Current Progress on Marine Microplastics Pollution Research: A Review on Pollution Occurrence, Detection, and Environmental Effects
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Identification and Quantification of Microplastics
3. Source and Distribution of Microplastics
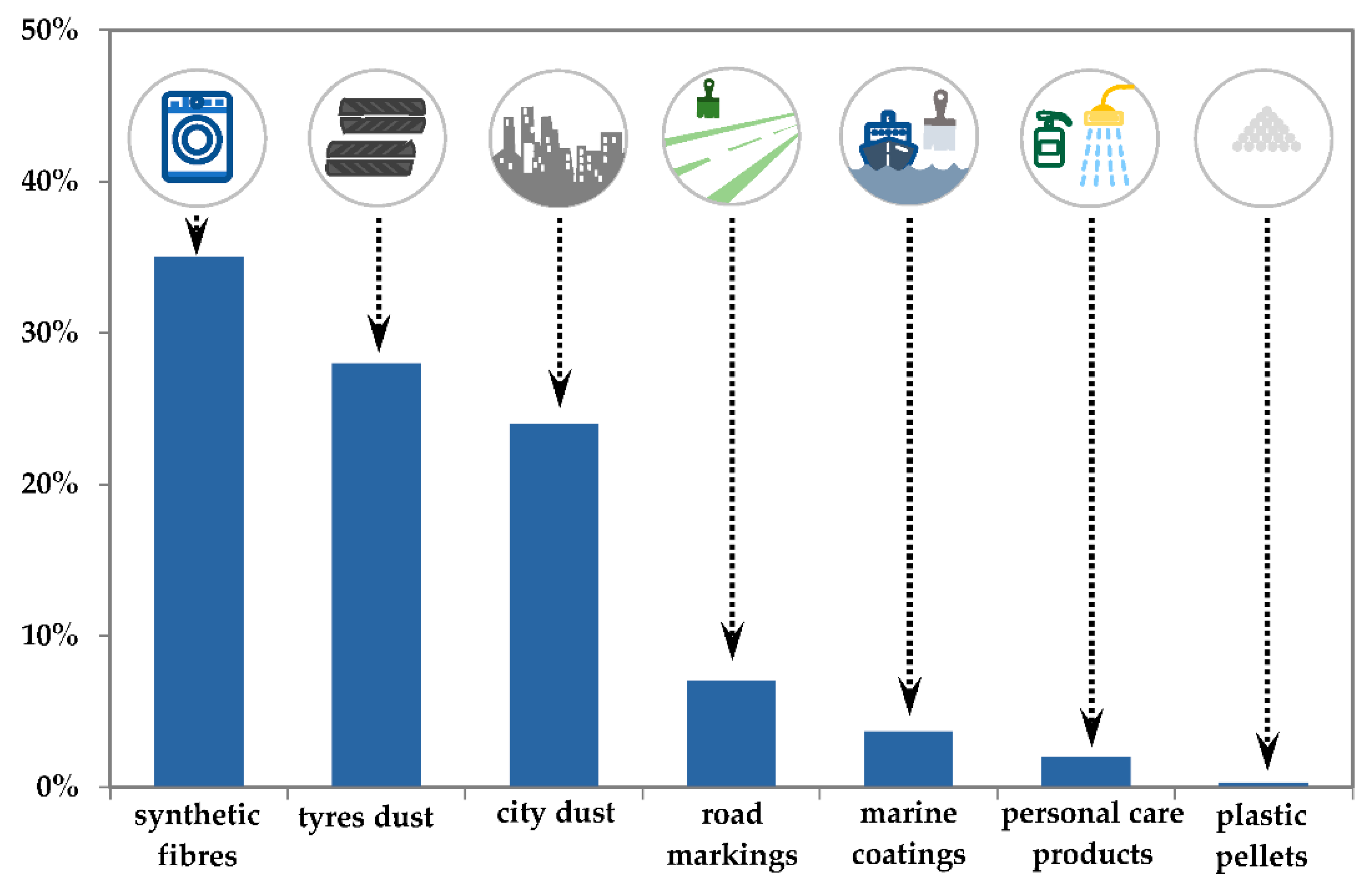
3.1. Source of Microplastics
3.2. Distribution and Abundance of Microplastics
| Regions | Sample Method | Identification Method | Microplastics Type | Microplastics Composition | Abundance | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Northwestern Mediterranean Sea | >333 μm | Microscopy | Filaments and films | PS | 0.116 particles/m2 | [26] |
| Central–western Mediterranean Sea | >200 μm | Microscopy + ATR FTIR | Fragments (93.2%), pellets (2.2%), films (1.6%), and foams (3.1%) | PE (52%), PP (16%), PA (4.7%), PVC (2.6%), PS (2.8%), PVA (1.2%), and paints (7.7%) | 1.25 particles/m2 | [50] |
| Northeast Levantine coast, Turkey | >333 μm | Microscopy | Fragments (60.1%), films (29.8%), filaments (7.3%), foams (2.7%), and granules (0.1%) | -- | 0.376 particles/m2 | [52] |
| Atlantic Ocean | >250 μm | Microscopy + FTIR | Fibers (94%) and fragments | PES (49%), PA or acrylic/PES (43%) | 1.15 particles/m3 | [61] |
| Bay of Brest, France | >335 μm | Microscopy + Raman | Fragments (53%), fibers (25%), foams (11%), films (8%) and pellets (3%) | PE (67.4%), PP (16.5%) and PS (16.1%) | 0.24 particles/m3 | [51] |
| San Francisco Bay | >333 μm | Microscopy | Central Bay: Fragment (34%), fiber (48%), pellet (1%), foam (5%) and film (1%); Southern Bay: Fragment (60%), fiber (22%), pellet (2%), foam (9%) and film (7%) | -- | 7.0 × 105 particles/km2 | [53] |
| Stockholm Archipelago, Baltic Sea | >335 μm | Microscopy + FTIR | Fibers (82%) and fragments | PE (24%), PP (53%), and PS (5%) | 4.2 × 105 particles/km2 | [54] |
| South Pacific subtropical gyre | >333 μm | Microscopy | Fragment (79%), pellet (2%), line (14%), and film (5%) | 2.69 × 104 particles/km2 | [28] | |
| North Atlantic subtropical gyre | >10 μm | Microscopy + Raman | Fibers (40%) and particles | PE (42%), PP (6%), PS (4%), PA (11%), PU (3%), PVC (1.8%), and PES (6%) | 13–501 particles/m3 | [25] |
| South Korea coastal areas | >20 μm | Microscopy + μ-FTIR | Fragments (81%) and fibers (18%) | PP and PE | 10–2000 particles/m3 | [55] |
| Goiana Estuary, Brazil | >45 μm | Microscopy | Soft plastic (41.08%), paint chips (29.11%), hard plastic (28.42%), and threads (1.4%) | -- | 0.26 particles/m3 | [70] |
| Sediment of Chang Jiang Estuary, China | -- | Microscopy + μ-FTIR | Fibers (93%), fragments (6%), and pellets (1%) | Rayon (63.1%), PES (18.5%), and acrylic (13.9%) | 121 particles/kg d.w. | [62] |
| Sediment of Lagoon of Venice, Italy | >32 μm | μ-FTIR + ESEM-EDS | Fragments (86%), fibers (11%), films (2%), and pellets/granules (1%) | PE, PP, and PS | 672–2175 particles/kg d.w. | [27] |
| Sediment of Bay of Brest, France | >335 μm | Microscopy + Raman | Fragments (71%), fibers (21%), and films (8%) | PE (53.3%), PP (30%), and PS (16.7%) | 0.97 particles/kg d.w. | [51] |
| Sediment of Belgian coast | >38 μm | Microscopy + FTIR | Fibers (59%), granules (25%), films (4%), and spherules (12%) | PP, PS, nylon, PVA, and PE | 390 particles/kg d.w. | [63] |
| Sediment of North Atlantic Ocean | >35 μm | Microscopy + μ-Raman | Particles | PE and PP | 3 particles/25 cm3 | [71] |
| Subalpine Lake Garda, Italy | >2.2 μm | Raman | -- | PE (33%), PS (33%), PP (25%), and PA (8%) | 75 particles/m2 | [6] |
| Lake Hovsgol, Mongolia | >333 μm | Microscopy | Fragment (40%), foam (38%), line/fiber (20%), pellet (1%), and film (1%) | -- | 2.0 × 104 particles/km2 | [56] |
| Lake Winnipeg, Canada | >333 μm | Microscopy + SEM-EDS | Fibers (>90%), films, and foam | -- | 1.93 × 105 particles/km2 | [57] |
| Kenkäveronniemi WWTPs, Finland | >250 μm | Microscopy + FTIR + Raman | Fibers (82.8%) and particles (11.4%) | PES (79.1%), PE (11.4%), and PA (3.7%) | Influent: 57.6 × 103 particles/m3 Effluent: 1.0 × 103 particles/m3 | [58] |
| WWTPs in Sydney, Australia | >25 μm | Microscopy + ATR-FTIR | PE, PET, Nylon, PP, PS, PVC | -- | Effluent: 1.5 × 103 particles/m3 | [60] |
| WWTPs in Glasgow, Scotland | >65 μm | Microscopy + FTIR | Flakes (67.3%), fibers (18.5%), film (9.9%), beads (3.0%), and foam (1.3%) | PES (28%), PA (20%), PP (12%), acrylic (12%), alkyd (8%), PE (4%), PS (4%), and PET (4%) | Influent: 15.7 × 103 particles/m3 Effluent: 0.25 × 103 particles/m3 | [11] |
| WWTPs in Lower Saxony, German | >10 μm | Microscopy + FTIR | -- | PP, PE, and PA | Effluent: 9 × 103 particles/m3 | [59] |
| Shark Galeus melastomus from western Mediterranean Sea | Filed study | Microscopy + FTIR | Filaments (86.36%), fragments (12.12%), and film (1.51%) | CP (33.33%), PET (27.27%), PP (12.12%), and polyacrylate (12.12%) | 0.34 ± 0.07 particles/individual | [64] |
| Fishes in Sydney Harbour, Australia | Filed study | Microscopy + ATR-FTIR | Fibers (83%) and granules (17%) | acrylic, PES, and rayon | 0.2–4.6 particles/individual | [65] |
| Hymenaster pellucidus from North Atlantic Ocean | Filed study | Microscopy + ATR-FTIR | Fibers (87%) and fragments (13%) | acrylic | 1.62 ± 0.9 particles/gram tissue | [72] |
| Shrimp Aristeus antennatus from northwestern Mediterranean Sea | Filed study | Microscopy + FTIR | Fibers | PET (57.1%), PA (28.6%), and rayon (14.3%) | -- | [73] |
| Molluscs from the Persian Gulf, Iran | Filed study | Microscopy + FTIR | Microfibers (>50%), fragments (26%), films (14%), and pellets (2%) | PE, PET, and nylon | 3.7–17.7 particles/individual | [67] |
| Mussels Mytilus edulis from UK | Filed study | Microscopy + μ-FTIR | Mostly fibers and a small number of fragments | PP and PES | 1.1–6.4 particles/individual | [66] |
| Cultured oysters from China | Filed study | Microscopy + μ-FTIR | Fibers (60.67%), fragments (19.95%), films (10.26%), and pellets (9.11%) | CP (41.34%), PE (22.97%), PET(15.19%), PP (9.89%), PA (4.95%), PS (2.47%), PC (1.77%), and PVC (1.41%) | 2.93 particles/individual | [69] |
| Cultured sea cucumbers from China | Filed study | Microscopy + μ-FTIR | Fibers, fragments, and pellets | CP | 10 particles/individual | [68] |
4. Fate and Effects of Microplastics in the Marine Environment
4.1. Effects of Microplastics on Marine Organisms
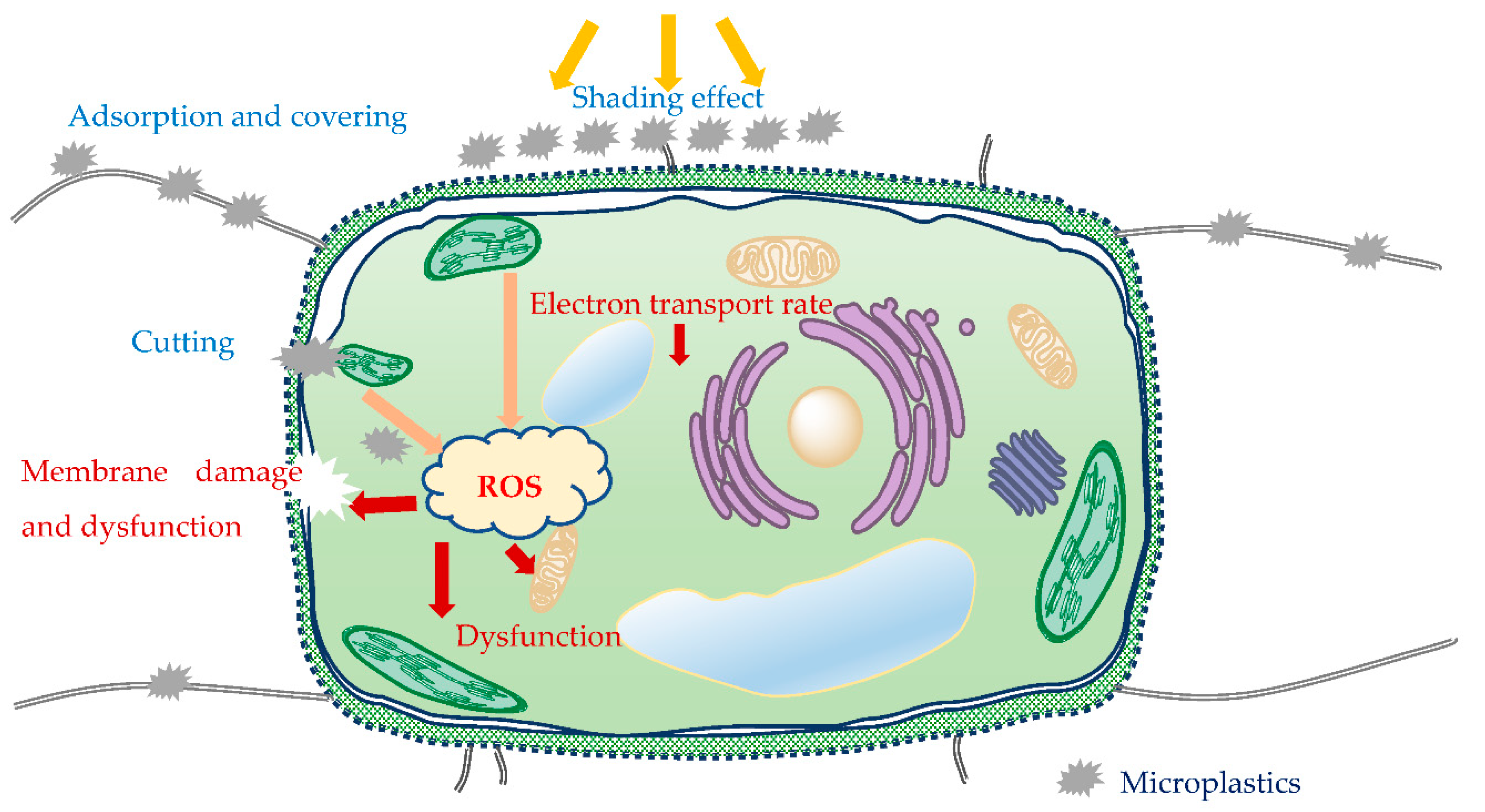
4.2. Toxic Effects of Microplastics on Marine Microalgae
4.3. Trophic Transfer of Microplastics in Marine Food Webs
4.4. Joint Toxicity of Microplastics with Other Chemicals
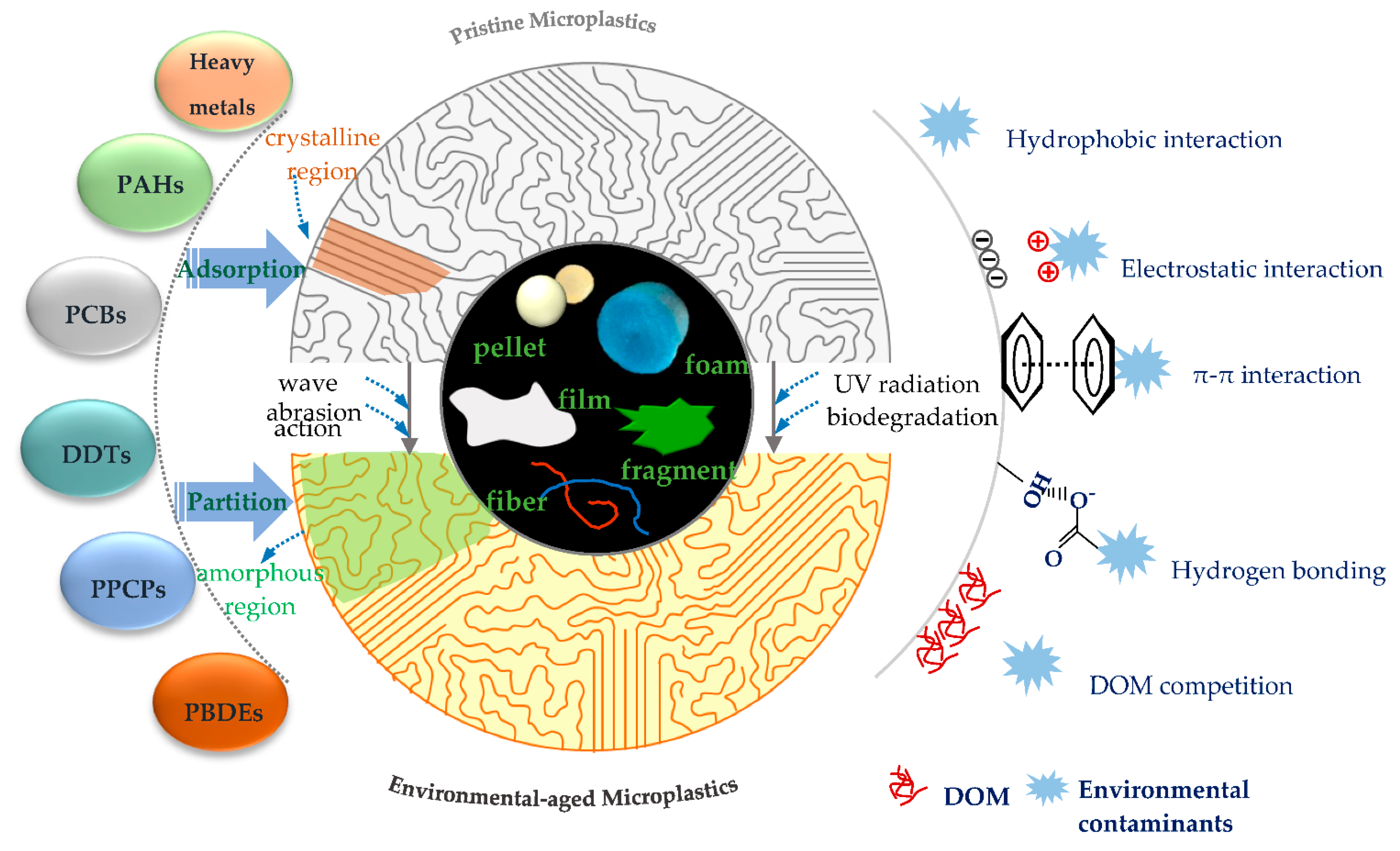
4.5. The Interactions between Microplastics and Contaminants
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- The current methods for the sampling and identification of microplastics need to be standardized. Efficient and adequate methods should be developed for the in-situ detection of microplastics.
- (2)
- Although we have gained some information on the distribution and abundance of microplastics, it is still not sufficient for the global regions. More survey studies are still needed to enrich the database of microplastics pollution.
- (3)
- As an important source for marine microplastics, investigation on the terrestrial pollution is not enough, especially for the WWTPs that we pointed out previously. Thus, the fate and transport of microplastics in WWTPs needs further study, and the microplastics-targeted treatment methods urgently need to be developed for reducing the amount of microplastics released from WWTPs to the environment.
- (4)
- There are not yet adequate studies on the impact of microplastics to microalgae, the marine environmental producer, which still need more research from the population level to the genetic level. In addition to the low trophic level organisms, the potential transfer of microplastics and the related contaminants from seafood products to human should also be carefully evaluated.
- (5)
- Considering the role of microplastics as vectors to transport pollutants, the chemicals adsorbed on environmentally collected microplastics should be analyzed to explore the formation of the microplastics–contaminants complex. Systematic studies are also needed to clarify the adsorption and desorption mechanisms of various chemicals on microplastics.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Andrady, A.L.; Neal, M.A. Applications and societal benefits of plastics. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. B Biol. Sci. 2009, 364, 1977–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hopewell, J.; Dvorak, R.; Kosior, E. Plastics recycling: Challenges and opportunities. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. B Biol. Sci. 2009, 364, 2115–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaposi, K.L.; Mos, B.; Kelaher, B.; Dworjanyn, S. Ingestion of microplastic has limited impact on a marine larva. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 1638–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Horton, A.A.; Walton, A.; Spurgeon, D.J.; Lahive, E.; Svendsen, C. Microplastics in freshwater and terrestrial environments: Evaluating the current understanding to identify the knowledge gaps and future research priorities. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 586, 127–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McCormick, A.; Hoellein, T.J.; Mason, S.A.; Schluep, J.; Kelly, J. Microplastic is an abundant and distinct microbial habitat in an urban river. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 11863–11871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imhof, H.K.; Laforsch, C.; Wiesheu, A.C.; Schmid, J.; Anger, P.M.; Niessner, R.; Ivleva, N.P. Pigments and plastic in limnetic ecosystems: A qualitative and quantitative study on microparticles of different size classes. Water Res. 2016, 98, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verster, C.; Minnaar, K.; Bouwman, H. Marine and freshwater microplastic research in South Africa. Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2017, 13, 533–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imhof, H.; Ivleva, N.P.; Schmid, J.; Niessner, R.; Laforsch, C. Contamination of beach sediments of a subalpine lake with microplastic particles. Curr. Biol. 2013, 23, R867–R868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schoof, R.A.; DeNike, J. Microplastics in the context of regulation of commercial shellfish aquaculture operations. Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2017, 13, 522–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Wang, J.; Cai, L. Current understanding of microplastics in the environment: Occurrence, fate, risks, and what we should do. Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2017, 13, 476–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, F.; Ewins, C.; Carbonnier, F.; Quinn, B. Wastewater treatment works (WwTW) as a source of microplastics in the aquatic environment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 5800–5808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Betts, K. Why small plastic particles may pose a big problem in the oceans. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 8995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladewig, S.; Bao, S.; Chow, A.T. Natural fibers: A missing link to chemical pollution dispersion in aquatic environments. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 12609–12610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidalgo-Ruz, V.; Gutow, L.; Thompson, R.C.; Thiel, M. Microplastics in the marine environment: A review of the methods used for identification and quantification. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 3060–3075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, M.; Lindeque, P.; Fileman, E.; Halsband, C.; Goodhead, R.; Moger, J.; Galloway, T.S. Microplastic ingestion by zooplankton. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 6646–6655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, P.K.; Hakkarainen, M.; Varma, I.K.; Albertsson, A.-C. Degradable polyethylene: Fantasy or reality. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 4217–4227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartmann, N.B.; Rist, S.; Bodin, J.; Jensen, L.H.S.; Schmidt, S.N.; Mayer, P.; Meibom, A.; Baun, A. Microplastics as vectors for environmental contaminants: Exploring sorption, desorption, and transfer to biota. Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2017, 13, 488–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gray, A.D.; Weinstein, J.E. Size- and shape-dependent effects of microplastic particles on adult daggerblade grass shrimp (Palaemonetes pugio). Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2017, 36, 3074–3080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghi, B.N.; Banaee, M. Effects of micro-plastic particles on paraquat toxicity to common carp (Cyprinus carpio): Biochemical changes. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2017, 14, 521–530. [Google Scholar]
- Kolandhasamy, P.; Su, L.; Li, J.; Qu, X.; Jabeen, K.; Shi, H. Adherence of microplastics to soft tissue of mussels: A novel way to uptake microplastics beyond ingestion. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 610–611, 635–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, F.; Garcia, A.R.; Pereira, B.P.; Fonseca, M.; Mestre, N.C.; Fonseca, T.G.; Ilharco, L.; Bebianno, M.J. Microplastics effects in Scrobicularia plana. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 122, 379–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.-Y.; Hu, X.-L.; Cheng, J.; Ma, Z.-X.; Gao, K. Growth inhibition and oxidative stress induced by 1-octyl-3-methylimidazolium bromide on the marine diatom Skeletonema costatum. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2016, 132, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, J.H.; Chang, S.; Hong, S.H.; Shim, W.J. Microplastics as a vector of hydrophobic contaminants: Importance of hydrophobic additives. Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2017, 13, 494–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esiukova, E. Plastic pollution on the Baltic beaches of Kaliningrad region, Russia. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 114, 1072–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enders, K.; Lenz, R.; Stedmon, C.A.; Nielsen, T.G. Abundance, size and polymer composition of marine microplastics ≥10μm in the Atlantic Ocean and their modelled vertical distribution. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 100, 70–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collignon, A.; Hecq, J.-H.; Galgani, F.; Voisin, P.; Collard, F.; Goffart, A. Neustonic microplastic and zooplankton in the North Western Mediterranean Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2012, 64, 861–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vianello, A.; Boldrin, A.; Guerriero, P.; Moschino, V.; Rella, R.; Sturaro, A.; Da Ros, L. Microplastic particles in sediments of Lagoon of Venice, Italy: First observations on occurrence, spatial patterns and identification. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2013, 130, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksen, M.; Maximenko, N.; Thiel, M.; Cummins, A.; Lattin, G.; Wilson, S.; Hafner, J.; Zellers, A.; Rifman, S. Plastic pollution in the South Pacific subtropical gyre. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2013, 68, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potthoff, A.; Oelschlägel, K.; Schmitt-Jansen, M.; Rummel, C.D.; Kühnel, D. From the sea to the laboratory: Characterization of microplastic as prerequisite for the assessment of ecotoxicological impact. Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2017, 13, 500–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisner, M.; Majer, A.P.; Balthazar-Silva, D.; Gorman, D.; Turra, A. Quantifying microplastic pollution on sandy beaches: The conundrum of large sample variability and spatial heterogeneity. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 13732–13740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Käppler, A.; Fischer, D.; Oberbeckmann, S.; Schernewski, G.; Labrenz, M.; Eichhorn, K.-J.; Voit, B. Analysis of environmental microplastics by vibrational microspectroscopy: FTIR, Raman or both? Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2016, 408, 8377–8391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oßmann, B.E.; Sarau, G.; Schmitt, S.W.; Holtmannspötter, H.; Christiansen, S.; Dicke, W. Development of an optimal filter substrate for the identification of small microplastic particles in food by micro-Raman spectroscopy. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2017, 409, 4099–4109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fries, E.; Dekiff, J.H.; Willmeyer, J.; Nuelle, M.-T.; Ebert, M.; Remy, D. Identification of polymer types and additives in marine microplastic particles using pyrolysis-GC/MS and scanning electron microscopy. Environ. Sci. Proc. Impacts 2013, 15, 1949–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fischer, M.; Scholz-Böttcher, B.M. Simultaneous trace identification and quantification of common types of microplastics in environmental samples by pyrolysis-gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 5052–5060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dümichen, E.; Barthel, A.-K.; Braun, U.; Bannick, C.G.; Brand, K.; Jekel, M.; Senz, R. Analysis of polyethylene microplastics in environmental samples, using a thermal decomposition method. Water Res. 2015, 85, 451–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, J.; Hou, S.; Sun, H. A simple method for quantifying polycarbonate and polyethylene terephthalate microplastics in environmental samples by liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2017, 4, 530–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boucher, J.; Friot, D. Primary Microplastics in the Oceans: A global Evaluation of Sources; IUCN: Gland, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Carr, S.A. Sources and dispersive modes of micro-fibers in the environment. Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2017, 13, 466–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesa, F.S.; Turra, A.; Baruque-Ramos, J. Synthetic fibers as microplastics in the marine environment: A review from textile perspective with a focus on domestic washings. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 598, 1116–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rochman, C.M.; Kross, S.M.; Armstrong, J.B.; Bogan, M.T.; Darling, E.S.; Green, S.J.; Smyth, A.R.; Veríssimo, D. Scientific evidence supports a ban on microbeads. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 10759–10761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Carr, S.A.; Liu, J.; Tesoro, A.G. Transport and fate of microplastic particles in wastewater treatment plants. Water Res. 2016, 91, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jambeck, J.R.; Geyer, R.; Wilcox, C.; Siegler, T.R.; Perryman, M.; Andrady, A.; Narayan, R.; Law, K.L. Plastic waste inputs from land into the ocean. Science 2015, 347, 768–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liu, H.; Chen, J.P. Microplastics in freshwater systems: A review on occurrence, environmental effects, and methods for microplastics detection. Water Res. 2018, 137, 362–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welden, N.A.; Cowie, P.R. Degradation of common polymer ropes in a sublittoral marine environment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 118, 248–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andrady, A.L. Microplastics in the marine environment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 62, 1596–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.K.; Hong, S.H.; Jang, M.; Han, G.M.; Jung, S.W.; Shim, W.J. Combined effects of UV exposure duration and mechanical abrasion on microplastic fragmentation by polymer type. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 4368–4376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davidson, T.M. Boring crustaceans damage polystyrene floats under docks polluting marine waters with microplastic. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2012, 64, 1821–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welden, N.A.; Lusher, A.L. Impacts of changing ocean circulation on the distribution of marine microplastic litter. Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2017, 13, 483–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Auta, H.S.; Emenike, C.U.; Fauziah, S.H. Distribution and importance of microplastics in the marine environment: A review of the sources, fate, effects, and potential solutions. Environ. Int. 2017, 102, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suaria, G.; Avio, C.G.; Mineo, A.; Lattin, G.L.; Magaldi, M.G.; Belmonte, G.; Moore, C.J.; Regoli, F.; Aliani, S. The Mediterranean plastic soup: Synthetic polymers in Mediterranean surface waters. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 37551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Frère, L.; Paul-Pont, I.; Rinnert, E.; Petton, S.; Jaffré, J.; Bihannic, I.; Soudant, P.; Lambert, C.; Huvet, A. Influence of environmental and anthropogenic factors on the composition, concentration and spatial distribution of microplastics: A case study of the Bay of Brest (Brittany, France). Environ. Pollut. 2017, 225, 211–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gündoğdu, S.; Çevik, C. Micro- and mesoplastics in Northeast Levantine coast of Turkey: The preliminary results from surface samples. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 118, 341–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton, R.; Mason, S.A.; Stanek, S.K.; Willis-Norton, E.; Wren, I.F.; Box, C. Microplastic contamination in the San Francisco Bay, California, USA. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 109, 230–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gewert, B.; Ogonowski, M.; Barth, A.; MacLeod, M. Abundance and composition of near surface microplastics and plastic debris in the Stockholm Archipelago, Baltic Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 120, 292–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.K.; Hong, S.H.; Eo, S.; Jang, M.; Han, G.M.; Isobe, A.; Shim, W.J. Horizontal and vertical distribution of microplastics in Korean coastal waters. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 12188–12197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Free, C.M.; Jensen, O.P.; Mason, S.A.; Eriksen, M.; Williamson, N.J.; Boldgiv, B. High-levels of microplastic pollution in a large, remote, mountain lake. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 85, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, P.J.; Warrack, S.; Langen, V.; Challis, J.K.; Hanson, M.L.; Rennie, M.D. Microplastic contamination in Lake Winnipeg, Canada. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 225, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lares, M.; Ncibi, M.C.; Sillanpää, M.; Sillanpää, M. Occurrence, identification and removal of microplastic particles and fibers in conventional activated sludge process and advanced MBR technology. Water Res. 2018, 133, 236–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mintenig, S.; Int-Veen, I.; Löder, M.; Primpke, S.; Gerdts, G. Identification of microplastic in effluents of waste water treatment plants using focal plane array-based micro-Fourier-transform infrared imaging. Water Res. 2017, 108, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziajahromi, S.; Neale, P.A.; Rintoul, L.; Leusch, F.D.L. Wastewater treatment plants as a pathway for microplastics: Development of a new approach to sample wastewater-based microplastics. Water Res. 2017, 112, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanhai, L.D.K.; Officer, R.; Lyashevska, O.; Thompson, R.C.; O’Connor, I. Microplastic abundance, distribution and composition along a latitudinal gradient in the Atlantic Ocean. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 115, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, G.; Zhu, B.; Yang, D.; Su, L.; Shi, H.; Li, D. Microplastics in sediments of the Changjiang Estuary, China. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 225, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claessens, M.; Meester, S.D.; Landuyt, L.V.; Clerck, K.D.; Janssen, C.R. Occurrence and distribution of microplastics in marine sediments along the Belgian coast. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 62, 2199–2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alomar, C.; Deudero, S. Evidence of microplastic ingestion in the shark Galeus melastomus Rafinesque, 1810 in the continental shelf off the western Mediterranean Sea. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 223, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halstead, J.E.; Smith, J.A.; Carter, E.A.; Lay, P.A.; Johnston, E.L. Assessment tools for microplastics and natural fibres ingested by fish in an urbanised estuary. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 234, 552–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Green, C.; Reynolds, A.; Shi, H.; Rotchell, J.M. Microplastics in mussels sampled from coastal waters and supermarkets in the United Kingdom. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 241, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naji, A.; Nuri, M.; Vethaak, A.D. Microplastics contamination in molluscs from the northern part of the Persian Gulf. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 235, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohsen, M.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, L.; Sun, L.; Lin, C.; Yang, H. Microplastic ingestion by the farmed sea cucumber Apostichopus japonicus in China. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 245, 1071–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, J.; Wang, Q.; Ran, W.; Wu, D.; Liu, Y.; Sun, S.; Liu, H.; Cao, R.; Zhao, J. Microplastic in cultured oysters from different coastal areas of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 653, 1282–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, A.R.A.; Costa, M.F.; Barletta, M. Distribution patterns of microplastics within the plankton of a tropical estuary. Environ. Res. 2014, 132, 146–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Cauwenberghe, L.; Vanreusel, A.; Mees, J.; Janssen, C.R. Microplastic pollution in deep-sea sediments. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 182, 495–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courtene-Jones, W.; Quinn, B.; Gary, S.F.; Mogg, A.O.; Narayanaswamy, B.E. Microplastic pollution identified in deep-sea water and ingested by benthic invertebrates in the Rockall Trough, North Atlantic Ocean. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 231, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Carreras-Colom, E.; Constenla, M.; Soler-Membrives, A.; Cartes, J.E.; Baeza, M.; Padrós, F.; Carrassón, M. Spatial occurrence and effects of microplastic ingestion on the deep-water shrimp Aristeus antennatus. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 133, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canniff, P.M.; Hoang, T.C. Microplastic ingestion by Daphnia magna and its enhancement on algal growth. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 633, 500–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cole, M.; Galloway, T.S. Ingestion of nanoplastics and microplastics by Pacific oyster larvae. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 14625–14632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ory, N.C.; Gallardo, C.; Lenz, M.; Thiel, M. Capture, swallowing, and egestion of microplastics by a planktivorous juvenile fish. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 240, 566–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ašmonaitė, G.; Sundh, H.; Asker, N.; Almroth, B.M.C. Rainbow trout maintain intestinal transport and barrier functions following exposure to polystyrene microplastics. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 14392–14401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawson, A.; Huston, W.; Kawaguchi, S.; King, C.; Cropp, R.; Wild, S.; Eisenmann, P.; Townsend, K.; Bengtson Nash, S. Uptake and depuration kinetics influence microplastic bioaccumulation and toxicity in Antarctic krill (Euphausia superba). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 3195–3201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, M.; Lindeque, P.; Fileman, E.; Halsband, C.; Galloway, T.S. The impact of polystyrene microplastics on feeding, function and fecundity in the marine copepod Calanus helgolandicus. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 1130–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.-W.; Shim, W.J.; Kwon, O.Y.; Kang, J.-H. Size-dependent effects of micro polystyrene particles in the marine copepod Tigriopus japonicus. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 11278–11283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardon, T.; Reisser, C.; Soyez, C.; Quillien, V.; Le Moullac, G. Microplastics affect energy balance and gametogenesis in the pearl oyster Pinctada margaritifera. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 5277–5286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Von Moos, N.; Burkhardt-Holm, P.; Köhler, A. Uptake and effects of microplastics on cells and tissue of the blue mussel Mytilus edulis L. after an experimental exposure. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 11327–11335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Deng, Y.; Jiang, W.; Zhao, Y.; Geng, J.; Ding, L.; Ren, H. Uptake and accumulation of polystyrene microplastics in zebrafish (Danio rerio) and toxic effects in liver. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 4054–4060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, C.-B.; Won, E.-J.; Kang, H.-M.; Lee, M.-C.; Hwang, D.-S.; Hwang, U.-K.; Zhou, B.; Souissi, S.; Lee, S.-J.; Lee, J.-S. Microplastic size-dependent toxicity, oxidative stress induction, and p-JNK and p-p38 activation in the monogonont rotifer (Brachionus koreanus). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 8849–8857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Ni, X.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, L.; Lin, S. Acute microplastic exposure raises stress response and suppresses detoxification and immune capacities in the scleractinian coral Pocillopora damicornis. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 243, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watts, A.J.R.; Urbina, M.M.A.; Goodhead, R.M.; Moger, J.; Lewis, C.; Galloway, T.S. Effect of microplastic on the gills of the shore crab Carcinus maenas. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 5364–5369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Della Torre, C.; Bergami, E.; Salvati, A.; Faleri, C.; Cirino, P.; Dawson, K.A.; Corsi, I. Accumulation and embryotoxicity of polystyrene nanoparticles at early stage of development of sea urchin embryos Paracentrotus lividus. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 12302–12311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, L.; Wang, X.; Zheng, H.; Liu, L.; Luo, X.; Li, F. Differential toxicity of functionalized polystyrene microplastics to clams (Meretrix meretrix) at three key development stages of life history. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 139, 346–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Chae, Y.; An, Y.-J. Mixture toxicity of nickel and microplastics with different functional groups on Daphnia magna. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 12852–12858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Hu, Y.; Cheng, H.; Tao, S. Releases of brominated flame retardants (BFRs) from microplastics in aqueous medium: Kinetics and molecular-size dependence of diffusion. Water Res. 2019, 151, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.-X.; Getzinger, G.J.; Ferguson, P.L.; Orihuela, B.; Zhu, M.; Rittschof, D. Effects of toxic leachate from commercial plastics on larval survival and settlement of the barnacle Amphibalanus amphitrite. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 924–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliviero, M.; Tato, T.; Schiavo, S.; Fernández, V.; Manzo, S.; Beiras, R. Leachates of micronized plastic toys provoke embryotoxic effects upon sea urchin Paracentrotus lividus. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 247, 706–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobre, C.R.; Santana, M.; Maluf, A.; Cortez, F.; Cesar, A.; Pereira, C.; Turra, A. Assessment of microplastic toxicity to embryonic development of the sea urchin Lytechinus variegatus (Echinodermata: Echinoidea). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 92, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gandara e Silva, P.P.; Nobre, C.R.; Resaffe, P.; Pereira, C.D.S.; Gusmão, F. Leachate from microplastics impairs larval development in brown mussels. Water Res. 2016, 106, 364–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coffin, S.; Dudley, S.; Taylor, A.; Wolf, D.; Wang, J.; Lee, I.; Schlenk, D. Comparisons of analytical chemistry and biological activities of extracts from North Pacific gyre plastics with UV-treated and untreated plastics using in vitro and in vivo models. Environ. Int. 2018, 121, 942–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.; Gao, P.; Li, H.; Huang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Ding, H.; Zhang, W. Mechanism of the inhibition and detoxification effects of the interaction between nanoplastics and microalgae Chlorella pyrenoidosa. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 783, 146919–146929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Zhao, W.; Chen, X.; Zhao, T.; Tan, L.; Wang, J. Growth inhibition of the microalgae Skeletonema costatum under copper nanoparticles with microplastic exposure. Mar. Environ. Res. 2020, 158, 105005–105011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wangjin, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, N.; Wang, Y.; Meng, G.; Chen, Y. The toxicity of virgin and UV-aged PVC microplastics on the growth of freshwater algae Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 749, 141603–141609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Chen, X.H.; Wang, J.T.; Tan, L.J. Toxic effects of microplastic on marine microalgae Skeletonema costatum: Interactions between microplastic and algae. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 220, 1282–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Tan, L.J.; Huang, W.Q.; Wang, J.T. The interactions between micro polyvinyl chloride (mPVC) and marine dinoflagellate Karenia mikimotoi: The inhibition of growth, chlorophyll and photosynthetic efficiency. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 247, 883–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Tan, L.; Zhu, X.; Huang, W.; Wang, J. Size-dependent oxidative stress effect of nano/micro-scaled polystyrene on Karenia mikimotoi. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 154, 111074–111084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.; Gao, X.; Wu, Y.; Wan, L.; Tan, L.; Yuan, S.; Ding, H.; Zhang, W. The combined toxicity influence of microplastics and nonylphenol on microalgae Chlorella pyrenoidosa. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 195, 110484–110493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjollema, S.B.; Redondo-Hasselerharm, P.; Leslie, H.A.; Kraak, M.H.; Vethaak, A.D. Do plastic particles affect microalgal photosynthesis and growth? Aquat. Toxicol. 2016, 170, 259–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Fernández, C.; Toullec, J.; Lambert, C.; Le Goïc, N.; Seoane, M.; Moriceau, B.; Huvet, A.; Berchel, M.; Vincent, D.; Courcot, L.; et al. Do transparent exopolymeric particles (TEP) affect the toxicity of nanoplastics on Chaetoceros neogracile? Environ. Pollut. 2019, 250, 873–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Zhang, W.; Yuan, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, X.; Fan, Z. Growth inhibition, toxin production and oxidative stress caused by three microplastics in Microcystis aeruginosa. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 208, 111575–111583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prata, J.C.; Lavorante, B.R.; Montenegro, M.D.; Guilhermino, C.B.; Guilhermino, L. Influence of microplastics on the toxicity of the pharmaceuticals procainamide and doxycycline on the marine microalgae Tetraselmis chuii. Aquat. Toxicol. 2018, 197, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Z.-L.; Wang, S.-C.; Zhao, F.-F.; Wang, S.-G.; Liu, F.-F.; Liu, G.-Z. Joint toxicity of microplastics with triclosan to marine microalgae Skeletonema costatum. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 246, 509–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, X.; Chi, T.; Li, Z.; Wang, J.; Yu, M.; Wu, M.; Zhou, H. Combined effect of polystyrene plastics and triphenyltin chloride on the green algae Chlorella pyrenoidosa. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 15011–15018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wang, Y.; Liang, Y.; Cao, W.; Sun, C.; Ju, P.; Zheng, L. The interactions between microplastic polyvinyl chloride and marine diatoms: Physiological, morphological, and growth effects. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 203, 111000–111007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, C.; Liu, Z.; Wang, C.; Li, S.; Kitamura, Y. Different interaction performance between microplastics and microalgae: The bio-elimination potential of Chlorella sp. L38 and Phaeodactylum tricornutum MASCC-0025. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 723, 138146–138155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Liang, Z.; Zheng, X.; Zhao, W.; Wu, M.; Wang, Z. Toxicity of nano-TiO2 on algae and the site of reactive oxygen species production. Aquat Toxicol 2015, 158, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Chen, X.; Wang, J.; Tan, L. Toxicity of zinc oxide nanoparticles on marine microalgae possessing different shapes and surface structures. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2018, 35, 785–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Ouyang, S.; Mu, L.; An, J.; Zhou, Q. Effects of graphene oxide and oxidized carbon nanotubes on the cellular division, microstructure, uptake, oxidative stress, and metabolic profiles. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 10825–10833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawson, A.L.; Kawaguchi, S.; King, C.K.; Townsend, K.A.; King, R.; Huston, W.M.; Bengtson Nash, S.M. Turning microplastics into nanoplastics through digestive fragmentation by Antarctic krill. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Costa, J.P.; Santos, P.S.; Duarte, A.; Rocha-Santos, T. (Nano)plastics in the environment—Sources, fates and effects. Sci Total Environ. 2016, 566–567, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nichols, E.C.; Lavers, J.L.; Archer-Rand, S.; Bond, A.L. Assessing plastic size distribution and quantity on a remote island in the South Pacific. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 167, 112366–112374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llorca, M.; Vega-Herrera, A.; Schirinzi, G.; Savva, K.; Abad, E.; Farré, M. Screening of suspected micro(nano)plastics in the Ebro Delta (Mediterranean Sea). J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 404, 124022–124030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwab, F.; Bucheli, T.D.; Lukhele, L.P.; Magrez, A.; Nowack, B.; Sigg, L.; Knauer, K. Are carbon nanotube effects on green algae caused by shading and agglomeration? Environ. Sci Technol. 2011, 45, 6136–6144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aruoja, V.; Dubourguier, H.-C.; Kasemets, K.; Kahru, A. Toxicity of nanoparticles of CuO, ZnO and TiO2 to microalgae Pseudokirchneriella subcapitata. Sci. Total. Environ. 2009, 407, 1461–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.; Jiang, R.; You, J.; Muir, D.C.G.; Zeng, E.Y. Microplastic impacts on microalgae growth: Effects of size and humic acid. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 1782–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eslick, E.M.; Beilby, M.J.; Moon, A.R. A study of the native cell wall structures of the marine alga Ventricaria ventricosa (Siphonocladales, Chlorophyceae) using atomic force microscopy. Microscopy (Oxf.) 2014, 63, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nolte, T.M.; Hartmann, N.B.; Kleijn, J.M.; Garnaes, J.; van de Meent, D.; Hendriks, A.J.; Baun, A. The toxicity of plastic nanoparticles to green algae as influenced by surface modification, medium hardness and cellular adsorption. Aquat. Toxicol. 2017, 183, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Y.; Jiang, X.; Liao, Y.; Zhao, W.; Zhao, P.; Li, M. Adverse physiological and molecular level effects of polystyrene microplastics on freshwater microalgae. Chemosphere 2020, 255, 126914–126921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiu, R.-F.; Vazquez, C.I.; Chiang, C.-Y.; Chiu, M.-H.; Chen, C.-S.; Ni, C.-W.; Gong, G.-C.; Quigg, A.; Santschi, P.H.; Chin, W.-C. Nano- and microplastics trigger secretion of protein-rich extracellular polymeric substances from phytoplankton. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 748, 141469–141478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, P.; Lin, S.J.; Turner, J.P.; Ke, P.C. Physical adsorption of charged plastic nanoparticles affects algal photosynthesis. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 16556–16561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Li, S.; Lu, Y.; Li, Q.; Yu, S. The influence of humic acid on the toxicity of nano-ZnO and Zn2+ to the Anabaena sp. Environ. Toxicol. 2015, 30, 895–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wang, S.; Fang, H.; Ye, N.; Wang, D. Ecotoxicological effects on Scenedesmus obliquus and Danio rerio Co-exposed to polystyrene nano-plastic particles and natural acidic organic polymer. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2019, 67, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, B.; Chen, B.; Sun, X.; Qu, K.; Ma, F.; Du, M. Interaction of TiO2 nanoparticles with the marine microalga Nitzschia closterium: Growth inhibition, oxidative stress and internalization. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 508, 525–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Liu, M.; Wang, J.; Huang, J.; Wang, J. Polystyrene nanoplastics cause growth inhibition, morphological damage and physiological disturbance in the marine microalga Platymonas helgolandica. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 158, 111403–111410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.F.; Ai, H.N.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Zeng, P.; Kang, L.; Li, W.; Gu, W.K.; He, Q.; Li, H. Phytoplankton response to polystyrene microplastics: Perspective from an entire growth period. Chemosphere 2018, 208, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hazeem, L.J.; Yesilay, G.; Bououdina, M.; Perna, S.; Cetin, D.; Suludere, Z.; Barras, A.; Boukherroub, R. Investigation of the toxic effects of different polystyrene micro-and nanoplastics on microalgae Chlorella vulgaris by analysis of cell viability, pigment content, oxidative stress and ultrastructural changes. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 156, 111278–111287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, W.; Huang, Q.-S.; Sun, J.; Wang, J.-Y.; Wu, S.-L.; Ni, B.-J. Polyvinyl chloride microplastics affect methane production from the anaerobic digestion of waste activated sludge through leaching toxic bisphenol-A. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 2509–2517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, S.; Zheng, H.; Xu, Q.; Sun, C.; Shi, M.; Wang, Z.; Li, F. Comparative toxicity of the plasticizer dibutyl phthalate to two freshwater algae. Aquat. Toxicol. 2017, 191, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Xiang, Y.; He, D.; Li, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, S.; Pan, X. Leaching behavior of fluorescent additives from microplastics and the toxicity of leachate to Chlorella vulgaris. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 678, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, A.; Becker, R.; Dorgerloh, U.; Simon, F.-G.; Braun, U. The effect of polymer aging on the uptake of fuel aromatics and ethers by microplastics. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 240, 639–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mai, L.; Bao, L.-J.; Shi, L.; Liu, L.-Y.; Zeng, E.Y. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons affiliated with microplastics in surface waters of Bohai and Huanghai Seas, China. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 241, 834–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Rong, L.; Xu, J.; Lian, J.; Wang, L.; Sun, H. Sorption of five organic compounds by polar and nonpolar microplastics. Chemosphere 2020, 257, 127206–127214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.M.; Qin, Q.D.; Hu, Z.X.; Yan, L.; Ieong, U.I.; Xu, Y. Adsorption of chlorophenols on polyethylene terephthalate microplastics from aqueous environments: Kinetics, mechanisms and influencing factors. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 265, 114926–114935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, H. Adsorption of antibiotics on microplastics. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 237, 460–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, B.; Liu, F.; Brookes, P.C.; Xu, J. Microplastics play a minor role in tetracycline sorption in the presence of dissolved organic matter. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 240, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Pleiter, M.; Pedrouzo-Rodriguez, A.; Verdú, I.; Leganés, F.; Marco, E.; Rosal, R.; Fernández-Pinas, F. Microplastics as vectors of the antibiotics azithromycin and clarithromycin: Effects towards freshwater microalgae. Chemosphere 2021, 268, 128824–128831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, W.K.; Law, J.C.; Zhang, T.; Leung, K.S. Effects of weathering on the sorption behavior and toxicity of polystyrene microplastics in multi-solute systems. Water. Res. 2020, 187, 116419–116428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrell, P.; Nelson, K. Trophic level transfer of microplastic: Mytilus edulis (L.) to Carcinus maenas (L.). Environ. Pollut. 2013, 177, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setälä, O.; Fleming-Lehtinen, V.; Lehtiniemi, M. Ingestion and transfer of microplastics in the planktonic food web. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 185, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chagnon, C.; Thiel, M.; Antunes, J.; Ferreira, J.L.; Sobral, P.; Ory, N.C. Plastic ingestion and trophic transfer between Easter Island flying fish (Cheilopogon rapanouiensis) and yellowfin tuna (Thunnus albacares) from Rapa Nui (Easter Island). Environ. Pollut. 2018, 243, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelms, S.E.; Galloway, T.S.; Godley, B.J.; Jarvis, D.S.; Lindeque, P.K. Investigating microplastic trophic transfer in marine top predators. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 238, 999–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cedervall, T.; Hansson, L.-A.; Lard, M.; Frohm, B.; Linse, S. Food chain transport of nanoparticles affects behaviour and fat metabolism in fish. PLoS ONE 2012, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chae, Y.; Kim, D.; Kim, S.W.; An, Y.-J. Trophic transfer and individual impact of nano-sized polystyrene in a four-species freshwater food chain. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coffin, S.; Huang, G.-Y.; Lee, I.; Schlenk, D. Fish and seabird gut conditions enhance desorption of estrogenic chemicals from commonly-ingested plastic items. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 4588–4599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nor, N.H.M.; Koelmans, A.A. Transfer of PCBs from microplastics under simulated gut fluid conditions is biphasic and reversible. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 1874–1883. [Google Scholar]
- Batel, A.; Linti, F.; Scherer, M.; Erdinger, L.; Braunbeck, T. Transfer of benzo[a]pyrene from microplastics to Artemia nauplii and further to zebrafish via a trophic food web experiment: CYP1A induction and visual tracking of persistent organic pollutants. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2016, 35, 1656–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diepens, N.J.; Koelmans, A.A. Accumulation of plastic debris and associated contaminants in aquatic food webs. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 8510–8520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grigorakis, S.; Drouillard, K.G. Effect of microplastic amendment to food on diet assimilation efficiencies of PCBs by fish. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 10796–10802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herzke, D.; Anker-Nilssen, T.; Nøst, T.H.; Götsch, A.; Christensen-Dalsgaard, S.; Langset, M.; Fangel, K.; Koelmans, A.A. Negligible impact of ingested microplastics on tissue concentrations of persistent organic pollutants in northern fulmars off coastal Norway. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 1924–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koelmans, A.A.; Bakir, A.; Burton, G.; Janssen, C.R. Microplastic as a vector for chemicals in the aquatic environment: Critical review and model-supported reinterpretation of empirical studies. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 3315–3326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wardrop, P.; Shimeta, J.; Nugegoda, D.; Morrison, P.D.; Miranda, A.; Tang, M.; Clarke, B.O. Chemical pollutants sorbed to ingested microbeads from personal care products accumulate in fish. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 4037–4044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, M.; Ribeiro, A.; Hylland, K.; Guilhermino, L. Single and combined effects of microplastics and pyrene on juveniles (0+ group) of the common goby Pomatoschistus microps (Teleostei, Gobiidae). Ecol. Indic. 2013, 34, 641–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochman, C.M.; Hoh, E.; Kurobe, T.; Teh, S.J. Ingested plastic transfers hazardous chemicals to fish and induces hepatic stress. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 3263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochman, C.M.; Kurobe, T.; Flores, I.; Teh, S.J. Early warning signs of endocrine disruption in adult fish from the ingestion of polyethylene with and without sorbed chemical pollutants from the marine environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 493, 656–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luís, L.G.; Ferreira, P.; Fonte, E.; Oliveira, M.; Guilhermino, L. Does the presence of microplastics influence the acute toxicity of chromium(VI) to early juveniles of the common goby (Pomatoschistus microps)? A study with juveniles from two wild estuarine populations. Aquat. Toxicol. 2015, 164, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bakir, A.; O’Connor, I.A.; Rowland, S.J.; Hendriks, A.J.; Thompson, R.C. Relative importance of microplastics as a pathway for the transfer of hydrophobic organic chemicals to marine life. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 219, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beiras, R.; Tato, T. Microplastics do not increase toxicity of a hydrophobic organic chemical to marine plankton. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 138, 58–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ašmonaitė, G.; Larsson, K.; Undeland, I.; Sturve, J.; Carney Almroth, B. Size matters: Ingestion of relatively large microplastics contaminated with environmental pollutants posed little risk for fish health and fillet quality. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 14381–14391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Huang, A.; Cao, S.; Sun, F.; Wang, L.; Guo, H.; Ji, R. Effects of nanoplastics and microplastics on toxicity, bioaccumulation, and environmental fate of phenanthrene in fresh water. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 219, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antunes, J.C.; Frias, J.G.L.; Micaelo, A.C.; Sobral, P. Resin pellets from beaches of the Portuguese coast and adsorbed persistent organic pollutants. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2013, 130, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frias, J.; Sobral, P.; Ferreira, A. Organic pollutants in microplastics from two beaches of the Portuguese coast. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2010, 60, 1988–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camacho, M.; Herrera, A.; Gomez, M.; Acosta-Dacal, A.; Martinez, I.; Alberto Henriquez-Hernandez, L.; Luzardo, O.P. Organic pollutants in marine plastic debris from Canary Islands beaches. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 662, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jasna, M.-L.; Jelena, L.; Pero, T.; Dubravka, B.V.; Jasna, S.; Josko, P. Levels of trace metals on microplastic particles in beach sediments of the island of Vis, Adriatic Sea, Croatia. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 137, 231–236. [Google Scholar]
- Munier, B.; Bendell, L.I. Macro and micro plastics sorb and desorb metals and act as a point source of trace metals to coastal ecosystems. PLoS ONE 2018, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prunier, J.; Maurice, L.; Perez, E.; Gigault, J.; Wickmann, A.-C.P.; Davranche, M.; ter Halle, A. Trace metals in polyethylene debris from the North Atlantic subtropical gyre. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 245, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vedolin, M.C.; Teophilo, C.Y.S.; Turra, A.; Figueira, R.C.L. Spatial variability in the concentrations of metals in beached microplastics. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 129, 487–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.; Wang, X.; Zhou, X.; Kong, X.; Tao, S.; Xing, B. Sorption of four hydrophobic organic compounds by three chemically distinct polymers: Role of chemical and physical composition. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 7252–7259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.-F.; Liu, G.-Z.; Zhu, Z.-L.; Wang, S.-C.; Zhao, F.-F. Interactions between microplastics and phthalate esters as affected by microplastics characteristics and solution chemistry. Chemosphere 2019, 214, 688–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Shih, K.; Li, X.Y. The partition behavior of perfluorooctanesulfonate (PFOS) and perfluorooctanesulfonamide (FOSA) on microplastics. Chemosphere 2015, 119, 841–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wang, J. Comparative evaluation of sorption kinetics and isotherms of pyrene onto microplastics. Chemosphere 2018, 193, 567–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Wang, J. Different partition of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon on environmental particulates in freshwater: Microplastics in comparison to natural sediment. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 147, 648–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hueffer, T.; Hofmann, T. Sorption of non-polar organic compounds by micro-sized plastic particles in aqueous solution. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 214, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascall, M.A.; Zabik, M.E.; Zabik, M.J.; Hernandez, R.J. Uptake of polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) from an aqueous medium by polyethylene, polyvinyl chloride, and polystyrene films. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 164–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Pang, J.; Chen, S.; Jia, H. Sorption properties of tylosin on four different microplastics. Chemosphere 2018, 209, 240–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velzeboer, I.; Kwadijk, C.J.A.F.; Koelmans, A.A. Strong sorption of PCBs to nanoplastics, microplastics, carbon nanotubes, and fullerenes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 4869–4876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Liu, X.; Liu, G.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, H.; Cui, B.; Bai, J.; Zhang, W. Size effect of polystyrene microplastics on sorption of phenanthrene and nitrobenzene. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 173, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Chen, M.; Zhang, L.; Wang, K.; Yu, X.; Zheng, Z.; Zheng, R. Sorption behaviors of phenanthrene on the microplastics identified in a mariculture farm in Xiangshan Bay, southeastern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 628–629, 1617–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, Z.; Wang, J.; Peng, J.; Xie, Q.; Huang, Y.; Gao, Y. Sorption of 3,3′,4,4′-tetrachlorobiphenyl by microplastics: A case study of polypropylene. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 110, 559–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Zheng, M.; Yin, X.; Wang, L.; Lou, Y.; Qu, L.; Liu, X.; Zhu, H.; Qiu, Y. Sorption of 3,6-dibromocarbazole and 1,3,6,8-tetrabromocarbazole by microplastics. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 138, 458–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Zheng, M.; Wang, L.; Lou, Y.; Shi, L.; Jiang, S. Sorption of three synthetic musks by microplastics. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 126, 606–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koelmans, A.A.; Besseling, E.; Shim, W.J. Nanoplastics in the Aquatic Environment. Critical Review, in Marine Anthropogenic Litter; Bergmann, M., Gutow, L., Klages, M., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 325–340. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Ma, Y.; Zhu, D.; Xia, T.; Qi, Y.; Yao, Y.; Guo, X.; Ji, R.; Chen, W. Polystyrene nanoplastics-enhanced contaminant transport: Role of irreversible adsorption in glassy polymeric domain. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 2677–2685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jahnke, A.; Arp, H.P.H.; Escher, B.I.; Gewert, B.; Gorokhova, E.; Kühnel, D.; Ogonowski, M.; Potthoff, A.; Rummel, C.; Schmitt-Jansen, M.; et al. Reducing uncertainty and confronting ignorance about the possible impacts of weathering plastic in the marine environment. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2017, 4, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Zhu, Z.; Yang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Yu, F.; Ma, J. Sorption behavior and mechanism of hydrophilic organic chemicals to virgin and aged microplastics in freshwater and seawater. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 246, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mato, Y.; Isobe, T.; Takada, H.; Kanehiro, H.; Ohtake, C.; Kaminuma, T. Plastic resin pellets as a transport medium for toxic chemicals in the marine environment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2001, 35, 318–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, L.A.; Turner, A.; Thompson, R.C. Interactions between trace metals and plastic production pellets under estuarine conditions. Mar. Chem. 2014, 167, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hüffer, T.; Weniger, A.-K.; Hofmann, T. Sorption of organic compounds by aged polystyrene microplastic particles. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 236, 218–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Qian, L.; Wang, H.; Zhan, X.; Lu, K.; Gu, C.; Gao, S. New insights into the aging behavior of microplastics accelerated by advanced oxidation processes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 3579–3588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rummel, C.D.; Jahnke, A.; Gorokhova, E.; Kühnel, D.; Schmitt-Jansen, M. Impacts of biofilm formation on the fate and potential effects of microplastic in the aquatic environment. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2017, 4, 258–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Johansen, M.P.; Cresswell, T.; Davis, J.; Howard, D.; Howell, N.R.; Prentice, E. Biofilm-enhanced adsorption of strong and weak cations onto different microplastic sample types: Use of spectroscopy, microscopy and radiotracer methods. Water Res. 2019, 158, 392–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, P.; Ge, W.; Chai, C.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, T.; Xia, B. Sorption of polybrominated diphenyl ethers by microplastics. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 145, 260–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, J.; Zhou, B.; Zhou, Y.; Dai, Z.; Zhou, Q.; Christie, P.; Luo, Y. Enhanced adsorption of oxytetracycline to weathered microplastic polystyrene: Kinetics, isotherms and influencing factors. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 243, 1550–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.; Zhang, K.; Huang, X.; Liu, J. Sorption of pharmaceuticals and personal care products to polyethylene debris. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 8819–8826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llorca, M.; Schirinzi, G.F.; Martínez, M.; Barceló, D.; Farré, M. Adsorption of perfluoroalkyl substances on microplastics under environmental conditions. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 235, 680–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Liu, F.; Brookes, P.C.; Xu, J. The sorption kinetics and isotherms of sulfamethoxazole with polyethylene microplastics. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 131, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.-C.; Li, D.-C.; Sima, X.-F.; Cheng, H.-Y.; Jiang, H. The effects of environmental conditions on the enrichment of antibiotics on microplastics in simulated natural water column. Environ. Res. 2018, 166, 377–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Tan, H.; Zhang, L.; Wang, S.; Wang, Y.; Yu, K. The implications of water extractable organic matter (WEOM) on the sorption of typical parent, alkyl and N/O/S-containing polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) by microplastics. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 156, 176–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Ouyang, Z.-Y.; Qian, C.; Yu, H.-Q. Induced structural changes of humic acid by exposure of polystyrene microplastics: A spectroscopic insight. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 233, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, L.-Z.; Li, H.-X.; Lin, L.; Sun, Y.-X.; Diao, Z.-H.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Z.-Y.; Xu, X.-R. Sorption and desorption of phenanthrene on biodegradable poly(butylene adipate co-terephtalate) microplastics. Chemosphere 2019, 215, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakir, A.; Rowland, S.J.; Thompson, R.C. Enhanced desorption of persistent organic pollutants from microplastics under simulated physiological conditions. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 185, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; Lee, H.-J.; Kwon, J.-H. Estimating microplastic-bound intake of hydrophobic organic chemicals by fish using measured desorption rates to artificial gut fluid. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 651, 162–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, F.-F.; Wang, S.-C.; Zhu, Z.-L.; Liu, G.-Z. Current Progress on Marine Microplastics Pollution Research: A Review on Pollution Occurrence, Detection, and Environmental Effects. Water 2021, 13, 1713. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13121713
Liu F-F, Wang S-C, Zhu Z-L, Liu G-Z. Current Progress on Marine Microplastics Pollution Research: A Review on Pollution Occurrence, Detection, and Environmental Effects. Water. 2021; 13(12):1713. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13121713
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Fei-Fei, Su-Chun Wang, Zhi-Lin Zhu, and Guang-Zhou Liu. 2021. "Current Progress on Marine Microplastics Pollution Research: A Review on Pollution Occurrence, Detection, and Environmental Effects" Water 13, no. 12: 1713. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13121713
APA StyleLiu, F.-F., Wang, S.-C., Zhu, Z.-L., & Liu, G.-Z. (2021). Current Progress on Marine Microplastics Pollution Research: A Review on Pollution Occurrence, Detection, and Environmental Effects. Water, 13(12), 1713. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13121713





