Calibration Procedure for Water Distribution Systems: Comparison among Hydraulic Models
Abstract
:1. Introduction
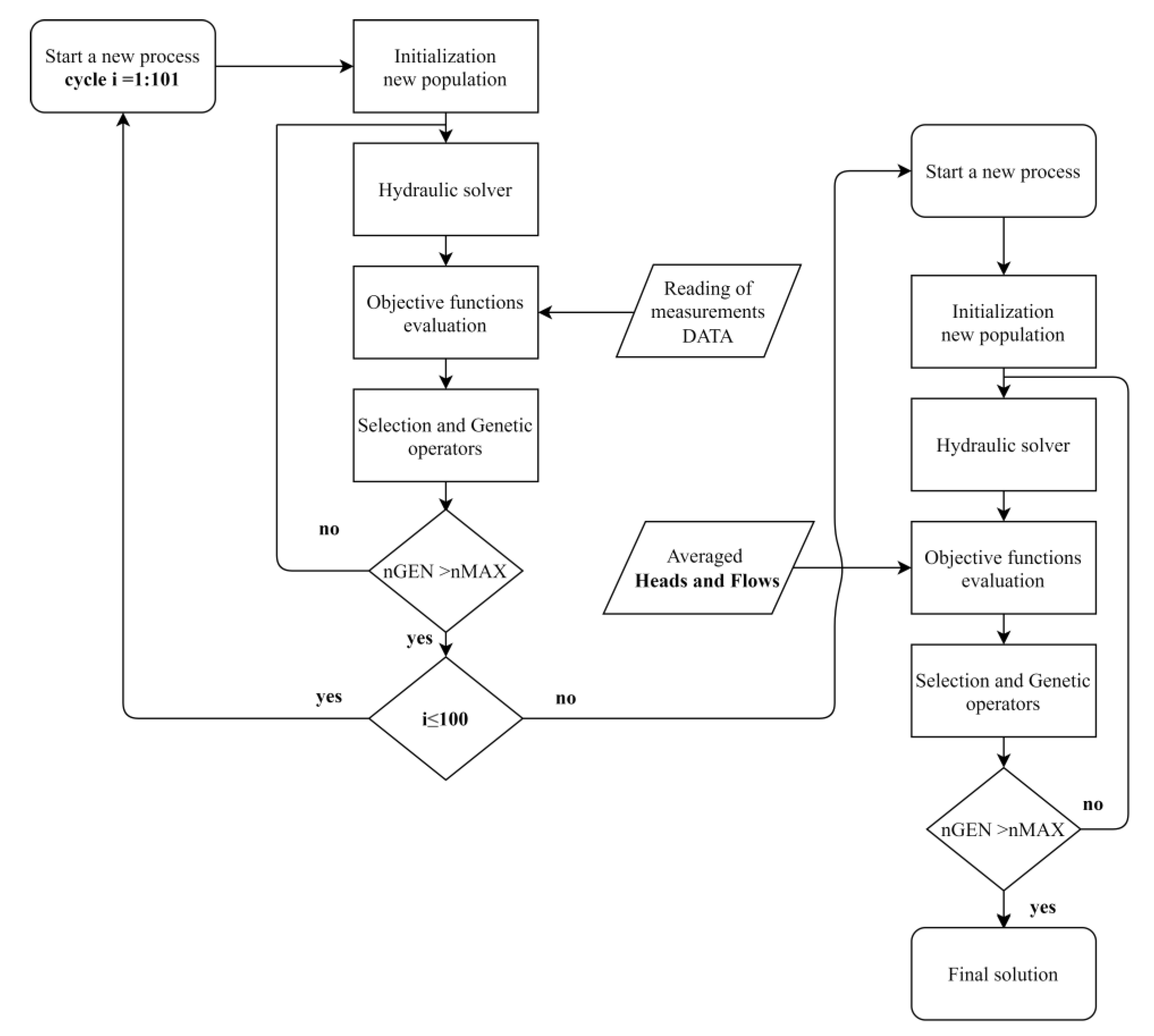
2. Methodology
2.1. Non-Uniqueness of the Solutions
2.2. Hydraulic Models
2.3. Decision Variables
2.4. Objective Functions
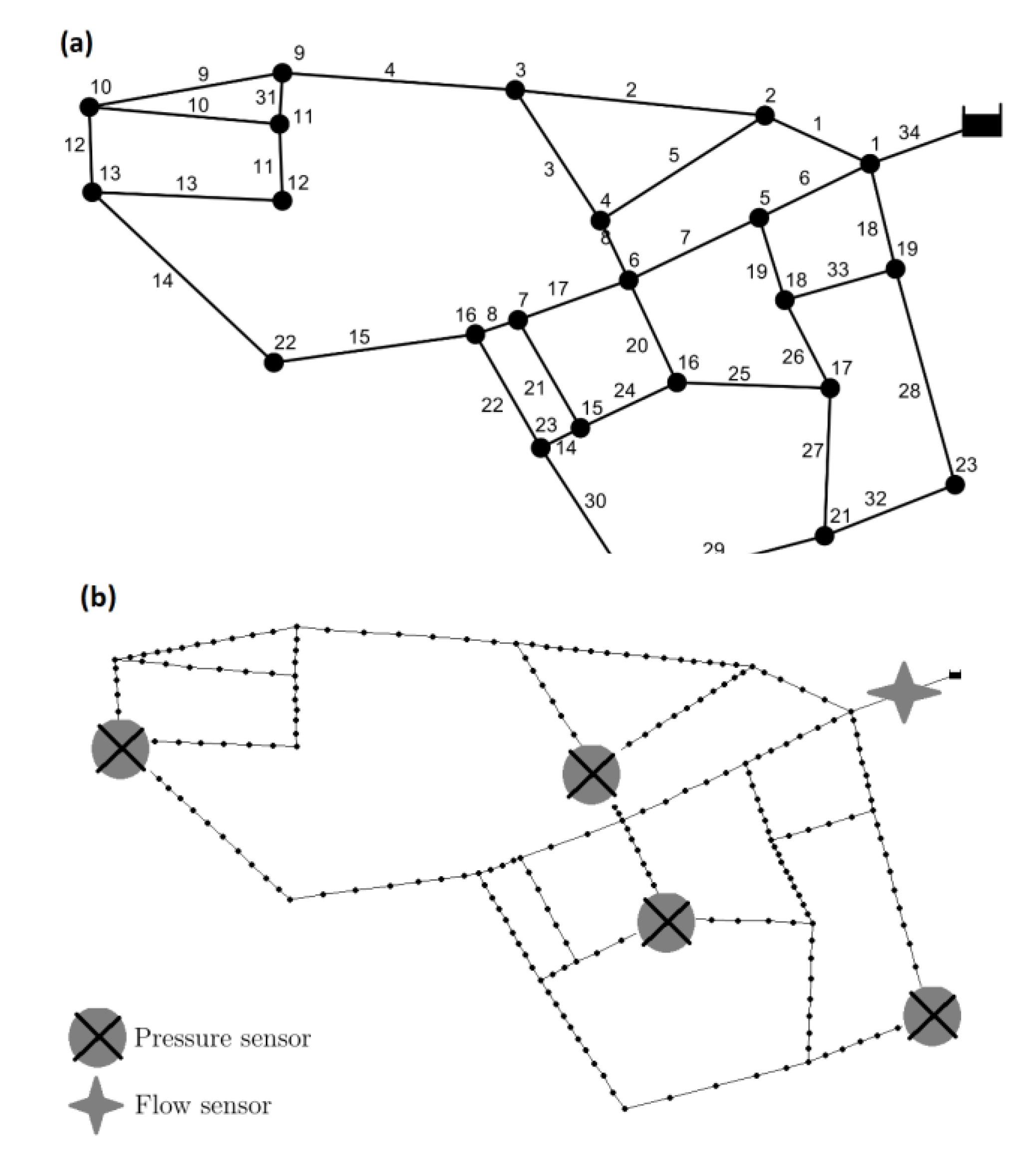
3. Test Case
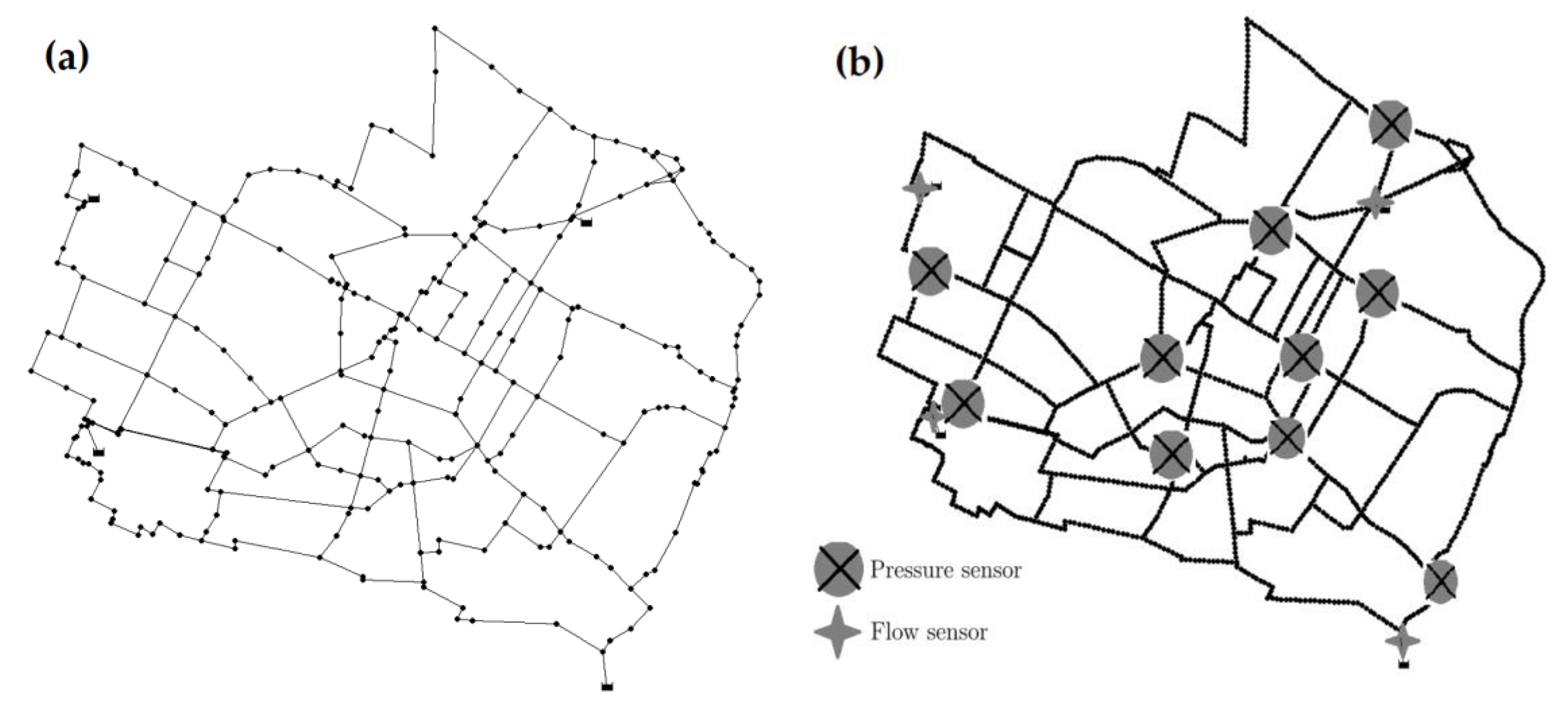
3.1. Data Generation and Sensor Placement
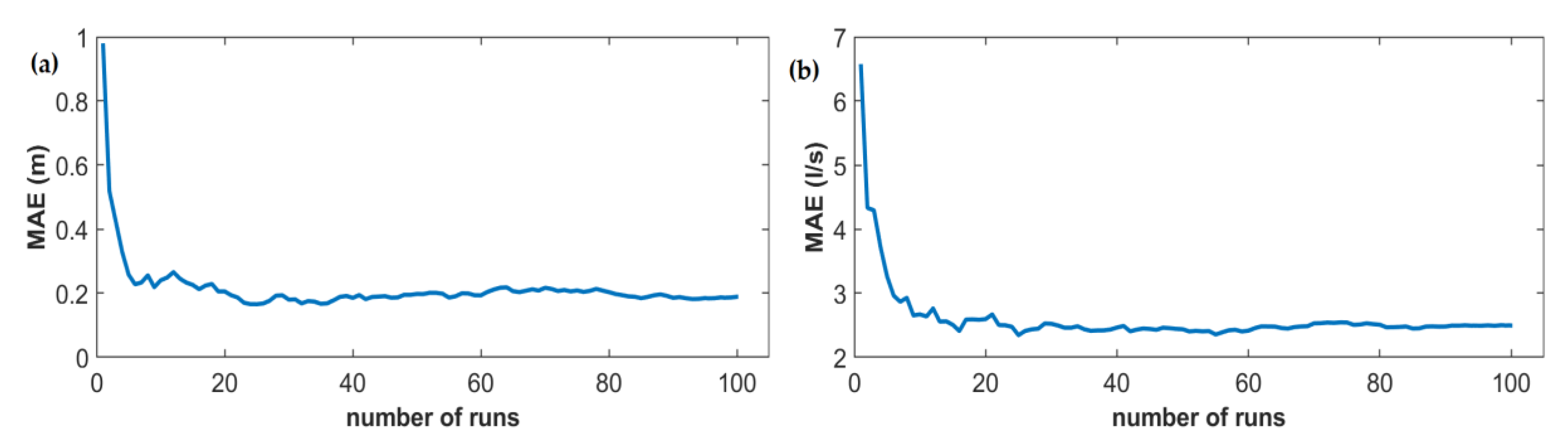
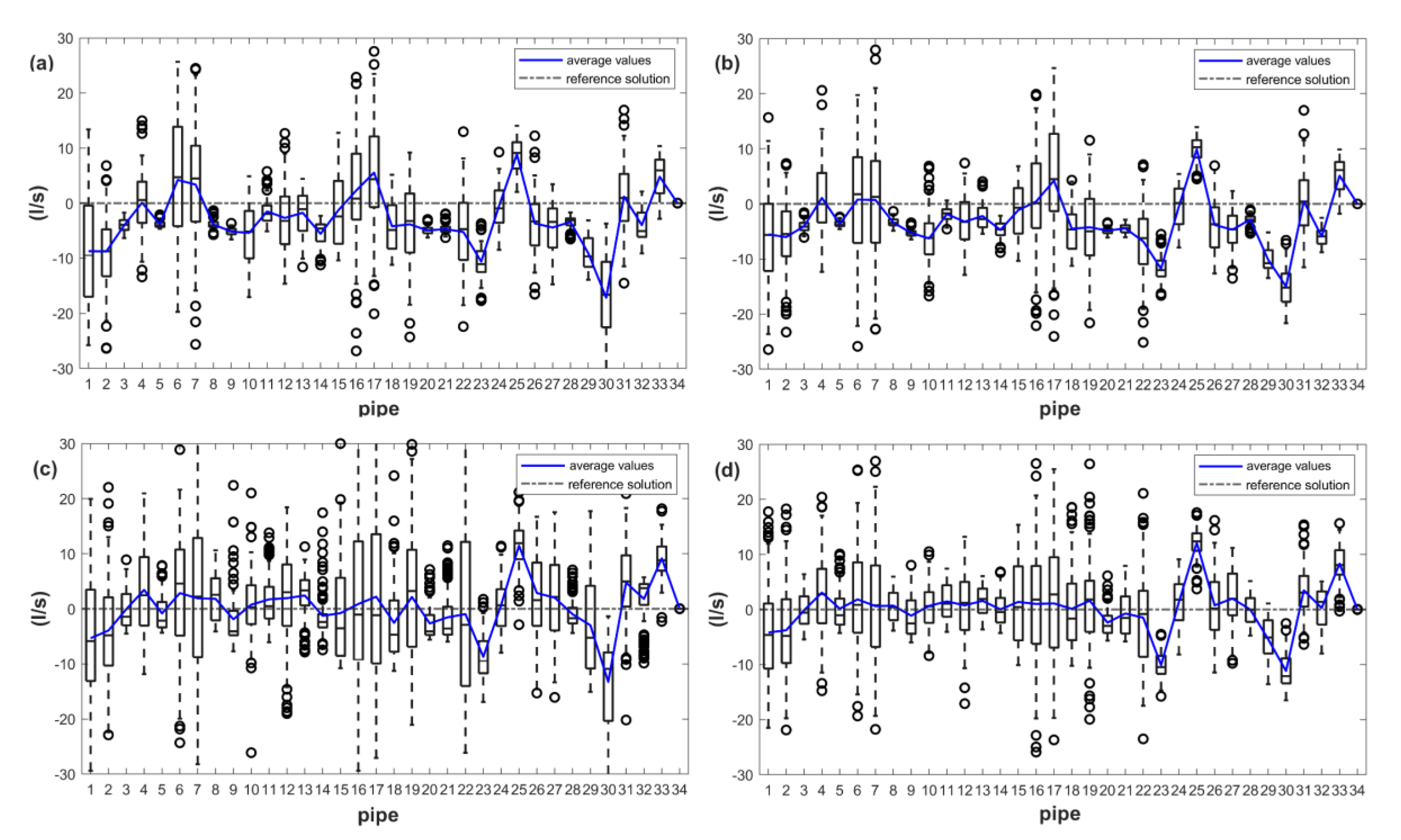
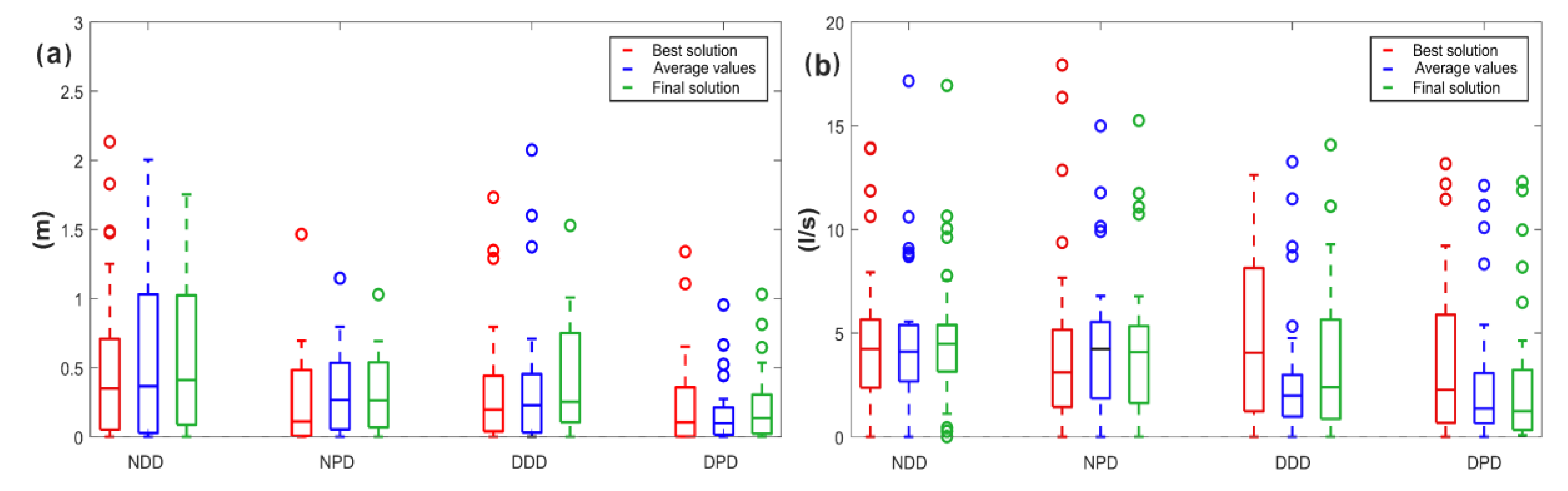
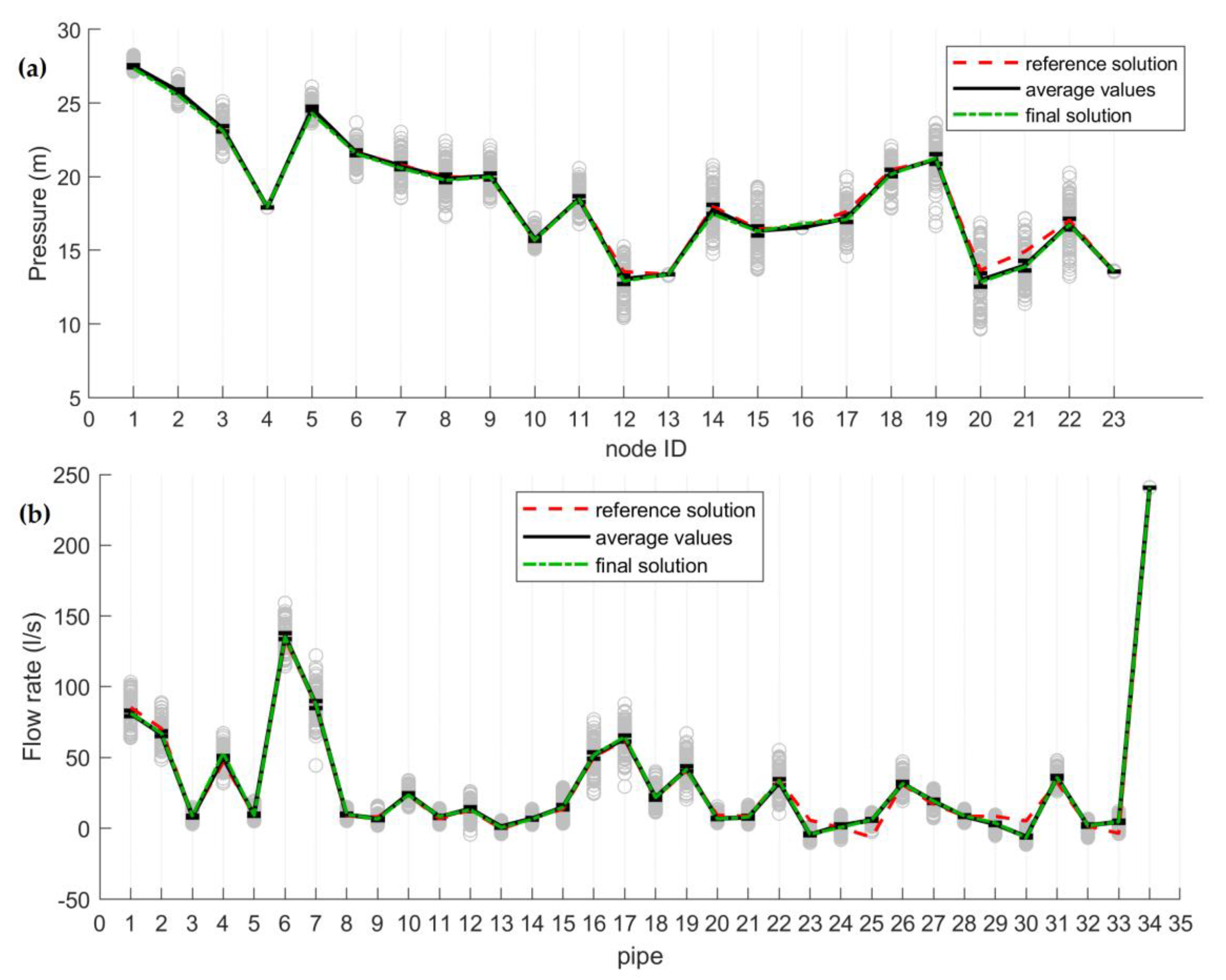
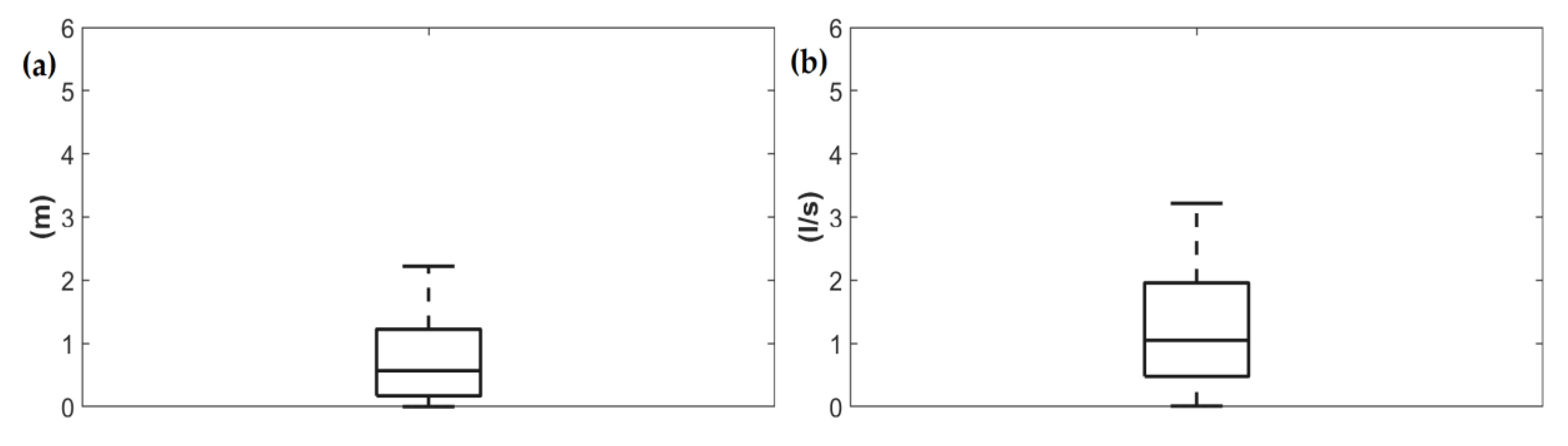
3.2. Results and Discussion
4. Test Case 2
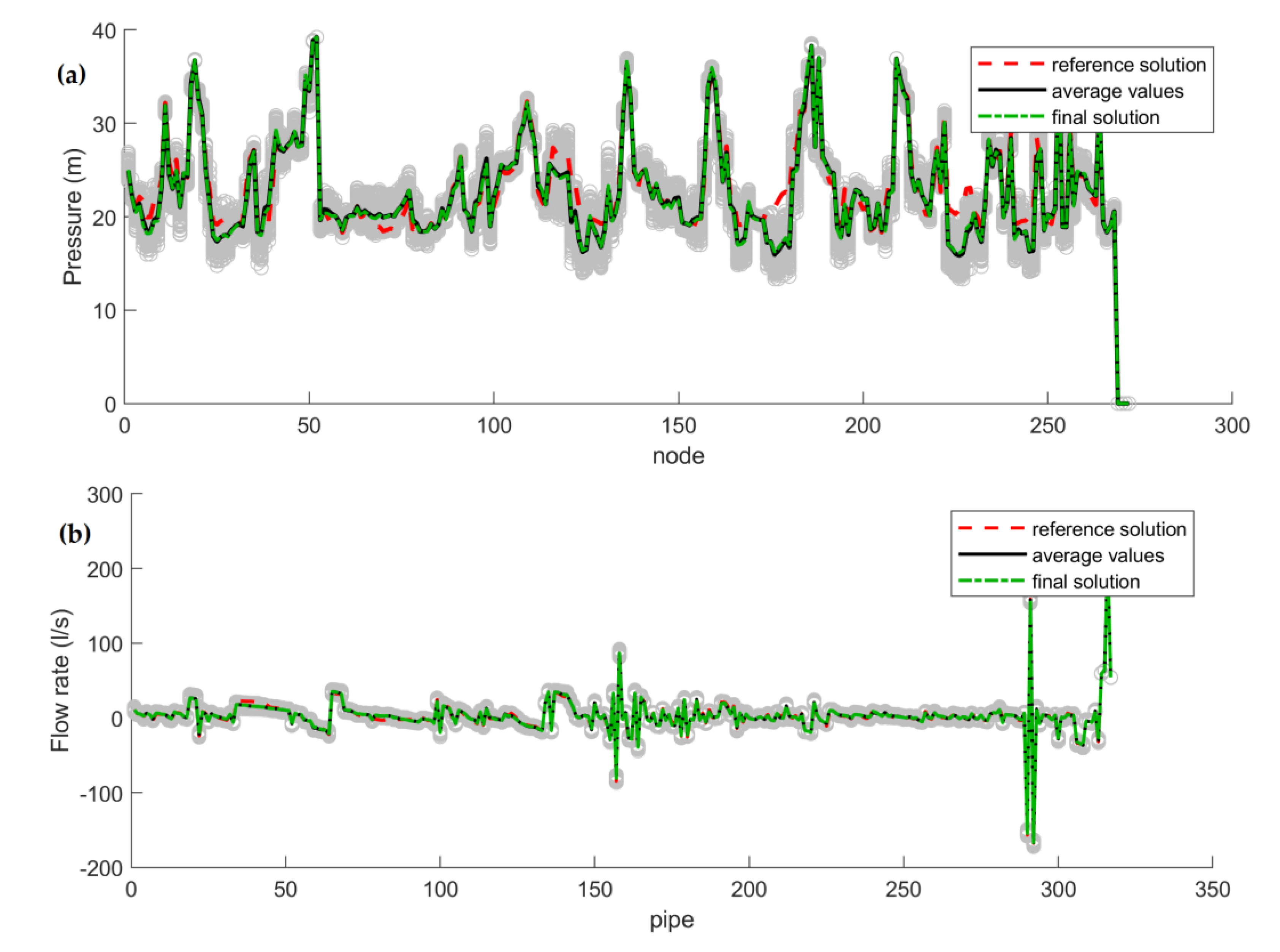
Results and Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Savic, D.; Kapelan, Z.S.; Jonkergouw, P.M. Quo vadis water distribution model calibration? Urban Water J. 2009, 6, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walski, T.M. Technique for Calibrating Network Models. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 1983, 109, 360–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhave, P.R. Calibrating Water Distribution Network Models. J. Environ. Eng. 1988, 114, 120–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ormsbee, L.E.; Wood, D.J. Explicit Pipe Network Calibration. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 1986, 112, 166–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Nardo, A.; Di Natale, M.; Gisonni, C.; Iervolino, M. A genetic algorithm for demand pattern and leakage estimation in a water distribution network. J. Water Supply Res. Technol. 2014, 64, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, N.C.; Simpson, A.R.; Deuerlein, J.W.; Piller, O. Calibration of Water Demand Multipliers in Water Distribution Systems Using Genetic Algorithms. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2016, 142, 04016044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabesh, M.; Jamasb, M.; Moeini, R. Calibration of water distribution hydraulic models: A comparison between pressure dependent and demand driven analyses. Urban Water J. 2011, 8, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.Y.; Walski, T.; Mankowski, R.; Herrin, G.; Gurrieri, R.; Tryby, M. Calibrating water distribution model via genetic algorithms. In Proceedings of the 2002 AWWA IMTech Conference, Kansas City, MO, USA, 14–17 April 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Laucelli, D.; Berardi, L.; Giustolisi, O.; Vamvakeridou-Lyroudia, L.S.; Kapelan, Z.; Savic, D.; Barbaroand, G. Calibration of Water Distribution System Using Topological Analysis. In Water Distribution Systems Analysis; American Society of Civil Engineers: Tucson, AZ, USA, 2011; pp. 1664–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadzadeh, M.; Tolson, B.A.; McKillop, R. A Two Stage Optimization Approach for Calibrating Water Distribution Systems. In Water Distribution Systems Analysis; American Society of Civil Engineers: Tucson, AZ, USA, 2011; pp. 1682–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meirelles, G.; Manzi, D.; Brentan, B.M.; Goulart, T.; Junior, E.L. Calibration Model for Water Distribution Network Using Pressures Estimated by Artificial Neural Networks. Water Resour. Manag. 2017, 31, 4339–4351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, N.C.; Simpson, A.R.; Deuerlein, J.; Piller, O. Particle Filter–Based Model for Online Estimation of Demand Multipliers in Water Distribution Systems under Uncertainty. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2017, 143, 04017065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, X.; Xu, W.; Xin, K.; Yan, H.; Tao, T. Self-Adaptive Calibration of Real-Time Demand and Roughness of Water Distribution Systems. Water Resour. Res. 2018, 54, 5536–5550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutton, C.J.; Kapelan, Z.; Vamvakeridou-Lyroudia, L.; Savic, D. Dealing with Uncertainty in Water Distribution System Models: A Framework for Real-Time Modeling and Data Assimilation. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2014, 140, 169–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puust, R.; Kapelan, Z.; Savic, D.; Koppel, T. A review of methods for leakage management in pipe networks. Urban Water J. 2010, 7, 25–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Covelli, C.; Cozzolino, L.; Cimorelli, L.; Della Morte, R.; Pianese, D. A model to simulate leakage through joints in water distribution systems. Water Supply 2015, 15, 852–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Covelli, C.; Cimorelli, L.; Cozzolino, L.; Della Morte, R.; Pianese, D. Reduction in water losses in water distribution systems using pressure reduction valves. Water Supply 2016, 16, 1033–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kang, D.; Lansey, K. Demand and Roughness Estimation in Water Distribution Systems. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2011, 137, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letting, L.; Hamam, Y.; Abu-Mahfouz, A.M. Estimation of Water Demand in Water Distribution Systems Using Particle Swarm Optimization. Water 2017, 9, 593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rossman, L.A. EPANET 2: Users Manual. 2000. Available online: https://epanet.es/wp-content/uploads/2012/10/EPANET_User_Guide.pdf (accessed on 15 January 2020).
- Sophocleous, S.; Savic, D.; Kapelan, Z.; Giustolisi, O. A Two-stage Calibration for Detection of Leakage Hotspots in a Real Water Distribution Network. Procedia Eng. 2017, 186, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todini, E.; Pilati, S. A gradient algorithm for the analysis of pipe networks. In Computer Applications in Water Supply: Vol. 1—Systems Analysis and Simulation; Research Studies Press Ltd.: Baldock, UK, 1988; pp. 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Collins, M.; Cooper, L.; Helgason, R.; Kennington, J.; Leblanc, L. Solving the Pipe Network Analysis Problem Using Optimization Techniques. Manag. Sci. 1978, 24, 747–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giustolisi, O.; Savic, D.; Kapelan, Z. Pressure-Driven Demand and Leakage Simulation for Water Distribution Networks. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2008, 134, 626–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Siew, C.; Tanyimboh, T.T. Pressure-Dependent EPANET Extension. Water Resour. Manag. 2012, 26, 1477–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Berardi, L.; Giustolisi, O.; Todini, E. Accounting for uniformly distributed pipe demand in WDN analysis: Enhanced GGA. Urban Water J. 2010, 7, 243–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menapace, A.; Avesani, D.; Righetti, M.; Bellin, A.; Pisaturo, G.R. Uniformly Distributed Demand EPANET Extension. Water Resour. Manag. 2018, 32, 2165–2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menapace, A.; Avesani, D. Global Gradient Algorithm Extension to Distributed Pressure Driven Pipe Demand Model. Water Resour. Manag. 2019, 33, 1717–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Todini, E. Extending the global gradient algorithm to unsteady flow extended period simulations of water distribution systems. J. Hydroinform. 2010, 13, 167–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Avesani, D.; Righetti, M.; Righetti, D.; Bertola, P. The extension of EPANET source code to simulate unsteady flow in water distribution networks with variable head tanks. J. Hydroinform. 2012, 14, 960–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deb, K.; Agrawal, S.; Pratap, A.; Meyarivan, T. A fast elitist non-dominated sorting genetic algorithm for multi-objective optimization: NSGA-II. In International Conference on Parallel Problem Solving from Nature; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2000; pp. 849–858. [Google Scholar]
- Germanopoulos, G. A technical note on the inclusion of pressure dependent demand and leakage terms in water supply network models. Civ. Eng. Syst. 1985, 2, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.; Bhave, P.R. Comparison of Methods for Predicting Deficient-Network Performance. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 1996, 122, 214–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanyimboh, T.T.; Templeman, A.B. Seamless pressure-deficient water distribution system model. Proc. Inst. Civ. Eng.-Water Manag. 2010, 163, 389–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, Z.Y.; Clark, C. Evolving Effective Hydraulic Model for Municipal Water Systems. Water Resour. Manag. 2008, 23, 117–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siew, C.; Tanyimboh, T.T. Augmented Gradient Method for Head Dependent Modelling of Water Distribution Networks. In World Environmental and Water Resources Congress 2009: Great Rivers; American Society of Civil Engineers: Kansas City, MO, USA, 2009; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giustolisi, O.; Kapelan, Z.; Savic, D. Extended Period Simulation Analysis Considering Valve Shutdowns. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2008, 134, 527–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giustolisi, O.; Todini, E. On the approximation of distributed demands as nodal demands in WDN analysis. In Proceedings of the XXXI National Hydraulics and Hydraulic Construction Conference, Perugia, Italy, 9–12 September 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Giustolisi, O.; Todini, E. Pipe hydraulic resistance correction in WDN analysis. Urban Water J. 2009, 6, 39–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menapace, A.; Righetti, M.; Avesani, D. Application of Distributed Pressure Driven Modelling in Water Supply System. In Proceedings of the WDSA/CCWI Joint Conference Proceedings, Kingston, ON, Canada, 23–25 July 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Sharp, W.W.; Walski, T.M. Predicting Internal Roughness in Water Mains. J. Am. Water Work. Assoc. 1988, 80, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Righetti, M.; Bort, C.M.G.; Bottazzi, M.; Menapace, A.; Zanfei, A. Optimal Selection and Monitoring of Nodes Aimed at Supporting Leakages Identification in WDS. Water 2019, 11, 629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bragalli, C.; D’Ambrosio, C.; Lee, J.; Lodi, A.; Toth, P. Water Network Design by MINLP; Rep No RC24495; IBM Res.: Yorktown Heights, NY, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]

| Node (ID) | Pressure (m) |
|---|---|
| 4 | 17.92 |
| 13 | 13.37 |
| 16 | 16.55 |
| 23 | 13.57 |
| Pipe ID | Flow Rate (L/s) |
| 34 | 240.82 |
| Solution | Best Solution | Average Values | Final Solution | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Approach | (m) | (m) | (m) | |
| NDD | 0.57 | 0.60 | 0.62 | |
| NPD | 0.28 | 0.34 | 0.34 | |
| DDD | 0.52 | 0.41 | 0.46 | |
| DPD | 0.28 | 0.19 | 0.24 | |
| Solution | Best Solution | Average Values | Final Solution | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Approach | (L/s) | (L/s) | (L/s) | |
| NDD | 4.60 | 4.66 | 4.76 | |
| NPD | 4.29 | 4.33 | 4.34 | |
| DDD | 4.95 | 2.98 | 3.63 | |
| DPD | 3.57 | 2.49 | 2.55 | |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zanfei, A.; Menapace, A.; Santopietro, S.; Righetti, M. Calibration Procedure for Water Distribution Systems: Comparison among Hydraulic Models. Water 2020, 12, 1421. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12051421
Zanfei A, Menapace A, Santopietro S, Righetti M. Calibration Procedure for Water Distribution Systems: Comparison among Hydraulic Models. Water. 2020; 12(5):1421. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12051421
Chicago/Turabian StyleZanfei, Ariele, Andrea Menapace, Simone Santopietro, and Maurizio Righetti. 2020. "Calibration Procedure for Water Distribution Systems: Comparison among Hydraulic Models" Water 12, no. 5: 1421. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12051421
APA StyleZanfei, A., Menapace, A., Santopietro, S., & Righetti, M. (2020). Calibration Procedure for Water Distribution Systems: Comparison among Hydraulic Models. Water, 12(5), 1421. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12051421







