Anthropogenic Impact on Tropical Perennial River in South India: Snapshot of Carbon Dynamics and Bacterial Community Composition
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling and Field Analyses
2.2. Analysis of Pharmaceutical Compounds
2.3. Analysis of Bacterial Community Structure
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
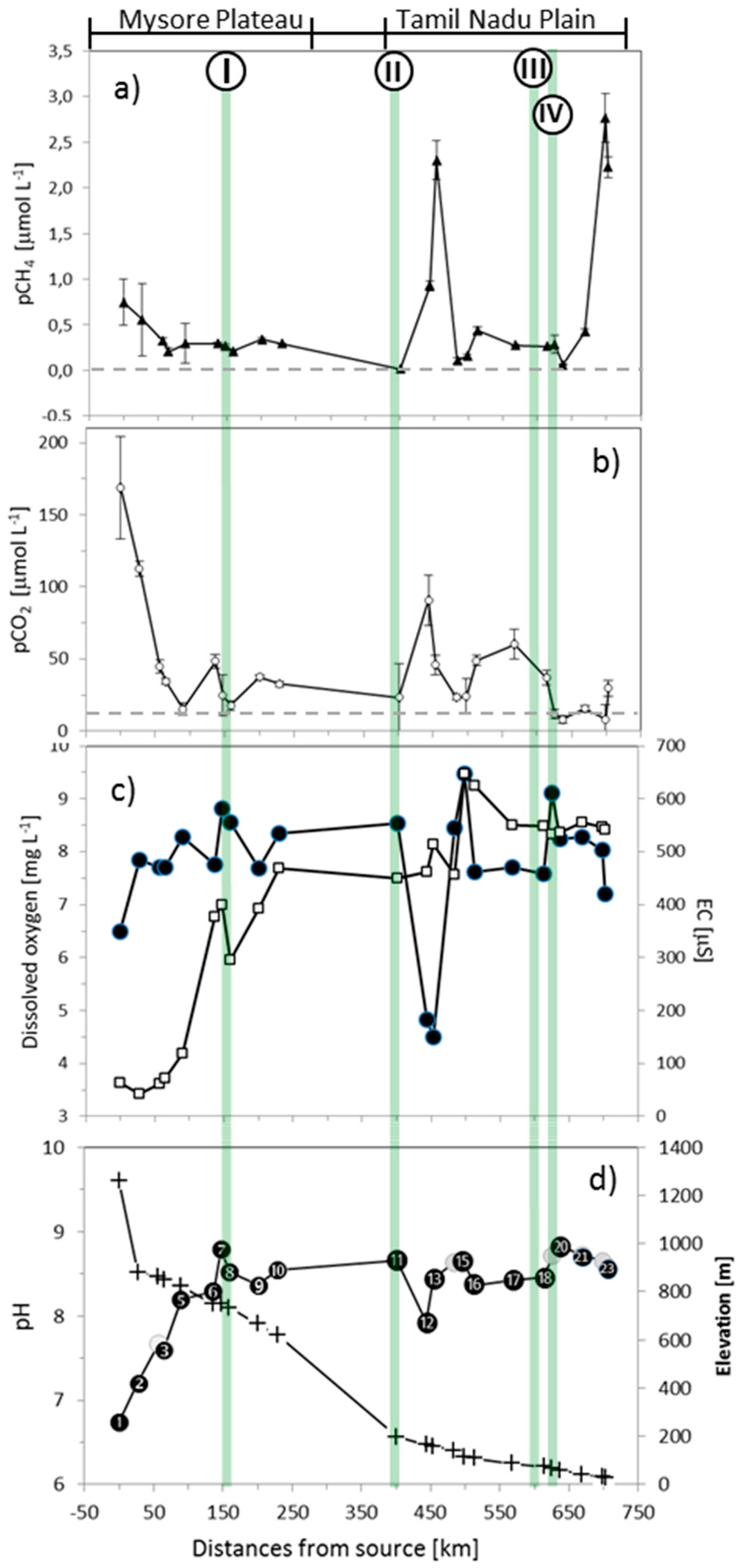
3.1. General Characteristics and Spatial Variations of Water Chemistry
3.2. Spatial Pattern of pCO2 and pCH4 Concentrations Along the Gradient
3.3. Pharmaceuticals
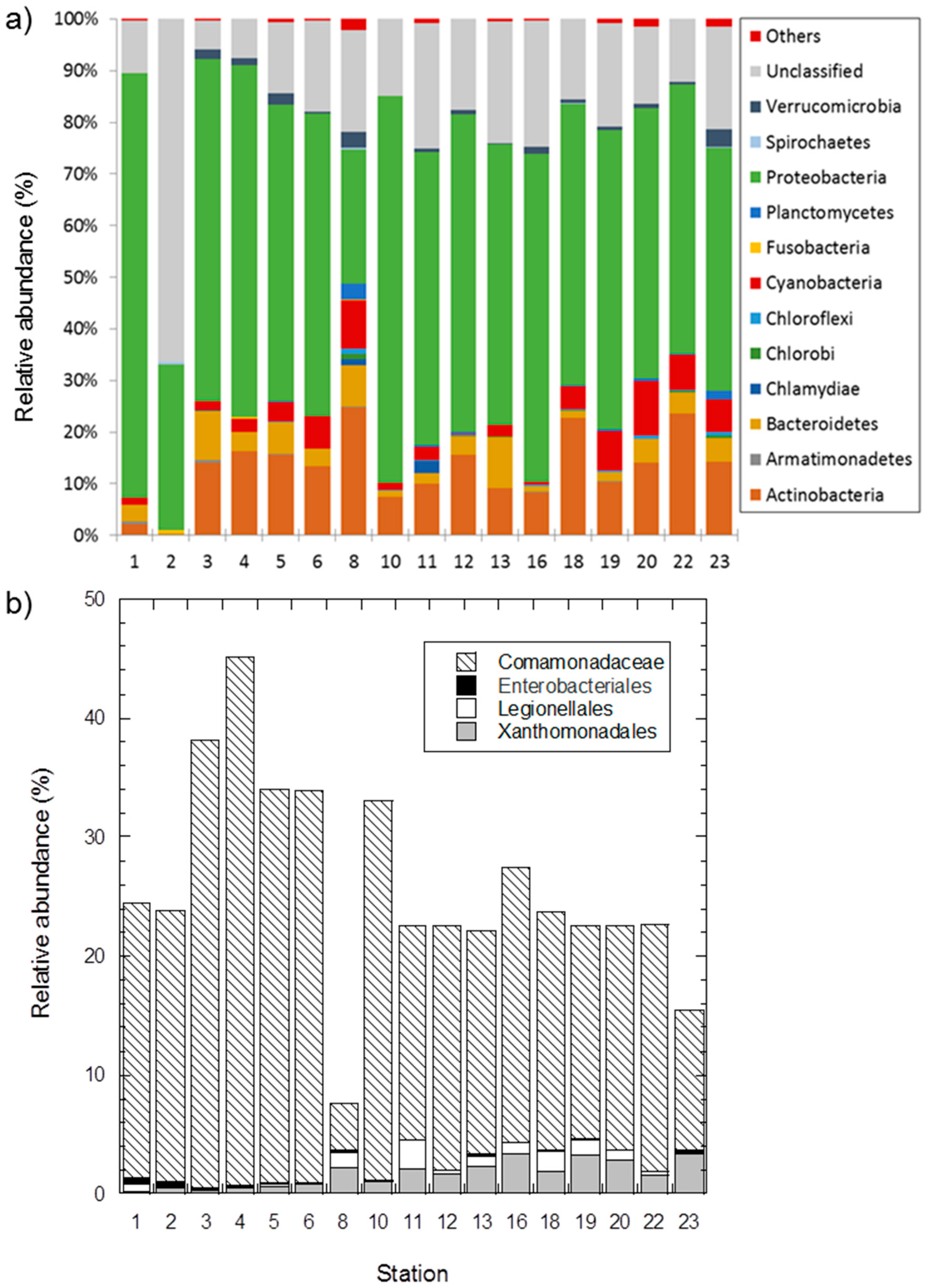
3.4. Changes in Bacterial Community
4. Discussion
4.1. Links between Greenhouse Gases and Water Quality, and their Connection to Urbanization
4.2. Pharmaceuticals in the Cauvery River Compared to Global Rivers
4.3. Possible Reasons for Bacterial Community Changes
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ramakrishnaiah, C.R.; Sadashivaiah, C.; Ranganna, G. Assessment of Water Quality Index for the Groundwater in Tumkur Taluk, Karnataka State, India. J. Chem. 2009, 6, 523–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridoutt, B.G.; Pfister, S. A revised approach to water footprinting to make transparent the impacts of consumption and production on global freshwater scarcity. Glob. Environ. Chang. Hum. Policy Dimens. 2010, 20, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gheewala, S.H.; Silalertruksa, T.; Nilsalab, P.; Mungkung, R.; Perret, S.R.; Chaiyawannakarn, N. Implications of the biofuels policy mandate in Thailand on water: The case of bioethanol. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 150, 457–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Downing, J.A.; Prairie, Y.T.; Cole, J.J.; Duarte, C.M.; Tranvik, L.J.; Striegl, R.G.; McDowell, W.H.; Kortelainen, P.; Caraco, N.F.; Melack, J.M.; et al. The global abundance and size distribution of lakes, ponds, and impoundments. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2006, 51, 2388–2397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Yadava, M.G.; Ahmad, M.Z.; Mohapatra, P.P.; Laskar, A.H.; Doradla, S.; Saravanavel, J.; Kumanan, C.J. Fertile farmlands in Cauvery delta: Evolution through LGM. Curr. Sci. 2015, 108, 218–225. [Google Scholar]
- Balakrishna, K.; Rath, A.; Praveenkumarreddy, Y.; Guruge, K.S.; Subedi, B. A review of the occurrence of pharmaceuticals and personal cue products in Indian water bodies. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 137, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, J.J.; Prairie, Y.T.; Caraco, N.F.; McDowell, W.H.; Tranvik, L.J.; Striegl, R.G.; Duarte, C.M.; Kortelainen, P.; Downing, J.A.; Middelburg, J.J.; et al. Plumbing the global carbon cycle: Integrating inland waters into the terrestrial carbon budget. Ecosystems 2007, 10, 171–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battin, T.J.; Luyssaert, S.; Kaplan, L.A.; Aufdenkampe, A.K.; Richter, A.; Tranvik, L.J. The boundless carbon cycle. Nat. Geosci. 2009, 2, 598–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tranvik, L.J.; Downing, J.A.; Cotner, J.B.; Loiselle, S.A.; Striegl, R.G.; Ballatore, T.J.; Dillon, P.; Finlay, K.; Fortino, K.; Knoll, L.B.; et al. Lakes and reservoirs as regulators of carbon cycling and climate. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2009, 54, 2298–2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raymond, P.A.; Hartmann, J.; Lauerwald, R.; Sobek, S.; McDonald, C.; Hoover, M.; Butman, D.; Striegl, R.; Mayorga, E.; Humborg, C.; et al. Global carbon dioxide emissions from inland waters. Nature 2013, 503, 355–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.R.; Schoups, G.; van de Giesen, N. Organic pollution of rivers: Combined threats of urbanization, livestock farming and global climate change. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodmer, P.; Heinz, M.; Pusch, M.T.; Singer, G.; Premke, K. Carbon dynamics and their link to DOM quality across contrasting stream ecosystems. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 553, 574–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attermeyer, K.; Flury, S.; Jayakumar, R.; Fiener, P.; Steger, K.; Arya, V.; Wilken, F.; van Geldern, R.; Premke, K. Invasive floating macrophytes reduce greenhouse gas emissions from a small tropical lake. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gudasz, C.; Bastviken, D.; Steger, K.; Premke, K.; Sobek, S.; Tranvik, L.J. Temperature-controlled organic carbon mineralization in lake sediments. Nature 2010, 466, 478–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobek, S.; Durisch-Kaiser, E.; Zurbruegg, R.; Wongfun, N.; Wessels, M.; Pasche, N.; Wehrli, B. Organic carbon burial efficiency in lake sediments controlled by oxygen exposure time and sediment source. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2009, 54, 2243–2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regnier, P.; Friedlingstein, P.; Ciais, P.; Mackenzie, F.T.; Gruber, N.; Janssens, I.A.; Laruelle, G.G.; Lauerwald, R.; Luyssaert, S.; Andersson, A.J.; et al. Anthropogenic perturbation of the carbon fluxes from land to ocean. Nat. Geosci. 2013, 6, 597–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvam, B.P.; Natchimuthu, S.; Arunachalam, L.; Bastviken, D. Methane and carbon dioxide emissions from inland waters in India—Implications for large scale greenhouse gas balances. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2014, 20, 3397–3407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommer, U.; Gliwicz, Z.M.; Lampert, W.; Duncan, A. The Peg-model of Seasonal Succession of Planktonic Events in Fresh Waters. Archiv. Fur. Hydrobiol. 1986, 106, 433–471. [Google Scholar]
- Crump, B.C.; Kling, G.W.; Bahr, M.; Hobbie, J.E. Bacterioplankton community shifts in an arctic lake correlate with seasonal changes in organic matter source. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 2253–2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibekwe, A.M.; Leddy, M.B.; Bold, R.M.; Graves, A.K. Bacterial community composition in low-flowing river water with different sources of pollutants. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2012, 79, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Nie, S.; Liang, J.; Zeng, G.M.; Wu, H.P.; Hua, S.S.; Liu, J.Y.; Yuan, Y.J.; Xiao, H.B.; Deng, L.J.; et al. Effects of heavy metals and soil physicochemical properties on wetland soil microbial biomass and bacterial community structure. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 557, 785–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sirota, J.; Baiser, B.; Gotelli, N.J.; Ellison, A.M. Organic-matter loading determines regime shifts and alternative states in an aquatic ecosystem. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 7742–7747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baquero, F.; Martinez, J.L.; Canton, R. Antibiotics and antibiotic resistance in water environments. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2008, 19, 260–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skariyachan, S.; Mahajanakatti, A.B.; Grandhi, N.J.; Prasanna, A.; Sen, B.; Sharma, N.; Vasist, K.S.; Narayanappa, R. Environmental monitoring of bacterial contamination and antibiotic resistance patterns of the fecal coliforms isolated from Cauvery River, a major drinking water source in Karnataka, India. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnaswamy, J.; Baruah, A.; Wickramasinghe, N.; Srinivas, V. Beyond the Tsunami: Trends and Patterns in Hydrology and Water Quality in Coastal Ecosystems and Upstream Catchments in Tamil Nadu, India; UNDP/UNTRS, Chennai and ATREE: Bangalore, India, 2008; p. 74. [Google Scholar]
- Drozd, J.; Novak, J. Headspace gas-analysis by gas-chromatography. J. Chromatogr. 1979, 165, 141–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klindworth, A.; Pruesse, E.; Schweer, T.; Peplles, J.; Quast, C. Evaluation of general 16S ribosomal RNA gene PCR primers for classical and next-generation sequencing-based diversity studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Primerlink. Available online: https://support.illumina.com/documents/documentation/chemistry_documentation/16s/16s-metagenomic-library-prep-guide-15044223-b.pdf (accessed on 18 March 2016).
- Verma, D.; Srivastava, S.P.; Bhanumati, P.; Kumar Maurya, S.R.; Jain, K.; Kumar, S.; Panwar, S.R.; Sokhi, K.; Ravi Kumar, S.R. Selected Socio-Economic Statistics, India; Social Statistics Division, Central Statistics Office, Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation: New Delhi, India, 2017; p. 15.
- Li, S.Y.; Bush, R.T. Revision of methane and carbon dioxide emissions from inland waters in India. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2015, 21, 6–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halbedel, S.; Koschorreck, M. Regulation of CO2 emissions from temperate streams and reservoirs. Biogeosciences 2013, 10, 7539–7551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rantakari, M.; Kortelainen, P. Interannual variation and climatic regulation of the CO2 emission from large boreal lakes. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2005, 11, 1368–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roehm, C.L.; Prairie, Y.T.; del Giorgio, P.A. The pCO (2) dynamics in lakes in the boreal region of northern Quebec, Canada. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2009, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasera, M.; Krusche, A.V.; Richey, J.E.; Ballester, M.V.R.; Victoria, R.L. Spatial and temporal variability of pCO (2) and CO2 efflux in seven Amazonian Rivers. Biogeochemistry 2013, 116, 241–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, W.D.; Dai, M.H.; Cai, W.J.; Wang, Y.C.; Wang, Z.H. High partial pressure of CO2 and its maintaining mechanism in a subtropical estuary: The Pearl River estuary, China. Mar. Chem. 2005, 93, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weyhenmeyer, G.A.; Kosten, S.; Wallin, M.B.; Tranvik, L.J.; Jeppesen, E.; Roland, F. Significant fraction of CO2 emissions from boreal lakes derived from hydrologic inorganic carbon inputs. Nat. Geosci. 2015, 8, 933–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotchkiss, E.R.; Hall, R.O.; Sponseller, R.A.; Butman, D.; Klaminder, J.; Laudon, H.; Rosvall, M.; Karlsson, J. Sources of and processes controlling CO2 emissions change with the size of streams and rivers. Nat. Geosci. 2015, 8, 696–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marce, R.; Obrador, B.; Morgui, J.-A.; Lluis Riera, J.; Lopez, P.; Armengol, J. Carbonate weathering as a driver of CO2 supersaturation in lakes. Nat. Geosci. 2015, 8, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeburgh, W.S. Oceanic methane biogeochemistry. Chem. Rev. 2007, 107, 486–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferry, J.G. How to Make a Living by Exhaling Methane. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2010, 64, 453–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGinnis, D.F.; Bilsley, N.; Schmidt, M.; Fietzek, P.; Bodmer, P.; Premke, K.; Lorke, A.; Flury, S. Deconstructing Methane Emissions from a Small Northern European River: Hydrodynamics and Temperature as Key Drivers. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 11680–11687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richey, J.E.; Devol, A.H.; Wofsy, S.C.; Victoria, R.; Riberio, M.N.G. Biogenic gases and the oxidation and reduction of carbon in Amazon River and floodplain waters. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1988, 33, 551–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, J.B.; Mulholland, P.J. Influence of drainage basin topography and elevation on carbon dioxide and methane supersaturation of stream water. Biogeochemistry 1998, 40, 57–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matousu, A.; Rulik, M.; Tuser, M.; Bednarik, A.; Simek, K.; Bussmann, I. Methane dynamics in a large river: A case study of the Elbe River. Aquat. Sci. 2019, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pattanaik, J.K.; Balakrishnan, S.; Bhutani, R.; Singh, P. Estimation of weathering rates and CO2 drawdown based on solute load: Significance of granulites and gneisses dominated weathering in the Kaveri River basin, Southern India. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2013, 121, 611–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulandaivel, A.R.K.; Kumar, P.E.; Perumaland, V.; Magudeswaran, P.N. Water Quality Index of River Cauvery at Erode Region, Tamilnadu, India. Nat. Environ. Pollut. Technol. 2009, 8, 343–346. [Google Scholar]
- Gowda, A.; Srikantaswamy, S.; Rajasekhara Reddy, K.; Abhilash, M.R.; Shiva Kumar, D.; Jagadish, K. Impact of Anthropological Activities on the Water Quality of Cauvery River, Karnataka, India. Int. J. Res. Sci. Innov. 2016, 3, 6–15. [Google Scholar]
- Krishna, M.S.; Prasad, M.H.K.; Rao, D.B.; Viswanadham, R.; Sarma, V.; Reddy, N.P.C. Export of dissolved inorganic nutrients to the northern Indian Ocean from the Indian monsoonal rivers during discharge period. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2016, 172, 430–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beshiru, A.; Okareh, O.T.; Chigor, V.N.; Igbinosa, E.O. Assessment of water quality of rivers that serve as water sources for drinking and domestic functions in rural and pre-urban communities in Edo North, Nigeria. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2018, 190, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odey, M.O.; Ibor, O.R.; Andem, A.B.; Ettah, I.; Chukwuka, A.V. Drinking water quality and risk implications for community health: A case study of shallow water wells and boreholes in three major communities in Northern Cross-River, Southern Nigeria. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. 2018, 24, 427–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahunsi, S.O.; Owamah, H.I.; Ayandiran, T.A.; Oranusi, S.U. Drinking Water Quality and Public Health of Selected Towns in South Western Nigeria. Water Qual. Expo. Health 2014, 6, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.C. Occurrence, sources, and fate of pharmaceuticals in aquatic environment and soil. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 187, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, A.; Pradhan, S.; Mohapatra, G.; Mohapatra, J. Drug-related problems associated with self-medication and medication guided by prescription: A pharmacy-based survey. Indian J. Pharmacol. 2016, 48, 515–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, Y.; Ryu, J.; Oh, J.; Choi, B.G.; Snyder, S.A. Occurrence of endocrine disrupting compounds, pharmaceuticals, and personal care products in the Han River (Seoul, South Korea). Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 636–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Togola, A.; Budzinski, H. Analytical development for analysis of pharmaceuticals in water samples by SPE and GC-MS. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2007, 388, 627–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patrolecco, L.; Ademollo, N.; Grenni, P.; Tolomei, A.; Caracciolo, A.B.; Capri, S. Simultaneous determination of human pharmaceuticals in water samples by solid phase extraction and HPLC with UV-fluorescence detection. Microchem. J. 2013, 107, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanmugam, G.; Sampath, S.; Selvaraj, K.K.; Larsson, D.G.J.; Ramaswamy, B.R. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in Indian rivers. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 921–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.W.; Jang, H.S.; Kim, J.G.; Ishibashi, H.; Hirano, M.; Nasu, K.; Ichikawa, N.; Takao, Y.; Shinohara, R.; Arizono, K. Occurrence of Pharmaceutical and Personal Care Products (PPCPs) in Surface Water from Mankyung River, South Korea. J. Health Sci. 2009, 55, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutiyar, P.K.; Gupta, S.K.; Mittal, A.K. Fate of pharmaceutical active compounds (PhACs) from River Yamuna, India: An ecotoxicological risk assessment approach. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 150, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fram, M.S.; Belitz, K. Occurrence and concentrations of pharmaceutical compounds in groundwater used for public drinking-water supply in California. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 3409–3417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agunbiade, F.O.; Moodley, B. Pharmaceuticals as emerging organic contaminants in Umgeni River water system, KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2014, 186, 7273–7291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebele, A.J.; Abdallahab, M.A.-E.; Harrad, S. Pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs) in the freshwater aquatic environment. Emerg. Contam. 2017, 3, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.L.; Mao, G.N.; Liu, J.; Gao, G.H.; Zou, C.L.; Bartlam, M.G.; Wang, Y.Y. Spatial-Temporal Changes of Bacterioplankton Community along an Exhorheic River. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.L.; Yu, N.; Chen, L.Q.; Jiang, C.H.; Tao, Y.J.; Zhang, T.; Chen, J.; Xue, D. Structure and seasonal dynamics of bacterial communities in three urban rivers in China. Aquat. Sci. 2012, 74, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carney, R.L.; Mitrovic, S.M.; Jeffries, T.; Westhorpe, D.; Curlevski, N.; Seymour, J.R. River bacterioplankton community responses to a high inflow event. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2015, 75, 187–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glockner, F.O.; Zaichikov, E.; Belkova, N.; Denissova, L.; Pernthaler, J.; Pernthaler, A.; Amann, R. Comparative 16S rRNA analysis of lake bacterioplankton reveals globally distributed phylogenetic clusters including an abundant group of actinobacteria. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2000, 66, 5053–5065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zwart, G.; Crump, B.C.; Agterveld, M.; Hagen, F.; Han, S.K. Typical freshwater bacteria: An analysis of available 16S rRNA gene sequences from plankton of lakes and rivers. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2002, 28, 141–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwart, G.; Hiorns, W.D.; Methe, B.A.; Van Agterveld, M.P.; Huismans, R.; Nold, S.C.; Zehr, J.P.; Laanbroek, H.J. Nearly identical 16S rRNA sequences recovered from lakes in North America and Europe indicate the existence of clades of globally distributed freshwater bacteria. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 1998, 21, 546–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberto, A.A.; Van Gray, J.B.; Leff, L.G. Sediment bacteria in an urban stream: Spatiotemporal patterns in community composition. Water Res. 2018, 134, 353–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, R.P.; Vorholter, F.J.; Potnis, N.; Jones, J.B.; Van Sluys, M.A.; Bogdanove, A.J.; Dow, J.M. Pathogenomics of Xanthomonas: Understanding bacterium-plant interactions. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2011, 9, 344–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Hunag, S.; Sun, G.; Xu, Z.; Xu, M. Phytoplanktonic diversity, composition and distribution of bacterioplankton community in the Dongjiang River, China. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2012, 80, 30–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Yang, M.; Li, Z.L.; Qi, R.; He, J.Z.; Liu, H.J. Change of bacterial communities in sediments along Songhua River in Northeastern China after a nitrobenzene pollution event. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2008, 65, 494–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopes, F.A.C.; Catao, E.C.P.; Santana, R.H.; Cabral, A.D.; Paranhos, R.; Rangel, T.P.; de Rezende, C.E.; Edwards, R.A.; Thompson, C.C.; Thompson, F.L.; et al. Microbial Community Profile and Water Quality in a Protected Area of the Caatinga Biome. PLoS ONE 2016, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.; Cai, L.; Yang, Y.; Ju, F.; Li, X.D.; Yu, Y.L.; Zhang, T. Metagenomic analysis reveals potential biodegradation pathways of persistent pesticides in freshwater and marine sediments. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 470, 983–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hahn, M.W.; Lang, E.; Brandt, U.; Lunsdorf, H.; Wu, Q.L.; Stackebrandt, E. Polynucleobacter cosmopolitanus sp nov., free-living planktonic bacteria inhabiting freshwater lakes and rivers. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2010, 60, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hahn, M.W.; Lang, E.; Brandt, U.; Wu, Q.L.; Scheuerl, T. Emended description of the genus Polynucleobacter and the species Polynucleobacter necessarius and proposal of two subspecies, P. necessarius subsp. necessarius subsp nov and P. necessarius subsp asymbioticus subsp nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2009, 59, 2002–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
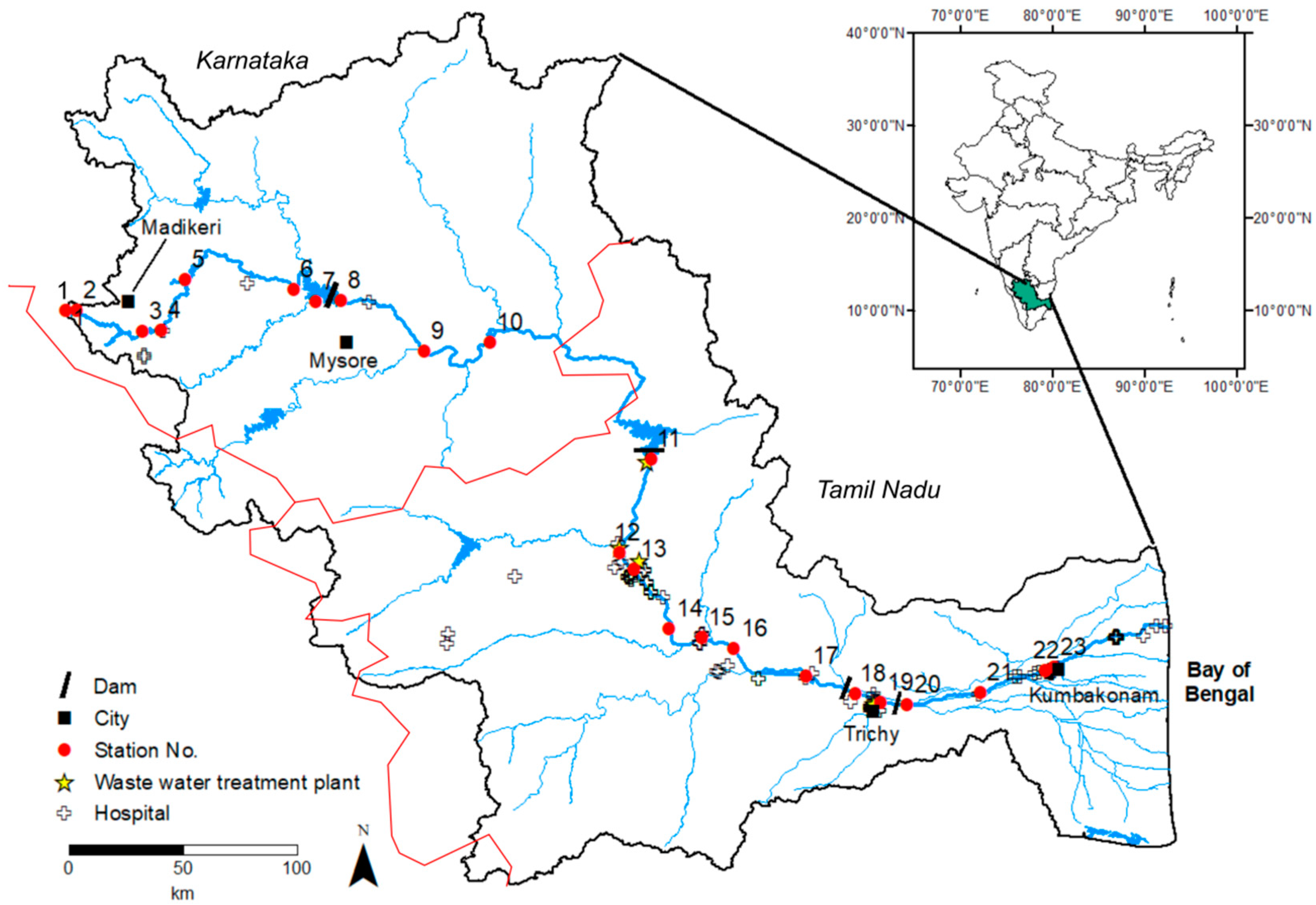


| Station No. | Station Name | State | Coordinates | DfS (km) | El (m) | Place of Importance | T (°C) | DIC (μmol L−1) | TOC (mg L−1) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Latitude | Longitude | |||||||||
| 1 | Tala Kaveri | KA | 12.429065 | 75.778851 | 0 | 1260 | Source, Pilgrimage, Touristic spot | 22.5 | 671.9 ± 184.6 | 15.7 |
| 2 | Bhagamandala | KA | 12.384406 | 75.533703 | 27 | 881 | Pilgrimage | 20.7 | 706.49 ± 94.1 | 11.1 |
| 3 | Kondangeri | KA | 12.302576 | 75.793159 | 57 | 863 | Small village | 23.7 | 565.69 ± 160.3 | 10.8 |
| 4 | Siddapura | KA | 12.305524 | 75.868617 | 65 | 849 | Taluk head quarters | 23.7 | 1052.29 ± 80.5 | 8.8 |
| 5 | Kanive | KA | 12.508369 | 75.962233 | 90 | 822 | Small village | 24 | 1161.79 ± 217 | 29.0 |
| 6 | Yedathore | KA | 12.468035 | 76.391969 | 137 | 749 | Small village | 24.1 | 2948.59 ± 131.6 | 11.9 |
| 7 | Honnavalli | KA | 12.418893 | 76.480502 | 148 | 751 | Taluk head quarters | 25.1 | 2891.09 ± 249.1 | 10.7 |
| 8 | KRS Dam | KA | 12.424884 | 76.581608 | 159 | 734 | Reservoir, touristic spot | 24.3 | 2255.29 ± 193.4 | 10.8 |
| 9 | T. Narasipura | KA | 12.225215 | 76.908996 | 200 | 666 | Pilgrimage, Touristic spot, confluence of 3 rivers | 25.6 | 2885.6 ± 108.9 | 17.2 |
| 10 | Shivana-samudra | KA | 12.260447 | 77.170415 | 229 | 619 | Touristic spot | 25.7 | 34629 ± 120.8 | 13.6 |
| 11 | Mettur Dam | TN | 11.797182 | 77.807326 | 401 | 198 | Reservoir, touristic spot | 26.1 | 1347.49 ± 205.3 | 16.7 |
| 12 | Bhavani | TN | 11.431789 | 77.682326 | 444 | 165 | Municipal town | 27.8 | 1245.4 ± 250.8 | 11.4 |
| 13 | Pallipalayam | TN | 1.136503 | 77.740134 | 454 | 159 | Municipal town | 28 | 1127.69 ± 100.6 | 10.6 |
| 14 | Unjalur | TN | 11.128925 | 77.879335 | 484 | 142 | Panchayat town | 28.4 | 1216.69 ± 654.3 | 5.9 |
| 15 | Paramathy Velur | TN | 11.094799 | 78.006123 | 498 | 116 | Town | 29.5 | 918.89 ± 180.7 | 13.1 |
| 16 | Mohanur | TN | 11.052458 | 78.135368 | 513 | 110 | Panchayat town | 28.6 | 1083.49 ± 365.7 | 11.0 |
| 17 | Kulithalai | TN | 10.946181 | 78.419337 | 568 | 88 | Town | 26.9 | 1260.09 ± 849.7 | 7.5 |
| 18 | Jeeyapuram | TN | 10.873914 | 78.613688 | 614 | 74 | Village | 28.7 | 1541.59 ± 179 | 12.8 |
| 19 | Trichy | TN | 10.840277 | 78.714369 | 625 | 66 | District head quarters | 29.6 | 2970.89 ± 146 | 8.8 |
| 20 | Grand Anaicut | TN | 10.831584 | 7.882052 | 637 | 60 | Reservoir & touristic spot | 28.69 | 13399 ± 270.9 | 17.9 |
| 21 | Thiruvaiyaru | TN | 10.879106 | 79.109731 | 652 | 43 | Panchayat town | 30.3 | 1672.2 ± 116.3 | 12.2 |
| 22 | Melacavery, Kumbakonam | TN | 10.966.264 | 79.365.665 | 682 | 31 | Municipal town | 28.6 | 1422.5 ± 82.4 | 6.2 |
| 23 | Chettimandapam, Kumbakonam | TN | 10.979.208 | 79.400.201 | 686 | 28 | Municipal town | 28.2 | 2009.6 ± 379 | 8.6 |
| Parameter | Distance | pH | Temp | DO | EC | TOC | DIC | pCO2 | pCH4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Distance | 1 | ||||||||
| pH | 0.67 ** | 1 | |||||||
| Temp | 0.91 ** | 0.72 ** | 1 | ||||||
| DO | 0.05 | 0.62 ** | 0.18 | 1 | |||||
| EC | 0.89 ** | 0.60 ** | 0.91 ** | 0.05 | 1 | ||||
| TOC | −0.27 | –0.07 | –0.18 | 0.04 | –0.14 | 1 | |||
| DIC | 0.35 | 0.54 ** | 0.28 | 0.33 | 0.22 | –0.00 | 1 | ||
| pCO2 | −0.47 * | –0.76 ** | –0.47 ** | –0.68 ** | –0.26 | –0.03 | –0.39 | 1 | |
| pCH4 | 0.03 | −0.38 | −0.08 | –0.63 ** | 0.01 | –0.18 | –0.11 | 0.40 | 1 |
| Phyla | Proteobacteria | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Class | S1 | S2 | S3 | S4 | S5 | S6 | S8 | S10 | S11 | S12 | S13 | S16 | S18 | S19 | S20 | S22 | S23 | Median |
| Alpha | 9.5 | 0.5 | 2.3 | 0.5 | 2.2 | 1 | 3.5 | 0.4 | 3.9 | 2.3 | 3.1 | 3.4 | 1.7 | 2.5 | 3.7 | 1.6 | 3.1 | 2.3 |
| Beta | 70.2 | 29.6 | 62.3 | 66.5 | 52.2 | 54.3 | 15.6 | 49.6 | 36.9 | 42.8 | 35.9 | 40.4 | 45.1 | 38 | 40.5 | 47 | 34.7 | 42.8 |
| Gamma | 2.3 | 1.5 | 1 | 1.1 | 2.7 | 3.3 | 4.6 | 24.5 | 15.5 | 16 | 15 | 18.8 | 7.4 | 17 | 7.2 | 3.1 | 7.8 | 7.2 |
| Delta | 0.2 | 0.5 | 0.7 | 0 | 0.3 | 0 | 1.9 | 0 | 0 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0 | 0.5 | 0.7 | 0 | 1 | 0.2 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Premke, K.; Dharanivasan, G.; Steger, K.; Nitzsche, K.N.; Jayavignesh, V.; Nambi, I.M.; Seshadri, S. Anthropogenic Impact on Tropical Perennial River in South India: Snapshot of Carbon Dynamics and Bacterial Community Composition. Water 2020, 12, 1354. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12051354
Premke K, Dharanivasan G, Steger K, Nitzsche KN, Jayavignesh V, Nambi IM, Seshadri S. Anthropogenic Impact on Tropical Perennial River in South India: Snapshot of Carbon Dynamics and Bacterial Community Composition. Water. 2020; 12(5):1354. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12051354
Chicago/Turabian StylePremke, Katrin, Gunasekaran Dharanivasan, Kristin Steger, Kai Nils Nitzsche, Vijayan Jayavignesh, Indumathi M Nambi, and Sundaram Seshadri. 2020. "Anthropogenic Impact on Tropical Perennial River in South India: Snapshot of Carbon Dynamics and Bacterial Community Composition" Water 12, no. 5: 1354. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12051354
APA StylePremke, K., Dharanivasan, G., Steger, K., Nitzsche, K. N., Jayavignesh, V., Nambi, I. M., & Seshadri, S. (2020). Anthropogenic Impact on Tropical Perennial River in South India: Snapshot of Carbon Dynamics and Bacterial Community Composition. Water, 12(5), 1354. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12051354





