Determination of Empirical Rainfall Thresholds for Shallow Landslides in Slovenia Using an Automatic Tool
Abstract
:1. Introduction
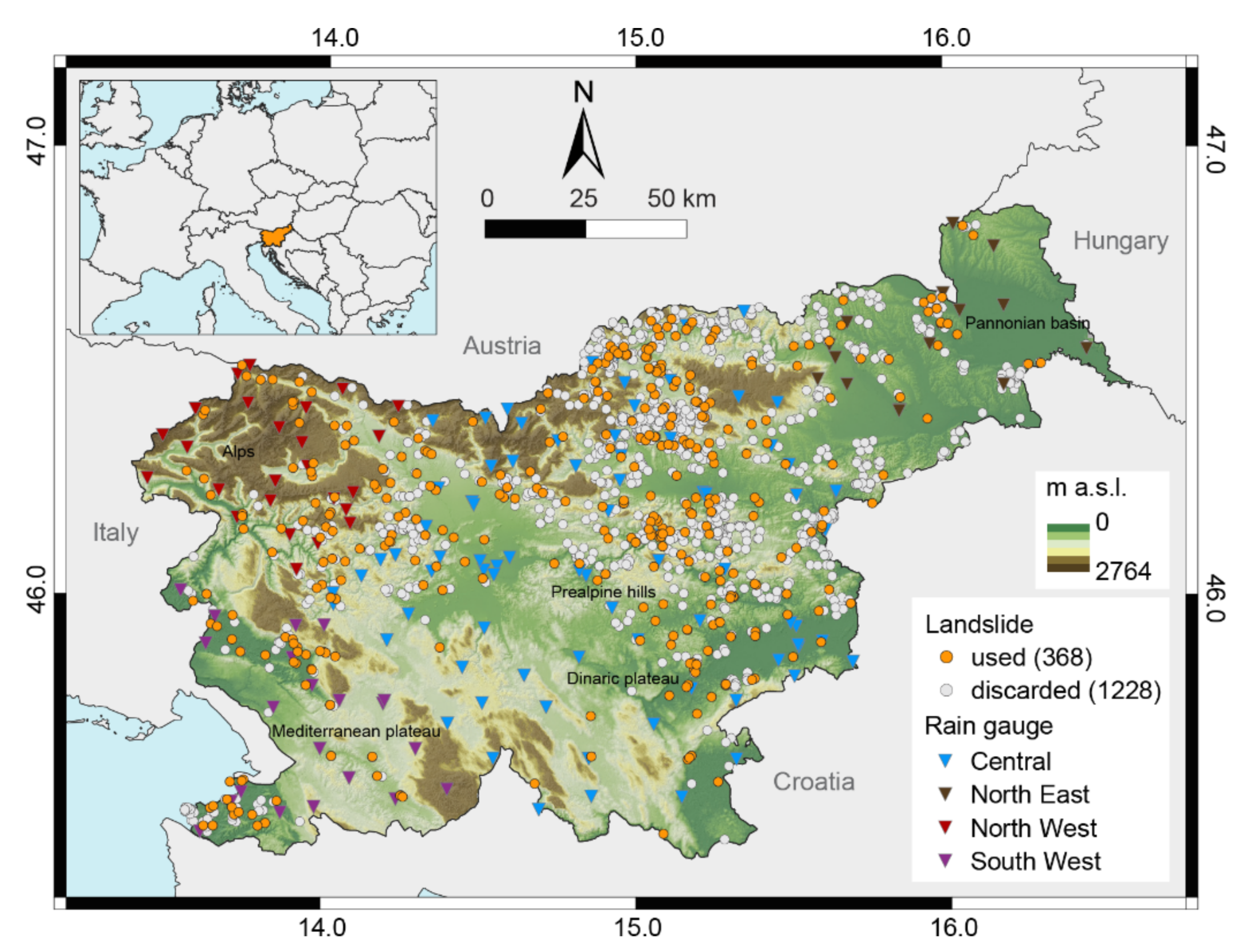
2. Study Area
3. Methods and Data
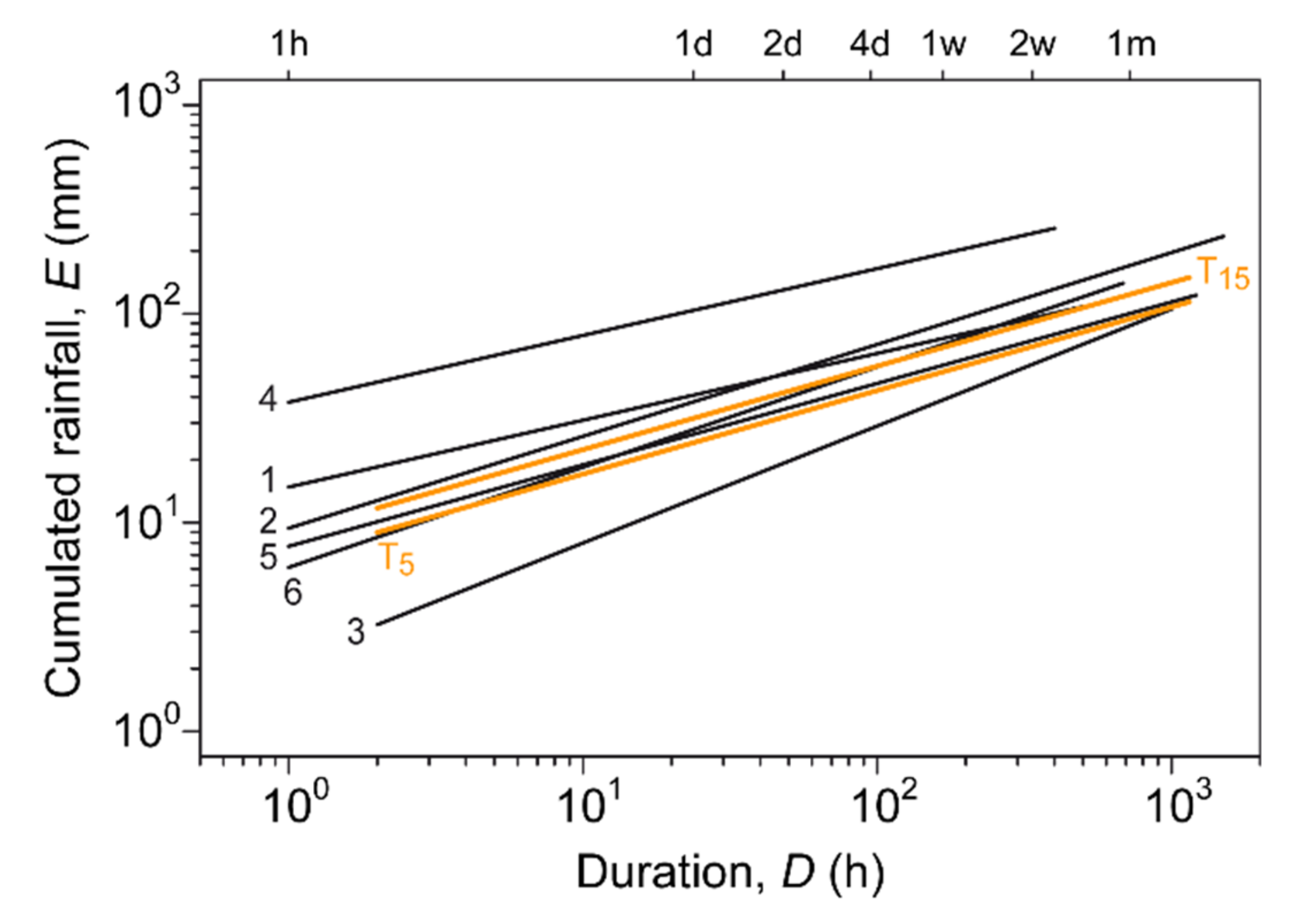
3.1. CTRL-T Tool and Threshold Equation
3.2. Landslide Data
3.3. Rainfall Data
4. Results and Discussion
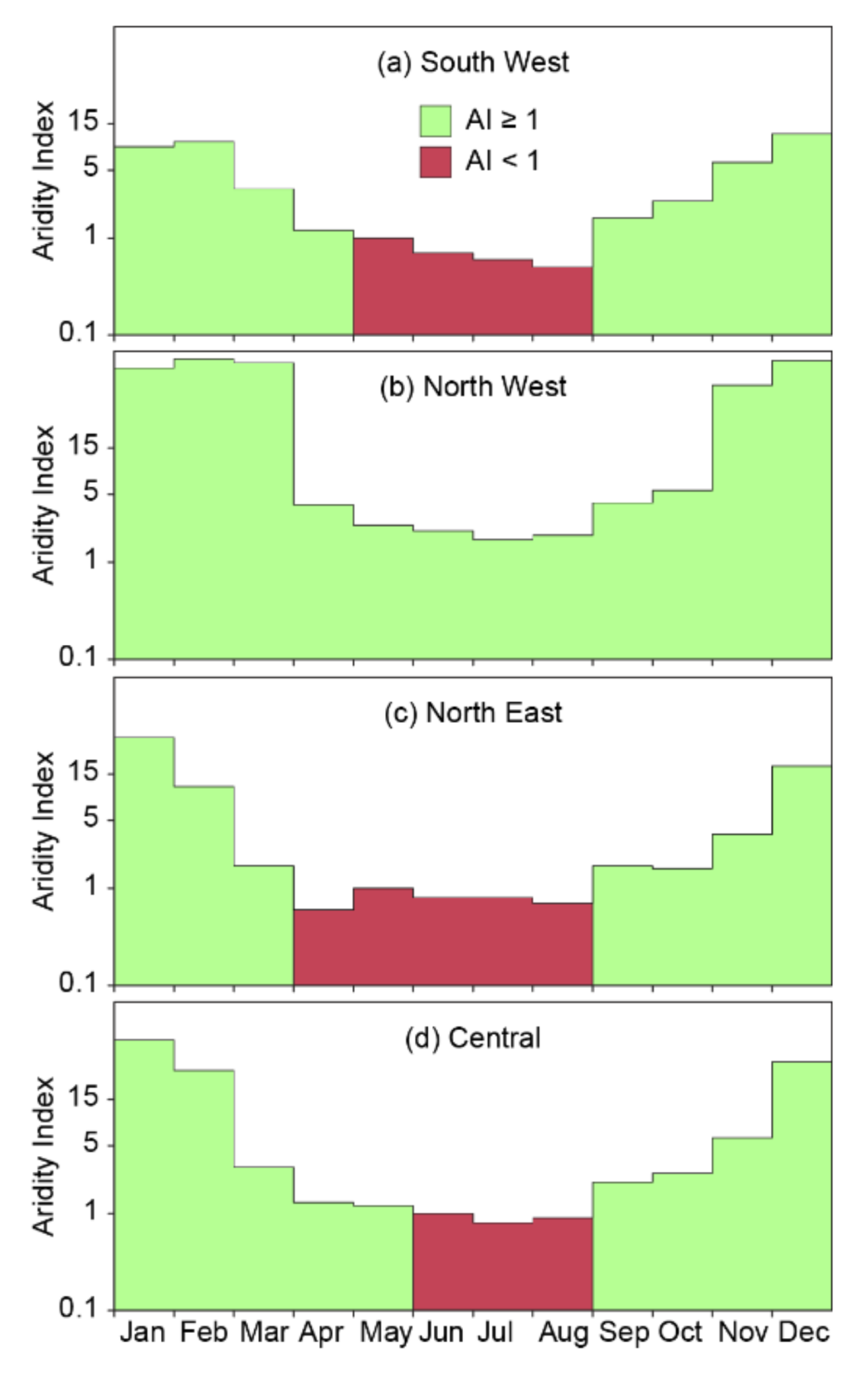
4.1. Definition of the Dry and Wet Season
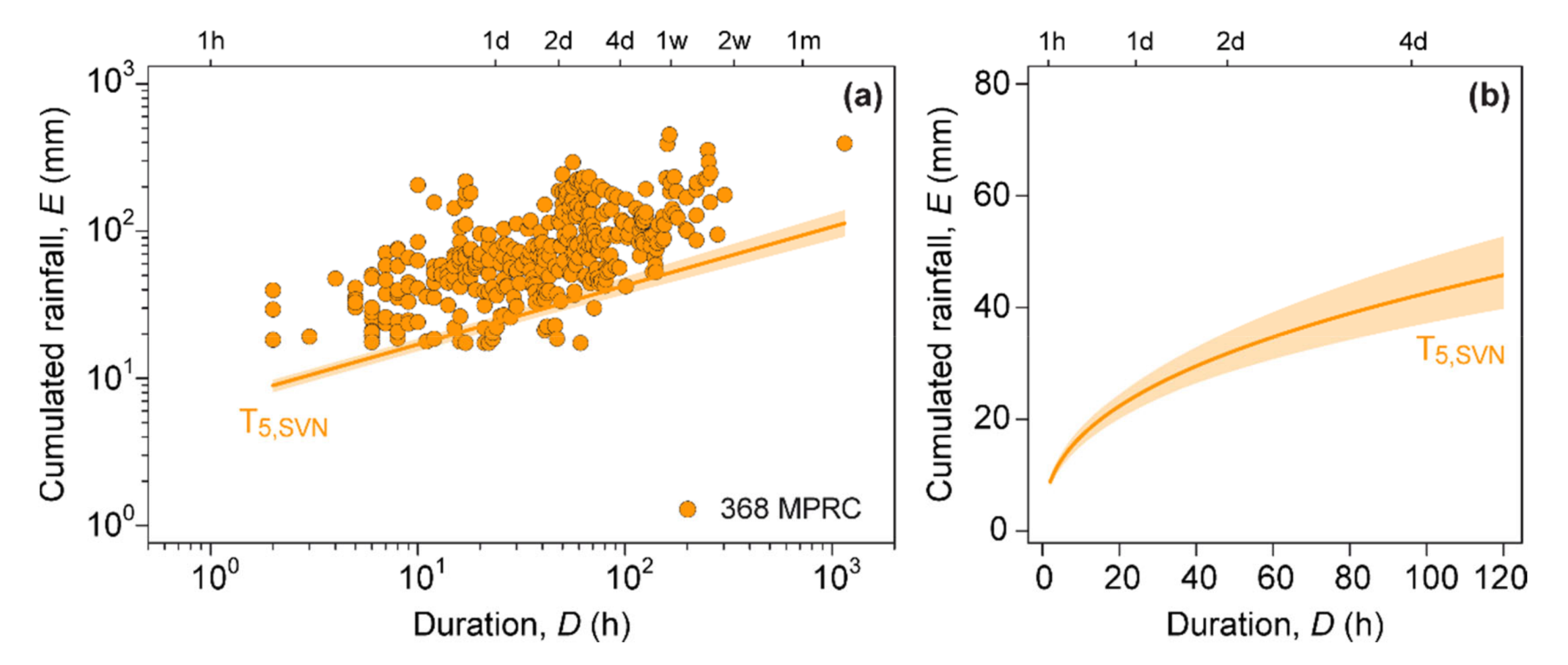
4.2. Threshold Calculation
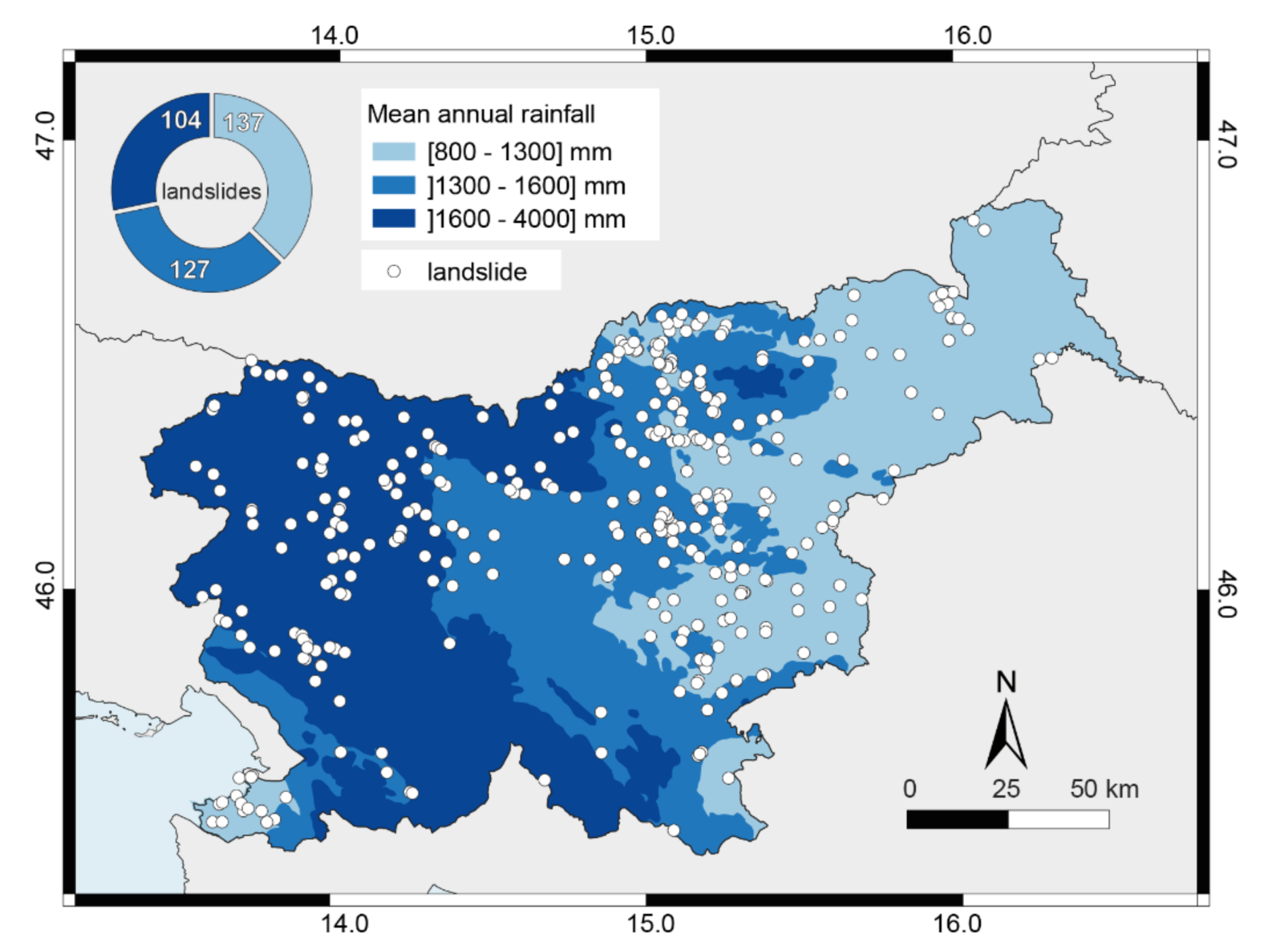
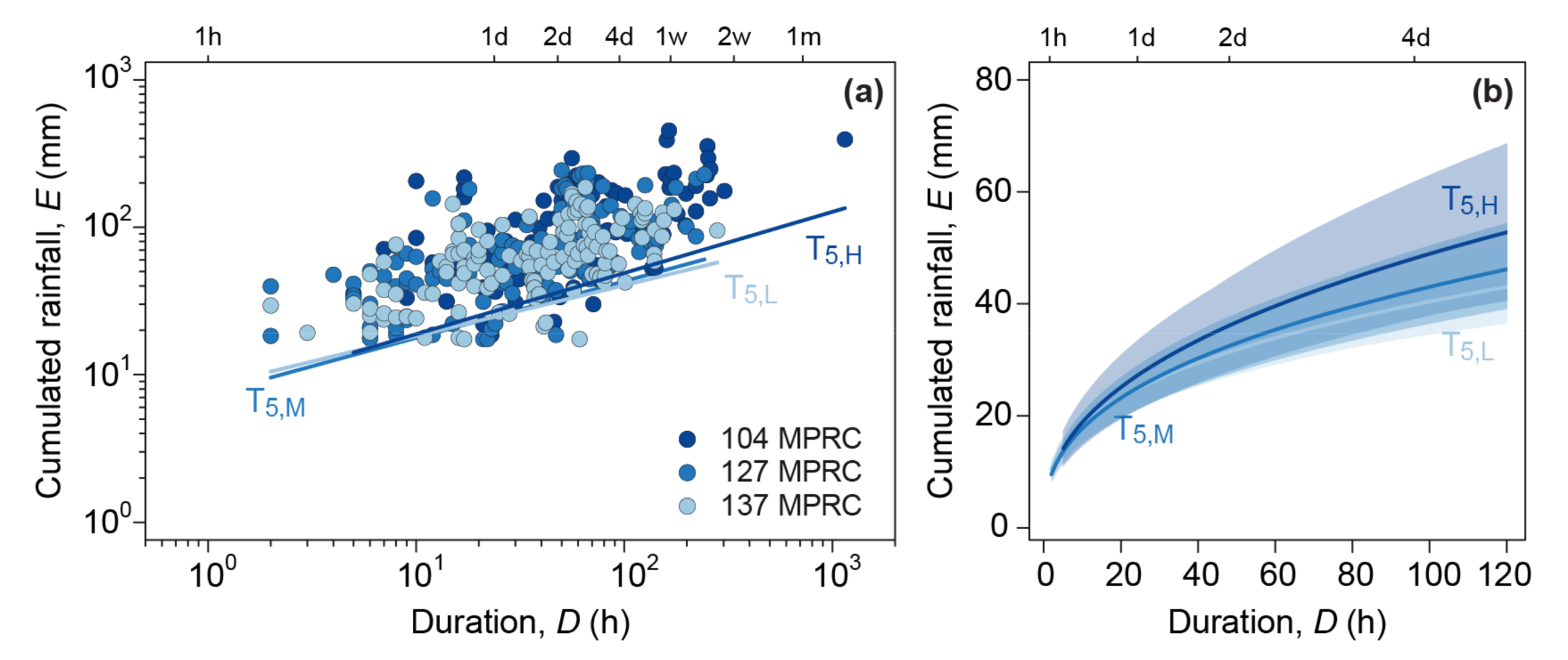
4.2.1. Thresholds for Different Mean Annual Rainfall Classes
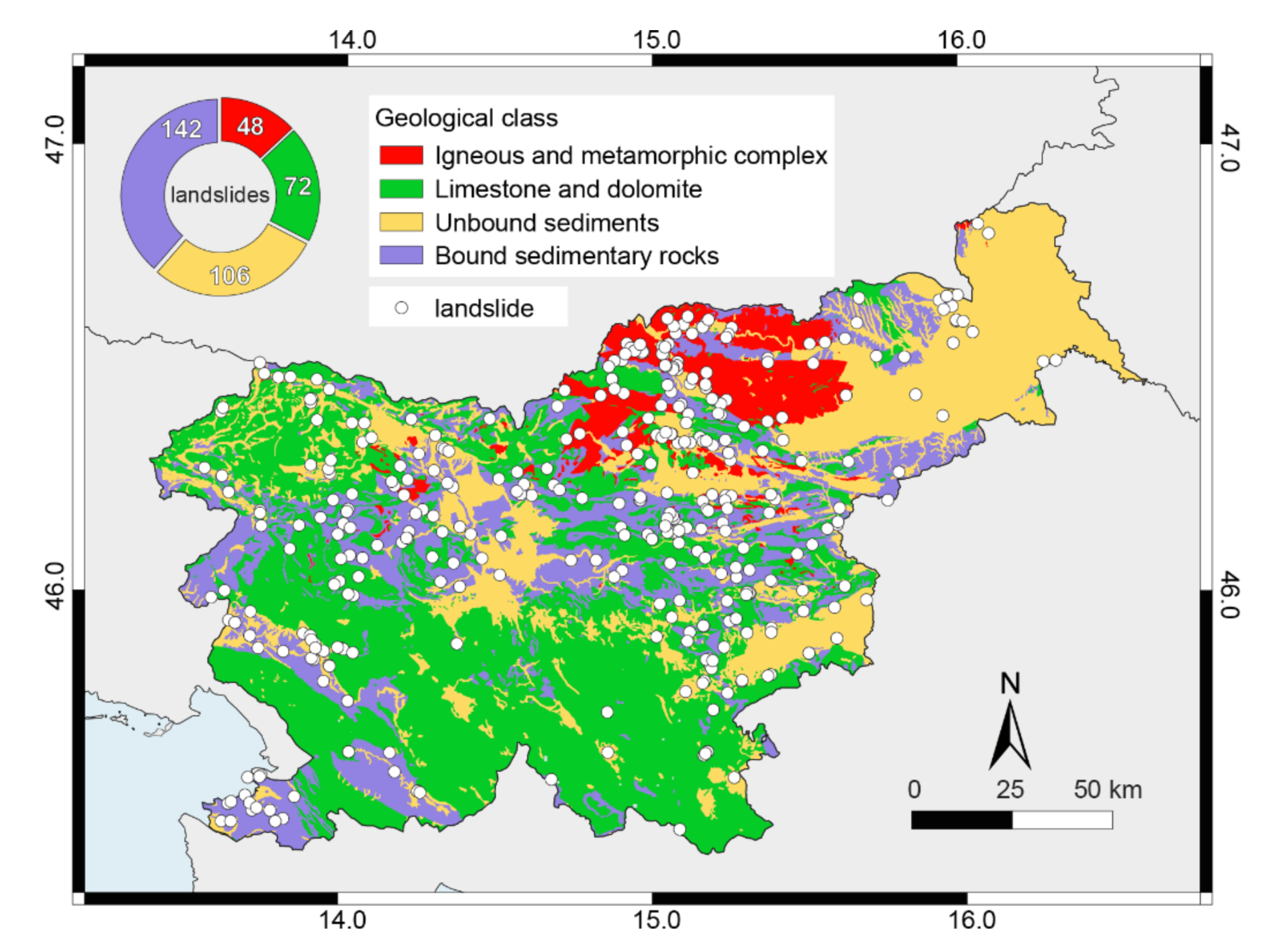
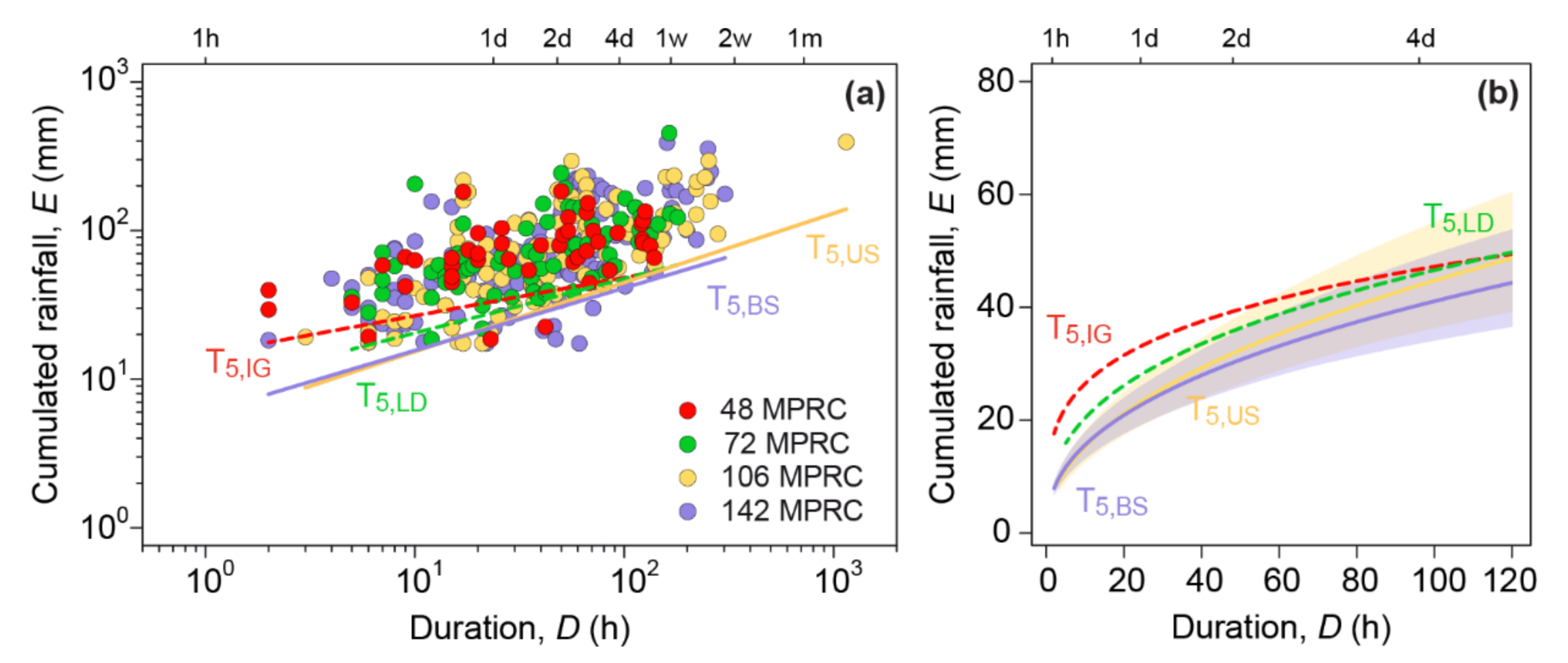
4.2.2. Thresholds for Lithological Classes
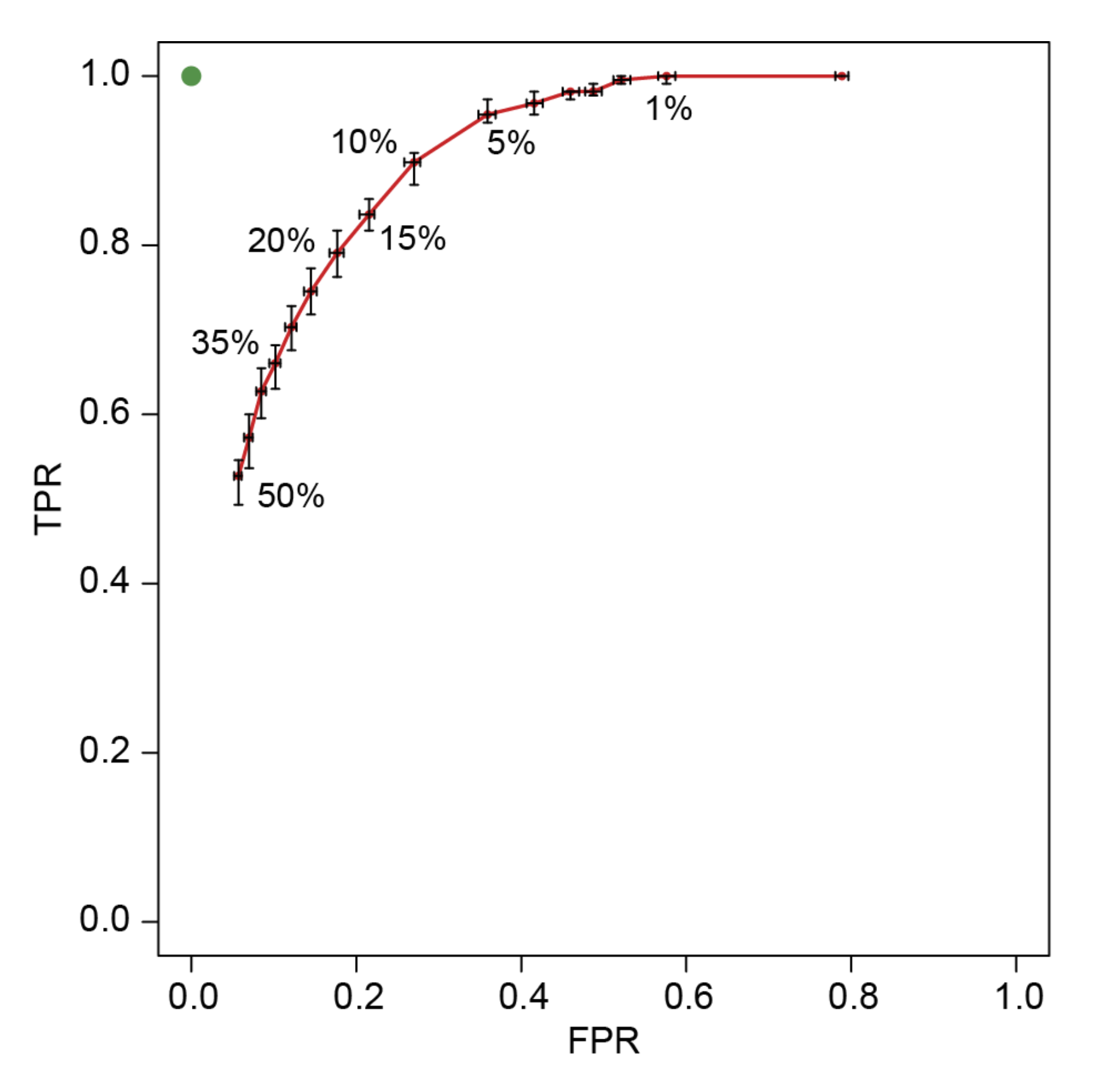
4.3. Threshold Validation
4.4. Comparison with Other Thresholds
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Komac, M. Intenzivne padavine kot sprožilni dejavnik pri pojavljanju plazov v Sloveniji=Rainstorms as a landslide-triggering factor in Slovenia. Geologija 2005, 48, 263–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gariano, S.L.; Guzzetti, F. Landslides in a changing climate. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2016, 162, 227–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Campbell, R.H. Soil Slips, Debris Flows, and Rainstorms in the Santa Monica Mountains and Vicinity, Southern California; US Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1975; Volume 851, p. 51. [Google Scholar]
- Nilsen, T.H.; Turner, B.L. Influence of Rainfall and Ancient Landslide Deposits on Recent Landslides (1950-71) in Urban Areas of Contra Costa County, California; Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1975; Volume 1388, p. 18. [Google Scholar]
- Caine, N. The rainfall intensity: Duration control of shallow landslides and debris flows. Geogr. Ann. 1980, 62, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzzetti, F.; Peruccacci, S.; Rossi, M.; Stark, C.P. Rainfall thresholds for the initiation of landslides in central and southern Europe. Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 2007, 98, 239–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzzetti, F.; Peruccacci, S.; Rossi, M.; Stark, C.P. The rainfall intensity-duration control of shallow landslides and debris flows: An update. Landslides 2008, 5, 3–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segoni, S.; Piciullo, L.; Gariano, S.L. A review of the recent literature on rainfall thresholds for landslide occurrence. Landslides 2018, 15, 1483–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piciullo, L.; Calvello, M.; Cepeda, J.M. Territorial early warning systems for rainfall-induced landslides. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2018, 179, 228–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzzetti, F.; Gariano, S.L.; Peruccacci, S.; Brunetti, M.T.; Marchesini, I.; Rossi, M.; Melillo, M. Geographical landslide early warning systems. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2020, 200, 102973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannon, S.H.; Ellen, S.D. Rainfall conditions for abundant debris avalanches, San Francisco Bay region, California. Calif. Geol. Surv. 1985, 38, 267–272. [Google Scholar]
- Wieczorek, G.F. Effect if rainfall intensity and duration on debris flows in central Santa Cruz Mountains. In Debris Flow/Avalanches: Process, Recognition, and Mitigation; Costa, J.E., Wieczorek, G.F., Eds.; Geological Society of America: Reviews in Engineering Geology: Boulder, CO, USA, 1987; Volume 7, pp. 93–104. [Google Scholar]
- Ortigao, B.; Justi, M.G. Rio-watch: The Rio de Janeiro Landslide Alarm System. Geotech. News 2004, 22, 28–31. [Google Scholar]
- Calvello, M.; d’Orsi, R.N.; Piciullo, L.; Paes, N.; Magalhaes, M.; Lacerda, W.A. The Rio de Janeiro early warning system for rainfall-induced landslides: Analysis of performance for the years 2010–2013. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2015, 12, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakob, M.; Weatherly, H. A hydroclimatic threshold for landslide initiation on the North Shore Mountains of Vancouver, British Columbia. Geomorphology 2003, 54, 137–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.-W.; Huang, C.-M.; Chen, H.; Lee, C.-T.; Chi, C.-C.; Chiu, C.-L. Adopting the I3-R24 rainfall index and landslide susceptibility for the establishment of an early warning model for rainfall-induced shallow landslides. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. 2018, 18, 1717–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rossi, M.; Marchesini, I.; Tonelli, G.; Peruccacci, S.; Brunetti, M.T.; Luciani, S.; Ardizzone, F.; Balducci, V.; Bianchi, C.; Cardinali, M.; et al. TXT-tool 2.039-1.1 Italian national early warning system. In Landslide Dynamics: ISDR-ICL Landslide Interactive Teaching Tools; Sassa, K., Guzzetti, F., Yamagishi, H., Arbanas, Ž., Casagli, N., McSaveney, M., Dang, K., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segoni, S.; Rosi, A.; Fanti, R.; Gallucci, A.; Monni, A.; Casagli, N. A Regional-Scale Landslide Warning System Based on 20 Years of Operational Experience. Water 2018, 10, 1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aleotti, P. A warning system for rainfall-induced shallow failures. Eng. Geol. 2004, 73, 247–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosi, A.; Segoni, S.; Catani, F.; Casagli, N. Statistical and environmental analyses for the definition of a regional rainfall threshold system for landslide triggering in Tuscany (Italy). J. Geogr. Sci. 2012, 22, 617–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segoni, S.; Rosi, A.; Rossi, G.; Catani, F.; Casagli, N. Analysing the relationship between rainfalls and landslides to define a mosaic of triggering thresholds for regional scale warning systems. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. 2014, 14, 2637–2648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rosi, A.; Lagomarsino, D.; Rossi, G.; Segoni, S.; Battistini, A.; Casagli, N. Updating EWS rainfall thresholds for the triggering of landslides. Nat. Hazards 2015, 78, 297–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brigandì, G.; Aronica, G.T.; Bonaccorso, B.; Gueli, R.; Basile, G. Flood and landslide warning based on rainfall thresholds and soil moisture indexes: The HEWS (Hydrohazards EarlyWarning System) for Sicily. ADGEO 2017, 44, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jemec Auflič, M.; Komac, M. Rainfall patterns for shallow landsliding in perialpine Slovenia. Nat. Hazards 2011, 67, 1011–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosi, A.; Peternel, T.; Jemec Auflič, M.; Komac, M.; Casagli, N. Rainfall thresholds for rainfall-induced landslides in Slovenia. Landslides 2016, 13, 1571–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segoni, S.; Rossi, G.; Rosi, A.; Catani, F. Landslides triggered by rainfall: A semi-automated procedure to define consistent intensity-duration thresholds. Comput. Geosci. 2014, 63, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezak, N.; Šraj, M.; Mikoš, M. Copula-based IDF curves and empirical rainfall thresholds for flash floods and rainfall-induced landslides. J. Hydrol. 2016, 541, 272–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezak, N.; Jemec Auflič, M.; Mikoš, M. Application of hydrological modelling for temporal prediction of rainfall-induced shallow landslides. Landslides 2019, 16, 1273–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jordanova, G.; Verbovšek, T.; Jemec Auflič, M. Validation and proposal of new rainfall thresholds for shallow landslide prediction in Posavsko hills, Eastern Slovenia. In Proceedings of the 4th Regional Symposium on Landslides in the Adriatic-Balkan Region, Sarajevo, Bosnia and Herzegovina, 23–25 October 2019; Uljarević, M., Zekan, S., Salković, S., Ibrahimović, D., Eds.; Geotechnical Society of Bosnia and Herzegovina: Sarajevo, Bosnia and Herzegovina, 2019; pp. 37–42. [Google Scholar]
- Jemec Auflič, M.; Šinigoj, J.; Krivic, M.; Podboj, M.; Peternel, T.; Komac, M. Landslide prediction system for rainfall induced landslides in Slovenia (Masprem). Geologija 2016, 59, 259–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jemec Auflič, M.; Šinigoj, J. Validation of the Slovenian national landslide forecast system using contingency matrices. Geophys. Res. Abstr. 2019, 21, 1. Available online: https://meetingorganizer.copernicus.org/EGU2019/EGU2019-13338.pdf (accessed on 30 April 2020).
- Melillo, M.; Brunetti, M.T.; Peruccacci, S.; Gariano, S.L.; Roccati, A.; Guzzetti, F. A tool for the automatic calculation of rainfall thresholds for landslide occurrence. Environ. Model. Softw. 2018, 105, 230–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gariano, S.L.; Melillo, M.; Peruccacci, S.; Brunetti, M.T. How much does the rainfall temporal resolution affect rainfall thresholds for landslide triggering? Nat. Hazards 2020, 100, 655–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Melillo, M.; Brunetti, M.T.; Peruccacci, S.; Gariano, S.L.; Guzzetti, F. An algorithm for the objective reconstruction of rainfall events responsible for landslides. Landslides 2015, 12, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melillo, M.; Brunetti, M.T.; Peruccacci, S.; Gariano, S.L.; Guzzetti, F. Rainfall thresholds for the possible landslide occurrence in Sicily (Southern Italy) based on the automatic reconstruction of rainfall events. Landslides 2016, 13, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordoni, M.; Corradini, B.; Lucchelli, L.; Valentino, R.; Bittelli, M.; Vivaldi, V.; Meisina, C. Empirical and Physically Based Thresholds for the Occurrence of Shallow Landslides in a Prone Area of Northern Italian Apennines. Water 2019, 11, 2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Teja, T.S.; Dikshit, A.; Satyam, N. Determination of Rainfall Thresholds for Landslide Prediction Using an Algorithm-Based Approach: Case Study in the Darjeeling Himalayas, India. Geosciences 2019, 9, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gariano, S.L.; Sarkar, R.; Dikshit, A.; Dorji, K.; Brunetti, M.T.; Peruccacci, S.; Melillo, M. Automatic calculation of rainfall thresholds for landslide occurrence in Chukha Dzongkhag, Bhutan. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2019, 78, 4325–4332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peruccacci, S.; Brunetti, M.T.; Gariano, S.L.; Melillo, M.; Rossi, M.; Guzzetti, F. Rainfall thresholds for possible landslide occurrence in Italy. Geomorphology 2017, 290, 39–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palladino, M.R.; Viero, A.; Turconi, L.; Brunetti, M.T.; Peruccacci, S.; Melillo, M.; Deganutti, A.M.; Guzzetti, F. Rainfall thresholds for the activation of shallow landslides in the Italian Alps: The role of environmental conditioning factors. Geomorphology 2018, 303, 53–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komac, M.; Ribičič, M. Landslide susceptibility map of Slovenia at scale 1:250,000. Geologija 2006, 49, 295–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ARSO. Mean Annual Measured Precipitation between 1981 and 2010. Ministry for Environment and Spatial Planning. Environmental Agency of the Republic of Slovenia. 2016. Available online: http://www.meteo.si/uploads/probase/www/climate/image/sl/by_variable/precipitation/mean-annual-measured-precipitation_81-10.png (accessed on 18 December 2019).
- Thornthwaite, C.W. An approach toward a rational classification of climate. Geogr. Rev. 1948, 38, 55–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thornthwaite, C.W.; Mather, J.R. Instructions and tables for computing potential evapotranspiration and the water balance. Publ. Climatol. Lab. Climatol. Drexel Inst. Technol. 1957, 10, 185–311. [Google Scholar]
- Dragoni, W.; Cambi, C.; Di Matteo, L.; Giontella, C.; Melillo, M.; Valigi, D. Possible response of two water systems in central Italy to climatic changes. In Advances in Watershed Hydrology; Moramarco, T., Barbetta, S., Brocca, L., Eds.; Water Resources Publications, LLC: Denver, CO, USA, 2015; pp. 397–424. ISBN 13 978-1-887-20185-8. [Google Scholar]
- Brunetti, M.T.; Peruccacci, S.; Rossi, M.; Luciani, S.; Valigi, D.; Guzzetti, F. Rainfall thresholds for the possible occurrence of landslides in Italy. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. 2010, 10, 447–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peruccacci, S.; Brunetti, M.T.; Luciani, S.; Vennari, C.; Guzzetti, F. Lithological and seasonal control of rainfall thresholds for the possible initiation of landslides in central Italy. Geomorphology 2012, 139, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peres, D.J.; Cancelliere, A.; Greco, R.; Bogaard, T.A. Influence of uncertain identification of triggering rainfall on the assessment of landslide early warning thresholds. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. 2018, 18, 633–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ribičič, M.; Komac, M.; Kumelj, Š.; Novak, M. Splošna Inženirsko-Geološka Karta Slovenije (General Engineering Geology Map of Slovenia). Geološki Zavod Slovenije—Geological Survey of Slovenia, 2008. Scale 1:1.000.000. Available online: http://www.egeologija.si/geonetwork/srv/eng/catalog.search#/metadata/d179cbc6-75fa-4a07-9096-814b07ff95a3 (accessed on 30 April 2020).
- Vennari, C.; Gariano, S.L.; Antronico, L.; Brunetti, M.T.; Iovine, G.; Peruccacci, S.; Terranova, O.; Guzzetti, F. Rainfall thresholds for shallow landslide occurrence in Calabria, southern Italy. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. 2014, 14, 317–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gariano, S.L.; Brunetti, M.T.; Iovine, G.; Melillo, M.; Peruccacci, S.; Terranova, O.; Vennari, C.; Guzzetti, F. Calibration and validation of rainfall thresholds for shallow landslide forecasting in Sicily, southern Italy. Geomorphology 2015, 228, 653–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Name | Region | Area (km2) | Number of MPRC* | Threshold Equation | Duration Range (h) | Δα/α (%) | Δγ/γ (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T5,SVN | Slovenia | 20,273 | 368 | E = (6.8 ± 0.7)∙D(0.40 ± 0.02) | 2–1149 | 10.3 | 5.0 |
| T1,SVN | Slovenia | 20,273 | 368 | E = (4.7 ± 0.5)∙D(0.40 ± 0.02) | 2–1149 | 10.6 | 5.0 |
| T10,SVN | Slovenia | 20,273 | 368 | E = (8.2 ± 0.8)∙D(0.40 ± 0.02) | 2–1149 | 9.8 | 5.0 |
| T15,SVN | Slovenia | 20,273 | 368 | E = (8.9 ± 0.9)∙D(0.40 ± 0.02) | 2–1149 | 10.1 | 5.0 |
| T20,SVN | Slovenia | 20,273 | 368 | E = (10.5 ± 1.0)∙D(0.40 ± 0.02) | 2–1149 | 9.5 | 5.0 |
| T50,SVN | Slovenia | 20,273 | 368 | E = (16.5 ± 1.6)∙D(0.40 ± 0.02) | 2–1149 | 9.7 | 5.0 |
| T5,L | 800 ≤ MAR ≤ 1300 mm | 6538 | 137 | E = (8.3 ± 1.1)∙D(0.34 ± 0.04) | 2–280 | 13.2 | 11.8 |
| T5,M | 1300 ≤ MAR ≤ 1600 mm | 6018 | 127 | E = (7.3 ± 1.1)∙D(0.38 ± 0.04) | 2–243 | 15.0 | 10.5 |
| T5,H | 1600 ≤ MAR ≤ 4000 mm | 7717 | 104 | E = (7.2 ± 1.6)∙D(0.41 ± 0.05) | 5–1149 | 22.2 | 11.9 |
| T5,IG | Igneous-metamorphic complex | 1444 | 48 | E = (14.8 ± 3.3)∙D(0.25 ± 0.05) | 2–139 | 22.3 | 20.0 |
| T5,LD | Limestone and dolomite | 8803 | 72 | E = (8.9 ± 2.2)∙D(0.36 ± 0.06) | 5–180 | 24.7 | 16.7 |
| T5,US | Unbound sediments | 5601 | 106 | E = (5.3 ± 0.9)∙D(0.47 ± 0.04) | 3–1149 | 17.0 | 8.5 |
| T5,BS | Bound sedimentary rocks | 4425 | 142 | E = (5.9 ± 0.9)∙D(0.42 ± 0.04) | 2–303 | 15.2 | 9.5 |
| NEP | TP | FN | FP | TN | TPR | FPR | TSS | δ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 109 | 1 | 5475 | 5009 | 0.99 | 0.52 | 0.47 | 0.52 |
| 5 | 105 | 5 | 3761 | 6723 | 0.96 | 0.36 | 0.60 | 0.36 |
| 10 | 98 | 12 | 2815 | 7669 | 0.89 | 0.27 | 0.63 | 0.29 |
| 15 | 92 | 18 | 2235 | 8249 | 0.84 | 0.21 | 0.63 | 0.27 |
| 20 | 86 | 23 | 1842 | 8642 | 0.79 | 0.18 | 0.61 | 0.28 |
| 35 | 72 | 37 | 1062 | 9423 | 0.66 | 0.10 | 0.94 | 0.36 |
| 50 | 57 | 52 | 590 | 9894 | 0.52 | 0.06 | 0.46 | 0.48 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jordanova, G.; Gariano, S.L.; Melillo, M.; Peruccacci, S.; Brunetti, M.T.; Jemec Auflič, M. Determination of Empirical Rainfall Thresholds for Shallow Landslides in Slovenia Using an Automatic Tool. Water 2020, 12, 1449. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12051449
Jordanova G, Gariano SL, Melillo M, Peruccacci S, Brunetti MT, Jemec Auflič M. Determination of Empirical Rainfall Thresholds for Shallow Landslides in Slovenia Using an Automatic Tool. Water. 2020; 12(5):1449. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12051449
Chicago/Turabian StyleJordanova, Galena, Stefano Luigi Gariano, Massimo Melillo, Silvia Peruccacci, Maria Teresa Brunetti, and Mateja Jemec Auflič. 2020. "Determination of Empirical Rainfall Thresholds for Shallow Landslides in Slovenia Using an Automatic Tool" Water 12, no. 5: 1449. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12051449






