Influence of Season, Occupancy Pattern, and Technology on Structure and Composition of Nitrifying and Denitrifying Bacterial Communities in Advanced Nitrogen-Removal Onsite Wastewater Treatment Systems
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Systems
2.2. Sample Collection
2.3. Sample Processing
2.4. Downstream Analysis and Statistics
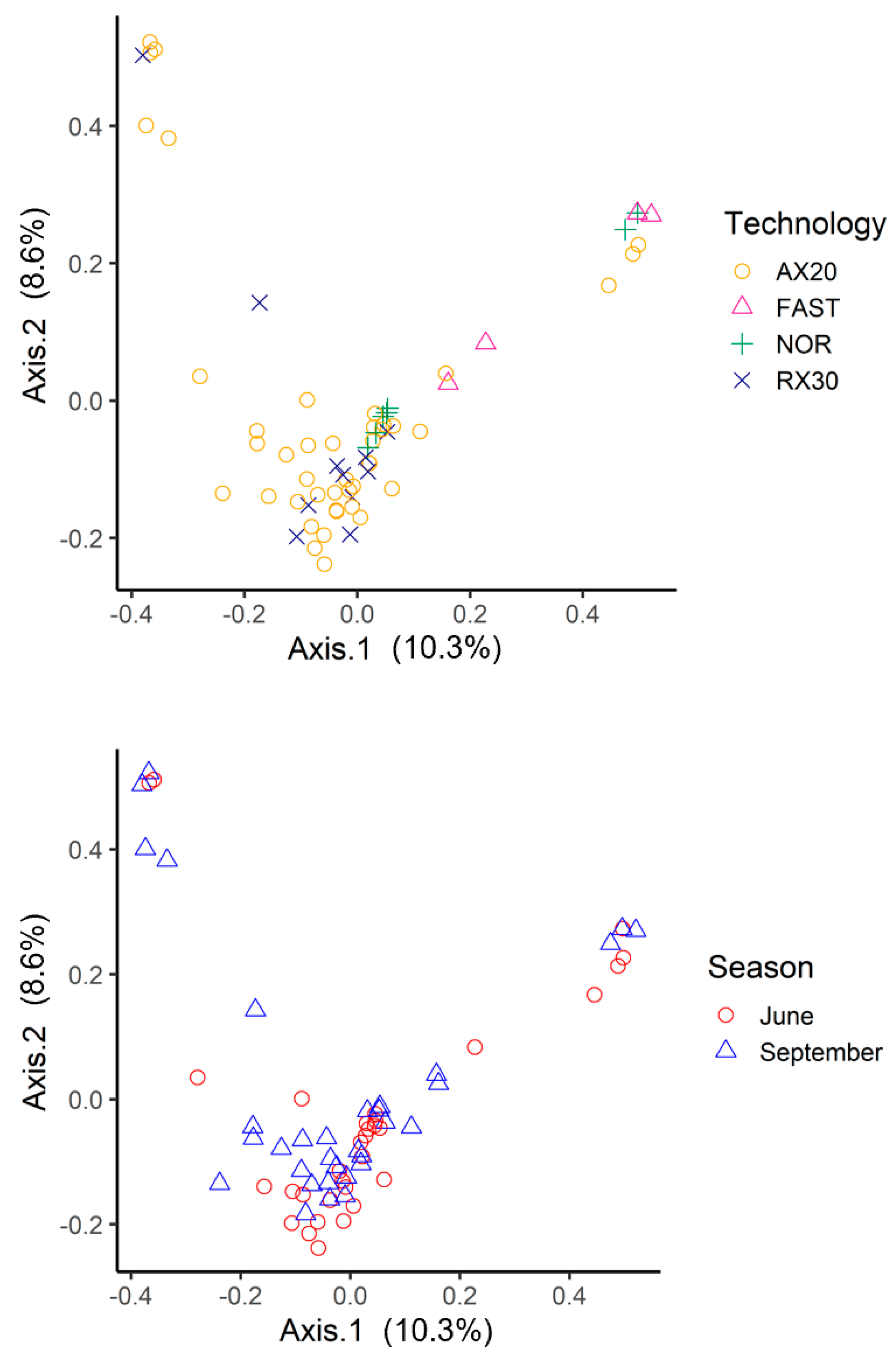
3. Results and Discussion
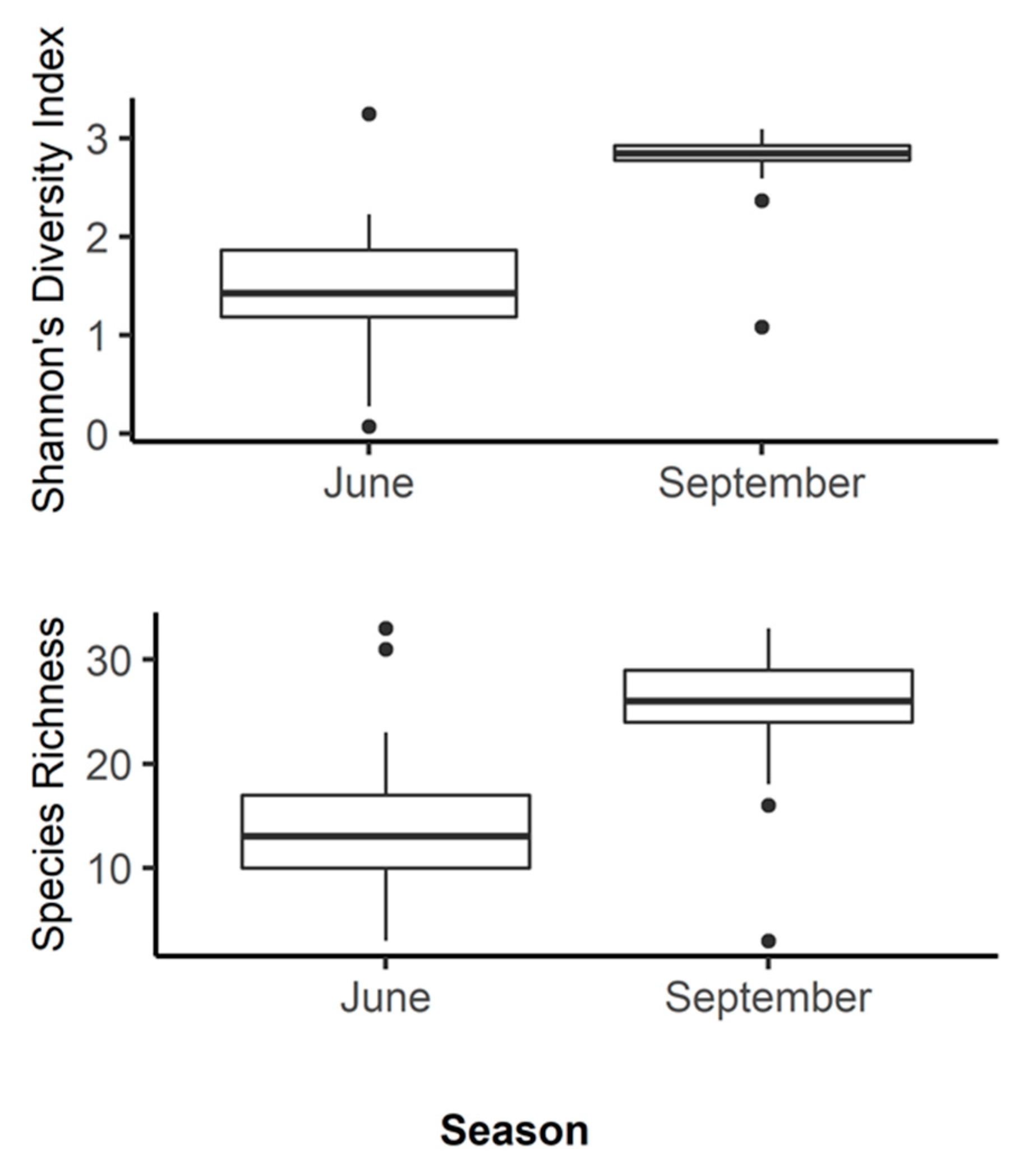
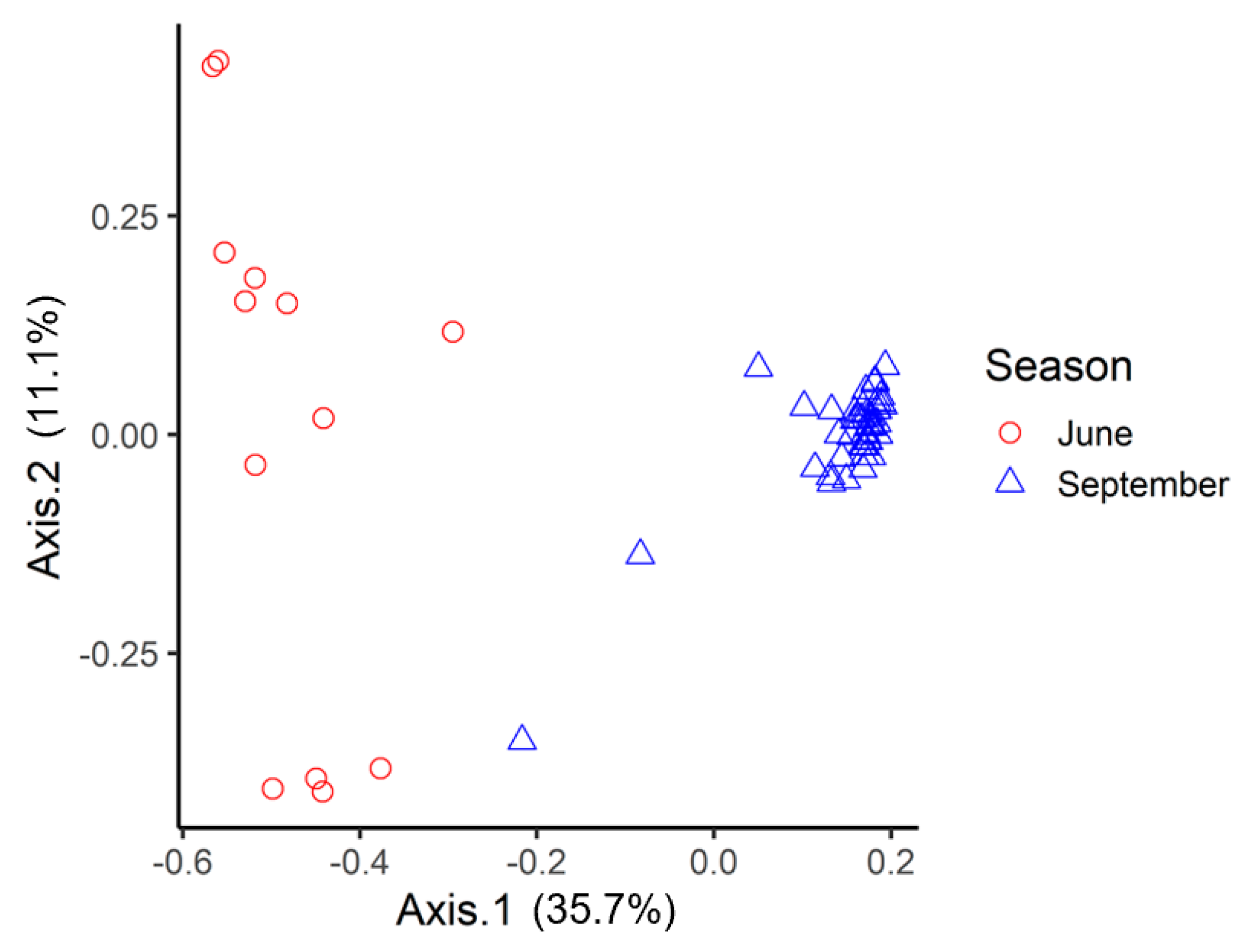
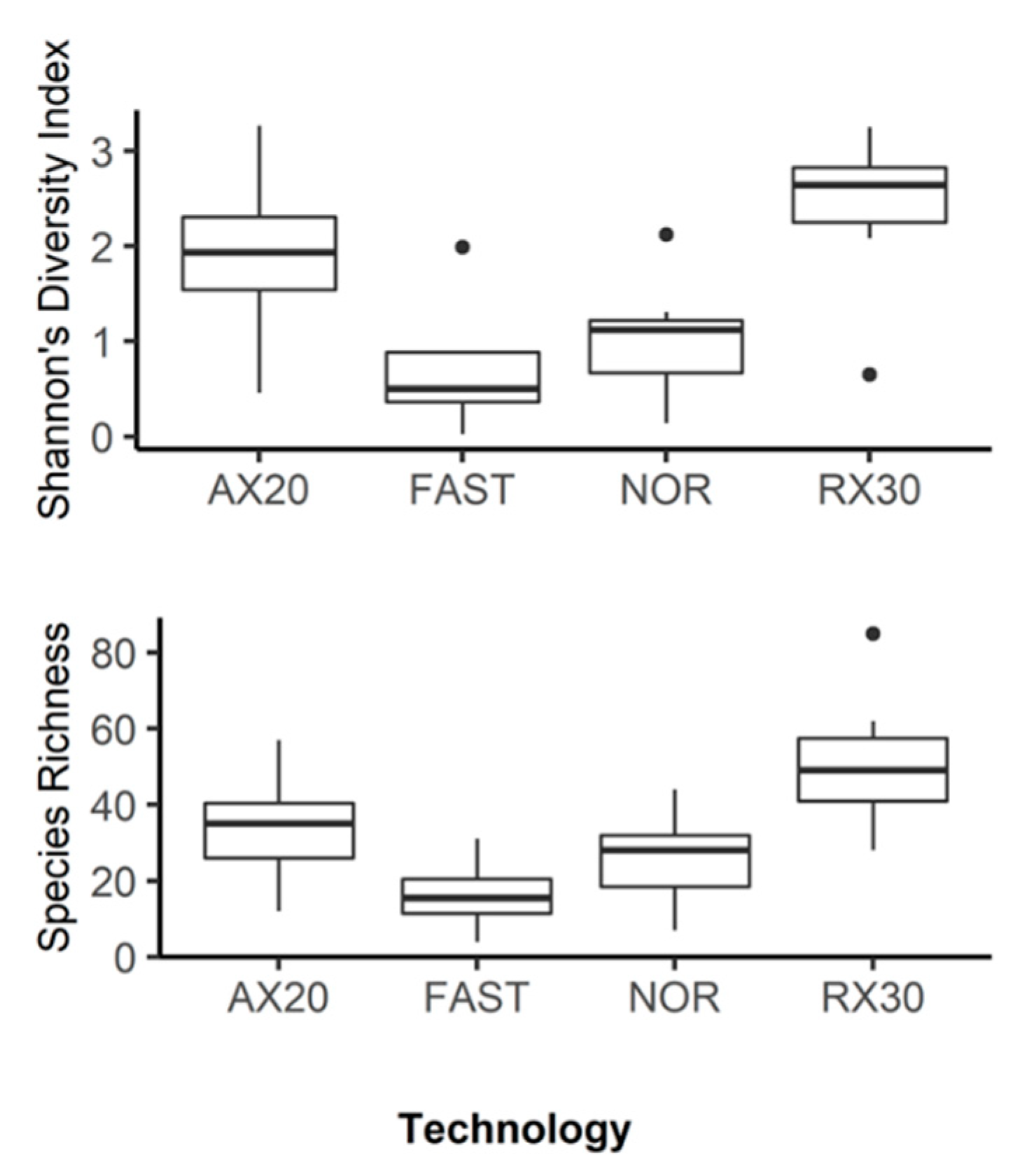
3.1. amoA: Species Richness and Diversity
3.2. nosZ: Species Richness and Diversity
3.3. amoA: Taxonomy
3.4. nosZ: Taxonomy
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
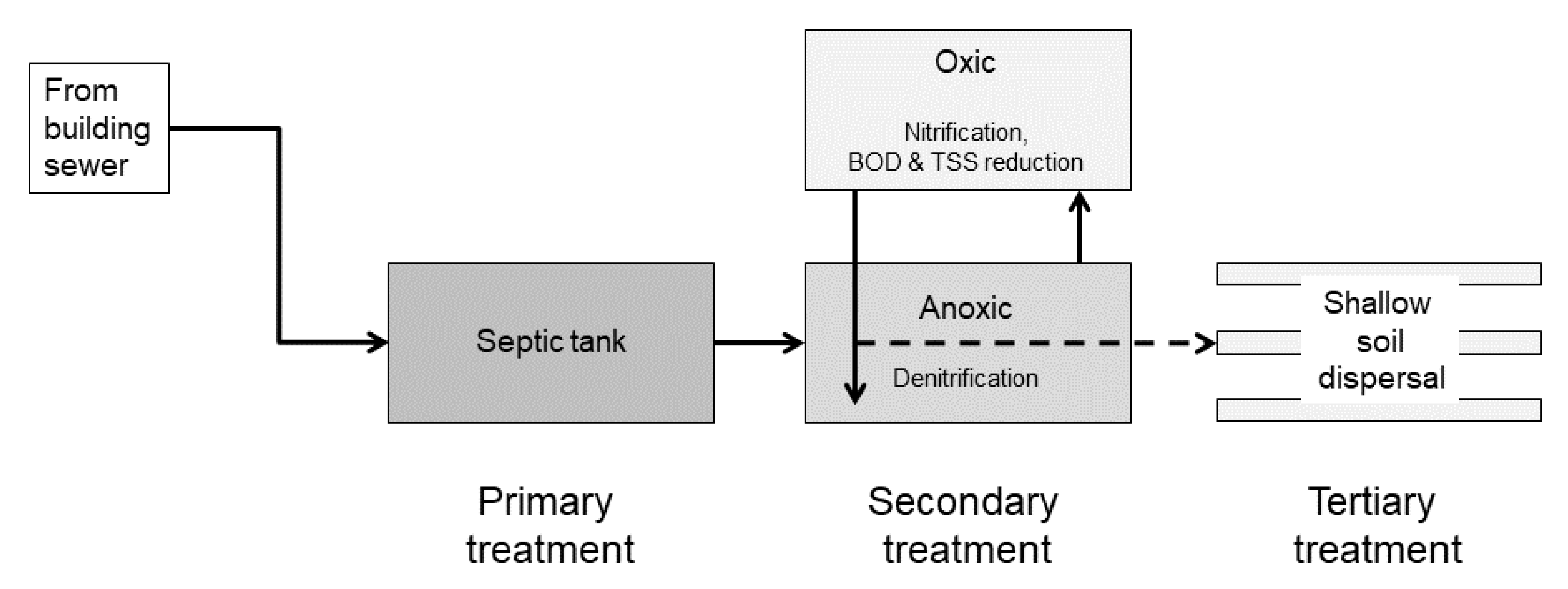
Appendix A.1. Technology Descriptions
Appendix A.2. DNA Extraction and PCR
| Parameter | June | September | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | Min | Median | Max | n | Min | Median | Max | |
| pH | 45 | 3.8 | 7.0 | 8.1 | 45 | 4.7 | 6.9 | 7.8 |
| Temperature | 45 | 12.6 | 16.1 | 20.9 | 44 | 18.9 | 21.2 | 25.4 |
| BOD5 | 20 | 0 | 0 | 54 | 20 | 0 | 0 | 76 |
| Dissolved oxygen | 45 | 1.1 | 6.8 | 9.9 | 44 | 0 | 5.8 | 8.7 |
| Ammonium-N | 42 | 0 | 0 | 41.6 | 38 | 0 | 0.1 | 51.6 |
| Nitrate-N | 43 | 0 | 8.4 | 32.8 | 40 | 0.1 | 9.4 | 25.3 |
| Total N | 43 | 3.6 | 18.7 | 60.9 | 41 | 0.6 | 11.9 | 52.0 |
References
- Amador, J.A.; Görres, J.H.; Loomis, G.W.; Lancellotti, B.V. Nitrogen loading from onsite wastewater treatment systems in the greater narragansett bay (Rhode Island, USA) watershed: Magnitude and reduction strategies. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2018, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.D.; Wells, G.F.; Bae, H.; Criddle, C.S.; Francis, C.A. Occurrence of ammonia-oxidizing archaea in wastewater treatment plant bioreactors. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 5643–5647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Annavajhala, M.K.; Kapoor, V.; Santo-Domingo, J.; Chandran, K. Structural and functional interrogation of selected biological nitrogen removal systems in the United States, Denmark, and Singapore using shotgun metagenomics. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Luo, X.; Wu, G.; Li, T.; Peng, Y. Abundance and diversity based on amoA genes of ammonia-oxidizing archaea and bacteria in ten wastewater treatment systems. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 3339–3354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oakley, S.M.; Gold, A.J.; Oczkowski, A.J. Nitrogen control through decentralized wastewater treatment: Process performance and alternative management strategies. Ecol. Eng. 2010, 36, 1520–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhode Island Department of Environmental Management (RIDEM). Rules Establishing Minimum Standards Relating to Location, Design, Construction and Maintenance of Onsite Wastewater Treatment Systems. 2016. Available online: http://www.dem.ri.gov/programs/benviron/water/permits/isds/pdfs/owts-250-150-10-6.pdf (accessed on 2 June 2020).
- BCDHE. Barnstable County Department of Health and Environment. Innovative/Alternative Septic System Tracking. 2012. Available online: http://www.barnstablecountyhealthorg/programs-and-services/ia-septic-systemtracking (accessed on 3 February 2020).
- Tomarken, J.L.; Dawydiak, W. Standards Promulgated under Article 19 for the Approval and Management of Innovative and Alternative Onsite Wastewater Treatment Systems. 2017. Available online: http://www.reclaimourwater.info/Portals/60/docs/Article_19_IA_OWTS_Standard_Final_12-29-17.pdf (accessed on 3 February 2020).
- Lancellotti, B.V.; Loomis, G.W.; Hoyt, K.P.; Avizinis, E.; Amador, J.A. Evaluation of nitrogen concentration in final effluent of advanced nitrogen-removal Onsite Wastewater Treatment Systems (OWTS). Water Air Soil Pollut. 2017, 228, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brannon, E.Q.; Moseman-Valtierra, S.M.; Lancellotti, B.V.; Wigginton, S.K.; Amador, J.A.; McCaughey, J.C.; Loomis, G.W. Comparison of N O emissions and gene abundances between wastewater nitrogen removal systems. J. Environ. Qual. 2017, 46, 931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ross, B.N.; Lancellotti, B.V.; Brannon, E.Q.; Loomis, G.W.; Amador, J.A. Greenhouse gas emissions from advanced nitrogen-removal onsite wastewater treatment systems. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 737, 140399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geets, J.; de Cooman, M.; Wittebolle, L.; Heylen, K.; Vanparys, B.; De Vos, P.; Verstraete, W.; Boon, N. Real-time PCR assay for the simultaneous quantification of nitrifying and denitrifying bacteria in activated sludge. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2007, 75, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siripong, S.; Rittmann, B.E. Diversity study of nitrifying bacteria in full-scale municipal wastewater treatment plants. Water Res. 2007, 41, 1110–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaranowska, P.; Cydzik-Kwiatkowska, A.; Zielińska, M. Configuration of biological wastewater treatment line and influent composition as the main factors driving bacterial community structure of activated sludge. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 29, 1145–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, B.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Xu, H.; Song, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, F.; Liu, Y.; Bai, J. Correlating microbial community structure with operational conditions in biological aerated filter reactor for efficient nitrogen removal of municipal wastewater. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 250, 374–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Feng, J.; Chen, S.; Zhao, Z.; Li, B.; Wang, Y.; Jia, J.; Li, S.; Wang, Y.; Yan, M.; et al. Geographical patterns of nirs gene abundance and nirs-type denitrifying bacterial community associated with activated sludge from different wastewater treatment plants. Microb. Ecol. 2019, 77, 304–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wigginton, S.; Brannon, E.; Kearns, P.J.; Lancellotti, B.; Cox, A.; Loomis, G.W.; Amador, J.A. Nitrifying and denitrifying bacterial communities in advanced nitrogen-removal onsite wastewater treatment systems. J. Environ. Qual. 2018, 47, 1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, B.N.; Hoyt, K.P.; Loomis, G.W.; Amador, J.A. Assessing drivers of nitrogen removal in advanced onsite wastewater treatment systems in a Rhode Island coastal community. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2020, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Cox, A.H.; Wigginton, S.K.; Amador, J.A. Structure of greenhouse gas-consuming microbial communities in surface soils of a nitrogen-removing experimental drainfield. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 739, 140362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. 2017. Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 3 February 2020).
- Fierer, N.; Nemergut, D.; Knight, R.; Craine, J.M. Changes through time: Integrating microorganisms into the study of succession. Res. Microbiol. 2010, 161, 635–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wigginton, S.K.; Brannon, E.Q.; Kearns, P.J.; Lancellotti, B.V.; Cox, A.; Moseman-Valtierrra, S.; Loomis, G.W.; Amador, J.A. Microbial communities in centralized and decentralized biological nitrogen removal wastewater treatment systems. Water 2020, 12, 1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, A.J.; Marcus, D.N.; Ijaz, U.Z.; Bautista-de Lose Santos, Q.M.; Dick, G.J.; Raskin, L. Metagenomic evidence for the presence of comammox Nitrospira-like bacteria in a drinking water system. Msphere 2016, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Ma, L.; Mao, Y.; Jiang, X.; Xia, Y.; Yu, K.; Zhang, T. Comammox in drinking water systems. Water Res. 2017, 116, 332–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limpiyakorn, T.; Sonthiphand, P.; Rongsayamanont, C.; Polprasert, C. Abundance of amoA genes of ammonia-oxidizing archaea and bacteria in activated sludge of full-scale wastewater treatment plants. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 3694–3701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mertoglu, B. Long-term assessment of nitrification in a full-scale wastewater treatment plant. J. Environ. Sci. Health 2008, 43, 538–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dionisi, H.M.; Layton, A.C.; Harms, G.; Gregory, I.R.; Robinson, K.G.; Sayler, G.S. Quantification of Nitrosomonas oligotropha-like ammonia-oxidizing bacteria and Nitrospira spp. from full-scale wastewater treatment plants by competitive PCR. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 68, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aigle, A.; Prosser, J.I.; Gubry-RanginC. The application of high-throughput sequencing technology to analysis of amoA phylogeny and environmental niche specialisation of terrestrial bacterial ammonia-oxidisers. Environ. Microbiome 2019, 14, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thomsen, T.R.; Kong, Y.; Nielsen, P.H. Ecophysiology of abundant denitrifying bacteria in activated sludge. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2007, 60, 370–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, M.; Huang, G.; Zhao, Z.; Dang, C.; Liu, W.; Zheng, M. Newly designed primer pair revealed dominant and diverse comammox amoA gene in full-scale wastewater treatment plants. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 270, 580–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, M.; Amann, R.; Rossello, R.A.; Schleifer, K. The abundance of zoogloea ramigera in sewage treatment plants. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1995, 61, 702–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kraigher, B.; Kosjek, T.; Heath, E.; Kompare, B.; Mandic-mulec, I. Influence of pharmaceutical residues on the structure of activated sludge bacterial communities in wastewater treatment bioreactors. Water Res. 2008, 42, 4578–4588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulzel, R.; Spring, S.; Amann, R.; Huber, I.; Ludwigl, W.; Schleiferl, K.; Kampfer, P. Appued microbiology genotypic diversity of acidovorax strains isolated from activated sludge and description of acidovorax defluvii sp. nov. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 1999, 214, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellini, M.I.; Gutiérrez, L.; Tarlera, S.; Scavino, A.F. Isolation and functional analysis of denitrifiers in an aquifer with high potential for denitrification. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2013, 36, 505–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, B.N.; Loomis, G.W.; Hoyt, K.P.; Amador, J.A. User-based photometer analysis of effluent from advanced nitrogen-removal onsite wastewater treatment systems. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2018, 229, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
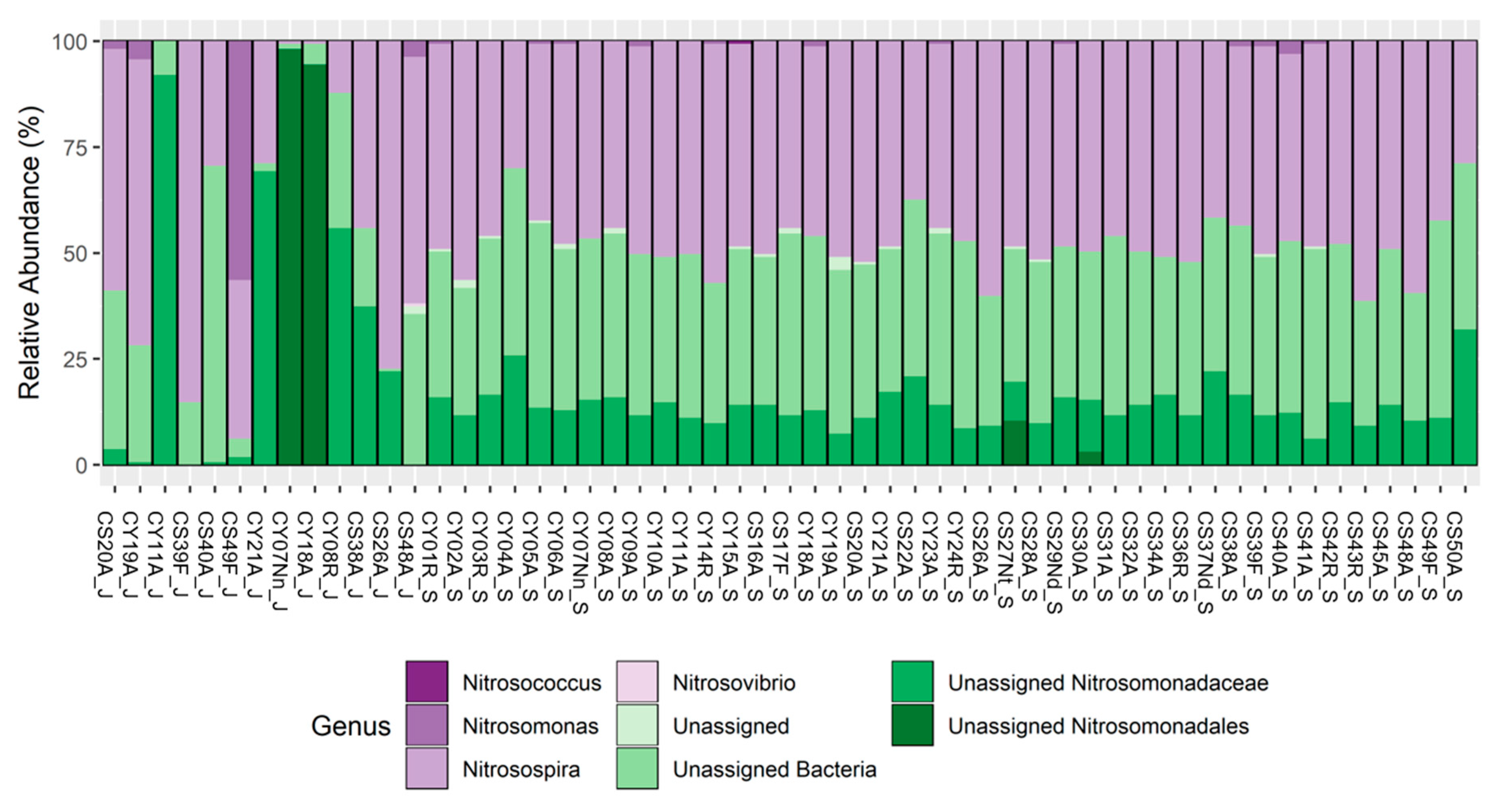
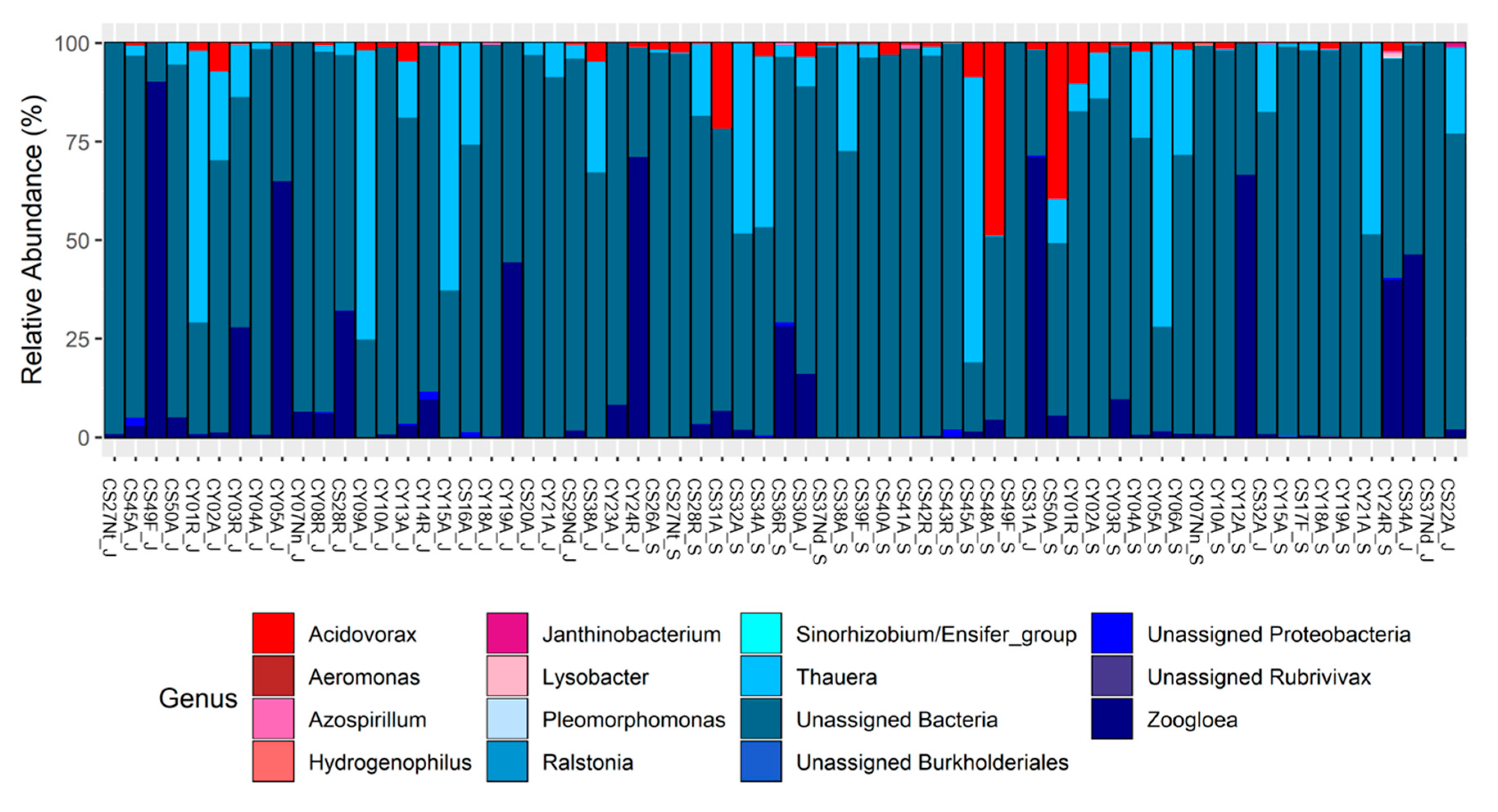
| Genus | Technology | Occupancy Pattern | Season | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AX20 | RX30 | FAST | NOR | Year Round | Seasonal | June | September | |
| U.A. Nitrosomonadaceae | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x |
| U.A. Bacteria | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x |
| Nitrosospira | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | |
| U.A. Bacteria | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x |
| Nitrosospira | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x |
| Nitrosospira | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x |
| Nitrosospira | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | |
| Nitrosospira | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | |
| U.A. Nitrosomonadales | x | x | x | x | x | x | ||
| Nitrosospira | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x |
| U. A. Bacteria | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x |
| Nitrosospira | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x |
| Nitrosospira | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x |
| Nitrosospira | x | x | x | x | x | x | ||
| Nitrosospira | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | |
| Nitrosospira | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x |
| U.A. Bacteria | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | |
| U.A. Bacteria | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x |
| U.A. Bacteria | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | |
| U.A. Bacteria | x | x | x | x | ||||
| Genus | Technology | Occupancy Pattern | Season | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AX20 | RX30 | FAST | NOR | Year Round | Seasonal | June | September | |
| U.A. Bacteria | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x |
| U.A. Bacteria | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x |
| U.A. Bacteria | x | x | x | x | x | x | ||
| Thauera | x | x | x | x | x | x | ||
| Zoogloea | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | |
| Thauera | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x |
| Thauera | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x |
| U.A. Bacteria | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | |
| U.A. Bacteria | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x |
| U.A. Bacteria | x | x | x | x | x | x | ||
| U.A. Bacteria | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | |
| U.A. Bacteria | x | x | x | x | x | x | ||
| U.A. Bacteria | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x |
| Zoogloea | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x |
| U.A. Bacteria | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | |
| Zoogloea | x | x | x | x | x | |||
| U.A. Bacteria | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | |
| U.A. Bacteria | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x |
| U.A. Bacteria | x | x | x | x | x | |||
| Acidovorax | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ross, B.N.; Wigginton, S.K.; Cox, A.H.; Loomis, G.W.; Amador, J.A. Influence of Season, Occupancy Pattern, and Technology on Structure and Composition of Nitrifying and Denitrifying Bacterial Communities in Advanced Nitrogen-Removal Onsite Wastewater Treatment Systems. Water 2020, 12, 2413. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12092413
Ross BN, Wigginton SK, Cox AH, Loomis GW, Amador JA. Influence of Season, Occupancy Pattern, and Technology on Structure and Composition of Nitrifying and Denitrifying Bacterial Communities in Advanced Nitrogen-Removal Onsite Wastewater Treatment Systems. Water. 2020; 12(9):2413. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12092413
Chicago/Turabian StyleRoss, Bianca N., Sara K. Wigginton, Alissa H. Cox, George W. Loomis, and Jose A. Amador. 2020. "Influence of Season, Occupancy Pattern, and Technology on Structure and Composition of Nitrifying and Denitrifying Bacterial Communities in Advanced Nitrogen-Removal Onsite Wastewater Treatment Systems" Water 12, no. 9: 2413. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12092413
APA StyleRoss, B. N., Wigginton, S. K., Cox, A. H., Loomis, G. W., & Amador, J. A. (2020). Influence of Season, Occupancy Pattern, and Technology on Structure and Composition of Nitrifying and Denitrifying Bacterial Communities in Advanced Nitrogen-Removal Onsite Wastewater Treatment Systems. Water, 12(9), 2413. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12092413







