Mechanistic Study of Pb2+ Removal from Aqueous Solutions Using Eggshells
Abstract
1. Introduction
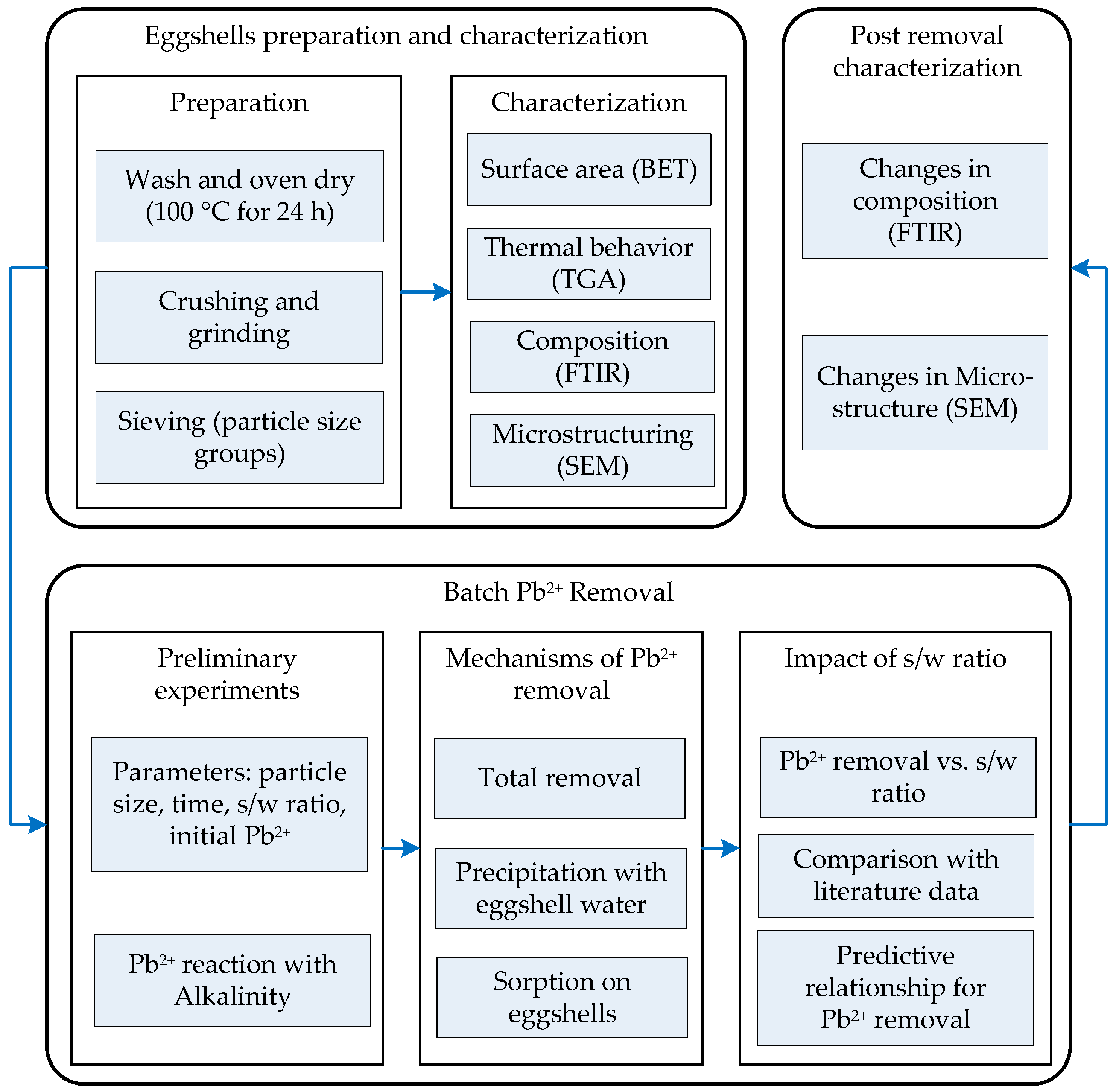
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Eggshells
2.3. Eggshells Characterization
2.4. Pb2+ Removal Experiments
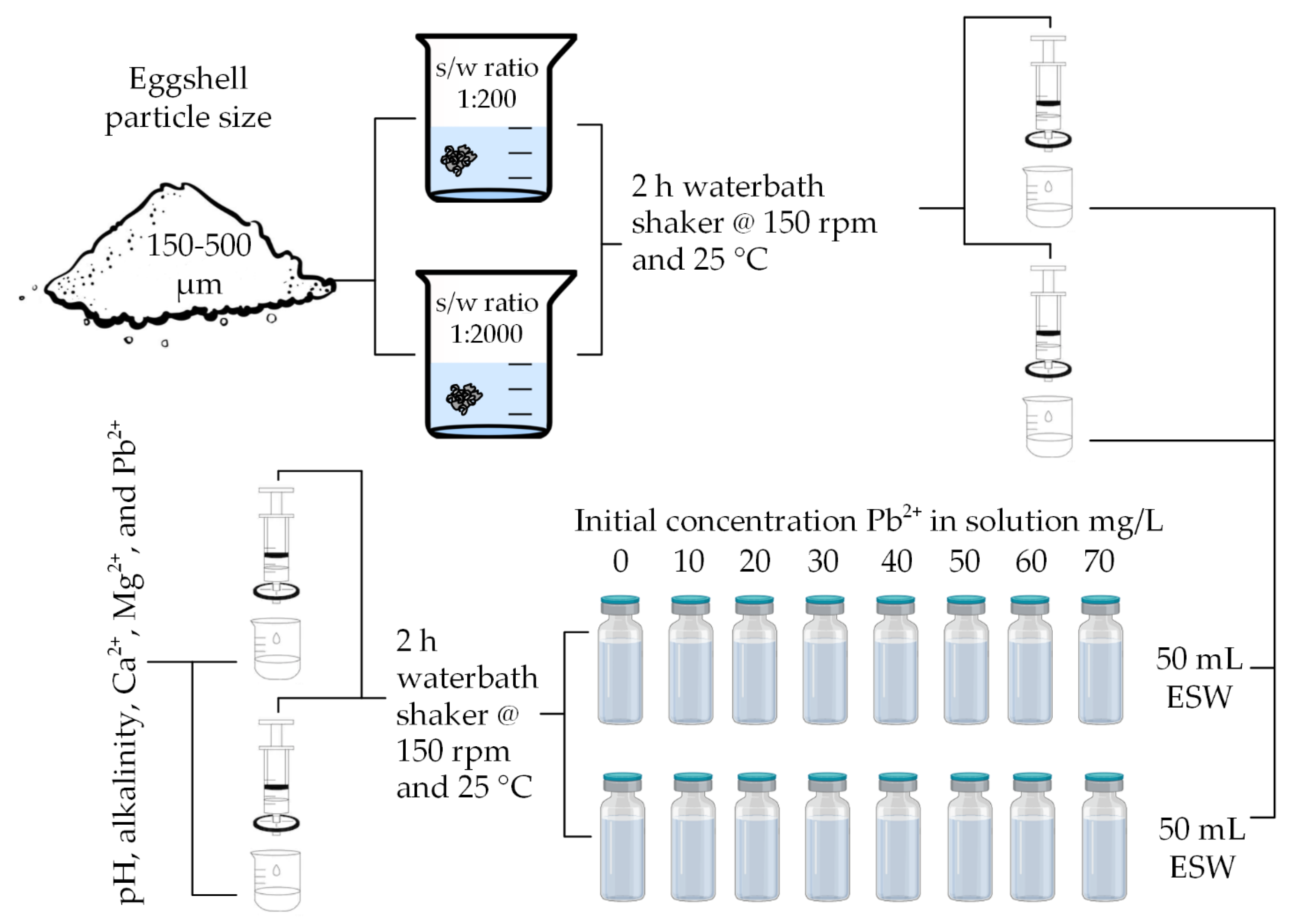
2.5. Preliminary Investigation of Pb2+ Removal
2.6. Effect of Particle Size and s/w Ratio on Removal of Pb2+
2.7. Differentiation between Removal of Pb2+ by Sorption and Precipitation
2.8. Microstructure Characterization of Pb2+ Removal
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Raw Eggshells Characterization
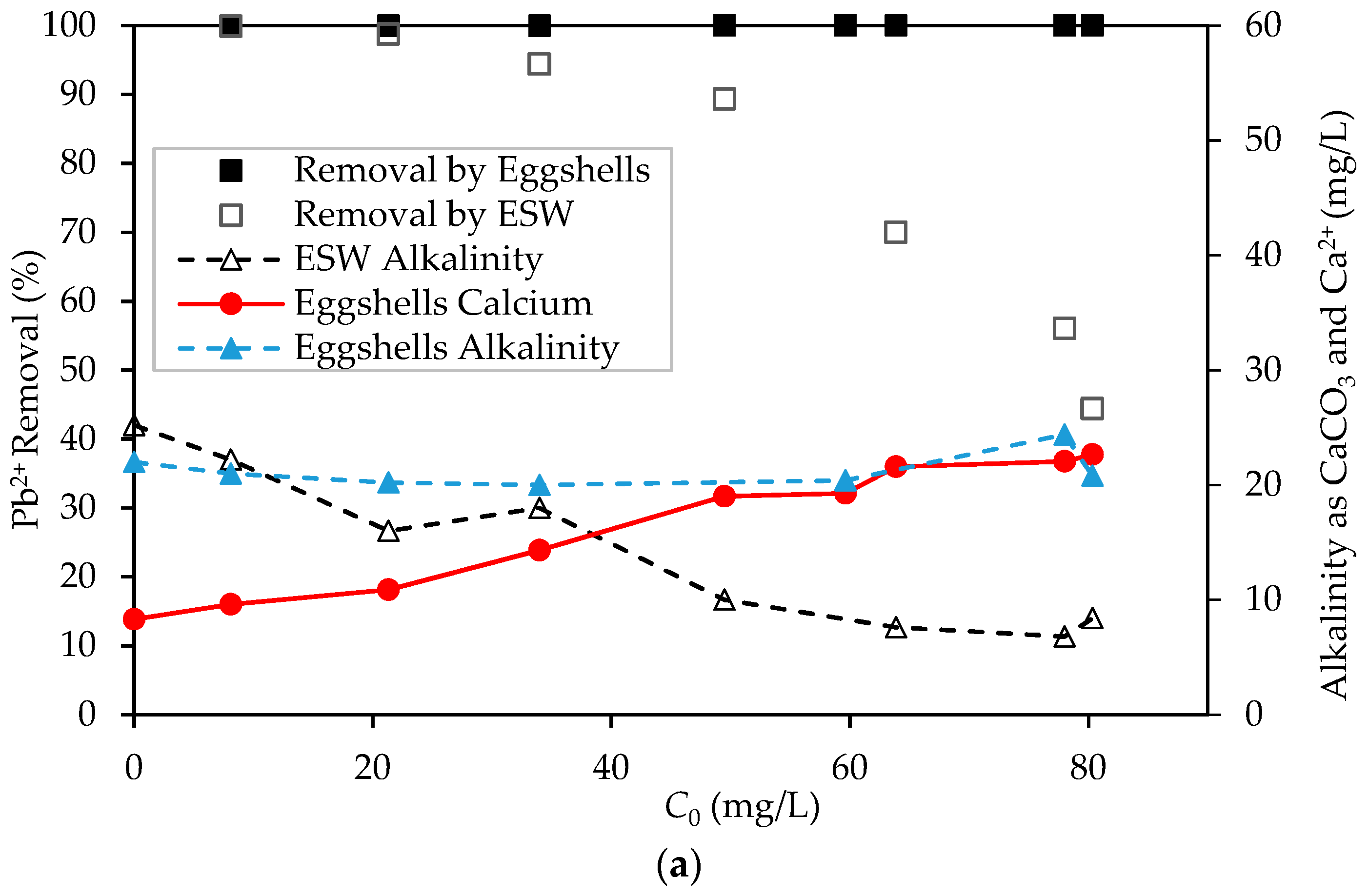
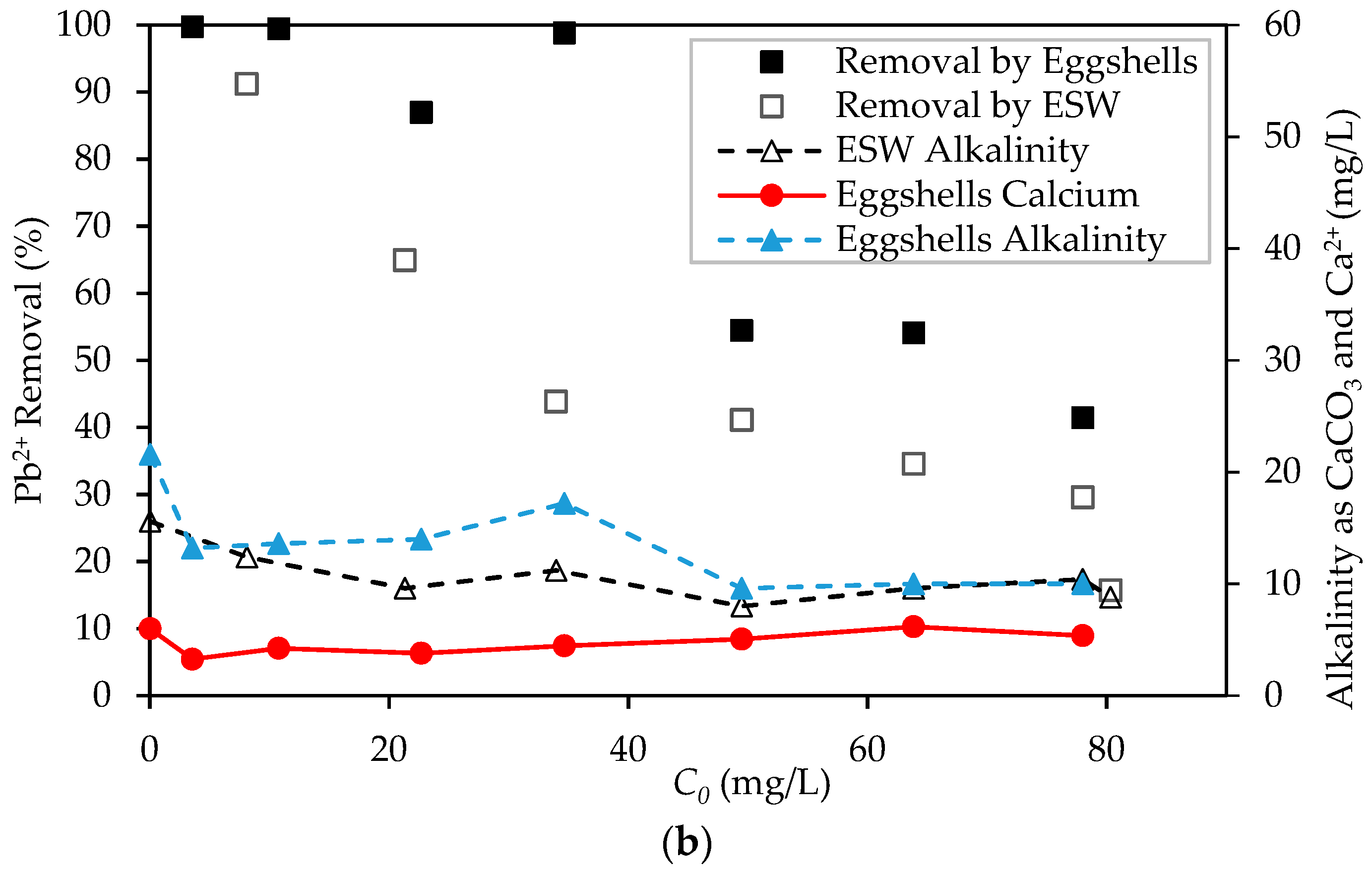
3.2. Preliminary Pb2+ Removal Experiments
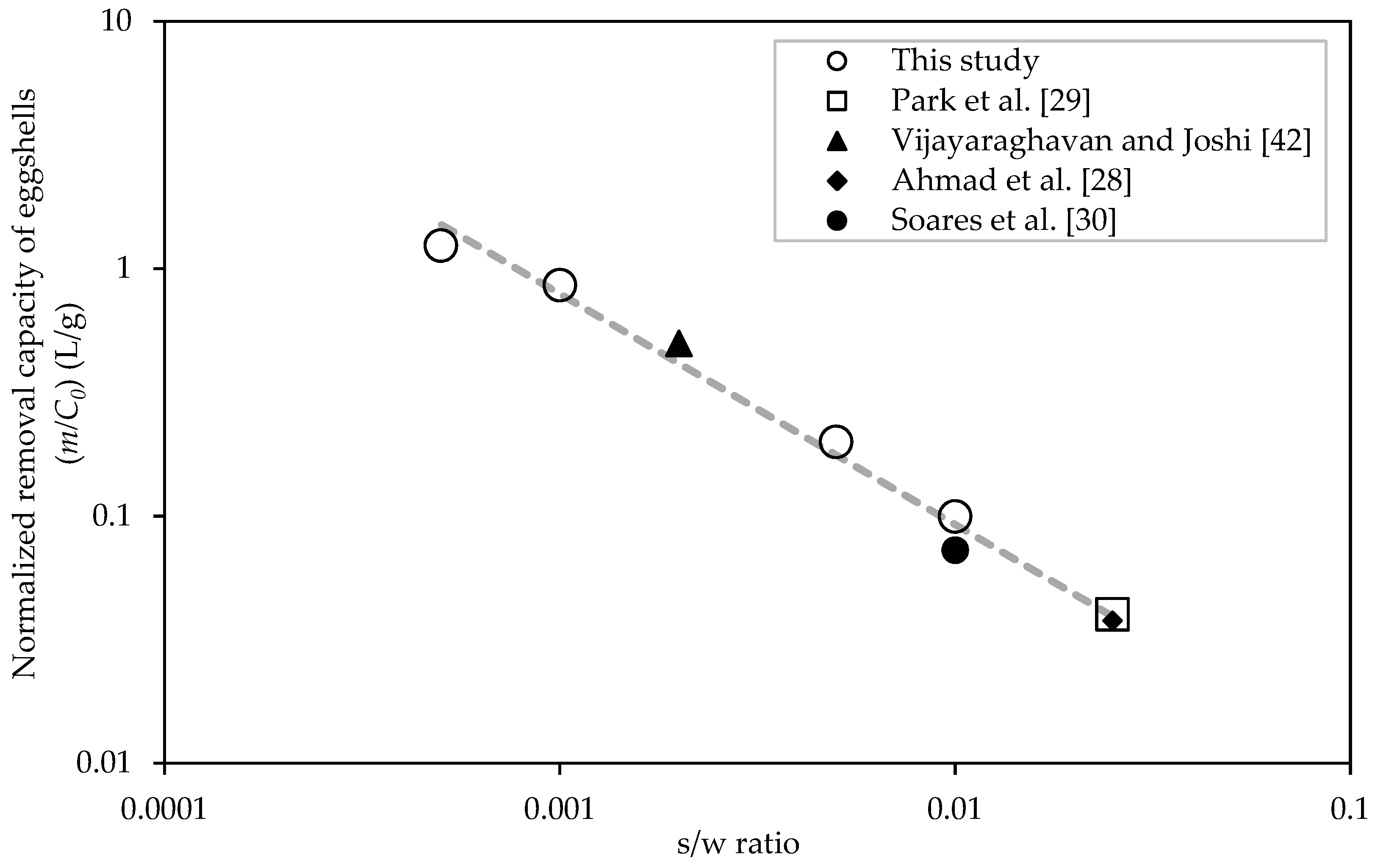
3.3. Effect of Particle Size and s/w Ratio on Removal of Pb2+
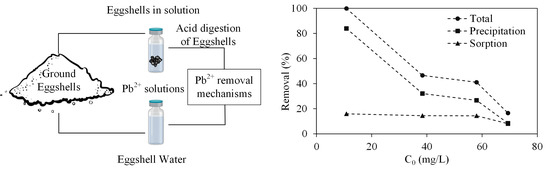
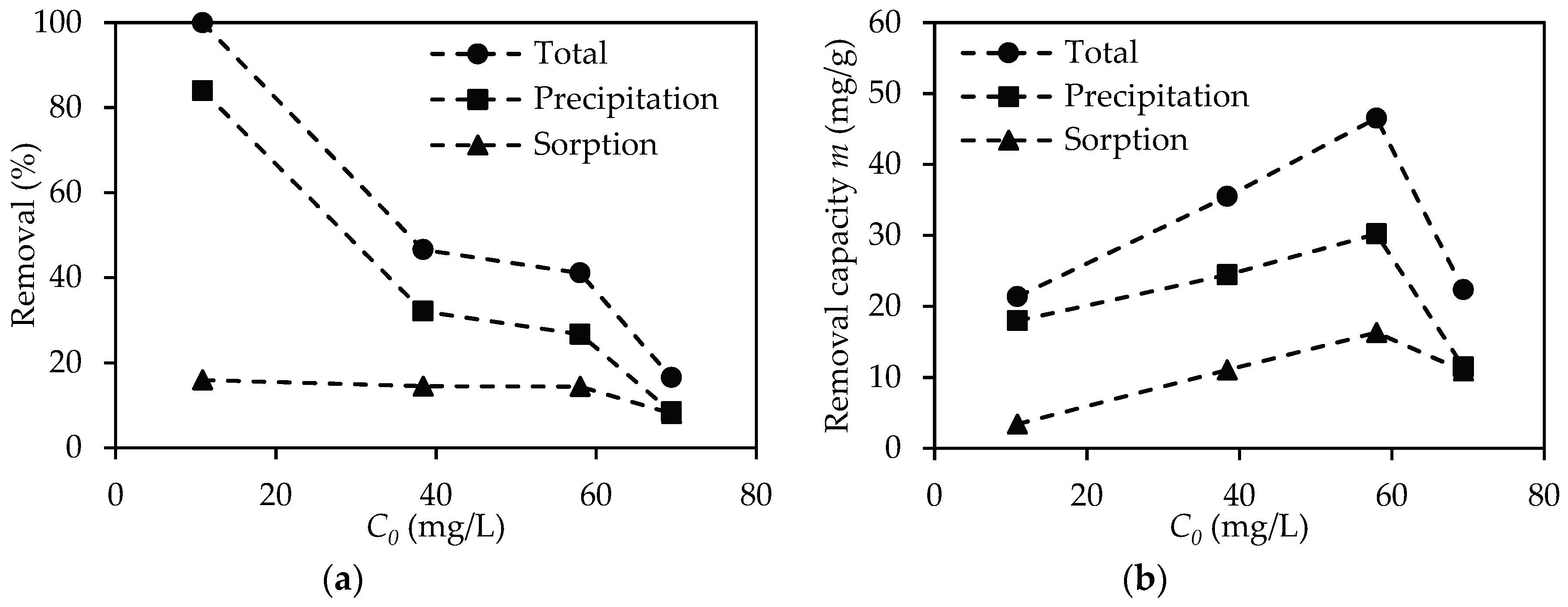
3.4. Differentiation between Removal of Pb2+ by Sorption and Precipitation
3.5. Thermodynamic and Stiochiometric Analysis
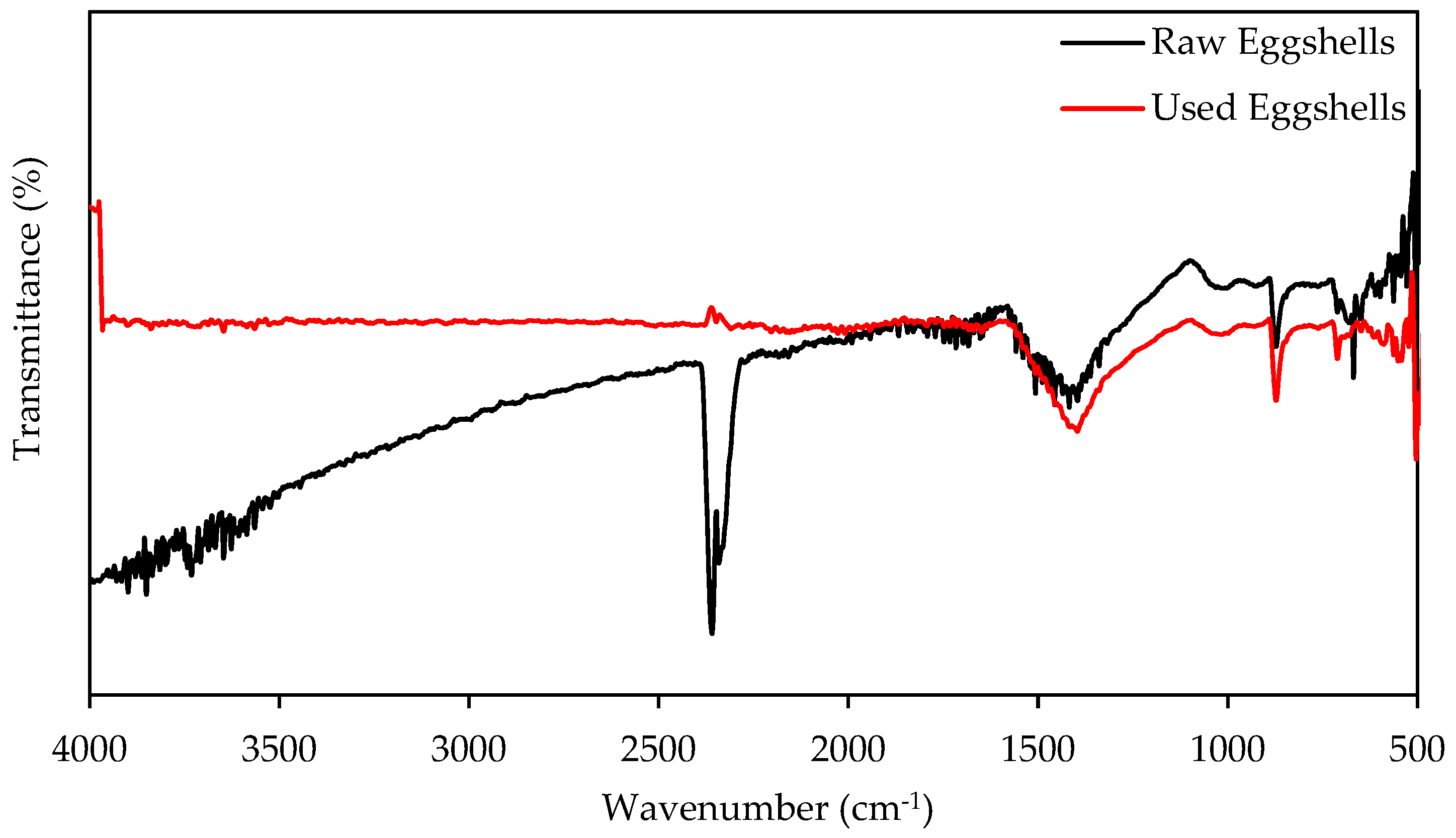
3.6. FTIR Analysis
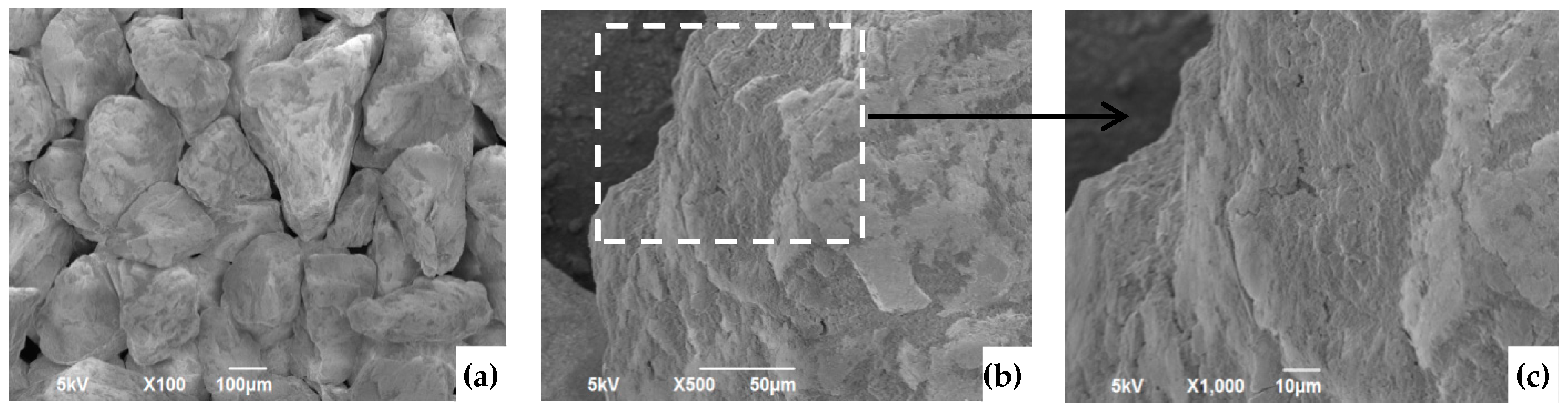
3.7. SEM Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Anantha, R.K.; Kota, S. Removal of lead by adsorption with the renewable biopolymer composite of feather (Dromaius novaehollandiae) and chitosan (Agaricus bisporus). Environ. Technol. Innov. 2016, 6, 11–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, V.K.; Agarwal, S.; Saleh, T.A. Synthesis and characterization of alumina-coated carbon nanotubes and their application for lead removal. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 185, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ritchey, A.K.; O’Brien, S.H.; Keller, F.G. Chapter 152—Hematologic manifestations of childhood illness. In Hematology, 7th ed.; Hoffman, R., Benz, E.J., Silberstein, L.E., Heslop, H.E., Weitz, J.I., Anastasi, J., Salama, M.E., Abutalib, S.A., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 2215–2237.e9. ISBN 978-0-323-35762-3. [Google Scholar]
- Burke, D.M.; Morris, M.A.; Holmes, J.D. Chemical oxidation of mesoporous carbon foams for lead ion adsorption. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2013, 104, 150–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canfield, R.L.; Henderson, C.R.; Cory-Slechta, D.A.; Cox, C.; Jusko, T.A.; Lanphear, B.P. Intellectual impairment in children with blood lead concentrations below 10 µg per deciliter. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 348, 1517–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanphear, B.P.; Matte, T.D.; Rogers, J.; Clickner, R.P.; Dietz, B.; Bornschein, R.L.; Succop, P.; Mahaffey, K.R.; Dixon, S.; Galke, W.; et al. The contribution of lead-contaminated house dust and residential soil to children’s blood lead levels: A pooled analysis of 12 epidemiologic studies. Environ. Res. 1998, 79, 51–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, W.C.; Wong, O.; Kheifets, L. Mortality among employees of lead battery plants and lead-producing plants, 1947–1980. Scand. J. Work Environ. Health 1985, 11, 331–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lancranjan, I.; Popescu, H.I.; GAvănescu, O.; Klepsch, I.; Serbănescu, M. Reproductive ability of workmen occupationally exposed to lead. Arch. Environ. Health 1975, 30, 396–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanphear, B.P.; Roghmann, K.J. Pathways of lead exposure in urban children. Environ. Res. 1997, 74, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, M.T.; Hamouda, M.A.; Al Kendi, R.R.; Mohamed, M.M. Health risk assessment of household drinking water in a district in the UAE. Water 2018, 10, 1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Health Canada. Guidelines for Canadian Drinking Water Quality—Summary Table; Water and Air Quality Bureau; Healthy Environments and Consumer Safety Branch, Health Canada: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 2019.
- US EPA. National Primary Drinking Water Regulations; EPA 816-F-09-004; Office of Water United States Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2009.
- Arunlertaree, C.; Kaewsomboon, W.; Kumsopa, A.; Pokethitiyook, P.; Panyawathanakit, P. Removal of lead from battery manufacturing wastewater by egg shell. Songklanakarin J. Sci. Technol. 2007, 29, 13. [Google Scholar]
- Dermentzis, K.; Valsamidou, E.; Marmanis, D. Simultaneous removal of acidity and lead from acid lead battery wastewater by aluminum and iron electrocoagulation. J. Eng. Sci. Technol. Rev. 2012, 5, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaoya, S.; Pancharoen, U. Removal of lead (II) from battery industry wastewater by HFSLM. Int. J. Chem. Eng. Appl. 2012, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macchi, G.; Pagano, M.; Santori, M.; Tiravanti, G. Battery industry wastewater: Pb removal and produced sludge. Water Res. 1993, 27, 1511–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. A Compendium of Standards for Wastewater Reuse in the Eastern Mediterranean Region; World Health Organization, Regional Office for the Eastern Mediterranean: Cairo, Egypt, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Babel, S.; Kurniawan, T.A. Low-cost adsorbents for heavy metals uptake from contaminated water: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2003, 97, 219–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweidan, H.; Hamouda, M.; El-Hassan, H.; Maraqa, M. A framework for the investigation of biowaste materials as potential adsorbents for water treatment. In Proceedings of the 4th World Congress on Civil, Structural, and Environmental Engineering, Rome, Italy, 7–9 April 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Podstawczyk, D.; Witek-Krowiak, A.; Chojnacka, K.; Sadowski, Z. Biosorption of malachite green by eggshells: Mechanism identification and process optimization. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 160, 161–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eba, F.; Biboutou, R.K.; Nlo, J.N.; Bibalou, Y.G.; Oyo, M. Lead removal in aqueous solution by activated carbons prepared from Cola edulis shell (Alocacée), Pentaclethra macrophylla husk (Mimosaceae) and Aucoumea klaineana sawdust (Burseraceae). Afr. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 5, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Naas, M.H.; Al-Rub, F.A.; Ashour, I.; Al Marzouqi, M. Effect of competitive interference on the biosorption of lead(II) by Chlorella vulgaris. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 2007, 46, 1391–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashed, M.N. Fruit stones from industrial waste for the removal of lead ions from polluted water. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2006, 119, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekar, M.; Sakthi, V.; Rengaraj, S. Kinetics and equilibrium adsorption study of lead(II) onto activated carbon prepared from coconut shell. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2004, 279, 307–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, T.; Luo, X.; Lin, X.; Yang, J. Preparation, characterization and adsorption properties for lead (II) of alkali-activated porous leather particles. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2017, 512, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritchie, H.; Roser, M. Meat and Dairy Production. Available online: https://ourworldindata.org/meat-production (accessed on 7 September 2020).
- Stadelman, W.J. EGGS|Structure and Composition. In Encyclopedia of Food Sciences and Nutrition, 2nd ed.; Caballero, B., Ed.; Academic Press: Oxford, UK, 2003; pp. 2005–2009. ISBN 978-0-12-227055-0. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, M.; Usman, A.R.A.; Lee, S.S.; Kim, S.-C.; Joo, J.-H.; Yang, J.E.; Ok, Y.S. Eggshell and coral wastes as low cost sorbents for the removal of Pb2+, Cd2+ and Cu2+ from aqueous solutions. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2012, 18, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.J.; Jeong, S.W.; Yang, J.K.; Kim, B.G.; Lee, S.M. Removal of heavy metals using waste eggshell. J. Environ. Sci. 2007, 19, 1436–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, M.; Marto, S.; Quina, M.; Gando-Ferreira, L.; Quinta-Ferreira, R. Evaluation of eggshell-rich compost as biosorbent for removal of Pb(II) from aqueous solutions. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2016, 227, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayaraghavan, K.; Jegan, J.; Palanivelu, K.; Velan, M. Removal and recovery of copper from aqueous solution by eggshell in a packed column. Miner. Eng. 2005, 18, 545–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeddou, N.; Bensmaili, A. Equilibrium and kinetic modelling of iron adsorption by eggshells in a batch system: Effect of temperature. Desalination 2007, 206, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Tu, Z.; Lu, G.; Duan, X.; Yi, X.; Guo, C.; Dang, Z. Removal of heavy metals from acid mine drainage using chicken eggshells in column mode. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 188, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pramanpol, N.; Nitayapat, N. Adsorption of reactive dye by eggshell and its membrane. Agric. Nat. Resour. 2006, 40, 192–197. [Google Scholar]
- Tsai, W.T.; Yang, J.M.; Lai, C.W.; Cheng, Y.H.; Lin, C.C.; Yeh, C.W. Characterization and adsorption properties of eggshells and eggshell membrane. Bioresour. Technol. 2006, 97, 488–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witek-Krowiak, A.; Chojnacka, K.; Podstawczyk, D.; Dawiec, A.; Pokomeda, K. Application of response surface methodology and artificial neural network methods in modelling and optimization of biosorption process. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 160, 150–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, M.P.; Sakuma, H.; Stipp, S.L.S. Strontium, nickel, cadmium, and lead substitution into calcite, studied by density functional theory. Langmuir 2014, 30, 6129–6133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, A.D.; Webb, C.J.; Sorensen, J.L.; Dixon, D.J.; Hudson, R. Geochemical thermodynamics of cadmium removal from water with limestone. Environ. Earth Sci. 2018, 77, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.-C.; Kim, E.J.; Yang, J.-W.; Shin, H.-J. Removal of malachite green by adsorption and precipitation using aminopropyl functionalized magnesium phyllosilicate. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 192, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.; Giammar, D.E. Effects of flow and water chemistry on lead release rates from pipe scales. Water Res. 2011, 45, 6525–6534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, L.; Giammar, D.E. Chapter 13 Influence of phosphate on adsorption and surface precipitation of lead on iron oxide surfaces. In Developments in Earth and Environmental Sciences; Barnett, M.O., Kent, D.B., Eds.; Adsorption of Metals by Geomedia II: Variables, Mechanisms, and Model Applications; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007; Volume 7, pp. 349–373. [Google Scholar]
- Vijayaraghavan, K.; Joshi, U.M. Chicken eggshells remove Pb(II) ions from synthetic wastewater. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2013, 30, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- APHA; AWWA; WEF. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 23rd ed.; Rice, E.W., Baird, R.B., Eaton, A.D., Eds.; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- U.S. EPA. Method 3050B: Acid Digestion of Sediments, Sludges, and Soils, Revision 2; U.S. EPA: Washington, DC, USA, 1996.
- Spagnoli, A.A.; Giannakoudakis, D.A.; Bashkova, S. Adsorption of methylene blue on cashew nut shell based carbons activated with zinc chloride: The role of surface and structural parameters. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 229, 465–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Lara, M.A.; Blázquez, G.; Ronda, A.; Pérez, A.; Calero, M. Development and characterization of biosorbents to remove heavy metals from aqueous solutions by chemical treatment of olive stone. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2013, 52, 10809–10819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Mendieta, A.; Olguín, M.T.; Solache-Ríos, M. Biosorption properties of green tomato husk (Physalis philadelphica Lam) for iron, manganese and iron–manganese from aqueous systems. Desalination 2012, 284, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Queirós, M.V.A.; Bezerra, M.N.; Feitosa, J.P.A. Composite superabsorbent hydrogel of acrylic copolymer and eggshell: Effect of biofiller addition. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2017, 28, 2004–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva Castro, L.; Barañano, A.G.; Pinheiro, C.J.G.; Menini, L.; Pinheiro, P.F. Biodiesel production from cotton oil using heterogeneous CaO catalysts from eggshells prepared at different calcination temperatures. Green Process. Synth. 2019, 8, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habte, L.; Shiferaw, N.; Mulatu, D.; Thenepalli, T.; Chilakala, R.; Ahn, J.W. Synthesis of nano-calcium oxide from waste eggshell by sol-gel method. Sustainability 2019, 11, 3196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godelitsas, A.; Astilleros, J.M.; Hallam, K.; Harissopoulos, S.; Putnis, A. Interaction of calcium carbonates with lead in aqueous solutions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 3351–3360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macchi, G.; Marani, D.; Pagano, M.; Bagnuolo, G. A bench study on lead removal from battery manufacturing wastewater by carbonate precipitation. Water Res. 1996, 30, 3032–3036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, P.; Lopata, V.J. Stability and solubility relationships between some solids in the system PbO–CO2–H2O. Can. J. Chem. 1984, 62, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, K.J.; Brown, P.L.; Byrne, R.H.; Gajda, T.; Hefter, G.; Leuz, A.-K.; Sjöberg, S.; Wanner, H. Chemical speciation of environmentally significant metals with inorganic ligands. Part 3: The Pb2+ + OH–, Cl–, CO32–, SO42–, and PO43– systems (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2009, 81, 2425–2476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snoeyink, V.L.; Jenkins, D. Water Chemistry; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1980; ISBN 978-0-471-05196-1. [Google Scholar]
- Bilinski, H.; Schindler, P. Solubility and equilibrium constants of lead in carbonate solutions (25 °C, I = 0.3 mol dm−3). Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1982, 46, 921–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Yang, D.-P.; Chen, Y.; Du, Z.; Guo, Y.; Huang, J.; Li, Q. Waste eggshells to valuable Co3O4/CaCO3 materials as efficient catalysts for VOCs oxidation. Mol. Catal. 2020, 483, 110766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abeywardena, M.R.; Elkaduwe, R.K.W.H.M.K.; Karunarathne, D.G.G.P.; Pitawala, H.M.T.G.A.; Rajapakse, R.M.G.; Manipura, A.; Mantilaka, M.M.M.G.P.G. Surfactant assisted synthesis of precipitated calcium carbonate nanoparticles using dolomite: Effect of pH on morphology and particle size. Adv. Powder Technol. 2020, 31, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, S.; Ahmed, A.S.; Anr, R.; Hamdan, S. Biodiesel production from castor oil by using calcium oxide derived from mud clam shell. J. Renew. Energy 2016, 2016, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seignez, N.; Gauthier, A.; Bulteel, D.; Buatier, M.; Recourt, P.; Damidot, D.; Potdevin, J.L. Effect of Pb-rich and Fe-rich entities during alteration of a partially vitrified metallurgical waste. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 149, 418–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, D.-Q.; Lin, Y.-P. Effects of pH value, chloride and sulfate concentrations on galvanic corrosion between lead and copper in drinking water. Environ. Chem. 2015, 13, 602–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

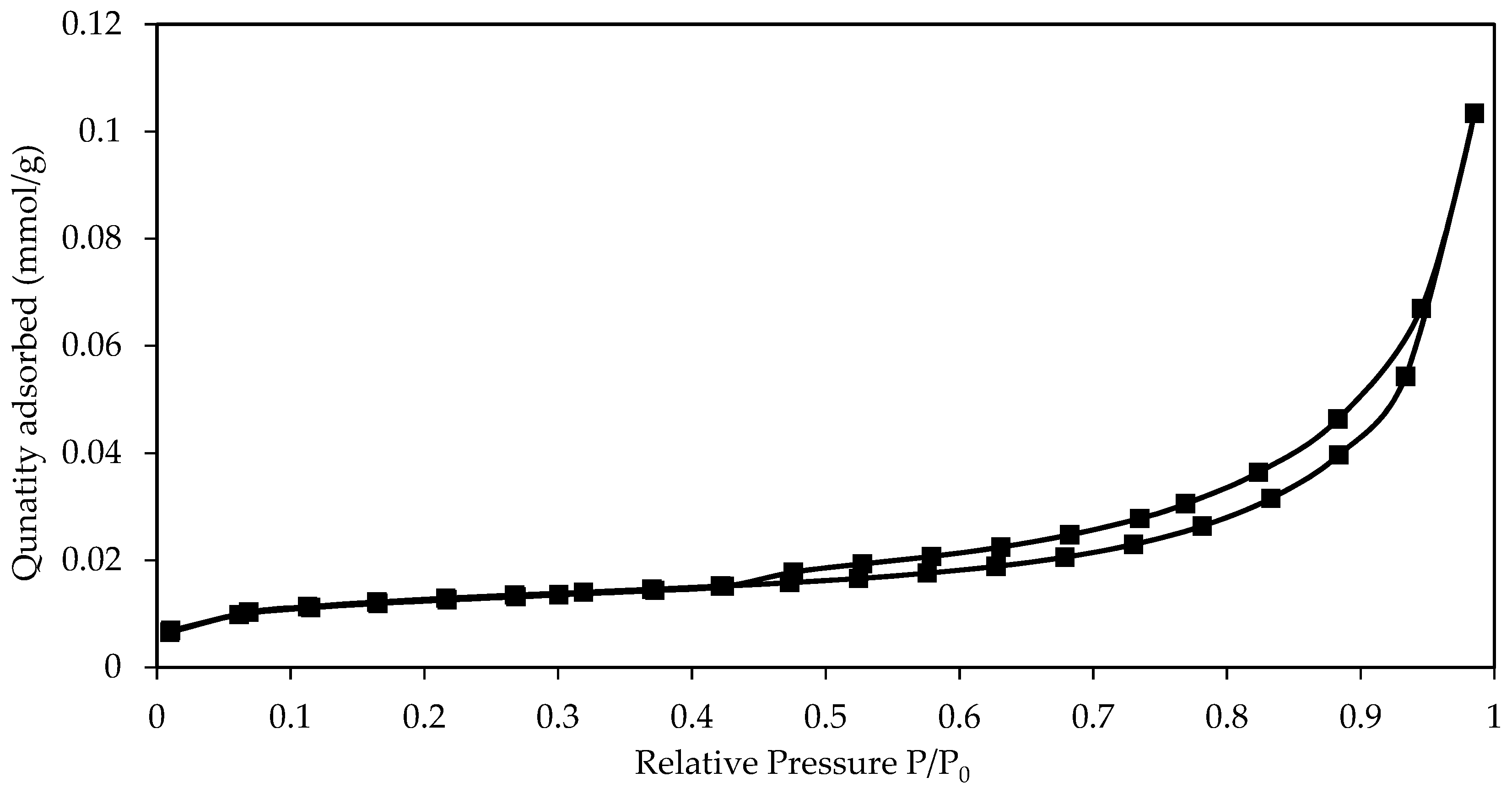





| Material | Size (µm) | Surface Area (m2/g) | Pore Volume (103 cm3/g) | Pore Size (nm) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eggshells | <150 | 0.977 | 3.544 | 14.8 | This work |
| 150–500 | 0.056 | - | - | This work | |
| Eggshells | 77.9 | 1.023 | 6.5 | - | [35] |
| Olive stones | <1000 | 0.163 | 1.84 | 45.302 | [46] |
| Tomato husks | 75–150 | 0.68 | 0.0015 | - | [47] |
| Study | Eggshell Size (µm) | s/w Ratio | pH | C0 (mg/L) | m (mg/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [42] a | 750 | 1:500 | 5.0 | 523, 1045 | 156 |
| [28] | <1000 | 1:40 | 5.5 | 10–150 | 2.24 |
| [30] b | <500 | 1:100 | 5.0 | 100–1435 | 12.9 |
| [29] | 210–400 | 1:40 | NA | 3 | 0.12 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hamouda, M.A.; Sweidan, H.; Maraqa, M.A.; El-Hassan, H. Mechanistic Study of Pb2+ Removal from Aqueous Solutions Using Eggshells. Water 2020, 12, 2517. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12092517
Hamouda MA, Sweidan H, Maraqa MA, El-Hassan H. Mechanistic Study of Pb2+ Removal from Aqueous Solutions Using Eggshells. Water. 2020; 12(9):2517. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12092517
Chicago/Turabian StyleHamouda, Mohamed A., Haliemeh Sweidan, Munjed A. Maraqa, and Hilal El-Hassan. 2020. "Mechanistic Study of Pb2+ Removal from Aqueous Solutions Using Eggshells" Water 12, no. 9: 2517. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12092517
APA StyleHamouda, M. A., Sweidan, H., Maraqa, M. A., & El-Hassan, H. (2020). Mechanistic Study of Pb2+ Removal from Aqueous Solutions Using Eggshells. Water, 12(9), 2517. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12092517