Evaluating Impacts of Irrigation and Drought on River, Groundwater and a Terminal Wetland in the Zayanderud Basin, Iran
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
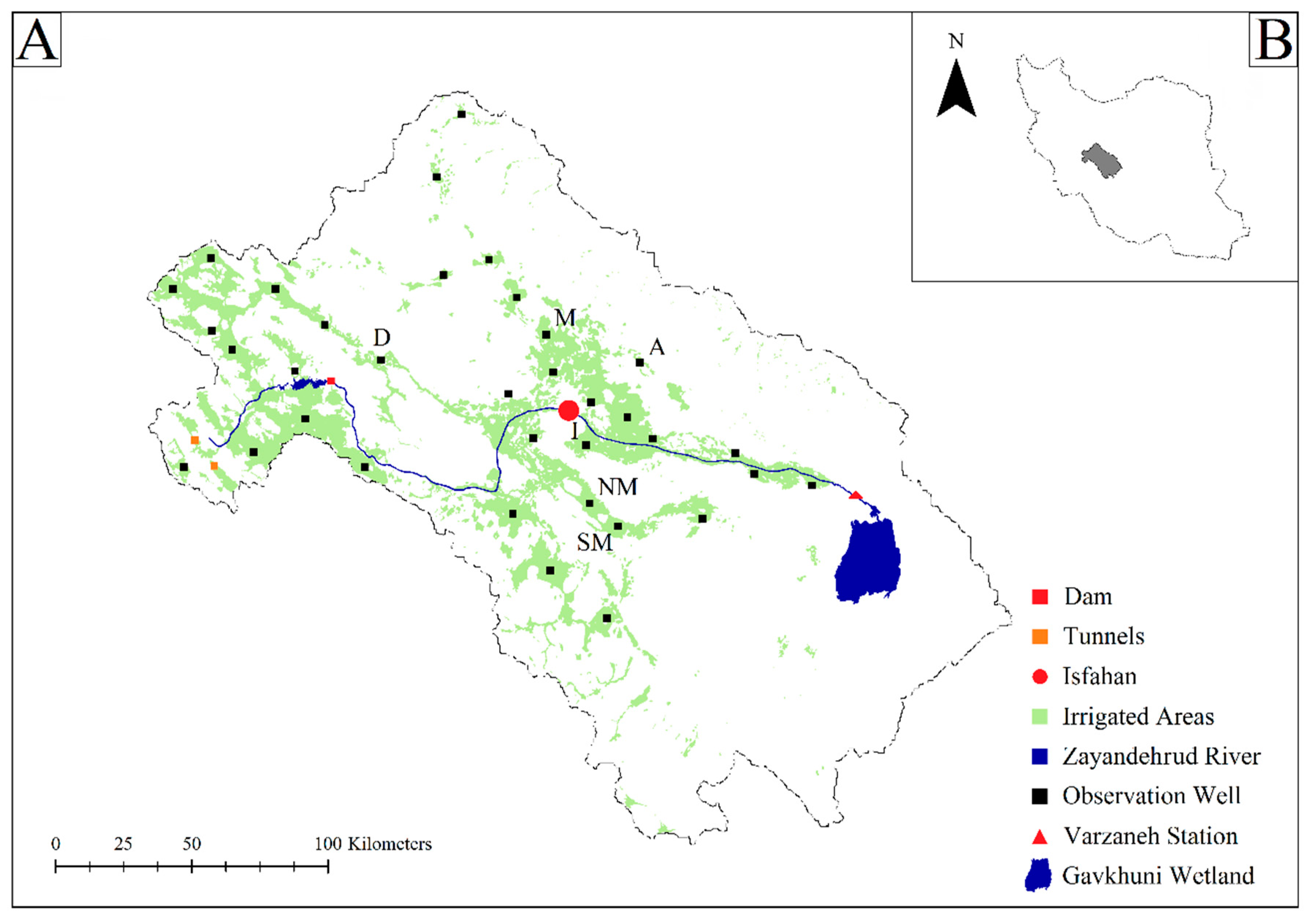
2.1. Study Area and Data
2.2. Monitoring the Meteorological and Hydrological Drought in the Zayanderud Basin
2.3. Monitoring Water Mass Depletion in the Zayanderud Basin
2.4. Using Normalized Difference Water Index (NDWI) to Monitor the Gavkhuni Wetland Water Mass Fluctuation
3. Results
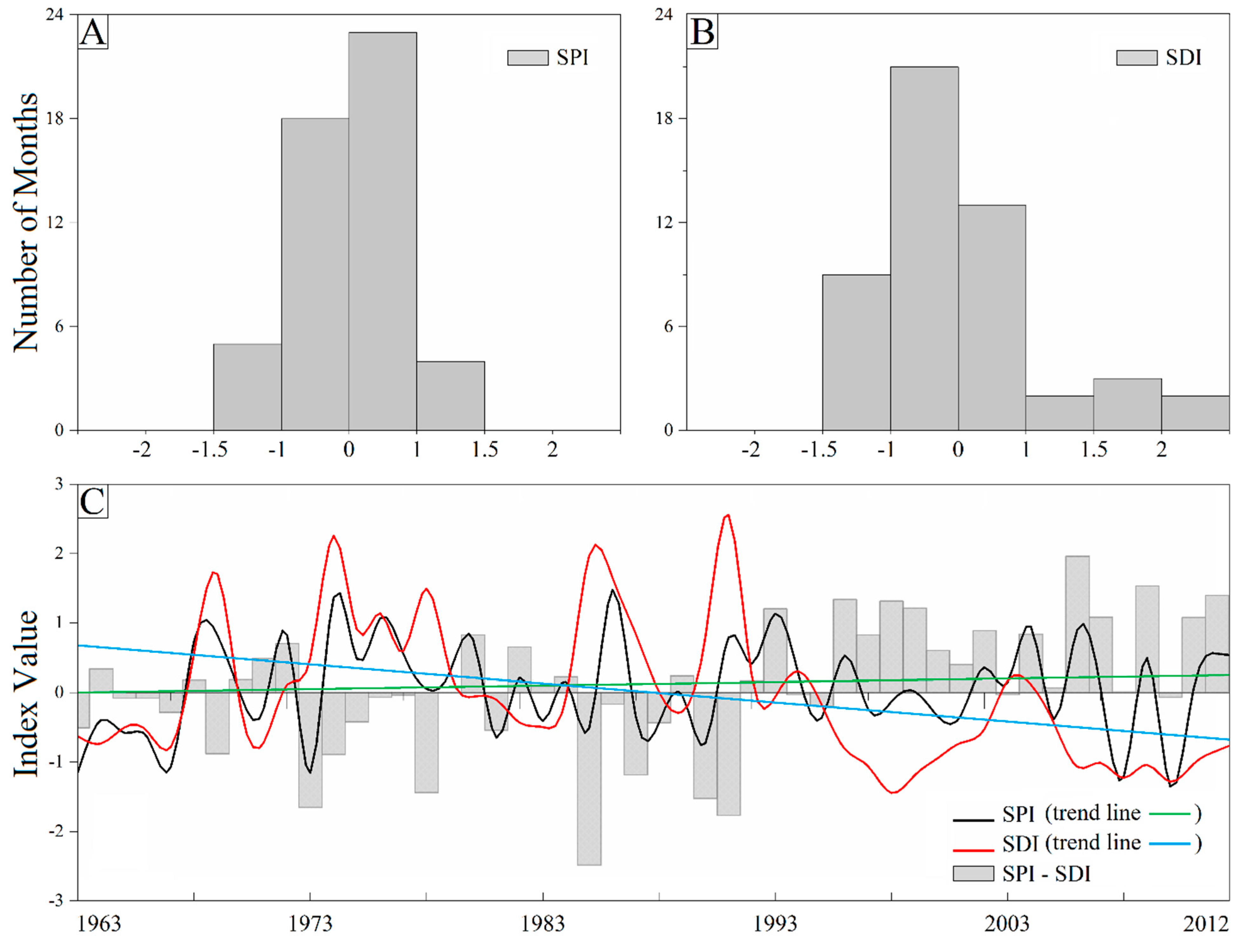
3.1. Meteorological and Hydrological Drought Occurrence Frequencies in the Zayanderud Basin
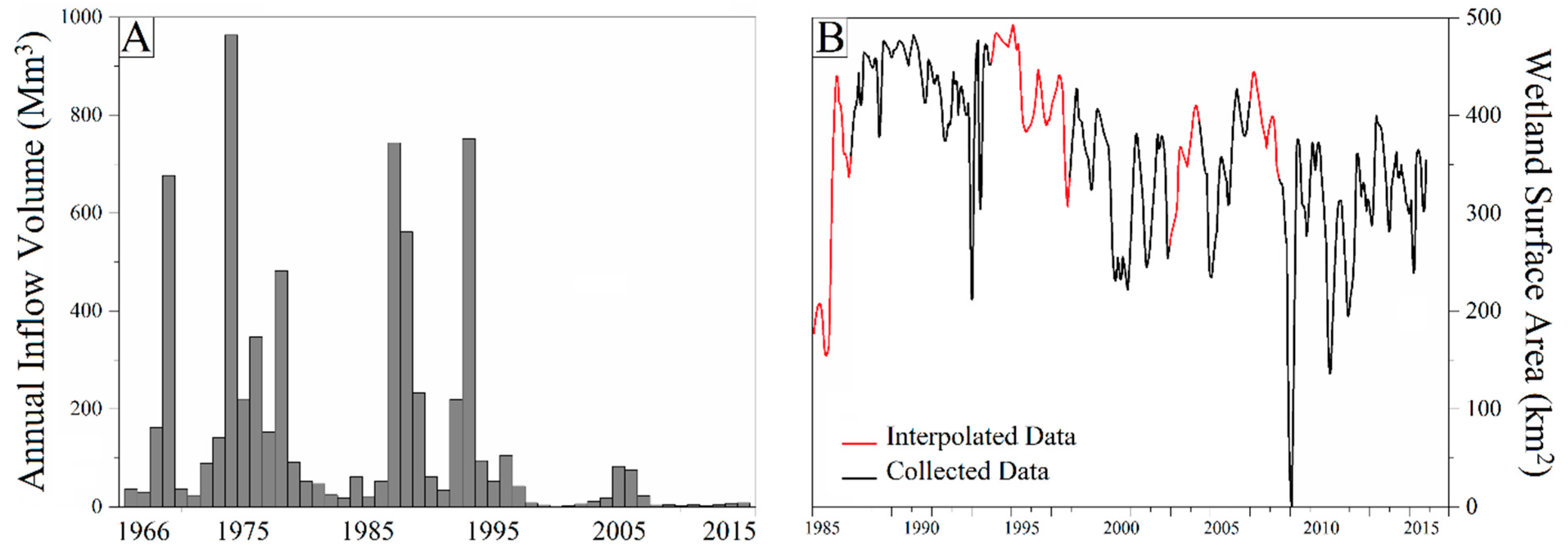
3.2. Water Mass and Groundwater Depletion in the Zayanderud Basin
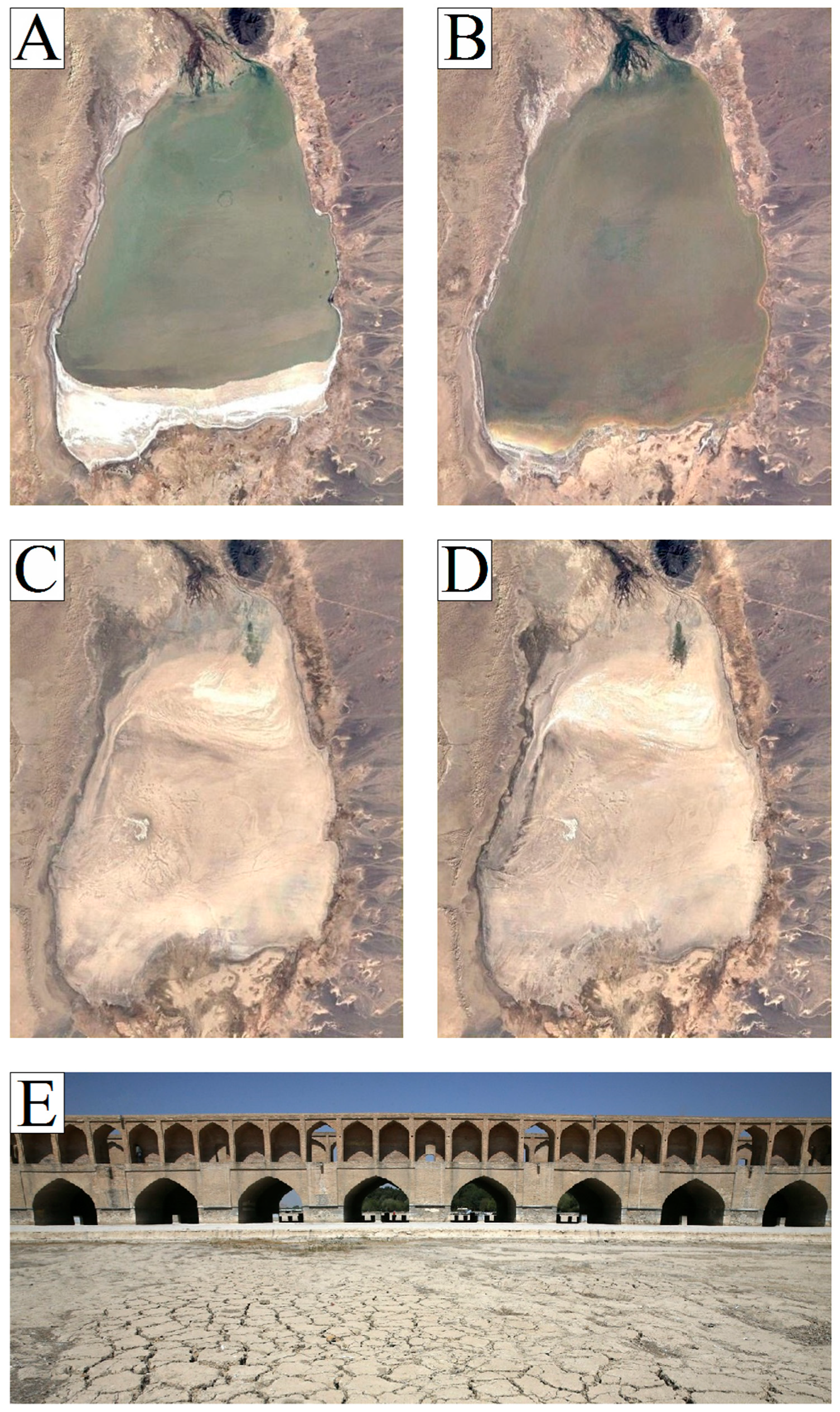
3.3. Gavkhuni Wetland Water Mass Fluctuation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Atlas of Desertification. 2020. Available online: www.wad.jrc.ec.europa.eu (accessed on 26 April 2020).
- Manap, N.; Ismail, N. Land Irrigation and Food Production in Dry-Land Developing Countries. Int. J. Agric. For. Plant. 2017, 5, 7–14. [Google Scholar]
- Deryng, D.; Sacks, W.J.; Barford, C.C.; Ramankutty, N. Simulating the effects of climate and agricultural management practices on global crop yield. Global Biogeochem. Cycles. 2011, 25, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, G.; Tang, Q.; Rayburg, S. Climate change impacts on meteorological, agricultural and hydrological droughts in China. Global Planet. Change 2015, 126, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orimoloye, I.R.; Kalumba, A.M.; Mazinyo, S.P.; Nel, W. Geospatial analysis of wetland dynamics: Wetland depletion and biodiversity conservation of Isimangaliso Wetland, South Africa. J. King Saud Univ.-Sci. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wada, Y.; Van Beek, L.P.; Van Kempen, C.M.; Reckman, J.W.; Vasak, S.; Bierkens, M.F. Global depletion of groundwater resources. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2010, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fazel, N.; Torabi Haghighi, A.; Kløve, B. Analysis of land use and climate change impacts by comparing river flow records in headwater and lowland streams of lake Urmia basin, Iran. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2017, 158, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haghighi, A.T.; Kløve, B. Design of environmental flow regimes to maintain lakes and wetlands in regions with high seasonal irrigation demand. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 100, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abou Zaki, N.; Torabi Haghighi, A.; Rossi, P.; Xenarios, S.; Kløve, B. An Index-Based Approach to Assess the Water Availability for Irrigated Agriculture in Sub-Saharan Africa. Water 2018, 10, 896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akbari, M.; Torabi Haghighi, A.; Aghayi, M.M.; Javadian, M.; Tajrishy, M.; Kløve, B. Assimilation of satellite-based data for hydrological mapping of precipitation and direct runoff coefficient for the Lake Urmia Basin in Iran. Water 2019, 11, 1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hoff, H.; Bonzi, C.; Joyce, B.; Tielbörger, K. A water resources planning tool for the Jordan River Basin. Water 2011, 3, 3–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyamfi, C.; Ndambuki, J.M.; Salim, R.W. Hydrological responses to land use/cover changes in the Olifants Basin, South Africa. Water 2016, 8, 588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godinez-Madrigal, J.; Van Cauwenbergh, N.; Van der Zaag, P. Production of competing water knowledge in the face of water crises: Revisiting the IWRM success story of the Lerma-Chapala Basin, Mexico. Geoforum 2019, 103, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enouist, P.; Zhou, Y.; Wensley, D.; Lewis, A. Ecological planning practices of the yellow river national wetland park in Jinan section. Landsc. Archit. Front. 2019, 7, 88–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahajan, D.R.; Dodamani, B.M. Trend analysis of drought events over upper Krishna basin in Maharashtra. Aquat. Procedia 2015, 4, 1250–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darvishi, E.; Mehraban, A.; Fanaei, H. Investigate the effects of water deficit stress on seed yield and wheat yield components under the influence of different amounts of super absorbent polymer. Int. J. Farming Allied Sci. 2014. Available online: http://ijfas.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/03/268-273.pdf (accessed on 20 January 2020).
- Rosenthal, G.G. The Mediterranean Basin: Its Political Economy and Changing International Relations; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Richards, N. Water Users Associations in Tanzania: Local Governance for Whom? Water 2019, 11, 2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hekmatpanah, M.; Nasri, M.; Sardu, F.S. Effect of industrial and agricultural pollutants on the sustainability of Gavkhuni lagoon wetland ecosystem. Afr. J. Agric. Res. 2012, 7, 3049–3059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soffianian, A.; Madanian, M. Monitoring land cover changes in Isfahan Province, Iran using Landsat satellite data. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Famiglietti, J.S.; Lo, M.; Ho, S.L.; Bethune, J.; Anderson, K.J.; Syed, T.H.; Swenson, S.C.; De Linage, C.R.; Rodell, M. Satellites measure recent rates of groundwater depletion in California’s Central Valley. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2011, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feng, W.; Zhong, M.; Lemoine, J.M.; Biancale, R.; Hsu, H.T.; Xia, J. Evaluation of groundwater depletion in North China using the Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment (GRACE) data and ground-based measurements. Water Resour. Res. 2013, 49, 2110–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voss, K.A.; Famiglietti, J.S.; Lo, M.; De Linage, C.; Rodell, M.; Swenson, S.C. Groundwater depletion in the Middle East from GRACE with implications for transboundary water management in the Tigris-Euphrates-Western Iran region. Water Resour. Res. 2013, 49, 904–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jia, K.; Liang, S.; Wei, X.; Yao, Y.; Su, Y.; Jiang, B.; Wang, X. Land cover classification of Landsat data with phenological features extracted from time series MODIS NDVI data. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 11518–11532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shao, Y.; Lunetta, R.S.; Wheeler, B.; Iiames, J.S.; Campbell, J.B. An evaluation of time-series smoothing algorithms for land-cover classifications using MODIS-NDVI multi-temporal data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 174, 258–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tourian, M.J.; Reager, J.T.; Sneeuw, N. The total drainable water storage of the Amazon River Basin: A first estimate using GRACE. Water Resour. Res. 2018, 54, 3290–3312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou Zaki, N.; Torabi Haghighi, A.; Rossi, P.M.J.; Tourian, M.; Kløve, B. Monitoring Groundwater Storage Depletion Using Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment (GRACE) Data in Bakhtegan Catchment, Iran. Water 2019, 11, 1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, G.; Yao, T.; Shum, C.K.; Yi, S.; Yang, K.; Xie, H.; Feng, W.; Bolch, T.; Wang, L.; Behrangi, A.; et al. Lake volume and groundwater storage variations in Tibetan Plateau’s endorheic basin. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 5550–5560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, L.; Wang, H.; Steffen, H.; Wu, P.; Jia, L.; Jiang, L.; Shen, Q. Groundwater storage changes in the Tibetan Plateau and adjacent areas revealed from GRACE satellite gravity data. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2016, 449, 228–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Madani, K.; Mariño, M.A. System dynamics analysis for managing Iran’s Zayandeh-Rud river basin. Water Resour. Manage. 2009, 23, 2163–2187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbari, M.; Toomanian, N.; Droogers, P.; Bastiaanssen, W.; Gieske, A. Monitoring irrigation performance in Esfahan, Iran, using NOAA satellite imagery. Agric. Water Manage. 2007, 88, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molle, F.; Ghazi, I.; Murray-Rust, H. Buying respite: Esfahan and the Zayandeh-Rud river basin, Iran. River Basin Traject. Soc. Environ. Dev. 2009, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bijani, M.; Hayati, D. Farmers’ Perceptions toward Agricultural Water Conflict: The Case of Doroodzan Dam Irrigation Network, Iran. J. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2015, 17, 561–575. [Google Scholar]
- Madani Larijani, K. A system dynamics approach, case study: Zayandeh-Rud River Basin, Iran. Watershed Manag. Sustain. 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harandi, M.F.; De Vries, M.J. An appraisal of the qualifying role of hydraulic heritage systems: A case study of Qanats in central Iran. Water Sci. Technol. Water Supply 2014, 14, 1124–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gohari, A.; Eslamian, S.; Abedi-Koupaei, J.; Bavani, A.M.; Wang, D.; Madani, K. Climate change impacts on crop production in Iran’s Zayandeh-Rud River Basin. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 442, 405–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iranian Metrological Organization. 2016. Available online: www.irimo.ir (accessed on 20 January 2020).
- Iranian Water Resources Management Company. 2016. Available online: www.wrm.ir (accessed on 20 January 2020).
- Irannezhad, M.; Haghighi, A.T.; Chen, D.; Kløve, B. Variability in dryness and wetness in central Finland and the role of teleconnection patterns. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2015, 122, 471–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diani, K.; Kacimi, I.; Zemzami, M.; Torabi Haghighi, A. Evaluation of meteorological drought using the Standardized Precipitation Index (SPI) in the High Ziz River basin, Morocco. Limnol. Rev. 2019, 19, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Torabi Haghighi, A.; Abou Zaki, N.; Rossi, P.M.; Noori, R.; Hekmatzadeh, A.A.; Saremi, H.; Kløve, B. Unsustainability Syndrome - From Meteorological to Agricultural Drought in Arid and Semi-Arid Regions. Water 2020, 12, 838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McKee, T.B.; Doesken, N.J.; Kleist, J. The relationship of drought frequency and duration to time scales. In Proceedings of the 8th Conference on Applied Climatology, Boston, MA, USA, 17–22 January 1993; 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd-Hughes, B.; Saunders, M.A. A drought climatology for Europe. Int. J. Climatl. J. R. Meteorolog. Soc. 2002, 22, 1571–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Drought Management Center. SPI Generator. 2018. Available online: https://drought.unl.edu/droughtmonitoring/SPI/SPIProgram.aspx. (accessed on 20 February 2020).
- Nalbantis, I.; Tsakiris, G. Assessment of hydrological drought revisited. Water Resour. Manag. 2009, 23, 881–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, M.; Taple, B.D.; Ries, J.C. Deceleration in the earth’s oblateness. J. Geophys. Res. 2013, 118, 740–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swenson, S.; Chambers, D.; Wahr, J. Estimating geocenter variations from a combination of GRACE and ocean model output. J. Geophys. Res. 2008, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tourian, M.J. Application of Spaceborne Geodetic Sensors for Hydrology. Ph.D. Thesis, University if Stuttgart, Stuttgart, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Wahr, J.; Zhong, S. Computations of the viscoelastic response of a 3-D compressible Earth to surface loading: An application to Glacial Isostatic Adjustment in Antarctica and Canada. Geophys. J. Int. 2012, 192, 557–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swenson, S.; Wahr, J. Estimating large-scale precipitation minus evapotranspiration from GRACE satellite gravity measurements. J. Hydrometeorol. 2006, 7, 252–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vishwakarma, B.D.; Horwath, M.; Devaraju, B.; Groh, A.; Sneeuw, N. A data driven approach for repairing the hydrological catchment signal damage due to filtering of GRACE products. Water Resour. Res. 2017, 53, 9824–9844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFeeters, S.K. The use of the Normalized Difference Water Index (NDWI) in the delineation of open water features. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1996, 17, 1425–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H. Modification of normalised difference water index (NDWI) to enhance open water features in remotely sensed imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2006, 27, 3025–3033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrishamchi, A.; Tajrishy, M. Interbasin water transfers in Iran. National Academy of Sciences. Water Conservation, Reuse, and Recycling. Proc. Iran. Am. Workshop 2002, 252–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doostmohammadi, M.; Jafari, A.; Asghari, O. Geostatistical modeling of uniaxial compressive strength along the axis of the Behesht-Abad tunnel in Central Iran. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2015, 74, 789–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarhadi, A.; Soltani, S. Determination of water requirements of the Gavkhuni wetland, Iran: A hydrological approach. J. Arid Environ. 2013, 98, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, C.A. Water Bankruptcy. Minnesota Law Rev. 2012, 97, 560. [Google Scholar]
- Oftadeh, E.; Shourian, M.; Saghafian, B. Evaluation of the Bankruptcy Approach for Water Resources Allocation Conflict Resolution at Basin Scale, Iran’s Lake Urmia Experience. Water Resour. Manag. 2016, 30, 10–3519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, R.; Kennedy, K. Bankrupt Rivers. UCDL Rev. 2015, 49, 1335. [Google Scholar]
- Schneier-Madanes, G.; Valdes, J.B.; Curley, E.F.; Maddock, T.; Marsh, S.; Hartfield, K.A. Water and urban development challenges in the Tucson metropolitan area: An interdisciplinary perspective. Water Bankruptcy Land Plenty 2017, 141–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Guo, P. A coupled random fuzzy two-stage programming model for crop area optimization—A case study of the middle Heihe River basin, China. Agric. Water Manag. 2015, 155, 53–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; He, W.; Degefu, D.M.; Liao, Z.; Wu, X. Water allocation model in the Lancing-Mekong River basin based on bankruptcy theory and bargaining game. World Environ. Water Resour. Congr. 2017, 78–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghadimi, S.; Ketabchi, H. Possibility of cooperative management in groundwater resources using an evolutionary hydro-economic simulation-optimization model. J. Hydrol. 2019, 578, 124094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Criterion | Description of State |
|---|---|
| SPI ≥ 2.0 | Extremely Wet |
| 1.5 ≤ SPI < 2.0 | Severely Wet |
| 1.0 ≤ SPI < 1.5 | Moderately Wet |
| 0 ≤ SPI < 1.0 | Normally Wet |
| −1.0 ≤ SPI < 0 | Normally Dry |
| −1.5 ≤ SPI < −1.0 | Moderately Dry |
| −2.0 ≤ SPI < −1.5 | Severely Dry |
| SPI < −2.0 | Extremely Dry |
| Criterion | Description of State |
|---|---|
| SDI ≥ 0.0 | No Drought |
| −1.0 ≤ SDI < 0.0 | Mild Drought |
| −1.5 ≤ SDI < −1.0 | Moderate Drought |
| −2.0 ≤ SDI < −1.5 | Severe Drought |
| SDI < −2.0 | Extreme Drought |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abou Zaki, N.; Torabi Haghighi, A.; Rossi, P.M.; Tourian, M.J.; Bakhshaee, A.; Kløve, B. Evaluating Impacts of Irrigation and Drought on River, Groundwater and a Terminal Wetland in the Zayanderud Basin, Iran. Water 2020, 12, 1302. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12051302
Abou Zaki N, Torabi Haghighi A, Rossi PM, Tourian MJ, Bakhshaee A, Kløve B. Evaluating Impacts of Irrigation and Drought on River, Groundwater and a Terminal Wetland in the Zayanderud Basin, Iran. Water. 2020; 12(5):1302. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12051302
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbou Zaki, Nizar, Ali Torabi Haghighi, Pekka M. Rossi, Mohammad J. Tourian, Alireza Bakhshaee, and Bjørn Kløve. 2020. "Evaluating Impacts of Irrigation and Drought on River, Groundwater and a Terminal Wetland in the Zayanderud Basin, Iran" Water 12, no. 5: 1302. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12051302
APA StyleAbou Zaki, N., Torabi Haghighi, A., Rossi, P. M., Tourian, M. J., Bakhshaee, A., & Kløve, B. (2020). Evaluating Impacts of Irrigation and Drought on River, Groundwater and a Terminal Wetland in the Zayanderud Basin, Iran. Water, 12(5), 1302. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12051302






