Abstract
Adequate environmental management in tropical aquatic ecosystems is imperative. Given the lack of knowledge about functional diversity and bioassessment programs, management is missing the needed evidence on pollution and its effect on biodiversity and functional ecology. Therefore, we investigated the composition and distribution of the macroinvertebrate community along two rivers. Specifically, 15 locations were sampled in the Coca and Aguarico Rivers (Ecuadorian Amazon) and the macroinvertebrates were used to indicate water quality (WQ), expressed as the Biological Monitoring Working Party Colombia (BMWP-Col) classes. Results indicate that elevation, pH, temperature, width, and water depth played an important role in the taxa and functional feeding groups (FFG) composition. The results show that diversity of taxa and FFG were generally scarce but were more abundant in good quality sites. Collector-gathers (CG) were, in general, dominant and were particularly abundant at low WQ and downstream sites. Scrapers (SC) were the second most abundant group, dominating mostly at good WQ and upstream sites. Predators (PR) were homogeneously distributed among the sites, without clear dominance, and their abundance was slightly higher in sites with medium-low WQ and downstream sites. Lastly, both shredders (SH) and collector-filterers (CF) were almost absent and were more abundant in good quality sites. The findings of this research can be used as baseline information in the studied region since a dam was constructed two years after the sampling campaign, which has been operating since. Furthermore, the results can be used to fill the knowledge gaps related to the bioassessments of other similar systems, particularly for a tropical rainforest.
1. Introduction
The pollution of aquatic ecosystems is currently one of the main environmental problems that humanity faces [1,2,3]. Specifically, rivers, as a surface water ecosystem, are exposed to multiple pressures mainly related to deforestation, agriculture, sedimentation and livestock cultivation, eutrophication/organic pollution, urbanization, and physical and hydrological modifications [4]. For instance, rivers are susceptible to pollution discharges of anthropogenic origin including point sources (i.e., wastewater from urban and industrial areas) and diffuse sources (runoff from livestock and agriculture). Both have led to a notable decline in water quality (WQ) [5,6,7]. In developing countries, such as Ecuador, these pollution problems in rivers are even more worrisome and have accelerated due to the lack of wastewater treatment plants or similar technologies in many towns. Raw sewage is most often directly discharged into water bodies [8,9]. In the Ecuadorian Amazon region, other sources of pollution are also present, such as, e.g., discharges from (legal or illegal) mining operations or oil exploitation [10,11,12,13]. Headwaters of the Amazon River, particularly those that originate in the Andes, usually accumulate different kinds of physical, chemical, or microbiological pollutants, which exceed the system’s capacity for self-purification and resilience despite the large amount of water it usually transports [14,15,16]. This problem makes the ecosystems increasingly fragile, even more in the context of climate change [17,18]. The persistence of this problem resulted in the loss or deterioration of key ecosystem services (i.e., food production, erosion prevention, tourism, water provisioning, and energy production) needed for the local and regional development and sustainability in these areas and also with the fulfillment of the Sustainable Development Goals [19,20,21,22,23].
Water quality in rivers has in general been evaluated by physical and chemical parameters (i.e., [24,25,26]). Beyond the advantages of these methods, their main limitation is they only provide a time-specific state of the ecosystem, but they do not integrate the changes in water quality over time [27,28,29]. As a solution, biological indices are used, which are more representative of water quality status over time [30,31]. Generally, aquatic macroinvertebrates are used as biomonitoring organisms of lotic ecosystems, including groups such as crustaceans, molluscs, and insects [32,33]. The use of organisms found in the environment combined with other metrics, such as species abundance, diversity, distribution, dispersion, and reproductive success, allows to detect changes in the ecosystem as a result of pollution or hydromorphological modifications [34]. The worldwide experience up to now has shown the effectiveness of benthic communities in the evaluation, monitoring, and even prediction of a lotic ecosystem’s quality and functioning (i.e., [35,36,37]). Macroinvertebrates are sensitive to different ranges of anthropogenic contamination, so their fluctuation, presence, or absence in the environment allow to classify the levels of disturbances [5]. Macroinvertebrates have usually a length of greater than 1 mm (visible with naked eyes) and are frequently used in biomonitoring since sampling them is simple, they have a low mobility, and their life span is relatively long when compared with other aquatic invertebrates (i.e., phytoplankton or rotifers) [38]. The study of these organisms allows the calculation of indices, by means of the ordering and weighting of the species obtained in the sampling campaigns, in which one of the most prominent indices for the neotropical region is the BMWP-Col [4,39,40]. The use and application of benthic invertebrates as bioindicators of water quality has been increasing these recent years as a tool that leads to the management, prediction, or protection of aquatic environments and the ecosystem services they provide [22,27,41].
The taxonomic approach is traditionally used to estimate the impact of human disturbances and some environmental conditions (i.e., climate change) on rivers, lakes, and streams by comparing the occurring species between disturbed and undisturbed sites [42,43]. It is known that some factors influence the distribution and composition of macroinvertebrates: for instance, some taxa are sensitive to high velocity as they potentially drift, which triggers responses in their abundance and densities, while oxygen deficiency in water is a deleterious factor for these organisms [44,45,46].
The use of the biological traits of these communities has often provided an organized understanding of the anthropogenic stressors impacts [41]. Among these traits, functional feeding groups (FFG) are directly associated with the metabolic resources that individuals need [47,48], which results in the shifts of FFG along the longitudinal profile as predicted by the River Continuum Concept (RCC) [49]. Although the longitudinal variations in FFG are generally consistent with the RCC predictions, these variations are also often affected by water quality, land use, and other local stressors [50,51].
The current study aims to better understand the human impacts in the Ecuadorian Amazon region based on several river characteristics, including physicochemical and biological (macroinvertebrates) water quality. We assume that locations with a low geographical distance are characterised by similar macroinvertebrate assemblages at both the taxonomic and the functional feeding groups (FFG) level, while local variables affect local and downstream FFG compositions. For this, we investigated: (i) the taxonomic similarity among sites, (ii) the similarity in functional feeding group among sites, (iii) the difference in FFG among Biological Monitoring Working Party-Colombia (BMWP-Col) WQ classes, and (iv) the most influential hydromorphological and physicochemical variables over the former macroinvertebrate community patterns. The outcomes of this study can be used to steer baseline information for future water management strategies and prioritise restoration activities locally and in similar river systems at the Amazon.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Site Selection
We performed a sampling campaign in the Coca (5705 km2) and Aguarico (10,290 km2) River basins in July 2014, during the wet season [52]. Both river basins are sub-basins of the Ecuadorian Amazon basin and are located in the north-eastern part of Ecuador (Figure 1). According to Köppen climate classification, this region has an equatorial climate (Af) of tropical rainforest [53]. The climate here is characterized by heavy rainfall throughout the year. The average annual precipitation during the hydrological year is around 3500 mm, with an average of 19 rainy days per month, although it is possible to distinguish, slightly, a rainy season that occurs from April to July from a less marked dry season from November to February [54].
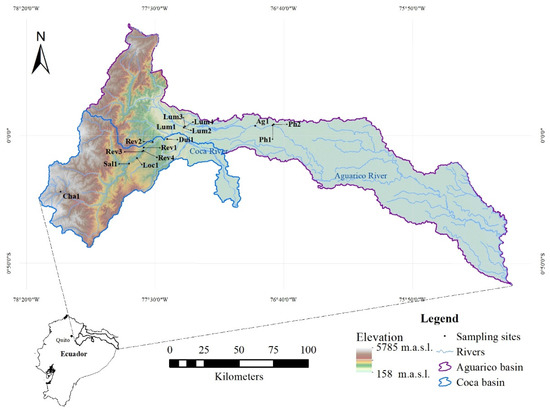
Figure 1.
Map of study area with sampling locations. For the Coca River basin tributaries, the sampling sites codes used were: Cha1 (Chalpichico stream), Sal1 (Salado stream), Loc1 (Loco stream), Rev1-Rev2-Rev3-Rev4 (Reventador stream) and Dui1 (Dui stream), whereas for Aguarico River basin tributaries: Lum1-Lum2-Lum3-Lum4 (Lumbaqui River), Ph1-Ph2 (Parahimayco stream) and Ag1 (Aguarico River).
The Coca River basin (CRB) is surrounded by three volcanoes: Cayambe, Antisana, and Reventador. The highest point in this river basin coincides with the mountain Cayambe in the Andes Cordillera with a summit of 5790 m above sea level. The CRB mouth is in the Puerto Francisco de Orellana city (254 m.a.s.l.), where it discharges an average of 219 m3·s−1 typically during the dry season and this increases to as much as 389 m3·s−1 at its peak flow in the wet season [55]. The Aguarico River basin (ARB) originates in the Pimampiro mountain range (3746 m.a.s.l.) west of the Sucumbíos province and runs almost entirely through this province. The Aguarico River is 390 km long, of which the last 50 km extend along the natural border between Ecuador and Perú. The ARB usually discharges an average of 1258 m3·s−1 during the wet season, and this decreases to 440 m3·s−1 in the dry season [56].
Both the CRB and ARB discharge the water into the Napo River within the Ecuadorian territory before joining the Amazon River. The highland rivers from the Napo basin (such as Coca, Tiputini, Yasuní, Aguarico) are known as “aguas blancas” (white waters) [54]. The whitewater systems originate in the Andean snowmelts and high altitude paramo grasslands at elevations over 4000 m, and have a muddy colour caused by drainage carrying heavy sediment loads from eroding uplands [57]. These rivers run through some protected areas of great biological biodiversity, as is the case of the CRB (originating in the Cayambe-Coca National Parks and Antisana Ecological Reserve and crossing the Sumaco Napo-Galeras National Park) and the ARB (originating in the Cayambe-Coca National Park and crossing the Cuyabeno Wildlife Production Reserve). Both basins are estimated to support over 500 freshwater fish species, many of which are endemic to the region [57]. It is also one of the most biologically diverse ecoregions in the world for amphibians, birds, and mammals [58,59]. This high diversity can be attributed to several factors including its high altitudinal gradient (100–5500 m), which provides a great variety of physical and climatic conditions [60] and an incredible heterogeneity of habitats.
The study area covers three provinces (Sucumbíos, Napo, and Orellana), and both river basins run through some medium-big cities such as El Chacho (3000 inhabitants), San Sebastián del Coca (11,369 inhabitants), Puerto Francisco de Orellana (45,163 inhabitants), Lumbaqui (8599 inhabitants), Cascales (11,104 inhabitants), Nueva Loja (71,914 inhabitants), and Shushufindi (44,328 inhabitants) (Prefectura de Sucumbíos, 2016; Prefectura del Napo, 2018). As oil is the main export of Ecuador and the largest reserves of the country are located in the Amazon basin, the main cities and towns emerged where the oil industry set up camps and stations. All the big cities in the Ecuadorian Amazon share this origin [61]. The initial oil exploration and production was owned by Texaco in the 1960s and, currently, there are 112 active oil blocks (parcels of land that organize oil exploitation) active in the Ecuadorian Amazon (32 of them are within these catchments) [62].
Beyond oil-related activities, other types of human activity are present in these basins: dams, mining, agriculture, livestock, and fishing. At the origin of the CRB river, there is a dam, the Coca Codo Sinclair Dam, built in 2010, generating 1500 megawatts since 2015, which represents 35% of the country’s electricity, being the largest in Ecuador. In total, the dam project covers an area of 3600 km2, including a compensating reservoir with a storage capacity of 880,000 m3 [63]. In both basins, there are also some illegal mining activities (specifically artisanal mining and alluvial gold mining). Legal mining or authorized concessions in the sector are very scarce [10,64]. Other anthropic activities identified in these basins are agriculture, especially short-crop species (i.e., cassava, cocoa, coffee, corn, banana, palm), livestock (specifically cattle, pigs, and breeding of chickens), and to a lesser extent fishing (for self-consumption purposes rather than trade) [65,66].
A total of 15 sites were selected: eight sites were situated in the Coca River basin and seven in the Aguarico River basin. The sites were located in the following streams: Aguarico (Ag), Parahimayco (Ph), and Lumbaqui (Lum) streams, which are tributaries of the Aguarico River; and Chalpichico (Cha), Salado (Sal), Loco (Loc), Reventador (Rev), and Dui (Dui) streams, which are tributaries of the Coca River (Figure 1). The sites range from highland in the Andes (Reventador mountain) with Chalpichico stream as the highest site (2872+ m.a.s.l.), through mid-altitude, to the low-land Amazonian region with the Parahimayco stream as the lowest site (263 m.a.s.l.). In general, sampling sites were chosen based on their accessibility as well as on their surrounding land use and the presence/absence of human activities. We hypothesized that the ecological water quality would decrease from source to mouth due to increasing human activities.
2.2. Data Collection
2.2.1. Physical Chemical Analysis
Water temperature, dissolved oxygen (DO), dissolved oxygen saturation, pH, and conductivity were measured “on site” with a field probe (type: Three-Multi 3430 IDS, WTW GmbH). The measurements were executed directly in the water body. Water samples were collected to determine the nutrient content and chemical oxygen demand (COD) in the water. The water samples were stored in plastic bottles for nutrient analysis. For COD analysis, drops of concentrated sulfuric acid were added to lower the pH to 2. Acidification was verified via litmus paper. Nitrate-N, nitrite-N, ammonium-N, phosphate-P, total N, total P, and COD were analysed and measured using the DR3500 Hach lab spectrophotometer (HACH Company, Loveland, CO, USA) and Hach kits in the “Laboratorio de Análisis Físicos Químicos y Microbiológicos de Aguas” in Universidad Técnica del Norte (UTN), Ibarra. The elevation of the sampling sites was measured using the Garmin Etrex GPS (Global Positioning System) equipment (Garmin Legend; Garmin Ltd., Olathe, KS, USA). Stream velocity at each site was measured several times at different points using a handheld Höntzsch probe (HFA-model; Höntzsch, Waiblingen, Germany). Furthermore, as hydromorphological variables, the depth and width of the rivers were measured. To observe the correlation between the variables, as well as with the BMWP-Col index, the Spearman correlation analysis was performed.
2.2.2. Macroinvertebrate Data Collection
Samples of macroinvertebrates were collected from each sampling site immediately after determining the physicochemical water quality variables. Macroinvertebrates were collected with a standard hand net consisting of a metal frame holding a conical net (mesh size 500 µm). Macroinvertebrates were collected using the kick-net sampling technique for 5 min stratified over the different microhabitats present at the sampling site [33]. Samples were sieved (500 µm mesh size) in the field and sorted in white trays. Macroinvertebrates from each location were placed in separate small plastic vials containing 96% ethanol to reach a final concentration of 70% ethanol. After sorting, organisms were identified and counted under a stereomicroscope. Macroinvertebrates were identified using the identification keys developed by Domínguez & Fernández [38]. Identification occurred at the family level only, for two reasons: firstly, previous research has shown that using biotic indices based on family level provides sufficient information to assess biological water quality [35,67,68], and, secondly, there are no detailed keys available enabling identification to lower taxonomic levels.
2.2.3. BMWP-Score Calculation for River Assessment
In each sampling site, ecological water quality was assessed using the Biological Monitoring Working Party (BMWP) index adapted for Colombia (BMWP-Col) [40], based on Álvarez [39]. The BMWP-Col was used since Ecuador does not have its own water quality index based on macroinvertebrates. This index is considered an appropriate index for Ecuador since Colombia has relatively similar environmental conditions to Ecuador. Moreover, Dominguez-Granda et al. [35] and Damanik-Ambarita et al. [27] also used the BMWP-Col to assess the water quality in the Chaguana and Guayas River basins in Ecuador, respectively. The BMWP-Col calculation was performed based on the macroinvertebrate community composition, wherein each macroinvertebrate taxon is associated with a certain tolerance score. The tolerance score ranged from 1 to 10, with low scores representing tolerant taxa and high scores representing sensitive taxa. A BMWP-Col score of ≥100, 61–100, 36–60, 16–35, and 0–15 represents good, moderate, poor, bad, and very bad ecological quality, respectively [39].
2.2.4. Trait-Allocation
Information on the traits of each macroinvertebrate was congregated from various databases [27,69,70,71,72,73,74,75]. As each taxon was identified to the family level, which is of a higher level than the one most often given in the trait database, the traits of the most dominant and/or common species found were used as identified by the taxonomy expert. We only focussed on the feeding habit trait as this trait (i) has been considered as an indispensable factor in structuring invertebrate communities [76] and (ii) is normally analysed, probably due to the link between feeding strategy and ecosystem functions [77]. The taxon enlisted in Table A1 was assigned to a specific functional feeding group (FFG) according to the databases previously cited. The abundance of each taxon was also allocated as the abundance of the taxon’s assigned FFG.
2.2.5. Data Analysis
A non-metric multidimensional scaling (NMDS) analysis was performed to analyse the similarity among study sites, the BMWP-Col index, the FFG, and the physical-chemical variables. Pie charts were developed to graphically represent the FFGs’ relative abundance of sites grouped per water quality class, expressed as BMWP-Col classes.
In each site, the relative abundance of each FFG was calculated. Subsequently, the relative abundance of FFGs per site was plotted in a bar chart as a function of elevation and sites were arranged based on decreasing elevation.
Similarity among sampling sites was inferred from clustering based on Euclidean distances among sample sites and subsequent Lance Williams algorithm applying Ward’s minimum variance method to determine the difference between clusters. Low distance values represent close linkages. Cluster analysis was performed based on the presence and abundances of taxa (after log(1 + x) transformation). Step-wise cluster analysis allowed to evaluate the evolution of the within-group sum of squares (WGSS) when going from one to ten clusters. With an increasing number of clusters, a decrease in WGSS is expected, which provides a trade-off between the number of clusters versus the variability within the clusters (WGSS). Subsequently, pie charts were developed to graphically represent the FFGs’ relative abundance of sites grouped per clusters. Cluster and NMDS analyses were implemented in R-Studio via the cluster, factoextra and vegan, lattice packages, respectively [78,79].
3. Results
3.1. Physical Chemical Analysis
The descriptive statistics of the main physicochemical variables are presented in Table 1. The temperature varied from 9.4 °C to 24.2 °C, due to differences in the time of sampling (early morning or midday) and also due to the vertical thermal gradient in which low temperature is normally observed in high altitude locations, which was also reflected in the temperature’s negative correlation with elevation (−0.80, p < 0.05). There was also a significant negative correlation (p < 0.05) between temperature and pH (−0.56), conductivity (−0.58), DO (−0.60), and DO saturation (−0.69), which is related to the low oxygen solubility at high elevation. The lowest conductivity was observed at the Parahimayco1-Ph1 (15.3 µS·cm−1), while the highest was at a small tributary of the CRB, the Reventador2-Rev2 (902 µS·cm−1). Conductivity is usually related to the presence of ionic compounds such as pollutants from mining [80]. Conductivity had a positive correlation with the pH (0.70, p < 0.05), total P (0.59), and elevation (0.65). The pH ranged from 6.5 to 8.35, and it had a significant positive correlation with DO (0.57, p < 0.05), DO saturation (0.81), and the presence of phosphorus, phosphate (0.56), and total P (0.69). The slowest flow velocity was measured at Ph1 (0.14 m·s−1), where also the lowest conductivity and pH were found. At Rev2, the highest flow velocity, pH, and conductivity were found. Nitrogen and phosphorus are commonly associated with organic pollutants and nutrient runoff from agricultural activities so their presence is often indicative of nearby sources of organic and fertiliser contaminants. In these basins, total phosphorus ranged from 0.12 mg·L−1 to 2.11 mg·L−1, with the lowest value observed at a medium stream location of a small tributary of the CRB, the Lumbaqui1 (Lum1), and the highest value was observed at the Aguarico1 (Ag1). DO ranged between 6.42 mg·L−1 and 8.98 mg·L−1, with the highest value observed at the location where the highest total p values were measured. DO was significantly related to phosphate (0.57, p < 0.05). The lowest oxygen concentration was observed at a tributary of the CRB, at the Dui1 site. Low oxygen solubility and saturation levels are usually related to the high elevation of most locations. But in this case a positive association between elevation and DO saturation (0.72, p < 0.05) was found. Table A2 presents the Spearman correlation coefficients between variables.

Table 1.
Mean, minimum (Min), maximum (Max), and standard deviation (Std) of continuous variables measured in 15 sampling sites (asl = above sea level).
3.2. BMWP-Col Score Calculation for River Assessment
In total, 1426 macroinvertebrates were sorted and identified, which led to 50 different families. The highest abundance and richness were observed in five locations situated in mountainous areas (1250 to 1650 m.a.s.l.) near the Reventador mountain in CRB, each containing more than 74 individuals and belonging to 14 to 20 different families, respectively. Leptophlebiidae and Chironomidae were the most frequently encountered taxa, followed by Baetidae and Elmidae (10 and 9 sites, respectively). Baetidae was also the most abundant family, succeeded by Leptophlebiidae and Leptohyphidae (in total 336, 193 and 192 animals, respectively). Table A3 presents the list of encountered taxa, their tolerance scores based on BMWP-Col by Álvarez [39], their total abundance in the basins, and the number of sampling sites where they were found.
The WQ for all 15 sampling sites based on the BMWP-Col ranged from 3 to 125 (Figure 2). The best biological water quality is found at an elevation from 1250 to 1650 m.a.s.l., coinciding with the high abundance and richness of species and showing a significant positive correlation with elevation (0.62, p < 0.05). The index had high values at sites with a temperature around 17 °C. Bad BMWP-Col was indicated by sites with a low concentration of DO and low values of pH; however, the pH and DO values were not in a range of toxic concentrations. Although the Spearman’s rank correlation coefficients were generally low between physicochemical parameters and the BMWP-Col, we found a positive correlation between the index and DO, DO saturation, pH, conductivity, phosphate, and total P. BMWP-Col also showed a negative correlation with temperature, ammonium–N, nitrite–N, and total N. Nitrate–N and COD could not be evaluated as all the measured values were under the detection value (Table A2).

Figure 2.
Map depicting the water quality of the sampled sites. Only the main rivers within the Coca River basin (CRB) and Aguarico River basin (ARB) are represented. Both the Coca River and Aguarico River are tributaries to the Napo River, which is one of the tributaries to the Amazon River.
Figure 3 shows that the worst biological WQ, expressed as BMWP-Col score, is related to the hydromorphological variables depth and average width of rivers. The greater the depth (up to 0.3 m), the worse is the water quality as observed in the sites Lum3 (bad WQ) and Dui1, Ag1, and Ph1 (very bad WQ). Likewise, the higher the temperature, the worse is the water quality. It is also observed that wide rivers (>5 m) had poor to very bad WQ: the sites Lum1, Ph2, and Lum4 had poor WQ; the site Lum3 had bad WQ; and the sites Ag1 and Ph1 had very bad WQ. In addition to the insights gained that river depth, temperature, and width were related to the decrease in the biological quality of the water, this decline in biological quality is also linked to the accumulation of polluting substances at the lower river courses from the upper courses.
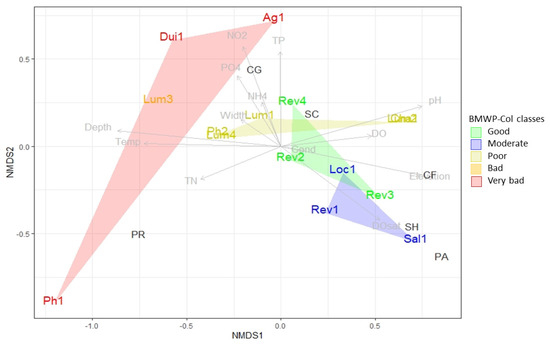
Figure 3.
Non-metric multidimensional scaling (NMDS) diagram of freshwater rivers within Coca River basin (CRB) and Aguarico River basin (ARB) sampled in June 2014. The associations between the sites with the same classes of the BMWP-Col index are shown in colours, according to their water quality. The main physical-chemical and two hydromorphological representative variables are indicated in grey letters (see Table 1). FFG are represented in black letters, where PA = parasites, CF = collector-filterers, SH = shredders, SC = scrapers, PR = predators, and CG = collector-gatherers.
3.3. Biological Water Quality and Functional Feeding Groups
The NMDS analysis shows that the sites with better WQ (Sal1, Loc1, and Rev sites) were related to the presence of the shredders (SH), collector-filterers (CF), and scrapers (SC) (Figure 3). Clusters based on water quality indicating the relative proportion of FFG (Figure 4) confirmed that the relative presence of SH decreased as the water quality decreased from 14% (good WQ) to 2% (poor WQ) and none in the worst WQ. The same trend was observed with SC (from 35% to 11%), although they were present in very bad quality sites (4%). CF showed a higher abundance in sites with poor WQ (10%) than in those of better quality (≤4%), but absent in sites of poorer quality. An opposite pattern is observed with the collector-gatherers (CG). As the WQ decreased, their abundance increased (from 17% to 86%), being very dominant in poor, bad, and very bad WQ classes. Predators showed a fair relative presence regardless of the BMWP-Col class, that is, their percentages were very similar in good quality (30%) and bad quality sites (33%). If we look at the distribution of the FFG by cluster according to the biological WQ, it was evident that there was more diversity of traits with better quality, without a clear dominance. This trend changed as the WQ is becoming worse and the CG were becoming dominant.

Figure 4.
Relative abundance of functional feeding groups clustered based on BMWP-Col water quality classes where CF, SH, SC, PA, PR, and CG refers to the collector-filterers, shredders, scrapers, parasites, predators, and collector-gatherers, respectively.
NMDS analysis and Spearman’s correlation showed that elevation is positively correlated to BMWP-Col values (see Table A2 and Figure 3). Figure 5 indicates that there was a higher diversity of FFGs at the higher altitudes (up to 1000 m.a.s.l.), which indeed was associated with good biological water quality. The sites with the best scores Rev1 (125), Loc1 (120), and Sal1 (114) had a high taxa richness (20, 18, and 17, respectively). We also observed that the higher is the taxa richness, the more diverse is the FFG as well. As indicated in Figure 4, the most abundant FFG in these locations were CF, SC, and SH. Among the high-altitude sites, Rev4 site had a high BMWP-Col score (98) even though more than 75% are CGs. This observation can be explained by the abundance of individuals (184) and taxa (15). On the other hand, Cha1 site, despite having the highest altitude (2872 m.a.s.l.), had a poor WQ (BMWP-Col score of 42). The site had a medium abundance of individuals (18) and a low number of taxa (8), which is dominated by more than 60% by CG. Sites below 1000 m.a.s.l. showed low WQ values. In these sites, they were dominated by PR and CG, which exceeded 60% of the community composition in most of these sites. The Dui1 site had the highest relative abundance of CG (almost 100%), being at a medium altitude (1030 m.a.s.l.), while the Ph1 site had only PR and the lowest BMWP-Col score (3), number of individuals, and taxa in comparison to other locations (See Figure A1 for further sites details).
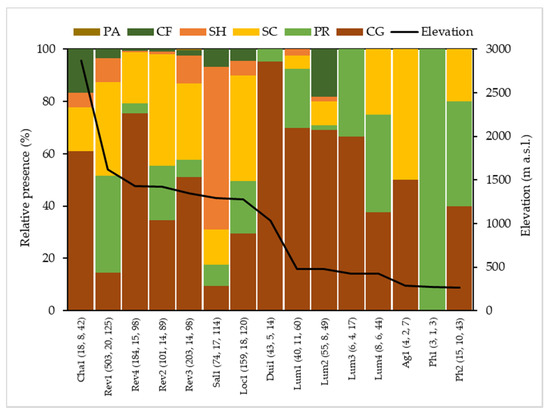
Figure 5.
Functional feeding group composition per studied sites. Numbers in parenthesis indicate the total number of encountered individuals, number of taxa, and BMWP-Col score, respectively. Locations are ordered based on a decreasing elevation. CF, SH, SC, PA, PR, and CG refers to the collector-filterers, shredders, scrapers, parasites, predators, and collector-gatherers, respectively.
Clustering analysis based on FFG composition showed that locations were divided into two groups (higher relative distance difference between base and first split) and provided different site linkages. Two sampling sites arose from the first group. The second one gave rise to the largest number of clusters and sites (13 out of 15). In Figure 6, the community-based FFG clusters have been represented. The distance between sampling sites based on the presence and abundance of taxa is represented on the axes. Six clusters were found, represented by C1–C6. Three of them had good WQ: C1, C2, and C3 (but each one was represented by a single site), one had moderate WQ: C5, one had poor WQ: C4, and, lastly, C6 had 8 sites consisting of worse WQ. Remarkably, Lum1 site, which is grouped in C4, was clustered separately from other Lum sites which are in the C6 group. Similarly, Cha1 belongs to C6 cluster despite being the highest altitude location and having good physical-chemical conditions (i.e., high oxygen concentrations and low temperature).

Figure 6.
Community-based clustering of locations. Axes represent the distance among sampling sites based on abundances (discrete values). The BMWP-Col class for each site is shown in coloured circles, where blue = good, green = moderate, yellow = poor, orange = bad, and red = very bad quality.
The distribution of the FFG is displayed in Figure 7 for the community-based clustering. The sites in the first three clusters had good water quality. These clusters also had the greatest diversity of FFG. There was a dominance of scrapers in C1 (36%) and C2 (40%), as well as a relatively high abundance in C3 and C5. The latter represented sites with good water quality (moderate in BMWP-Col index). Shredders dominated the C3 cluster with 62% (Sal1—good water quality) and had relatively similar abundance in the other clusters with good quality (C1, C2, and C5). Similar to other previous analyses, predators showed an equitable distribution in each cluster, indicating that they adapted very well to different environmental conditions, their dominance being slightly higher in the C6 cluster with lower WQ, than being composed of a greater number of sites. Their absolute abundance is greater than what their relative abundance represents with respect to other clusters. Collector-gatherers dominated in the C4 and C6 clusters with 70% and 69% relative abundance, respectively, although they were also highly abundant in the C5 cluster (moderate WQ). Its presence in the clusters on the left of Figure 7 was relatively low compared to its dominance at the other sites.

Figure 7.
Functional feeding group distribution per cluster for community-based clustering analyScheme 6. CF, SH, SC, PA, PR, and CG refers to the collector-filterers, shredders, scrapers, parasites, predators, and collector-gatherers, respectively. Cluster 1 represents the leftmost cluster, while Cluster 6 represents the rightmost cluster in Figure 6.
4. Discussion
Instream variability of macroinvertebrate functional feeding group composition is usually linked with chemical interactions and site-specific conditions of which the impact is hard to be unscrambled by biotic indices [20]. Multiple chemical (e.g., nitrogen, conductivity, oxygen) and site-specific (e.g., elevation, velocity, depth, width) variables were identified as potential variables explaining the difference in functional feeding group composition among clusters in the CRB and ARB. The elevation ranges might be also considered as an influential variable as the longitudinal gradient of the river is affected by upstream locations and surrounding land use [81]. In short, our results are in line with the findings of previously reported research, which shows that these variables are not only important for taxonomic diversity but also influence functional diversity [20,82,83,84].
There is a need for a global assessment system using cost-effective bioindicators that track changes in ecosystem health and composition, in which this system could be achievable in a short-term perspective for riverine ecosystems [4]. Bioindicators and ecological knowledge are applied to assess stream quality. Both have contributed to the improvement of the ecological status of many riverine ecosystems [85].
Approximately 40% of the studies applied sensitivity metrics in river assessments, and the majority of these studies (31%) used a variant of the Biological Monitoring Working Party (BMWP) and Average Score Per Taxon (ASPT) [4,86]. When applying the BMWP-Col index, it seems that the more biodiverse the aquatic community, the higher the BMWP-Col, the better the WQ. The index is not affected by the number of individuals. That is, if you have 6 taxa, even though there are only a few individuals (8) present, such as the case of the Lum4 site, it still obtained a better BMWP-Col score (44). On the other hand, the Dui1 site, which is located on a higher elevation, only obtained a WQ score of 14, despite the presence of 5 taxa and 43 individuals. Similarly, Rev2 was classified as the site with good WQ, although the site had the least number of individuals compared to the rest of the Rev sites. It was expected, though, that Rev2 obtained a lower score since a lower taxa diversity and abundance were observed. A possible cause of this decrease in quality could have been the presence of upstream tilapia farms, which can contribute to turbidity and loss of water quality (i.e., wastewater, improper management, excess fish and removal of sediment, modification of the river habitat to adapt the fish farm). Although this problem was not seen at this sampling point, it could be considered that the anthropic impact by piscicolas in the Ecuadorian Amazon region is not significant.
The best WQ was found at sites above 1200 m.a.s.l. (except for the Cha1 site). The Loc1, Sal1, and specifically Rev1 sites had the best BMWP-Col score since they were very pristine and had very diverse macroinvertebrate communities. Rev1 is a site with high biodiversity and good water quality, in which 503 individuals and 20 taxa were collected. The site had also a good diversity of traits (with a certain dominance of scrapers and predators). Cha1 was classified as poor water quality, although it looks pristine and has high elevation. A probable explanation for this observation is the exceptionally high water velocity in Cha1 due to the presence of a waterfall, resulting in the presence of a few invertebrates that are tolerant to this high flow velocity. The sites located on the Lumbaqui River (a tributary of the Aguarico River) have a poor to bad WQ and both of them have an elevation of 500 m.a.s.l. Both sites had wide width (Lum3 = 10 m or Lum4 = 100 m) for which the macroinvertebrates were collected on the banks. It appears that the hydromorphological variables depth and width were correlated to turbidity, and were also related to sites with worse water quality. These sites may have experienced a cumulative impact from anthropogenic activities as both are downstream sites. The sites with the worst water quality according to the BMWP-Col WQ classification were Dui1, Ag1, and Ph1. Dui1 had high turbidity (brown water), which can be attributed to its sediment, which is clayey, and its location in the middle of the jungle, wherein there is constant precipitation or permanent flooding. High water quality would be expected at the Dui1 site, but that was not the case. It is known that turbidity makes it more difficult for fishes and macroinvertebrates to breathe (the gills of the fishes and the trachea of the macroinvertebrates get obstructed). Thus, without macroinvertebrates, there was bad BMWP, although, physicochemically, the water might be of superior quality. The Ag1 site, located at 285 m.a.s.l., also had high turbidity, which possibly resulted in a low number of taxa and individuals, which gave rise to very poor WQ. The environmental impact on the Ph1 site was very evident. The sampling site had been affected by a recent oil spill and, despite the cleaning and decontamination, there were still drops of oil emerging from the aquatic sediment. This contamination explained the separation of this site from others in the analyses, in which Ph1 had the lowest diversity (only three individuals of predators) resulting in a very bad WQ. The Ph2 site, although being relatively close to Ph1, was not directly affected by the oil spill and could thus be considered as a lesser-impacted site in comparison with Ph1, since the former’s BMWP-Col score, taxonomic diversity, and abundance are much higher than the latter. We can therefore infer the considerable effects of oil spills on lotic ecosystems from these two sites.
Anthropic impacts have different levels of impact depending on their severity, temporality, persistence, and possible treatment. Commonly considered minor impacts are those that come from diffuse or isolated pollution such as a tilapia farm (Rev2), wastewater from small towns, isolated homes in the middle of the forest/jungle (Ph2 and Lumbaqui sites), or even from small agricultural plots (sites below 1000 m.a.s.l.) [63,65,66]. This type of disturbance usually generates inconveniences in the biological communities that inhabit the rivers and therefore can lead to the decrease of biodiversity and abundance. However, the case of oil or mining exploitation can be even more devastating because their impacts persist over time and are more complex and challenging to remove from the environment [10,11,12,13,64]. The impact of the latter type of stressors is very severe and interrupts the dynamics and ecological functions that normally are given by the site-specific conditions, the seasonal fluctuations of the physical-chemical variables, or the temporal patterns of rainfall, which determine the composition of aquatic invertebrate communities. Instead, biological communities decline dramatically in terms of abundance and diversity, and, in some cases, they even disappear from the impacted systems [9,54,61]. Comparable findings are reported in several similar studies in other tropical regions (e.g., [87,88,89,90,91]).
Trait metrics were used in 25% of freshwater assessment studies in tropical countries and, of those studies, feeding habits were mostly investigated (85%) [4]. The cluster analysis in general shows high linkages between closely located sampling sites and BMWP-Col score quality, indicating a fluctuating community composition and trait distribution.
In this study area, the most representative FFGs were scrapers, shredders, collector-filterers, predators, and collector-gatherers. There seems to be a specific distribution relationship not only between elevation gradient and temperature but also with the chemical quality of the water and the hydromorphological conditions. The FFG association with WQ is evident considering that the diversity and dominance of some feeding traits completely change as the degree of disturbance increases. Thus, in sites with good quality all the FFG are present, with a slight dominance of SC and PR, while in the sites with poorer quality the diversity of FFG is reduced with a dominance of CG. Tor et al. [4] pointed out that FFGs were often successful in detecting river degradation: the authors found ecologically meaningful changes in the composition of traits that could be related to perturbations; however, the responses were sometimes also unexpected. In general, these observed patterns of FFG composition along the CRB and ARB can be summarised as follows: (i) CG were in general dominant and were more abundant at low WQ and downstream sites; (ii) SC were the second most abundant group, dominating mostly high WQ and upstream sites; (iii) PR were homogeneously distributed among the sites, without clear dominance, and their presence was slightly higher in sites with medium-low WQ and downstream; and (iv) SH and CF were almost absent and their abundance was greater in good quality sites. These patterns are almost in line with the river continuum concept (RCC) [49], but instead of determining the FFG composition in the stream orders, our study mainly investigates the different water quality classes. Some of the sites in this study are at low stream order, while others are high order streams. The deviations from the RCC are attributed to the presence of different kinds of stressors, which resulted in altered FFG composition.
The high abundances of CG and the distribution of SH are potentially linked with altitude and temperature. Fierro et al. [92] show that CG are very abundant at altitudes below 1000 m.a.s.l. and prefer warmer temperatures (such as the warm climate of the Amazon in medium-low mountains), while the SH are more abundant in colder temperatures (e.g., the high mountains). The absence of shredders can also be attributed to environmental conditions such as the season with no leaf shedding and continuously high temperatures in the Amazon region, supporting microbial growth and related degradation of coarse organic matter [20]. These factors limit the overall food availability for shredders and influence the food chain. Moreover, high flow velocities due to extreme rain events can flush out the accumulated coarse particulate organic matter (CPOM) stock and, with some taxa being more vulnerable than others, alter the community composition and decrease the overall taxa richness, requiring a process of recolonization during the limited dry periods there [93]. However, a common problem was that shredders often behaved in unpredictable ways, especially in tropical regions. Although leaf litter is available throughout the year, shredders are still scarce [94] and not always correlated with the amount of leaf material [4]. The reasons for this may be the low nutritional quality of some tropical riparian plants, which are unpalatable and unattractive to shredders [95]. The CRB and ARB are not considered large-sized rivers, but neither are they small in comparison to other tropical rivers. In this regard, Marques & Barbosa [90] mentioned that the abundance of shredders may also be naturally low in medium- and large-sized rivers and change seasonally in response to stormy weather with an increase of allochthonous matter input [92]. The limited presence of shredders is not only the case for the CRB and ARB but has also been observed in other tropical rivers [69,96]. The relative distribution of predators is potentially linked with the possible absence of some perturbations, such as deforestation, intensified land-use, the input of nutrients, and organic effluents [4,83]. It may be also related to seasonality, that is, higher predator diversity and abundance had been already reported in Ecuadorian high-altitude streams during the dry season compared to the wet season [97].
Macroinvertebrate community composition in tropical regions with pronounced wet and dry seasons is expected to be better explained by the flood pulse concept [98] than by the RCC [49]. Within this concept, it is stated that the annual flooding and increased water level influence nutrient dynamics and, consequently, the complete food chain. For instance, when the water level rises, mineralised nutrients in the aquatic-terrestrial transition zone will be dissolved and transported downstream, being readily available for phytoplankton and related filter feeders. When the water level decreases again, suspended solids will settle, providing a new food source. At the same time, the higher flow velocity during the flood will drag along a fraction of the original macroinvertebrate community, locally changing the FFG distributions. Thus, the combination of new food sources and an altered community composition causes the development of a new community composition until the next flooding period [20]. But, on the other hand, as the RCC explains, shredders are more abundant in headwaters (stream order 1 to 3), with low rates of photosynthesis and allochthonous CPOM. Scrapers and collectors are more abundant in midreaches (stream order 4–6), with a photosynthesis and respiration (P:R) ratio > 1 and the presence of periphyton and other autochthonous organic materials. While in the lower reaches (stream order > 6), with the ratio again less than 1 (P:R < 1), a lot of turbidity and a surface film from suspended fine particulate organic matter (FPOM), the macroinvertebrate community in these areas is made up of almost exclusively collectors, as well as a small share of predators [20,36,49]. This is exactly the situation observed within the study area, although with the relatively low abundance of SH and with the almost ubiquitous presence of PR along the rivers.
The integration of biotic indices and traits to the physical-chemical analysis of water has proven to be an important tool in monitoring, evaluation, water management, and decision-making for researchers and stakeholders (e.g., [30,99,100]). The use of the biological traits has often provided a structured understanding of the anthropogenic stressors impacts [101], enabling the comparison of species groups from different systems and assemblages [7]. For instance, in this study, they indicate how feeding habits are directly associated with the metabolic resources that individuals need and, therefore, to the dominant productivity pathways that operate in a given water space, such as primary or secondary productivity, as also explained by the RCC [49,82,102]. Nevertheless, some challenges associated with the application of traits are the low taxonomical resolution of the data (often family), a general lack of autecological knowledge for many taxa [4,103], and the absence of a standardized methodology for trait allocation in this specific Ecuadorian Amazon region [36]. Altogether, the use of traits offers great potential in water assessments but, currently, more research is needed if used in routine monitoring covering larger areas and river typologies, especially in the Amazon regions due to the unexplored areas and the difficulty in accessing these regions.
The information collected in this work can be useful as a baseline for future work in this study area. These data can be used as a comparison for future sampling campaigns in the region, to determine the long-term effect of the oil spill, and to verify the areas that might be endangered due to new environmental stressors that may worsen the water quality, such as a dam the was constructed within the study area in 2010 and was operational in 2016. Furthermore, it is noteworthy to examine if the feeding habits of macroinvertebrates will follow the same patterns as observed in this study (i.e., CG dominance in places with poorer water quality) after the construction and operation of dams. Considering the fragility and increasing anthropic pressure to which these aquatic ecosystems are subjected, continuous and systematized biomonitoring needs to be proposed and executed. At this point, this work can lay the methodological and technical bases of some variables to study such as physical, chemical, hydromorphological, and even biological (aquatic invertebrates) ones.
Riverine macroinvertebrates have an excellent track record as indicators of common human perturbations to rivers, acting alone or in synergy, by using relatively simple and cost-effective biomonitoring methods. The current and projected future land-use [104] is of much concern for the integrity of rivers, especially in developing economies, where natural ecosystems are particularly exposed to stressors and do not have the resources for biomonitoring of surface waters [4]. In the region, in addition to economic, political, and administrative issues, there are still some challenges to be overcome in terms of biological, hydrological, ecological, and limnological knowledge in order to develop continuous and adequate biomonitoring to the characteristics of tropical lotic ecosystems. The application of systematic and periodic monitoring could fill the gaps around the use of specific macroinvertebrate indices, being able to even create indices for the Ecuadorian Amazon region (considering the diversity of ecosystems, altitude, latitude, land use, topography, river typologies, etc.). Furthermore, it is also valuable to develop trait-based metrics and a trait database applicable for species found in the Amazon region. Once that baseline has been developed and implemented, these databases can be included in the national and supra-national structures, relying on reproducible and standardized assessment methods for comparable assessment across spatial and temporal scales [4].
5. Conclusions
The macroinvertebrate community composition of the Coca and Aguarico River basins (Ecuadorian Amazon) changes from the source to the mouth. A similarity in taxa abundance and feeding group composition was observed between sites of the same or near-similar water quality (using the BMWP-Col index), except in a few cases. Diversity of taxa and functional feeding groups (FFG) were generally scarce but were more abundant in good quality sites. Collector-gathers (CG) were, in general, dominant and were particularly abundant at low WQ and downstream sites. Scrapers (SC) were the second most abundant group, dominating mostly at good WQ and upstream sites. Both shredders (SH) and collector-filterers (CF) were almost absent and were more abundant in good quality sites. It was determined that elevation, pH, depth, and temperature play an important role in explaining the distribution and abundance of taxa and traits. Generally, the higher sites, with better water quality, and a priori without external stressors have a higher diversity of taxa and FFG, while the downstream sites with greater depth and average width are correlated with low water quality, which could be due to the cumulative impact of various stressors. It could be observed through the physicochemical and especially biological variables that the worst water quality was linked to an oil spill, significantly limiting the diversity of macroinvertebrates. Therefore, taking this last circumstance as an example, it is possible to use this research as a baseline and reference information for possible future bioassessment campaigns and to disentangle the effect of anthropogenic disturbance from natural changes to adjust the values of biotic indexes to different sections of the rivers. The aquatic environments of the Amazon region lack in-depth knowledge on both taxonomic and functional diversity, complementary with the physical and chemical data. This shortfall impedes the development of useful mechanisms and tools for stakeholders. Thus, this research aims to fill this void.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.C., C.V.d.h., M.A.E.F. and P.L.M.G.; methodology, S.C., C.V.d.h., M.A.E.F., M.V. and P.L.M.G.; field sampling, C.V.d.h., M.A.E.F., T.O., M.G. and P.L.M.G.; software, M.A.E.F.; validation, C.V.d.h.; formal analysis, S.C., M.A.E.F., M.V. and C.V.d.h.; investigation, S.C., C.V.d.h., M.A.E.F. and P.L.M.G.; resources, P.L.M.G., M.G. and C.V.d.h.; data curation, K.L., C.V.d.h., S.C. and M.A.E.F.; writing—original draft preparation, S.C., M.A.E.F., P.L.M.G. and C.V.d.h.; writing—review and editing, S.C., M.A.E.F., P.L.M.G. and C.V.d.h.; visualization, S.C. and M.A.E.F.; supervision, C.V.d.h. and P.L.M.G.; project administration, C.V.d.h. and P.L.M.G.; funding acquisition, C.V.d.h. and P.L.M.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by VLIR UOS SI ZEIN2014Z155 assigned to Christine Van der heyden. Additionally, financial support was provided through the Flemish Interuniversity Council and University Development Cooperation (VLIR-UOS) and the VLIR Ecuador Biodiversity Network project.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable as the research does not involve human subject.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available in the Appendix A.
Acknowledgments
We thank the biotechnology and natural resource students of the Universidad Técnica del Norte, who joined and assisted the sampling campaign.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Appendix A

Table A1.
List of all orders, families, and functional feeding group (FFG) assigned based on available information, encountered in the Coca and Aguarico River basins. Cited reference (a) Damanik-Amabrita et al. [27], (b) Ramirez & Gutierrez [71], (c) Tomanova et al. [72], (d) Yang et al. [74], (e) Wehrtmann et al. [73], (f) Nessimian et al. [75], (g) Dudgeon & Gao [69] and (h) Niu & Dudgeon [70]. The bold “c” letters indicate the FFG that Tomanova et al. [72] assigns the highest feeding habit.
Table A1.
List of all orders, families, and functional feeding group (FFG) assigned based on available information, encountered in the Coca and Aguarico River basins. Cited reference (a) Damanik-Amabrita et al. [27], (b) Ramirez & Gutierrez [71], (c) Tomanova et al. [72], (d) Yang et al. [74], (e) Wehrtmann et al. [73], (f) Nessimian et al. [75], (g) Dudgeon & Gao [69] and (h) Niu & Dudgeon [70]. The bold “c” letters indicate the FFG that Tomanova et al. [72] assigns the highest feeding habit.
| Order | Family | Parasite (PA) | Collector-Filterer (CF) | Shredder (SH) | Scraper (SC) | Predator (PR) | Collector-Gatherer (CG) | Piercer (PI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acari | Acari | a | ||||||
| Amphipoda | Hyalellidae | a | ||||||
| Architaenioglossa | Ampullariidae | a | ||||||
| Coleoptera | Dryopidae | b | a,b | |||||
| Elmidae | b,c | a,b,c | b,c | |||||
| Hydrophilidae | c | a,b,c | b,c | |||||
| Lampyridae | a,b | |||||||
| Psephenidae | a,b,c | c | ||||||
| Ptilodactylidae | a,b | |||||||
| Scirtidae | b | b | a,b | b | ||||
| Decapoda | Pseudothelphusidae | d | e | |||||
| Diptera | Blephariceridae | a,b | ||||||
| Chironomidae NTP | b | c | c | b,c | a,b,c | |||
| Chironomidae TP | b | c | c | b,c | a,b,c | |||
| Dixidae | a | |||||||
| Dolichopodidae | b | |||||||
| Limoniidae | a | |||||||
| Muscidae | b | |||||||
| Psychodidae | c | c | b,c | |||||
| Simuliidae | a,b,c | b,c | b | b | ||||
| Tipulidae | b,c | c | c | b,c | c | |||
| Ephemeroptera | Baetidae | c | a,b,c | b,c | ||||
| Leptohyphidae | b | c | c | a,b,c | ||||
| Leptophlebiidae | b,c | c | b,c | a,b,c | ||||
| Oligoneuriidae | a,b | |||||||
| Haplotaxida | Tubificidae | a | ||||||
| Hemiptera | Hebridae | a,b | ||||||
| Naucoridae | a,b,c | c | ||||||
| Veliidae | a,b | |||||||
| Hirudinida | Glossiphoniidae | a | ||||||
| Lepidoptera | Pyralidae | c | c | c | ||||
| Littorinimorpha | Hydrobiidae | a | ||||||
| Megaloptera | Corydalidae | a,b,c | ||||||
| Odonata | Calopterygidae | a,b | ||||||
| Coenagrionidae | a,b,c | |||||||
| Libellulidae | a,b,c | |||||||
| Polythoridae | b | |||||||
| Opisthopora | Lumbricidae | f | ||||||
| Plecoptera | Perlidae | a,b,c | ||||||
| Sorbeoconcha | Pachychilidae | g,h | ||||||
| Trichoptera | Calamoceratidae | a,b,c | b | c | ||||
| Ecnomidae | b | |||||||
| Helicopsychidae | a,b,c | c | ||||||
| Hydrobiosidae | a,b | |||||||
| Hydropsychidae | a,b,c | c | b | b | c | |||
| Philopotamidae | a,b,c | c | ||||||
| Polycentropodidae | b | c | b,c | a | ||||
| Sericostomatidae | b | |||||||
| Xiphocentronidae | b,c | |||||||
| Tricladida | Dugesiidae | a |

Table A2.
Spearman’s rank correlation matrix of 11 environmental variables of the CRB and ARB dataset. * means significant correlations (p < 0.05) and a moderate correlation (up to 0.5) are marked in bold.
Table A2.
Spearman’s rank correlation matrix of 11 environmental variables of the CRB and ARB dataset. * means significant correlations (p < 0.05) and a moderate correlation (up to 0.5) are marked in bold.
| Temp | DO | DO sat | pH | Cond | NH4 | NO2 | Total N | Phosphate | Total P | Elevation | BMWP-Col | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature | 1.00 | |||||||||||
| DO | −0.60 * | 1.00 | ||||||||||
| DO saturation | −0.69 * | 0.68 * | 1.00 | |||||||||
| pH | −0.56 * | 0.57 * | 0.81 * | 1.00 | ||||||||
| Conductivity | −0.58 * | 0.06 | 0.47 | 0.70 * | 1.00 | |||||||
| Ammonium-N | 0.18 | 0.16 | −0.42 | −0.14 | −0.25 | 1.00 | ||||||
| Nitrite–N | 0.10 | −0.09 | −0.20 | 0.16 | 0.35 | 0.40 | 1.00 | |||||
| Total N | 0.20 | −0.35 | −0.53 * | −0.36 | −0.07 | 0.21 | 0.11 | 1.00 | ||||
| Phosphate | −0.02 | 0.57 * | 0.49 | 0.56 * | 0.16 | 0.15 | 0.17 | −0.43 | 1.00 | |||
| Total P | −0.24 | 0.27 | 0.38 | 0.69 * | 0.59 * | 0.28 | 0.59 * | −0.41 | 0.52 | 1.00 | ||
| Elevation | −0.80 * | 0.23 | 0.72 * | 0.51 | 0.65 * | −0.65 * | −0.28 | −0.23 | −0.07 | 0.06 | 1.00 | |
| BMWP-Col | −0.51 | 0.11 | 0.43 | 0.33 | 0.39 | −0.23 | −0.28 | −0.43 | 0.03 | 0.26 | 0.62 * | 1.00 |

Table A3.
List of encountered taxa with their total abundance in the basins, number of sampling sites where they were found, and their tolerance scores based on BMWP-Col by Alvarez [39].
Table A3.
List of encountered taxa with their total abundance in the basins, number of sampling sites where they were found, and their tolerance scores based on BMWP-Col by Alvarez [39].
| Order | Family | Total Abundance | Number of Sampling Sites | BMWP-Col Tolerance Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acari | Acari | 2 | 2 | - |
| Amphipoda | Hyalellidae | 1 | 1 | 7 |
| Architaenioglossa | Ampullariidae | 1 | 1 | 6 |
| Coleoptera | Dryopidae | 1 | 1 | 6 |
| Elmidae | 46 | 9 | 7 | |
| Hydrophilidae | 10 | 5 | 4 | |
| Lampyridae | 1 | 1 | 10 | |
| Psephenidae | 12 | 2 | 10 | |
| Ptilodactylidae | 115 | 5 | 9 | |
| Scirtidae | 1 | 1 | 6 | |
| Decapoda | Pseudothelphusidae | 1 | 1 | 8 |
| Diptera | Blephariceridae | 7 | 4 | 10 |
| Chironomidae NTP | 54 | 10 | 2 | |
| Chironomidae TP | 32 | 1 | 2 | |
| Dixidae | 1 | 1 | 4 | |
| Dolichopodidae | 1 | 1 | 4 | |
| Limoniidae | 40 | 7 | - | |
| Muscidae | 1 | 1 | 5 | |
| Psychodidae | 1 | 1 | 4 | |
| Simuliidae | 11 | 2 | 6 | |
| Tipulidae | 2 | 2 | 5 | |
| Ephemeroptera | Baetidae | 336 | 9 | 5 |
| Leptohyphidae | 192 | 8 | 7 | |
| Leptophlebiidae | 193 | 10 | 8 | |
| Oligoneuriidae | 1 | 1 | 10 | |
| Haplotaxida | Tubificidae | 25 | 6 | 1 |
| Hemiptera | Hebridae | 1 | 1 | - |
| Naucoridae | 5 | 2 | 5 | |
| Veliidae | 6 | 5 | 6 | |
| Hirudinida | Glossiphoniidae | 2 | 1 | 3 |
| Lepidoptera | Pyralidae | 1 | 1 | 4 |
| Littorinimorpha | Hydrobiidae | 1 | 1 | 7 |
| Megaloptera | Corydalidae | 27 | 6 | 9 |
| Odonata | Calopterygidae | 1 | 1 | 7 |
| Coenagrionidae | 3 | 1 | 6 | |
| Libellulidae | 6 | 5 | 5 | |
| Polythoridae | 4 | 2 | 10 | |
| Opisthopora | Lumbricidae | 1 | 1 | - |
| Plecoptera | Perlidae | 206 | 6 | 10 |
| Sorbeoconcha | Pachychilidae | 2 | 2 | - |
| Trichoptera | Calamoceratidae | 2 | 2 | 10 |
| Ecnomidae | 1 | 1 | - | |
| Helicopsychidae | 9 | 4 | 9 | |
| Hydrobiosidae | 14 | 3 | 9 | |
| Hydropsychidae | 27 | 6 | 5 | |
| Philopotamidae | 9 | 3 | 9 | |
| Polycentropodidae | 2 | 1 | 7 | |
| Sericostomatidae | 6 | 3 | - | |
| Xiphocentronidae | 1 | 1 | 9 | |
| Tricladida | Dugesiidae | 1 | 1 | 6 |



Figure A1.
Photographs of the sampling sites on the Coca and Aguarico Rivers. The letters distinguish the place where the images were taken, being (a) the Rev2 site, (b) the Loc1 and Sal1 sites, (c) the Cha1, (d) the Lum3 and Lum4 sites, (e) the Dui1 site, and (f) the Ph1 and Ph2 sites.
References
- Ganoulis, J.; Fried, J. Towards A “Good” Transboundary Hydro-Governance: From Conflict to Shared Management, 1st ed.; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; ISBN 9783319786247. [Google Scholar]
- Giri, S. Water quality prospective in Twenty First Century: Status of water quality in major river basins, contemporary strategies and impediments: A review. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 271, 116332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushal, S.S.; McDowell, W.H.; Wollheim, W.M.; Johnson, T.A.N.; Mayer, P.M.; Belt, K.T.; Penninov, M.J. Urban evolution: The role of water. Water 2015, 7, 4063–4087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksen, T.E.; Brittain, J.E.; Søli, G.; Jacobsen, D.; Goethals, P.; Friberg, N. A global perspective on the application of riverine macroinvertebrates as biological indicators in Africa, South-Central America, Mexico and Southern Asia. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, D. Water Quality Assessments—A Guide to Use of Biota, Sediments and Water in Environmental Monitoring, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: London, UK, 1996; ISBN1 0 419 21590 5 (HB). ISBN2 0 419 21600 6 (PB). [Google Scholar]
- Helson, J.E.; Williams, D.D. Development of a macroinvertebrate multimetric index for the assessment of low-land streams in the neotropics. Ecol. Indic. 2013, 29, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joao, C.; Perez-Bilbao, A.; Garrido, J. Macroinvertebrates as Indicators of Water Quality in Running Waters: 10 Years of Research in Rivers with Different Degrees of Anthropogenic Impacts. Ecol. Water Qual. Water Treat. Reuse 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borja-Serrano, P.; Ochoa-Herrera, V.; Maurice, L.; Morales, G.; Quilumbaqui, C.; Tejera, E.; Machado, A. Determination of the microbial and chemical loads in rivers from the Quito capital province of Ecuador (Pichincha)—A preliminary analysis of microbial and chemical quality of the main rivers. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 5048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celi, J.E.; Villamarín, F. Freshwater ecosystems of mainland Ecuador: Diversity, issues and perspectives. Acta Limnol. Bras. 2020, 32, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capparelli, M.V.; Moulatlet, G.M.; Abessa, D.M.d.S.; Lucas-Solis, O.; Rosero, B.; Galarza, E.; Tuba, D.; Carpintero, N.; Ochoa-Herrera, V.; Cipriani-Avila, I. An integrative approach to identify the impacts of multiple metal contamination sources on the Eastern Andean foothills of the Ecuadorian Amazonia. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 709, 136088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaderne Houssou, N.L.; Cordero, J.D.; Bouadjio-Boulic, A.; Morin, L.; Maestripieri, N.; Ferrant, S.; Belem, M.; Peláez, J.I.; Saenz, M.; Lerigoleur, E.; et al. Synchronizing histories of exposure and demography: The construction of an agent- based model of the ecuadorian amazon colonization and exposure to oil pollution hazards. JASSS 2019, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, B.G.; Veiga, M.M.; Kaplan, R.J.; Adler Miserendino, R.; Schudel, G.; Bergquist, B.A.; Guimarães, J.R.D.; Sobral, L.G.S.; Gonzalez-Mueller, C. Evidence of transboundary mercury and other pollutants in the Puyango-Tumbes River basin, Ecuador-Peru. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2018, 20, 632–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, J.; Coomes, O.T.; Mainville, N.; Mergler, D. Mercury Contamination in an Indicator Fish Species from Andean Amazonian Rivers Affected by Petroleum Extraction. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2015, 95, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antunes, A.P.; Fewster, R.M.; Venticinque, E.M.; Peres, C.A.; Levi, T.; Rohe, F.; Shepard, G.H. Empty forest or empty rivers? A century of commercial hunting in Amazonia. Sci. Adv. 2016, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaiswal, D.; Pandey, J. River ecosystem resilience risk index: A tool to quantitatively characterize resilience and critical transitions in human-impacted large rivers. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 268, 115771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sá-Oliveira, J.C.; Isaac, V.J.; Ferrari, S.F. Fish community structure as an indicator of the long-term effects of the damming of an Amazonian river. Environ. Biol. Fishes 2015, 98, 273–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escanilla-Minchel, R.; Alcayaga, H.; Soto-Alvarez, M.; Kinnard, C.; Urrutia, R. Evaluation of the impact of climate change on runoff generation in an andean glacier watershed. Water 2020, 12, 3547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wongchuig, S.C.; Mello, C.R.; Chou, S.C. Projections of the impacts of climate change on the water deficit and on the precipitation erosive indexes in Mantaro River Basin, Peru. J. Mt. Sci. 2018, 15, 264–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casagrande, E.; Recanati, F.; Rulli, M.C.; Bevacqua, D.; Melià, P. Water balance partitioning for ecosystem service assessment. A case study in the Amazon. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Echelpoel, W.; Van Forio, E.; Butsel, J.; Van Lock, K.; Dueñas, J.; Dominguez-granda, L.; Goethals, P.L.M. Macroinvertebrate functional feeding group structure along an impacted tropical river: The Portoviejo River (Ecuador). Limnologica 2018, 73, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forio, M.A.; Landuyt, D.; Bennetsen, E.; Lock, K.; Hanh, T.; Nguyen, T.; Naomi, M.; Ambarita, D.; Liz, P.; Musonge, S.; et al. Bayesian belief network models to analyse and predict ecological water quality in rivers. Ecol. Modell. 2015, 312, 222–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forio, M.A.; Goethals, P.L.M. An Integrated Approach of Multi-Community Monitoring and Assessment of Aquatic Ecosystems to Support Sustainable Development. Sustainanility 2020, 12, 5603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubach, M.N.; Ashauer, R.; Buchwalter, D.B.; De Lange, H.J.; Hamer, M.; Preuss, T.G.; Töpke, K.; Maund, S.J. Framework for traits-based assessment in ecotoxicology. Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2011, 7, 172–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koklu, R.; Sengorur, B.; Topal, B. Water quality assessment using multivariate statistical methods-a case study: Melen river system (Turkey). Water Resour. Manag. 2010, 24, 959–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matoušková, M.; Dvořák, M. Assessment of physical habitat modification in the Bílina River Basin. Limnetica 2011, 30, 293–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wepener, V.; van Dyk, C.; Bervoets, L.; O’Brien, G.; Covaci, A.; Cloete, Y. An assessment of the influence of multiple stressors on the Vaal River, South Africa. Phys. Chem. Earth 2011, 36, 949–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damanik-Ambarita, M.N.; Lock, K.; Boets, P.; Everaert, G.; Hanh, T.; Nguyen, T.; Anne, M.; Forio, E.; Liz, P.; Musonge, S.; et al. Ecological water quality analysis of the Guayas river basin (Ecuador) based on macroinvertebrates indices. Limnologica 2016, 57, 27–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damanik-Ambarita, M.N.; Boets, P.; Tien, H.; Thi, N.; Anne, M.; Forio, E.; Everaert, G.; Lock, K.; Liz, P.; Musonge, S.; et al. Impact assessment of local land use on ecological water quality of the Guayas river basin (Ecuador). Ecol. Inform. 2018, 48, 226–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sotomayor, G.; Hampel, H.; Vázquez, R.F.; Goethals, P.L.M. Multivariate-statistics based selection of a benthic macroinvertebrate index for assessing water quality in the Paute River basin (Ecuador). Ecol. Indic. 2020, 111, 106037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boonsoong, B.; Sangpradub, N.; Barbour, M.T.; Simachaya, W. An implementation plan for using biological indicators to improve assessment of water quality in Thailand. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2010, 165, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerves-Cobo, R.; Gonzalo, C.; Iñiguez-vela, X.; Catalina, D. Model-Based Analysis of the Potential of Macroinvertebrates as Indicators for Microbial Pathogens in Rivers. Water 2018, 10, 375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brittain, J.E.; Eikeland, T.J. Invertebrate drift—A review Invertebrate drift—A review. Hydrobiologia 1988, 166, 77–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabriels, W.; Lock, K.; Pauw, N.; De Goethals, P.L.M. Limnologica Multimetric Macroinvertebrate Index Flanders (MMIF) for biological assessment of rivers and lakes in Flanders (Belgium). Limnologica 2010, 40, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forio, M.A.; Mouton, A.; Lock, K.; Boets, P.; Thi, N.; Tien, H.; Naomi, M.; Ambarita, D.; Liz, P.; Musonge, S.; et al. Fuzzy modelling to identify key drivers of ecological water quality to support decision and policy making. Environ. Sci. Policy 2017, 68, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominguez-Granda, L.; Lock, K.; Goethals, P.L.M. Using multi-target clustering trees as a tool to predict biological water quality indices based on benthic macroinvertebrates and environmental parameters in the Chaguana watershed (Ecuador). Ecol. Inform. 2011, 6, 303–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forio, M.; Goethals, P.L.M.; Lock, K.; Asio, V.; Bande, M.; Thas, O. Model-based analysis of the relationship between macroinvertebrate traits and environmental river conditions. Environ. Model. Softw. 2018, 106, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holguin-Gonzalez, J.E.; Boets, P.; Alvarado, A.; Cisneros, F.; Carrasco, M.C.; Wyseure, G.; Nopens, I.; Goethals, P.L.M. Integrating hydraulic, physicochemical and ecological models to assess the effectiveness of water quality management strategies for the River Cuenca in Ecuador. Ecol. Modell. 2013, 254, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez, E.; Fernández, H.R. Macroinvertebrados Bentónicos Sudamericanos; Fundación Miguel Lillo: San Miguel de Tucumán, Argentina, 2009; ISBN 9789506680152. [Google Scholar]
- Álvarez, L.F. Metodología para la Utilización de los Macroinvertebrados Acuáticos como Indicadores de la Calidad del Agua; Alexander von Humboldt Biological Resources Research Institute: Bogotá, Colombia, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Roldán-Pérez, G. Bioindicación de la Calidad del Agua en Colombia. Uso del método BMWP/Col; Universidad de Antioquia: Medellín, Colombia, 2003; 170p. [Google Scholar]
- Verberk, W.C.E.P.; Noordwijk, C.G.E.; Van Hildrew, A.G. Delivering on a promise: Integrating species traits to transform descriptive community ecology into a predictive science. Freshw. Sci. 2013, 32, 531–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menezes, S.; Baird, D.J.; Soares, A.M.V.M. Beyond taxonomy: A review of macroinvertebrate trait-based community descriptors as tools for freshwater biomonitoring. J. Appl. Ecol. 2010, 47, 711–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tall, L.; Méthot, G.; Armellin, A.; Pinel-alloul, B. Bioassessment of Benthic Macroinvertebrates in Wetland Habitats of Lake Saint-Pierre (St. Lawrence River). J. Great Lakes Res. 2008, 34, 599–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calapez, A.R.; Serra, S.R.Q.; Santos, J.M.; Branco, P.; Ferreira, T.; Hein, T.; Brito, A.G.; Feio, M.J. The effect of hypoxia and flow decrease in macroinvertebrate functional responses: A trait-based approach to multiple-stressors in mesocosms. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 637–638, 647–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- James, A.B.W.; Dewson, Z.S.; Death, R.G. Do stream macroinvertebrates use instream refugia in response to severe short-term flow reduction in New Zealand streams ? Freshw. Biol. 2008, 53, 1316–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardo, I.; García, L. Abstraction in small lowland streams: Unforeseen hypoxia and anoxia effects. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 568, 226–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schäfer, R.B.; Kefford, B.J.; Metzeling, L.; Liess, M.; Burgert, S.; Marchant, R.; Pettigrove, V.; Goonan, P.; Nugegoda, D. A trait database of stream invertebrates for the ecological risk assessment of single and combined effects of salinity and pesticides in South-East Australia. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 2055–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boxall, A.B.A.; Rudd, M.A.; Brooks, B.W.; Caldwell, D.J.; Choi, K.; Hickmann, S.; Innes, E.; Ostapyk, K.; Staveley, J.P.; Verslycke, T.; et al. Pharmaceuticals and personal care products in the environment: What are the big questions? Environ. Health Perspect. 2012, 120, 1221–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vannote, R.L.; Minshall, G.W.; Cummins, K.W.; Sedell, J.R.; Cushing, C.E. The river continuum concept. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1980, 37, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foden, W.B.; Butchart, S.H.M.; Stuart, S.N.; Vié, J.C.; Akçakaya, H.R.; Angulo, A.; DeVantier, L.M.; Gutsche, A.; Turak, E.; Cao, L.; et al. Identifying the World’s Most Climate Change Vulnerable Species: A Systematic Trait-Based Assessment of all Birds, Amphibians and Corals. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, 5427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolédec, S.; Statzner, B.; Bournard, M. Species traits for fututre biomonitoring across ecoregions. Freshw. Biol. 1999, 42, 737–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, M.C.; Fierro, V.; Páez, S.; Plúa, F.; Carrera, M.I.; Moscoso, N.; Cazco, R.; Tamayo, G.; Ruiz, M.; Narváez, M.; et al. La Economía de los ecosistemas y la biodiversidad. Informe final: Resultados de las modelaciones biofísicas, valoración económica y propuesta de políticas. Cuenca del Río Coca, Ecuador; Quito, Ecuador. 2018. Available online: https://www.epn.edu.ec/wp-content/uploads/2018/03/Informe-Final-TEEB-Cuenca-Rio-Coca.pdf (accessed on 22 March 2021).
- Beck, H.E.; Zimmermann, N.E.; McVicar, T.R.; Vergopolan, N.; Berg, A.; Wood, E.F. Present and future köppen-geiger climate classification maps at 1-km resolution. Sci. Data 2018, 5, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexiades, A.V.; Encalada, A.C.; Lessmann, J.; Guayasamin, J.M. Spatial prediction of stream physicochemical parameters for the Napo River Basin, Ecuador. J. Freshw. Ecol. 2019, 34, 249–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez, S.; Terneus, F. Nexo agua—energía: Análisis del flujo hídrico del Proyecto Hidroeléctrico Coca Codo Sinclair The water-energy nexus: Analysis of the water flow of the Coca Codo Sinclair Hydroelectric Project. Ingenius 2019, 21, 53–62. [Google Scholar]
- Organization of American States (OAS). Plan de Ordenamiento y Manejo de las Cuencas de los Ríos San Miguel y Putumayo Indice Prefacio Instituciones citadas; Washington, DC, USA. 1987. Available online: https://www.oas.org/dsd/publications/Unit/oea49s/oea49s.pdf (accessed on 25 March 2021).
- Galacatos, K.; Barriga-Salazar, R.; Stewart, D. Seasonal and Habitat Influences on Fish Communities within the Lower Yasuni River Basin of the Ecuadorian Amazon. Environ. Biol. Fishes 2004, 71, 33–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bass, M.S.; Finer, M.; Jenkins, C.N.; Kreft, H.; Cisneros-Heredia, D.F.; McCracken, S.F.; Pitman, N.C.A.; English, P.H.; Swing, K.; Villa, G.; et al. Global conservation significance of Ecuador’s Yasuní National Park. PLoS ONE 2010, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lessmann, J.; Guayasamin, J.M.; Casner, K.L.; Flecker, A.S.; Funk, W.C.; Ghalambor, C.K.; Gill, B.A.; Jácome-Negrete, I.; Kondratieff, B.C.; Poff, L.R.N.; et al. Freshwater vertebrate and invertebrate diversity patterns in an Andean-Amazon basin: Implications for conservation efforts. Neotrop. Biodivers. 2016, 2, 99–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mena, C.F.; Bilsborrow, R.E.; McClain, M.E. Socioeconomic drivers of deforestation in the Northern Ecuadorian Amazon. Environ. Manag. 2006, 37, 802–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera-Parra, J.L.; Vizcarra, C.; Mora, K.; Mayorga, H.; Dueñas, J.C. Spatial distribution of oil spills in the north eastern Ecuadorian Amazon: A comprehensive review of possible threats. Biol. Conserv. 2020, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PetroAmazonas, E. Nuestra Producción. Available online: https://www.petroamazonas.gob.ec/ (accessed on 18 January 2021).
- López, V. El proyecto hidroeléctrico Coca Codo Sinclair y la gobernanza energética en la Amazonía ecuatoriana. Let. Verdes Rev. Latinoam. Estud. Socioambientales 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- van Teijlingen, K. Minería a gran escala, pluralismo territorial y contención: Un mapeo de encuentros y desencuentros en la amazonía ecuatoriana. Estud. Atacameños. Arqueol. Antropol. Surandinas 2019, 275–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, F.; Gray, C.; Bilsborrow, R.E.; Mena, C.F.; Erlien, C.M.; Bremner, J.; Barbieri, A.; Walsh, S.J. Contrasting Colonist and Indigenous Impacts on Amazonian Forests. Conserv. Biol. 2010, 24, 881–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdivia, G. On indigeneity, change, and representation in the northeastern Ecuadorian Amazon. Environ. Plan. A 2005, 37, 285–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everaert, G.; Neve, J.; De Boets, P.; Dominguez-granda, L.; Mereta, S.T.; Ambelu, A.; Hoang, T.H.; Goethals, P.L.M.; Thas, O. Comparison of the Abiotic Preferences of Macroinvertebrates in Tropical River Basins. PLoS ONE 2014, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mereta, S.T.; Boets, P.; De Meester, L.; Goethals, P.L.M. Development of a multimetric index based on benthic macroinvertebrates for the assessment of natural wetlands in Southwest Ethiopia. Ecol. Indic. 2013, 29, 510–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudgeon, D.; Gao, B.W. Biodiversity and ecosystem functioning in a species-poor guild: A test using tropical stream detritivores. Hydrobiologia 2010, 652, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, S.Q.; Dudgeon, D. The influence of flow and season upon leaf-litter breakdown in monsoonal Hong Kong streams. Hydrobiologia 2011, 663, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ramírez, A.; Gutiérrez-Fonseca, P.E. Functional feeding groups of aquatic insect families in Latin America: A critical analysis and review of existing literature. Rev. Biol. Trop. 2014, 62, 155–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomanova, A.; Moya, N.; Oberdorff, T. Using macroinvertebrate biological traits for assessing biotic integrity of Neotropical streams. River Res. Appl. 2008, 24, 1230–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wehrtmann, I.S.; Hernández-Díaz, D.; Cumberlidge, N. Freshwater crabs as predators and prey: The case of Ptychophallus uncinatus Campos & Lemaitre, 1999 (Brachyura, Pseudothelphusidae) from Costa Rica, Central America. Lat. Am. J. Aquat. Res. 2019, 47, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Wehrtmann, I.S.; Wenger, S.J.; Rugenski, A.T. Neotropical freshwater crabs (Decapoda: Pseudothelphusidae) shred leaves. Nauplius 2020, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nessimian, J.L.; Dorvillé, L.F.M.; Sanseverino, A.M.; Baptista, D.F. Relation between flood pulse and functional composition of the macroinvertebrate benthic fauna in the lower Rio Negro, Amazonas, Brazil. Amazoniana 1998, 15, 35–50. [Google Scholar]
- Pearson, T.; Rosenberg, R. Macrobenthic succession in relation to organic enrichment and pollution of the marine environment. Oceanogr. Mar. Biol. An Annu. Rev. 1978, 16, 229–331. [Google Scholar]
- Schmera, D.; Heino, J.; Podani, J.; Erős, T.; Dolédec, S. Functional diversity: A review of methodology and current knowledge in freshwater macroinvertebrate research. Hydrobiologia 2017, 787, 27–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing, 4.0.3 ed. Vienna, Austria. Available online: https://www.r-project.org/ (accessed on 28 December 2020).
- RStudio Team RStudio: Integrated Development for R. Available online: https://www.rstudio.com/ (accessed on 28 December 2020).
- Grande, J.A.; Jiménez, A.; Borrego, J.; de la Torre, M.L.; Gómez, T. Relationships Between Conductivity and pH in Channels Exposed to Acid Mine Drainage Processes: Study of a Large Mass of Data Using Classical Statistics. Water Resour. Manag. 2010, 24, 4579–4587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.; Boets, P.; Lock, K.; Anne, M.; Forio, E.; Echelpoel, W.; Van Butsel, J.; Van Dueñas, J.A.; Everaert, G.; Elvin, L.; et al. Water quality related macroinvertebrate community responses to environmental gradients in the Portoviejo River (Ecuador). Ann. Limnol. J. Limnol. 2017, 53, 203–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Brouwer, J.H.F.; Verdonschot, P.F.M.; Eekhout, J.P.C.; Verdonschot, R.C.M. Macroinvertebrate taxonomic and trait-based responses to large-wood reintroduction in lowland streams. Freshw. Sci. 2020, 39, 693–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, N.; Yang, W.; Zhou, Y.; González-Bergonzoni, I.; Zhang, J.; Chen, K.; Vidal, N.; Jeppesen, E.; Liu, Z.; Wang, B. Different responses of functional traits and diversity of stream macroinvertebrates to environmental and spatial factors in the Xishuangbanna watershed of the upper Mekong River Basin, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 574, 288–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statzner, B.; Bêche, L.A. Can biological invertebrate traits resolve effects of multiple stressors on running water ecosystems? Freshw. Biol. 2010, 55, 80–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friberg, N.; Bonada, N.; Bradley, D.C.; Dunbar, M.J.; Edwards, F.K.; Grey, J.; Hayes, R.B.; Hildrew, A.G.; Lamouroux, N.; Trimmer, M.; et al. Biomonitoring of Human Impacts in Freshwater Ecosystems. The Good, the Bad and the Ugly. 2011, 44, 1–68. [Google Scholar]
- Armitage, P.D.; Moss, D.; Wright, J.F.; Furse, M.T. The performance of a new biological water quality score system based on macroinvertebrates over a wide range of unpolluted running-water sites. Water Res. 1983, 17, 333–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buss, D.; Baptista, D.; Nessimian, J.; Egler, M. Substrate specificity, environmental degradation and disturbance structuring macroinvertebrate assemblages in neotropical streams. Hydrobiologia 2004, 518, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chukwu, L.; Nwachukwu, S. Impact of refined petroleum spills on water quality, macro-invertebrate and microbial communities of a tropical aquatic environment. Journal of environmental biology. J. Environ. Biol. 2005, 26, 449–458. [Google Scholar]
- Couceiro, S.R.M.; Hamada, N.; Forsberg, B.R.; Padovesi-Fonseca, C. Effects of anthropogenic silt on aquatic macroinvertebrates and abiotic variables in streams in the Brazilian Amazon. J. Soils Sediments 2010, 10, 89–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, M.M.; Barbosa, F. Biological quality of waters from an impacted tropical watershed (middle Rio Doce basin, southeast Brazil), using benthic macroinvertebrate communities as an indicator. Hydrobiologia 2001, 457, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinson, M.R.; Dinger, E.C.; Kotynek, J.; Dethier, M. Effects of oil pollution on aquatic macroinvertebrate assemblages in Gabon wetlands. Afr. J. Aquat. Sci. 2008, 33, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fierro, P.; Bertrán, C.; Mercado, M.; Peña-Cortés, F.; Tapia, J.; Hauenstein, E.; Caputo, L.; Vargas-Chacoff, L. Landscape composition as a determinant of diversity and functional feeding groups of aquatic macroinvertebrates in southern rivers of the Araucanía, Chile. Lat. Am. J. Aquat. Res. 2015, 43, 186–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brewin, P.A.; Buckton, S.T.; Ormerod, S.J. The seasonal dynamics and persistence of stream macroinvertebrates in Nepal: Do monsoon floods represent disturbance? Freshw. Biol. 2000, 44, 581–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesa, L.M. Influence of riparian quality on macroinvertebrate assemblages in subtropical mountain streams. J. Nat. Hist. 2014, 48, 1153–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buss, D.F.; Carlisle, D.M.; Chon, T.S.; Culp, J.; Harding, J.S.; Keizer-Vlek, H.E.; Robinson, W.A.; Strachan, S.; Thirion, C.; Hughes, R.M. Stream biomonitoring using macroinvertebrates around the globe: A comparison of large-scale programs. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wantzen, K.M.; Wagner, R.; Suetfeld, R.; Junk, W.J. How do plant-herbivore interactions of trees influence coarse detritus processing by shredders in aquatic ecosystems of different latitudes? SIL Proc. 1922–2010 2002, 28, 815–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobsen, D.; Encalada, A. The macroinvertebrate fauna of Ecuadorian highland streams in the wet and dry season. Arch. fur Hydrobiol. 1998, 142, 53–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junk, W.; Bayley, P.B.; Sparks, R.E. The Flood Pulse Concept in River-Floodplain Systems. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1989, 106, 110–127. [Google Scholar]
- Buss, D.; Salles, F. Using Baetidae species as biological indicators of environmental degradation in a Brazilian river basin. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2007, 130, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damanik-Ambarita, M.N.; Everaert, G.; Anne, M.; Forio, E.; Hanh, T.; Nguyen, T.; Lock, K.; Liz, P.; Musonge, S.; Suhareva, N.; et al. Generalized Linear Models to Identify Key Hydromorphological and Chemical Variables Determining the Occurrence of Macroinvertebrates in the Guayas River Basin (Ecuador). Water 2016, 8, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, N.; Thodsen, H.; Andersen, H.E.; Tornbjerg, H.; Baattrup-Pedersen, A.; Riis, T. Flow regimes filter species traits of benthic diatom communities and modify the functional features of lowland streams—A nationwide scale study. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 651, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merritt, R.W.; Cummins, K.W.; Berg, M.B.; Novak, J.A.; Higgins, M.J.; Wessell, K.J.; Lessard, J.L. Development and application of a macroinvertebrate functional-group approach in the bioassessment of remnant river oxbows in southwest Florida. J. N. Am. Benthol. Soc. 2002, 21, 290–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buss, D.F.; Vitorino, A.S. Rapid Bioassessment Protocols using benthic macroinvertebrates in Brazil: Evaluation of taxonomic sufficiency. J. N. Am. Benthol. Soc. 2010, 29, 562–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz, S.; Settele, J.; Brondízio, E. Summary for Policymakers of the Global Assessment Report on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services of the Intergovernmental Science-Policy Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services. The Intergovernmental Science-Policy Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services. 2019. Available online: https://www.ipbes.net/sites/default/files/downloads/spm_unedited_advance_for_posting_htn.pdf (accessed on 2 April 2021).
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).