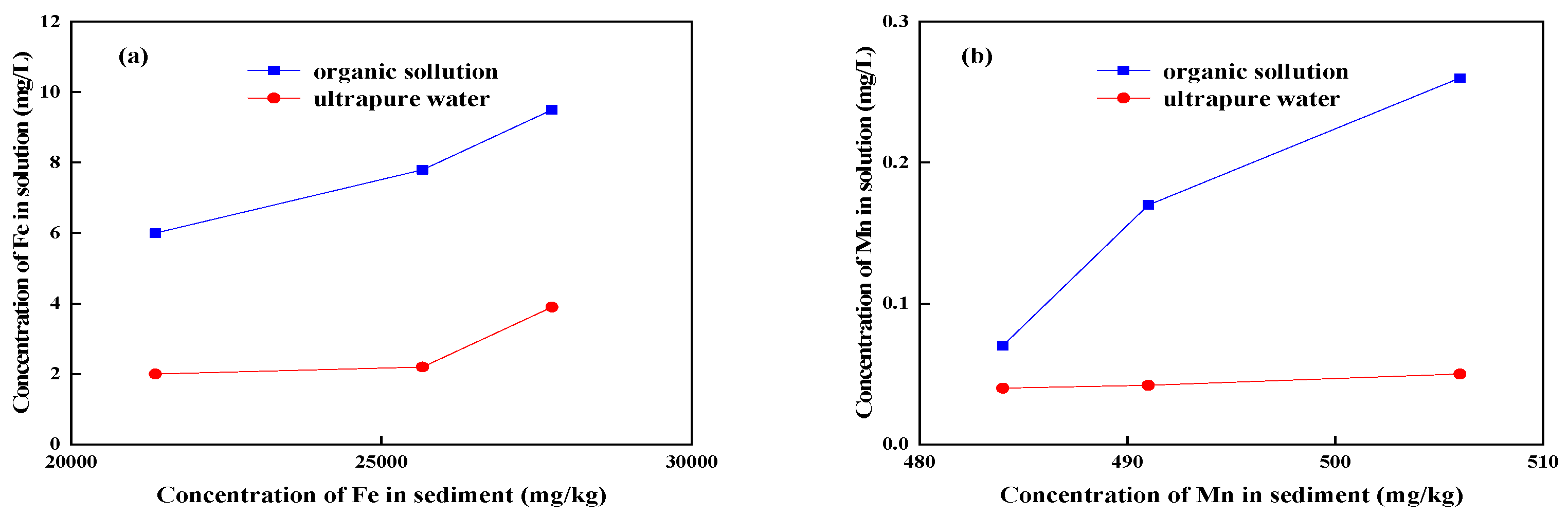
3.1. Changes of Fe/Mn with Sediments
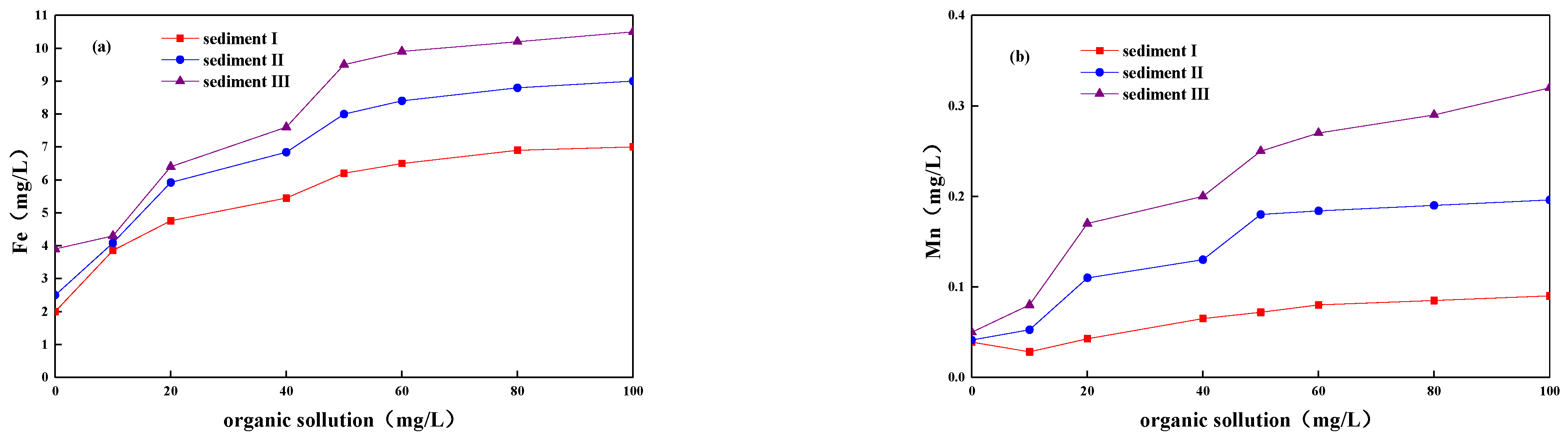
3.2. Changes of Fe/Mn with Organics
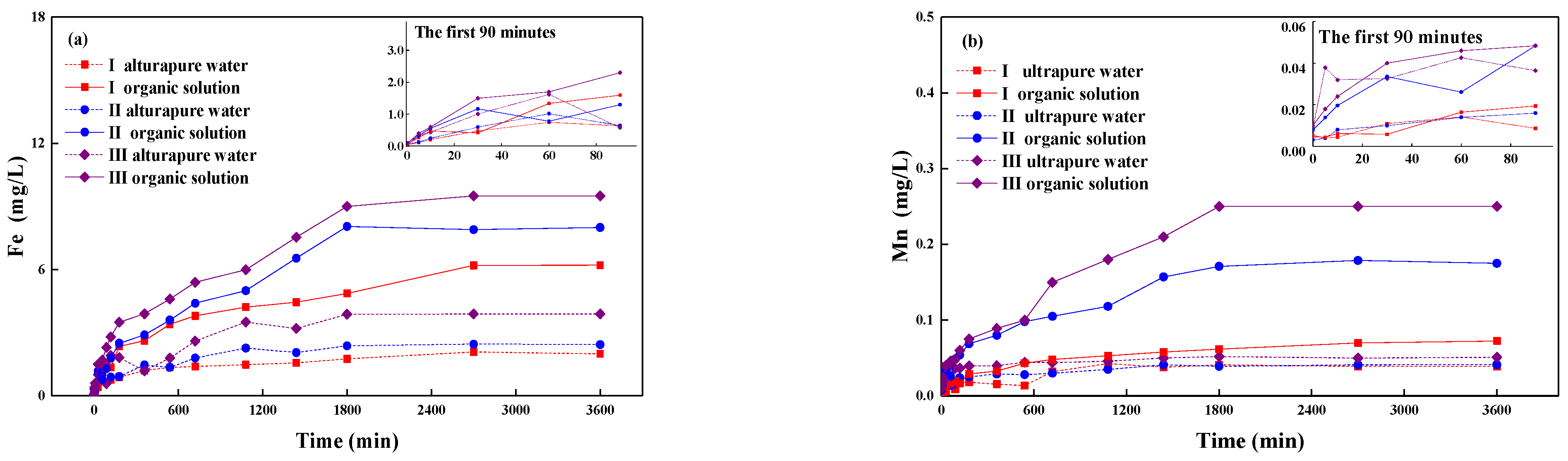
3.3. Changes of Fe/Mn with Time
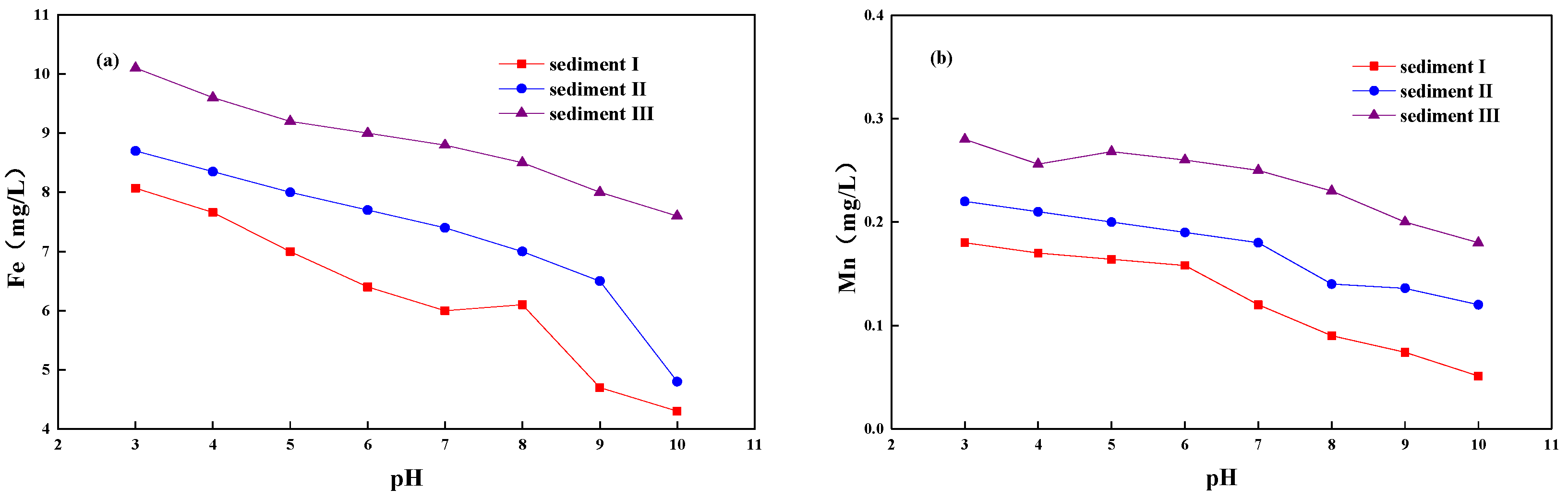
3.4. Changes of Fe/Mn with pH
4. Discussion
4.1. Input of Organics Increase Fe/Mn Release
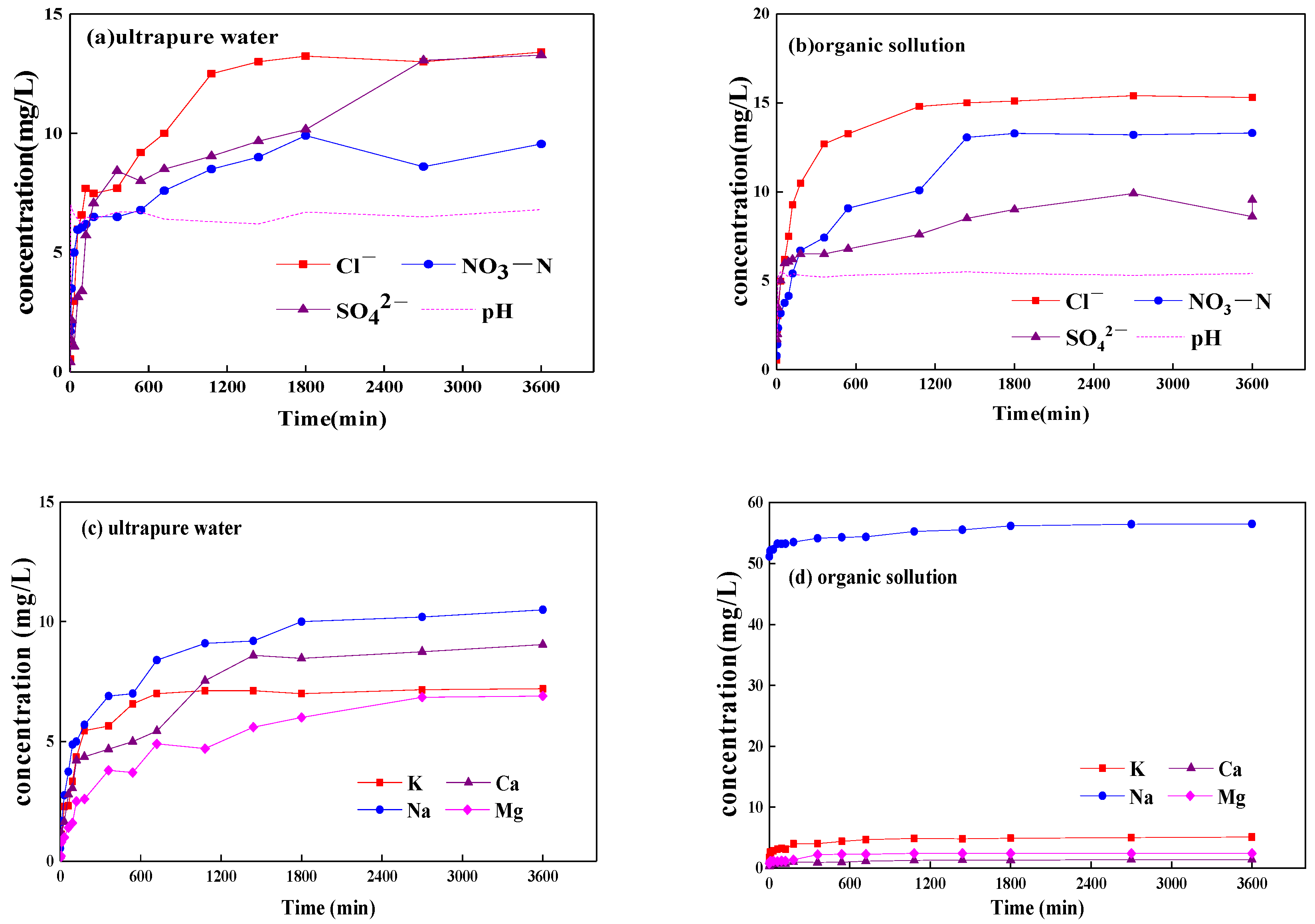
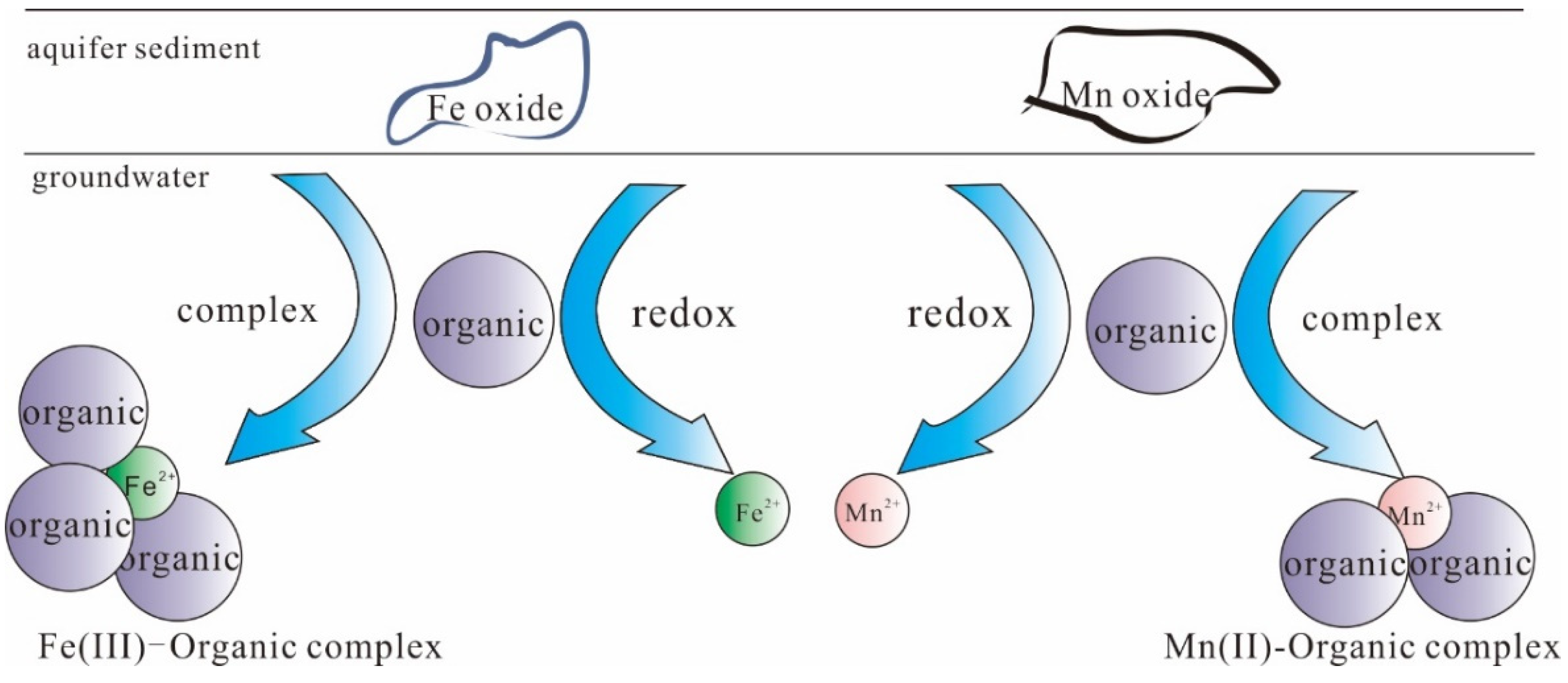
4.2. Cause of Enhanced Releases of Fe and Mn
4.3. Implications for Pollution Control
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, B.; Amelung, W.; Xing, Y.; Bol, R.; Berns, A.E. Iron cycling and isotope fractionation in terrestrial ecosystems. Earth Sci. Rev. 2019, 190, 323–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMahon, P.B.; Belitz, K.; Reddy, J.E.; Johnson, T.D. Elevated Manganese Concentrations in United States Groundwater, Role of Land Surface-Soil-Aquifer Connections. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dippong, T.; Mihali, C.; Hoaghia, M.A.; Cical, E.; Cosma, A. Chemical modeling of groundwater quality in the aquifer of Seini town—Somes Plain, Northwestern Romania. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 168, 88–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- VanTruc, N.; ThiDieuHien, V.; ThanhDai, T.; ThiNhuKhanh, N.; ThanhBinh, N.; BaoTrong, D.; XuanThanh, B. Arsenic-contaminated groundwater and its potential health risk: A case study in Long An and Tien Giang provinces of the Mekong Delta, Vietnam. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, W.; Qin, Y.; Ma, T.; Zhou, J.; Du, S. Fe-colloid cotransport through saturated porous media under different hydrochemical and hydrodynamic conditons Water Res. Water Res. 2019, 647, 494–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Socié, A.; Dubois, F.; Monerie, Y.; Perales, F. Multibody approach for reactive transport modeling in discontinuous-heterogeneous porous media. Computat. Geosci. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, S.C.; Schaefer, M.V.; Cock-Esteb, A.; Li, J.; Fendorf, S. Depth Stratification Leads to Distinct Zones of Manganese and Arsenic Contaminated Groundwater. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 8926–8932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, J.W.; Paradis, C.J.; Joyner, D.C.; von Netzer, F.; Majumder, E.L.; Dixon, E.R.; Podar, M.; Ge, X.; Walian, P.J.; Smith, H.J.; et al. Characterization of subsurface media from locations up- and down-gradient of a uranium-contaminated aquifer. Chemosphere 2020, 255, 126951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reyes-Toscano, C.A.; Alfaro-Cuevas-Villanueva, R.; Cortés-Martínez, R.; Morton-Bermea, O.; Hernández-Álvarez, E.; Buenrostro-Delgado, O.; Ávila-Olivera, J.A. Hydrogeochemical Characteristics and Assessment of Drinking Water Quality in the Urban Area of Zamora, Mexico. Water 2020, 12, 556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shrestha, S.; Sattar, H.; Khattak, M.S.; Wang, G.; Babur, M. Evaluation of adaptation options for reducing soil erosion due to climate change in the Swat River Basin of Pakistan. Ecol. Eng. 2020, 158, 106017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Xi, B.; Jiang, Y.; Guo, H.; Yang, Y.; Lian, X.; Han, S. Distribution, formation and human-induced evolution of geogenic contaminated groundwater in China: A review. Sci. Total. Environ. 2018, 643, 967–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.; Zhang, Y.; Knibbe, W.-J.; Feng, C.; Liu, W.; Medema, G.; van der Meer, W. Potential impacts of changing supply-water quality on drinking water distribution: A review. Water Res. 2017, 116, 135–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Ma, X.; Chen, R.; Yu, Y.; Tao, H.; Shi, B. Field studies of manganese deposition and release in drinking water distribution systems: Insight into deposit control. Water Res. 2019, 163, 114897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Ma, T.; Chen, J.; Xiao, C.; Liu, R.; Du, Y.; Fendorf, S. Contribution of clay-aquitard to aquifer iron concentrations and water quality. Sci. Total. Environ. 2020, 741, 140061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Y.; Lei, Y.; Wu, J.; Teng, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhao, X.; Pan, X. Does the groundwater nitrate pollution in China pose a risk to human health? A critical review of published data. Environ. Sci. Pollut. R 2016, 24, 3640–3653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Li, J.; Teng, Y.; Chen, H.; Wang, Y. A partition computing-based positive matrix factorization (PC-PMF) approach for the source apportionment of agricultural soil heavy metal contents and associated health risks. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 388, 121766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Y.; Zhao, X.; Teng, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, J.; Wu, J.; Zuo, R. Groundwater nitrate pollution and human health risk assessment by using HHRA model in an agricultural area, NE China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 137, 130–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Zhai, Y.; Teng, Y.; Wang, G.; Du, Q.; Wang, J.; Yang, G. Water supply safety of riverbank filtration wells under the impact of surface water-groundwater interaction: Evidence from long-term field pumping tests. Sci. Total. Environ. 2020, 711, 135141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Ma, T.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, J. Health risks associated with multiple metal(loid)s in groundwater: A case study at Hetao Plain, northern China. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 263, 114562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, C.D.; Nandi, A.; Joyner, T.A.; Luffman, I. Iron and Manganese in Groundwater: Using Kriging and GIS to Locate High Concentrations in Buncombe County, North Carolina. Ground Water 2018, 56, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dean, W.E.; Neff, B.P.; Rosenberry, D.O.; Winter, T.C.; Parkhurst, R. The Significance of Ground Water to the Accumulation of Iron and Manganese in the Sediments of Two Hydrologically Distinct Lakes in North-Central Minnesota: A Geological Perspective. Ground Water 2003, 41, 951–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vega, M.A.; Kulkarni, H.V.; Johannesson, K.H.; Taylor, R.J.; Datta, S. Mobilization of co-occurring trace elements (CTEs) in arsenic contaminated aquifers in the Bengal basin. Appl. Geochem. 2020, 122, 104709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degnan, J.R.; Lindsey, B.D.; Levitt, J.P.; Szabo, Z. The relation of geogenic contaminants to groundwater age, aquifer hydrologic position, water type, and redox conditions in Atlantic and Gulf Coastal Plain aquifers, eastern and south-central USA. Sci. Total. Environ. 2020, 723, 137835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloise, A.; Miriello, D.; de Rosa, R.; Vespasiano, G.; Fuoco, I.; de Luca, R.; Barrese, E.; Apollaro, C. Mineralogical and Geochemical Characterization of Asbestiform Todorokite, Birnessite, and Ranciéite, and Their host Mn-Rich Deposits from Serra D’Aiello (Southern Italy). Fibers 2020, 8, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhai, Y.; Zheng, F.; Zhao, X.; Xia, X.; Teng, Y. Identification of hydrochemical genesis and screening of typical groundwater pollutants impacting human health: A case study in Northeast China. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 252, 1202–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Zhang, H.; Guo, S.; Fu, K.; Liao, L.; Xu, Y.; Cheng, S. Groundwater pollution source apportionment using principal component analysis in a multiple land-use area in southwestern China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2020, 27, 9000–9011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; He, J.; He, B.; Sun, J. Assessment, formation mechanism, and different source contributions of dissolved salt pollution in the shallow groundwater of Hutuo River alluvial-pluvial fan in the North China Plain. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2019, 26, 35742–35756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Lu, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhang, M.; Yuan, J.; Zhang, A.; Song, S.; Baninla, Y.; Khan, K.; Wang, Y. Hydrogeochemistry and quality of surface water and groundwater in the drinking water source area of an urbanizing region. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 186, 109628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Wang, G.; Wang, H.; Shrestha, S.; Xue, B.; Sun, W.; Yu, J. Macrozoobenthos variations in shallow connected lakes under the influence of intense hydrologic pulse changes. J. Hydrol. 2020, 584, 124755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Hu, M.; Zhou, D.; Fan, W.; Wang, X.; Huo, M. Bioremoval of Cu2+ from CMP wastewater by a novel copper-resistant bacterium Cupriavidus gilardii CR3: Characteristics and mechanisms. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 18793–18802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Latif, A.; Sheng, D.; Sun, K.; Si, Y.; Azeem, M.; Abbas, A.; Bilal, M. Remediation of heavy metals polluted environment using Fe-based nanoparticles: Mechanisms, influencing factors, and environmental implications. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 264, 114728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.; Wu, J.; Yang, P.; Zhu, M. Coupled Manganese Redox Cycling and Organic Carbon Degradation on Mineral Surfaces. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallis, I.; Prommer, H.; Berg, M.; Siade, A.J.; Sun, J.; Kipfer, R. The river-groundwater interface as a hotspot for arsenic release. Nat. Geosci. 2020, 13, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Qian, K.; Xie, X. Indices of the dual roles of OM as electron donor and complexing compound involved in As and Fe mobilization in aquifer systems of the Datong Basin. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 262, 114305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryant, S.R.; Sawyer, A.H.; Briggs, M.A.; Saup, C.M.; Nelson, A.R.; Wilkins, M.J.; Christensen, J.N.; Williams, K.H. Seasonal manganese transport in the hyporheic zone of a snowmelt-dominated river (East River, Colorado, USA). Hydrogeol. J. 2020, 28, 1323–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Wang, Z.; Ma, T.; Chen, S. Spatial distribution characteristics and influencing factors of organic carbon in sediments of Tongshun River riparian zone. Chemosphere 2020, 252, 126322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papp, D.C.; Cociuba, I.; Baciu, C.; Cozma, A. Origin and Geochemistry of Mine Water and its Impact on the Groundwater and Surface Running Water in Post-mining Environments: Zlatna Gold Mining Area (Romania). Aquat. Geochem. 2017, 23, 247–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thayalakumaran, T.; Lenahan, M.J.; Bristow, K.L. Dissolved Organic Carbon in Groundwater Overlain by Irrigated Sugarcane. Ground Water 2015, 53, 525–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Wu, X.; Ge, J.; Liu, F.; Zhao, W.; Wu, C. Influence of mining activities on groundwater hydrochemistry and heavy metal migration using a self-organizing map (SOM). J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 257, 120664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Y.; Ma, T.; Zhou, J.; Li, X.; Liu, D.; Wang, Z.; Qin, Y.; Du, Q. Impacts of leachate of landfill on the groundwater hydrochemistry and size distributions and heavy metal components of colloids: A case study in NE China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. R 2019, 26, 5713–5723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Deng, Y.; Ma, T.; Xu, Y.; Tao, Y.; Huang, Y.; Liu, R.; Wang, Y. Enrichment of Geogenic Ammonium in Quaternary Alluvial-Lacustrine Aquifer Systems: Evidence from Carbon Isotopes and DOM Characteristics. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 6104–6114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barhoumi, B.; Beldean-Galea, M.S.; Al-Rawabdeh, A.M.; Roba, C.; Martonos, I.M.; Balc, R.; Kahlaoui, M.; Touil, S.; Tedetti, M.; Driss, M.R.; et al. Occurrence, distribution and ecological risk of trace metals and organic pollutants in surface sediments from a Southeastern European river (Somesu Mic River, Romania). Sci. Total. Environ. 2019, 660, 660–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, B.T.; Nguyen, T.M.T.; Bach, Q.-V. Assessment of groundwater quality based on principal component analysis and pollution source-based examination: A case study in Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam. Environ. Monit. Assess 2020, 192, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Hall, S.J.; Coward, E.; Thompson, A. Iron-mediated organic matter decomposition in humid soils can counteract protection. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yinglan, A.; Wang, G.; Liu, T.; Xue, B.; Kuczera, G. Spatial variation of correlations between vertical soil water and evapotranspiration and their controlling factors in a semi-arid region. J. Hydrol. 2019, 574, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Zhai, Y.; Du, Q.; Teng, Y.; Wang, J.; Yang, G. The impact of well drawdowns on the mixing process of river water and groundwater and water quality in a riverside well field, Northeast China. Hydrol. Process. 2019, 33, 945–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, H.; Pan, Y.; Zheng, L.; Li, X.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, C.; Huang, Z.; Li, Z.; Wang, H.; Zhou, C. Long-term groundwater storage changes and land subsidence development in the North China Plain (1971–2015). Hydrogeol. J. 2018, 26, 1417–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhai, Y.; Xia, X.; Yang, G.; Lu, H.; Ma, G.; Wang, G.; Teng, Y.; Yuan, W.; Shrestha, S. Trend, seasonality and relationships of aquatic environmental quality indicators and implications: An experience from Songhua River, NE China. Ecol. Eng. 2020, 145, 105706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Liu, H.; Wang, Z.; Cui, Y.; Chen, R.; Peng, Z.; Yuan, S.; Shi, L. Benzene promotes microbial Fe(III) reduction and flavins secretion. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2019, 264, 92–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.; Han, S. Study of multi-aquifer groundwater interaction in a coal mining area in China using stable isotopes and major-ion chemical data. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 76, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Hu, X.; Wan, Y.; Mahai, G.; Jiang, Y.; Huo, W.; Zhao, X.; Liang, G.; He, Z.; Xia, W.; et al. A nationwide study of the occurrence and distribution of atrazine and its degradates in tap water and groundwater in China: Assessment of human exposure potential. Chemosphere 2020, 252, 126533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMahon, P.B.; Chapelle, F.H. Redox processes and water quality of selected principal aquifer systems. Ground Water 2008, 46, 259–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D. Influence of Iron Speciation on Redox Cycling and Reactivity with Persistent Organic Contaminants. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, Champaign, IL, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Amarathunga, U.; Diyabalanage, S.; Bandara, U.G.C.; Chandrajith, R. Environmental factors controlling arsenic mobilization from sandy shallow coastal aquifer sediments in the Mannar Island, Sri Lanka. Appl. Geochem. 2019, 100, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.; Lu, S.; Yuan, W.; Woo, N.C.; Dai, Z.; Dong, W.; Du, S.; Zhang, X. Redox zonation for different groundwater flow paths during bank filtration: A case study at Liao River, Shenyang, northeastern China. Hydrogeol. J. 2018, 26, 1573–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sader, J.A.; Hattori, K.; Hamilton, S.; Brauneder, K. Metal binding to dissolved organic matter and adsorption to ferrihydrite in shallow peat groundwaters: Application to diamond exploration in the James Bay Lowlands, Canada. Appl. Geochem. 2011, 26, 1649–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, S.; Wang, X.; Xiang, Q.; Yin, H.; Tan, W.; Qiu, G.; Liu, F.; Zhang, J.; Feng, X. Mechanisms of Mn(II) catalytic oxidation on ferrihydrite surfaces and the formation of manganese (oxyhydr)oxides. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2017, 211, 79–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Guo, H.; Zheng, H.; Xiu, W.; He, W.; Ding, Q. Roles of different molecular weights of dissolved organic matter in arsenic enrichment in groundwater: Evidences from ultrafiltration and EEM-PARAFAC. Appl. Geochem. 2019, 104, 124–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broclawik, O.; Lukawska-Matuszewska, K.; Brodecka-Goluch, A.; Bolalek, J. Impact of methane occurrence on iron speciation in the sediments of the Gdansk Basin (Southern Baltic Sea). Sci. Total. Environ. 2020, 721, 137718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, S.; Fang, Q.; Duan, Y.; Ou, P.; Wang, L.; Chen, Z.; Wang, F. Implementation of long-term assessment of human health risk for metal contaminated groundwater: A coupled chemical mass balance and hydrodynamics model. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 180, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Li, J.; Sun, W.; Xue, B.; Yinglan, A.; Liu, T. Non-point source pollution risks in a drinking water protection zone based on remote sensing data embedded within a nutrient budget model. Water Res. 2019, 157, 238–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, K.; Song, Z. Cycling and total risks of multiple As fractions in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei area on the agricultural plain, China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 190, 110097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xia, J.; Ding, S.; Zhang, S.; Li, M.; Shang, Z.; Lu, J.; Ding, J. Removing organic matters from reverse osmosis concentrate using advanced oxidation-biological activated carbon process combined with Fe3+/humus-reducing bacteria. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 203, 110945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Yu, X.; Zhang, W.; Huan, Y.; Yu, J.; Zhang, Y. Risk Assessment of Groundwater Organic Pollution Using Hazard, Intrinsic Vulnerability, and Groundwater Value, Suzhou City in China. Expo. Health 2017, 10, 99–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, T.; Zeng, X.; Wu, J.; Wang, D.; Sun, Y.; Zhu, X.; Lin, J.; Long, Y. Groundwater contaminant source identification via Bayesian model selection and uncertainty quantification. Hydrogeol. J. 2019, 27, 2907–2918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jylhä-Ollila, M.; Laine-Kaulio, H.; Niinikoski-Fusswinkel, P.; Leveinen, J.; Koivusalo, H. Water quality changes and organic matter removal using natural bank infiltration at a boreal lake in Finland. Hydrogeol. J. 2020, 28, 1343–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ruhala, S.S.; Zarnetske, J.P.; Long, D.T.; Lee-Cullin, J.A.; Plont, S.; Wiewiora, E.R. Exploring dissolved organic carbon cycling at the stream-groundwater interface across a third-order, lowland stream network. Biogeochemistry 2017, 137, 105–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouser, P.J.; Liu, S.; Cluff, M.A.; McHugh, M.; Lenhart, J.J.; MacRae, J.D. Redox conditions alter biodegradation rates and microbial community dynamics of hydraulic fracturing fluid organic additives in soil-groundwater microcosms. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2016, 33, 827–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousi, M.; Liu, G.; Salinas-Rodriguez, S.G.; Chen, L.; Dusseldorp, J.; Wessels, P.; Schippers, J.C.; Kennedy, M.D.; van der Meer, W. Multi-parametric assessment of biological stability of drinking water produced from groundwater: Reverse osmosis vs. conventional treatment. Water Res. 2020, 186, 116317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Su, X.; Wang, J.; Lyu, H.; Gao, R.; Lu, S. Multi-isotope constraints on biogeochemical processes during bank filtration: A case study of the Liao River, Northeast China. Appl. Geochem. 2020, 122, 104762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Sediment | pH | NO3-N (mg/kg) | NO2-N (mg/kg) | TOC (mg/kg) | Total Fe (mg/kg) | Total Mn (mg/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | 5.87 | 25.5 | 0.105 | 1550 | 18540 | 384 |
| II | 6.24 | 22.6 | 0.134 | 6400 | 22664 | 451 |
| III | 6.11 | 27.5 | 0.12 | 7980 | 27749 | 506 |
| Group | Sediment | Sampling Time (min) | Organics (mg/L) | pH | Number of Samples |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | I | 0, 5, 10, 30, 60, 90, 120, 180, 360, 540, 720, 1080, 1440, 1800, 2700, 3600 | 50 | 16 | |
| II | |||||
| III | |||||
| B | I | 3600 | 10, 20, 40, 60, 80, 100 | 6 | |
| II | |||||
| III | |||||
| C | I | 50 | 3 | ||
| II | |||||
| III | |||||
| D | I | 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10 | 8 | ||
| II | |||||
| III |
| Item (Unit) | Detection Method | Level of Detection (Unit) |
|---|---|---|
| Fe (II) | O-phenanthroline spectrophotometry | 0.03 mg/L |
| TFe | ICP-AES (PerkinElmer Optima 8000) | 0.01 mg/L |
| TMn | ICP-AES (PerkinElmer Optima 8000) | 0.001 mg/L |
| Ion chromatography (Thermo ICS-2100) | 0.02 mg/L | |
| Cl | Ion chromatography (Thermo ICS-2100) | 0.02 mg/L |
| pH | Water quality analyzer (HANNA-HI9828) | — |
| K | ICP-AES (PerkinElmer Optima 8000) | 0.007 mg/L |
| Na | ICP-AES (PerkinElmer Optima 8000) | 0.004 mg/L |
| Ca | ICP-AES (PerkinElmer Optima 8000) | 0.0002 mg/L |
| Mg | ICP-AES (PerkinElmer Optima 8000) | 0.001 mg/L |
| Ion chromatography (Thermo ICS-2100) | 0.09 mg/L |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhai, Y.; Han, Y.; Xia, X.; Li, X.; Lu, H.; Teng, Y.; Wang, J. Anthropogenic Organic Pollutants in Groundwater Increase Releases of Fe and Mn from Aquifer Sediments: Impacts of Pollution Degree, Mineral Content, and pH. Water 2021, 13, 1920. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13141920
Zhai Y, Han Y, Xia X, Li X, Lu H, Teng Y, Wang J. Anthropogenic Organic Pollutants in Groundwater Increase Releases of Fe and Mn from Aquifer Sediments: Impacts of Pollution Degree, Mineral Content, and pH. Water. 2021; 13(14):1920. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13141920
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhai, Yuanzheng, Yifan Han, Xuelian Xia, Xindai Li, Hong Lu, Yanguo Teng, and Jinsheng Wang. 2021. "Anthropogenic Organic Pollutants in Groundwater Increase Releases of Fe and Mn from Aquifer Sediments: Impacts of Pollution Degree, Mineral Content, and pH" Water 13, no. 14: 1920. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13141920
APA StyleZhai, Y., Han, Y., Xia, X., Li, X., Lu, H., Teng, Y., & Wang, J. (2021). Anthropogenic Organic Pollutants in Groundwater Increase Releases of Fe and Mn from Aquifer Sediments: Impacts of Pollution Degree, Mineral Content, and pH. Water, 13(14), 1920. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13141920








