Evaluation of Thirty-Eight Models of Drippers Using Reclaimed Water: Effect on Distribution Uniformity and Emitter Clogging
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Laboratory Phase
2.1.1. Emitters Tested
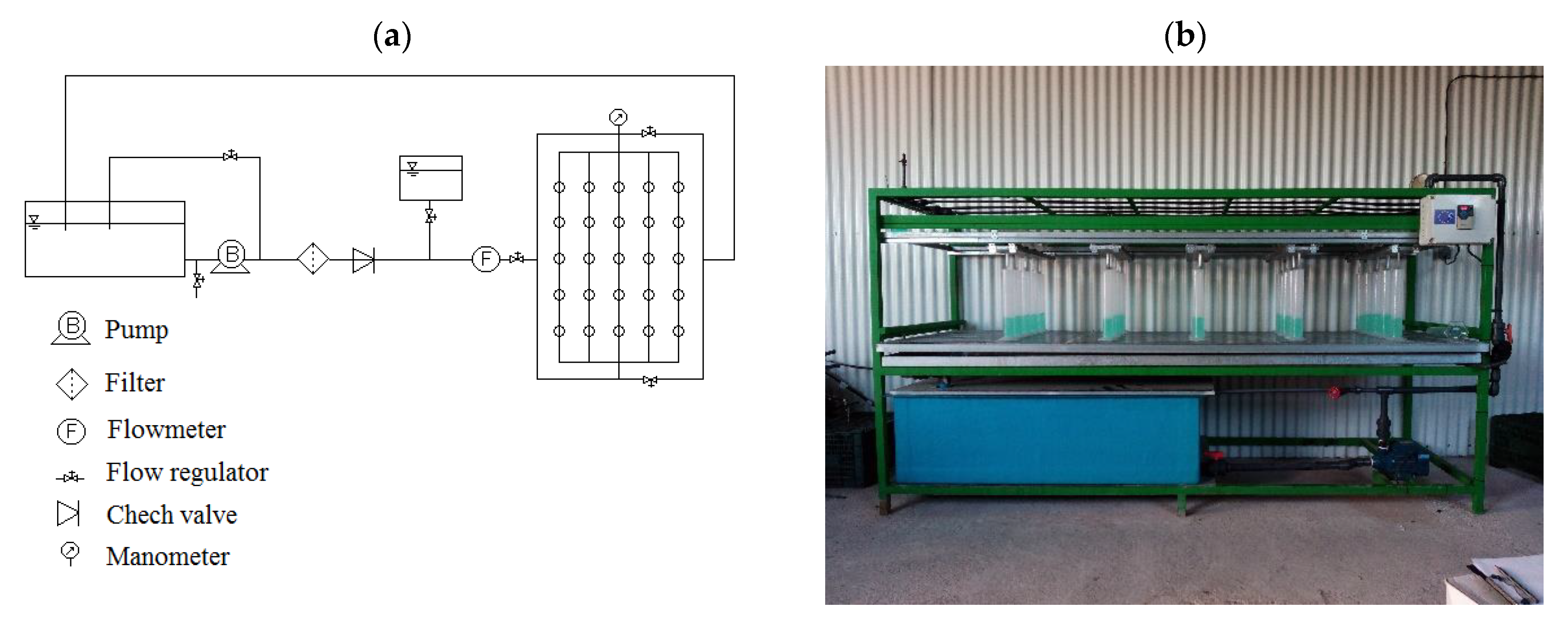
2.1.2. Test Set
2.1.3. Determinations
2.2. Greenhouse Condition Phase
2.2.1. Origin, Treatment, and Quality of Reclaimed Water
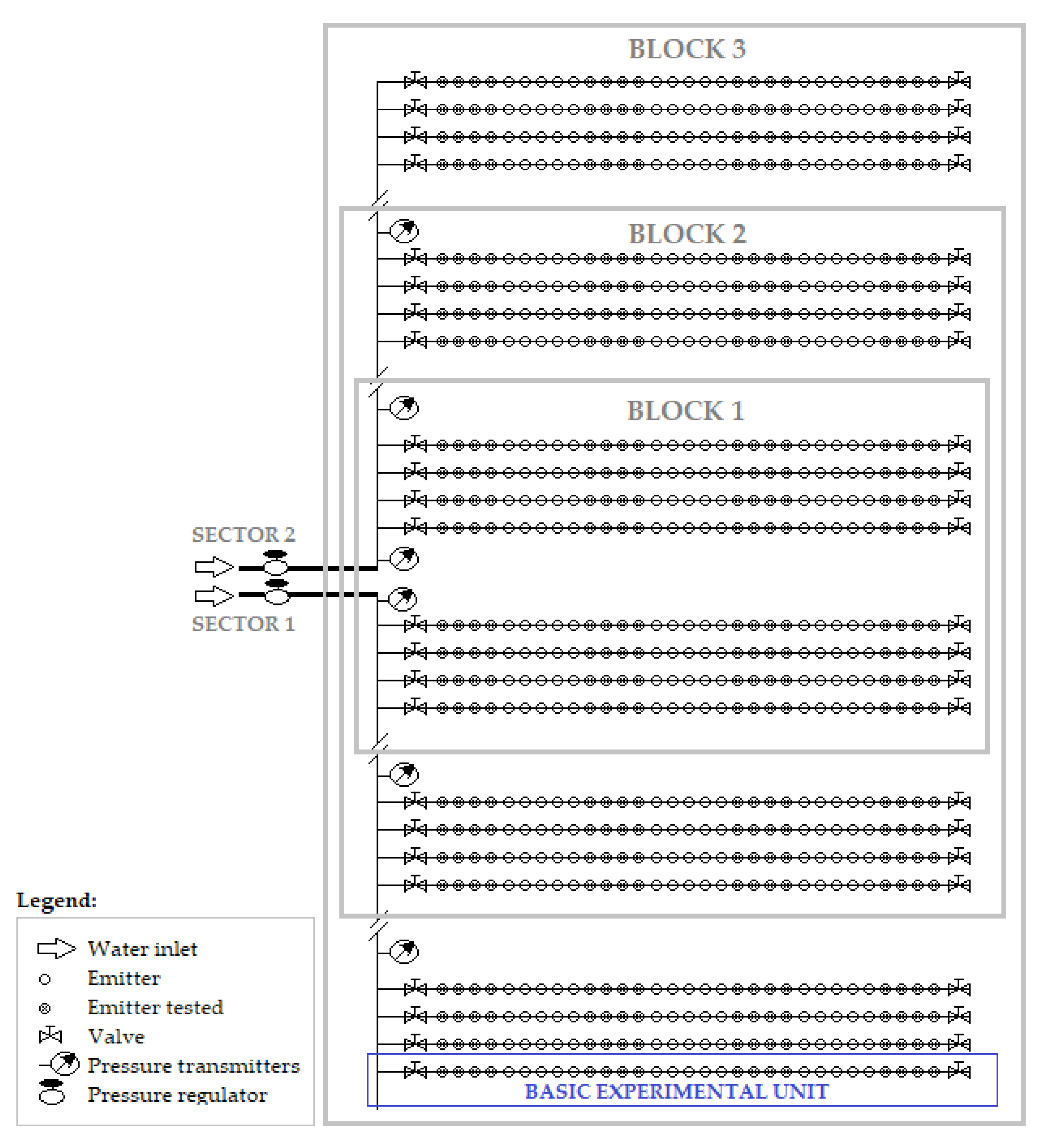
2.2.2. Equipment, Experimental Design, and Treatments
2.2.3. Determinations
2.2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
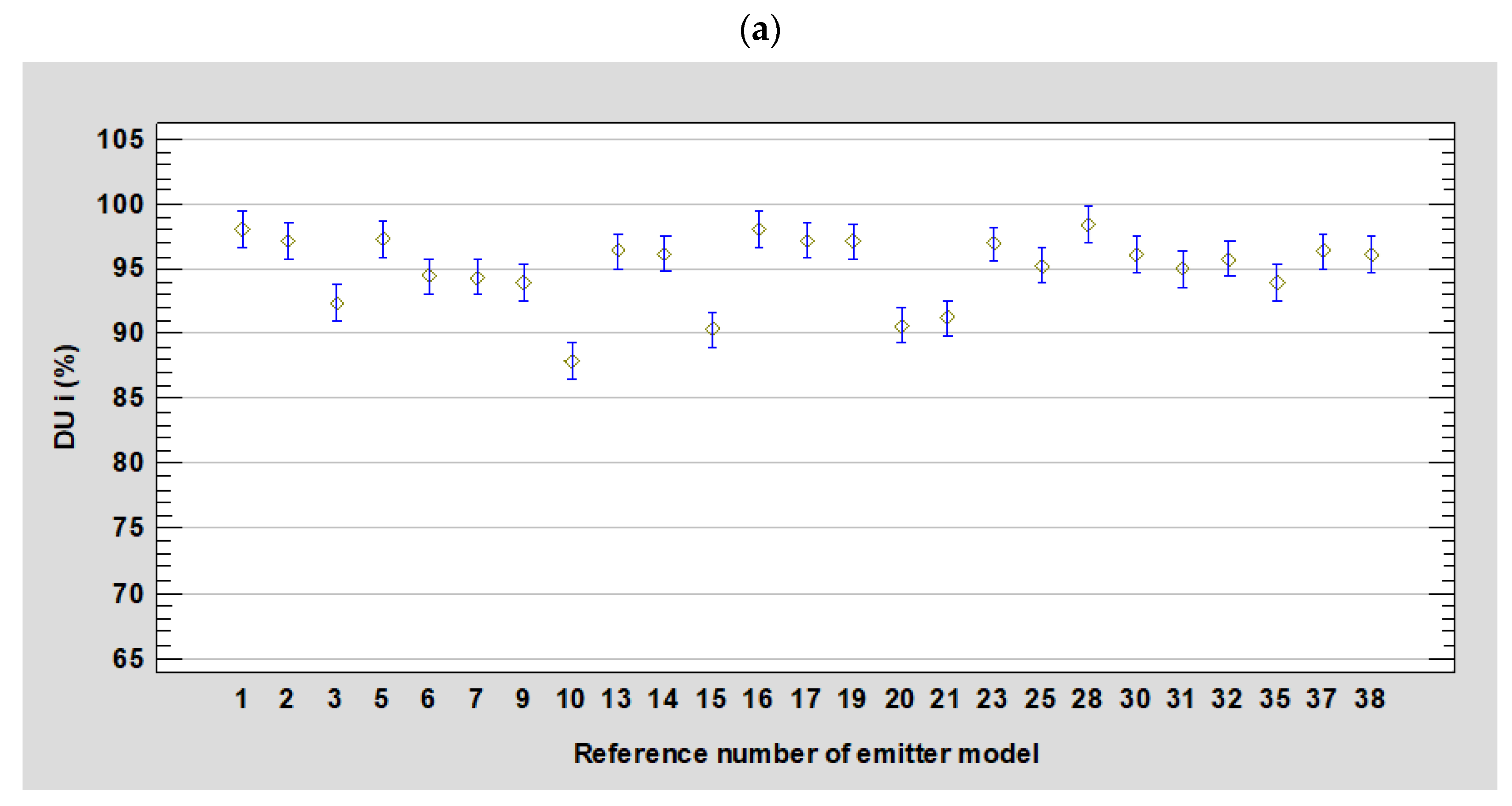
3.1. Manufacturer’s Coefficient of Variation (Cv) and Emitter Equation (Ee)
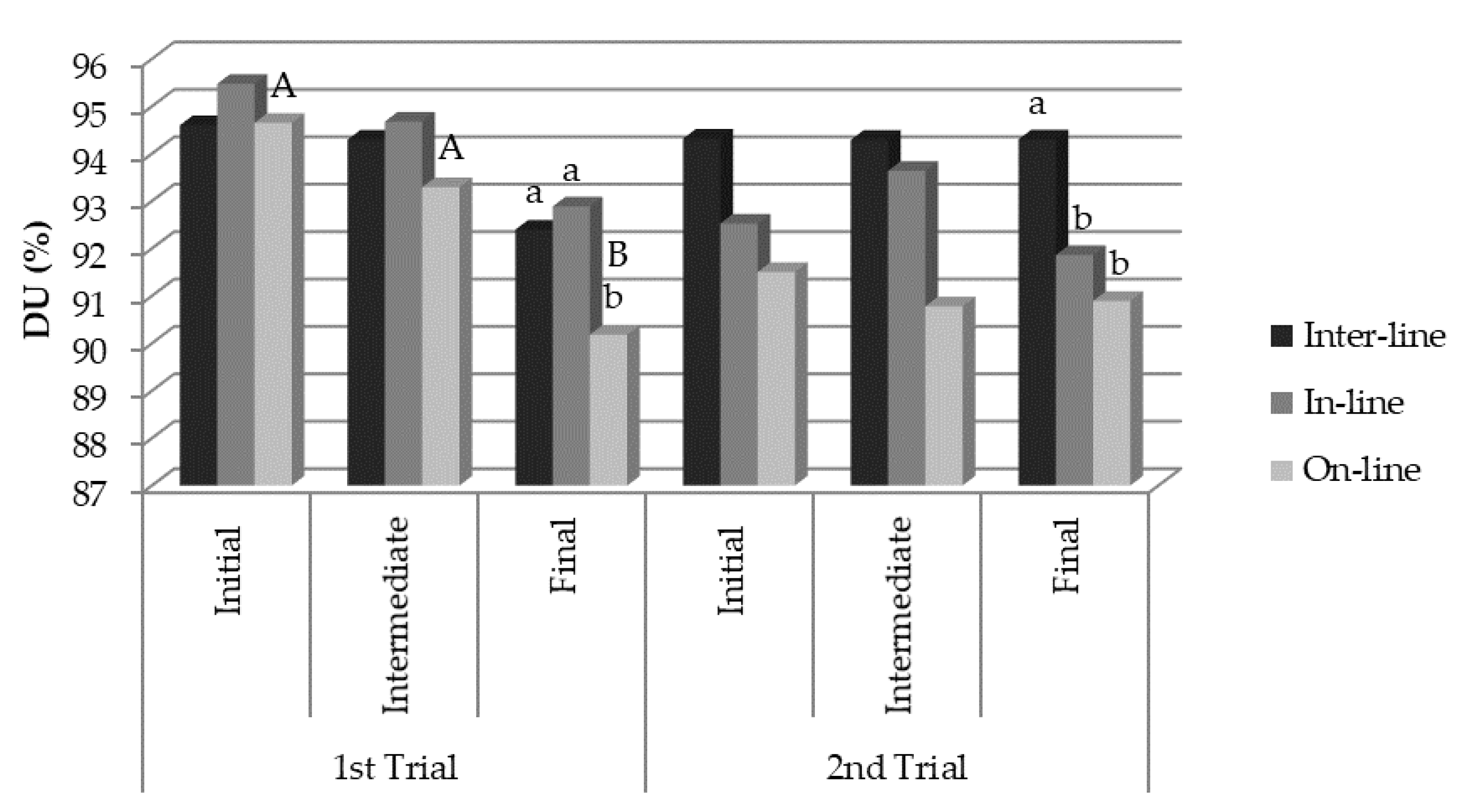
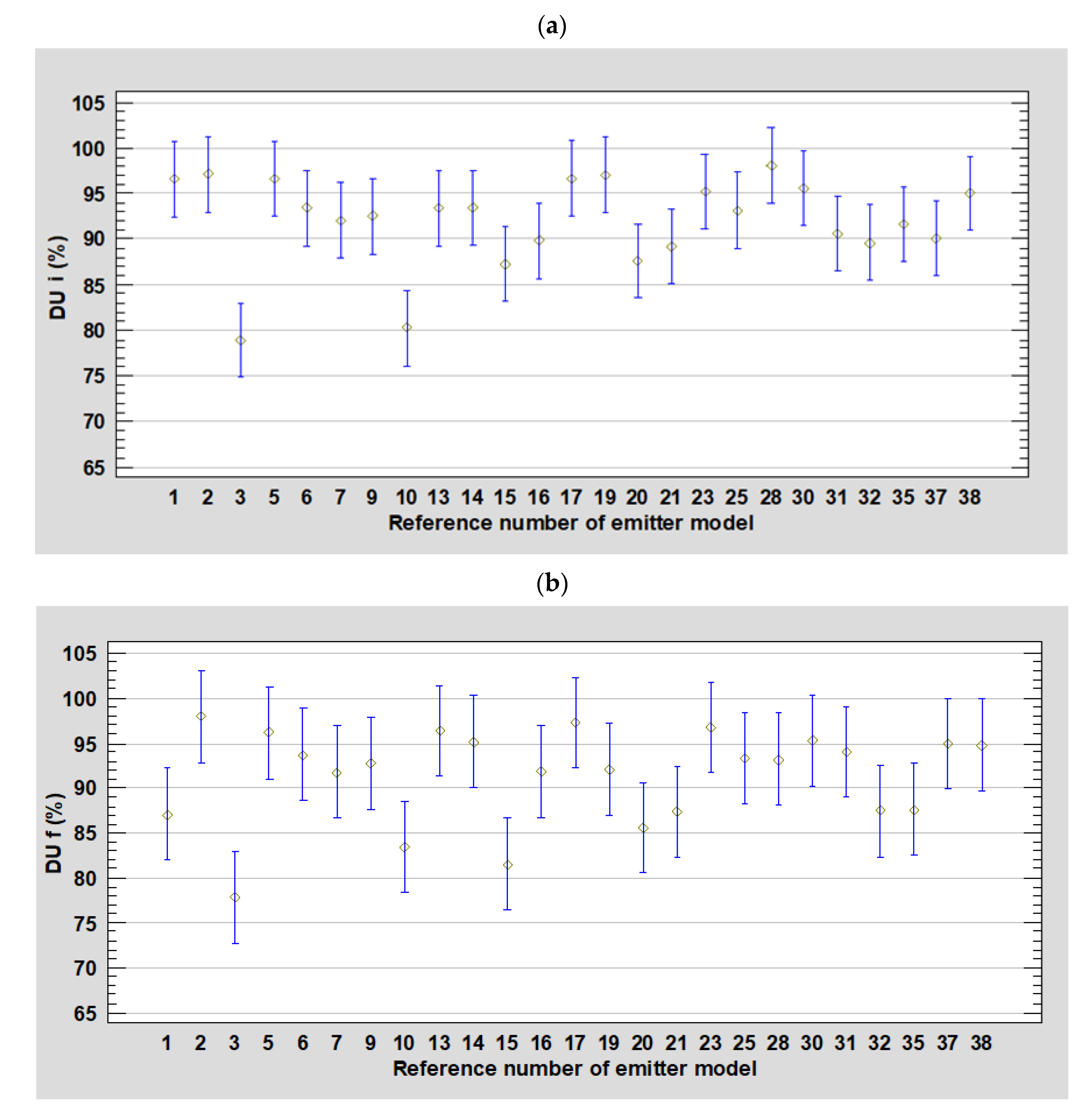
3.2. Distribution Uniformity Coefficient (DU)
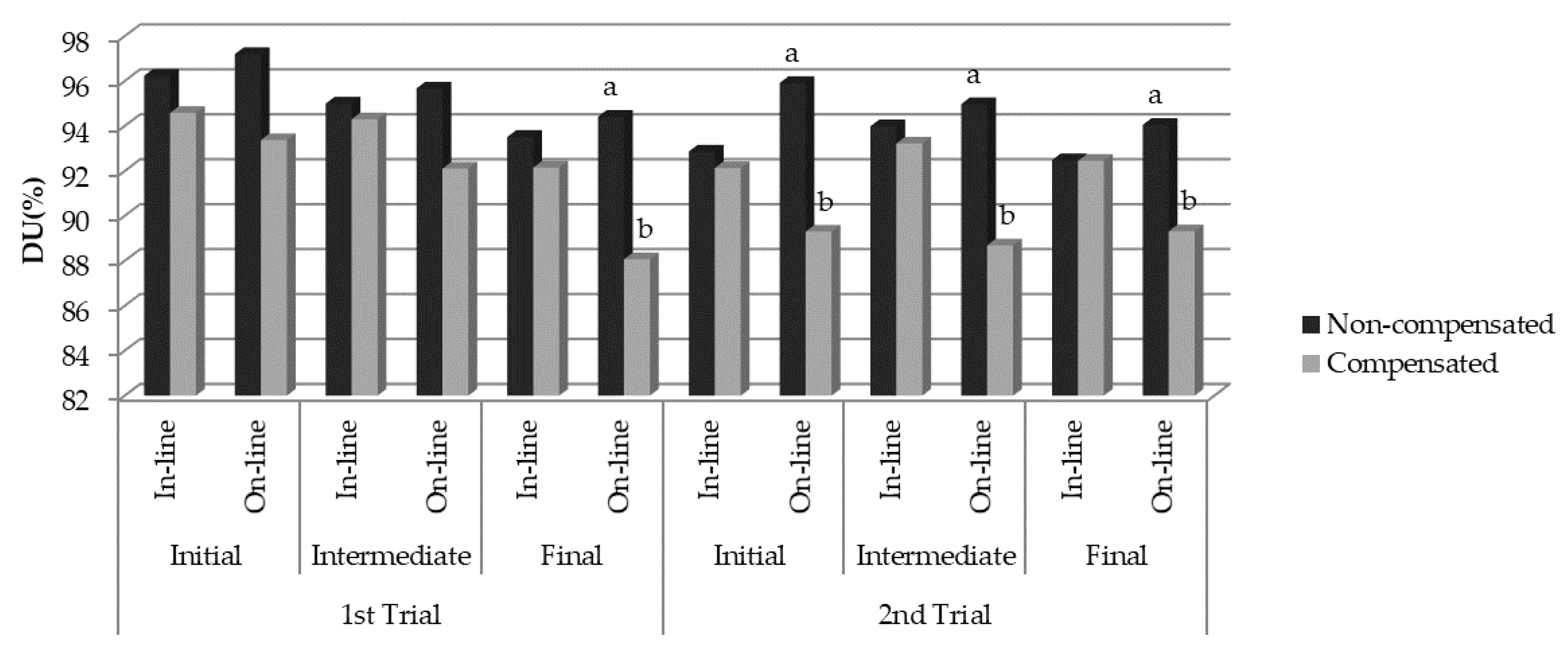
3.2.1. First Trial
3.2.2. Second Trial
3.3. Emitter Clogging (CE)
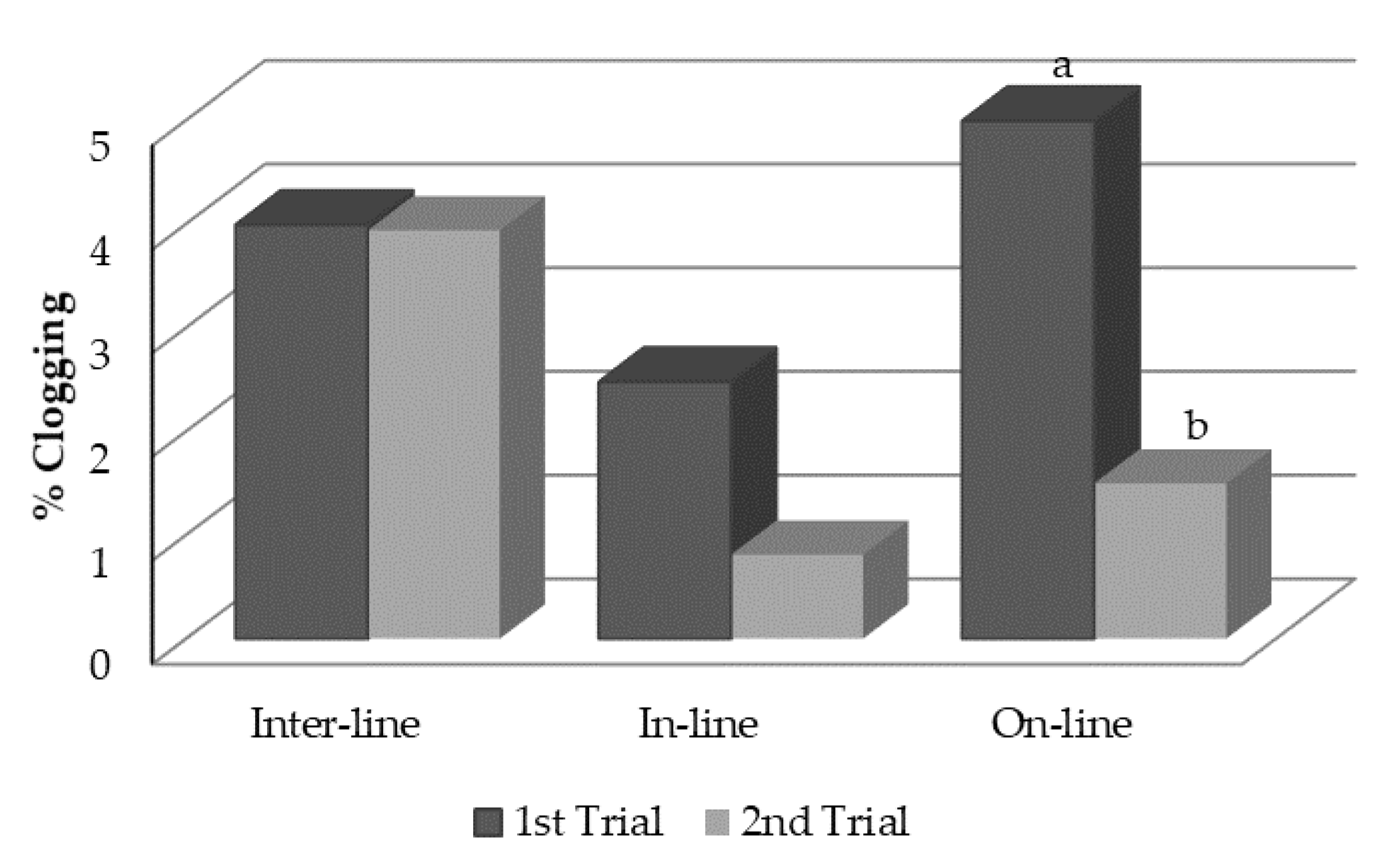
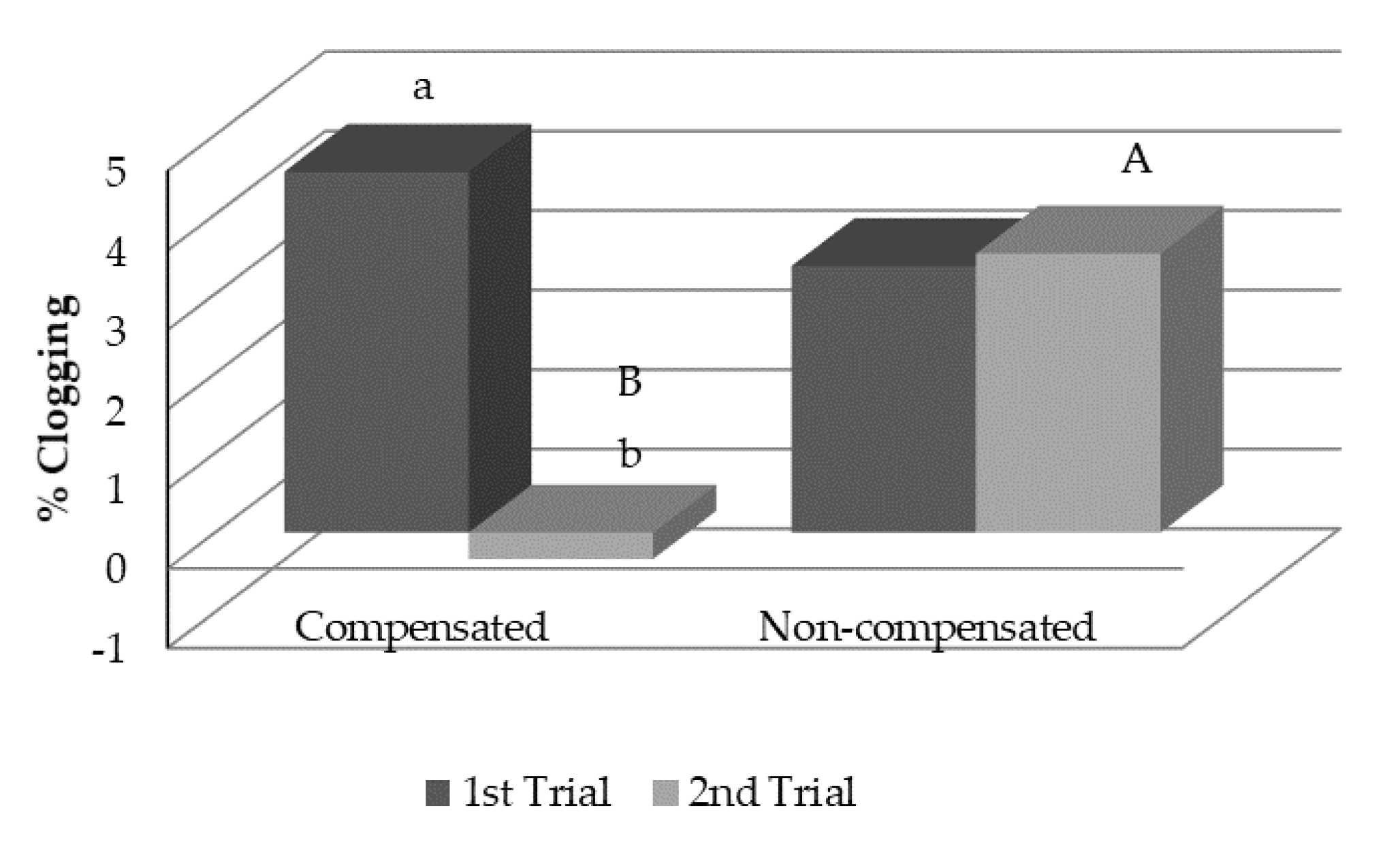
3.3.1. First Trial
3.3.2. Second Trial
4. Discussion
4.1. Regarding Water Quality
4.2. Regarding Type of Emitter
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Cv | Manufacturer’s Coefficient of Variation |
| Ee | Emitter equation |
| DU | Uniformity Distribution Coefficient |
| CE | Clogging of the Emitter |
References
- UNESDOC. Digital Library. Available online: https://unesdoc.unesco.org/ark:/48223/pf0000372985.locale=en (accessed on 12 April 2020).
- UNESCO. The Agenda 21 World Water Development Report 3: Water in a Changing World; World Water Assessment Programme; UNESCO: Paris, France, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Evans, R.G. Microirrigacion; 24106 North Bunn Roas Prosser; Washington State University, Irrigated Agriculture Research and Extension Center: Washington, DC, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Contreras, J.I.; Alonso, F.; Cánovas, G.; Baeza, R. Irrigation management of greenhouse zucchini with different soil matric potential level. Agronomic and environmental effects. Agric. Water Manag. 2017, 183, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Caparros, P.; Contreras, J.I.; Baeza, R.; Segura, M.L.; Lao, M.T. Integral management of irrigation water in intensive horticultural systems of Almería. Sustainability 2017, 9, 2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Instituto Geográfico Nacional. Available online: https://www.ign.es/espmap/mapas_rural_bach/Rural_Mapa_06.htm (accessed on 12 April 2020).
- Corominas, J. Los Nuevos Planes Hidrológicos de las Cuencas Andaluzas; Observatorio del Agua de la Fundación Botín: Madrid, Spain, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Pujol, J.; Duran-Ros, M.; Arbat, G.; Ramirez de Cartagena, F.; Puig-Bargues, J. Private micro-irrigation costs using reclaimed water. Span. J. Agric. Res. 2011, 9, 1120–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- BOE. Royal Decree 1620/2007, of December 7, by Establishing the Legal Regime Reuse of Treated Water; Boletín Oficial del Estado No. 294; BOE: Madrid, Spain, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- EUR-lex. Access to European Union Law. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/procedure/ES/2018_169?uri=PROCEDURE:2018_169 (accessed on 12 April 2020).
- García-Delgado, C.; Eymar, E.; Contreras, J.I.; Segura, M.L. Effects of fertigation with purified urban wastewater on soil and pepper plant (Capsicum annuum L.) production, fruit quality and pollutant contents. Span. J. Agric. Res. 2012, 10, 209–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Contreras, J.I.; Eymar, E.; Lopez, J.G.; Lao, M.T.; Segura, M.L. Influences of nitrogen and potassium fertigation on nutrient uptake, production, and quality of pepper irrigated with disinfected urban wastewater. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2013, 44, 767–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contreras, J.I.; López, J.G.; Lao, M.T.; Eymar, E.; Segura, M.L. Dry-matter allocation and nutrient uptake dynamic in pepper plant irrigated with recycled water by different nitrogen and potassium rate. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2013, 44, 758–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baeza, R.; Gavilán, P.; Del Castillo, N.; Berenguel, P.; López, J.G. Programa de evaluación y asesoramiento en instalaciones de riego en invernadero con uso de dos fuentes distintas de agua: Subterránea y regenerada. In Proceedings of the XXVIII Congreso Nacional de Riegos, León, Spain, 15–17 June 2010; pp. 111–112. [Google Scholar]
- Baeza, R.; Cánovas, G.; Alonso, F.; Contreras, J.I. Evaluación de las instalaciones de riego en cultivos hortícolas intensivos del sureste de Andalucía. In El Agua en Andalucía. El agua, clave medioambiental y socioeconómica. Tomo II; SIAGA; Instituto Geológico y Minero de España: Málaga, Spain, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Ravina, I.; Paz, E.; Sofer, Z.; Marm, A.; Schischa, A.; Sagi, G.; Yechialy, Z.; Lev, Y. Control of clogging in drip irrigation with stored treated municipal sewage effluent. Agric. Water Manag. 1997, 33, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Chen, L.; Li, Y. Comparison of clogging in drip emitters during application of sewage effluent and groundwater. Trans ASABE 2009, 52, 1203–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, R.G.; Nakayama, F.S.; Bucks, D.A.; French, O.F.; Adamson, K.C. Trickle irrigation: Emitter clogging and flow problems. Agric. Water Manag. 1981, 3, 159–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitts, D.J.; Haman, D.Z.; Smajstrla, A.G. Causes and prevention of emitter plugging in micro irrigation systems. Bull.-Fla. Coop. Ext. Serv. 1990, 258. [Google Scholar]
- Coelho, R.D.; Resende, R.S. Biological Clogging of nEtafim’s Drippers and Recovering Process through Chlorination Impact Treatment; ASAE Paper Number: 012231; ASAE: Sacramento, CA, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert, R.G.; Ford, H.W. Operational principles emitter clogging. In Trickle Irrigation for Crop Production: Design, Operation and Management; Nakayama, F.S., Bucks, D.A., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1986; pp. 142–163. [Google Scholar]
- Guan, H.; Li, J.; Li, Y. Effects of drip system uniformity and irrigation amount on cotton yield and quality under arid conditions. Agric. Water Manag. 2013, 124, 37–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, J.; Li, Y. Effects of drip system uniformity and nitrogen application rate on yield and nitrogen balance of spring maize in the North China Plain. Field Crops Res. 2014, 159, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Ortolá, M.; Daccache, A.; Hess, T.M.; Knox, J.W. Simulating impacts of irrigation heterogeneity on onion (Allium cepa L.) yield in a humid climate. Irrig. Sci. 2015, 33, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, C.E. Efecto de la Uniformidad de Riego sobre la Productividad del Cultivo de Calabacín en Invernadero. Master’s Thesis, Universidad de Almería, Almería, Spain, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Mateos, L.; Mantovani, E.C.; Villalobos, F.J. Cotton response to non-uniformity of conventional sprinkler irrigation. Irrig. Sci. 1997, 17, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordovsky, J.P.; Porter, D.O. Effect of subsurface drip irrigation system uniformity on cotton production in the Texas High Plains. Appl. Eng. Agric. 2008, 24, 465–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Li, J.; Li, Y.; Yin, J. Effects of drip system uniformity on yield and quality of Chinese cabbage heads. Agric. Water Manag. 2012, 110, 118–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adin, A.; Sacks, M. Dripper-clogging factors in wastewater irrigation. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 1991, 117, 813–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.Q. Some advice on the application of micro irrigation. Beijing Water Technol. 1993, 4, 23–24. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, W.; Xue, S. Effect of optimization forms of flow path on emitter hydraulic and anti-clogging performance in drip irrigation system. Irrig. Sci. 2018, 36, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhangzhong, L.; Yang, P.; Li, Y.; Ren, S. Effects of flow path geometrical parameters on flow characteristics and hydraulic performance of drip irrigation emitters. Irrig. Drain. 2016, 65, 426–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Li, Y.; Song, P.; Xu, Z.; Bralts, V. A kinetic model for biofilm growth inside non-PC emitters under reclaimed water drip irrigation. Agric. Water Manag. 2016, 168, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, B.; Shi, Z.; Jiang, Y. Eight emitters clogging characteristics and its suitability under on-site reclaimed water drip irrigation. Irrig. Sci. 2014, 32, 141–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bounoua, S.; Tomas, S.; Labille, J.; Molle, B.; Granier, J.; Haldenwang, P.; Izzati, S.N. Understanding physical clogging in drip irrigation: In situ, in-lab and numerical approaches. Irrig. Sci. 2016, 34, 327–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Li, Y.; Zhou, B.; Liu, Z.; Feng, J.; Xiao, Y. An in-situ accelerated experimental testing method for drip irrigation emitter clogging with inferior water. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 212, 136–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baeza, R.; Contreras, J.I.; Martin, F.; Zapata, A.; López, J.G. Estudio prospectivo de los emisores de riego localizado instalados en la zona regable del Bajo Andarax con aguas residuales urbanas regenerada. In Proceedings of the XXX Congreso Nacional de Riegos, Albacete, Spain, 12–14 June 2012; pp. 89–90. [Google Scholar]
- Lorenzo, P.; Sánchez-Guerrero, M.C.; Medrano, E.; Garcia, M.L.; Caparros, I.; Coelho, G.; Giménez, M. Climate control in the summer season: A comparative study of external mobile shading and fog system. Act. Hort. 2004, 659, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, M.D.; Bonachela, S.; Orgaz, F.; Thompson, R.; López, J.C.; Granados, M.R.; Gallardo, M.; Fereres, E. Measurement and estimation of plastic greenhouse reference evapotranspiration in a Mediterranean climate. Irrig. Sci. 2010, 28, 497–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Merriam, J.L.; Keller, J. Farm Irrigation System Evaluation: A Guide for Management; UTAH State University: Logan, UT, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Ravina, I.; Paz, E.; Sofer, Z.; Marcu, A.; Shisha, A.; Sagi, G. Control of emitter clogging in drip irrigation with reclaimed wastewater. Irrig. Sci. 1992, 13, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capra, A.; Scicolone, B. Management of emitter clogging with municipal wastewater. In Wastewater Management for Irrigation: Principles and Practices; Goyal, M.R., Tripathi, V.K., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016; Volume 4, pp. 81–96. [Google Scholar]
- Lili, Z.; Yang, P.; Ren, S.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Xia, Y. Chemical clogging of emitters and evaluation of their suitability for saline water drip irrigation. Irrig. Drain. 2016, 65, 439–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Li, Y.; Song, P.; Zhou, Y.; Yu, Y.; Bralts, V. Anti-clogging evaluation for drip irrigation emitters using reclaimed water. Irrig. Sci. 2017, 35, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baeza, R.; Contreras, J.I.; Cánovas, G.; Alonso, F.; Reyes-Requena, R.; Roldán-Cañas, J.; Moreno-Pérez, M.F. Study of the uniformity of emitters in drip irrigation using regenerated wastewater under different management practices. In Geophysical Research Abstracts; EGU General Assembly: Vienna, Austria, 2019; Volume 21. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, D.; Yang, P.; Rowan, M.; Ren, S.; Pitts, D. Biofilm accumulation and structure in the flow path of drip emitters using reclaimed wastewater. Trans. ASABE 2010, 53, 751–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Solé-Torres, C.; Duran-Ros, M.; Arbat, G.; Pujol, J.; Ramírez de Cartagena, F.; Puig-Bargués, J. Assessment of Field Water Uniformity Distribution in a Microirrigation System Using a SCADA System. Water 2019, 11, 1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Capra, A.; Scicolone, B. Recycling of poor quality urban wastewater by drip irrigation systems. J. Clean Prod. 2007, 15, 1529–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Xu, F.; Pei, Y.; Wang, Z. Effect of drip irrigation frequency on emitter clogging using reclaimed water. Irrig. Sci. 2015, 33, 221–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamri, S.; Soric, A.; Tomas, S.; Molle, B.; Roche, N. Biofilm development in micro-irrigation emitters for wastewater reuse. Irrig. Sci. 2014, 32, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, M.F.; Molle, B.; Alves, D.G.; Ait-Mouheb, N.; Camargo, A.P.D.; Frizzone, J.A. Flow rate dynamics of pressure-compensating drippers under clogging effect. Rev. Bras. Eng. Agríc. Ambient. 2017, 21, 304–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ebrahimi, H.; Hamzee, G.H.; Farsheh, T.A.; Nazarjani, M. Evaluation of emitter clogging in trickle irrigation with wastewater. J. Basic Appl. Sci. Res. 2012, 2, 5288–5291. [Google Scholar]
- Puig-Bargues, J.; Arbat, G.; Elbana, M.; Duran-Ros, M.; Barragán, J.; De Cartagena, F.R.; Lamm, F.R. Effect of flushing frequency on emitter clogging in microirrigation with effluents. Agric. Water Manag. 2010, 97, 883–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]




| N 1 | Commercial Name | Manufacturer | Pipeline Insertion | Pressure Compensation | Emitter Equation 2 (Q = k Hx) | Manufacturer’s Coefficient of Variation (Cv) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | JainEmitter | NaanDanJain Ibérica | On-line | Non-compensated | Q = 4.2358 H 0.482271 | 0.03 |
| 2 | Twin DropsAdvanced | Mondragon Soluciones | On-line | Non-compensated | Q = 3.98369 H 0.388491 | 0.01 |
| 3 | Key Orvel | ExtrulineSystems | On-line | Compensated | Q = 4.75822 H 0.153382 | 0.06 |
| 4 | Interline 12 | ExtrulineSystems | Inter-line | Non-compensated | Q = 3.40393 H 0.51944 | 0.03 |
| 5 | Demountable perforated | Hidroten | On-line | Non-compensated | Q = 4.17937 H 0.506763 | 0.02 |
| 6 | MB Escober GE3 | Marbroer | On-line | Compensated | Q = 3.19962 H −0.0745321 | 0.03 |
| 7 | ADO Metzerplas | ExtrulineSystems | On-line | Compensated | Q = 4.52218 H −0.0141037 | 0.05 |
| 8 | Interline 12 | Amacom | Inter-line | Non-compensated | Q = 3.26627 H 0.521201 | 0.03 |
| 9 | MB Escober GAE3 | Marbroer | On-line | Compensated | Q = 2.96746 H −0.0362502 | 0.01 |
| 10 | Pinchado autocompensante | Hidroten | On-line | Compensated | Q = 4.36964 H 0.121575 | 0.07 |
| 11 | Interline 12 | Hidroten | Inter-line | Non-compensated | Q = 3.22552 H 0.487763 | 0.02 |
| 12 | NYA | Prima-Ram | Inter-line | Non-compensated | Q = 3.48498 H 0.535236 | 0.04 |
| 13 | PCJ | Netafim | On-line | Compensated | Q =3.13308 H −0.0166151 | 0.03 |
| 14 | Demountable conical | Hidroten | On-line | Non-compensated | Q = 3.75943 H 0.430399 | 0.04 |
| 15 | Acuario | Gestirriego | On-line | Compensated | Q = 5.14509 H 0.0318056 | 0.05 |
| 16 | J-Turboline | NaanDanJain Ibérica | In-line | Non-compensated | Q = 3.06543 H 0.474679 | 0.02 |
| 17 | PC-CNL | Netafim | On-line | Compensated | Q = 2.86158 H 0.0914451 | 0.03 |
| 18 | IT-S Interline | Marbroer | Inter-line | Non-compensated | Q = 3.36957 H 0.484893 | 0.07 |
| 19 | Hydrogol | Rivulis | In-line | Non-compensated | Q = 2.96926 H 0.490086 | 0.03 |
| 20 | NaanPC | NaanDanJain Ibérica | On-line | Compensated | Q = 3.27609 H 0.104834 | 0.06 |
| 21 | Starcomp | Comercial Agrícola de Riegos | In-line | Compensated | Q = 4.38239 H 0.0246694 | 0.06 |
| 22 | AGR | Azud | Inter-line | Non-compensated | Q = 3.15374 H 0.498693 | 0.02 |
| 23 | AmnomDrip | NaanDanJain Ibérica | In-line | Compensated | Q = 1.99524 H 0.0276302 | 0.02 |
| 24 | Interline 16 | Hidroten | Inter-line | Non-compensated | Q = 3.79157 H 0.513929 | 0.05 |
| 25 | LIN | ExtrulineSystems | In-line | Non-compensated | Q = 3.15383 H 0.480486 | 0.04 |
| 26 | Interline 16 | Comercial Agrícola de Riegos | Inter-line | Non-compensated | Q = 3.29897 H 0.472523 | 0.07 |
| 27 | Interline 16 | Amacom | Inter-line | Non-compensated | Q = 3.21973 H 0.498309 | 0.02 |
| 28 | PRO | Azud | In-line | Non-compensated | Q = 4.18379 H 0.473664 | 0.03 |
| 29 | Interline 16 | ExtrulineSystems | Inter-line | Non-compensated | Q = 3.77026 H 0.508657 | 0.05 |
| 30 | Megadrip | Mondragon Soluciones | In-line | Compensated | Q = 1.9288 H 0.0273114 | 0.03 |
| 31 | Tifdrip | NaanDanJain Ibérica | In-line | Non-compensated | Q = 3.70889 H 0.444218 | 0.03 |
| 32 | Irridrip | Mondragon Soluciones | In-line | Non-compensated | Q = 1.98437 H 0.474063 | 0.03 |
| 33 | Demountable interline | Hidroten | Inter-line | Non-compensated | Q = 4.02549 H 0.528695 | 0.03 |
| 34 | Interline 16 | NaanDanJain Ibérica | Inter-line | Non-compensated | Q = 3.60934 H 0.463382 | 0.06 |
| 35 | Cardrip | Comercial Agrícola de Riegos | In-line | Non-compensated | Q = 3.34583 H 0.485898 | 0.04 |
| 36 | IT-N Interline | Marbroer | Inter-line | Non-compensated | Q = 3.95558 H 0.454687 | 0.10 |
| 37 | Hydro-PC | Rivulis | In-line | Compensated | Q = 3.74919 H −0.00899392 | 0.01 |
| 38 | DripNet PC | Netafim | In-line | Compensated | Q = 3.33987 H −0.0207132 | 0.01 |
| Parameter | 1st Trial | 2nd Trial | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average Value | Range | Average Value | Range | |
| Turbidity (NTU) | 11.3 | 9.4–16.0 | 4.2 | 3.8–4.4 |
| Suspended solids (mg L−1) | 12.5 | 9.7–15.5 | 3.8 | 3.5–4.0 |
| pH | 8.2 | 8.1–8.3 | 7.8 | 7.7–7.9 |
| Biochemical oxygen demand—BOD5 (mg O2 L−1) | 8.6 | 7.5–11.2 | <5 | <5 |
| Chemical oxygen demand—COD (mg O2 L−1) | 35.3 | 30.1–45.7 | 22.1 | 20.1–25.3 |
| Electrical conductivity—EC (dS m−1) | 1.92 | 1.83–2.03 | 1.89 | 1.80–1.93 |
| DU | Classification |
|---|---|
| >95% | Excellent |
| 85–95% | Good |
| 80–85% | Fair |
| 70–80% | Poor |
| <70% | Unacceptable |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Baeza, R.; Contreras, J.I. Evaluation of Thirty-Eight Models of Drippers Using Reclaimed Water: Effect on Distribution Uniformity and Emitter Clogging. Water 2020, 12, 1463. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12051463
Baeza R, Contreras JI. Evaluation of Thirty-Eight Models of Drippers Using Reclaimed Water: Effect on Distribution Uniformity and Emitter Clogging. Water. 2020; 12(5):1463. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12051463
Chicago/Turabian StyleBaeza, Rafael, and Juana I. Contreras. 2020. "Evaluation of Thirty-Eight Models of Drippers Using Reclaimed Water: Effect on Distribution Uniformity and Emitter Clogging" Water 12, no. 5: 1463. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12051463
APA StyleBaeza, R., & Contreras, J. I. (2020). Evaluation of Thirty-Eight Models of Drippers Using Reclaimed Water: Effect on Distribution Uniformity and Emitter Clogging. Water, 12(5), 1463. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12051463






