A Stable Isotope Approach for Estimating the Contribution of Recycled Moisture to Precipitation in Lanzhou City, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data and Method
2.1. Sampling Network
2.2. Laboratory Testing
2.3. Three-Component Mixing Model
3. Results
3.1. The Path of Renshoushan—Anning—LREVC—Yuzhong
3.2. The Path of Yongdeng–Daheng/Gaolan
3.3. Spatial and Monthly Patterns of Recycling Fraction
4. Discussion
4.1. Potential Spatial Controls of Recycling Fraction
4.2. Model Uncertainty Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Savenije, H.H. New definitions for moisture recycling and the relationship with land-use changes in the Sahel. J. Hydrol. 1995, 167, 57–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominguez, F.; Kumar, P.; Liang, X.-Z.; Ting, M. Impact of Atmospheric Moisture Storage on Precipitation Recycling. J. Clim. 2006, 19, 1513–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Ent, R.J.; Savenije, H.H.G.; Schaeflfli, B.; Steele-Dunne, S.C. Origin and fate of atmospheric moisture over continents. Water Resour. Res. 2010, 46, W09525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, Y.; Chen, F.; Miguez-Macho, G.; Li, X. Understanding precipitation recycling over the Tibetan Plateau using tracer analysis with WRF. Clim. Dyn. 2020, 55, 2921–2937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, M.; Che, Y.; Chen, F.; Qiang, F. Contribution of recycled moisture to precipitation in oases of arid central Asia: A stable isotope approach. Water Resour. Res. 2016, 52, 3246–3257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, P.; Ding, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, X. The characteristics of moisture recycling and its impact on regional precipitation against the background of climate warming over Northwest China. Int. J. Clim. 2019, 39, 5241–5255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.; Zhang, M.; Dong, Z.; Wang, S.; Yu, X.; Meng, H.; Che, C. Contribution of recycled moisture to precipitation in Northeastern Tibetan Plateau: A case study based on Bayesian estimation. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, S. A review of precipitation isotope studies in China: Basic pattern and hydrological process. J. Geogr. Sci. 2016, 26, 921–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, R.; Wang, C.; Wu, D. Changes in precipitation recycling over arid regions in the Northern Hemisphere. Theor. Appl. Clim. 2018, 131, 489–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hua, L.; Zhong, L.; Ke, Z. Characteristics of the precipitation recycling ratio and its relationship with regional precipitation in China. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2015, 127, 513–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aemisegger, F.; Pfahl, S.; Sodemann, H.; Lehner, I.; Seneviratne, S.I.; Wernli, H. Deuterium excess as a proxy for continental moisture recycling and plant transpiration. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2014, 14, 4029–4054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Lu, A.; Feng, Q.; Li, Z.; Liu, W.; Wang, S.; Tripathee, L.; Wang, X.; Cao, J. Recycled moisture in an enclosed basin, Guanzhong Basin of Northern China, in the summer: Contribution to precipitation based on a stable isotope approach. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 27926–27936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Y.; Pang, Z.; Froehlich, K. Quantifying recycled moisture fraction in precipitation of an arid region using deuterium excess. Tellus B Chem. Phys. Meteorol. 2013, 65, 19251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corcoran, M.C.; Thomas, E.K.; Boutt, D.F. Event-based precipitation isotopes in the Laurentian Great Lakes region reveal spatiotemporal patterns in moisture recycling. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2019, 124, 5463–5478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.J.; Wang, S.J. Precipitation isotopes in the Tianshan Mountains as a key to water cycle in arid central Asia. Sci. Cold Arid. Reg. 2018, 10, 27–37. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, T.R.; Liu, K.K.; Wang, C.H.; Chuang, K.H. A water isotope approach to assessing moisture recycling in the island-based precipitation of Taiwan: A case study in the western Pacific. Water Resour. Res. 2011, 47, W08507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Chen, Y.; Li, J.; Chen, W.; Li, X. Stable isotope variations in precipitation in the northwesternmost Tibetan Plateau related to various meteorological controlling factors. Atmos. Res. 2019, 227, 66–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Feng, Q.; Wang, Q.J.; Yanlong, K.; Aifang, C.; Song, Y.; Yongge, L.; Jianguo, L.; Xiaoyan, G. Contributions of local terrestrial evaporation and transpiration to precipitation using δ18O and D-excess as a proxy in Shiyang inland river basin in China. Global Planet. Chang. 2016, 146, 140–151. [Google Scholar]
- Good, S.P.; Noone, D.; Bowen, G. Hydrologic connectivity constrains partitioning of global terrestrial water fluxes. Science 2015, 349, 175–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Gentine, P.; Lin, C.; Zhou, S.; Sun, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Liu, J.; Zheng, C. A simple and objective method to partition evapotranspiration into transpiration and evaporation at eddy-covariance sites. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2019, 265, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, F.; Qiu, G.; Yang, Y.; Lü, Y.; Xiong, Y. Estimation of evapotranspiration and its partition based on an extended three-temperature model and MODIS products. J. Hydrol. 2013, 498, 210–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimura, K. Stable Water Isotopes in Climatology, Meteorology, and Hydrology: A Review. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. 2015, 93, 513–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, Q.; Jiang, D.; Lang, X.; Xu, B. Moisture sources of the Chinese Loess Plateau during 1979–2009. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclim. Palaeoecol. 2018, 509, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhao, C.; Yu, Z.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, A.; Zhang, X.; Feng, X.; Sun, X.; Shen, J. Western Pacific Ocean influences on monsoon precipitation in the southwestern Chinese Loess Plateau since the mid-Holocene. Clim. Dyn. 2020, 54, 3121–3134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.; An, Z.; Huh, C.-A.; Cai, Y.; Shen, C.-C.; Shiau, L.-J.; Yan, L.; Cheng, H.; Edwards, R.L. Cyclic precipitation variation on the western Loess Plateau of China during the past four centuries. Sci. Rep. 2015, 4, 6381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, F.; Zhang, M.; Wang, S.; Qiu, X.; Du, M. Environmental controls on stable isotopes of precipitation in Lanzhou, China: An enhanced network at city scale. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 609, 1013–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, F.; Zhang, M.; Wang, S.; Ma, Q.; Zhu, X.; Dong, L. Relationship between sub-cloud secondary evaporation and stable isotopes in precipitation of Lanzhou and surrounding area. Quat. Int. 2015, 380–381, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Zhang, M.; Argiriou, A.A.; Wang, S.; Zhou, X.; Liu, X. Deuterium Excess in Precipitation Reveals Water Vapor Source in the Monsoon Margin Sites in Northwest China. Water 2020, 12, 3315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Zhang, M.; Argiriou, A.A.; Wang, S.; Ma, Q.; Zhou, X.; Wu, X.; Chen, J. Modeling Insights into Precipitation Deuterium Excess as an Indicator of Raindrop Evaporation in Lanzhou, China. Water 2021, 13, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Zhang, M.; Wang, S.; Wang, Q.; Liu, W.; Li, F.; Chen, F. An investigation of moisture sources and secondary evaporation in Lanzhou, Northwest China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2013, 71, 3375–3385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brubaker, K.L.; Entekhabi, D.; Eagleson, P.S. Estimation of continental precipitation recycling. J. Clim. 1993, 6, 1077–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Friedman, I.; O’Neil, J.R. Compilation of Stable Isotope Fractionation Factors of Geochemical Interest; Data of Geochemistry; U. S. Department of the Interior: Washington, DC, USA, 1977. [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Criss, R.E. Principles of Stable Isotope Distribution; Oxford University: New York, NY, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Barnes, S.L. An empirical shortcut to the calculation of temperature and pressure at the lifted condensation level. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1968, 7, 511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Craig, H.; Gordon, L.I. Deuterium and Oxygen 18 Variations in the Ocean and the Marine Atmosphere in Stable Isotopes in Oceanographic Studies and Paleotemperatures; Laboratory of Geology and Nuclear Science: Pisa, France, 1965; pp. 9–130. [Google Scholar]
- Gat, J.R. Oxygen and hydrogen isotopes in the hydrologic cycle. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 1996, 24, 225–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, L.; Liu, X.; Wang, N.; Kong, Y.; Song, Y.; He, Z.; Liu, Q.; Wang, L. Contribution of recycled moisture to local precipitation in the inland Heihe River Basin. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2019, 271, 316–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Qu, D.; Duan, W.; Wang, J.; Su, P.; Guo, R. Water use strategies of dominant species (Caragana korshinskii and Reaumuria soongorica) in natural shrubs based on stable isotopes in the Loess Hill, China. Water 2020, 12, 1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Q.; Zhang, M.; Wang, S.; Argiriou, A.A.; Che, C.; Zhao, P.; Ma, Z.; Su, P. Plant water resource partitioning and xylem-to-leaf deuterium enrichment in Lanzhou, northwest China. Water Supply 2020, 20, 1127–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, C.; Zhang, M.; Argiriou, A.A.; Wang, S.; Du, Q.; Zhao, P.; Ma, Z.; Yung, P. The Stable Isotopic Composition of Different Water Bodies at the Soil–Plant–Atmosphere Continuum (SPAC) of the Western Loess Plateau, China. Water 2019, 11, 1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Z.L. An enhanced dual IDW method for high-quality geospatial interpolation. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 9903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.; Liu, D.S.; Tan, X.C.; Wang, J.; Chen, Y.P.; He, B.B. Explorations of the implementation of a parallel IDW interpolation algorithm in a Linux cluster-based parallel GIS. Comput. Geosci. 2011, 37, 426–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Zheng, C.; Chien, C.C. Cost-effective sampling network design for contaminant plume monitoring under general hydrogeological conditions. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2005, 77, 41–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
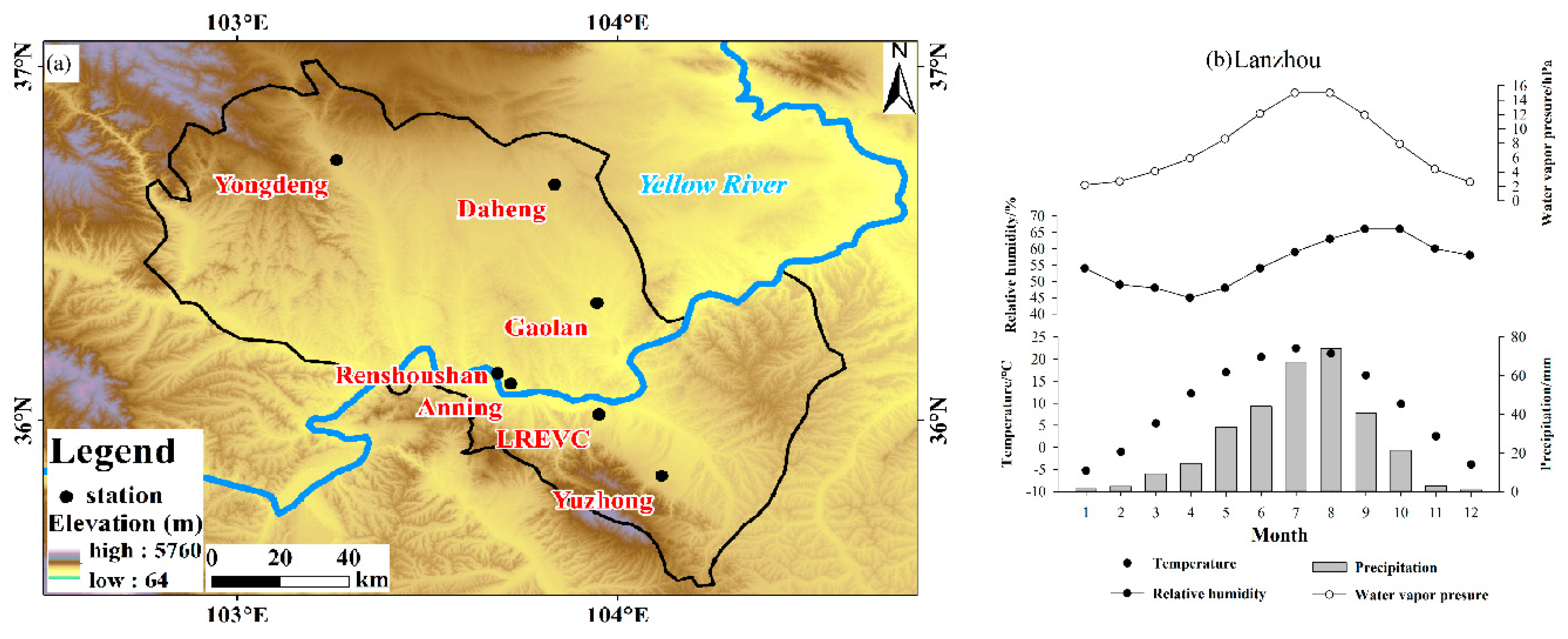
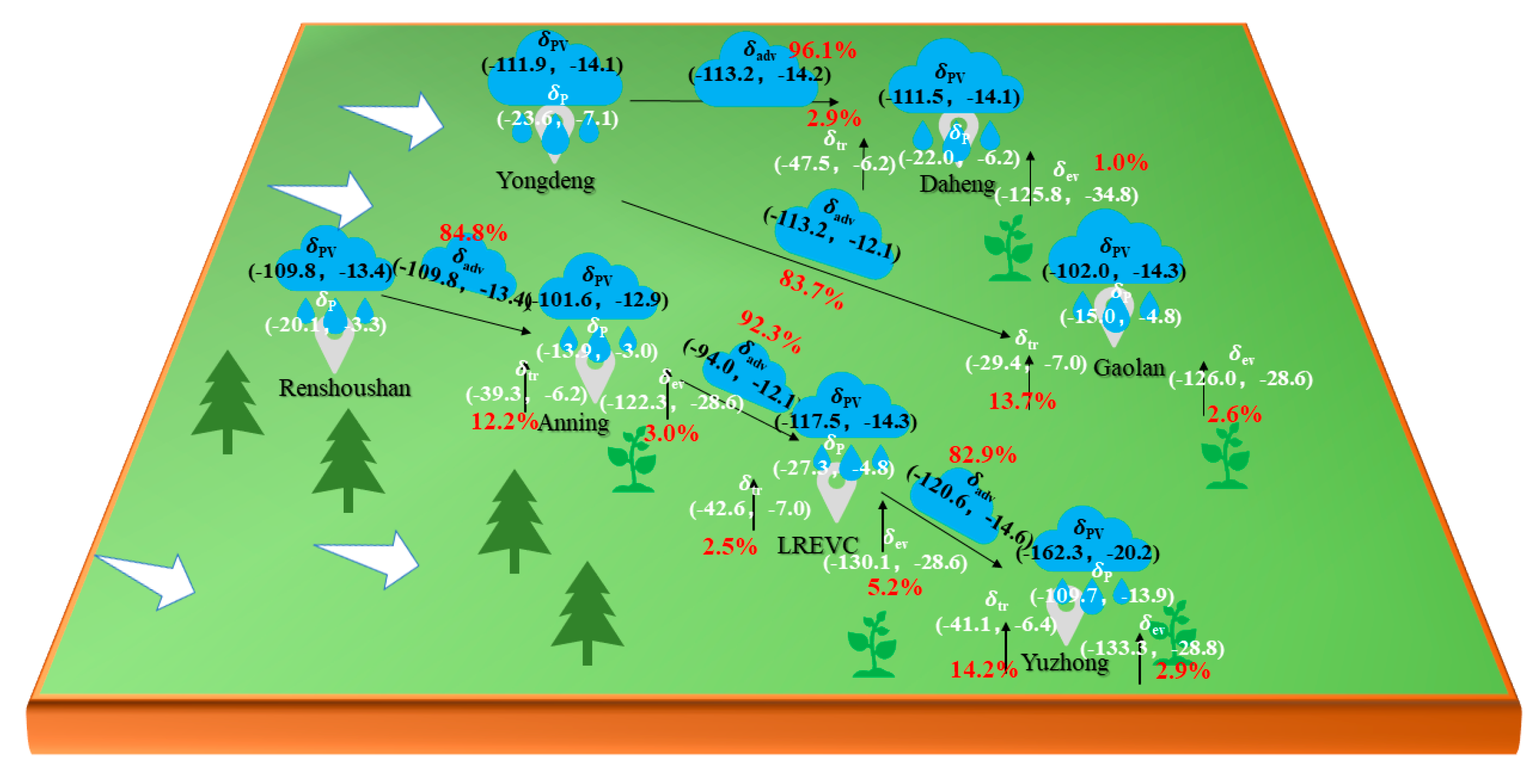
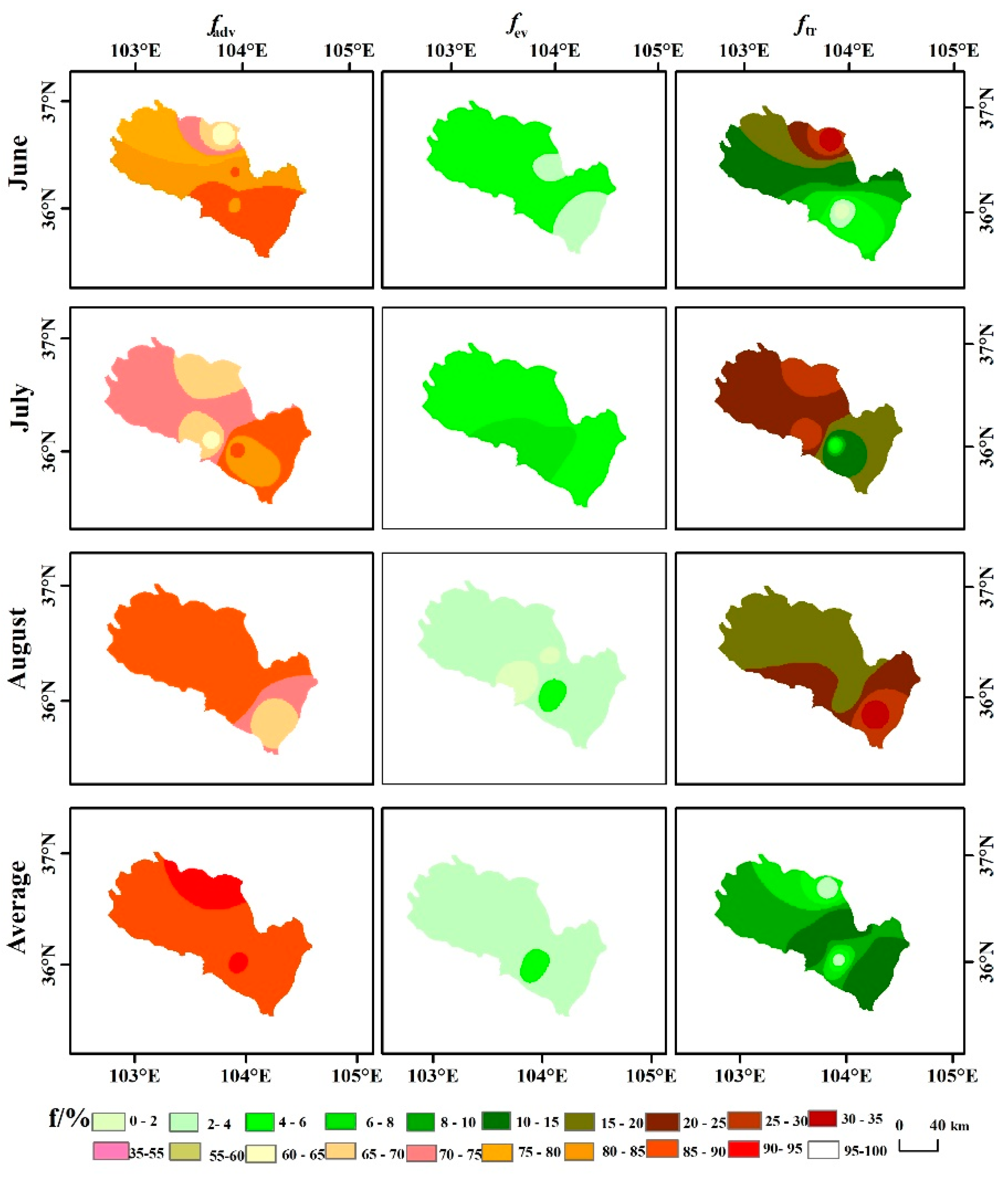
| Station | Latitude N | Longitude E | Altitude/m |
|---|---|---|---|
| Renshoushan | 36°08′ | 103°41′ | 1657 |
| Anning | 36°06′ | 103°44′ | 1548 |
| LREVC | 36°01′ | 103°57′ | 1725 |
| Yuzhong | 35°52′ | 104°09′ | 1874 |
| Yongdeng | 36°45′ | 103°15′ | 2119 |
| Daheng | 36°40′ | 103°50′ | 2029 |
| Gaolan | 36°21′ | 103°56′ | 1669 |
| Anning | LREVC | Yuzhong | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| δ2H | δ18O | δ2H | δ18O | δ2H | δ18O | |
| δp/‰ | −13.9 | −3.0 | −27.3 | −4.8 | −19.8 | −3.7 |
| δpv/‰ | −101.6 | −12.9 | −117.5 | −14.3 | −109.7 | −13.9 |
| δtr/‰ | −39.3 | −6.2 | −42.6 | −7.0 | −41.1 | −6.4 |
| δev/‰ | −122.3 | −28.6 | −130.1 | −28.6 | −133.3 | −28.8 |
| δadv/‰ | −109.8 | −13.4 | −94.0 | −12.1 | −120.6 | −14.6 |
| ftr/% | 12.2 | 2.5 | 14.2 | |||
| fev/% | 3.0 | 5.2 | 2.9 | |||
| fadv/% | 84.8 | 92.3 | 82.9 | |||
| Daheng | Gaolan | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| δ2H | δ18O | δ2H | δ18O | |
| δp/‰ | −22.0 | −6.2 | −15.0 | −4.8 |
| δpv/‰ | −111.5 | −14.1 | −102.0 | −14.3 |
| δtr/‰ | −47.5 | −6.2 | −29.4 | −7.0 |
| δev/‰ | −125.8 | −34.8 | −126.0 | −28.6 |
| δadv/‰ | −113.2 | −14.2 | −113.2 | −12.1 |
| ftr/% | 2.9 | 13.7 | ||
| fev/% | 1.0 | 2.6 | ||
| fadv/% | 96.1 | 83.7 | ||
| Upwind Station | Target Station | Month | ftr/% | fev/% | fadv/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Renshoushan | Anning | June | 7.4 | 5.2 | 87.4 |
| July | 32.0 | 6.4 | 61.6 | ||
| August | 24.4 | 0.3 | 75.3 | ||
| LREVC | June | 0.2 | 5.2 | 84.6 | |
| July | 4.0 | 7.9 | 88.1 | ||
| August | 13.9 | 6.2 | 79.9 | ||
| Yuzhong | June | 5.4 | 3.1 | 91.5 | |
| July | 15.0 | 4.0 | 81.0 | ||
| August | 34.2 | 2.1 | 63.7 | ||
| Yongdeng | Daheng | June | 33.6 | 4.7 | 61.7 |
| July | 30.5 | 4.5 | 65.5 | ||
| August | 14.5 | 4.0 | 81.5 | ||
| Gaolan | June | 11.3 | 3.4 | 85.3 | |
| July | 20.9 | 5.8 | 73.3 | ||
| August | 16.0 | 1.7 | 82.3 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, F.; Zhang, M.; Wu, X.; Wang, S.; Argiriou, A.A.; Zhou, X.; Chen, J. A Stable Isotope Approach for Estimating the Contribution of Recycled Moisture to Precipitation in Lanzhou City, China. Water 2021, 13, 1783. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13131783
Chen F, Zhang M, Wu X, Wang S, Argiriou AA, Zhou X, Chen J. A Stable Isotope Approach for Estimating the Contribution of Recycled Moisture to Precipitation in Lanzhou City, China. Water. 2021; 13(13):1783. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13131783
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Fenli, Mingjun Zhang, Xixi Wu, Shengjie Wang, Athanassios A. Argiriou, Xin Zhou, and Jufan Chen. 2021. "A Stable Isotope Approach for Estimating the Contribution of Recycled Moisture to Precipitation in Lanzhou City, China" Water 13, no. 13: 1783. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13131783
APA StyleChen, F., Zhang, M., Wu, X., Wang, S., Argiriou, A. A., Zhou, X., & Chen, J. (2021). A Stable Isotope Approach for Estimating the Contribution of Recycled Moisture to Precipitation in Lanzhou City, China. Water, 13(13), 1783. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13131783









