Effects of Distinct Revegetation Methods on Growth and Microbial Properties of Vallisneria natans
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
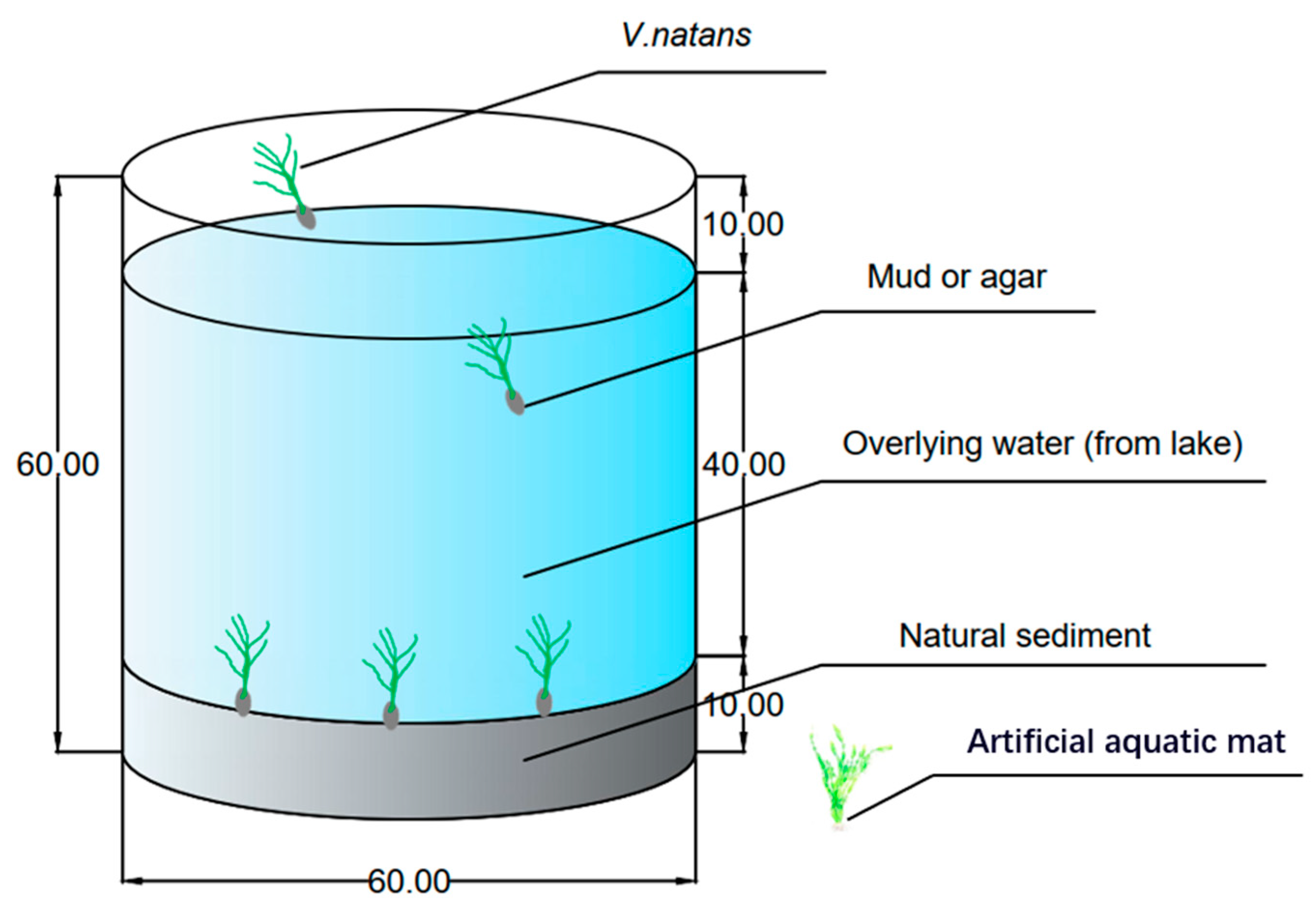
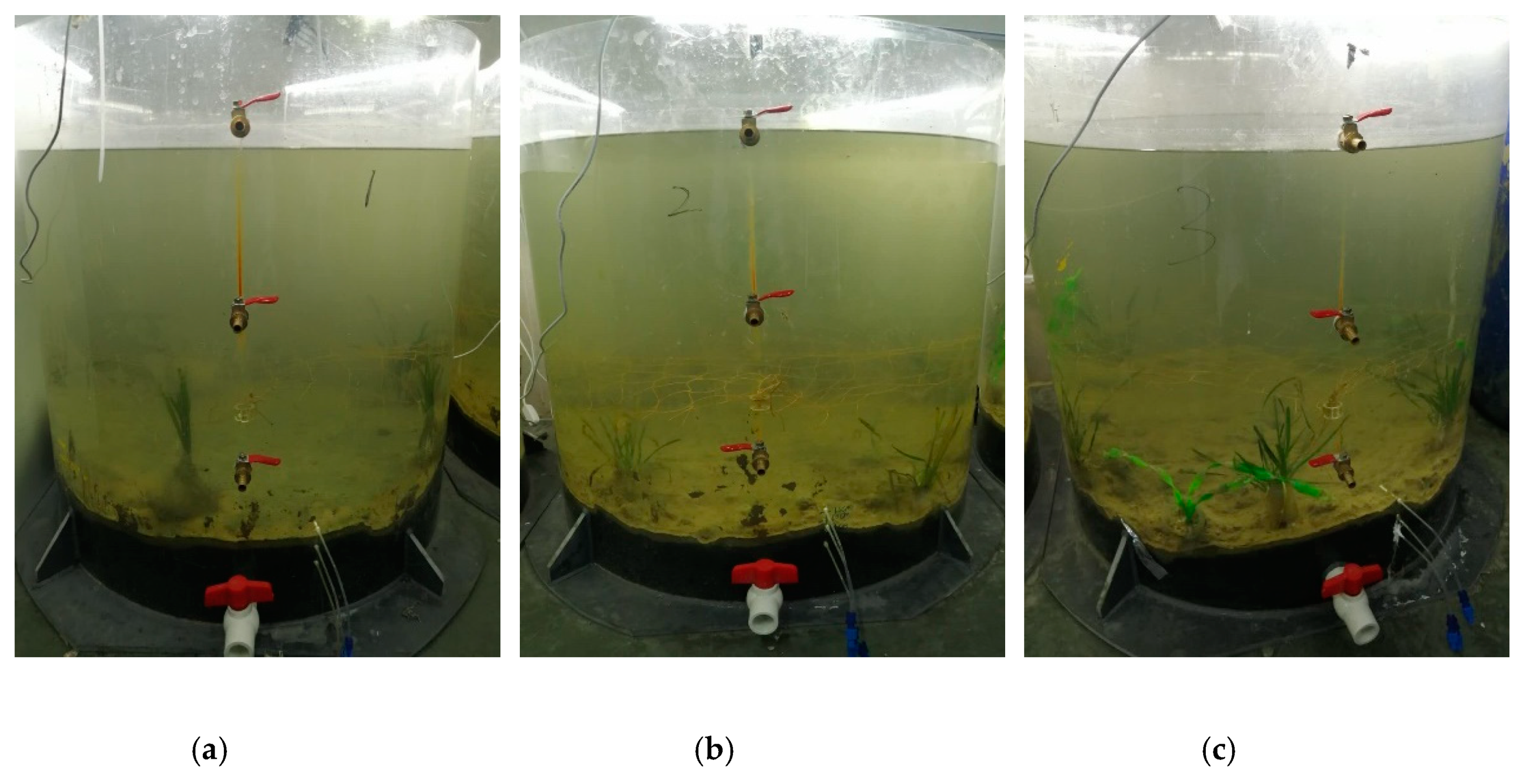
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Monitoring Plant Growth and Enzyme Activity
2.4. Water Quality Parameters
2.5. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) and Microbial Properties Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effects of Distinct Revegetation Methods on Growth, Physiological Parameters, and Enzyme Activity of V. natans
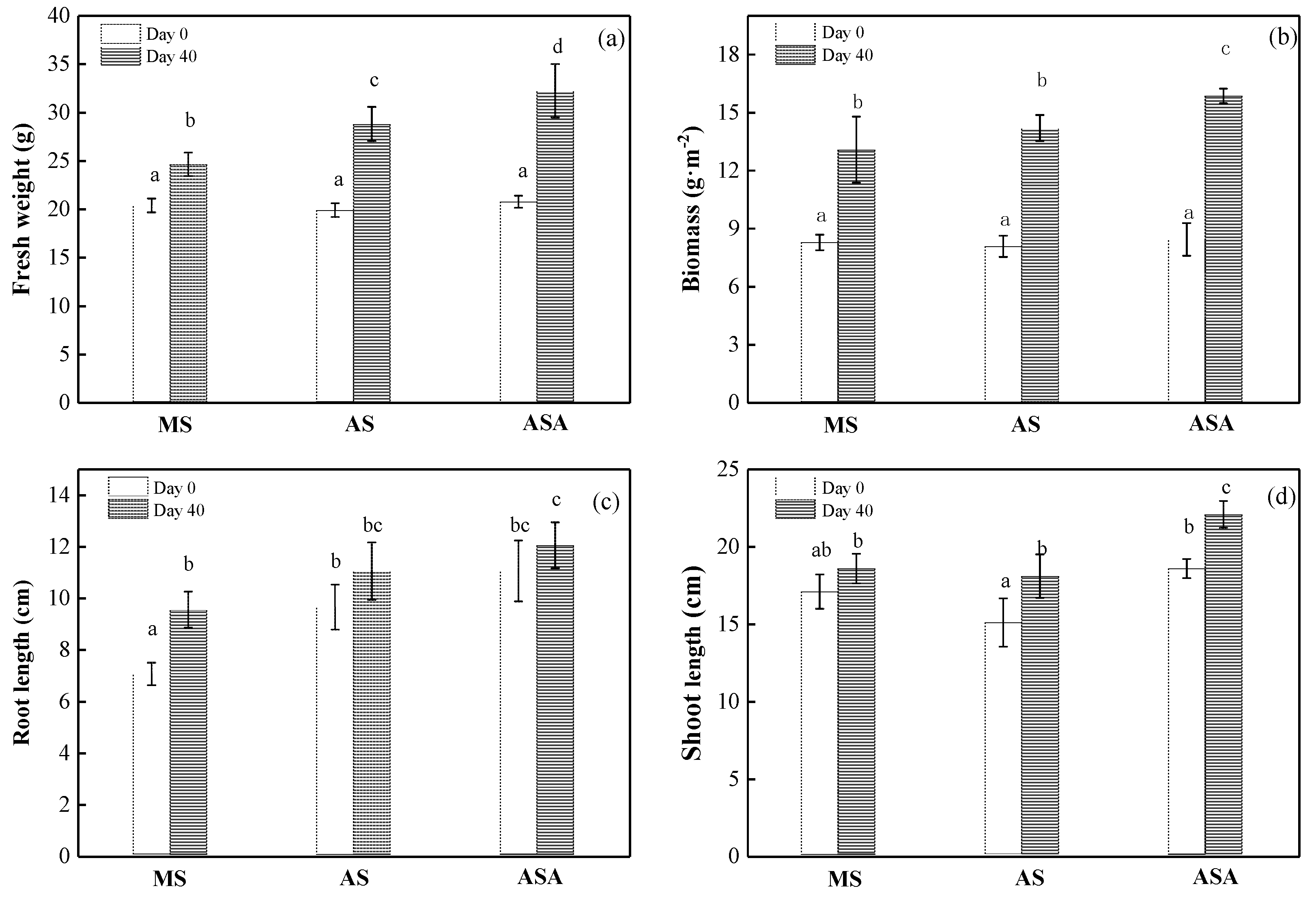
3.1.1. Growth of V. natans
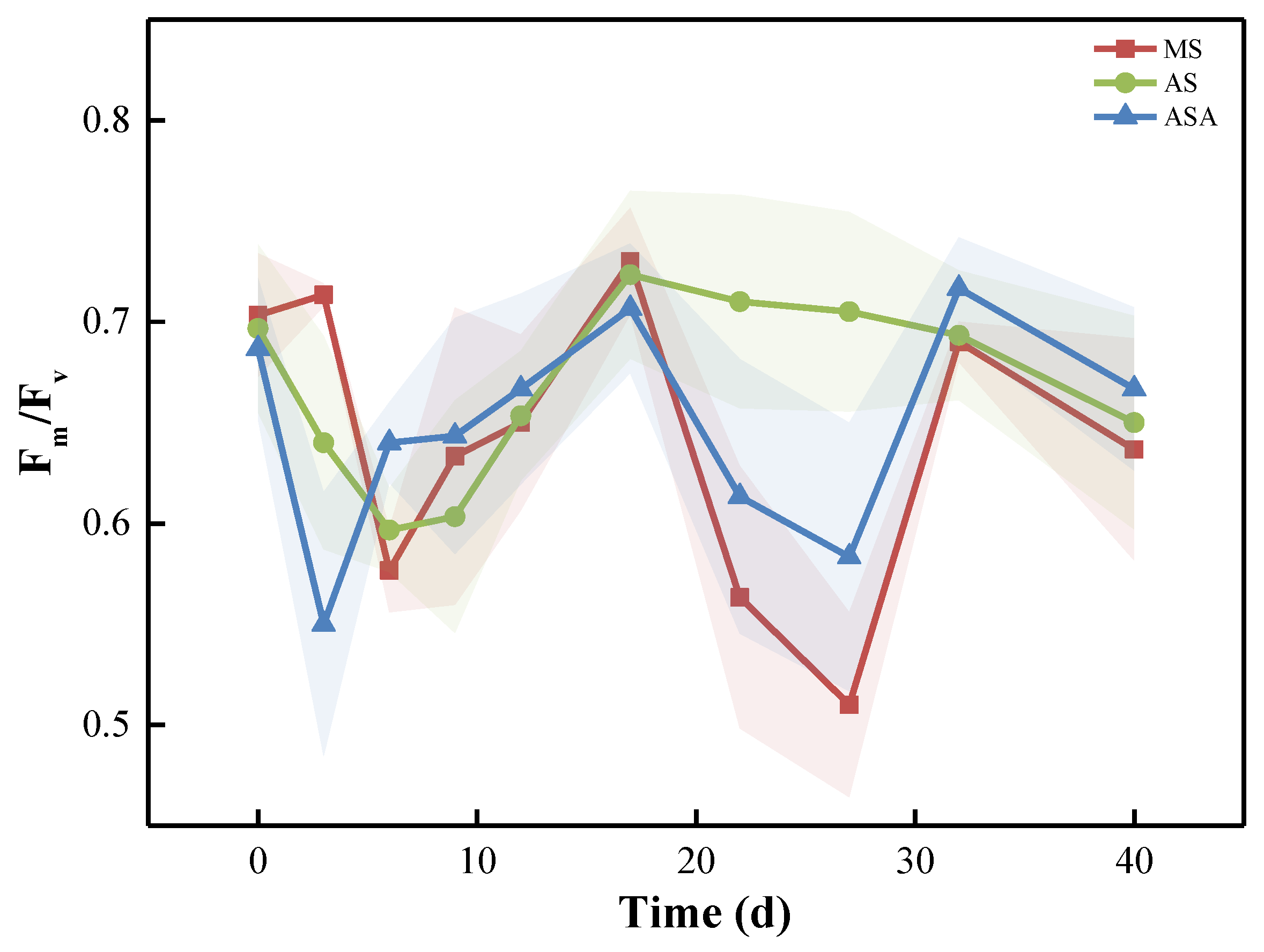
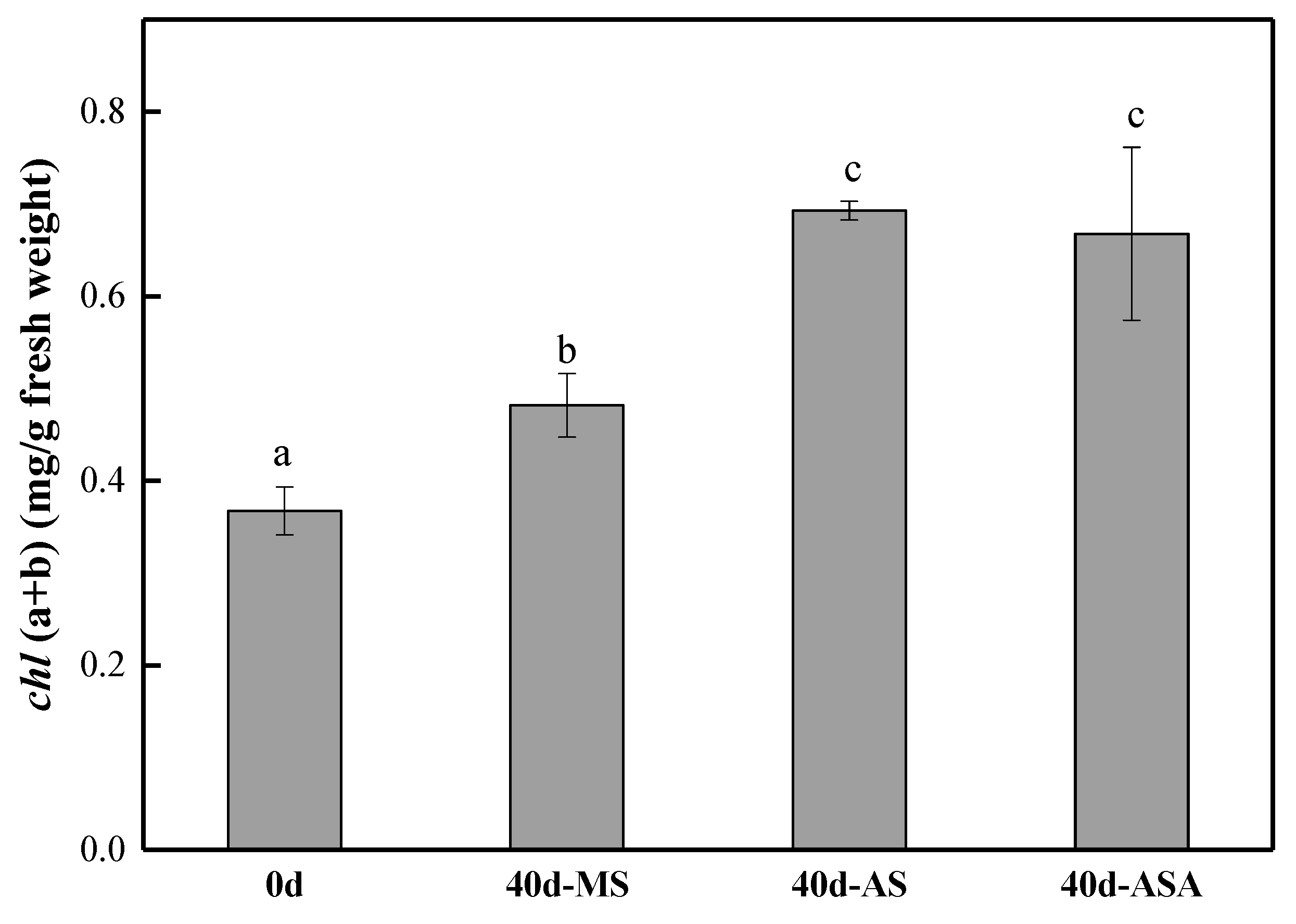
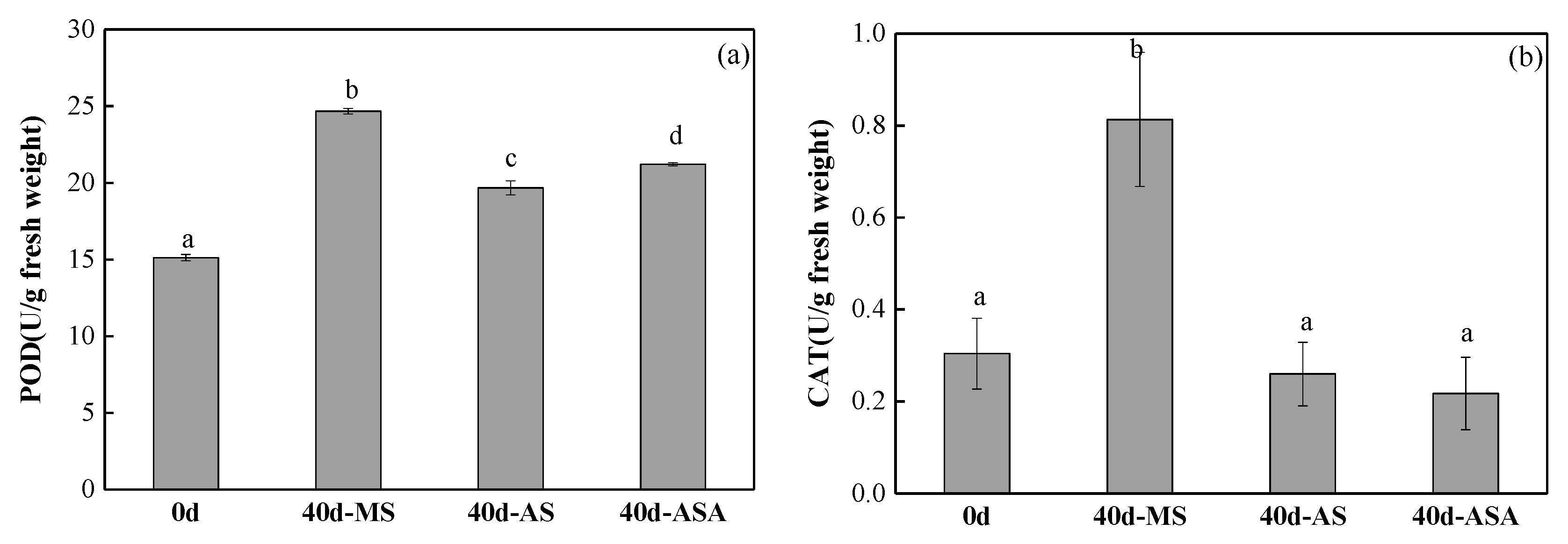
3.1.2. Physiological Parameters and Enzyme Activity of V. natans
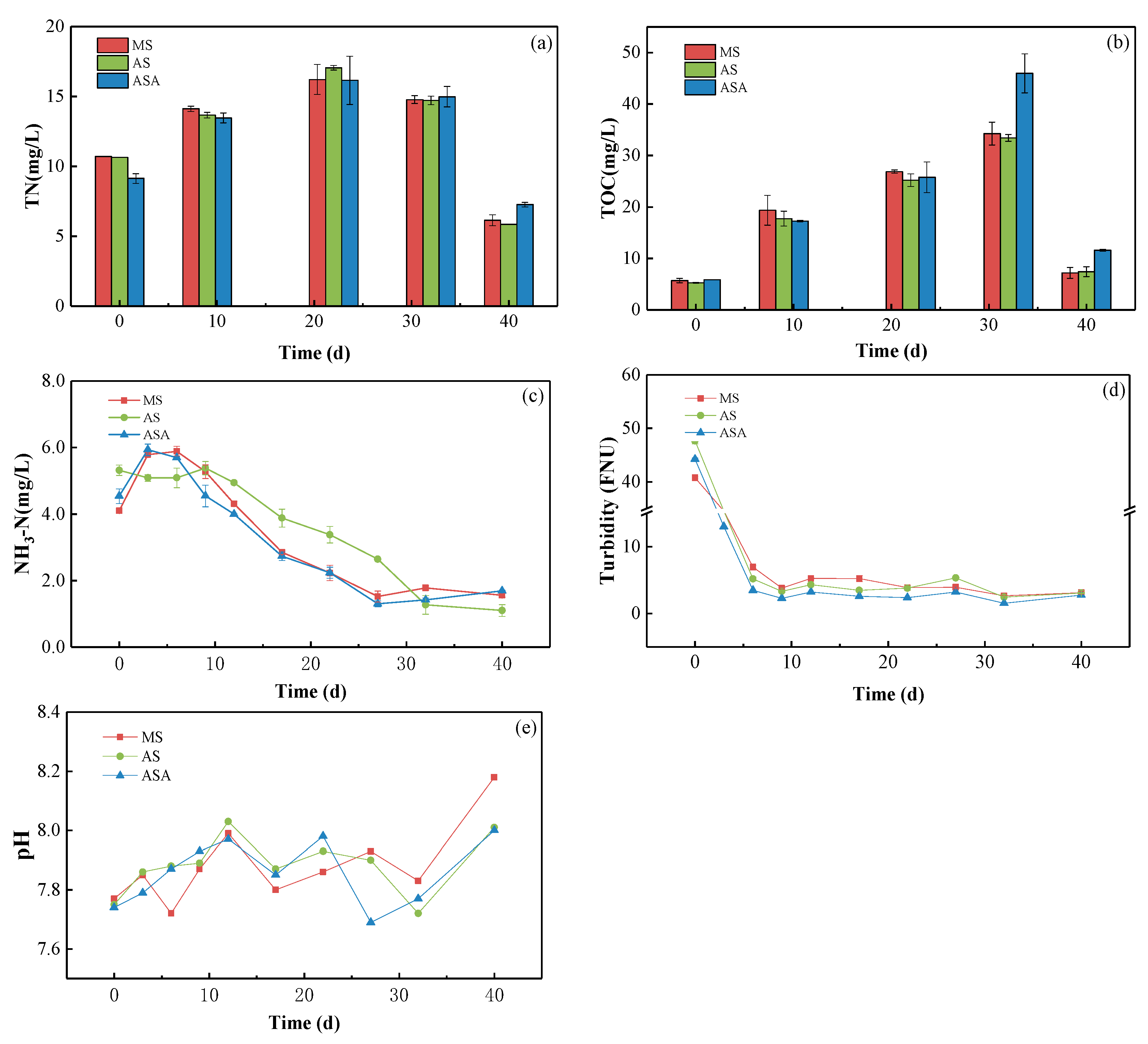
3.2. Effects of Distinct Revegetation Methods on the Results of Water Purification
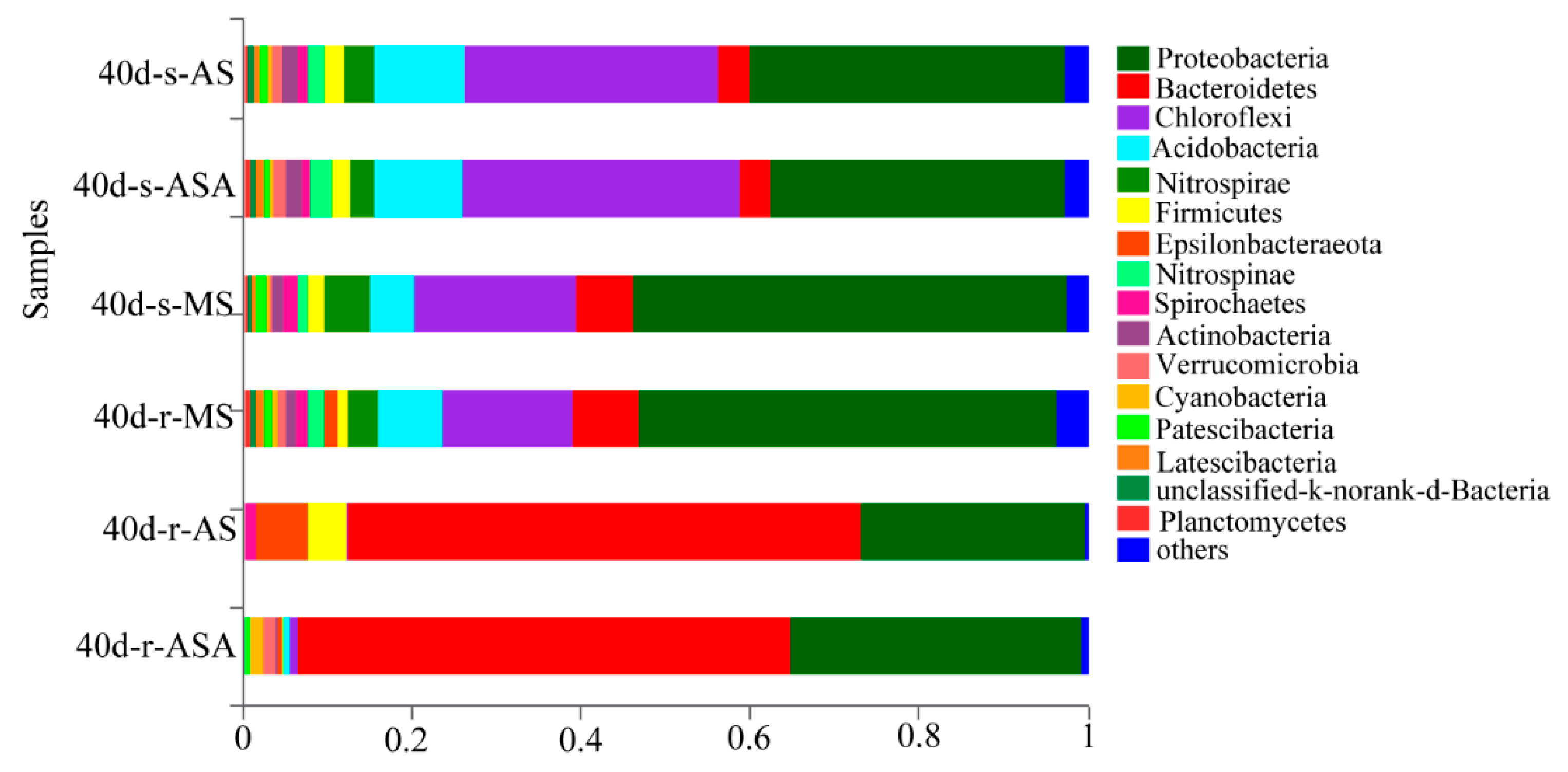
3.3. Effects of Distinct Revegetation Methods on the Microbial Properties of V. natans Root and Rhizosphere Soil
3.4. Biofilm Attached to the Leaves of V. natans
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Scheffer, M.; Hosper, S.H.; Meijer, M.L.; Moss, B.; Jeppesen, E. Alternative equilibria in shallow lakes. Trends Ecol. Evol. 1993, 8, 275–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, H.; Pan, J.Z.; Shen, Y.L.; Li, W.C.; Huang, F.; Zhao, H.G. Phosphorus threshold for the shift between grass-and algae-stable states in Dahong Harbor of Gehu Lake. J. Appl. Ecol. 2012, 23, 264. [Google Scholar]
- Cronin, G.; Lodge, D.M. Effects of light and nutrient availability on the growth, allocation, carbon/nitrogen balance, phenolic chemistry, and resistance to herbivory of two freshwater macrophytes. Oecologia 2003, 137, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hilt, S.; Gross, E.M.; Hupfer, M.; Morscheid, H.; Mählmann, J.; Melzer, A.; Poltz, J.; Sandrock, S.; Scharf, E.-M.; Schneider, S. Restoration of submerged vegetation in shallow eutrophic lakes–A guideline and state of the art in Germany. Limnologica 2006, 36, 155–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, Y.W.; Zhou, X.H.; Han, R.M.; Xu, X.G.; Wang, G.X.; Liu, X.S.; Bi, F.Z.; Feng, D.Y. Reproduction capacity of Potamogeton crispus fragments and its role in water purification and algae inhibition in eutrophic lakes. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 580, 1421–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.S. Research Status of Water Pollution Control by Aquatic Plants. Heilongjiang Agric. Sci. 2018, 8, 148–149. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, H.; Kong, W.; Wang, M.; Zongxue, X.U.; Yin, X.; Xuesen, L.I. Community structure and biotic integrity of aquatic plants along the North Canal in Beijing. Chin. J. Appl. Environ. Biol. 2018, 24, 260–268. [Google Scholar]
- Gulati, R.D.; Donk, E.V. Lakes in the Netherlands, their origin, eutrophication and restoration: State-of-the-art review. Hydrobiologia 2002, 478, 73–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egertson, C.J.; Kopaska, J.A.; Downing, J.A. A Century of Change in Macrophyte Abundance and Composition in Response to Agricultural Eutrophication. Hydrobiologia 2004, 524, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, T.; Zhang, H.; Hu, W.; Deng, J.; Zhu, G. Research on self-purification capacity of Lake Taihu. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 8201–8215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addisie, Y.; Medellin, A.C. Allelopathy in aquatic macrophytes: Effects on growth and physiology of phytoplankton. Afr. J. Plant Sci. 2012, 6, 270–276. [Google Scholar]
- Yi, Y.; Jie, S.; Yang, Y.; Yang, Z.; Tang, C.; Xuan, W.; Yang, Z. Habitat suitability evaluation of a benthic macroinvertebrate community in a shallow lake. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 90, 451–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeppesen, E.; Jensen, J.P.; Søndergaard, M.; Lauridsen, T.; Jensen, L. Top-down control in freshwater lakes: The role of nutrient state, submerged macrophytes and water depth. Hydrobiologia 1997, 342–343, 151–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciurli, A.; Zuccarini, P.; Alpi, A. Growth and nutrient absorption of two submerged aquatic macrophytes in mesocosms, for reinsertion in a eutrophicated shallow lake. Wetl. Ecol. Manag. 2009, 17, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, C.M.; Kalff, J. Influence of Lake Morphometry on the Response of Submerged Macrophytes to Sediment Fertilization. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2011, 45, 216–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Li, W.; Jeppesen, E. The response of two submerged macrophytes and periphyton to elevated temperatures in the presence and absence of snails: A microcosm approach. Hydrobiologia 2014, 738, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrow, M.R.; Moss, B.; Stansfield, J. Trophic interactions in a shallow lake following a reduction in nutrient loading: A long-term study. Hydrobiologia 1994, 275–276, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosper, S.H. Stable states, buffers and switches: An ecosystem approach to the restoration and management of shallow lakes in the Netherlands. Water Sci. Technol. 1998, 37, 151–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigo, M.A.; Rojo, C.; Alonso-Guillén, J.L.; Vera, P. Restoration of two small Mediterranean lagoons: The dynamics of submerged macrophytes and factors that affect the success of revegetation. Ecol. Eng. 2013, 54, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Feng, H.E.; Gao, X.H.; Kong, L.W.; Shenghua, H.U.; Xia, S.B.; Zhenbin, W.U. Restoration Efficiency of Submerged Macrophytes with Three Planting Patterns. Bull. Bot. Res. 2012, 32, 603–608. [Google Scholar]
- Stein, H.; Kellermann, C.; Schmidt, S.I.; Brielmann, H.; Griebler, C. The potential use of fauna and bacteria as ecological indicators for the assessment of groundwater quality. J. Environ. Monit. 2010, 12, 242–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dudley, N.; Bhagwat, S.A.; Harris, J.; Maginnis, S.; Moreno, J.G.; Mueller, G.M.; Oldfield, S.; Walters, G. Measuring progress in status of land under forest landscape restoration using abiotic and biotic indicators. Restor. Ecol. 2018, 26, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dan, H.; Lijuan, R.; Qinglong, W. Epiphytic bacterial communities on two common submerged macrophytes in Taihu Lake: Diversity and host-specificity. Chin. J. of Oceanol. Limnol. 2012, 30, 237–247. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zeng, L.; Liu, B.; Wu, Z.; He, F. Effects of different planting methods on the growth of Vallisneria natans (Lour) Hara in dynamic and static water environments. Plant Sci. J. 2017, 35, 691–698. [Google Scholar]
- Ke, X.; Li, W. Germination Requirement of Vallisneria natans Seeds: Implications for Restoration in Chinese Lakes. Hydrobiologia 2006, 559, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbiero, R.P. A multi-lake comparison of epilithic diatom communities on natural and artificial substrates. Hydrobiologia 2000, 438, 157–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, A.L.; Nicolas, N. Influence of the Degree of Solvent Impurity on the Spectrophotometric Determination of Chlorophylls in 80% Aqueous Acetone and Dimethyl formamide. Application to Non-Abrasive Extraction of Leaves of Citrus Aurantium. Photosynthetica 1998, 35, 545–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demmig, B. Comparison of the excessive light on chlorophyll fluorecence(77K) and photon yield of O2 evolution in higher plants. Planta 1987, 171, 171–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clesceri, L.S.; Greenberg, A.E.; Eaton, A.D. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, American Public Health Association; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, M.; Zhou, Y.; Ji, X.; Li, H.; Zheng, Z.; Zhang, J. Responses of leaf-associated biofilms on the submerged macrophyte Vallisneria natans during harmful algal blooms. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 246, 819–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulgarelli, D.; Rott, M.; Schlaeppi, K.; Ver Loren van Themaat, E.; Ahmadinejad, N.; Assenza, F.; Rauf, P.; Huettel, B.; Reinhardt, R.; Schmelzer, E.; et al. Revealing structure and assembly cues for Arabidopsis root-inhabiting bacterial microbiota. Nature 2012, 488, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niemi, R.M.; Heiskanen, I.; Wallenius, K.; Lindstrom, K. Extraction and purification of DNA in rhizosphere soil samples for PCR-DGGE analysis of bacterial consortia. J. Microbiol. Methods 2001, 45, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Gu, P.; Ji, X.Y.; Li, H.M.; Zhang, J.B.; Zheng, Z. Response of submerged macrophytes and periphyton biofilm to water flow in eutrophic environment: Plant structural, physicochemical and microbial properties. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 189, 109990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bécel, C.; Vercambre, G.; Pagès, L. Soil penetration resistance, a suitable soil property to account for variations in root elongation and branching. Plant Soil 2011, 353, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, L.; Zhang, S.; Chen, D.; Liu, K.; Lu, J. Response of biofilms-leaves of two submerged macrophytes to high ammonium. Chemosphere 2018, 192, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Yang, L.; Yin, D.; Wang, R.; Lu, X.; Qin, B. Vertical distribution of physicochemical characteristics and the microbial diversity in different spatial sediments samples in Lake Taihu. Environ. Sci. 2008, 29, 3537–3545. [Google Scholar]
- Best, E.P.H. Effects of nitrogen on the growth and nitrogenous compounds of Ceratophyllum demersum. Aquat. Bot. 1980, 8, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; An, S.; Wu, B. Resource allocation in the submerged plant Vallisneria natans related to sediment type, rather than water-column nutrients. Freshw. Biol. 2005, 50, 391–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz-De-Leon, F.; Klotz, K.L.; Lagrimini, L.M. Nucleotide Sequence of the Tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum) Anionic Peroxidase Gene. Plant Physiol. 1993, 101, 1117–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hilt, S.; Gross, E.M. Can allelopathically active submerged macrophytes stabilise clear-water states in shallow lakes? Basic Appl. Ecol. 2008, 9, 422–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dhote, S.; Dixit, S. Water quality improvement through macrophytes—A review. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2009, 152, 149–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Jia, C.; Liang, W.; Hu, S.; Wu, Z. Effects of the submerged macrophyte Ceratophyllum demersum L. on restoration of a eutrophic waterbody and its optimal coverage. Ecol. Eng. 2012, 40, 113–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozimek, T.; Donk, E.; Gulati, R.D. Growth and nutrient uptake by two species of Elodea in experimental. Hydrobiologia 1993, 251, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nayar, S.; Collings, G.J.; Miller, D.J.; Bryars, S.; Cheshire, A.C. Uptake and resource allocation of ammonium and nitrate in temperate seagrasses Posidonia and Amphibolis. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2010, 60, 1502–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, Y.; Shen, H.; Chen, J.; Xie, P.; Yang, X.; Tao, M.; Ma, Z.; Qi, M. Phytoplankton community succession shaping bacterioplankton community composition in Lake Taihu, China. Water Res. 2011, 45, 4169–4182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Shi, Q.; Wen, D.; Li, Z.; Jefferson, W.A.; Feng, C.; Tang, X. Bacterial communities in the sediments of Dianchi Lake, a partitioned eutrophic waterbody in China. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e37796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stratton, C.W.; Weeks, L.S.; Aldridge, K.E. Comparison of kill-kinetic studies with agar and broth microdilution methods for determination of antimicrobial activity of selected agents against members of the Bacteroides fragilis group. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1987, 4, 645–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beena, V.K.; Rao, S.; Kotian, M.; Shivananda, P.G. Fish meal extract bile esculin agar (FMBE) a selective medium for Bacteroides fragilis group. Indian J. Pathol. Microbiol. 1997, 3, 361–364. [Google Scholar]
- Brook, I. Growth of Bacteroides fragilis group in agar and broth media. J. Appl. Bacteriol. 1990, 5, 697–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayar, S.; Goh, B.P.L.; Chou, L.M. Settlement of marine periphytic algae in a tropical estuary. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2005, 64, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, C.S.; Eaton, J.W.; Hardwick, K. Responses of three invasive aquatic macrophytes to nutrient enrichment do not explain their observed field displacements. Aquat. Bot. 2006, 84, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
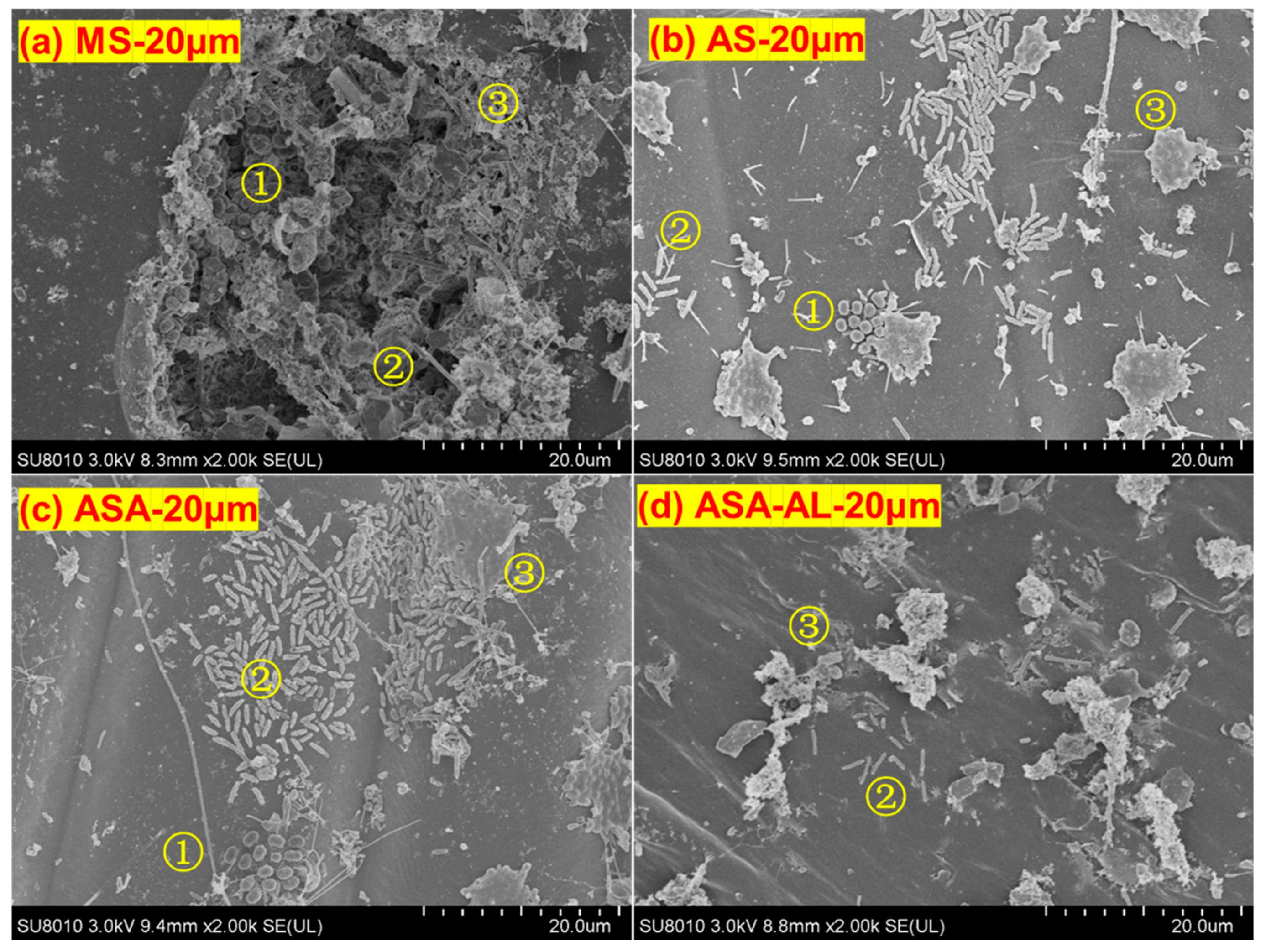
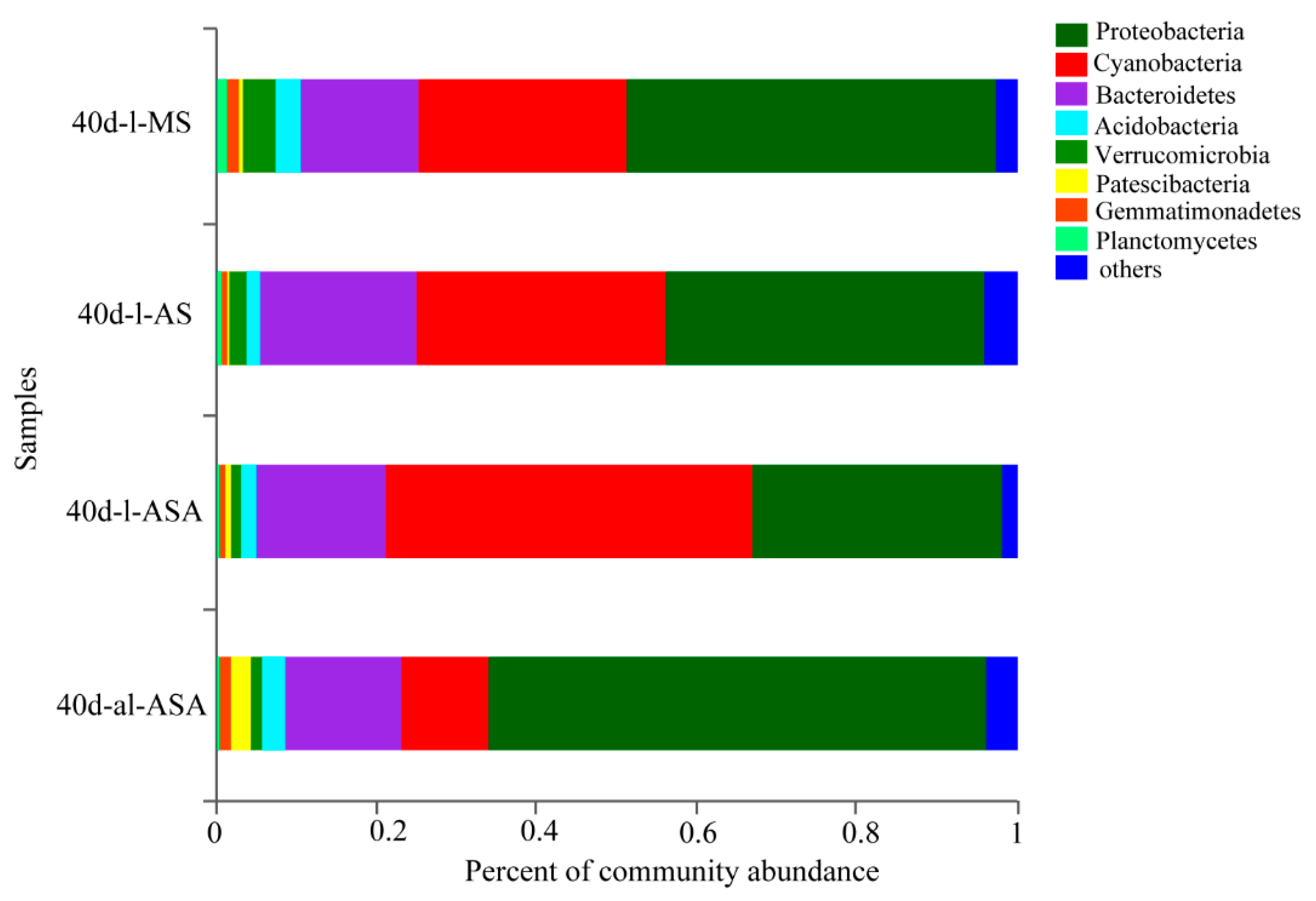
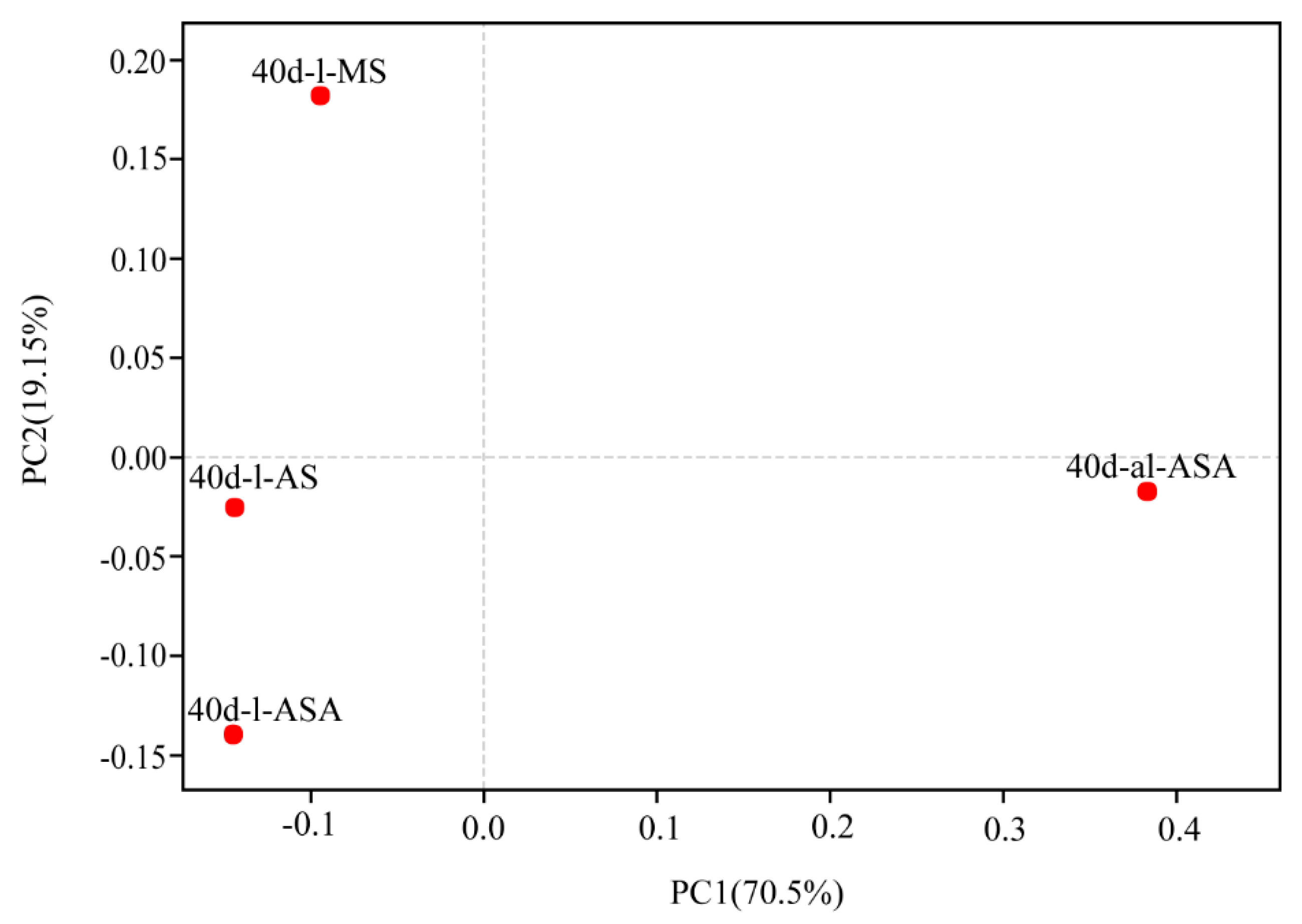
| Samples | Ace | Chao | Coverage | Shannon | Simpson | Sobs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 40d-s-MS | 3168.89 | 3083.75 | 0.97 | 6.08 | 0.011 | 2400.00 |
| 40d-s-AS | 3341.26 | 3252.70 | 0.98 | 6.24 | 0.007 | 2572.00 |
| 40d-s-ASA | 3351.64 | 3326.66 | 0.97 | 6.24 | 0.007 | 2564.00 |
| 40d-r-MS | 3747.64 | 3750.71 | 0.97 | 6.54 | 0.005 | 2912.00 |
| 40d-r-AS | 934.22 | 781.22 | 0.99 | 2.63 | 0.313 | 576.00 |
| 40d-r-ASA | 1648.57 | 1457.83 | 0.99 | 3.51 | 0.176 | 1037.00 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, N.; Li, Q.; Jiang, M.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, H.; Song, Q.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Zheng, Z. Effects of Distinct Revegetation Methods on Growth and Microbial Properties of Vallisneria natans. Water 2020, 12, 1294. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12051294
Wang N, Li Q, Jiang M, Zhang W, Zhang H, Song Q, Hu Z, Zhang J, Zheng Z. Effects of Distinct Revegetation Methods on Growth and Microbial Properties of Vallisneria natans. Water. 2020; 12(5):1294. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12051294
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Ning, Qi Li, Mengqi Jiang, Weizhen Zhang, Hao Zhang, Qixuan Song, Zhongda Hu, Jibiao Zhang, and Zheng Zheng. 2020. "Effects of Distinct Revegetation Methods on Growth and Microbial Properties of Vallisneria natans" Water 12, no. 5: 1294. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12051294
APA StyleWang, N., Li, Q., Jiang, M., Zhang, W., Zhang, H., Song, Q., Hu, Z., Zhang, J., & Zheng, Z. (2020). Effects of Distinct Revegetation Methods on Growth and Microbial Properties of Vallisneria natans. Water, 12(5), 1294. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12051294





